Analytical Determination and Influence Analysis of Stiffness Matrix of Ball Bearing under Different Load Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
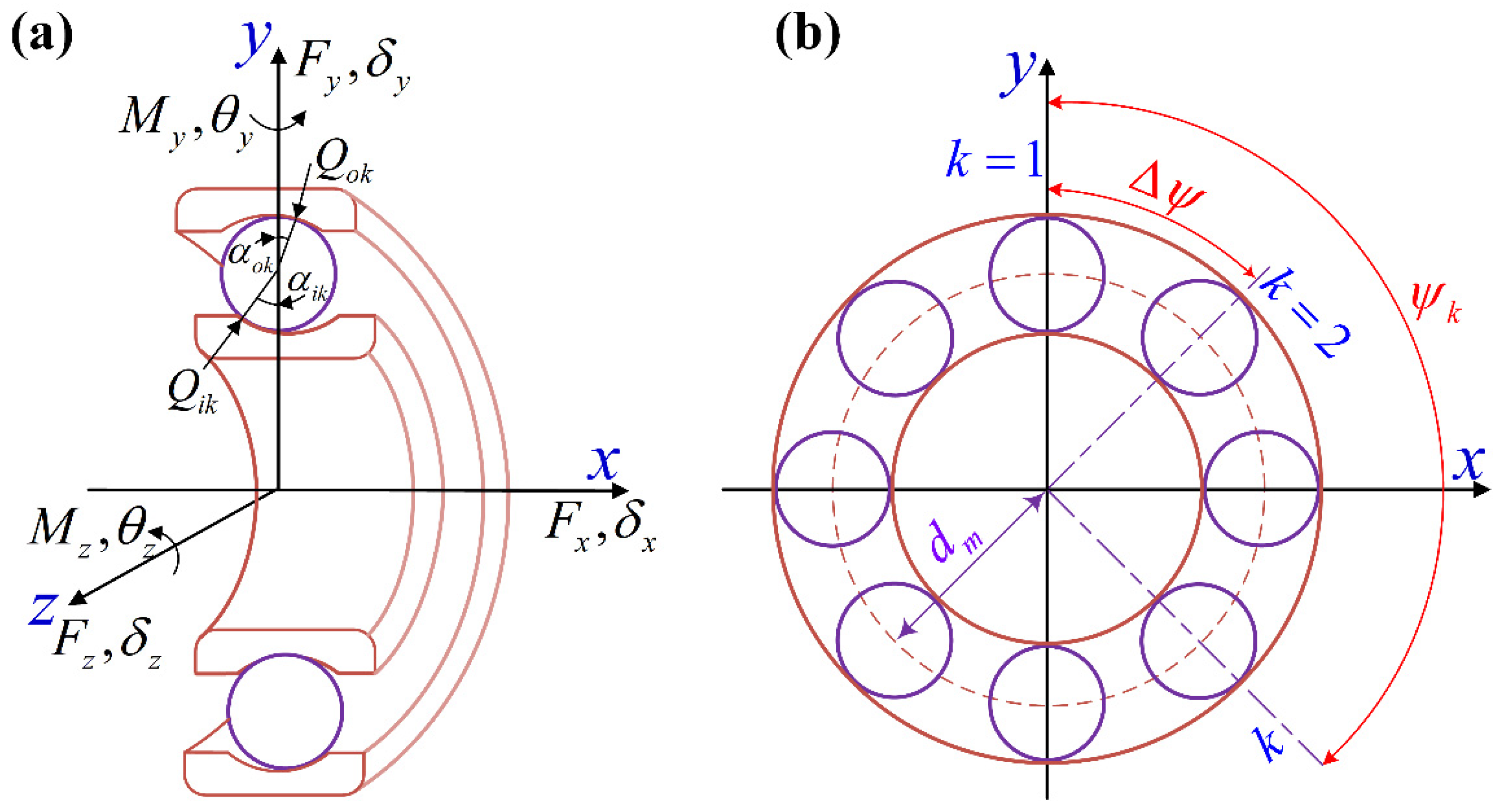
2. Theoretical Model
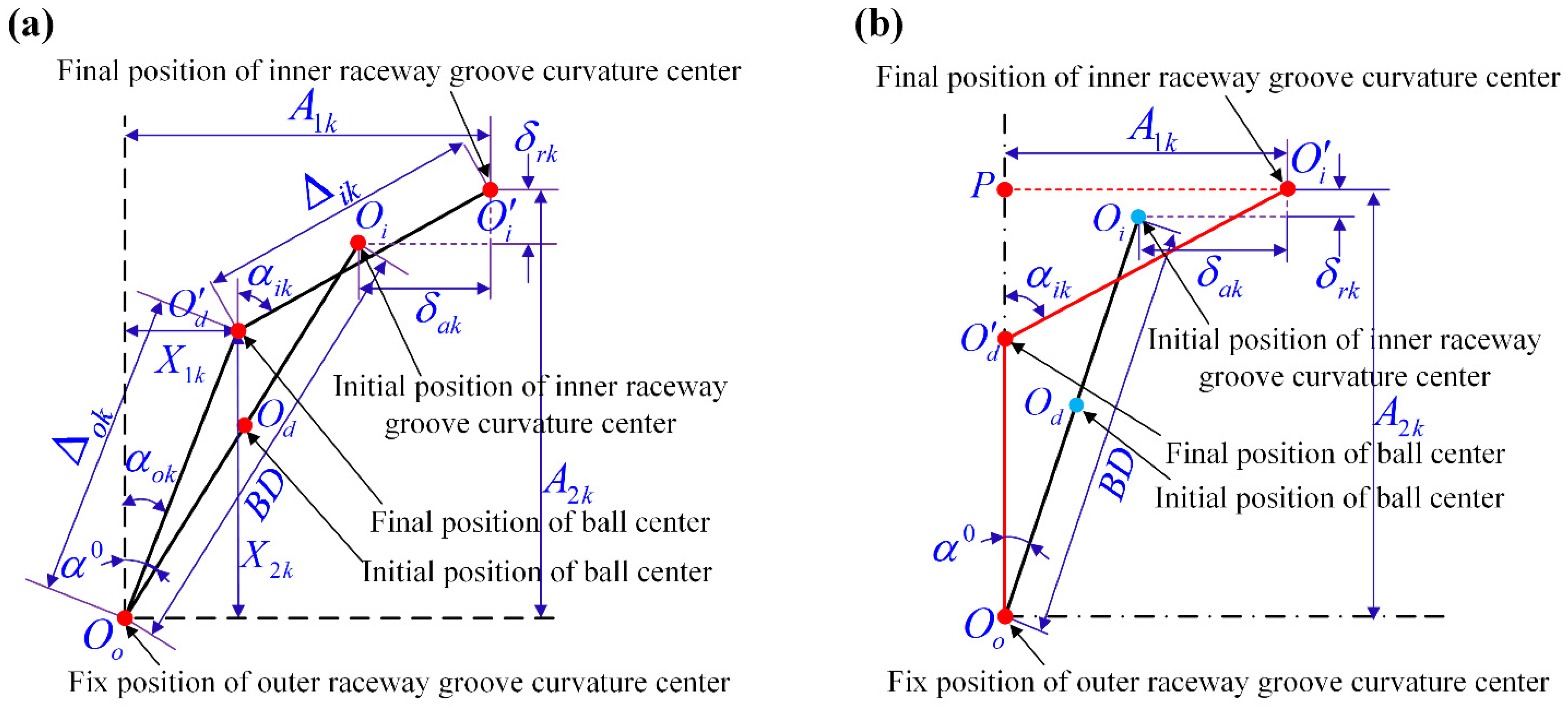
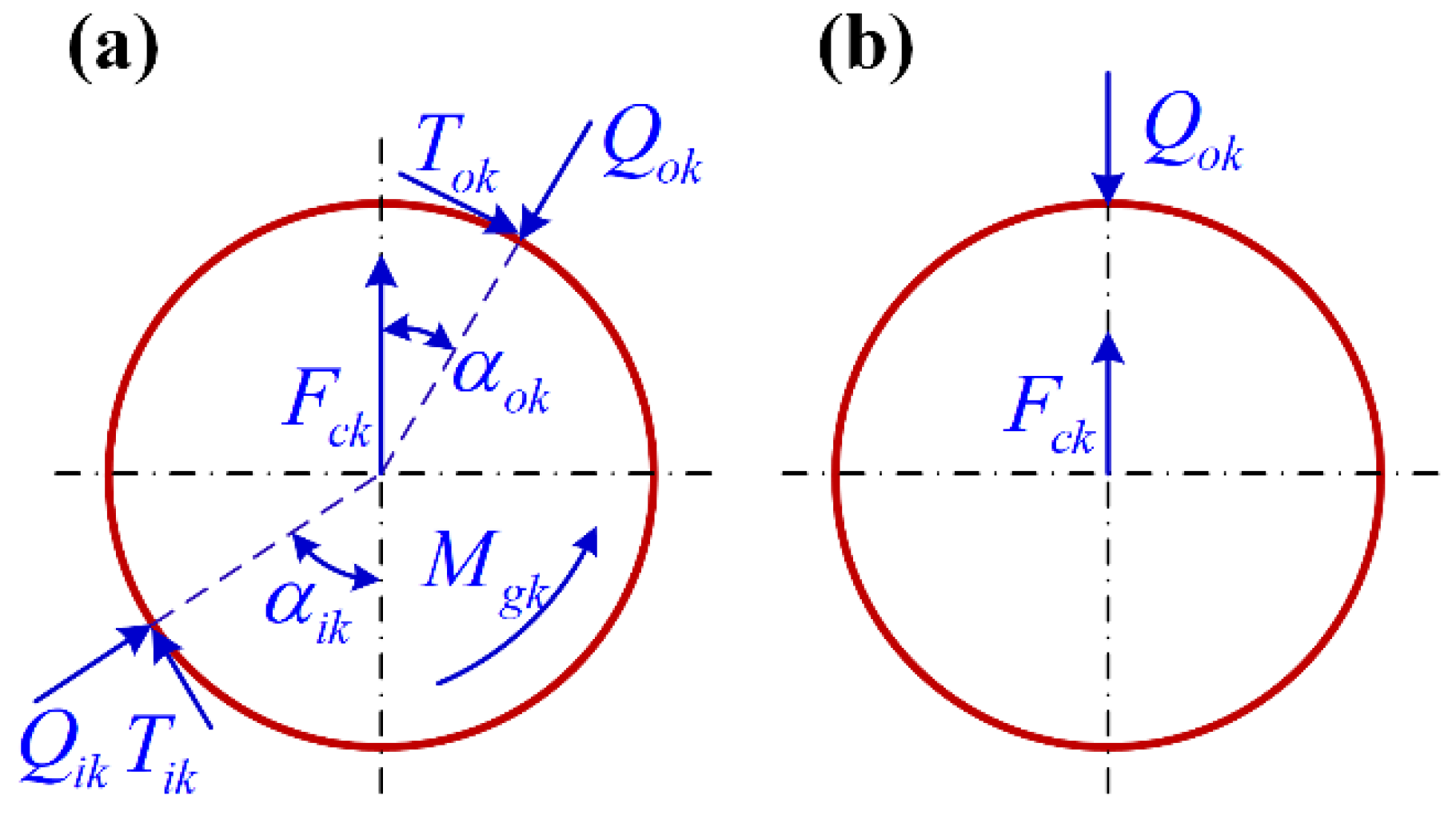
2.1. Quasi-Static Model of Ball Bearing
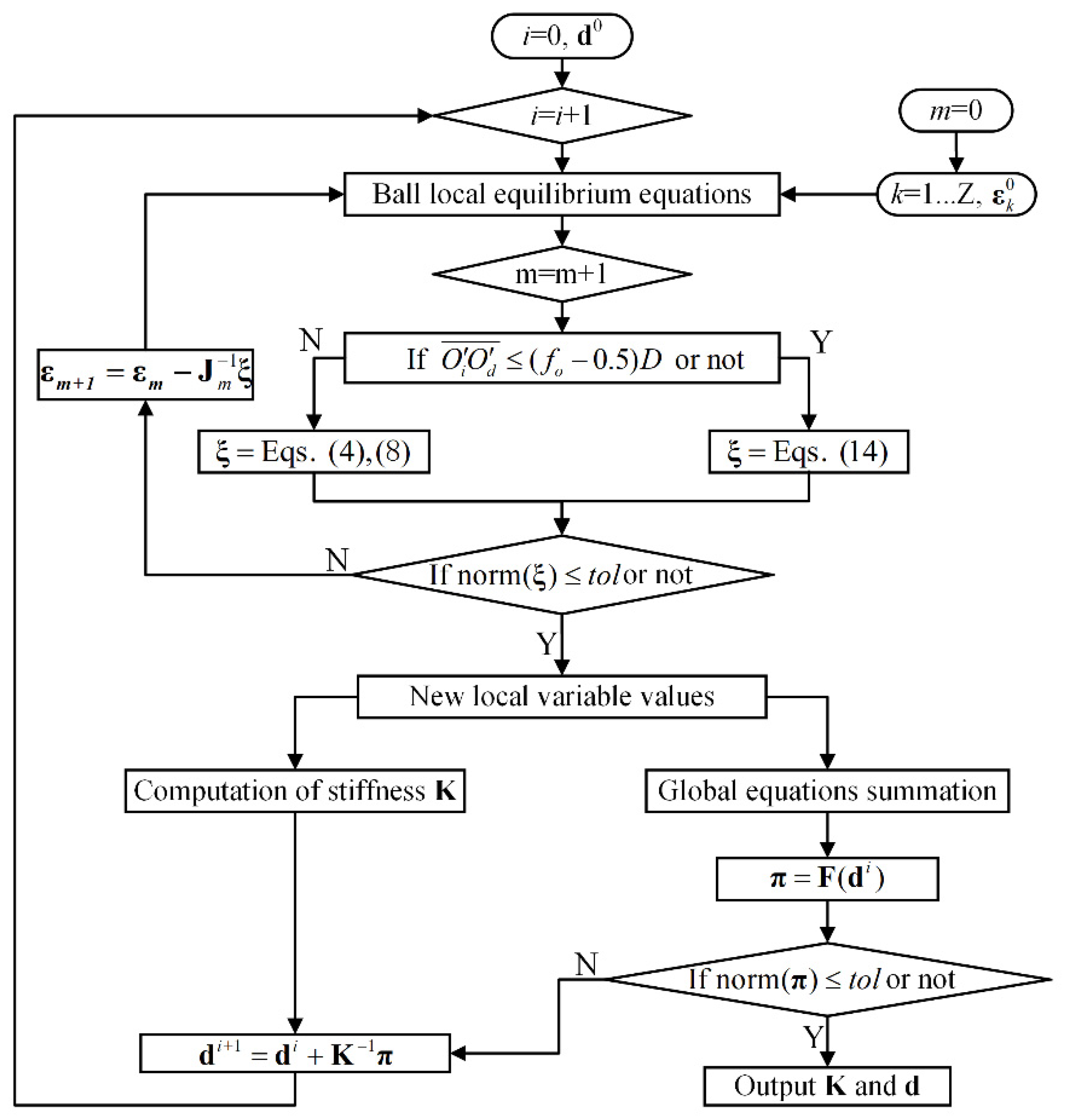
2.2. Computation of the Stiffness Matrix
3. Results
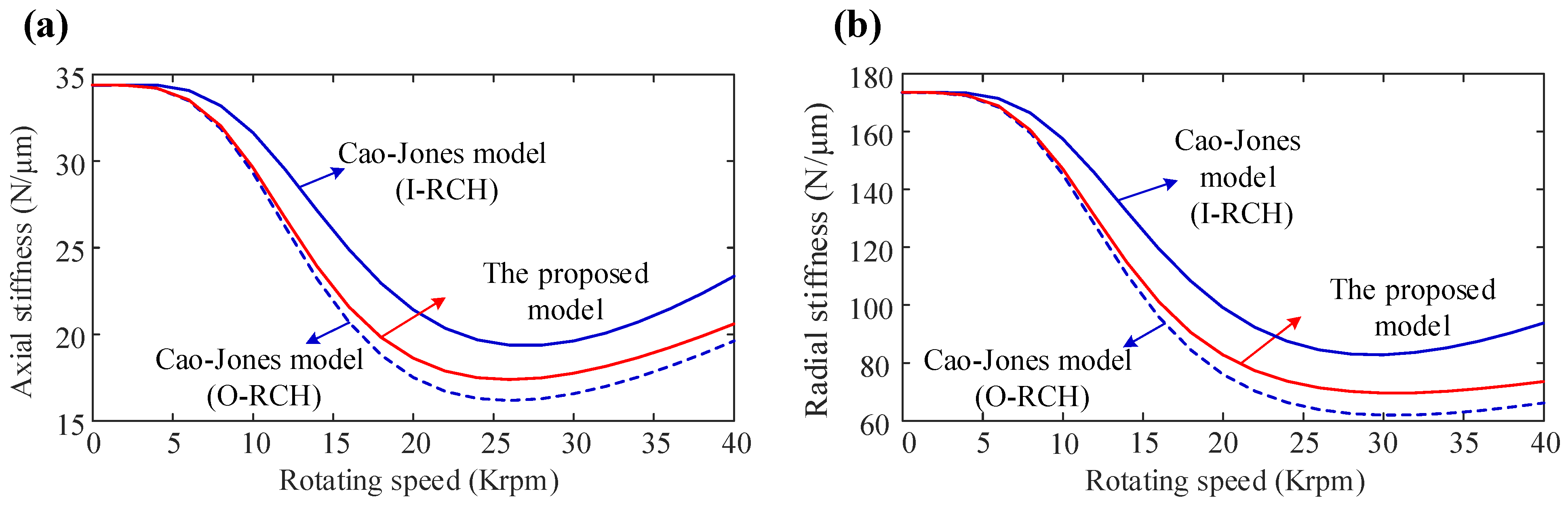
3.1. Comparison against Experimental and Theoretical Results
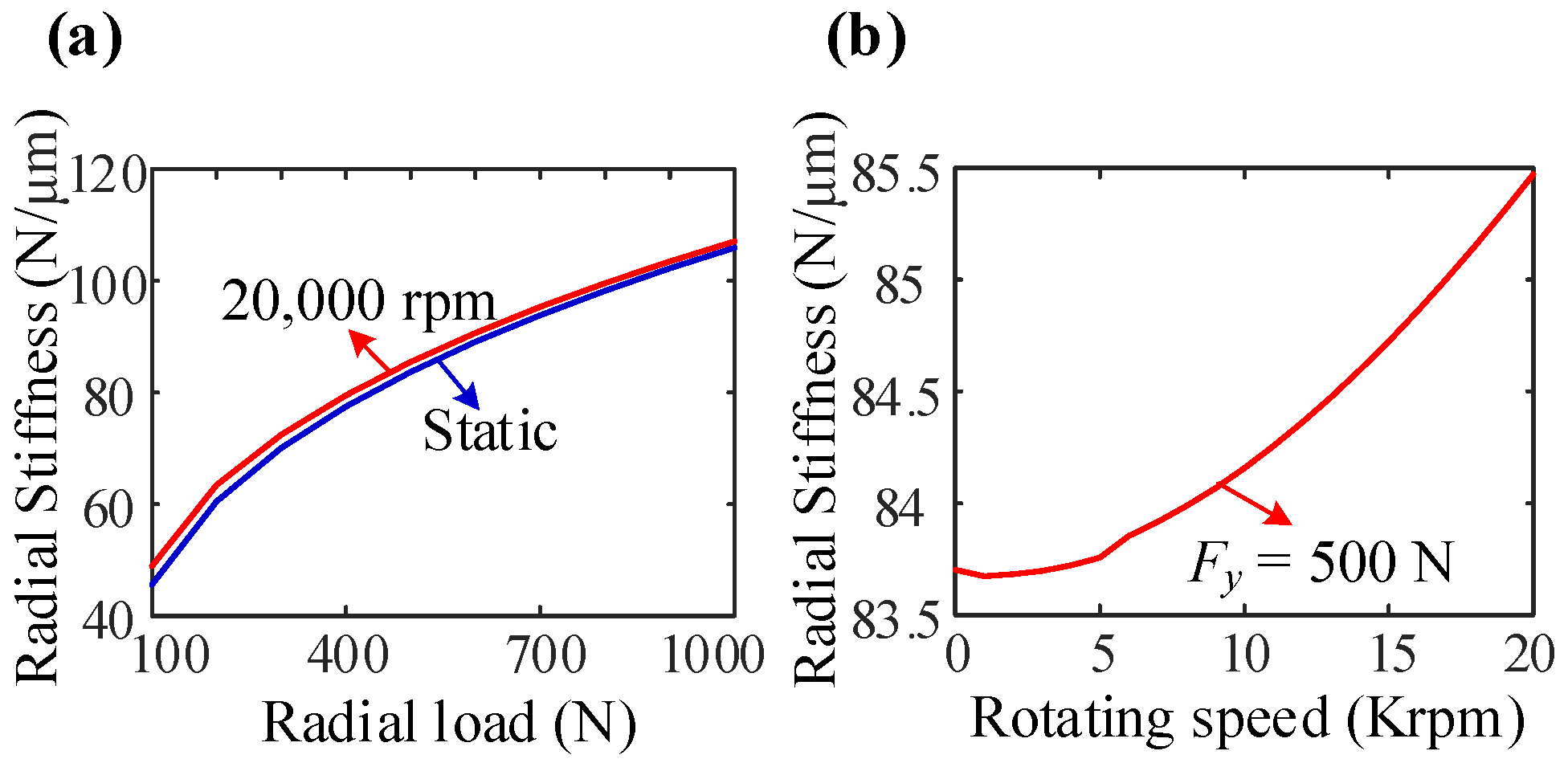
3.2. Stiffness Variation with Rotating Speed and Axial Preload
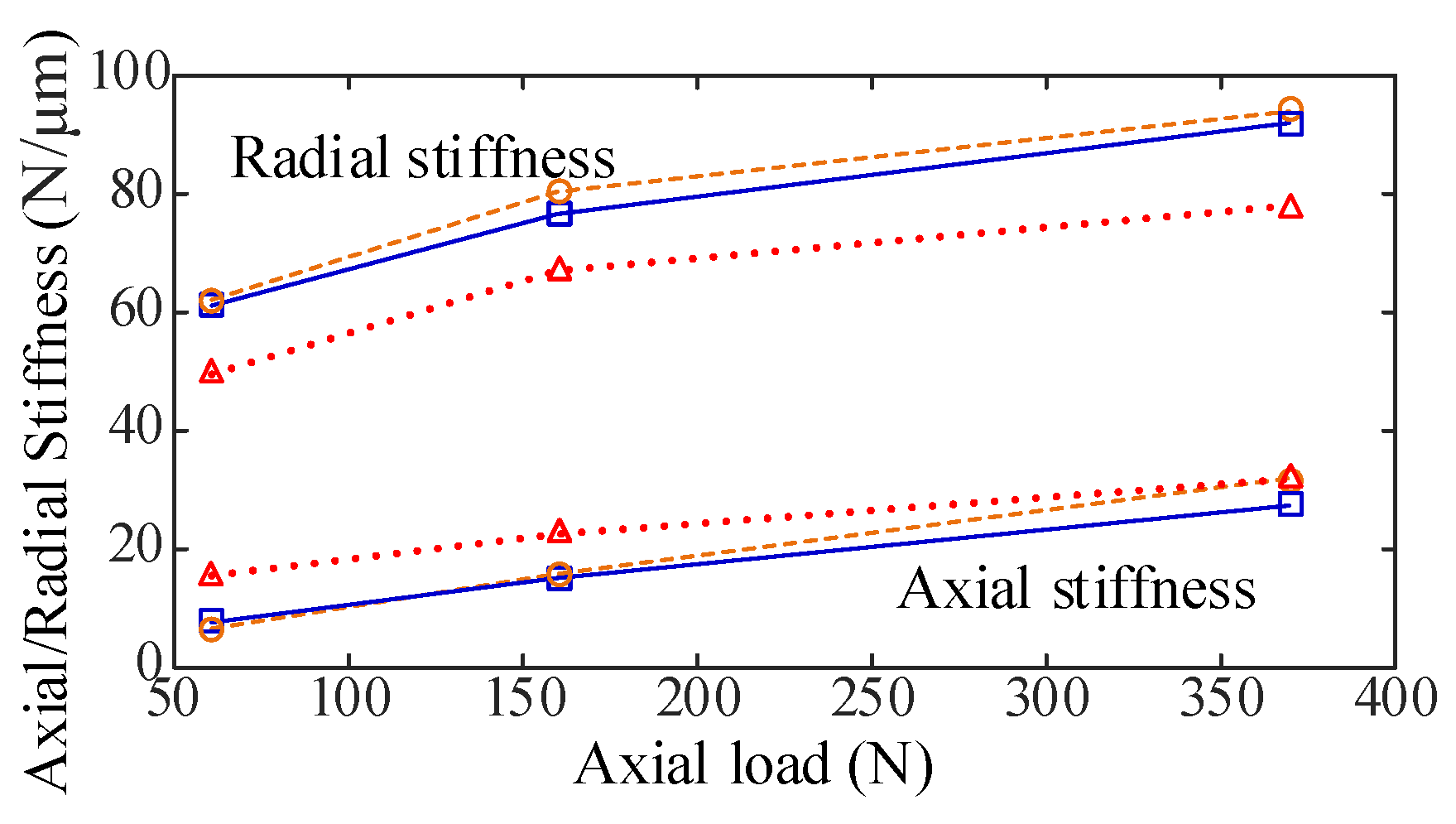
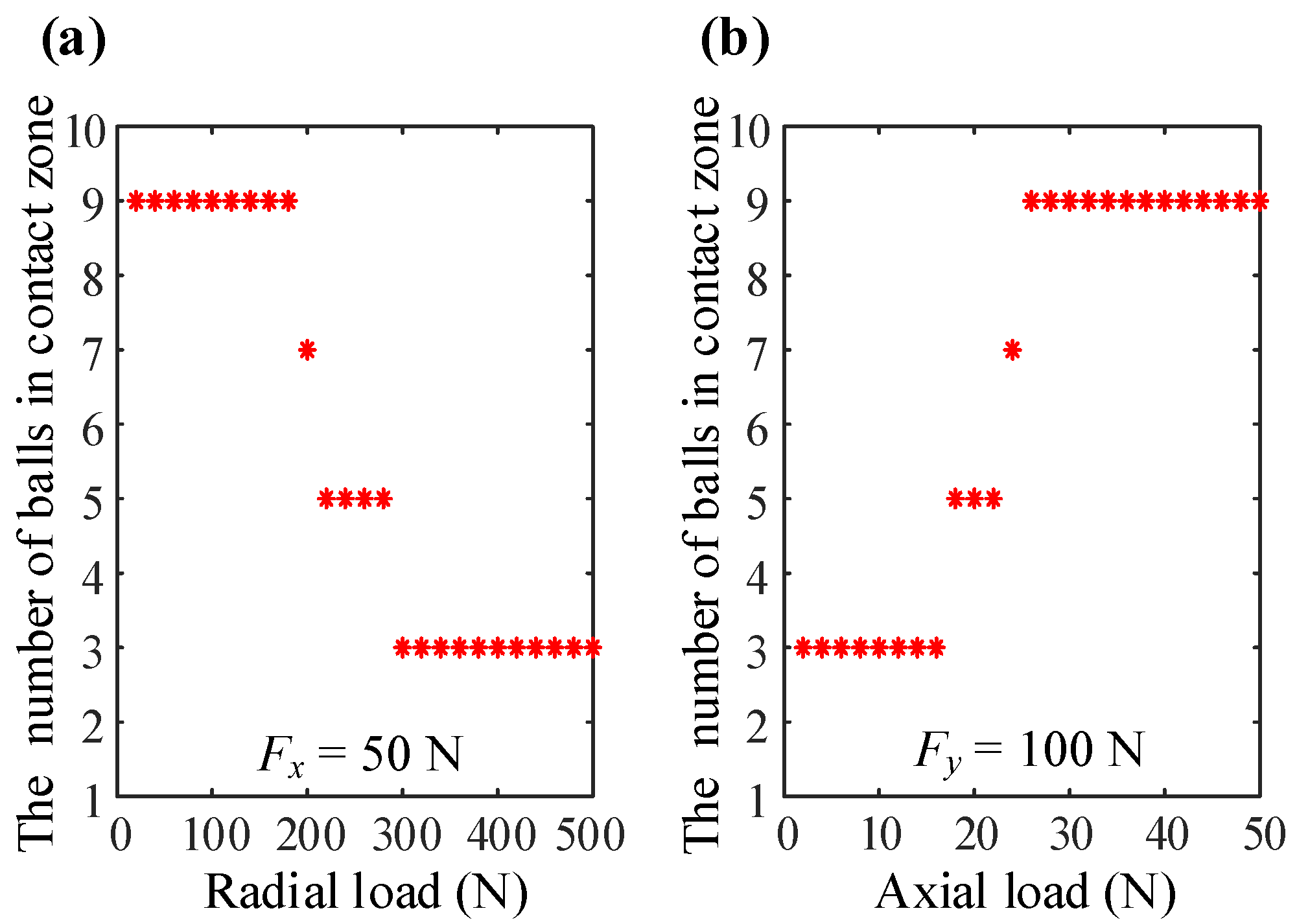
3.3. Stiffness Variation with Different Load Conditions
3.3.1. The Pure Radial Load Condition
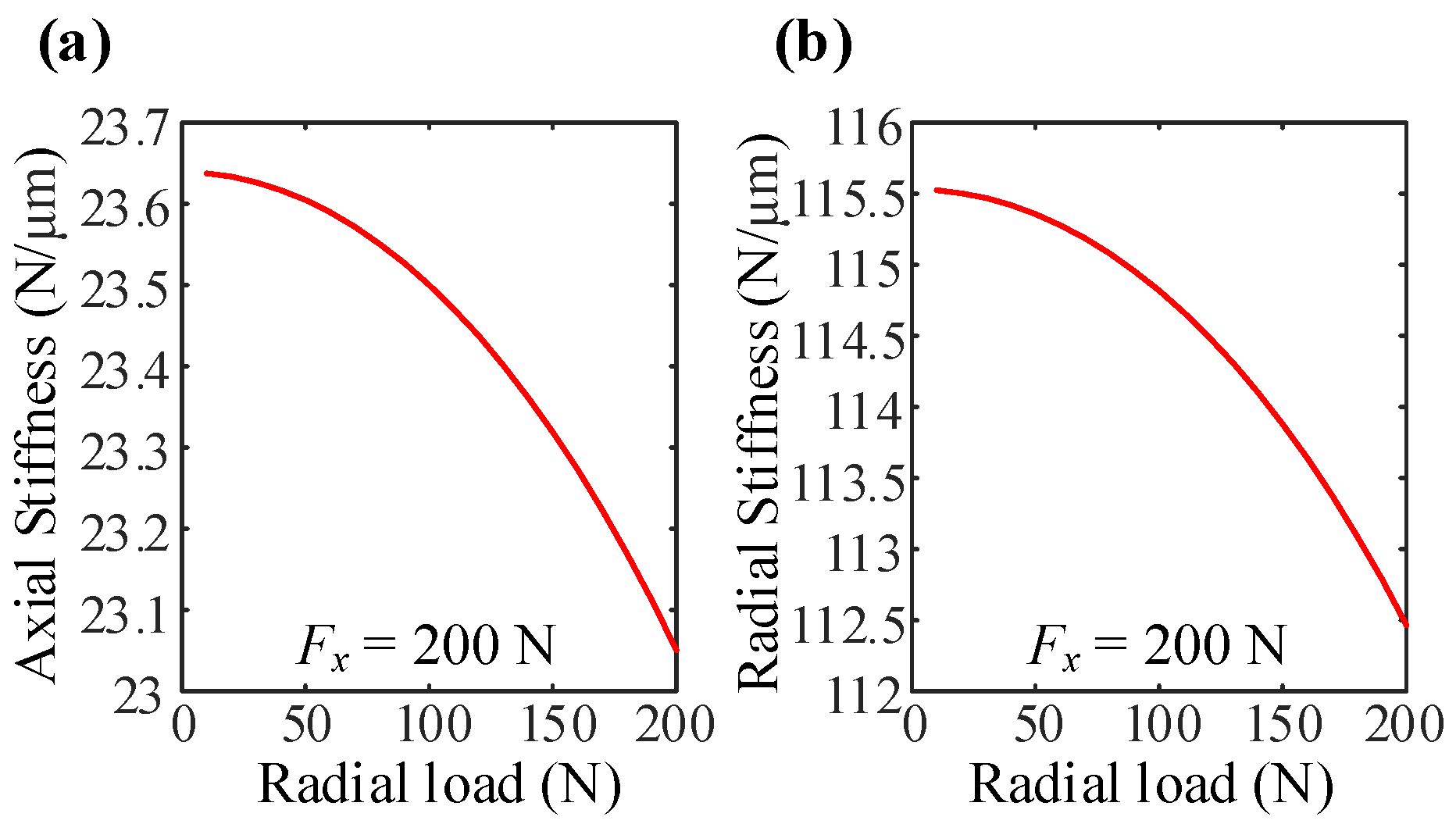
3.3.2. The Combined Large Axial Load and Small Radial Load Condition
3.3.3. The Combined Small Axial Load and Large Radial Load Condition
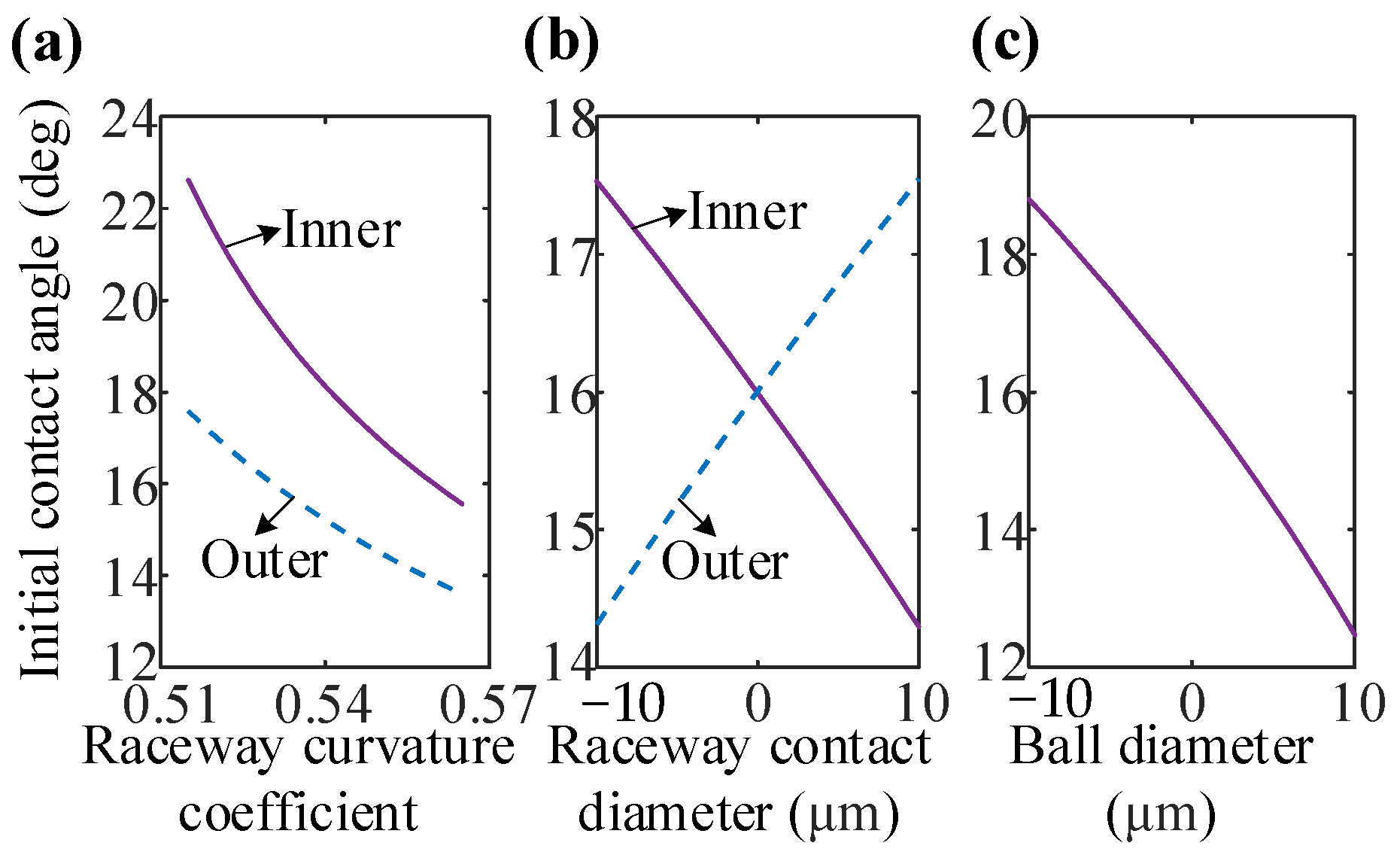
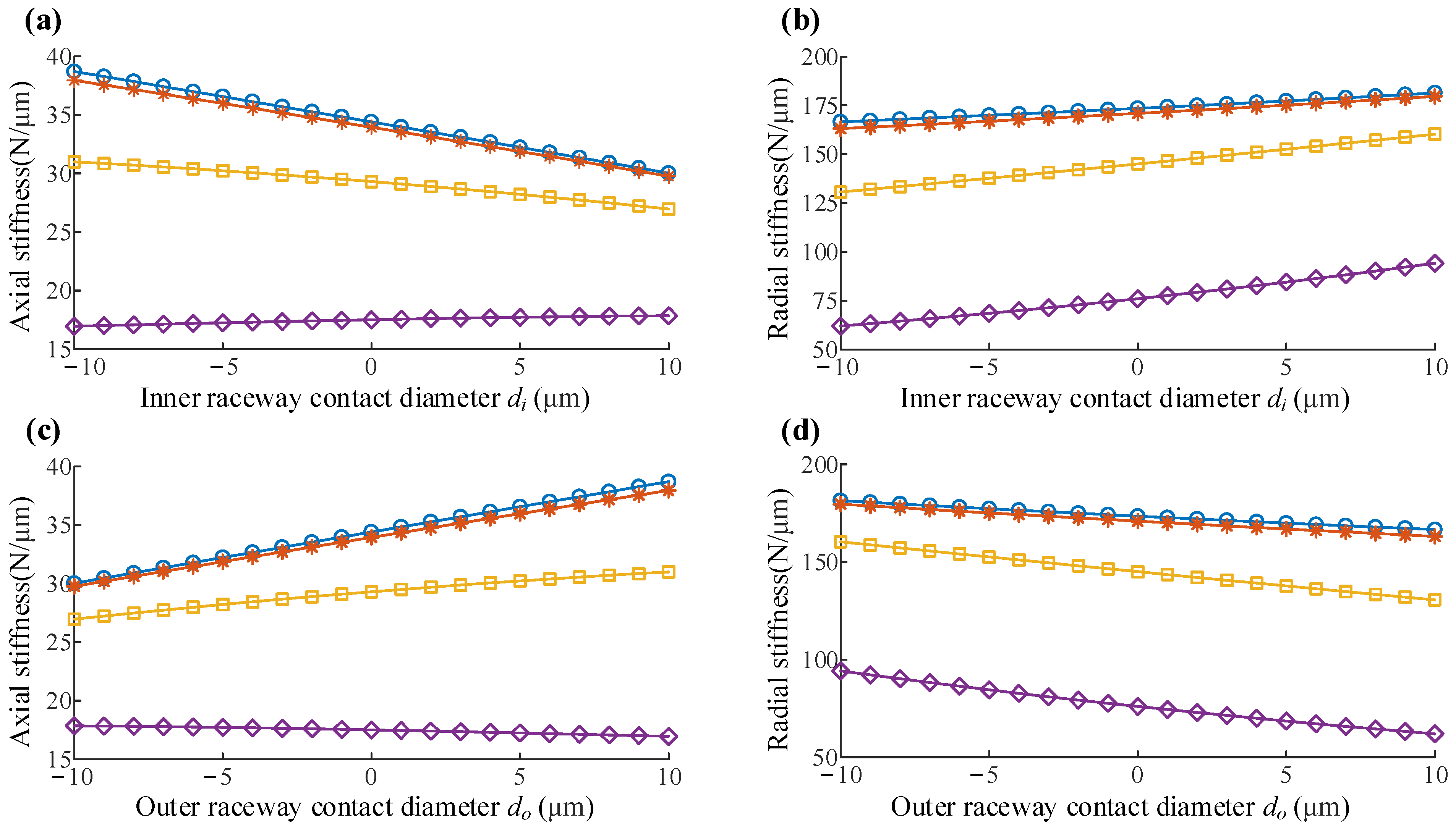
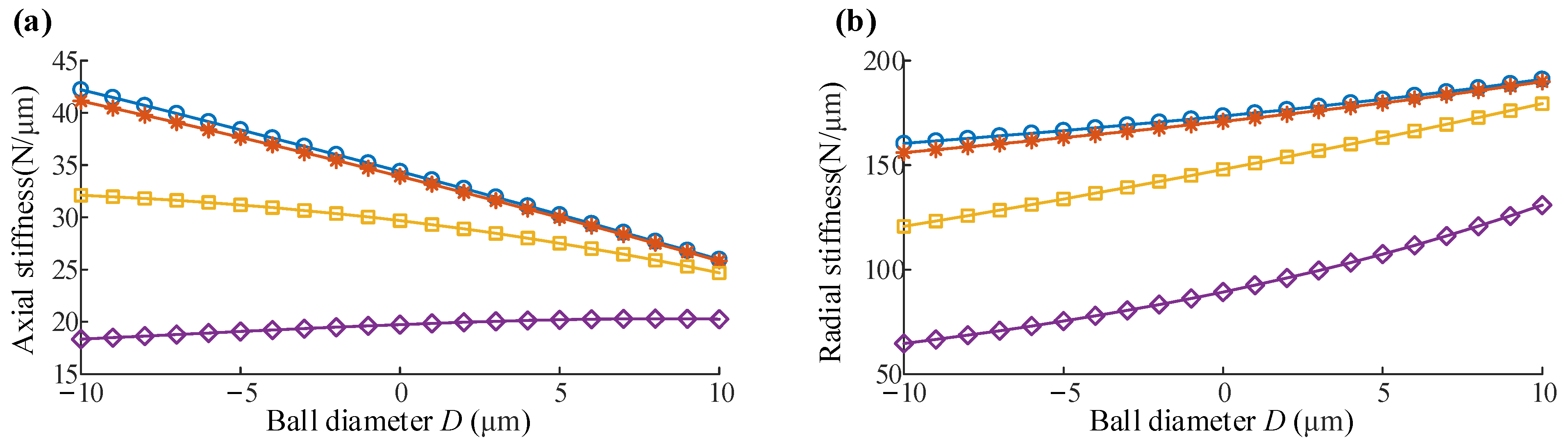
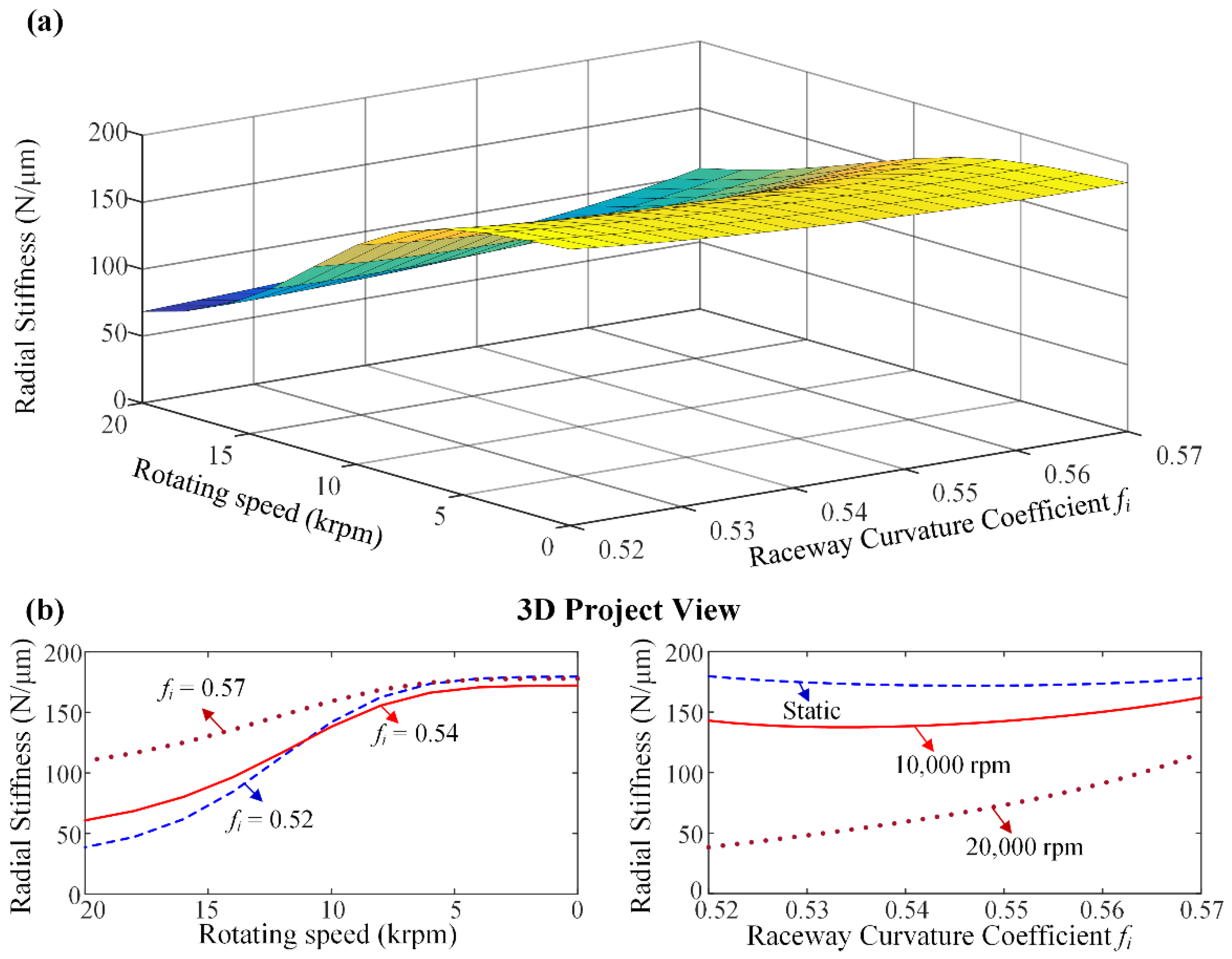
3.4. Stiffness Change with Internal Structural Parameters
3.4.1. Single Structural Parameter Variation
3.4.2. Constant Initial Contact Angle
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Property increasing the axial preload for ball bearing can effectively inhibit the stiffness attenuation phenomenon with rotating speed.
- The internal contact states of balls and raceways have significant effects on the stiffness variation.
- The influences of initial contact angle variation determined by different structure parameters on stiffness are different.
- A smaller raceway curvature coefficient of outer ring and a larger raceway curvature coefficient of inner ring can be designed for the high-speed ball bearing range to improve its stiffness property.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | distance between curvature centers of raceway groove |
| , | semi-major axes of the inner and outer ball–raceways contact |
| D | rolling ball diameter |
| di, do | contact diameter of inner/outer raceway |
| dm | pitch diameter |
| E | equivalent elastic modulus |
| centrifugal force of the kth ball | |
| , | The second kind of elliptic integral of the inner and outer ball–raceways contact |
| , | ; |
| J | mass moment of the ball |
| J | Jacobi determinant |
| Jacobian matrix of the ball local equations to ball local variables | |
| stiffness matrix | |
| , | load-deformation coefficients in the kth ball–inner/outer raceway contact |
| , | the second kind elliptic integral of the inner and outer ball–raceways contact |
| m | mass of the ball |
| gyroscopic moment of the kth ball | |
| internal radial clearance | |
| , | contact loads of the kth ball–inner/outer raceway |
| ri, ro | inner/outer raceway curvature radius |
| , | equivalent curvature radius of the inner and outer ball–raceways contact |
| , | frictions of the kth ball–inner/outer raceway |
| Z | number of rolling balls |
| initial contact angle | |
| , | contact angle of the kth ball |
| pitch angle of the kth ball | |
| , | The angular displacements of ball bearing |
| , | elastic deformations of the kth ball–inner/outer raceway contacts |
| , , | elative displacement of the inner and outer rings |
| , | the distribution factor of the contact load of the inner and outer ball–raceways contact |
| , | ; |
| rotating speed of inner ring | |
| spin angular speed of the kth ball | |
| revolution angular speed of the kth ball | |
| angular position of the kth rolling ball |
Appendix A. The Detailed Solution Process of Bearing Static Model
References
- Stribeck, R. Ball bearing for various loads. Trans. ASME 1907, 29, 420–463. [Google Scholar]
- Sjovall, H. The load distribution within ball and roller bearings under given external radial and axial load. Tek. Tidskr. 1933, 19, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, G.; Palmgren, A. Dynamic Capacity of Roller Bearings. Acta Polytechnica, Generalstabens Litograf. Anst. Förl. 1952, 2, 96–127. [Google Scholar]
- Palmgren, A.; Ruley, B. Ball and Roller Bearing Engineering; SKF Industries, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.B. A general theory for elastically constrained ball and radial roller bearings under arbitrary load and speed conditions. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.A. Rolling Bearing Analysis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 256–296. [Google Scholar]
- Foord, C.A. High-speed ball bearing analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2006, 220, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.-G.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Ai, S. Modeling angular contact ball bearing without raceway control hypothesis. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 82, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.A.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhan, L. Raceway control assumption and the determination of rolling element attitude angle. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. En. 2001, 37, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, C.T. Dynamics of ball bearings. J. Lubr. Technol. 1971, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Dynamics of rolling-element bearings—Part III: Ball-bearing analysis. J. Lubr. Technol. Trans. ASME 1979, 101, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Dynamics of rolling-element bearings—Part IV: Ball-bearing results. J. Lubr. Technol. Trans. ASME 1979, 101, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, C.R.; Ng, K.O. The dynamics of ball separators in ball bearings—Part I: Analysis. ASLE Trans. 1985, 28, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, C.R.; Long, T. Ball bearing dynamic analysis using computer methods—Part I: Analysis. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 1996, 118, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z. Investigation of skidding in angular contact ball bearings under high speed. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Nanda, P.; Mishra, D. Comparative study on optimum design of rolling element bearing. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shin, Y.C. Analysis of bearing configuration effects on high speed spindles using an integrated dynamic thermo-mechanical spindle model. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2004, 44, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Altintas, Y. A general method for the modelling of spindle-bearing systems. J. Mech. Des. Trans. ASME 2004, 126, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Holkup, T.; Altintas, Y. A comparative study on the dynamics of high speed spindles with respect to different preload mechanisms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2011, 57, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, E.P. A simple way to estimate bearing stiffness. Mach. Des. 1980, 52, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wardle, F.P.; Lacey, S.J.; Poon, S.Y. Dynamic and static characteristics of a wide speed range machine tool spindle. Precis. Eng. 1983, 5, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houpert, L. A uniform analytical approach for ball and roller bearings calculations. J. Tribol. 1997, 119, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernot, X.; Sartor, M.; Guillot, J. Calculation of the Stiffness Matrix of Angular Contact Ball Bearings by Using the Analytical Approach. J. Mech. Des. Trans ASME 2000, 122, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, C.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L. An analytical calculation method of the load distribution and stiffness of an angular contact ball bearing. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 142, 103597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C.; Singh, R. Vibration transmission through rolling element bearings, part I: Bearing stiffness formulation. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 139, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C.; Singh, R. Vibration transmission through rolling element bearings, part II: System studies. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 139, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C.; Singh, R. Vibration transmission through rolling element bearings, Part III: Geared rotor system studies. J. Sound Vib. 1991, 151, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, J.G.; Geiger, G. Analysis of the static and dynamic behavior of lathe spindles. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Des. Res. 1964, 3, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- While, M.F. Rolling Element Bearing Vibration Transfer Characteristics: Effect of Stiffness. J. Appl. Mech. 1979, 46, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Yu, T. Influence of structural parameters and tolerance on stiffness of high-speed ball bearings. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Man. 2016, 17, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yu, T. Effects of rolling bearing configuration on stiffness of machine tool spindle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 232, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, D.; Ritou, M.; Furet, B.; Le Loch, S. Complete Analytical Expression of the Stiffness Matrix of Angular Contact Ball Bearings. J. Tribol. Trans ASME 2013, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Yan, K.; Hong, J.; Zhang, J. A comprehensive study on the off-diagonal coupling elements in the stiffness matrix of the angular contact ball bearing and their influence on the dynamic characteristics of the rotor system. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 158, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, H. Calculation of ball bearing speed-varying stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 81, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, A.; Singh, R. Stiffness matrix formulation for double row angular contact ball bearings: Analytical development and validation. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 5898–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuha, N.; Cavalca, K.L. Stiffness and damping of elastohydrodynamic line contact applied to cylindrical roller bearing dynamic model. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 481, 115444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Parker, R.G. Stiffness matrix calculation of rolling element bearings using a finite element/contact mechanics model. Mech. Mac. Theory 2012, 51, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Peng, Z.; Chu, F. Stability analysis of a rotor–bearing system with time-varying bearing stiffness due to finite number of balls and unbalanced force. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 6768–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, D.; Howard, C.; Prime, Z. Varying stiffness and load distributions in defective ball bearings: Analytical formulation and application to defect size estimation. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 337, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, D.; Howard, C.; Sawalhi, N.; Ahmadi, A.M.; Singh, S. Analysis of bearing stiffness variations, contact forces and vibrations in radially loaded double row rolling element bearings with raceway defects. Mech. Syst. Signal. Processing 2015, 50–51, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.; Blech, J.J.; Braun, S.G. In Situ Determination of Rolling Bearing Stiffness and Damping by Modal Analysis. J. Vib. Acoust. 1987, 109, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.J.; Walford, T. The measurement of the radial stiffness of rolling element bearings under oscillating conditions. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1980, 22, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, M. Computational modelling of precision spindles supported by ball bearings. Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf. 1998, 28, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejewski, J.; Kwasny, W. Modelling of angular contact ball bearings and axial displacements for high-speed spindles. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 59, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, B.; Hong, J.; Zhu, Y. Effect of preload on ball-raceway contact state and fatigue life of angular contact ball bearing. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, J. A comparative study and stiffness analysis of angular contact ball bearings under different preload mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 115, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yan, K.; Hong, J.; Wang, M.Y. A comprehensive study on the speed-varying stiffness of ball bearing under different load conditions. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 136, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, B.; Kong, L.; Li, Y. Effect of the ring misalignment on the service characteristics of ball bearing and rotor system. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 151, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | NSK B7008C | NSK B7014C | SKF EEB3-2Z | SKF 6205 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The curvature radius of inner raceway ri (mm) | 4.000 | 5.330 | 2.064 | 4.108 |
| The curvature radius of outer raceway ro (mm) | 3.790 | 5.050 | 2.064 | 4.108 |
| The contact diameter of inner raceway di (mm) | 46.838 | 80.452 | 11.78 | 30.59 |
| The contact diameter of outer raceway do (mm) | 61.176 | 99.562 | 19.72 | 46.41 |
| The number of internal balls Z | 19 | 25 | 7 | 9 |
| The diameter of balls D (mm) | 7.144 | 9.522 | 3.969 | 7.900 |
| The initial contact angle of ball bearing (°) | 15.992 | 15.942 | 6.429 | 14.453 |
| The pitch diameter of ball bearing dm (mm) | 50.00 | 90.00 | 15.75 | 38.50 |
| Types | 7008C | 7014C | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preload (N) | 60 (EL) | 120 (L) | 10he290 (M) | 590 (H) | 145 (EL) | 290 (L) | 740 (M) | 1470 (H) | |
| Axial stiffness (N/µm) | Model | 37.5 | 48.7 | 72.5 | 99.3 | 65.1 | 83.9 | 124.4 | 170.1 |
| Manual | 39 | 51 | 77 | 110 | 68 | 88 | 135 | 190 | |
| error | 3.8% | 4.5% | 5.84% | 9.72% | 4.26% | 4.66% | 7.85% | 10.47% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Pei, S.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D. Analytical Determination and Influence Analysis of Stiffness Matrix of Ball Bearing under Different Load Conditions. Machines 2022, 10, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040238
Niu Q, Li Y, Zhu Y, Pei S, Yin Y, Wang D. Analytical Determination and Influence Analysis of Stiffness Matrix of Ball Bearing under Different Load Conditions. Machines. 2022; 10(4):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040238
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Qingbo, Yeteng Li, Yongsheng Zhu, Shiyuan Pei, Yanjing Yin, and Dongfeng Wang. 2022. "Analytical Determination and Influence Analysis of Stiffness Matrix of Ball Bearing under Different Load Conditions" Machines 10, no. 4: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040238
APA StyleNiu, Q., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Pei, S., Yin, Y., & Wang, D. (2022). Analytical Determination and Influence Analysis of Stiffness Matrix of Ball Bearing under Different Load Conditions. Machines, 10(4), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040238





