A Two-Stage Transfer Regression Convolutional Neural Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
- An end-to-end CNN classifier is firstly constructed for IF point identification, which can detect the IF point without the help of feature extractor.
- 2.
- A two-stage TR-CNN method is proposed based on transfer learning for bearing RUL prediction, which can help the method to be trained in a domain-invariant way by minimizing the probability distribution distance, namely the maximum mean discrepancy (MMD). Since the distributions of the bearing vibration datasets are usually different from each other, the proposed method is expected to be a promising method for RUL prediction.
- 3.
- Via proposing the regression loss, classification loss, MMD term and regularization term, a multiloss CNN model is constructed as the backbone architecture to extract the fault information from the fault diagnosis for RUL prediction, thus making full use of the historical data and increasing the performance of the proposed method.
- 4.
- Experimental results of the publicly available PRONOSTIA dataset [35] demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2. Proposed Approach
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. Convolutional Neural Network
2.2.1. Convolutional Layer
2.2.2. Pooling Layer
2.2.3. Fully Connected Layer
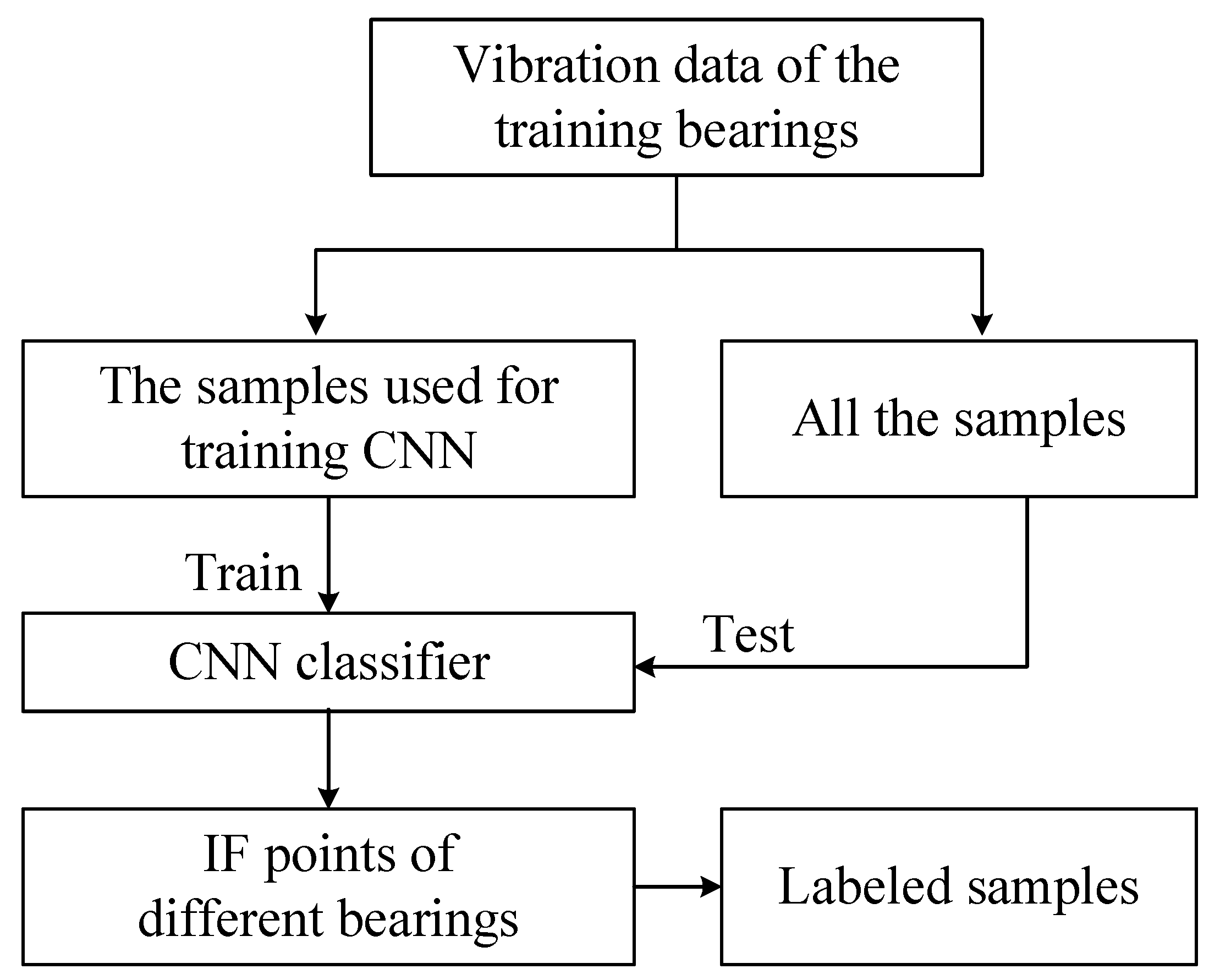
2.3. Incipient Fault Point Identification
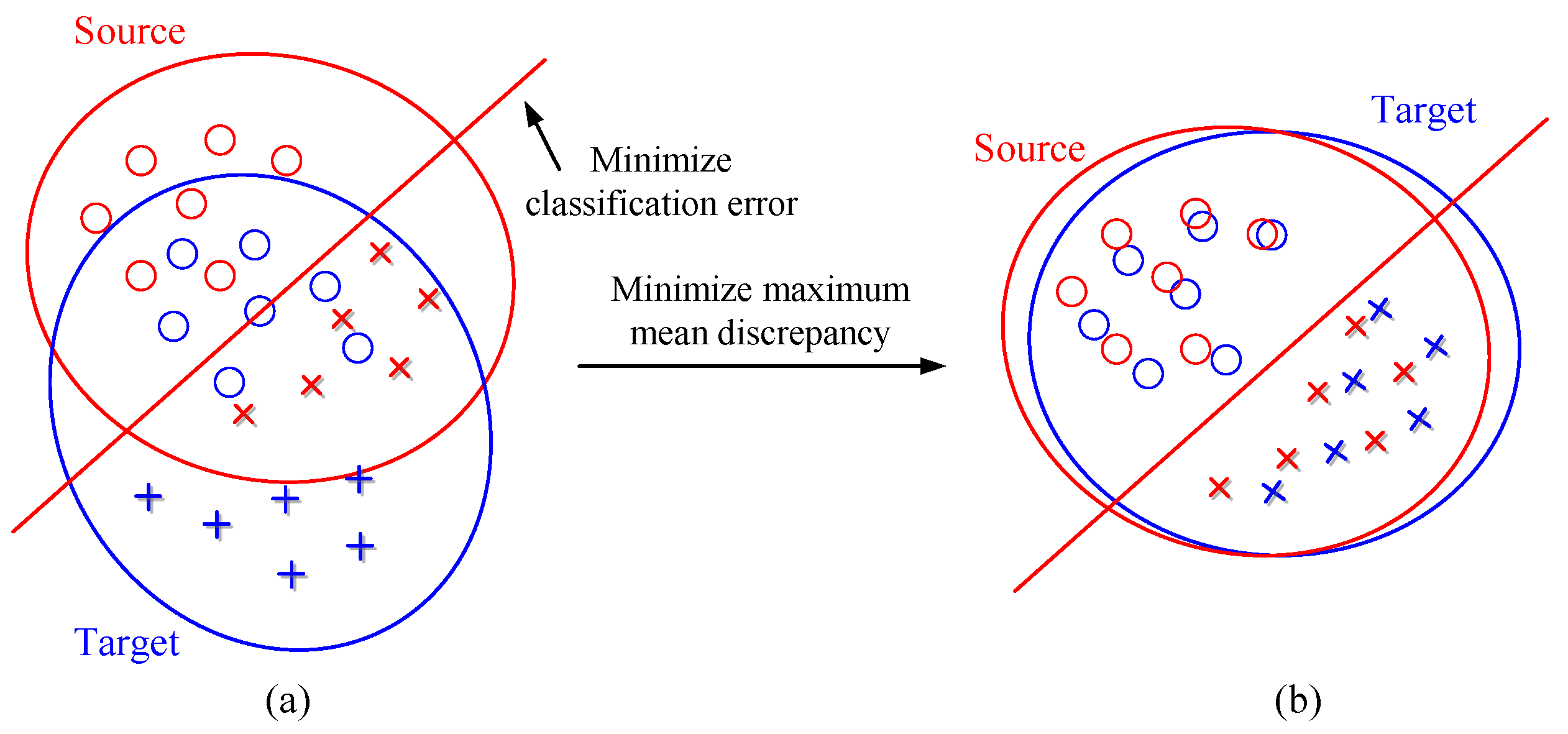
2.4. Maximum Mean Discrepancy
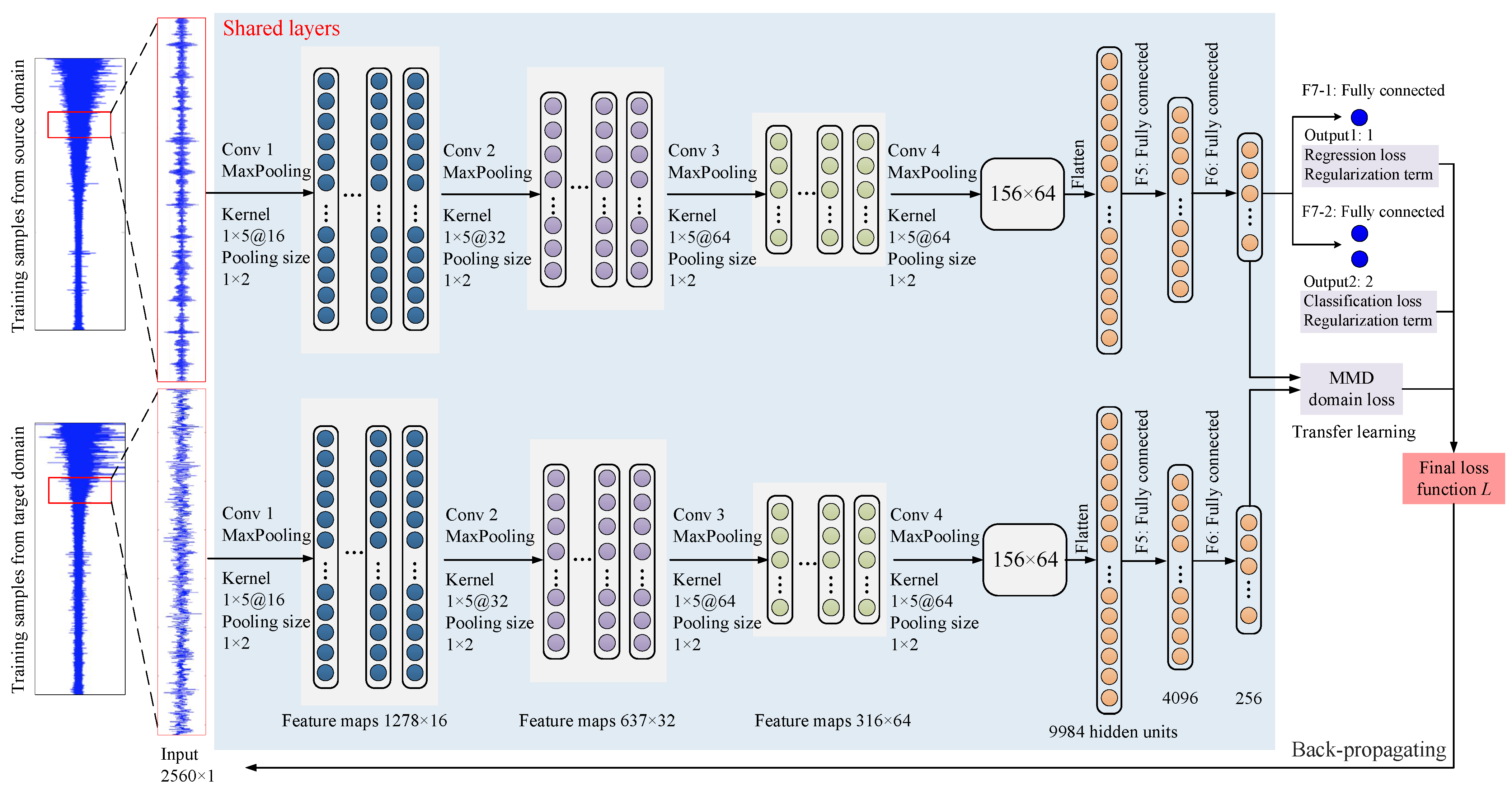
2.5. Transfer Regression Method
2.5.1. Regression Loss
2.5.2. Classification Loss
2.5.3. MMD Term
2.5.4. Regularization Term
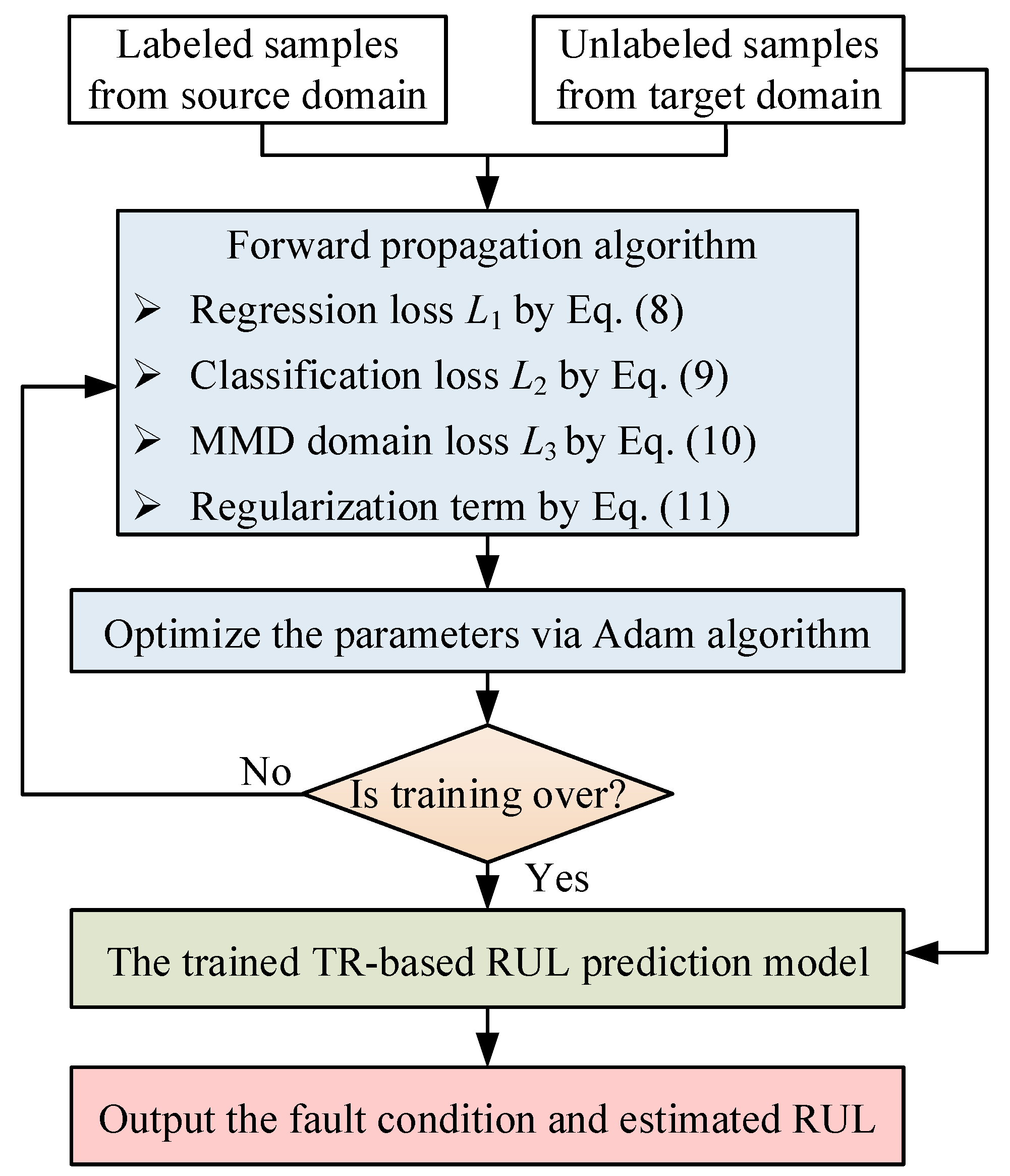
2.5.5. Final Loss Function
- 1.
- The regression loss ;
- 2.
- The classification loss of CNN model ;
- 3.
- The MMD term for domain adaption between the source domain and target domain.
- 4.
- The regularization term .
2.6. Training Process
3. Experiments, Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Setup and Data Description
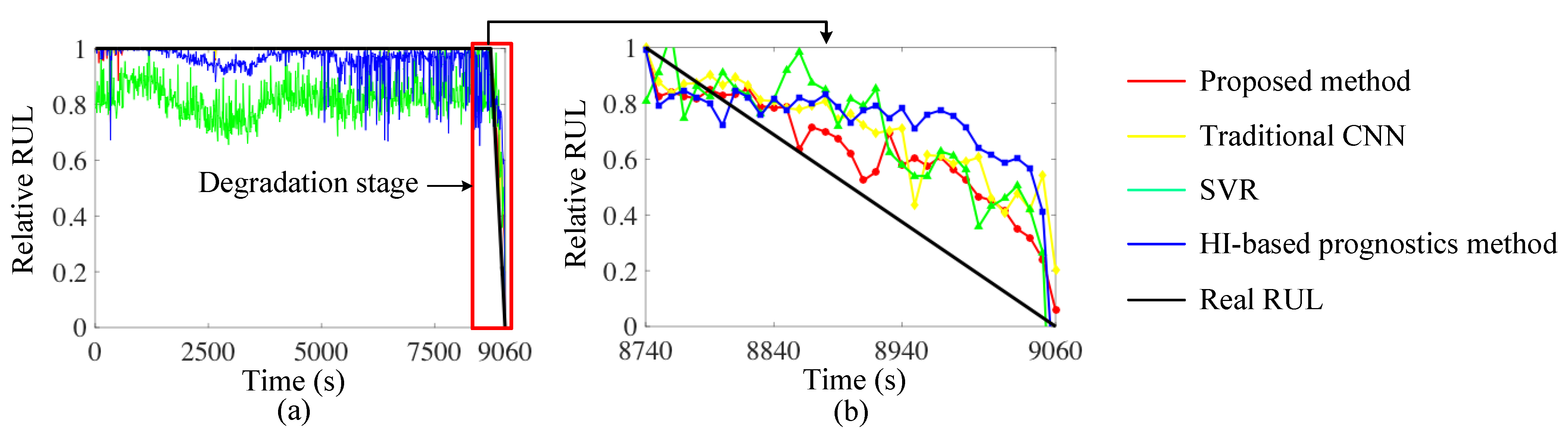
3.2. Case 1
3.3. Case 2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, H.; Wu, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on shift invariant sparse feature and optimized support vector machine. Machines 2021, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.C.; Hoang, D.T.; Tran, X.T.; Van, M.; Kang, H.J. A Bearing Fault Diagnosis Method Using Multi-Branch Deep Neural Network. Machines 2021, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Qu, L.; Qiao, W.; Hao, L. Enhanced Particle Filtering for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Wind Turbine Drivetrain Gearboxes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4738–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zi, Y. Switching State-Space Degradation Model With Recursive Filter/Smoother for Prognostics of Remaining Useful Life. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W. Multiscale Convolutional Attention Network for Predicting Remaining Useful Life of Machinery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 7496–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiahou, T.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y. Remaining Useful Life Prediction by Fusing Expert Knowledge and Condition Monitoring Information. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 2653–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Gontarz, S.; Lin, J.; Radkowski, S.; Dybala, J. A model-based method for remaining useful life prediction of machinery. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2016, 65, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, N.; Peng, W. Estimation of Bearing Remaining Useful Life Based on Multiscale Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3208–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Jin, Y.; Dang, X.; Deng, W. Feature Extraction for Data-Driven Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wu, J. A Neural Network-Based Joint Prognostic Model for Data Fusion and Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z. An artificial neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of equipment subject to condition monitoring. J. Intell. Manuf. 2012, 23, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, M.J. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gao, R.X.; Chen, X. Wavelets for fault diagnosis of rotary machines: A review with applications. Signal Process. 2014, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, R.; Chen, X. Fault diagnosis for a wind turbine generator bearing via sparse representation and shift-invariant K-SVD. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, R.; Chen, X. Sparse Time-Frequency Representation for Incipient Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Drive Train. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Bearing performance degradation assessment using locality preserving projections and Gaussian mixture models. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 2573–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wong, L.; Safaei, N. A neural network approach for remaining useful life prediction utilizing both failure and suspension histories. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2010, 24, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Vachtsevanos, G. Prediction of machine health condition using neuro-fuzzy and Bayesian algorithms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelif, R.; Chebel-Morello, B.; Malinowski, S.; Laajili, E.; Fnaiech, F.; Zerhouni, N. Direct remaining useful life estimation based on support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; He, D. A segmental hidden semi-Markov model (HSMM)-based diagnostics and prognostics framework and methodology. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2248–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yan, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.X. DCNN-Based Multi-Signal Induction Motor Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 2658–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, N. Deep neural networks: A promising tool for fault characteristic mining and intelligent diagnosis of rotating machinery with massive data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 72, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ming, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, A.; Chu, F. Cross-Operating Condition Degradation Knowledge Learning for Remaining Useful Life Estimation of Bearings. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; He, H.; Yan, J.; Xie, P. Multiscale Convolutional Neural Networks for Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Gearbox. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, R.; Zio, E. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on a Double-Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9521–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Dong, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y. Remaining useful life estimation of engineered systems using vanilla LSTM neural networks. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Yu, J. A Deep Domain Adaptative Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Machines Under Different Working Conditions and Fault Modes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A Comprehensive Survey on Transfer Learning. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lei, Y.; Jia, F.; Xing, S. An intelligent fault diagnosis approach based on transfer learning from laboratory bearings to locomotive bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, N.; Shen, C. A New Deep Transfer Learning Method for Bearing Fault Diagnosis Under Different Working Conditions. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8394–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ding, P.; Jia, M. A Novel Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method of Rolling Bearings Based on Deep Transfer Auto-Encoder. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; He, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, L. Prediction of Bearings Remaining Useful Life Across Working Conditions Based on Transfer Learning and Time Series Clustering. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135285–135303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, J. Transfer remaining useful life estimation of bearing using depth-wise separable convolution recurrent network. Measurement 2021, 176, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xuan, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, J. Dynamic Reweighted Domain Adaption for Cross-Domain Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Machines 2022, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nectoux, P.; Gouriveau, R.; Medjaher, K.; Ramasso, E.; Chebel-Morello, B.; Zerhouni, N.; Varnier, C. PRONOSTIA: An experimental platform for bearings accelerated degradation tests. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, PHM’12, IEEE Catalog Number: CPF12PHM-CDR, Denver, CO, USA, 18–21 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Guo, L.; Li, N.; Yan, T.; Lin, J. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 104, 799–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, K.M.; Gretton, A.; Rasch, M.J.; Kriegel, H.P.; Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, e49–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, B.; Hauptmann, A.G. Simultaneous Bearing Fault Recognition and Remaining Useful Life Prediction Using Joint Loss Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Habibullah, M.S.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Lim, P.; Nadarajan, S. Health index-based prognostics for remaining useful life predictions in electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Source Domain | Target Domain Dataset of Case 1 | Target Domain Dataset of Case 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 |
| Datasets | 1_1, 1_2, 1_3, 1_4 | 2_1 | 3_1 |
| Dataset | 1_1 | 1_2 | 1_3 | 1_4 | 2_1 | 3_1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | 871 | 1138 | 2448 | 2230 | 906 | 1637 |
| Proposed Method | CNN | SVR | HI-Based Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full life cycle | 0.0014 | 0.0023 | 0.381 | 0.0080 |
| Degradation stage | 0.0350 | 0.0617 | 0.0810 | 0.1007 |
| Proposed Method | CNN | SVR | HI-Based Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full life cycle | 0.0005 | 0.0015 | 0.0150 | 0.0031 |
| Degradation stage | 0.0105 | 0.0258 | 0.0413 | 0.0503 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Liu, R. A Two-Stage Transfer Regression Convolutional Neural Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Machines 2022, 10, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050369
Li X, Zhang K, Li W, Feng Y, Liu R. A Two-Stage Transfer Regression Convolutional Neural Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Machines. 2022; 10(5):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianling, Kai Zhang, Weijun Li, Yi Feng, and Ruonan Liu. 2022. "A Two-Stage Transfer Regression Convolutional Neural Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction" Machines 10, no. 5: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050369
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, K., Li, W., Feng, Y., & Liu, R. (2022). A Two-Stage Transfer Regression Convolutional Neural Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Machines, 10(5), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050369







