Temporal Cox Process with Folded Normal Intensity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Folded Normal Intensity Process
2.1. Definition
2.2. Properties
- (a)
- (mean value function)
- (b)
- (variance value function)
3. Properties of the CP-NFI
3.1. Process Density
3.2. Properties of the Process
- For the mean of over :
- For the variance of over :
- For the covariance of over :
- (a)
- (mean value function)
- (b)
- (variance value function)
- (c)
- (covariance value function)
- (a’)
- ;
- (b’)
- ;
- (c’)
- .
- (a)
- (mean value function)
- (b)
- (variance value function)with
- (c)
- (covariance value function)with
- (i)
- , defined in the Equation (13), is well defined;
- (ii)
- ;
- (iii)
- ;
- (iv)
- .
- (a)
- (mean value function)
- (b)
- (variance value function)
- (c)
- (covariance function)
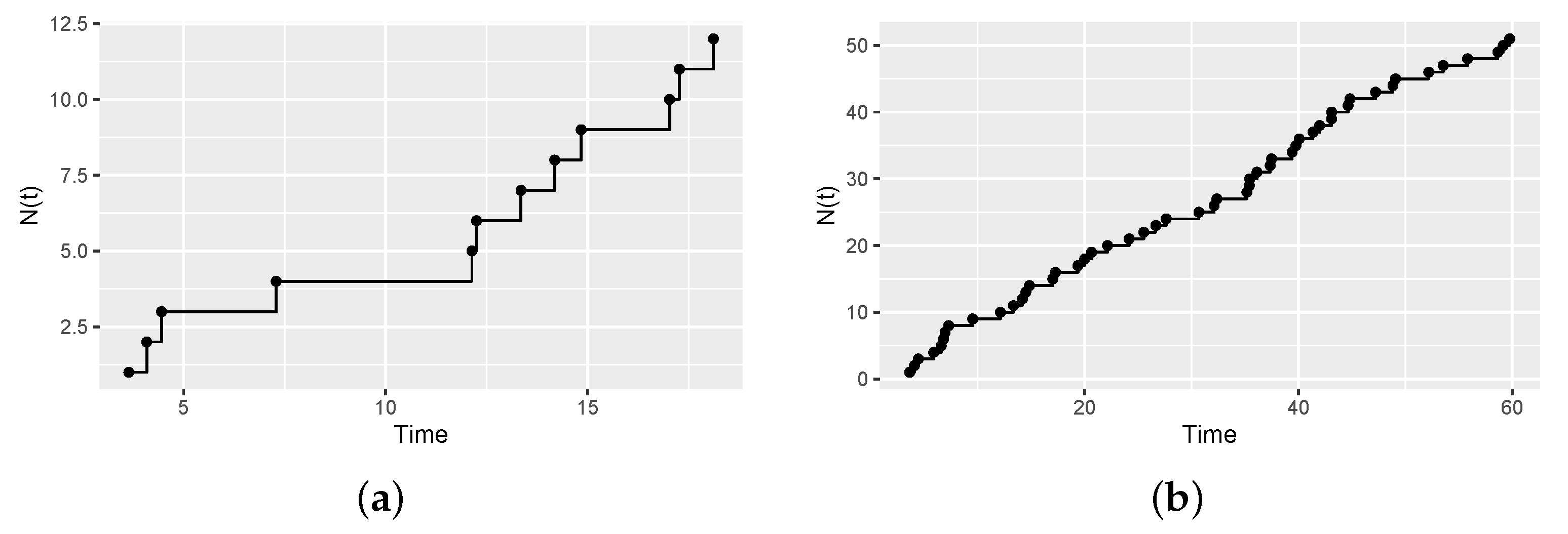
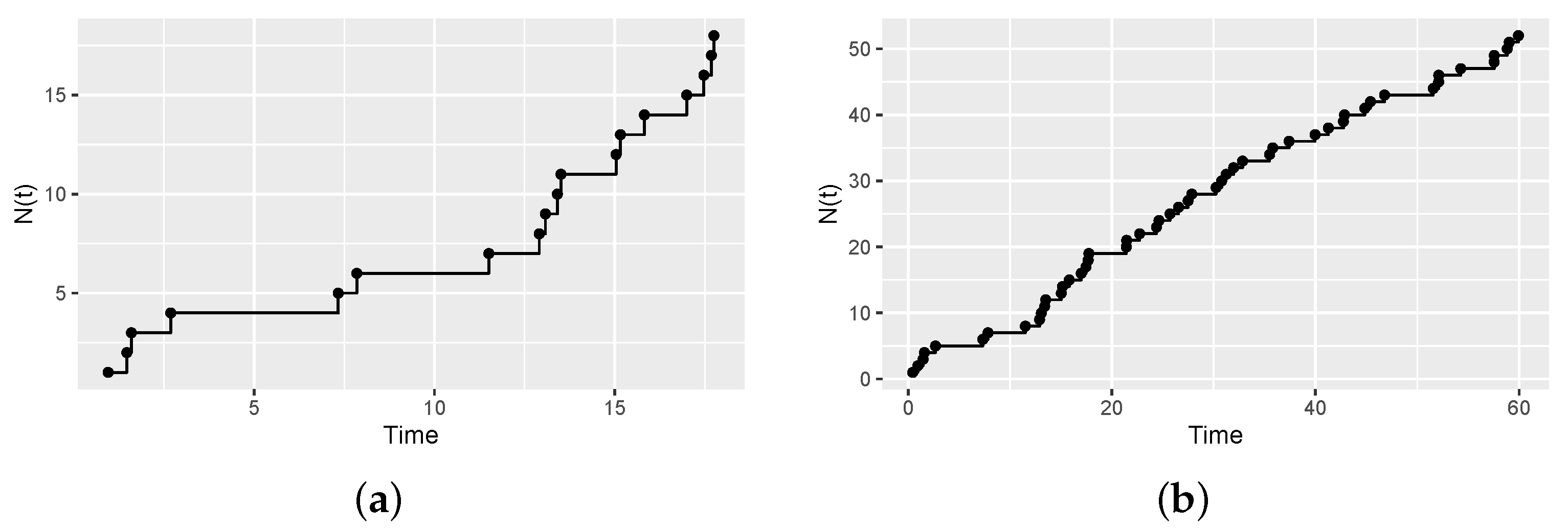
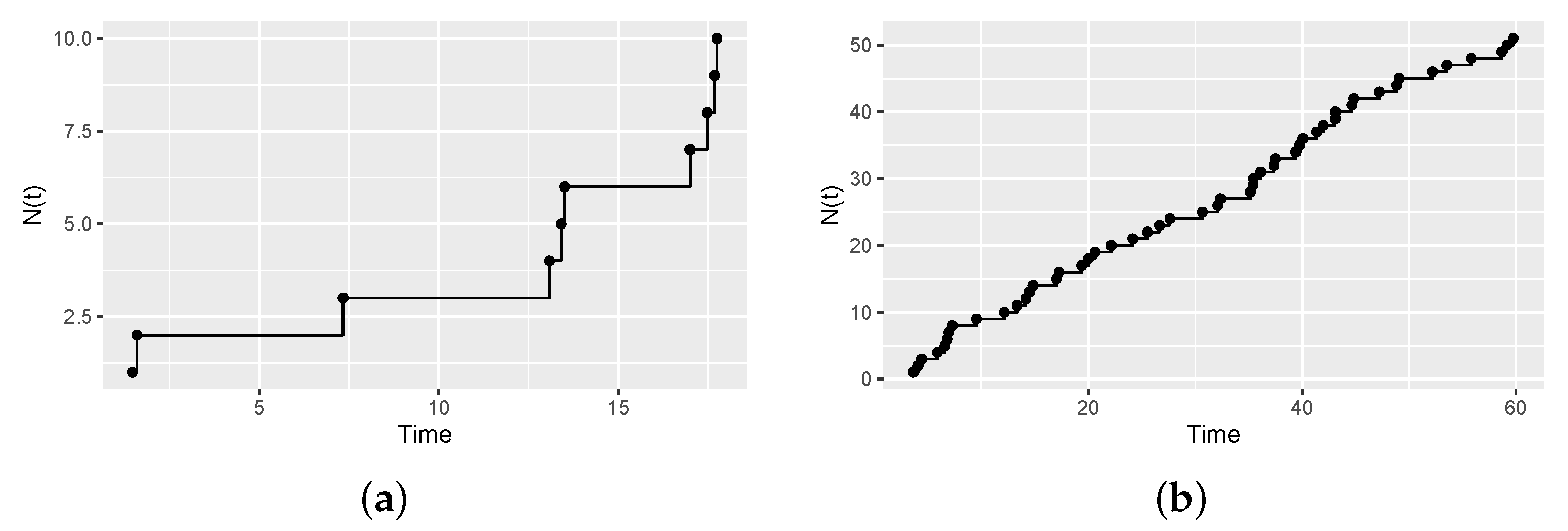
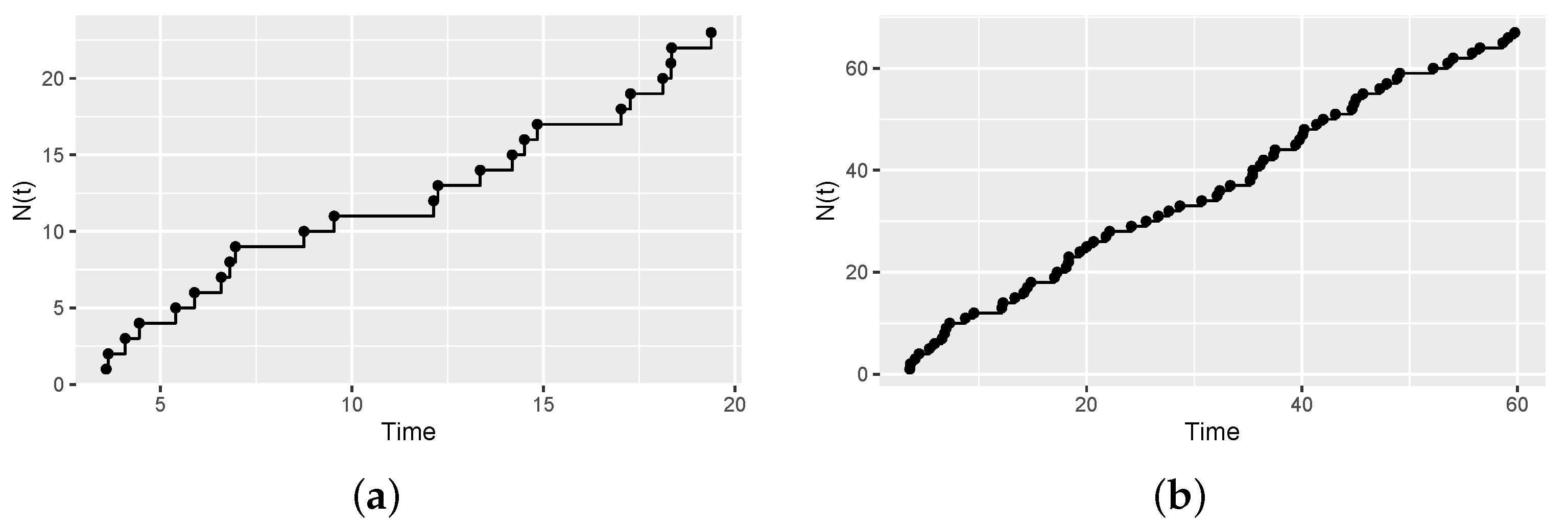
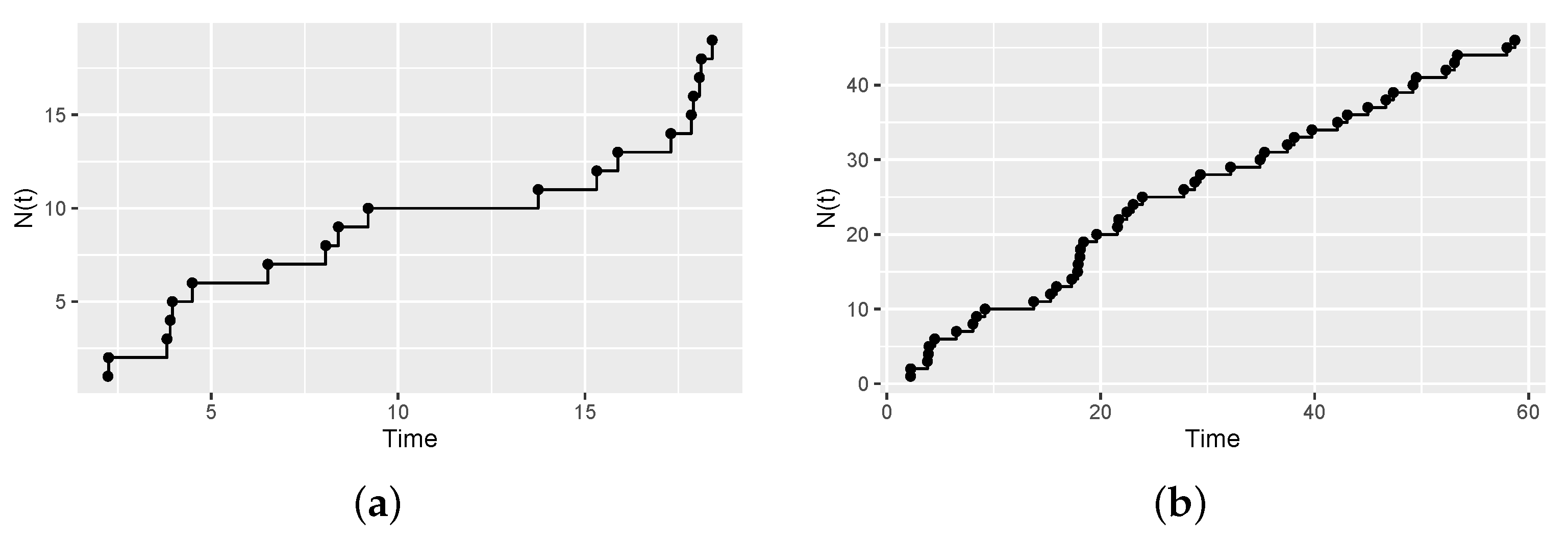
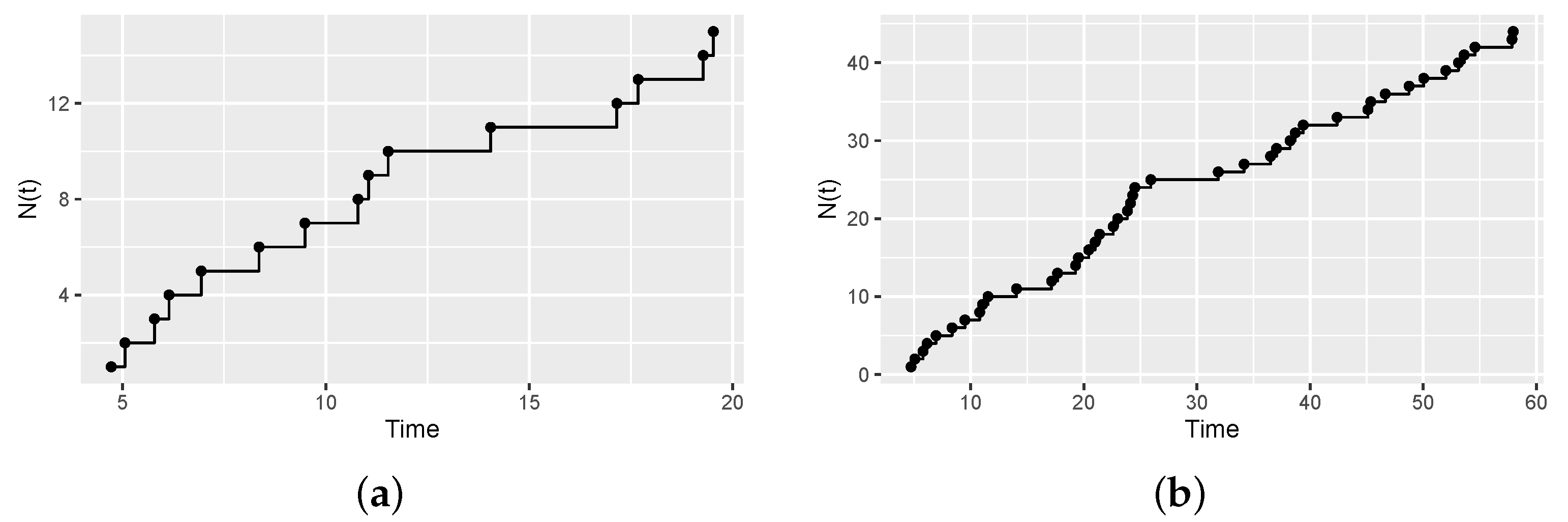
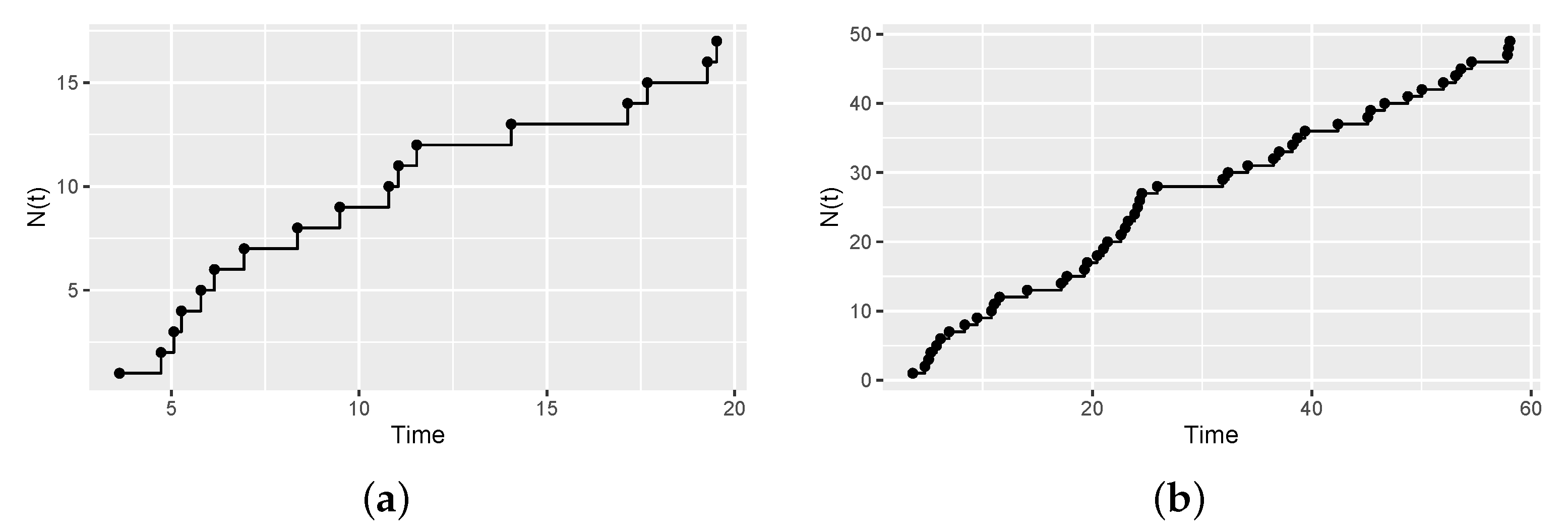
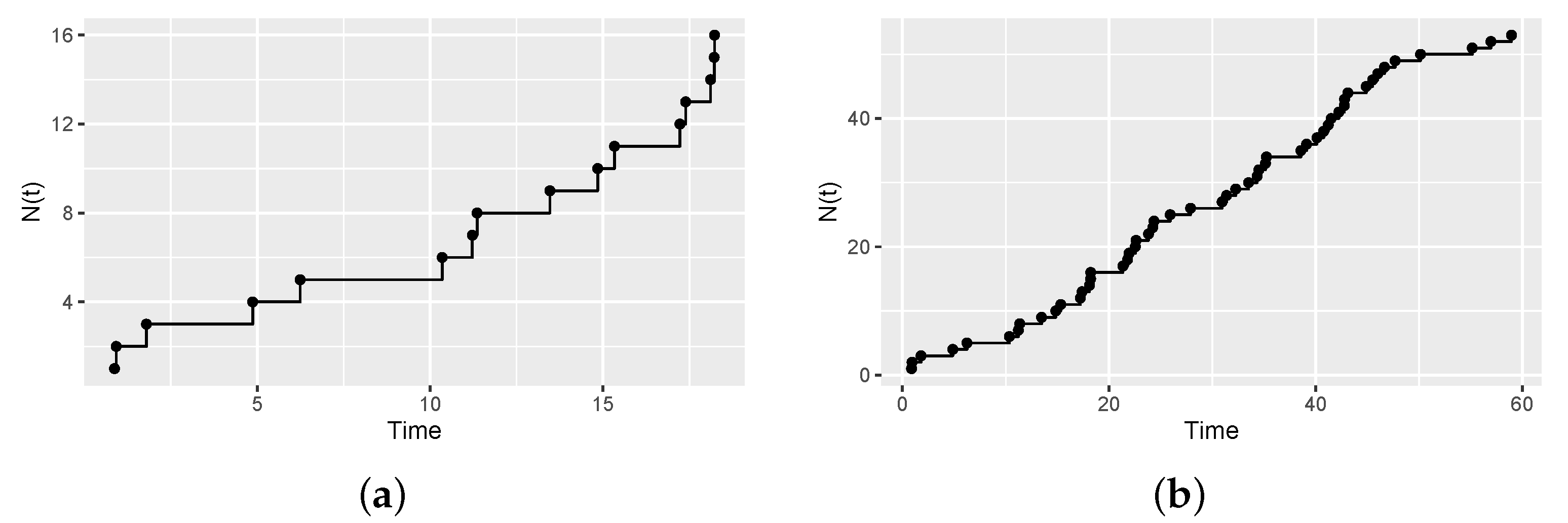
4. Simulation Studies
- Step 1
- Start and
- Step 2
- Generate
- Step 3
- Make . If , end up. Else, go to Step 4
- Step 4
- If , make y .
- Step 5
- Go to Step 2.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cox, D.R. Some statistical methods connected with series of events. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1955, 17, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, M.R. Introduction to Prabability Models, 8th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, R.J. Probabilidade: Um Curso em Naaível Intermediário; Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada-CNPq, Projeto Euclides: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.R.; Miller, H.D. The Theory of Stochastic Processes; Imperial College: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Parzen, E. Procesos Estocásticos; Holden Day Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Rozanov, Y.A. Procesos Aleatorios; Editorial Mir: Moscú, Russia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Daley, D.J.; Vere-Jones, D. An Introduction to the Theory of Point Processes, Volume I: Elementary Theory and Methods, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, J.; Syversveen, A.R.; Waagepetersen, R.P. Log Gaussian Cox processes. Scand. J. Stat. 2008, 25, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, P.J.; Moraga, P.; Rowlingson, B.; Taylor, B.M. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Log-Gaussian Cox Processes: Extending the Geostatistical Paradigm. Stat. Sci. 2013, 28, 542–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Pacheco, F.; Møller, J. Log Gaussian Cox processes on the sphere. Spat. Stat. 2018, 26, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, V.; Damoulas, T.; Bonilla, E. Efficient Inference in Multi-task Cox Process Models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09781. [Google Scholar]
- Waagepetersen, R.; Guan, D.Y.; Jalilian, A.; Mateu, J. Analysis of multi-species point patterns by using multivariate log-Gaussian Cox processes. J. R. Statist. Soc. C 2016, 65, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.P.; Torres-Signes, A.; Ruiz-Medina, M.D.; Mateu, J. Spatial Cox processes in an infinite-dimensional framework. TEST 2022, 31, 175–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, N.; Siino, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Adelfio, G. Local spatial log-Gaussian Cox processes for seismic data. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, V.; Bodlak, K.; Møller, J.; Waagepetersen, R. Application of log-Gaussian Cox processes in disease mapping. In ISI International Conference on Environmental Statistics and Health; University of Santiago de Compostela: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, J.; díaz-Avalos, C. Structured Spatio-Temporal Shot-Noise Cox Point Process Models, with a View to Modelling Forest Fires. Scand. J. Stat. 2010, 37, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirota, S.; Banerjee, S. Scalable Inference for Space-Time Gaussian Cox Processes. J. Time Ser. Anal. 2018, 40, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder, C.; Bishop, A. Gamma Gaussian Cox Processes. Methodology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaxman, S.; Teh, Y.W.; Sejdinovic, D. Poisson intensity estimation with reproducing kernels. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; Volume 54, pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.P.; Murray, I.; MacKay, D.J.C. Tractable nonparametric Bayesian inference in Poisson processes with gaussian process intensities. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML ’09), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, F.C.; Nelson, L.S.; Nottingham, R.B. The folded normal distribution. Technometrics 1961, 3, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagris, T.; Beneki, C.; Hassani, H. On the Folded Normal Distribution. Mathematics 2014, 2, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarakis, S.; Panaretos, J. On some bivariate extensions of the folded normal and the folded T distributions. J. Appl. Statist. Sci. 2001, 10, 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, A.K.; Chatterjee, M. On multivariate folded normal distribution. Sankhya Indian J. Stat. 2013, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, R.; Robotti, C. On Moments of Folded and Truncated Multivariate Normal Distributions. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2017, 26, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, S.; Bakar, A.; Anuar, S. New Folded Models for the Log-Transformed Norwegian Fire Claim Data. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2015, 44, 4408–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kozubowski, T.J. A folded Laplace distribution. J. Stat. Distrib. Appl. 2015, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotin, M.T. On the law of frequency of errors. Mat. Sb. 1923, 31, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, M.; Chakraborty, A.K. A simple algorithm for calculating values for folded normal distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2016, 86, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, G.L.; Fei, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Q. Folded normal regression models with applications in biomedicine. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 379, 112941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Wei, A. Gaussian integrals involving absolute value functions. Inst. Math. Stat. Collect. 2009, 5, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, J.; Waagepetersen, R.P. Statistical Inference for Cox Processes. In Spatial Cluster Modelling; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 37–60. [Google Scholar]
- Loéve, M. Probability Theory, 2nd ed.; Van Nostrand: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Tierney, L.; Kadane, J.B. Accurate Approximations for Posterior Moments and Marginal Densities. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Az-Zo’bi, E. An approximate analytic solution for isentropic flow of an inviscid gas equations. Arch. Mech. 2014, 66, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Az-Zo’bi, E. A reliable analytic study for higher-dimensional telegraph equation. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2019, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Az-Zo’bi, E.; Al-Amb, M.O.; Yildirim, A.; Alzoubi, W.A. Revised reduced differential transform method using Adomian’s polynomials with convergence analysis. Math. Eng. Sci. Aerosp. (MESA) 2020, 11, 827–840. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Gabriel, E. Représentation, Analyse et Simulation de Processus Ponctuels Spatio-Temporels; 1éres Rencontres R: Bordeaux, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, M.R. Simulation, Second Edition: Programming Methods and Applications (Statistical Modeling and Decision Science); Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dassios, A.; Jang, J. The Distribution of the Interval between Events of a Cox Process with Shot Noise Intensity. J. Appl. Math. Stoch. Anal. 2008, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinichiro, S.; Gelfand, A.E. Inference for log Gaussian Cox processes using an approximate marginal posterior. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.10359. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, M.; Nathoo, F.; Johnson, T. Bayesian Computation for Log-Gaussian Cox Processes—A Comparative Analysis of Methods. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2017, 87, 2227–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F.B.; Gamerman, D. Exact Bayesian inference in spatiotemporal Cox processes driven by multivariate Gaussian processes. J. R. Soc. Ser. B 2018, 80, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder, C.; Bishop, A.N. Fast Bayesian Intensity Estimation for the Permanental Process. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’17), Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kelling, C.; Murali, H. A two-stage Cox process model with spatial and nonspatial covariates. Spat. Stat. 2022, 51, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolis, O.; Riquelme Quezada, L.M.; Ibacache-Pulgar, G. Temporal Cox Process with Folded Normal Intensity. Axioms 2022, 11, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11100513
Nicolis O, Riquelme Quezada LM, Ibacache-Pulgar G. Temporal Cox Process with Folded Normal Intensity. Axioms. 2022; 11(10):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11100513
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolis, Orietta, Luis M. Riquelme Quezada, and Germán Ibacache-Pulgar. 2022. "Temporal Cox Process with Folded Normal Intensity" Axioms 11, no. 10: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11100513
APA StyleNicolis, O., Riquelme Quezada, L. M., & Ibacache-Pulgar, G. (2022). Temporal Cox Process with Folded Normal Intensity. Axioms, 11(10), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11100513





