A Reliable Computational Scheme for Stochastic Reaction–Diffusion Nonlinear Chemical Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Take into account the stochastic auto-catalytic Brusselator model subject to time-varying white noise.
- The underlying model’s smoothness properties have been determined.
- Examine the precision and reliability of such NSFD techniques for numerically solving the reaction–diffusion Brusselator model over time. Our findings have immediate implications for models in other fields, including ecology and finance, where they simulate the behavior of predators and prey and the fluctuations of financial markets, respectively.
- Keeping the solution’s positivity in mind, provide an alternate method that ensures first-order precision in time and second-order accuracy in space.
- Show that the proposed strategy is consistent and stable.
- Show the efficacy of the current NSFD technique and our suggested system using two simulated cases.
2. Smoothness Properties of the Stochastic Auto-Catalytic Brusselator Model
- (i)
- .
- (ii)
- is pre-compact.
3. Stochastic Numerical Scheme
4. Existing Stochastic NSFD
5. Stability Analysis of the Proposed Scheme
5.1. Consistency of the Proposed Stochastic Scheme
5.2. Consistency of Stochastic NSFD
5.3. Convergence of Stochastic Proposed Scheme
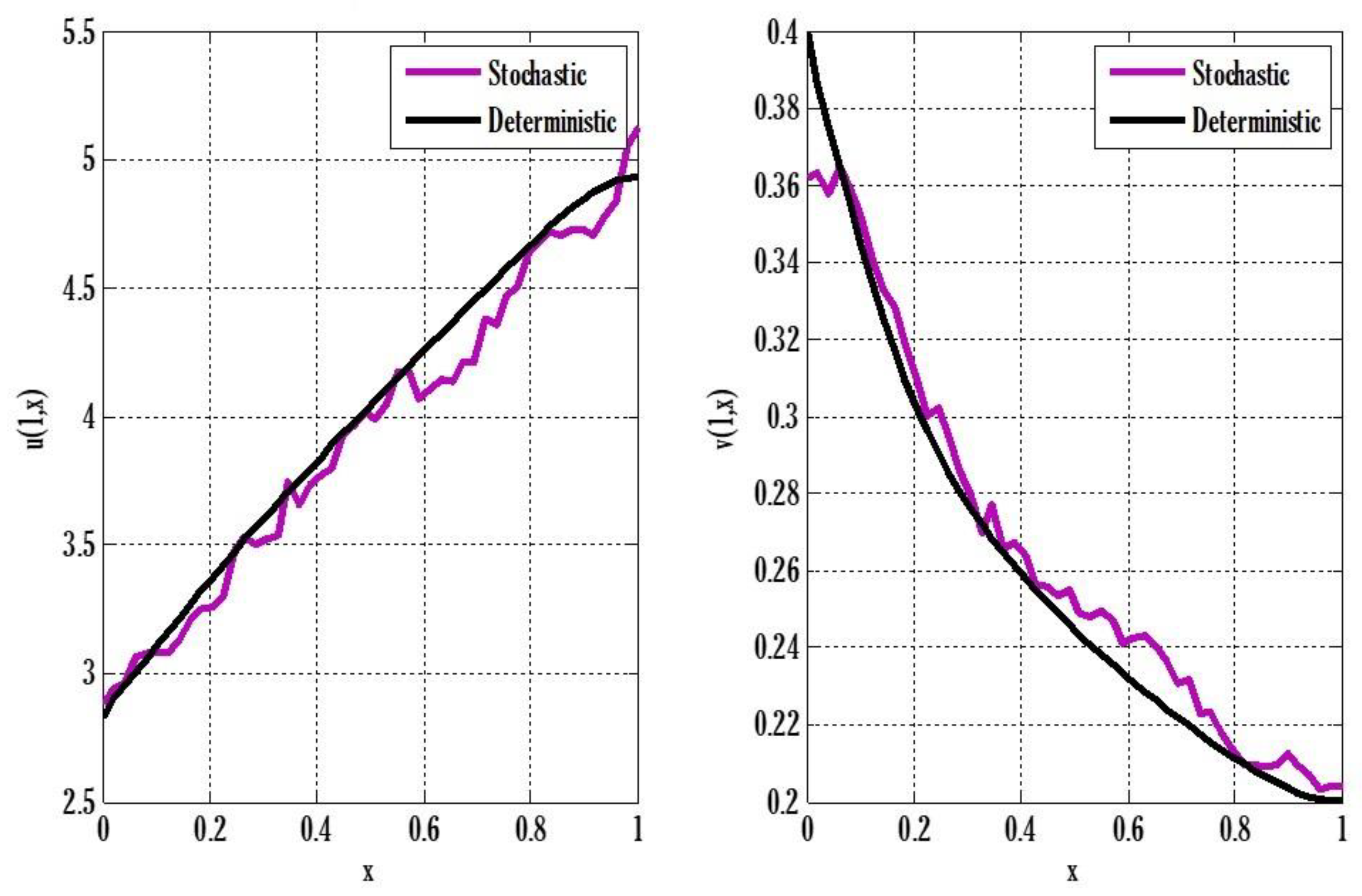
6. Numerical Experiment
| Algorithm 1 Pseudo code for the nonlinear problem. |
| ● Input the parameters and independent variables and . ● Start the constructing procedure of normal distribution using the command of “makedist,” with a mean of and a variance of . ● Start the “for” loop for the iterative method and input the initial conditions. ● Start the “for” loops for time and space. ● Input boundary conditions at both ends. ● Use the random of the normal distribution to choose a random value to find the solution of stochastic equations at each grid point and time level using the proposed scheme. ● End the “for” loops for space and time. ● Provide the stopping criteria to stop the iterative method. ● End the iterative “for” loop. |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolis, G.; Prigogine, I. Fluctuations in nonequilibrium systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Rafiq, M.; Baleanu, D.; Rehman, M.A. Spatio-temporal numerical modeling of auto-catalytic Brusselator model. Rom. J. Phys. 2019, 64, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Baleanu, D.; Korkmaz, A.; Rafiq, M.; Rehman, M.A.; Ali, M. Positivity preserving computational techniques for nonlinear autocatalytic chemical reaction model. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2020, 72, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Jawaz, M.; Rafiq, M.; Rehman, M.A.; Ali, M.; Ahmad, M.O. Numerical treatment of an epidemic model withspatial diffusion. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2018, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; S.S., T.; Imran, M.; Rafiq, M.; Rehman, M.A.; Younis, M. Numerical analysis of auto-catalytic glycolysis model. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 85213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.W.; Iqbal, M.S.; Ahmed, N.; Akgül, A.; Raza, A.; Rafiq, M.; Riaz, M.B. Numerical scheme and stability analysis of stochastic Fitzhugh-Nagumo model. Results Phys. 2022, 32, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.S.; Abodayeh, K.; Nawaz, Y. A Computational Scheme for Stochastic Non-Newtonian Mixed Convection Nanofluid Flow over Oscillatory Sheet. Energies 2023, 16, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, G.; Meade, D. A survey of spline collocation methods for the numerical solution of differential equations. In Mathematics for Large Scale Computing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 297–341. [Google Scholar]
- Arqub, O.A.; Al-Smadi, M. Fuzzy conformable fractional differential equations: Novel extended approach and new numerical solutions. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 12501–12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Ji, F.Y.; Mohammad-Sedighi, H. Difference equation versus differential equation on different scales. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2020, 31, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, G. Existence, uniqueness and space regularity of the adapted solutions of a backward. SPDE Stoch. Anal. Appl. 1996, 14, 461–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozzi, M.; López-Mimbela, J.A. Finite-time blowup and existence of global positive solutions of a semilinear. SPDE Stoch. Process. Appl. 2010, 120, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Yang, X. Existence and pathwise uniqueness to an SPDE driven by a-stable colored noise. Stoch. Process. Appl. 2019, 129, 2681–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeyer, R.; Bretschneider, T.; Janák, J.; Reiß, M. Parameter estimation in an SPDE model for cell repolarization SIAM/ASA. J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2022, 10, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyöngy, I.; Carles, R. On Lp-solutions of semilinear stochastic partial differential equations. Stoch. Process. Appl. 2000, 90, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, T. A stochastic partial differential equation with values in a manifold. J. Funct. Anal. 1992, 109, 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytnik, L. Stochastic partial differential equation driven bystable noise. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 2002, 123, 157–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Abdelmonem, A.; Li, Y. Mild solution of stochastic partial differential equation with nonlocal conditions and noncompact semigroups. Math. Slovaca 2019, 69, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyöngy, I.; Martínez, T. On numerical solution of stochastic partial differential equations of elliptic type Stochastics: An International. J. Probab. Stoch. Process. 2006, 78, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrani, M.; Hosseini, S.M. The role of coefficients of a general SPDE on the stability and convergence of a finite difference method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2010, 234, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.J.; Novosel, S.J.; Zhang, Z. Finite element and difference approximation of some linear stochastic partial differential equations. Stoch. Int. J. Probab. Stoch. Process. 1998, 64, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweilam, N.H.; ElSakout, D.M.; Muttardi, M.M. Numerical solution for stochastic extended Fisher-Kolmogorov equation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 151, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, F.; Rezaei, S.; Samadyar, N. Application of combination schemes based on radial basis functions and finite difference to solvestochastic coupled nonlinear time fractional sine-Gordon equations. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, W. Strongly convergent error analysis for aspatially semidiscrete approximation of stochastic partial differential equations with non-globally Lipschitz continuous coefficients. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 384, 113173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoomandan, M.; Soheili, A.R. Spectral collocation method forstochastic partial differential equations with fractional Brownian motion. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 389, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.; Iqbal, M.; Seadawy, A.; Baber, M.; Younis, M.; Rizvi, S. Numerical scheme and analytical solutions to the stochastic nonlinear advection diffusion dynamical model. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Nu-Merical Simulation 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Tunç, O.; ur Rahman, G.; Khan, H.; Nadia, E. Mathematical analysis of stochastic epidemic model of MERS-corona & application of ergodic theory. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 207, 130–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alzabut, J.; Alobaidi, G.; Hussain, S.; Madi, E.N.; Khan, H. Stochastic dynamics of influenza infection: Qualitative analysis and numerical results. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 10316–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Abdeljawad, T.; Din, A. Modeling the dynamics of stochastic norovirus epidemic model with time delay. FRACTALS 2022, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, R. Consistency and stability of a Milstein-Galerkin finite element scheme for semilinear. SPDE Stoch. Partial. Differ. Equ. Anal. Comput. 2014, 2, 471–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C. A combination of finite difference and Wong-Zakai methods for hyperbolic stochastic partial differential equations. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 2006, 24, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoo, M.; Mohebbian, A. Approximation of stochastic partial differential equations with Stochastic Crank-Nicolson method. In Proceedings of the 21st Seminar on Mathematical Analysis and its Applications, Hamedan, Iran, 26–27November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Mao, X.; Song, Q.; Wu, F.; Yin, G. Strong convergence of Euler-Maruyama schemes for McKean-Vlasov stochastic differential equations under local Lipschitz conditions of state variables. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 2022, 43, 1001–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, X.; Mao, X. Convergence rate and stability of the truncated Euler-Maruyama method forstochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 337, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Metwally, H.; Sohaly, M.A.; Elbaz, I.M. Mean-square stability of the zero equilibrium of the nonlinear delay differential equation: Nicholson’s blowflies application. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 105, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehry, A.S.; Shah, R.; Shah, N.A.; Dassios, I. A Reliable Technique for Solving Fractional Partial Differential Equation. Axioms 2022, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderremy, A.A.; Shah, R.; Shah, N.A.; Aly, S.; Nonlaopon, K. Comparison of two modified analytical approaches for the systems of time fractional partial differential equations. AIMS Math. 2023, 8, 7142–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Hamed, Y.S.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Chung, J.-D.; Shah, R.; Khan, A. A Comparative Analysis of Fractional-Order Kaup–Kupershmidt Equation within Different Operators. Symmetry 2022, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Agarwal, P.; Chung, J.D.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Hamed, Y.S. Analysis of Optical Solitons for Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation with Detuning Term by Iterative Transform Method. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, N.; Dassios, I.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D. Fractional System of Korteweg-De Vries Equations via Elzaki Transform. Mathematics 2021, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.; Ahmed, N.; Iqbal, M.S.; Rafiq, M.; Raza, A.; Akgül, A. Reliable numerical analysis for stochastic reaction-diffusion system. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 015209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S. Solutions of Boundary Value Problems for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations by Fixed Point Methods. Doctoral studies of engineering science, Graz University of Technology, Styria, Austria, 21 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shatanawi, W.; Raza, A.; Arif, M.S.; Rafiq, M.; Bibi, M.; Mohsin, M. Essential features preserving dynamics of stochastic Dengue model. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 126, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abodayeh, K.; Raza, A.; Arif, M.S.; Rafiq, M.; Bibi, M.; Mohsin, M. Stochastic numerical analysis for impact of heavy alcohol consumption on transmission dynamics of gonorrhoea epidemic. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 62, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Arif, M.S.; Rafiq, M. A reliable numerical analysis for stochastic gonorrhea epidemic model with treatment effect. Int. J. Biomath. 2019, 12, 1950072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.S.; Raza, A.; Shatanawi, W.; Rafiq, M.; Bibi, M. A stochastic numerical analysis for computer virus model with vertical transmission over the internet. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2019, 61, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib Arif, M.; Raza, A.; Abodayeh, K.; Rafiq, M.; Bibi, M.; Nazeer, A. A numerical efficient technique for the solution of susceptible infected recovered epidemic model. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 124, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, N.; SenGupta, I. Fractional Barndorff-Nielsen and Shephard model: Applications in variance and volatility swaps, and hedging. Ann. Financ. 2021, 17, 529–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
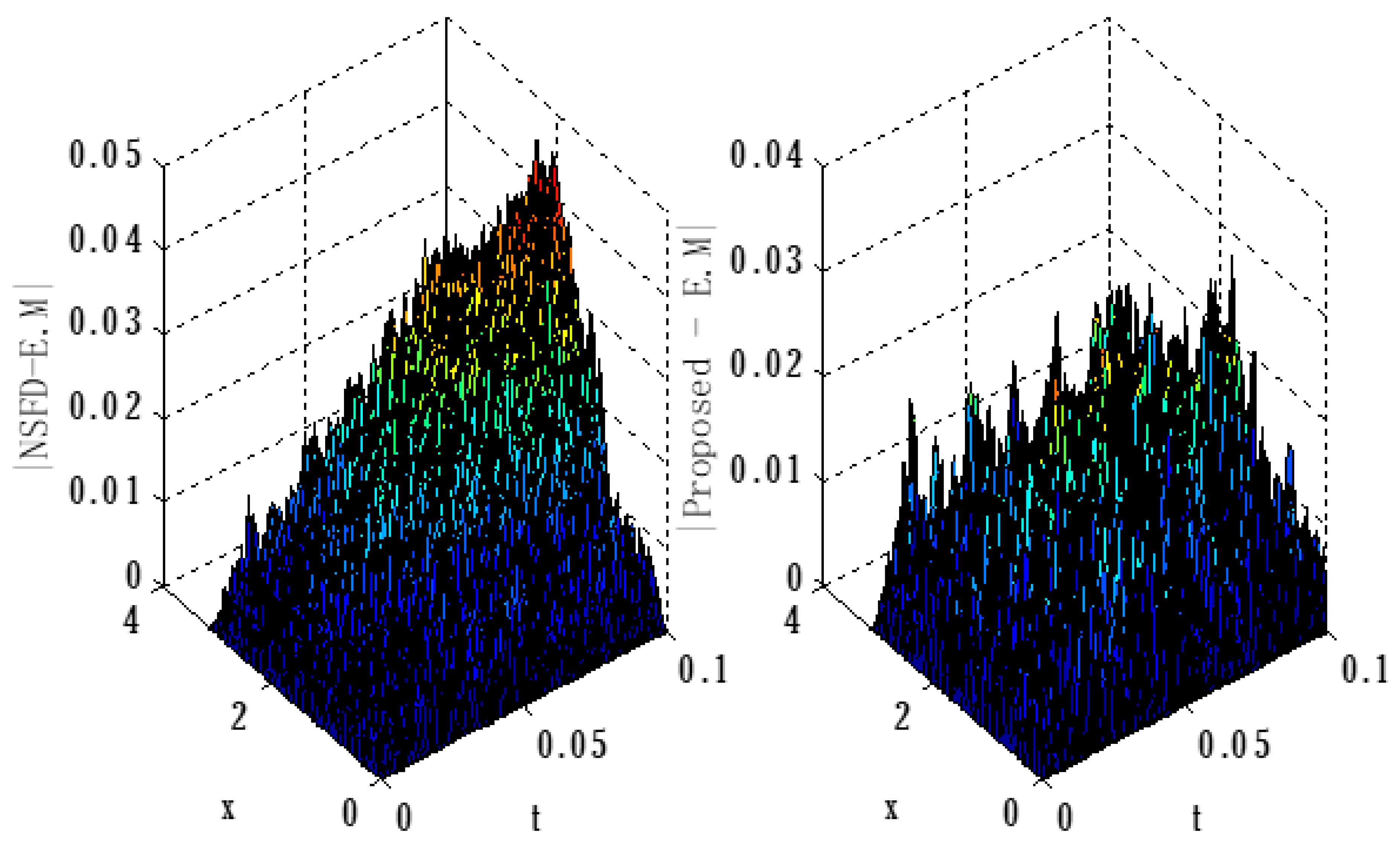
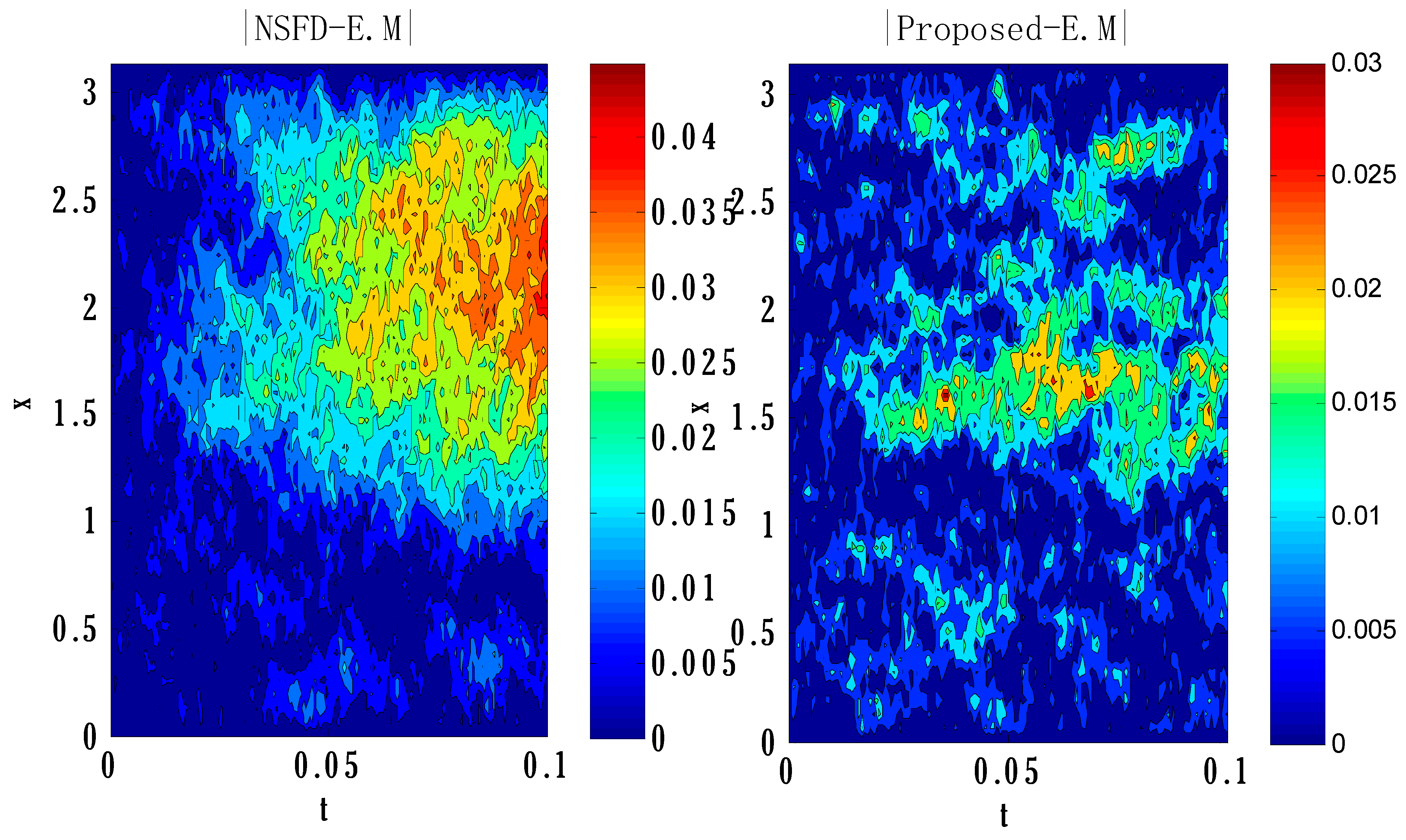

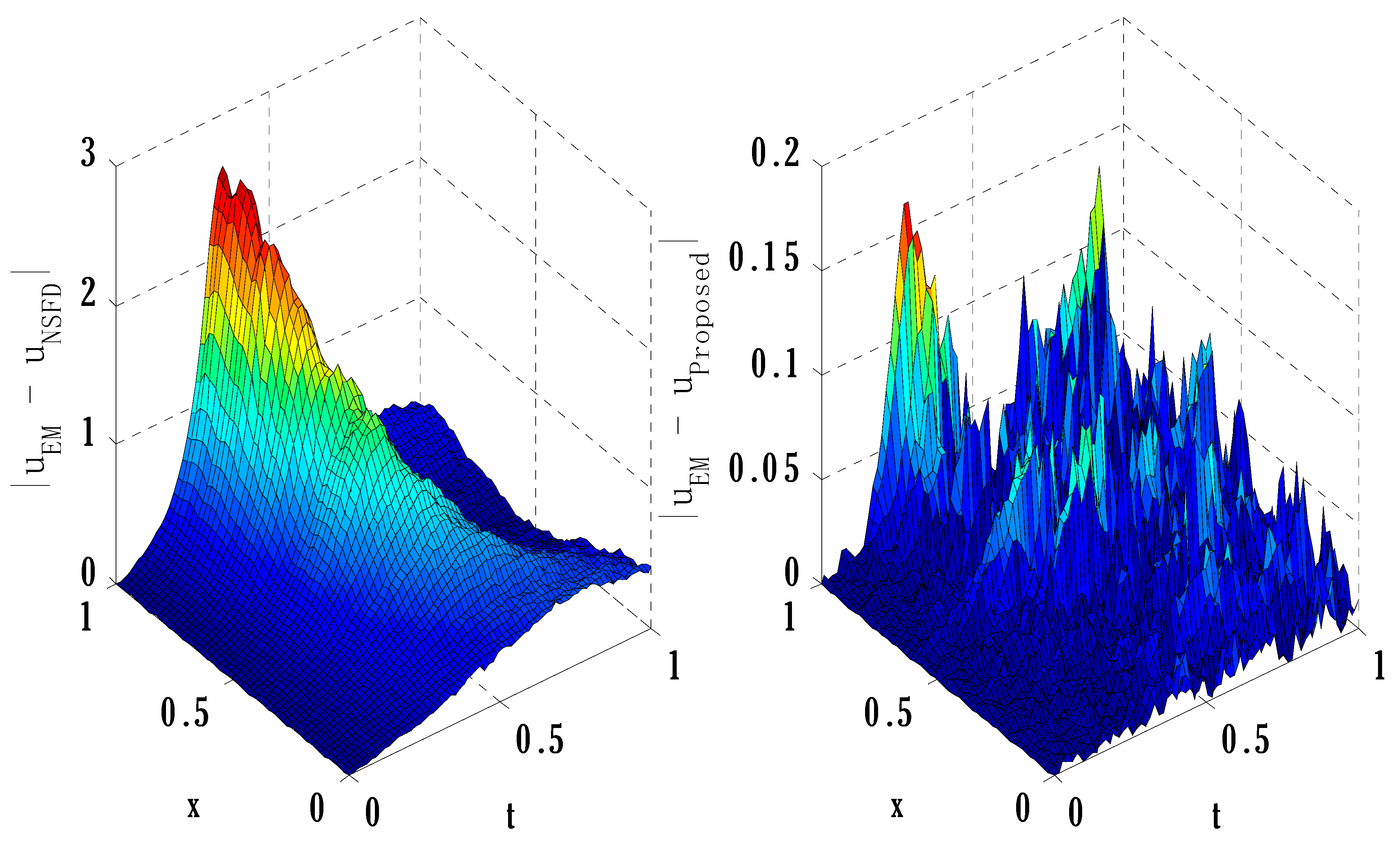
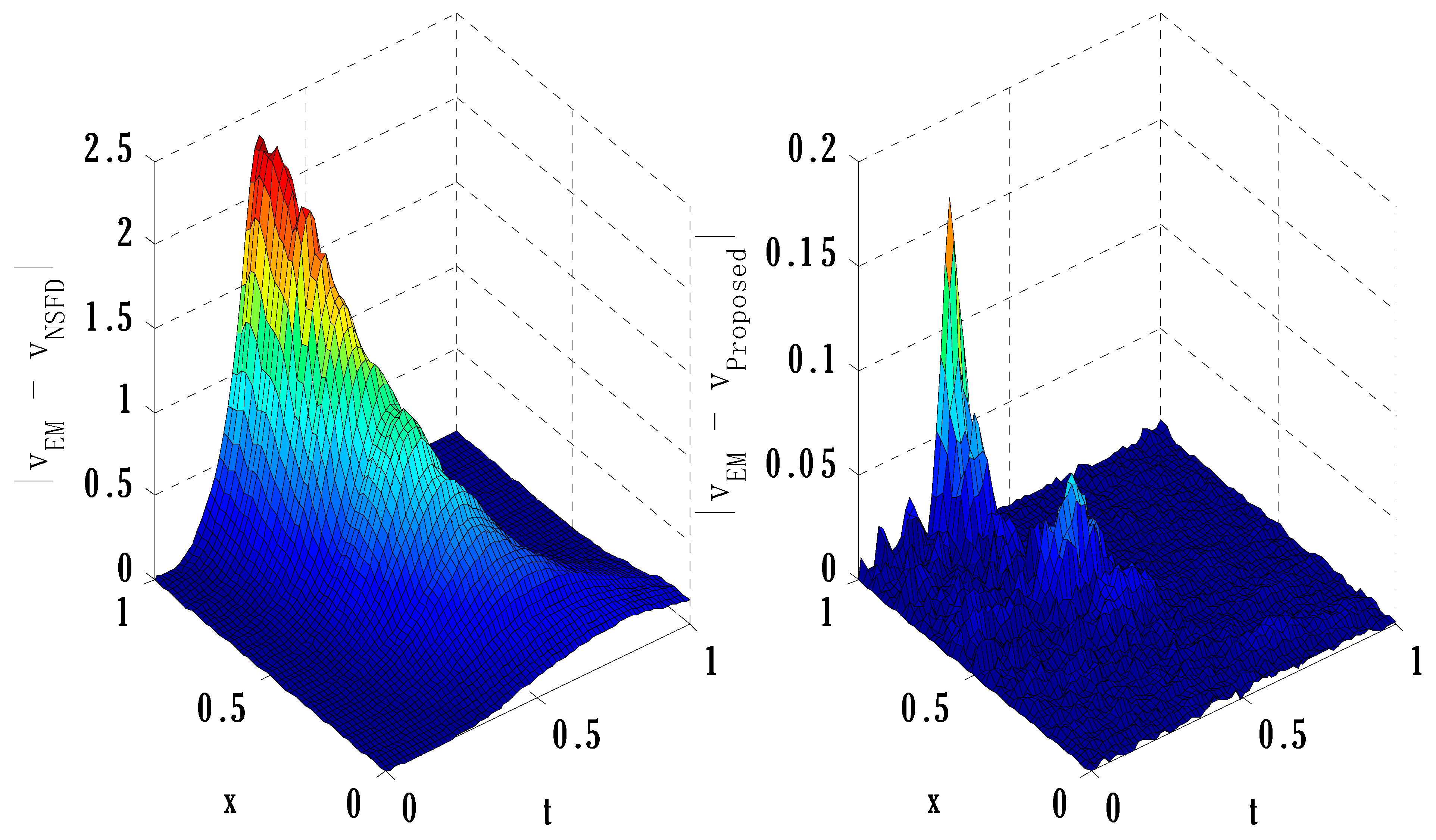
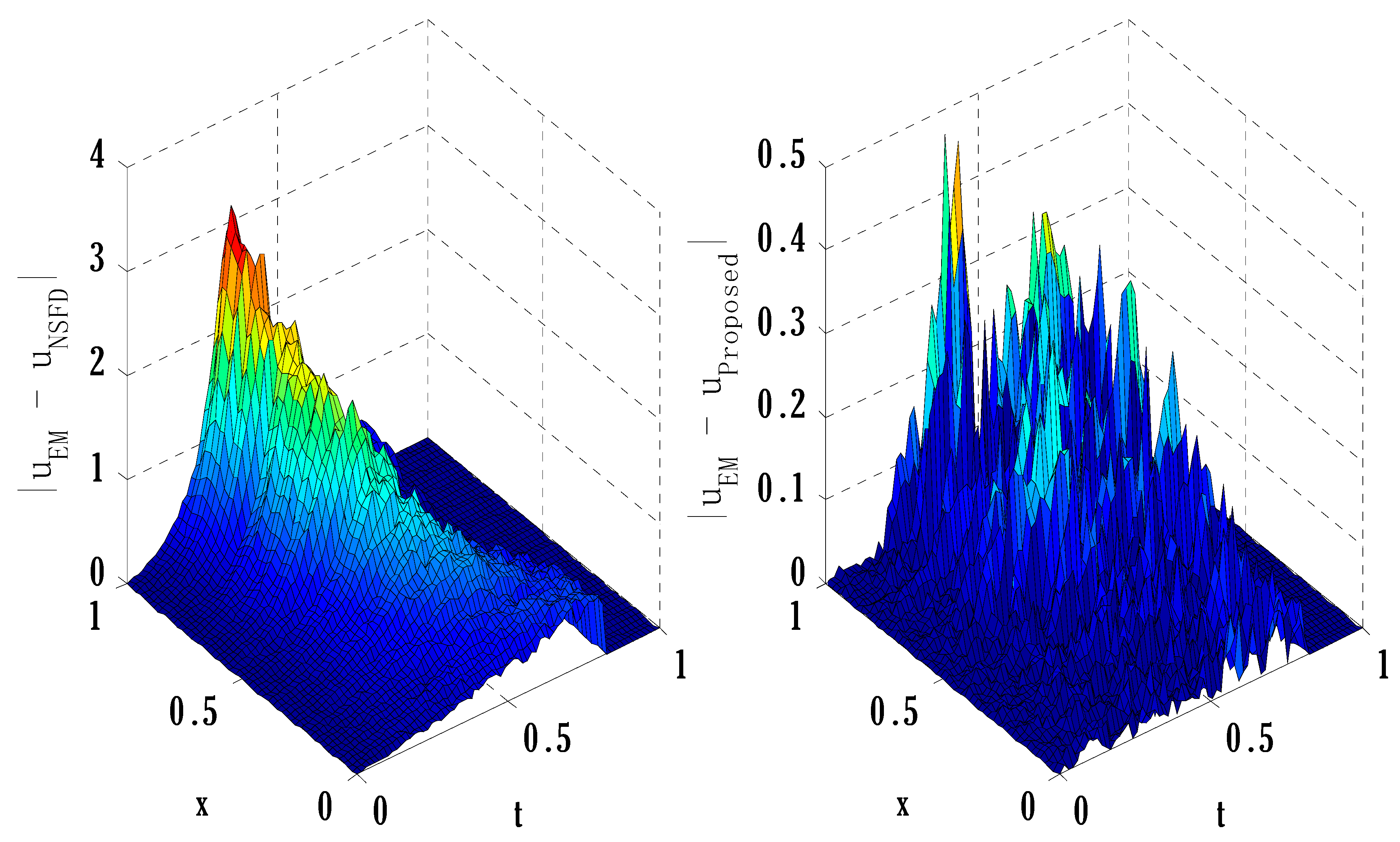
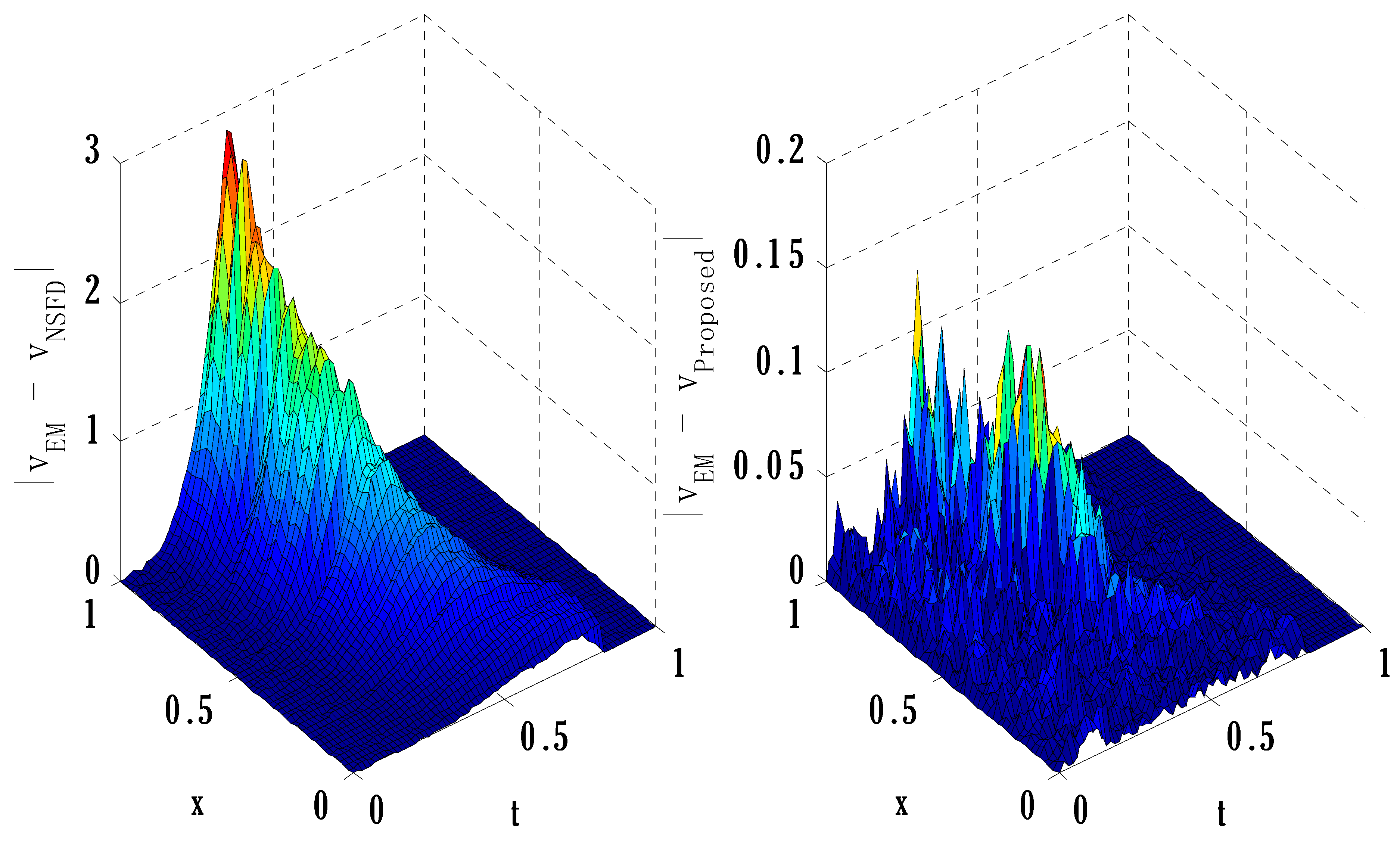
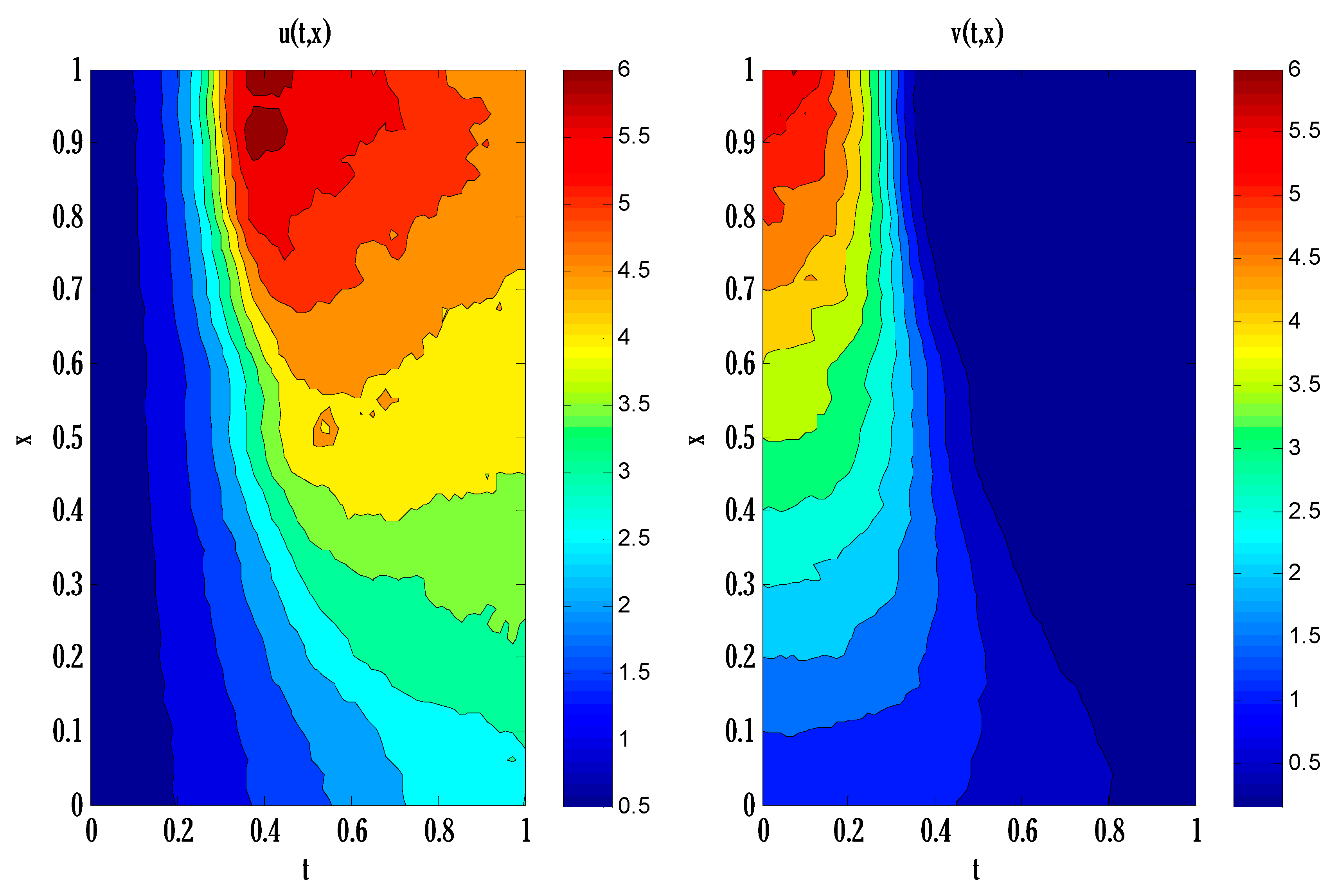
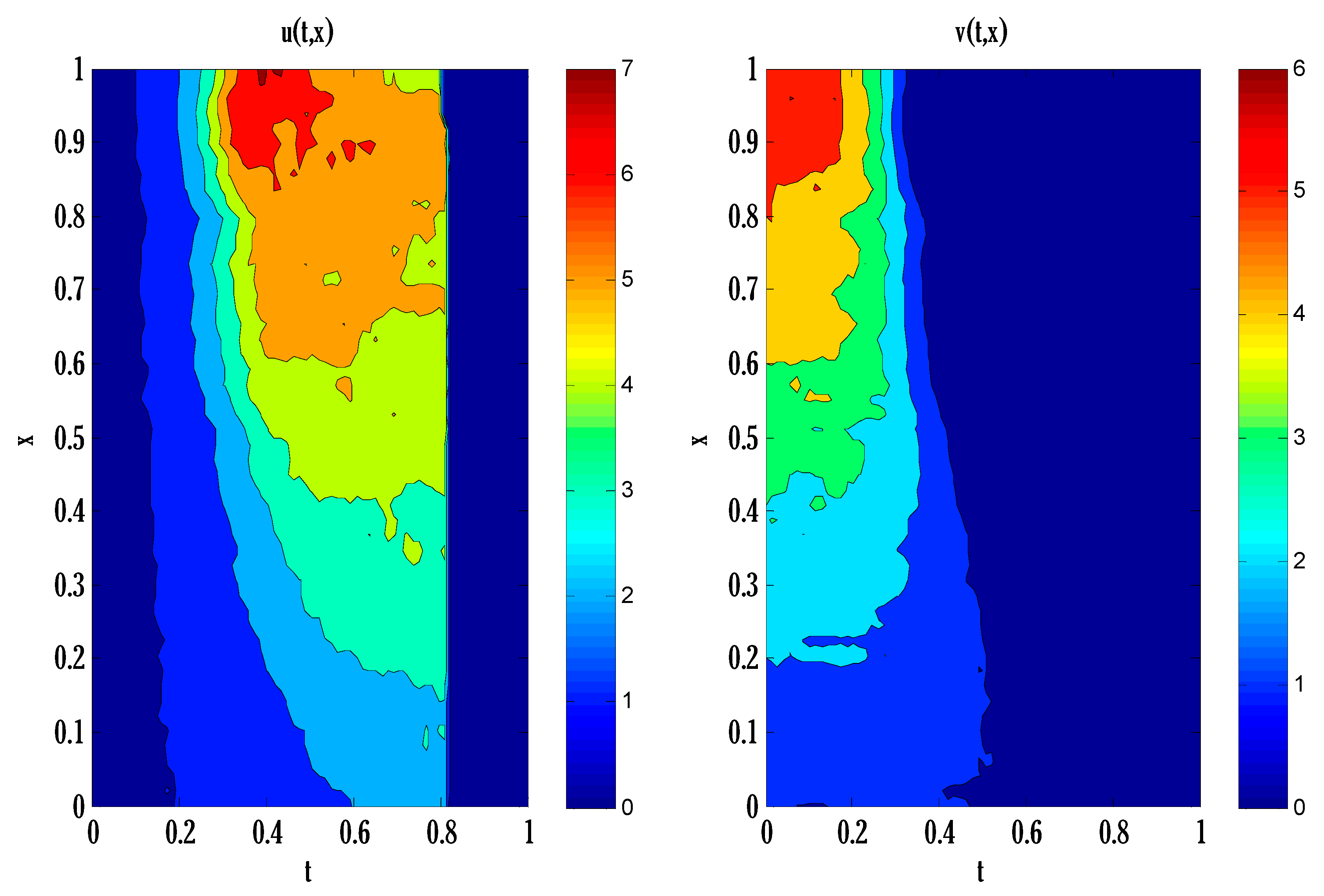
| Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stochastic Proposed | Stochastic NSFD | ||
| 25 | 150 | 0.0024 | 3.4370 |
| 300 | 0.0012 | 3.4520 | |
| 50 | 150 | 0.0078 | 5.0020 |
| 300 | 0.0197 | 4.9376 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arif, M.S.; Abodayeh, K.; Nawaz, Y. A Reliable Computational Scheme for Stochastic Reaction–Diffusion Nonlinear Chemical Model. Axioms 2023, 12, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050460
Arif MS, Abodayeh K, Nawaz Y. A Reliable Computational Scheme for Stochastic Reaction–Diffusion Nonlinear Chemical Model. Axioms. 2023; 12(5):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050460
Chicago/Turabian StyleArif, Muhammad Shoaib, Kamaleldin Abodayeh, and Yasir Nawaz. 2023. "A Reliable Computational Scheme for Stochastic Reaction–Diffusion Nonlinear Chemical Model" Axioms 12, no. 5: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050460
APA StyleArif, M. S., Abodayeh, K., & Nawaz, Y. (2023). A Reliable Computational Scheme for Stochastic Reaction–Diffusion Nonlinear Chemical Model. Axioms, 12(5), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050460









