Phase Relations in MAFSH System up to 21 GPa: Implications for Water Cycles in Martian Interior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
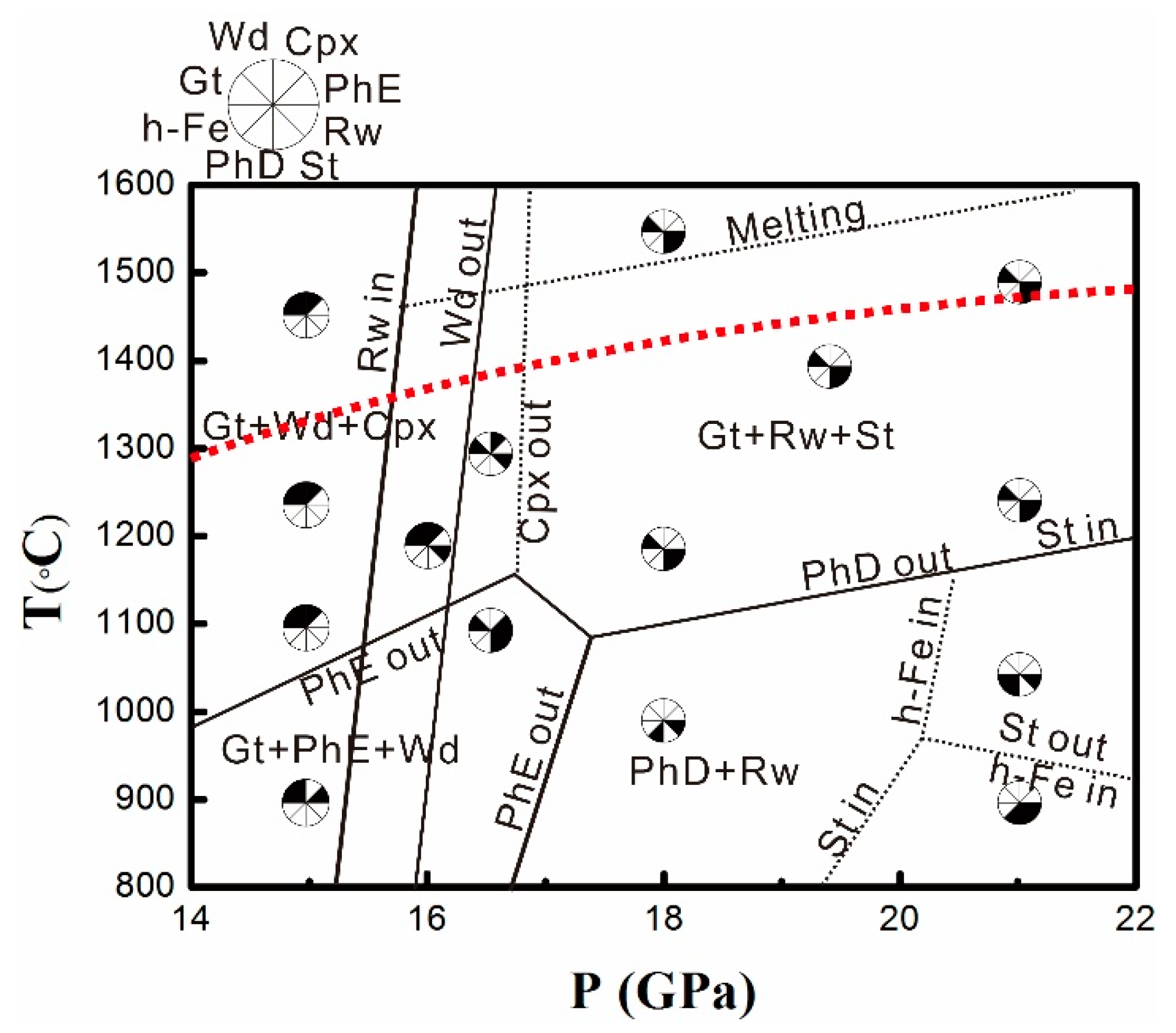
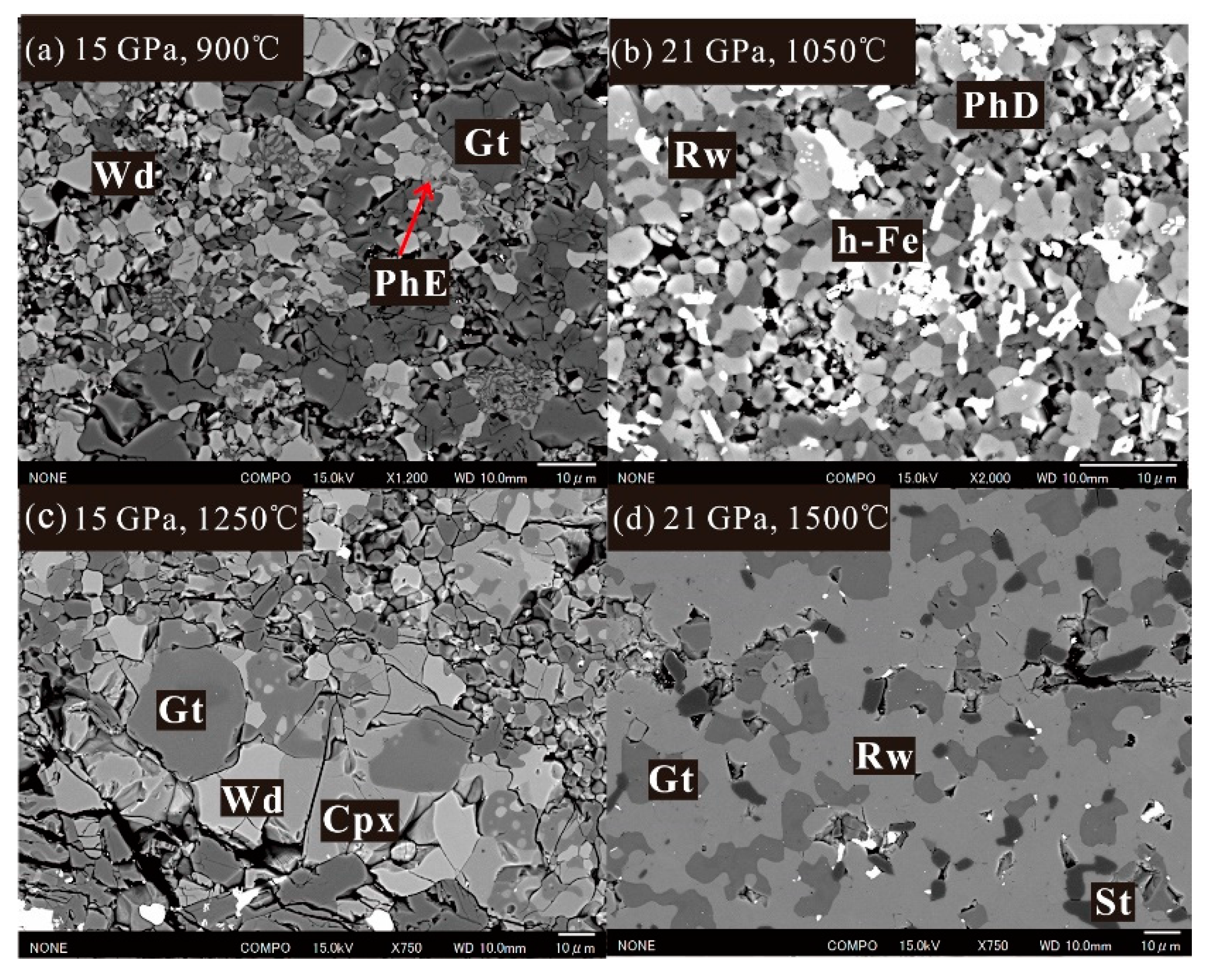
3.1. Phase Relations
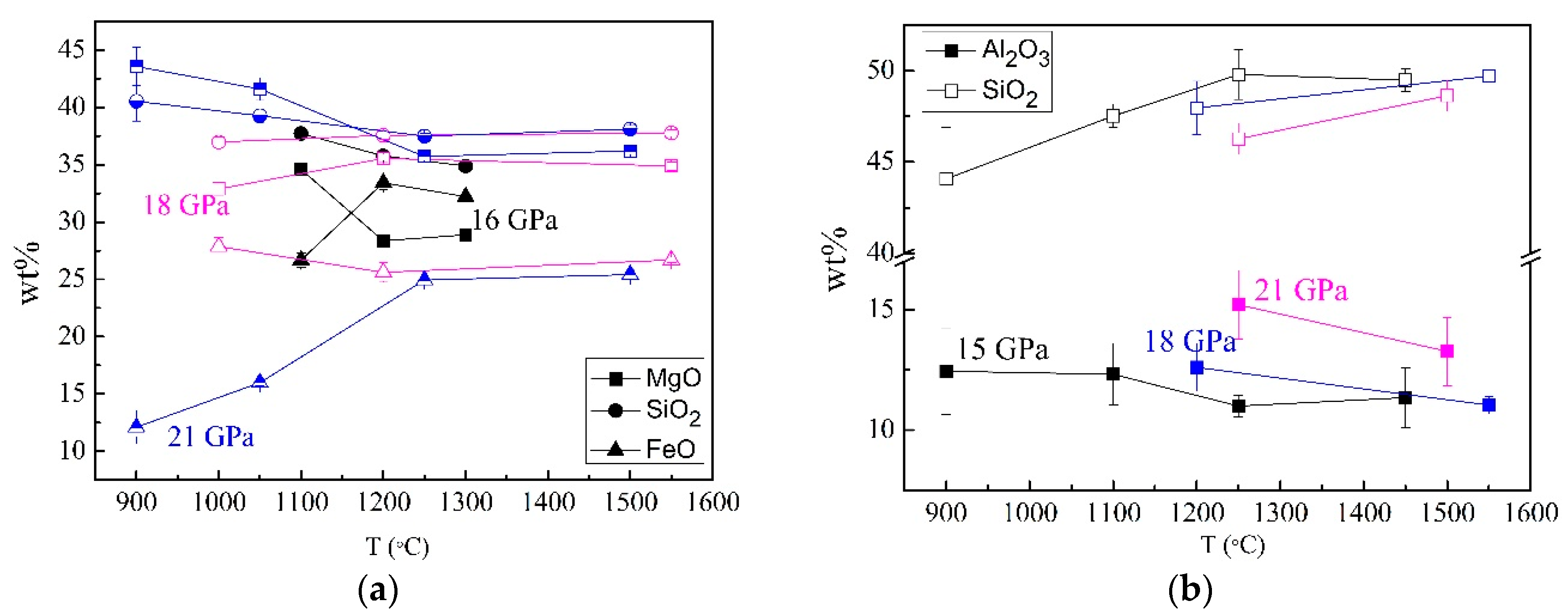
3.2. Mineral Chemistry in DHMSs, Wadsleyite, and Ringwoodite
3.3. Stability and Water Contents of Hydrous Phases in Iron-Rich Martian Mantle
4. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gasparik, T. The role of volatile in the transition zone. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 4287–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, E.; Touma, M.; Litasov, K.; Kubo, T.; Suzuki, A. Stability of hydrous phases and water storage capacity in the transitional zone and lower mantle. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2001, 124, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komabayashi, T.; Omori, S. Internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for dense hydrous magnesium silicates up to 35 GPa, 1600 °C: Implications for water circulation in the Earth’s deep mantle. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 2006, 156, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litasov, K.; Ohtani, E.; Sano, A.; Suzuki, A.; Funakoshi, K. Wet subduction versus cold subduction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Schmidt, M. Melting of phase D in the lower mantle and implications for recycling and storage of H2O in the deep mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 145, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, M.; Irifune, T.; Tsuchiya, J.; Tange, Y.; Nishihara, Y.; Fujino, K.; Higo, Y. Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamato, M.; Myhill, R.; Ballaran, T.; Frost, D.; Heidelbach, F.; Miyajima, N. Lower-mantle water reservoir implied by the extreme stability of a hydrous aluminosilicate. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.J.; Thomson, A.R.; Wang, W.; Lord, O.T.; Ross, J.; McMahon, S.C.; Baron, M.A.; Melekhova, E.; Kleppe, A.K.; Kohn, S.C. The stability of hydrous silicates in Earth’s lower mantle: Experimental constraints from the systems MgO–SiO2–H2O and MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O. Chem. Geol. 2015, 418, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Matsukage, K.; Nishihara, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Takahashi, E. Stability of the hydrous phases of Al-rich phase D and Al-rich phase H in deep subducted oceanic crust. Am. Mineral. 2019, 104, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T. Effect of water on melting phase relations and melt composition in the system Mg2SiO4-MgSiO3-H2O up to 15 GPa. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1994, 85, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, B.; Mohrig, D.; Goudge, T. Fluvial stratigraphy of valley fills at Aeolis Dorsa, Mars: Evidence for base-level fluctuations controlled by a downstream water body. GSA Bull. 2018, 130, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.; Perron, J.; Mitrovica, J.; Gomez, N. New Evidence of an Ancient Martian Ocean from the Global Distribution of Valley Networks. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Erkeling, G.; Hiesinger, H.; Bernhardt, H.; Reiss, D. Topography of the deuteronilus contact on mars: Evidence for an ancient water/mud ocean and long-wavelength topographic readjustments. Planet. Space Sci. 2017, 144, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.; Dundas, C.; Kennedy, M. Distribution of mid-latitude ground ice on Mars from new impact craters. Science 2009, 325, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, S.J.; Balme, M.R.; Kreslavsky, M.A.; Murray, J.B.; Towner, M.C. The comparison of topographic long profiles of gullies on Earth to gullies on Mars: A signal of water on Mars. Icarus 2016, 253, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Ehlmann, B. Aqueous Processes from Diverse Hydrous Minerals in the Vicinity of Amazonian-Aged Lyot Crater. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 1618–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, S.A.; Phillips, R.J. Thermal and crustal evolution of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, D.J.; Fei, Y.W. Stability of phase D at high pressure and high temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7463–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, I.; Ohtani, E.; Sakai, T.; Miyahara, M.; Hirao, N.; Ohishi, Y.; Nishijima, M. Stability of a hydrous δ-phase, AlOOH-MgSiO2(OH)2, and a mechanism for water transport into the base of lower mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 401, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreibus, G.; Wänke, H. Mars, a volatile-rich planet. Icarus 1987, 71, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, E.; Litasov, K.; Hosoya, T.; Kubo, T.; Kondo, T. Water transport into the deep mantle and formation of a hydrous transition zone. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2004, 143–144, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litasov, K.D.; Ohtani, E.; Sano, A. Influence of water on major phase transitions in the Earth’s mantle. In Earth Deep Water Cycle; Jacobsen, S.D., van der Lee, S., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 168, pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Akaogi, M.; Ito, E.; Navrotsky, A. Olivine-modified spinel-spinel transitions in the system Mg2SiO4–Fe2SiO4: Calorimetric measurements, thermochemical calculation, and geophysical application. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 15671–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litasov, K.; Ohtani, E. Stability of various hydrous phases in CMAS pyrolite-H2O system up to 25 GPa. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2003, 30, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertka, C.M.; Fei, Y.W. Mineralogy of Martian interior up to core-mantle boundary pressures. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5251–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, V.R. Water and the Martian landscape. Nature 2001, 412, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, P.; Carr, M.H.; Costard, F.; Greeley, R.; Hauber, E.; Jaumann, R. Geomorphologic evidence for liquid water. Space Sci. Rev. 2001, 96, 333–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkov, V.N.; Gudkova, T.V. Seismic model of Mars: Effects of hydration. Planet. Space Sci. 2014, 104, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raevskiy, S.N.; Gudkova, T.V.; Zharkov, V.N. Diagnostic possibilities of body waves for studying the interior structure of Mars. Izv-Phys. Solid Eart. 2015, 51, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composition | MgO | Al2O3 | FeO | SiO2 | H2O | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAFSH | 30.2 | 3.5 | 19.9 | 44.4 | 2 | 100 |
| Pressure (GPa) | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 900 | 240 | Gt, Wd, PhE |
| 15 | 1100 | 240 | Gt, Wd, Cpx |
| 15 | 1250 | 120 | Gt, Wd, Cpx |
| 15 | 1450 | 90 | Gt, Wd, Cpx |
| 16 | 1200 | 120 | Gt, Wd, Rw, Cpx |
| 16.5 | 1100 | 120 | Gt, Rw, PhE, St |
| 16.5 | 1300 | 90 | Gt, Rw, Cpx |
| 18 | 1000 | 240 | Rw, PhD |
| 18 | 1200 | 120 | Gt, Rw, St |
| 18 | 1550 | 40 | Gt, Rw, St, Melt |
| 19.5 | 1400 | 40 | Gt, Rw, St |
| 21 | 900 | 240 | Rw, PhD, St |
| 21 | 1050 | 240 | Rw, PhD, h-Fe |
| 21 | 1250 | 120 | Gt, Rw, St |
| 21 | 1500 | 40 | Gt, Rw, St |
| P (GPa) | T (°C) | Phase | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | FeO | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 1500 | Gt | 26.48 (54) | 13.27 (142) | 48.63 (84) | 12.33 (39) | 100.71 (23) |
| Rw | 36.20 (29) | 0 | 38.11 (32) | 25.42 (45) | 99.73 (66) | ||
| St | 0 | 1.45 (46) | 100.68 (81) | 0.77 (6) | 102.90 (52) | ||
| 1250 | Gt | 25.01 (60) | 15.21 (142) | 46.27 (85) | 12.34 (37) | 98.84 (33) | |
| Rw | 35.72 (33) | 0 | 37.49 (23) | 24.95 (43) | 98.15 (58) | ||
| St | 38.20 | 0.55 (38) | 99 (63) | 0.78 (33) | 100.33 (83) | ||
| 1050 | Rw | 41.60 (98) | 0 | 39.27 (62) | 15.99 (27) | 96.86 (88) | |
| PhD | 20.24 (42) | 4.71 (71) | 56.11 (85) | 4.79 (34) | 85.86 (145) | ||
| h-Fe | 7.25 (33) | 0 | 0.87 (60) | 81.74 (106) | 89.87 (120) | ||
| 900 | Rw | 43.57 (86) | 1.33 (7) | 40.54 (73) | 12.11 (87) | 96.22 (143) | |
| PhD | 29.36 (78) | 3.50 (48) | 52.95 (90) | 3.93 (48) | 89.74 (81) | ||
| St | 1.53 (71) | 0 | 99.08 (78) | 1.15 (27) | 101.72 (58) | ||
| 19.5 | 1400 | Gt | 26.02 (39) | 12.76 (65) | 47.78 (60) | 12.21 (39) | 98.78 (92) |
| Rw | 35.26 (13) | 0 | 36.96 (19) | 25.55 (34) | 97.77 (44) | ||
| St | 0 | 0.96 (47) | 98.42 (58) | 0.72 (32) | 100.10 (81) | ||
| 18 | 1550 | Gt | 27.78 (29) | 11.04 (37) | 49.70 (30) | 12.45 (80) | 100.45 (37) |
| Rw | 34.88 (37) | 2.05 (18) | 37.77 (30) | 26.70 (24) | 99.35 (58) | ||
| St | 0 | 1.54 (58) | 99.90 (97) | 0.62 (36) | 102.05 (63) | ||
| Melt | 20.65 | 1.62 | 16.45 | 16.57 | 55.31 | ||
| 18 | 1200 | Gt | 25.88 (90) | 12.61 (99) | 47.96 (67) | 12.41 (64) | 98.86 (76) |
| Rw | 35.55 (35) | 0 | 37.56 (34) | 25.61 (47) | 98.71 (79) | ||
| St | 0 | 0.58 (23) | 99.49 (71) | 0.70 (40) | 100.77 (82) | ||
| 18 | 1000 | Rw | 32.89 (61) | 0 | 36.98 (46) | 27.86 (81) | 97.73 (57) |
| PhD | 20.48 (75) | 7.86 (59) | 54.68 (73) | 4.57 (46) | 87.59 (53) | ||
| 16.5 | 1300 | Gt | 25.42 (32) | 11.23 (48) | 47.18 (29) | 12.76 (57) | 96.59 (50) |
| Rw | 28.89 (32) | 0 | 34.88 (27) | 32.21 (25) | 95.98 (64) | ||
| Cpx | 33.79 (24) | 19.19 (60) | 55.66 (53) | 6.98 (47) | 96.44 (95) | ||
| 16.5 | 1100 | Gt | 25.76 (80) | 12.81 (36) | 47.64 (77) | 14.74 (57) | 100.94 (63) |
| Rw | 34.59 (57) | 0 | 37.72 (17) | 26.67 (63) | 98.97 (37) | ||
| PhE | 38.42 (75) | 3.12 (20) | 37.82 (18) | 8.47 (28) | 87.82 (57) | ||
| St | 1.38 (67) | 0.76 (64) | 96.75 (75) | 1.14 (20) | 100.03 (27) | ||
| 16 | 1200 | Gt | 24.28 (47) | 13.42 (37) | 46.67 (33) | 14.26 (83) | 98.63 (44) |
| Rw | 28.36 (42) | 0 | 35.76 (39) | 33.43 (59) | 97.55 (69) | ||
| Wd * | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Cpx | 34.99 (51) | 20.70 (54) | 56.73 (58) | 6.52 (37) | 98.25 (37) | ||
| 15 | 1450 | Gt | 26.61 (71) | 11.35 (25) | 49.48 (61) | 13.10 (75) | 100.54 (82) |
| Wd | 34.43 (35) | 0 | 37.35 (33) | 27.61 (46) | 99.40 (81) | ||
| Cpx | 34.68 (74) | 0 | 58.09 (41) | 7.56 (70) | 100.34 (82) | ||
| 15 | 1250 | Gt | 27.39 (13) | 11 (54) | 49.79 (37) | 13.06 (34) | 101.24 (40) |
| Wd | 30.91 (34) | 0 | 36.54 (18) | 32.11 (47) | 99.55 (46) | ||
| Cpx | 35.80 (39) | 0 | 58.17 (57) | 6.65 (35) | 100.61 (67) | ||
| 15 | 1100 | Gt | 25.19 (57) | 12.32 (28) | 47.52 (64) | 13.08 (61) | 98.11 (81) |
| Wd | 31.03 (96) | 0 | 36.49 (80) | 30.23 (94) | 97.76 (46) | ||
| Cpx | 35.32 (70) | 30.91 (34) | 56.57 (72) | 6.27 (81) | 98.16 (13) | ||
| 15 | 900 | Gt | 27.61 (31) | 12.45 (79) | 44.08 (83) | 17.22 (96) | 101.35 (74) |
| Wd | 27.91 (46) | 0 | 36.15 (50) | 35.08 (27) | 99.14 (84) | ||
| PhE | 34.01 (84) | 4.54 (26) | 35.92 (47) | 12.79 (54) | 87.27 (79) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Inoue, T. Phase Relations in MAFSH System up to 21 GPa: Implications for Water Cycles in Martian Interior. Minerals 2019, 9, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090559
Xu C, Inoue T. Phase Relations in MAFSH System up to 21 GPa: Implications for Water Cycles in Martian Interior. Minerals. 2019; 9(9):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090559
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chaowen, and Toru Inoue. 2019. "Phase Relations in MAFSH System up to 21 GPa: Implications for Water Cycles in Martian Interior" Minerals 9, no. 9: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090559
APA StyleXu, C., & Inoue, T. (2019). Phase Relations in MAFSH System up to 21 GPa: Implications for Water Cycles in Martian Interior. Minerals, 9(9), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090559





