The Strike–Slip Fault Effect on a Reef–Shoal Reservoir in the Northern Sichuan Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
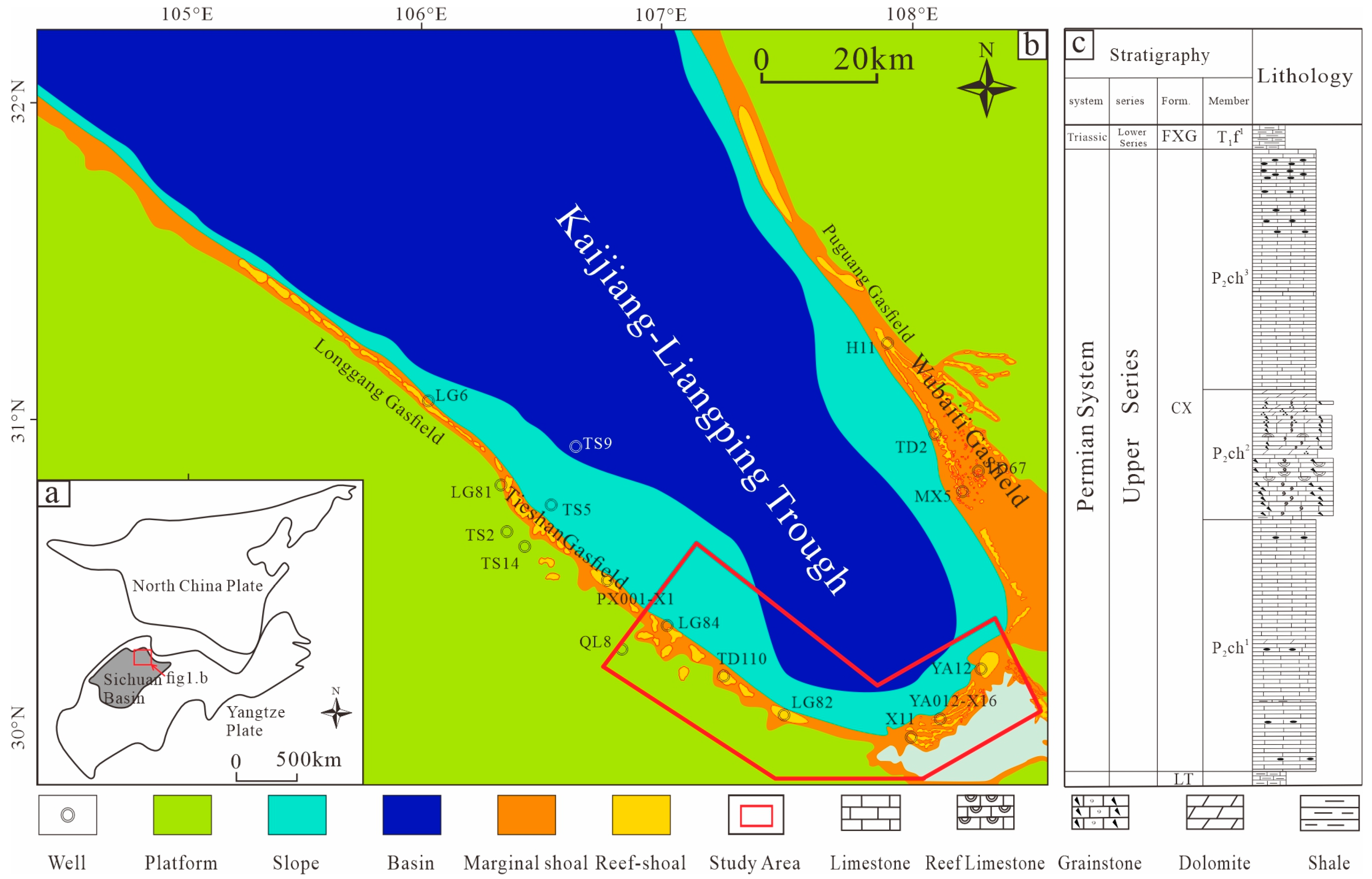
2. Geological Background
3. Data and Methods
4. Results
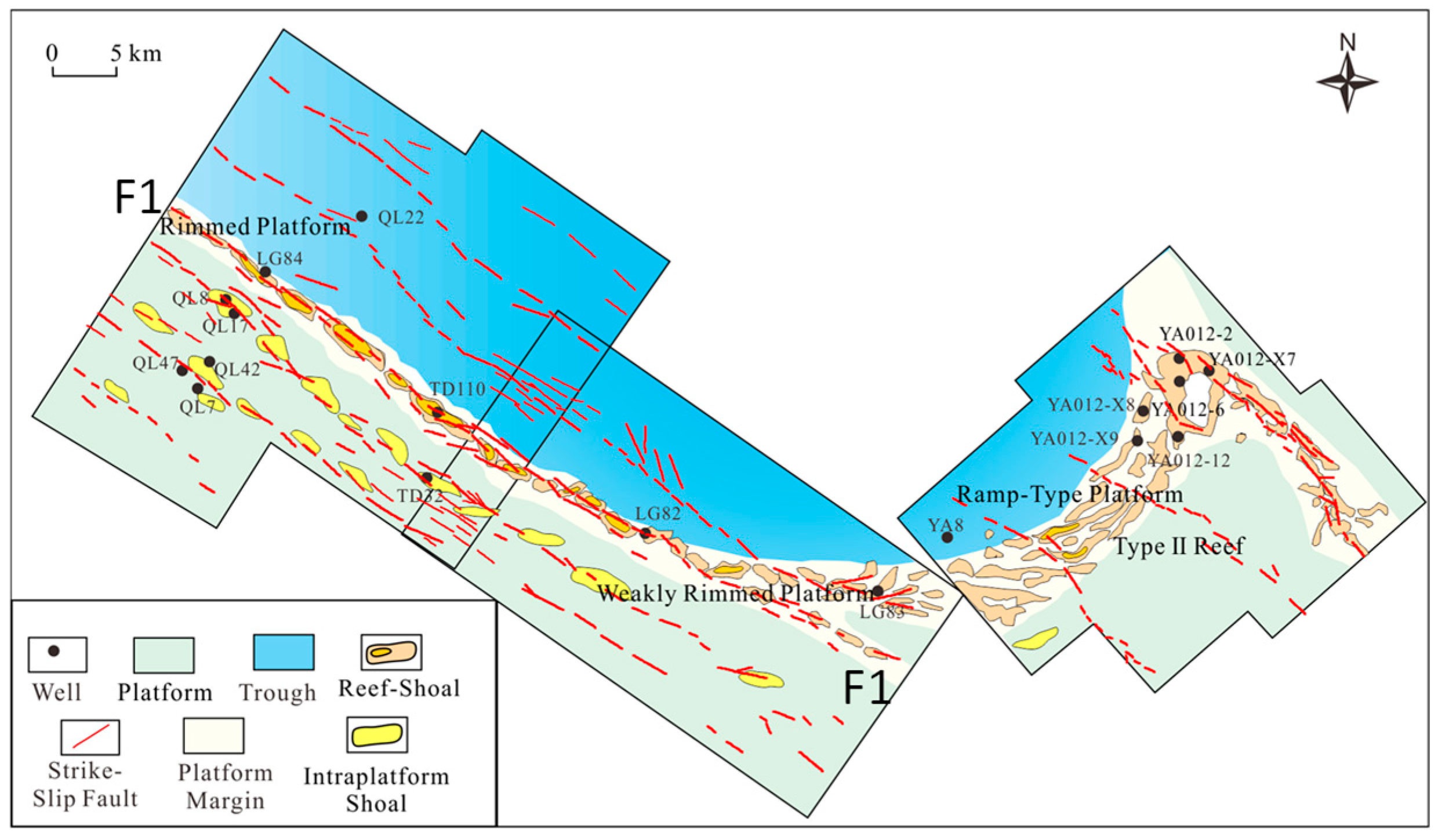
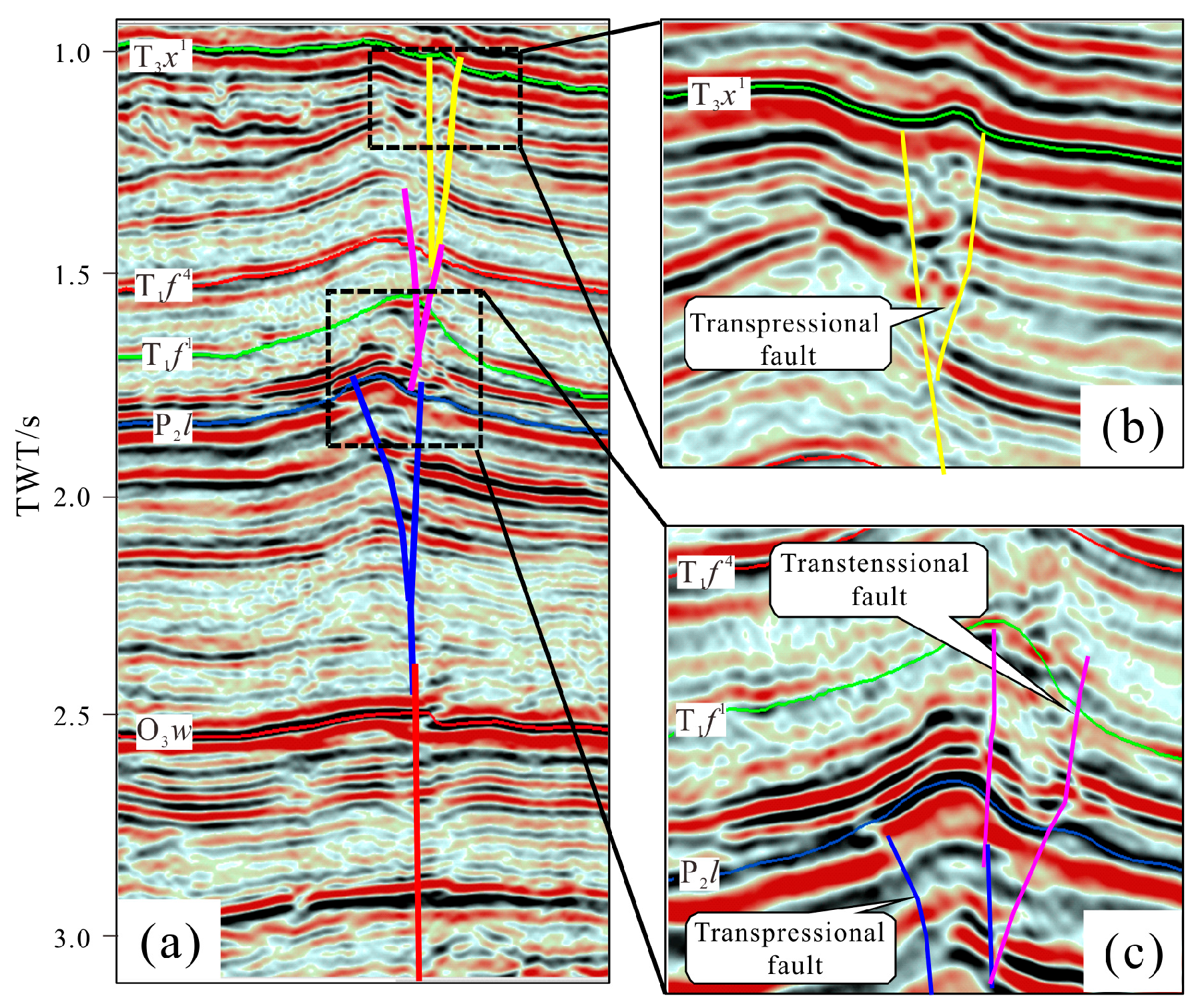
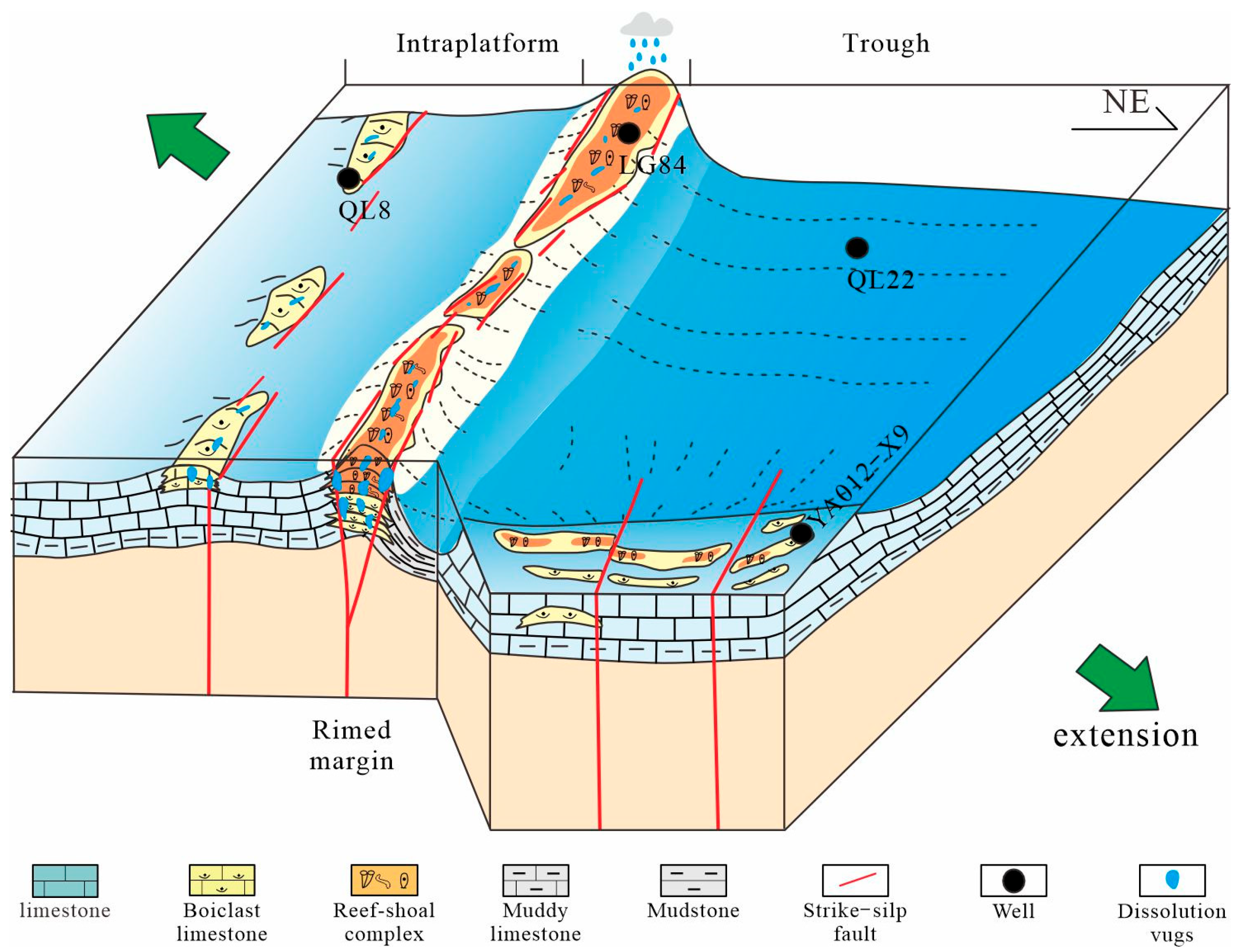
4.1. The Strike–Slip Fault Distribution in the Platform Margin
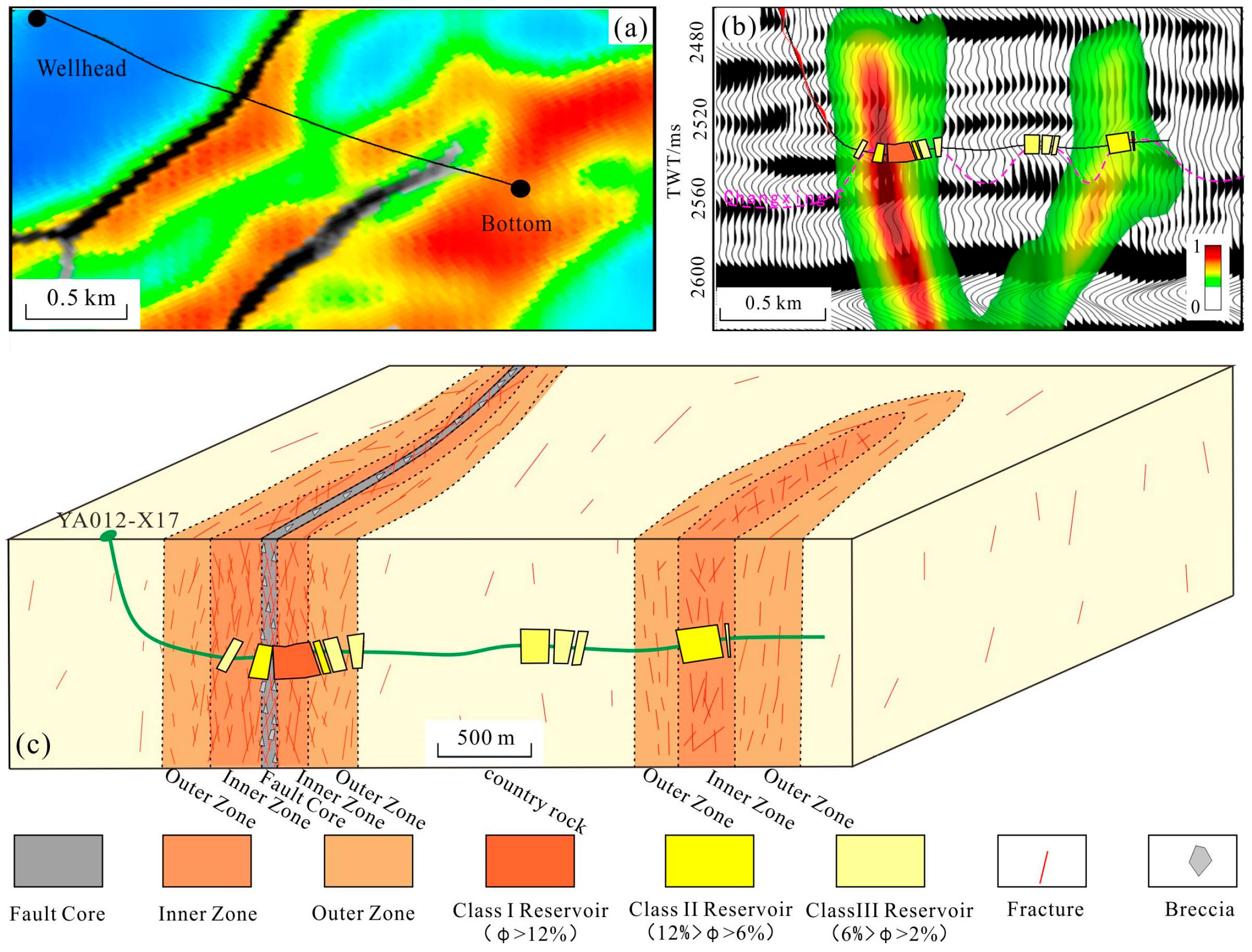
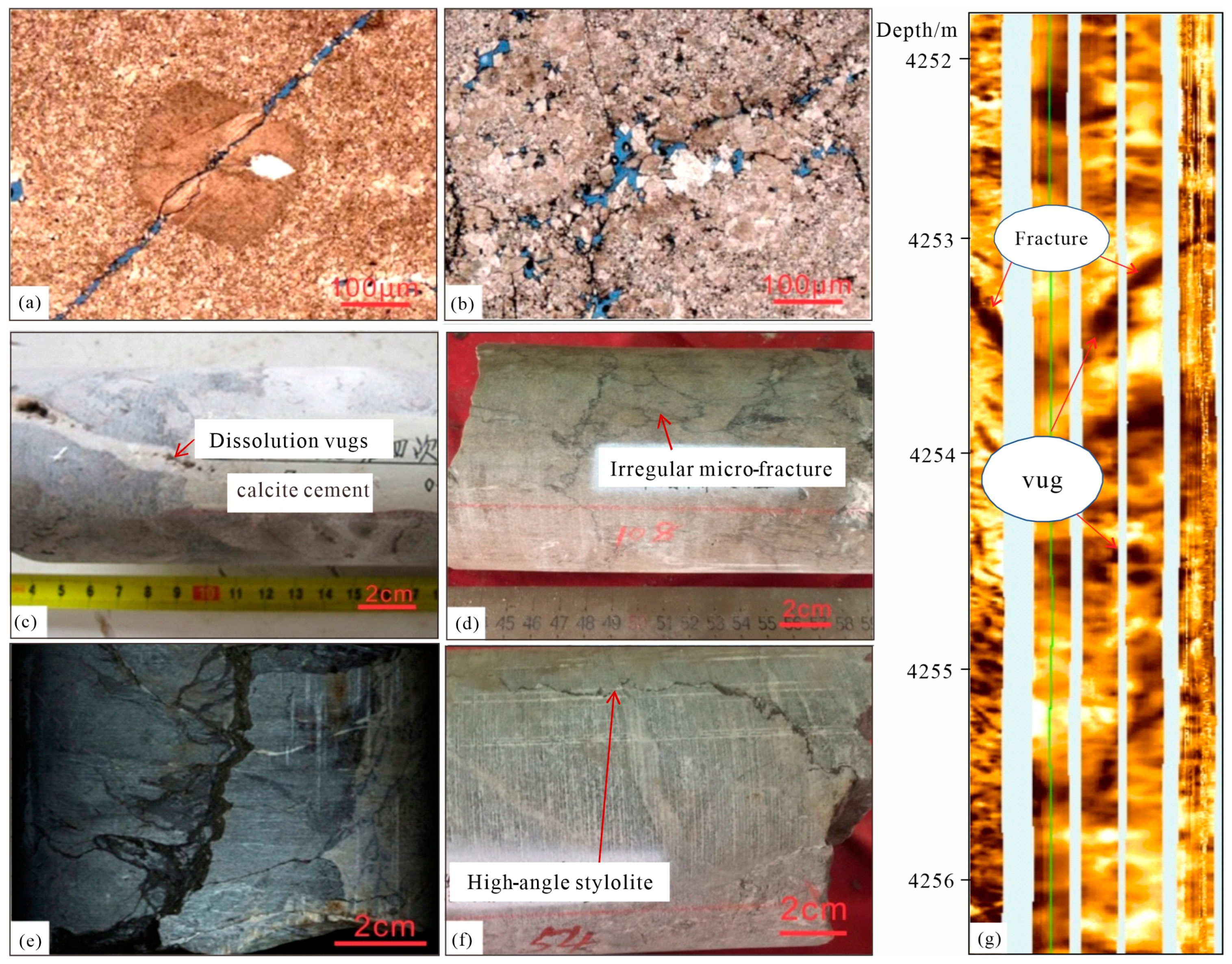
4.2. Characteristics of Micro-Fractures
4.3. Fracture Diagenesis
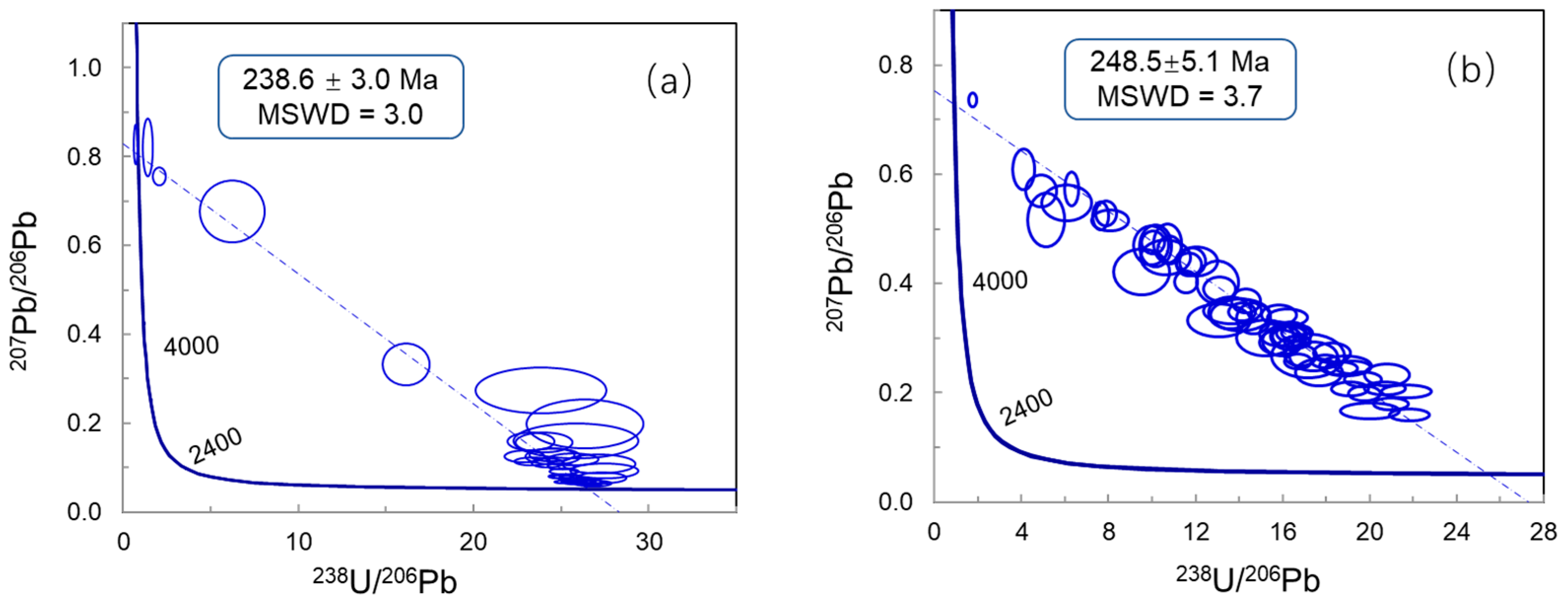
4.4. U–Pb Ages of Fracture Cements
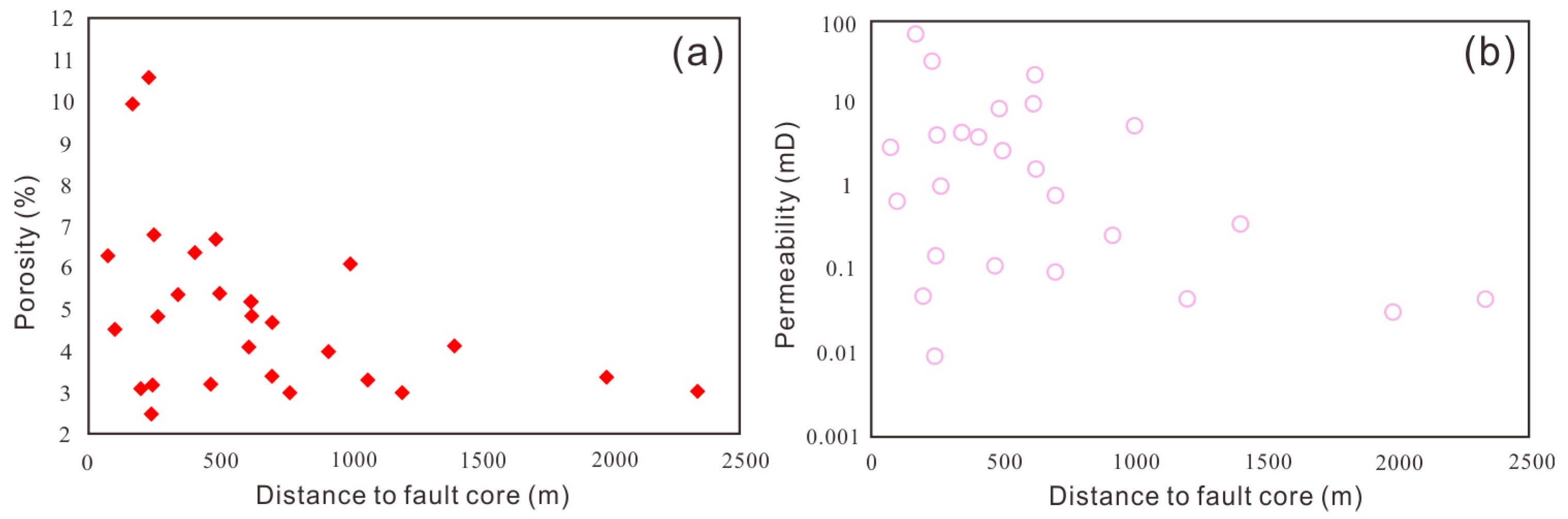
4.5. The Carbonate Reservoir
5. Discussion
5.1. Timing of the Fractured Reservoirs
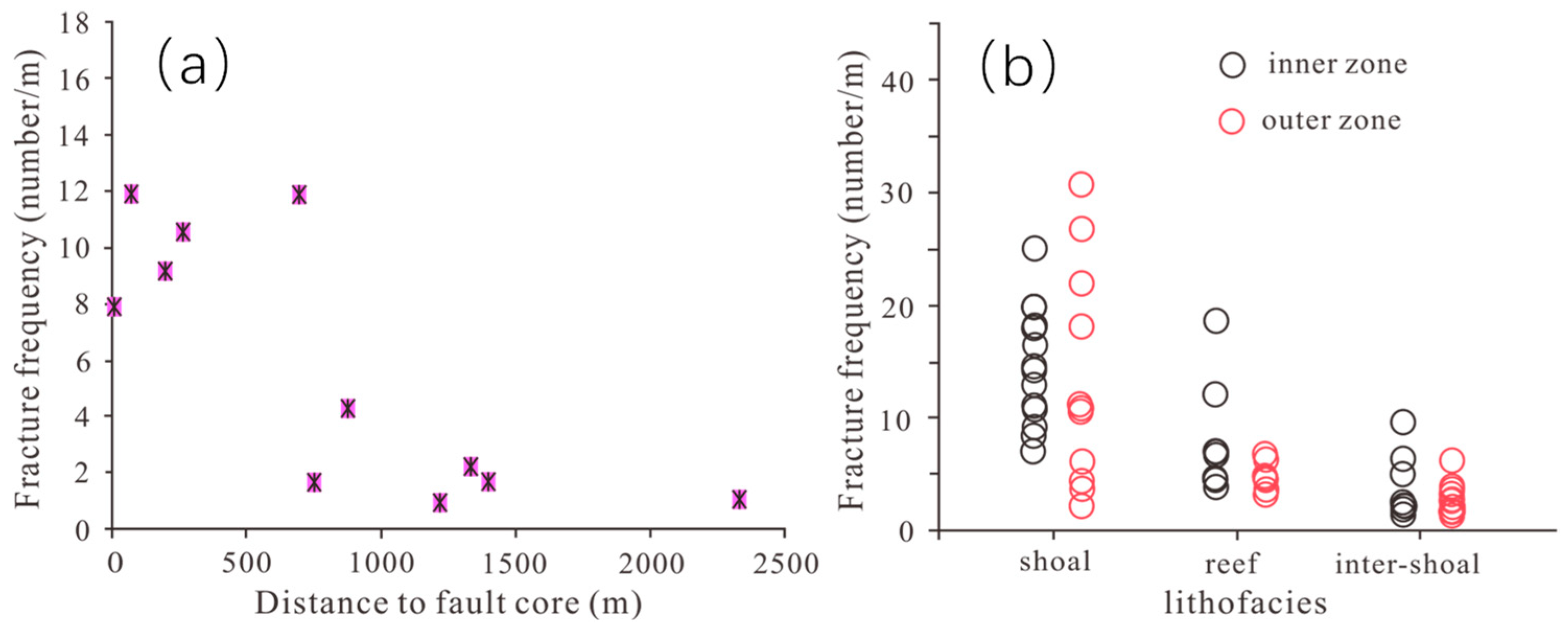
5.2. Fault Effect on Reef–Shoal Reservoirs
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Two faulting stages from transtensional (Late Permian) to transpressional (the end of the Middle Triassic) resulted in small-scale strike–slip faults along the platform margin in the northern Sichuan Basin. These faults produced wide damage zones and multi-stage fracture diagenesis.
- (2)
- Three principal stages of fracture diagenesis were identified, as follows: Late Permian syn-sedimentary fracturing and dissolution; extensive burial cementation during rapid subsidence in the Early–Middle Triassic; and limited reactivation and sealing prior to the Late Triassic.
- (3)
- Contemporaneous fracturing and dissolution at the end of the Permian generated fracture–vug “sweet spot” reservoirs within reef–shoal carbonates. This early fracture diagenesis exerted the most significant positive influence on reservoir quality. In contrast, subsequent burial diagenesis and compaction resulted in porosity loss and permeability reduction.
- (4)
- Even small-displacement strike–slip faults can create favorable fractured reservoirs when structural deformation is coupled with syn-depositional dissolution, providing critical implications for gas exploration in deep, tight reef–shoal reservoirs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydin, A.; Schultz, R.A. Effect of mechanical interaction on the development of strike-slip faults with echelon patterns. J. Struct. Geol. 1990, 12, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Sanderson, D.J. The relationship between displacement and length of faults. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 68, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, D.C.P.; Anderson, M.W. The scaling of pull-aparts and implications for fluid flow in areas with strike-slip faults. J. Pet. Geol. 2012, 35, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabia, A.; Berg, S.S. Scaling of fault attributes: A review. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1444–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayolle, S.; Soliva, R.; Dominguez, S.; Wibberley, C.; Caniven, Y. Nonlinear fault damage zone scaling revealed through analog modeling. Geology 2021, 49, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainge, A.M.; Davies, K.G. Reef exploration in the East Sengkang Basin, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1985, 2, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédir, M.; Boukadi, N.; Tlig, S.; Timzal, F.B.; Zitouni, L.; Alouani, R.; Slimane, F.; Bobier, C.; Zargouni, F. Subsurface Mesozoic basins in the central Atlas of Tunisia: Tectonics, Sequence deposit distribution, and hydrocarbon potential. AAPG Bull. 2001, 85, 885–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolting, A.; Fernández-Ibáñez, F. Stress states of isolated carbonate platforms: Implications for development and reactivation of natural fractures post burial. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 128, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Ran, Q.; Tian, W.; Liang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, Y.; Su, C.; Wu, G. Strike-slip fault effects on diversity of the Ediacaran mound-shoal distribution in the Central Sichuan intracratonic basin, China. Energies 2022, 15, 5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Scarselli, N.; Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Han, J. The strike-slip fault effects on tight Ordovician reef-shoal reservoirs in the central Tarim Basin (NW China). Energies 2023, 16, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, S.E.; Eichhubl, P.; Hilgers, C.; Lander, R.H. Structural diagenesis. J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Yasuhara, H. An evaluation of the effects of fracture diagenesis on hydraulic fracturing treatment. Geosystem Eng. 2013, 16, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Xie, E.; Zhang, Y.F.; Qing, H.R.; Luo, X.S.; Sun, C. Structural diagenesis in carbonate fault damage zones in the northern Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals 2019, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhubl, P.; Davatzes, N.C.; Becker, S.P. Structural and diagenetic control of fluid migration and cementation along the Moab fault, Utah. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 653–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeginste, V.; Swennen, R.; Allaeys, M.; Ellam, R.M.; Osadetz, K.; Roure, F. Challenges of structural diagenesis in foreland fold-and-thrust belts: A case study on paleofluid flow in the Canadian Rocky Mountains West of Calgary. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 35, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Paton, D.A.; Knipe, R.J.; Wu, K.Y. A review of fault sealing behaviour and its evaluation in siliciclastic rocks. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.T.; Goodwin, L.B.; Mozley, P.S. Diagenetic controls on the evolution of fault-zone architecture and permeability structure: Implications for episodicity of fault-zone fluid transport in extensional basins. GSA Bull. 2017, 129, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghani, M.M.A.; Zairi, M.; Radwan, A.E. Facies analysis, diagenesis, and petrophysical controls on the reservoir quality of the low porosity fluvial sandstone of the Nubian formation, east Sirt Basin, Libya: Insights into the role of fractures in fluid migration, fluid flow, and enhancing the permeability of low porous reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 147, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, B.C.; Reuning, L.; Schoenherr, J.; Lueders, V.; Kukla, P.A. Impacts of hydrothermal dolomitization and thermochemical sulfate reduction on secondary porosity creation in deeply buried carbonates: A case study from the Lower Saxony Basin, northwest Germany. AAPG Bull. 2016, 100, 597–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Zhao, K.Z.; Qu, H.Z.; Nicola, S.; Zhang, Y.T.; Han, J.F.; Xu, Y.F. Permeability distribution and scaling in multi-stages carbonate damage zones: Insight from strike-slip fault zones in the Tarim Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 114, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, H.H.; Ping, H.W.; Fang, X.J. Structural diagenesis and reservoir control analysis of tight sandstone in the strike-slip fault zones of the Chang 8 to Chang 6 Members in the Jinghe Oilfield. Bullet Geol. Sci. Technol. 2025, 44, 74–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhan, W.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, X.; Yuan, J. New fields, new types and resource potentials of hydrocarbon exploration in Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 2045–2069, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Xu, C.C.; Wang, T.S.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Bian, C.S.; Li, X. Comparative study of gas accumulations in the Permian Changxing reefs and Triassic Feixianguan oolitic reservoirs between Longgang and Luojiazhai-Puguang in the Sichuan Basin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3310–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.M.; Hu, Z.G.; Chen, S.Y.; Yuan, B.G.; Dai, X. Reef–shoal combinations and reservoir characteristics of the Changxing–Feixianguan Formation in the eastern Kaijiang–Liangping trough, Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 2021, 36, 00698-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.P.; Li, B.S.; Duan, J.B.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Zou, H.Y.; Hao, F. Sulfate sources of thermochemical sulfate reduction and hydrogen sulfide distributions in the Permian Changxing and Triassic Feixianguan formations, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 145, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Tang, S.; Luo, B.; Luo, X.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Wu, G. Seismic description of deep strike-slip fault damage zone by steerable pyramid method in the Sichuan Basin, China. Energies 2022, 15, 8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, G.; Luo, B. The fractured Permian reservoir and its significance in the gas exploitation in the Sichuan Basin, China. Energies 2023, 16, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.G.; Yang, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.W.; Jansa, L.; Li, J.X.; Song, J.M.; et al. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 213, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Li, B.; Wen, L.; Xu, L.; Xie, S.Y.; Du, Y.; Feng, M.Y.; Yang, X.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Pei, S.Q. Characteristics of “Guangyuan-Wangcang” trough during late Middle Permian and its petroleum geological significance in northern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Wu, G.H.; Tang, Q.S.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhao, Z.Y. Effects of intracratonic strike-slip fault on the differentiation of carbonate microfacies: A case study of a Permian platform margin in the Sichuan Basin (SW China). Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 936–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.S.; Liang, H.; Wu, G.H.; Tang, Q.S.; Tian, W.Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.L. Formation and evolution of the strike-slip faults in the central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.F.; Zheng, J.F.; Dai, K.; Hong, S.X.; Duan, J.M.; Liu, Y.M. Petrological, geochemical and chronological characteristics of dolomites in the Permian Maokou Formation and constraints to the reservoir genesis, central Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Jiang, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Qiu, C.; Liu, T.; Deng, M.; Tian, W. Timing and Effect of the Hidden Thrust Fault on the Tight Reservoir in the Southeastern Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.Y.; Shang, J.X.; Shen, A.J.; Wen, L.; Wang, X.Z.; Xu, L.; Liang, F.; Liu, X.H. Episodic hydrothermal alteration on Middle Permian carbonate reservoirs and its geological significance in southwestern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.S.; Zhou, R.J.; Mou, C.L.; Ge, X.Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, J.X.; Howard, D. Origins of the Upper Permian reef-dolostone and reservoir evolution in northern South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 162, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, P. Segmented, curved faults: The example of the Balduini Thrust Zone, Northern Apennines, Italy. J. Struct. Geol. 1999, 21, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.; Budai, T.; Győri, O.; Kele, S. Multiphase partial and selective dolomitization of Carnian reef limestone (Transdanubian Range, Hungary). Sedimentology 2014, 61, 836–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.D.; Yuan, J.; Liu, K.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Dong, D.T.; Ma, P.J.; Huang, C.Q. Diagenesis of the Paleogene sandstones in the DN2 Gas Field, Kuqa foreland basin and its link to tectonics. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, C.; Tang, Q.; Tian, W.; Wu, G. The strike-slip fault effects on the Ediacaran carbonate tight reservoirs in the central Sichuan Basin, China. Energies 2023, 16, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Shi, J.X.; Ma, Q.Y.; Lyu, W.Y.; Dong, S.Q.; Cao, D.S.; Wei, H.H. Strike-slip fault control on karst in ultra-deep carbonates, Tarim Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2024, 108, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Chen, L.X.; Su, Z.; Dong, H.Q.; Ma, B.S.; Zhao, B.; Lu, Z.D.; Zhang, M. Differential characteristics of conjugate strike-slip faults and their controls on fracture-cave reservoirs in the Halahatang area of the northern Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals 2024, 14, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Su, C.; Yu, Y. The Strike–Slip Fault Effect on a Reef–Shoal Reservoir in the Northern Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121284
Wen Y, Wu G, Liu J, Liu X, He B, Su C, Yu Y. The Strike–Slip Fault Effect on a Reef–Shoal Reservoir in the Northern Sichuan Basin. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121284
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yinyu, Guanghui Wu, Jiawei Liu, Xiaoxu Liu, Bing He, Chen Su, and Youliang Yu. 2025. "The Strike–Slip Fault Effect on a Reef–Shoal Reservoir in the Northern Sichuan Basin" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121284
APA StyleWen, Y., Wu, G., Liu, J., Liu, X., He, B., Su, C., & Yu, Y. (2025). The Strike–Slip Fault Effect on a Reef–Shoal Reservoir in the Northern Sichuan Basin. Minerals, 15(12), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121284






