Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions at Narra in Palawan, the Philippines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
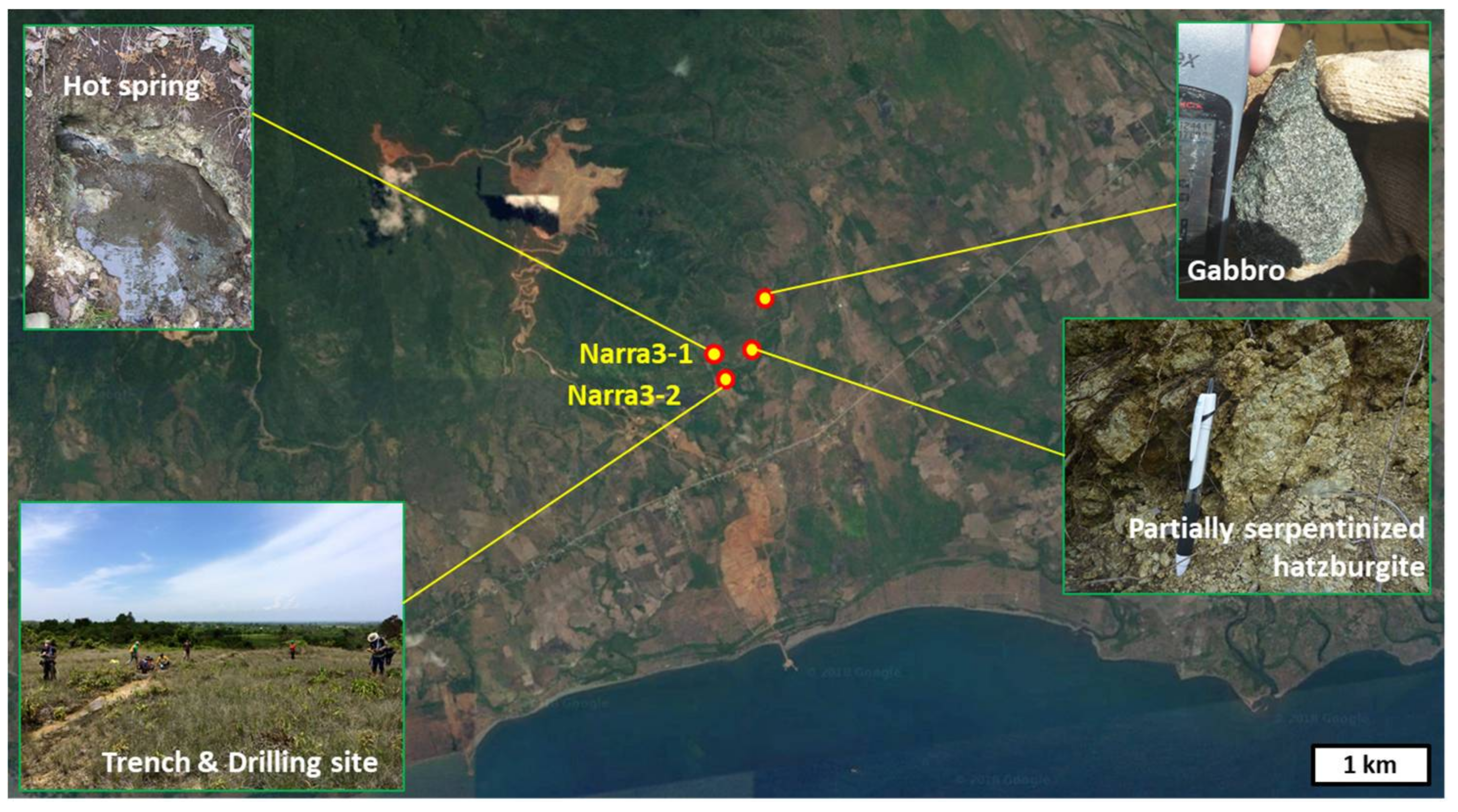
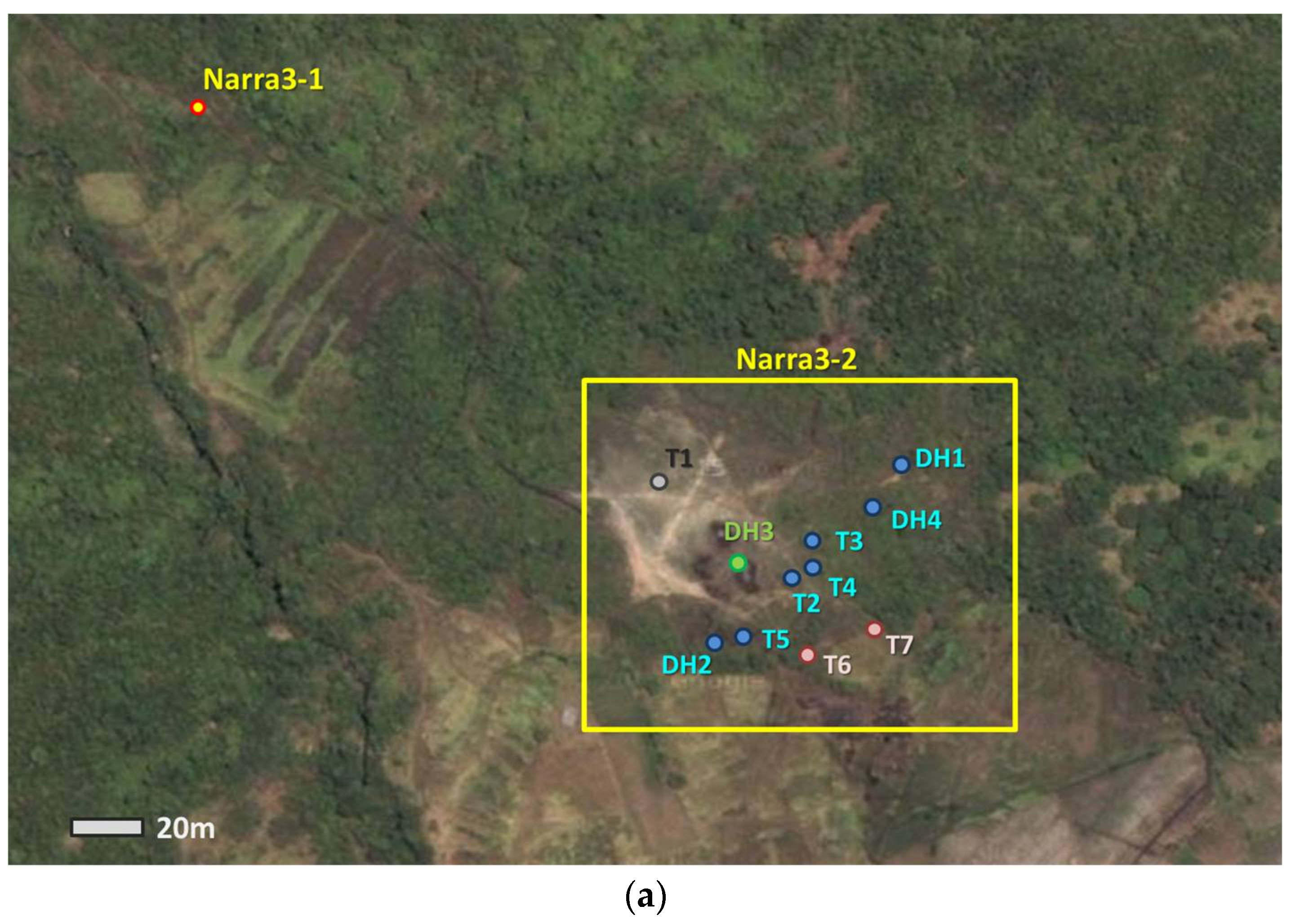
2. Geological Setting and Samples
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Fluids Analyses
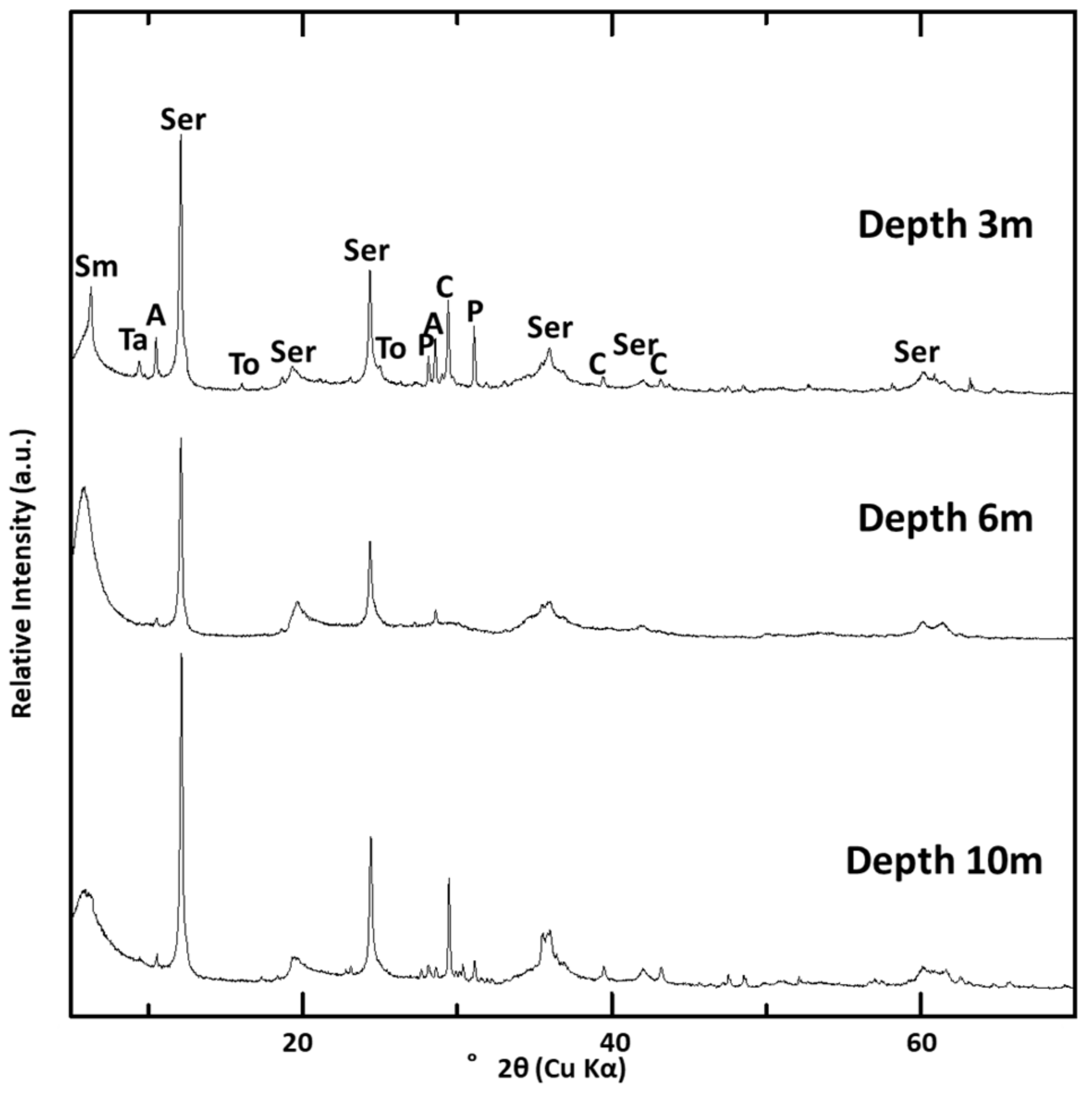
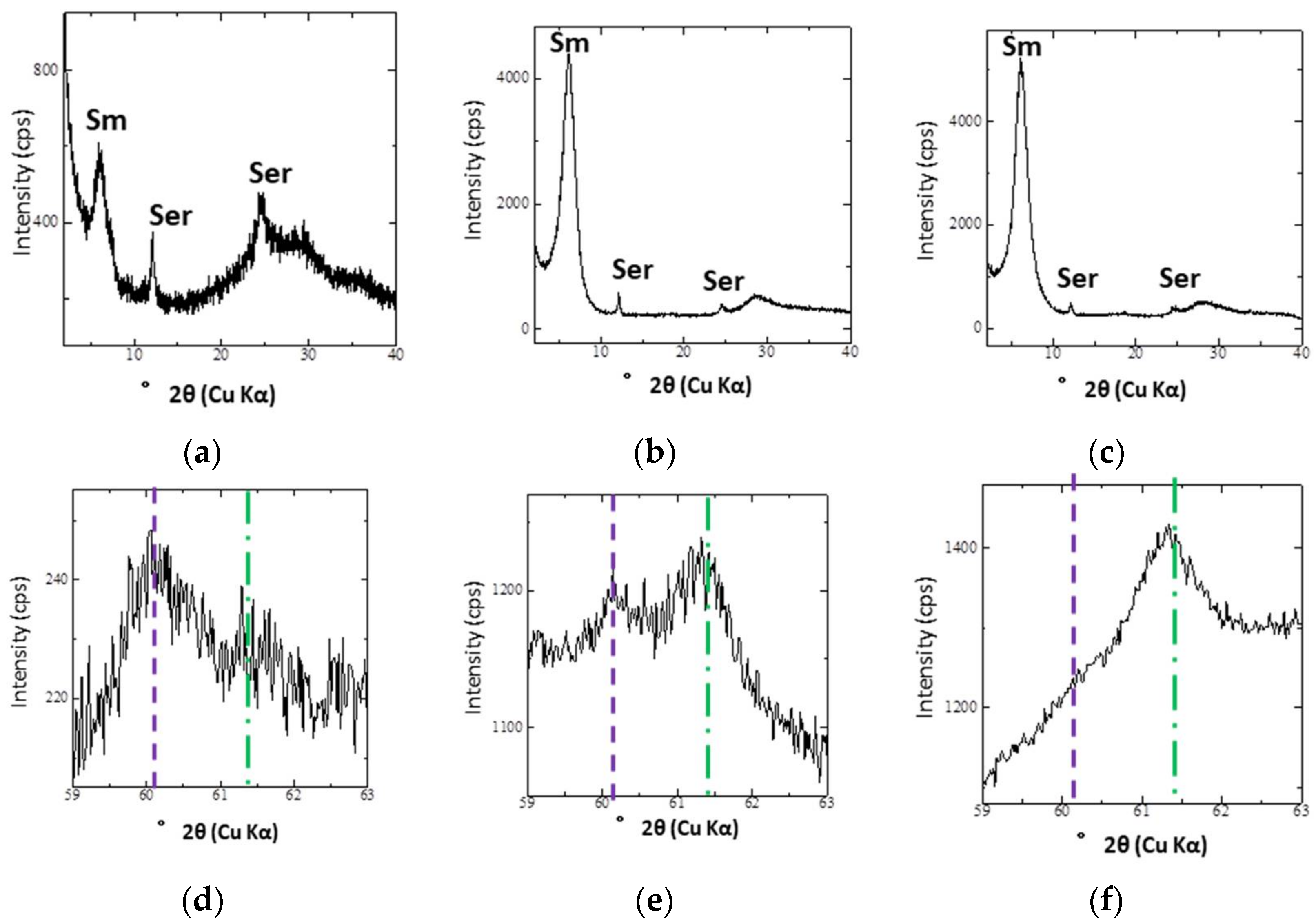
4.2. XRD Analyses
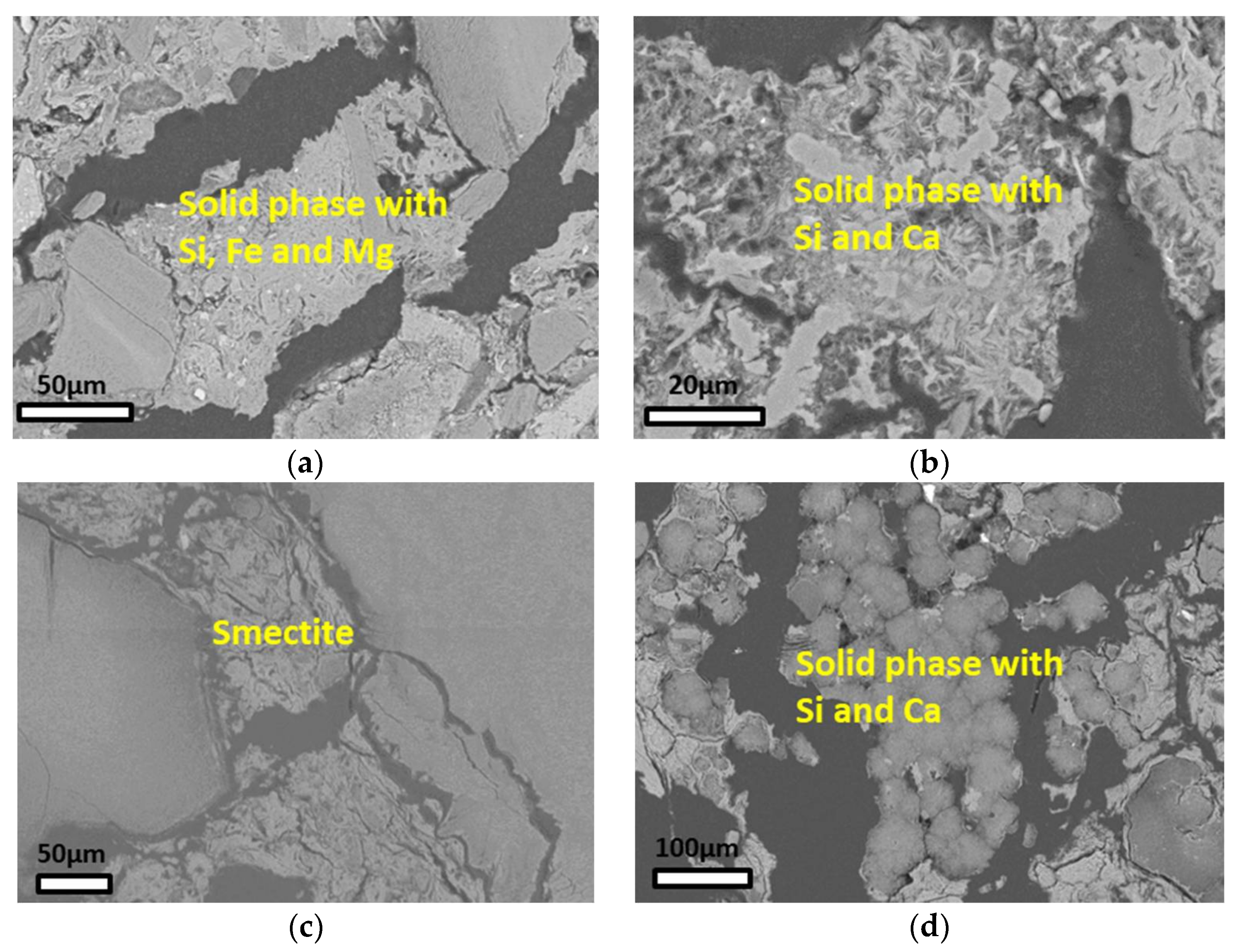
4.3. EPMA Analyses
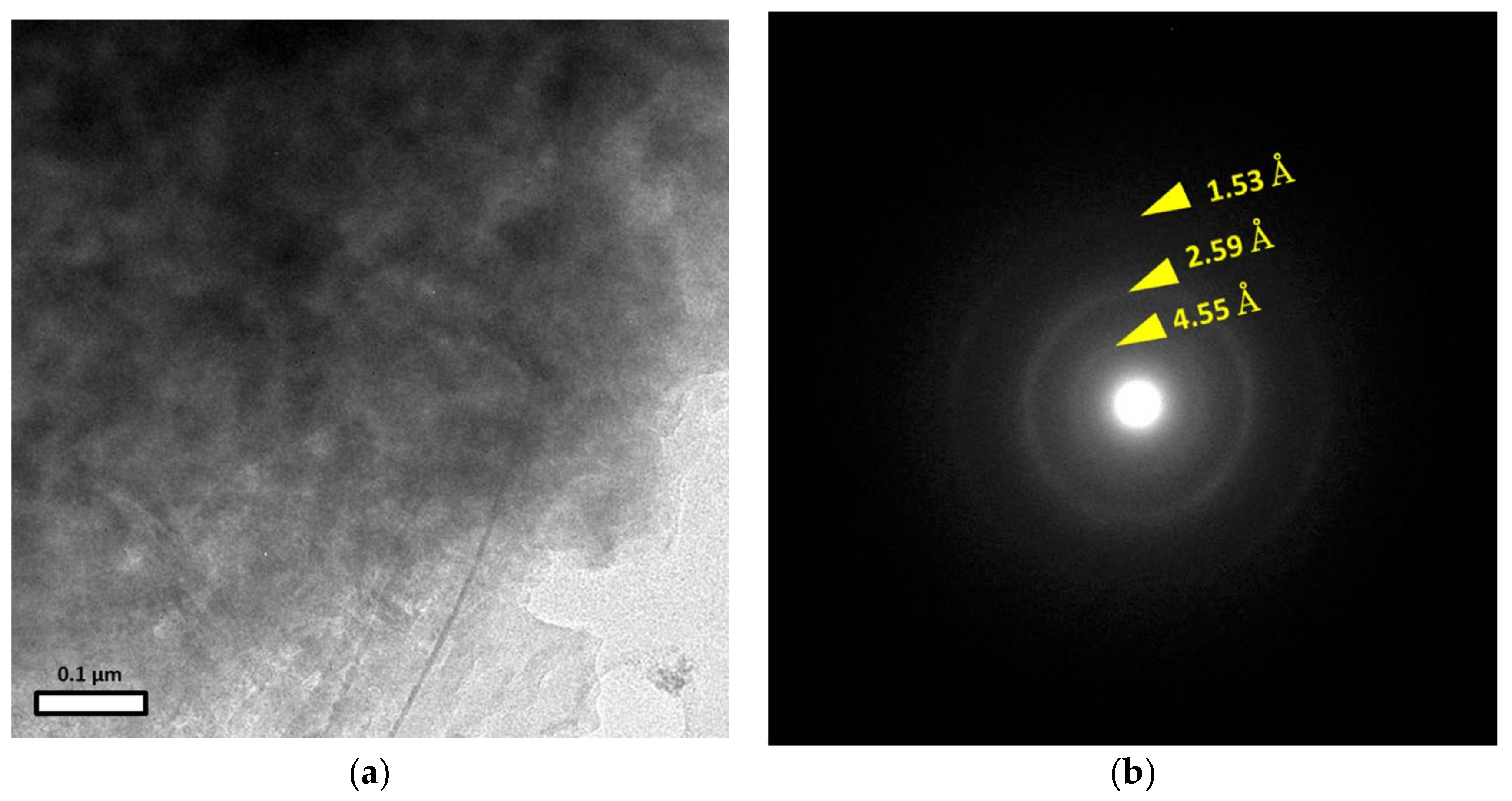
4.4. TEM Observations
4.5. 14C Dating
5. Discussion
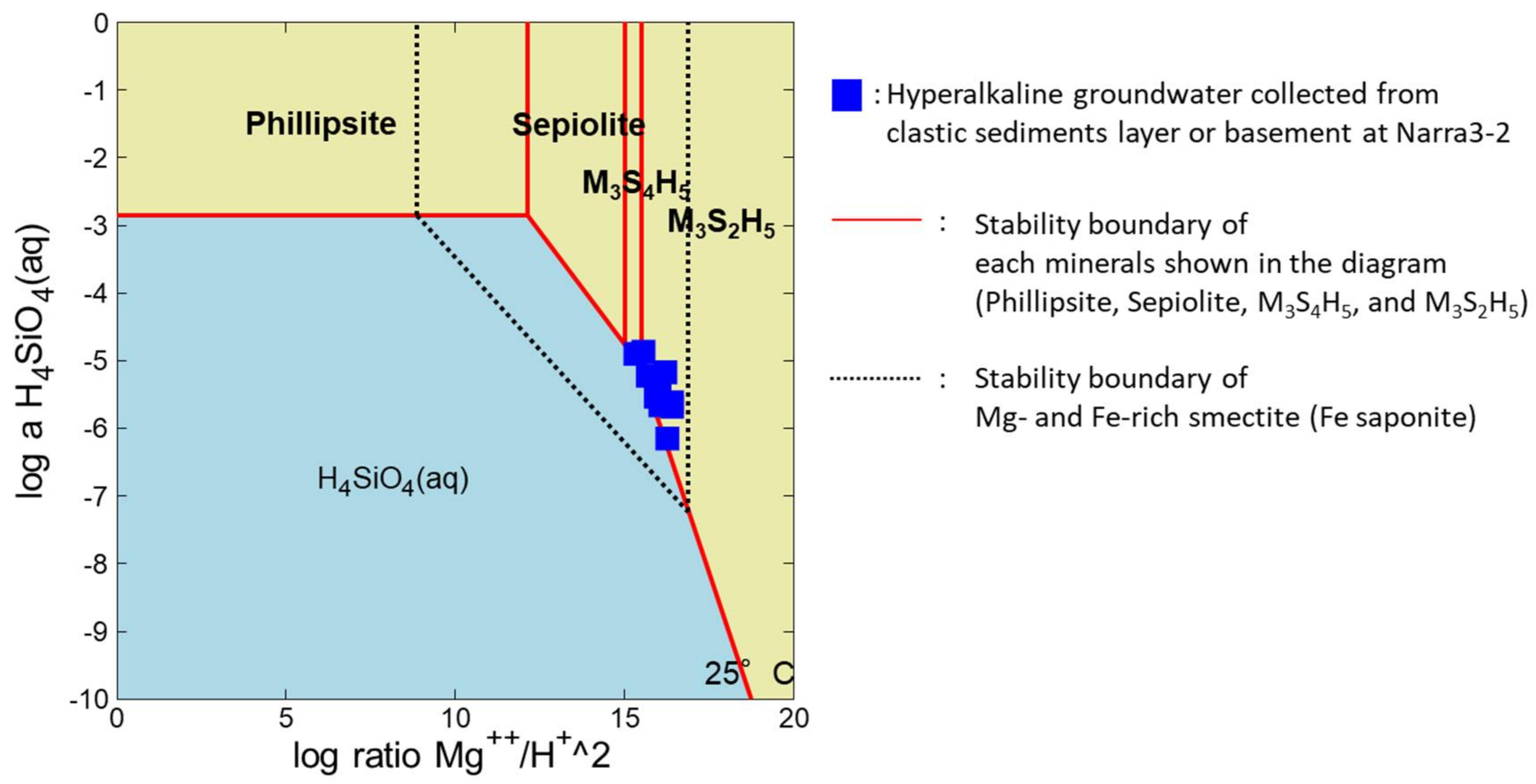
5.1. Origin of Hyperalkaline Groundwater and Its Relation to Alkaline Surface Water
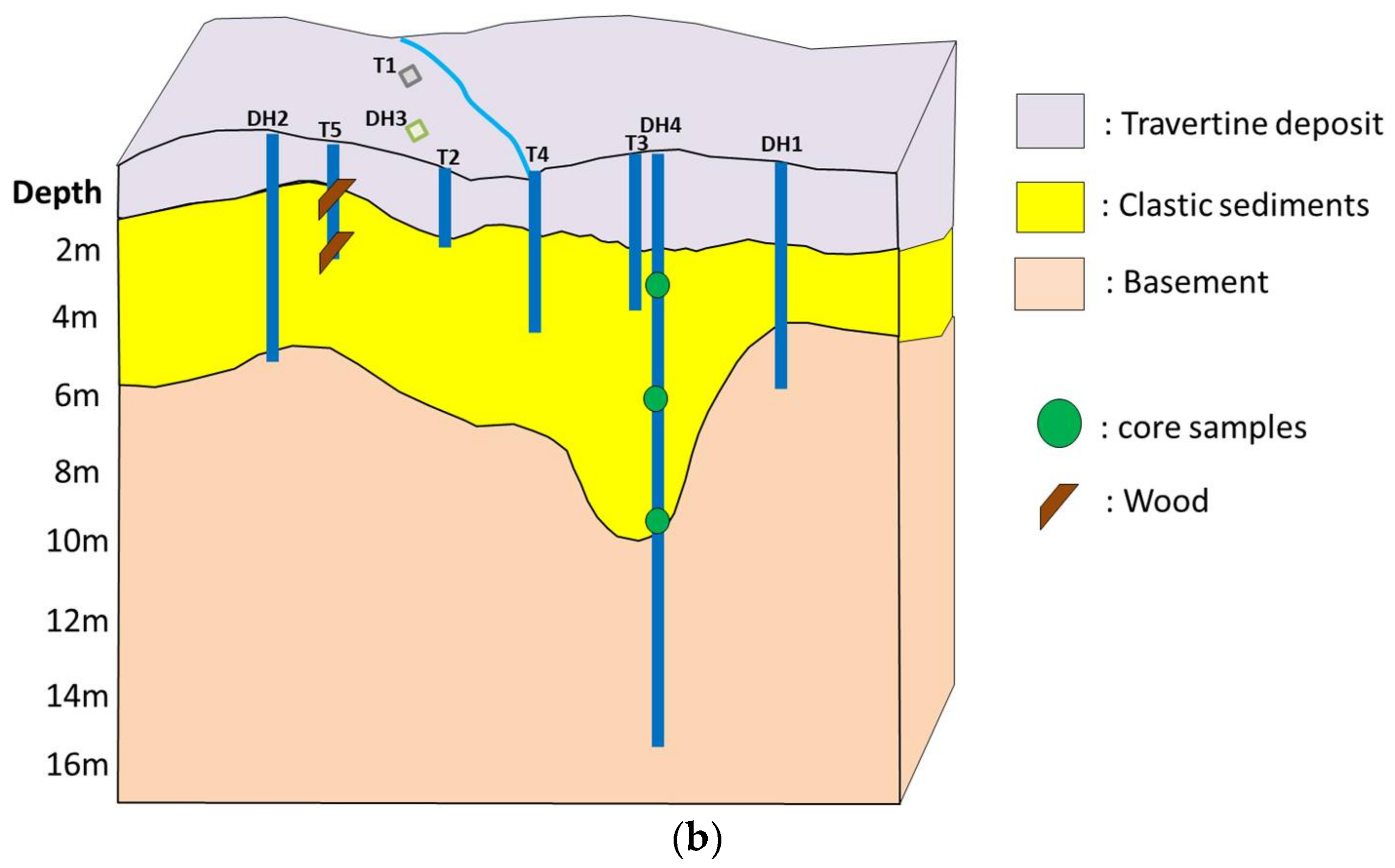
5.2. Evidence of the Interaction between Clastic Sediments and Hyperalkaline Groundwater
5.3. Identification of the Solid Phase with Si, Fe, and Mg
5.4. Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions
5.5. Implications of the Study
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernàndez, R.; Cuevas, J.; Sànchez, L.; Vigil de la Villa, R.; Santiago, L. Reactivity of the cement—Bentonite interface with alkaline solutions using transport cells. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil de la Villa, R.; Cuevas, J.; Ramîrez, S.; Leguey, S. Zeolite formation during the alkaline reaction of bentonite. Eur. J. Mineral. 2001, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.; Blanc, C.; Pesquera, C.; Gonzilez, F.; Lpez, J.L.; Benito, I. Zeolitization of a bentonite and its application to the removal of ammonium ion from waste water. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Yamakawa, M.; Shikazono, N.; Sato, T. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characterizations of Bentonite interacted with Alkaline Fluids generating in Zambales Ophiolite, Northwestern Luzons, Philippines. Geol. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 120, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.H.G.; Hernandez, F.; Dela Cruz, A.P. Cenozoic evolution of the Philippine Archipelago. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1986, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurelio, M.A.; Forbes, M.T.; Joy, K.; Taguibao, L.; Savella, R.B.; Bacud, J.A.; Franke, D.; Pubellier, M.; Savva, D.; Meresse, F.; et al. Middle to Late Cenozoic tectonic events in south and central Palawan (Philippines) and their implications to the evolution of the south-eastern margin of South China Sea: Evidence from onshore structural and offshore seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 58, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirozu, H. Introduction to Clay Mineralogy—Fundamentals for Clay Science; Asakura Bookseller: Tokyo, Japan, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, G.E.; Mitsis, I. A new Ni-rich stevensite from the ophiolite complex of Othrys, Central Greece. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nied, D.; Enemark-rasmussen, K.; Hopital, E.L.; Skibsted, J.; Lothenbach, B. Properties of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milodowski, A.E.; Norris, S.; Alexander, W.R. Minimal alteration of montmorillonite following long-term interaction with natural alkaline groundwater: Implications for geological disposal of radioactive waste. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 66, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, S.; Matsubara, I.; Morimoto, K.; Sato, T. Geochemical Factors for Secondary Mineral Formation at Naturally-Occurring Hyperalkaline Spring in Oman Ophiolite. J. Clay Sci. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 55, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, I.; Neil, J.R.O. The Relationship between Fluids in Some Fresh Alpine-Type Ultramafics and Possible Modern Serpentinization, Western United States. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1969, 80, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, J.; Canepa, M.; Chiodini, G.; Cioni, R.; Cipolli, F.; Longinelli, A.; Marini, L.; Ottonello, G.; Vetuschi, M. Irreversible water—Rock mass transfer accompanying the generation of the neutral, Mg-HCO3 and high-pH, Ca-OH spring waters of the Genova province, Italy. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Sinn, E. 1.4 nm tobermorite-like calcium silicate hydrate prepared at room temperature from Si(OH)4 and CaCl2 solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1993, 12, 542–544. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Glasser, F.P. Alkali binding in cement pastes Part I. The C-S-H phase. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 29, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarreau, A.; Colin, F.; Herbillon, A.; Manceau, A.; Nahon, D.; Paquet, H.; Trauth-badaud, D.; Trescases, J.J. DOMAIN SEGREGATION IN Ni-Fe-Mg-SMECTITES. Clays Clay Miner. 1987, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainey, S.R.; Hausrath, E.M.; Adcock, C.T.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Xiao, Y.; Bartlett, C.L.; Tschauner, O.; Hurowitz, J.A. Clay mineral formation under oxidized conditions and implications for paleoenvironments and organic preservation on Mars. Nat. Commun. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosz, C.; Grangeon, S.; Blanc, P.; Montouillout, V.; Lothenbach, B.; Henocq, P.; Giffaut, E.; Vieillard, P.; Gaboreau, S. Crystal structure of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H): The relation with 2:1 Mg-Si phyllosilicates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Vandeperre, L.J.; Cheeseman, C.R. Formation of magnesium silicate hydrate (M-S-H) cement pastes using sodium hexametaphosphate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 65, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarreau, A.; Bonnin, D. Synthesis and Crystallogenesis at Low Temperature of Fe (III)-Smectites by Evolution of Coprecipitated Gels: Experiments in Partially Reducing Conditions. Clay Miner. 1986, 21, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, J.F.; Jones, B.F.; Veblen, D.R. An AEM-TEM study of weathering and diagenesis, Albert Lake, Oregon. I. Weathering reactions in the volcanics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Loizeau, D.; Mckeown, N.K.; Saper, L.; Dyar, M.D.; Des, D.J.; Parente, M.; Murchie, S.L. What the ancient phyllosilicates at Mawrth Vallis can tell us about possible habitability on early Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 2013, 86, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaniman, D.T.; Bish, D.L.; Ming, D.W.; Bristow, T.F.; Morris, R.V.; Blake, D.F.; Chipera, S.J.; Morrison, S.M.; Treiman, A.H.; Rampe, E.B.; et al. Mineralogy of a Mudstone at Yellowknife Bay, Gale Crater, Mars. Sciences 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemtob, S.M.; Nickerson, R.D.; Morris, R.V.; Agresti, D.G.; Catalano, J.G. Synthesis and structural characterization of Ferrous trioctahedral smectites: Implications for clay mineral genesis and detectability on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 1119–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretyazhko, T.S.; Sutter, B.; Morris, R.V.; Agresti, D.G.; Le, L.; Ming, D.W. Fe/Mg smectite formation under acidic conditions on early Mars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 173, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, H. The Role of Magnesium in the Formation of Smectite Minerals. Chem. Geol. 1971, 10, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, H. Nontronite Synthesis at Low Temperatures. Chem. Geol. 1976, 18, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, S.; Cuevas, J.; Vigil, R.; Leguey, S. Hydrothermal alteration of “La Serrata” bentonite (Almeria, Spain) by alkaline solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 21, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E. Genesis and compositional heterogeneity of smectites. Part III: Alteration of basic pyroclastic rocks—A case study from the Troodos Ophiolite Complex, Cyprus. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | T (°C) | pH | ORP (mV) | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Fe(2+3)+ | Al3+ | Ca2+ | Si2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narra3-1 | 38.6 | 11.16 | −450 | 48.6 | 2.94 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 37.5 | 0.9 | 29.5 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
| T1 | 30.3 | 11.31 | −176 | 44.6 | 2.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 32.2 | 0.7 | 25.6 | 0.08 | 0.77 |
| DH2 | 35.9 | 11.18 | −113 | 40.3 | 2.66 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 24.8 | 5 | 31.3 | 0.10 | 5.6 |
| T5 | 29.9 | 11.36 | −152 | 48.2 | 2.24 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 44.8 | 4.1 | 27.8 | <0.01 | 3.6 |
| T6 | 27.2 | 10.96 | −107 | 50.1 | 2.46 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 24.6 | 5.77 | 28.5 | 1.92 | 9.2 |
| DH3 | 33.5 | 11.29 | −99 | 51.2 | 2.72 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 33.9 | 2.8 | 28.7 | 0.12 | 1.2 |
| T2 | 28.8 | 11.39 | −160 | 46.1 | 2.32 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 26.9 | 2.5 | 27.3 | 0.13 | 0.67 |
| T7 | 27.7 | 11.16 | −141 | 49.1 | 2.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 26.8 | 4.27 | 28.6 | 0.63 | 8.9 |
| T4 | 33.4 | 11.17 | −30 | 47.1 | 2.54 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 36.4 | 2.3 | 28.5 | 0.21 | 2.1 |
| T3 | 33.7 | 11.37 | −111 | 50.4 | 2.39 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 48.5 | 2.5 | 27.0 | 0.02 | <0.01 |
| DH4 | 33.0 | 11.39 | −119 | 51.8 | 2.96 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 22.4 | 2.9 | 21.1 | 0.14 | 2.8 |
| DH1 | 30.9 | 11.08 | −79 | 51.1 | 3.56 | <0.01 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 10.4 | 8 | 31.6 | 0.83 | 2.3 |
| Up-stream | 32.5 | 9.3 | 120 | 52.6 | 2.55 | 18.0 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 27.3 | 11 | 36.6 | 0.58 | 275.5 |
| Mid-stream | 33.2 | 9.64 | 120 | 52.4 | 2.55 | 16.0 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 22.9 | 10 | 36.2 | 0.53 | 105.9 |
| Down-stream | 32.4 | 9.73 | 115 | 51.7 | 2.42 | 5.00 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 9.2 | 4.2 | 35.3 | 0.34 | 100.4 |
| Typical Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite | Typical Serpentine | Ratio at 6 m | Ratio at 3 m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Fe + Mg)/Si | 0.5–0.8 | 1.5 | 0.55–0.88 | 1.24–1.51 |
| N | - | - | 14 | 16 |
| Minerals at Matrix from DH4 at Depth 3 m | M-S-H | Fe2+-Si Coprecipitates |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | 14–15.5 |
| 4.55 | 4.51 | 4.54 |
| - | 3.34 | 3.41 |
| 2.59 | 2.56 | 2.61 |
| - | - | 2.28 |
| - | - | 1.70 |
| 1.53 | 1.54 | 1.52 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimbashi, M.; Sato, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Fujii, N.; Otake, T. Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions at Narra in Palawan, the Philippines. Minerals 2018, 8, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8040155
Shimbashi M, Sato T, Yamakawa M, Fujii N, Otake T. Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions at Narra in Palawan, the Philippines. Minerals. 2018; 8(4):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8040155
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimbashi, Misato, Tsutomu Sato, Minoru Yamakawa, Naoki Fujii, and Tsubasa Otake. 2018. "Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions at Narra in Palawan, the Philippines" Minerals 8, no. 4: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8040155
APA StyleShimbashi, M., Sato, T., Yamakawa, M., Fujii, N., & Otake, T. (2018). Formation of Fe- and Mg-Rich Smectite under Hyperalkaline Conditions at Narra in Palawan, the Philippines. Minerals, 8(4), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8040155





