Parameter Estimation of the Exponentiated Pareto Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling and Simple Random Sampling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ranked Set Sampling
- Select units at random from a specified population.
- Rank these units with some expert judgment without measuring them.
- Retain the smallest judged unit and return the others.
- Continue the process until ordered units are measured.
- These ordered observations are called a cycle.
- Process repeated cycle to get observations.
3. Estimation Using Ranked Set Sampling
4. Simulation Study
- Based on , the bias and for estimates of and are more significant than that based on .
- For both methods of estimations, it is clear that the bias and decrease as set sizes increase for fixed values of .
- As the value of increases, the bias and increase in almost all cases.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.C.; Gupta, P.L.; Gupta, R.D. Modeling failure time data by Lehman alternatives. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1998, 27, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.L.; Kotz, S.; Balakrishnan, N. Continuous Univariate Distributions; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsanullah, M.; Nevzorov, V.B.; Shakil, M. Order Statistics: An Introduction; Handbook of statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 16, pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shawky, A.I.; Abu-Zinadah, H.H. Exponentiated Pareto distribution: Different method of estimations. Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci. 2009, 4, 677–693. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzinadah, H. A study on mixture of exponentiated pareto and exponential distributions. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 6, 358–376. [Google Scholar]
- Afify, W. On estimation of the exponentiated Pareto distribution under different sample schemes. Stat. Methodol. 2010, 7, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.D.; Kundu, D. Theory & methods: Generalized exponential distributions. Aust. New Zealand J. Stat. 1999, 41, 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.D.; Kundu, D. Generalized exponential distribution: Different method of estimations. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2001, 69, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.E.; Yhiea, N.M.; El-Said, S.M. Estimation of parameters for the exponentiated Pareto distribution based on progressively type-II right censored data. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 2016, 24, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzaghal, A. The Exponentiated Gamma-Pareto Distribution with Application to Bladder Cancer Susceptibility. J. Stat. Appl. Probab. Lett. 2020, 7, 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Makouei, R.; Khamnei, H.J.; Salehi, M. Moments of order statistics and k-record values arising from the complementary beta distribution with application. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 390, 113386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, G. A method for unbiased selective sampling, using ranked sets. Am. Stat. 2005, 59, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahasi, K.; Wakimoto, K. On unbiased estimates of the population mean based on the sample stratified by means of ordering. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1968, 20, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, T.R.; Clutter, J.L. Ranked set sampling theory with order statistics background. Biometrics 1972, 28, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samawi, H.M.; Ahmed, M.S.; Abu-Dayyeh, W. Estimating the population mean using extreme ranked set sampling. Biom. J. 1996, 38, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttlak, H. Median ranked set sampling. J. Appl. Stat. Sci. 1997, 6, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saleh, M.F.; Al-Kadiri, M.A. Double-ranked set sampling. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2000, 48, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Patil, G.P.; Sinha, A.K.; Taillie, C. Ranked set sampling: An annotated bibliography. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 1995, 2, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bai, Z.; Sinha, B. Ranked Set Sampling: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 176. [Google Scholar]
- Khamnei, H.J.; Mayan, S.R. Comparison of parameter estimation in the exponentiated Gumbel distribution based on ranked set sampling and simple random sampling. J. Math. Stat. Sci. 2016, 2016, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Khamnei, H.J.; Abusaleh, S. Estimation of parameters in the generalized logistic distribution based on ranked set sampling. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2017, 24, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sabry, M.H.; Almetwally, E.M. Estimation of the Exponential Pareto Distribution’s Parameters under Ranked and Double Ranked Set Sampling Designs. Pak. J. Stat. Oper. Res. 2021, 17, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Shabbir, J. On the use of ranked set sampling for estimating super-population total: Gamma population model. Sci. Iranica. Trans. E Ind. Eng. 2021, 28, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorniani, S.; Mohammadpour, A.; Nematollahi, N. Estimation of the parameter of Le’vy distribution using ranked set sampling. AUT J. Math. Comput. 2021, 2, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, K.E. An Introduction to Numerical Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
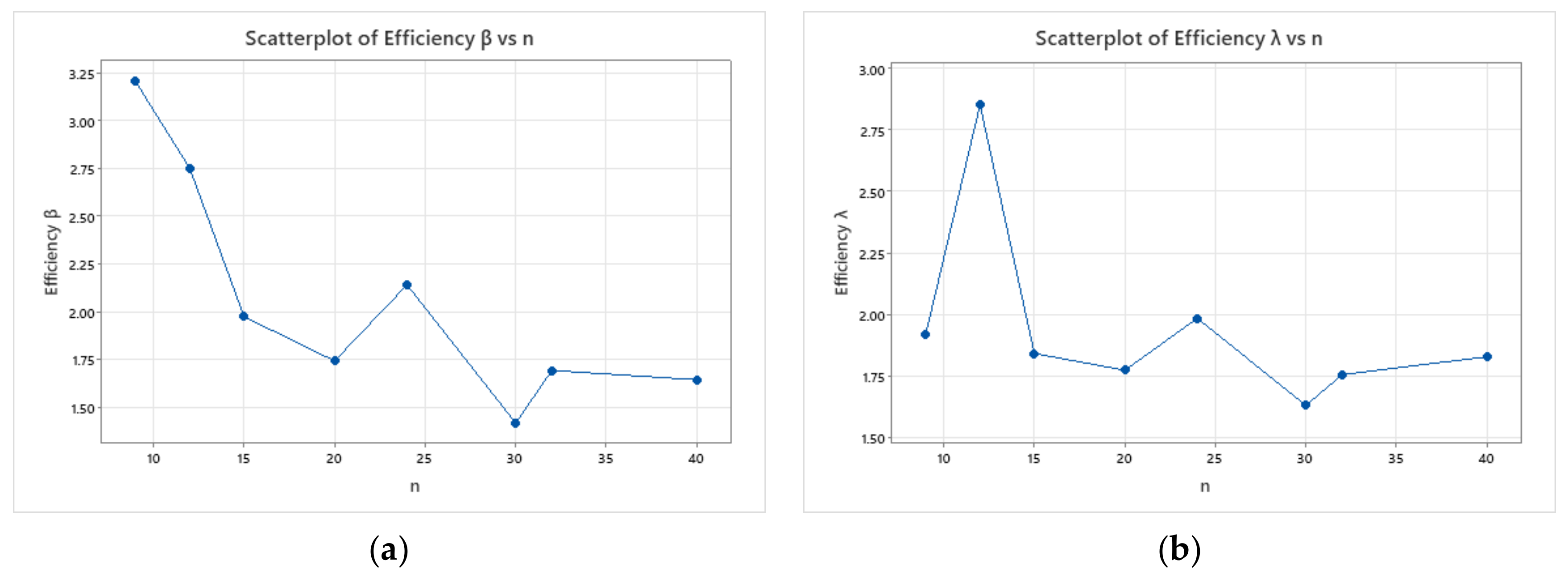

| (k, s) | RSS | n | Efficiency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3, 3) | 0.115 (0.091) | 0.328 (0.658) | 9 | 0.197 (0.291) | 0.493 (1.262) | 3.207 | 1.918 |
| (4, 3) | 0.072 (0.035) | 0.209 (0.298) | 12 | 0.127 (0.099) | 0.367 (0.819) | 2.751 | 2.851 |
| (3, 5) | 0.059 (0.031) | 0.171 (0.240) | 15 | 0.092 (0.057) | 0.282 (0.474) | 1.975 | 1.841 |
| (4, 5) | 0.043 (0.019) | 0.130 (0.149) | 20 | 0.063 (0.033) | 0.180 (0.260) | 1.744 | 1.773 |
| (3, 8) | 0.032 (0.013) | 0.087 (0.105) | 24 | 0.055 (0.025) | 0.180 (0.225) | 2.142 | 1.984 |
| (3, 10) | 0.026 (0.010) | 0.074 (0.082) | 30 | 0.036 (0.016) | 0.098 (0.116) | 1.419 | 1.630 |
| (4, 8) | 0.026 (0.009) | 0.077 (0.076) | 32 | 0.034 (0.015) | 0.108 (0.128) | 1.694 | 1.755 |
| (4, 10) | 0.021 (0.007) | 0.066 (0.057) | 40 | 0.031 (0.012) | 0.088 (0.094) | 1.645 | 1.828 |
| (k, s) | RSS | n | Efficiency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3, 3) | 0.318 (0.698) | 0.328 (0.320) | 9 | 0.552 (2.917) | 0.328 (0.563) | 1.759 | 4.180 |
| (4, 3) | 0.191 (0.233) | 0.147 (0.162) | 12 | 0.339 (0.721) | 0.243 (0.366) | 2.263 | 3.096 |
| (3, 5) | 0.155 (0.200) | 0.118 (0.131) | 15 | 0.239 (0.369) | 0.190 (0.231) | 1.765 | 1.847 |
| (4, 5) | 0.114 (0.121) | 0.092 (0.086) | 20 | 0.157 (0.194) | 0.122 (0.137) | 1.596 | 1.609 |
| (3, 8) | 0.081 (0.074) | 0.061 (0.061) | 24 | 0.140 (0.147) | 0.126 (0.120) | 1.964 | 2.989 |
| (3, 10) | 0.066 (0.058) | 0.052 (0.048) | 30 | 0.089 (0.087) | 0.069 (0.068) | 1.416 | 1.501 |
| (4, 8) | 0.068 (0.056) | 0.055 (0.045) | 32 | 0.085 (0.090) | 0.074 (0.073) | 1.542 | 1.616 |
| (4, 10) | 0.054 (0.039) | 0.047 (0.034) | 40 | 0.077 (0.068) | 0.062 (0.055) | 1.641 | 1.751 |
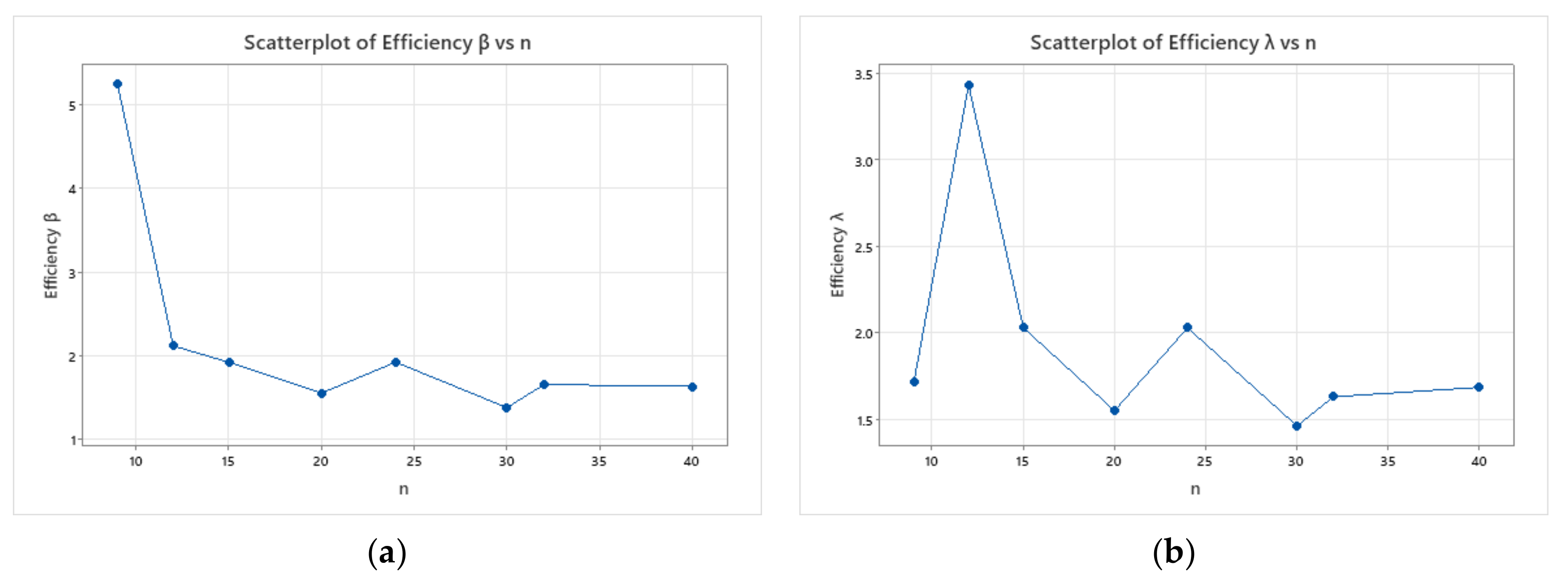
| (k, s) | RSS | n | Efficiency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3, 3) | 0.593 (2.496) | 0.193 (0.243) | 9 | 1.056 (3.094) | 0.280 (0.417) | 5.244 | 1.716 |
| (4, 3) | 0.345 (0.737) | 0.128 (0.127) | 12 | 0.620 (2.529) | 0.206 (0.269) | 2.121 | 3.432 |
| (3, 5) | 0.278 (0.624) | 0.103 (0.102) | 15 | 0.428 (0.426) | 0.108 (0.092) | 1.927 | 2.030 |
| (4, 5) | 0.204 (0.368) | 0.079 (0.068) | 20 | 0.277 (0.571) | 0.105 (0.106) | 1.558 | 1.551 |
| (3, 8) | 0.143 (0.210) | 0.053 (0.048) | 24 | 0.248 (0.426) | 0.108 (0.092) | 1.927 | 2.030 |
| (3, 10) | 0.117 (0.166) | 0.046 (0.039) | 30 | 0.155 (0.243) | 0.060 (0.054) | 1.384 | 1.463 |
| (4, 8) | 0.119 (0.161) | 0.047 (0.035) | 32 | 0.150 (0.262) | 0.063 (0.058) | 1.660 | 1.631 |
| (4, 10) | 0.095 (0.112) | 0.041 (0.027) | 40 | 0.133 (0.188) | 0.054 (0.044) | 1.637 | 1.686 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khamnei, H.J.; Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I.; Fathi, M.; Valackienė, A.; Ghorbani, S. Parameter Estimation of the Exponentiated Pareto Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling and Simple Random Sampling. Axioms 2022, 11, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060293
Khamnei HJ, Meidute-Kavaliauskiene I, Fathi M, Valackienė A, Ghorbani S. Parameter Estimation of the Exponentiated Pareto Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling and Simple Random Sampling. Axioms. 2022; 11(6):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060293
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhamnei, Hossein Jabbari, Ieva Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, Masood Fathi, Asta Valackienė, and Shahryar Ghorbani. 2022. "Parameter Estimation of the Exponentiated Pareto Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling and Simple Random Sampling" Axioms 11, no. 6: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060293
APA StyleKhamnei, H. J., Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I., Fathi, M., Valackienė, A., & Ghorbani, S. (2022). Parameter Estimation of the Exponentiated Pareto Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling and Simple Random Sampling. Axioms, 11(6), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060293








