Abstract
The effect of silica on the immobilization reaction of boron by magnesium oxide was investigated by laboratory experiments. In the absence of silica, due to dissolution of the magnesium oxide, boron was removed from solutions by the precipitation of multiple magnesium borates. In the presence of silica, magnesium silica hydrate (M-S-H) was formed as a secondary mineral, which takes up boron. Here 11B magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR) and Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) data show that a part of the boron would be incorporated into M-S-H structures by isomorphic substitution of silicon. Another experiment where magnesium oxide and amorphous silica were reacted beforehand and boron was added later showed that the shorter the reaction time of the preceding reaction, the higher the sorption ratio of boron. That is, boron was incorporated into the M-S-H mainly by coprecipitation. The experiments in the study here show that the sorption of boron in the presence of silica is mainly due to the incorporation of boron during the formation of the M-S-H structure, which suggests that boron would not readily leach out, and that stable immobilization of boron can be expected.
1. Introduction
Immobilization technology is often used to control mobility and reduce toxicity in metal contaminated soils. The primary role of the compounds used in the immobilization is to change the speciation of the metals in the soils from dissolved species to more geochemically stable species via adsorption and precipitation processes. Immobilization is a widely proven useful method because of the speedy and simple applicability, relatively low cost, and small amount of waste generated compared with other methods such as sealing or excavation [1]. In addition, it offers a lower risk of dispersing polluting components as there is no need to move the originally contaminated soil. However, detailed immobilization mechanisms have not been established and confirmed for most candidates for immobilization compounds. Particularly, the reaction between soil and immobilized components has not been sufficiently studied, it is not clear how the compounds to be immobilized react with soil in the process of immobilizing hazardous substances [2]. There is a clear need for knowing details of how hazardous elements are immobilized in the precipitated phases when making assessments of risks and long-term evaluations.
Many types of Magnesium-based immobilization compounds are commercially available and have attracted attention in recent years as highly efficient compounds for applications to immobilization technology. The main component of Magnesium-based compounds is magnesium oxide, which has been reported to be effective against many harmful elements [3,4]. Harmful elements have been immobilized by magnesium oxide by ion exchange, surface complex formation, and coprecipitation in simple laboratory experiments, however the detailed reaction mechanisms in the soil at the contaminated sites has not been exhaustively detailed or understood.
Boron is an essential element in the human body, however, toxicity to male reproductive organs and toxicity to developing embryos by long-term exposure has been established [5]. As a result, boron is designated as a pollutant by the Ministry of the Environment of Japan by analogy with lead, arsenic, fluoride, and others. Boron is not frequently identified in contaminated soils, but it is known as an element that is only immobilized with difficulty in soils. Boron is commonly present in the form of B(OH)3(aq), which is an electrically neutral dissolved species and so difficult to adsorb electrostatically on minerals in soil [6]. It is also considered to be difficult to immobilize by precipitation of little soluble salts because of the high solubility of borate salts [2]. Therefore, compounds and methods that are effective in immobilizing boron have not been identified.
Boron removal has been extensively studied in the field of wastewater treatment, and several methods such as chemical precipitation [7], adsorption [8], extraction [9], biological method [10] are known. As immobilization mechanisms for boron by magnesium oxide, precipitation of magnesium borates [11] and formation of an inner-sphere complex on the surface of brucite [12] have been reported. However, these results have been obtained with simple experimental systems using magnesium oxide and aqueous solutions of boric acid, and do not adequately explain the processes and states of the immobilized boron in soil as soils are complex. Various minerals are present in soils, generating a range of dissolved species in the pore water. Among these, dissolved silica is frequently the dominant species when magnesium oxide is mixed with the soils, as the solubility of silica minerals increases with increasing pH due to the dissolution of magnesium oxide. This suggests that dissolved silica in pore water would commonly be present and available for immobilization processes using magnesium oxide. Furthermore, it has been suggested that boron in soil interacts with silicates. Jin et al. [13] carried out sequential extraction on 14 types of soil and reported that 2.4 to 79.2 % in total boron was separated into the residual fraction, and residual boron was considered to be in association with soil silicates. In this context, our main hypothesis is that silica in the reaction system involves in the immobilization of boron.
In this study, the authors carried out an immobilization experiment for boron with magnesium oxide in the presence of silica and investigated the influence of silica on the immobilization of boron.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sorption Experiments for Boron Using Magnesium Oxide
In this study, B(OH)3 solutions of 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L were prepared by dissolving B(OH)3 (special grade; Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., Chuo-ku, Japan) into deionized water bubbled with N2 to remove CO2 from the solutions. With 80 mg of magnesium oxide (special grade; Kanto Chemical) added to 80 mL of the B(OH)3 solution in 100 mL polyethylene bottles, the suspensions were shaken with a horizontal shaker (120 rpm) in a water bath at 25 °C for one, 2, 5, 17, or 28 days. After these reaction times, the suspensions were filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter (cellulose nitrate ester). The solids remaining on the filter were rinsed with deionized water and freeze-dried for two days. The sorption ratios of boron were calculated from the differences between the initial boron concentrations and the equilibrium concentrations of the solutions.
2.2. Sorption Experiment for Boron Using Magnesium Oxide with Soluble Silica
To investigate how the presence of silica affects the sorption reaction, boron sorption experiments with silica in solutions were also conducted. Here, 80 mg of amorphous silica (special grade; Kanto Chemical) and 80 mg of magnesium oxide were added to the 80 mL of the B(OH)3 solution in 100 mL polyethylene bottles and the suspensions were shaken under the conditions detailed above.
2.3. Sorption Experiment for Boron Using Precipitates Reacting with Magnesium Oxide and Amorphous Silica
Further, other experiments were conducted to investigate the reactions when boron was reacted with the precipitates obtained by reacting magnesium oxide with amorphous silica. Here, 80 mg of amorphous silica and 80 mg of magnesium oxide were added to the 80 mL of the deionized water in the 100 mL polyethylene bottle under N2 bubbling. These samples were shaken like those of the sorption experiments and the suspensions were collected after 1, 5, and 28 days. Following this, 20 mg of precipitate was added to 20 mL of the 0.46 mmol/L B(OH)3 solution in 50 mL centrifuge tubes. These suspensions were shaken with a horizontal shaker (120 rpm) at room temperature for 7 days. After the reaction, the liquids and solids of the suspensions were separated by centrifugation (3000 rpm, 40 min.) and freeze-dried for two days.
2.4. Analysis of the Solutions
The concentrations of dissolved species in the solutions obtained in the above experiments were determined. Acidified samples were diluted 10–100 times and analyzed for B and Mg by inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) using a SHIMADZU ICPE-9000 (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan). Non-acidified samples were diluted 10–100 times and analyzed for dissolved silica by spectrophotometry using a JASCO V-550 (JASCO Corp., Hachioji, Japan) based on the formation of blue molybdosilicic acid.
2.5. Analysis of the Solid Phases
The solid samples were ground and analyzed for powder X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Corp., Akishima, Japan) to establish the mineral compositions using a Rigaku RINT2100 diffractometer operating at 30 kV and 20 mA, equipped with a Cu target. Diffraction profiles were collected from 10 to 70° 2θ.
The Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) spectra were obtained from 400 to 4000 cm−1 on a JASCO FTIR-4100 spectrometer (JASCO Corp., Hachioji, Japan) with 1.0 cm−1 spectral resolution. Pellets were prepared by mixing the samples with KBr at a 2.0 mg sample to 400 mg KBr ratio. The KBr was heated at 110 °C for 2 h prior to use to remove the contained water.
Solid-state 11B magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR) spectra were acquired on a JEOL ECA600II (JEOL Ltd., Akishima, Japan) using 3.2 mm probes and a single pulse method. The resonance frequency for 11B was 192.5 MHz at a field strength of 14.1 T. Typical acquisition parameters were spinning speed 12.5 kHz, relaxation delay 3 s, and 2048–12,000 scans depending on the boron concentration in the solid samples. The 11B chemical shift was referenced to a saturated H3BO3 solution at 19.6 ppm.
3. Results
3.1. Sorption Experiments Using Magnesium Oxide
3.1.1. Sorption Experiments with Boron and Magnesium Oxide Both Added Together
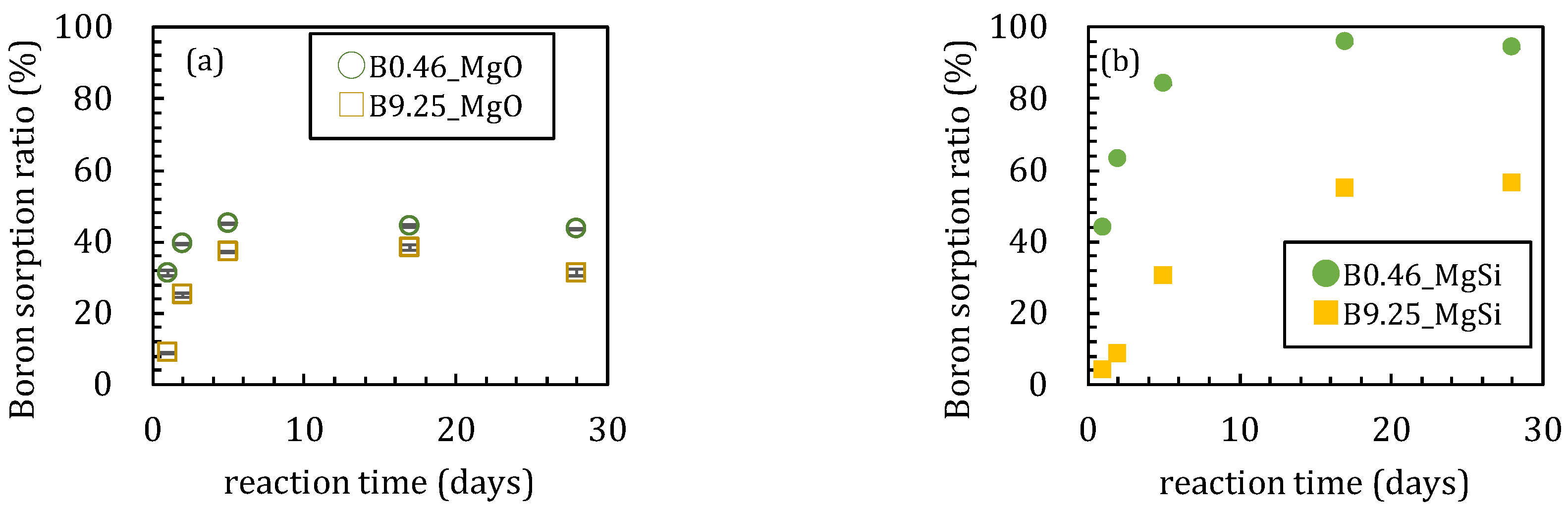
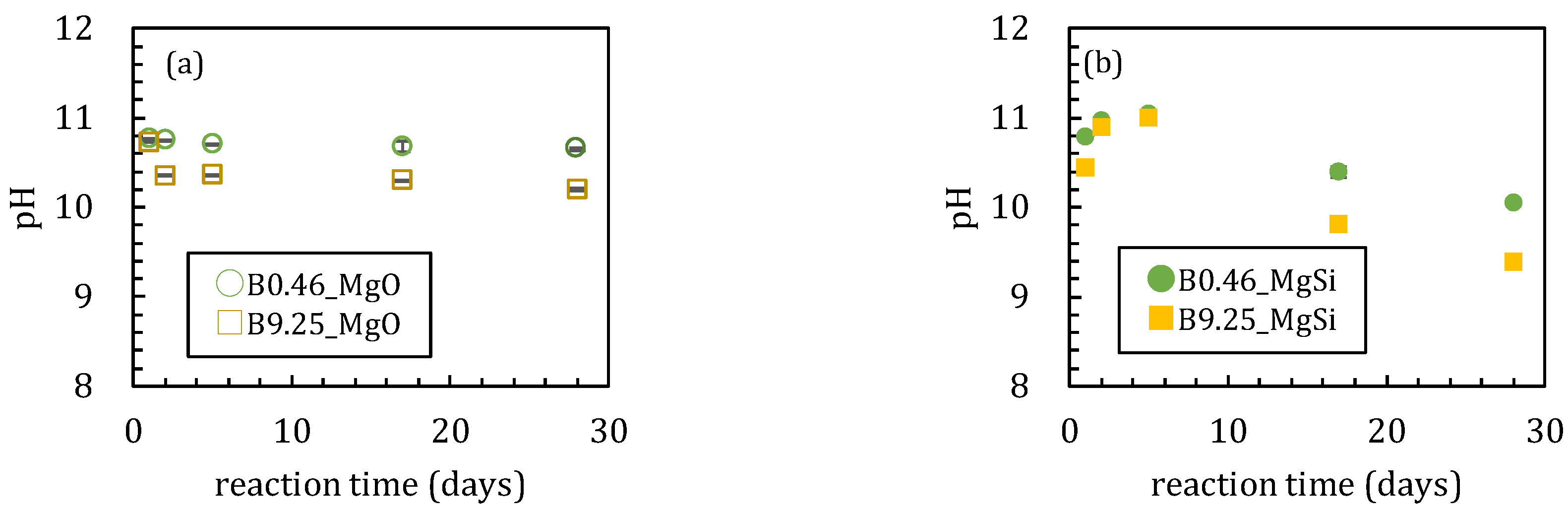
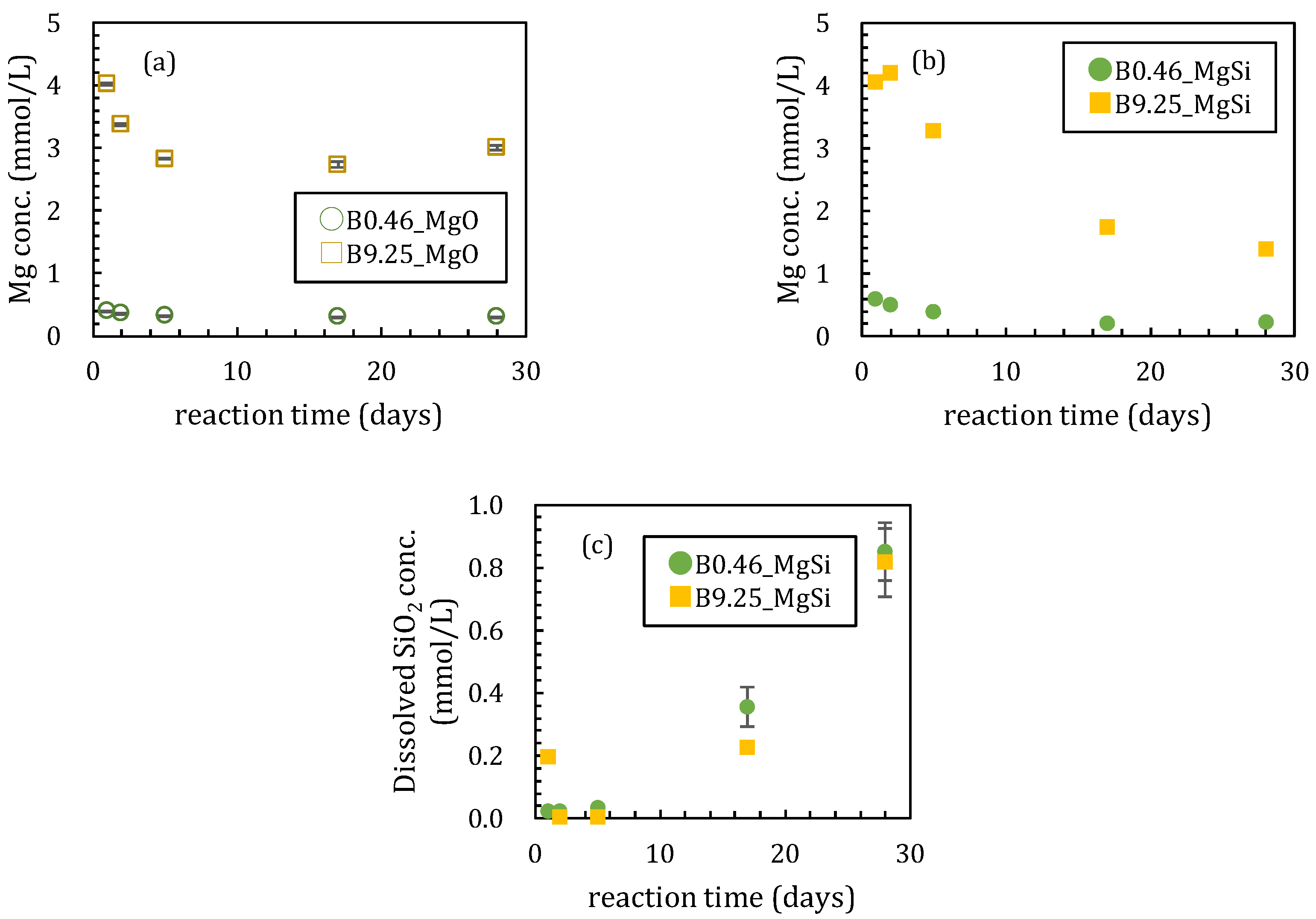
In the first series of sorption experiments where boron was added to magnesium oxide, the boron sorption ratios were different with or without amorphous silica (Figure 1). The boron sorption ratios reached the maximum values after 5 days when no silica was added to the solutions (Figure 1a). The maximum sorption ratios were 45 and 37% when the initial boron concentrations ([B]ini) were 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively. In the case of [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L, the boron sorption ratio gradually decreased after 5 days while it remained constant at 44 % in the [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L addition experiments. The pH of the experimental solutions decreased from 10.7 to 10.3 after 2 days for [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L and remained constant at pH 10.7 throughout the 28 days with [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L (Figure 2a). The dissolved magnesium concentration steadily decreased until 17 days from 0.39 mmol/L to 0.31 mmol/L and 4.02 mmol/L to 2.73 mmol/L for [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively (Figure 3a), then in the period between after 17 and 28 days, it increased to 3.00 mmol/L only for [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L.
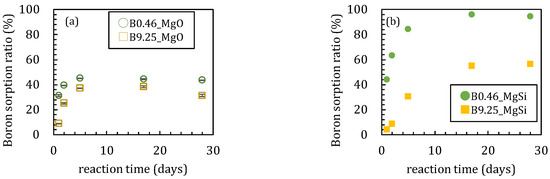
Figure 1.
Changes of boron sorption ratios with time for the sorption of 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L boron on MgO (a) without amorphous silica and (b) with amorphous silica. Data with error bars indicate the standard error of three samples.
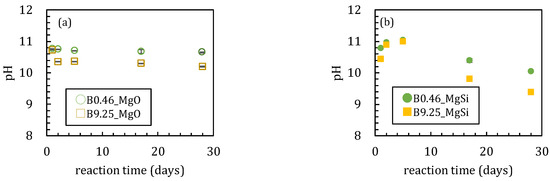
Figure 2.
Changes in pH during sorption for (a) without amorphous silica and (b) with amorphous silica. Data with error bars indicate the standard error of three samples.
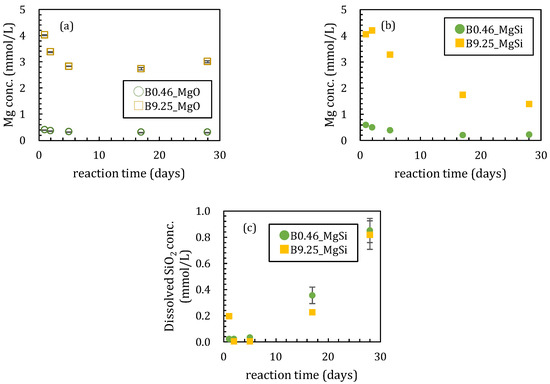
Figure 3.
Changes of concentration of dissolved species; (a) Mg without amorphous silica, (b) Mg and (c) SiO2 with amorphous silica. Data with error bars indicate the standard error of three samples.
The pH of the experimental solutions decreased from 10.7 to 10.3 after two days for [B]ini = 5 mg/L and remained constant at pH 10.7 throughout the 28 days with [B]ini = 100 mg/L (Figure 2a). The dissolved magnesium concentration steadily decreased until 17 days from 9.5 mg/L to 7.6 mg/L and 97.7 mg/L to 66.5 mg/L for [B]ini = 5 and 100 mg/L, respectively (Figure 3a), then in the period between after 17 and 28 days, it increased to 73.0 mg/L only for [B]ini = 100 mg/L.
These changes in the solution chemistry were very different when amorphous silica was added. For the boron sorption ratio, it took ~17 days to reach a steady state with high adsorption ratios, reaching maximum values of 95.8% and 56.6% for [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively (Figure 1b). After a slight pH increase until 5 days both with [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, pH kept decreasing to 10.0 and 9.4 for [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively (Figure 2b). Dissolved magnesium concentrations kept decreasing for 28 days to 0.23 mmol/L and 1.38 mmol/L for [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively (Figure 3b). The dissolved silica concentrations increased to 0.85 mmol/L and 0.82 mmol/L for [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L, respectively, after decreasing until five days (Figure 3c).
3.1.2. Characterization of the Precipitates
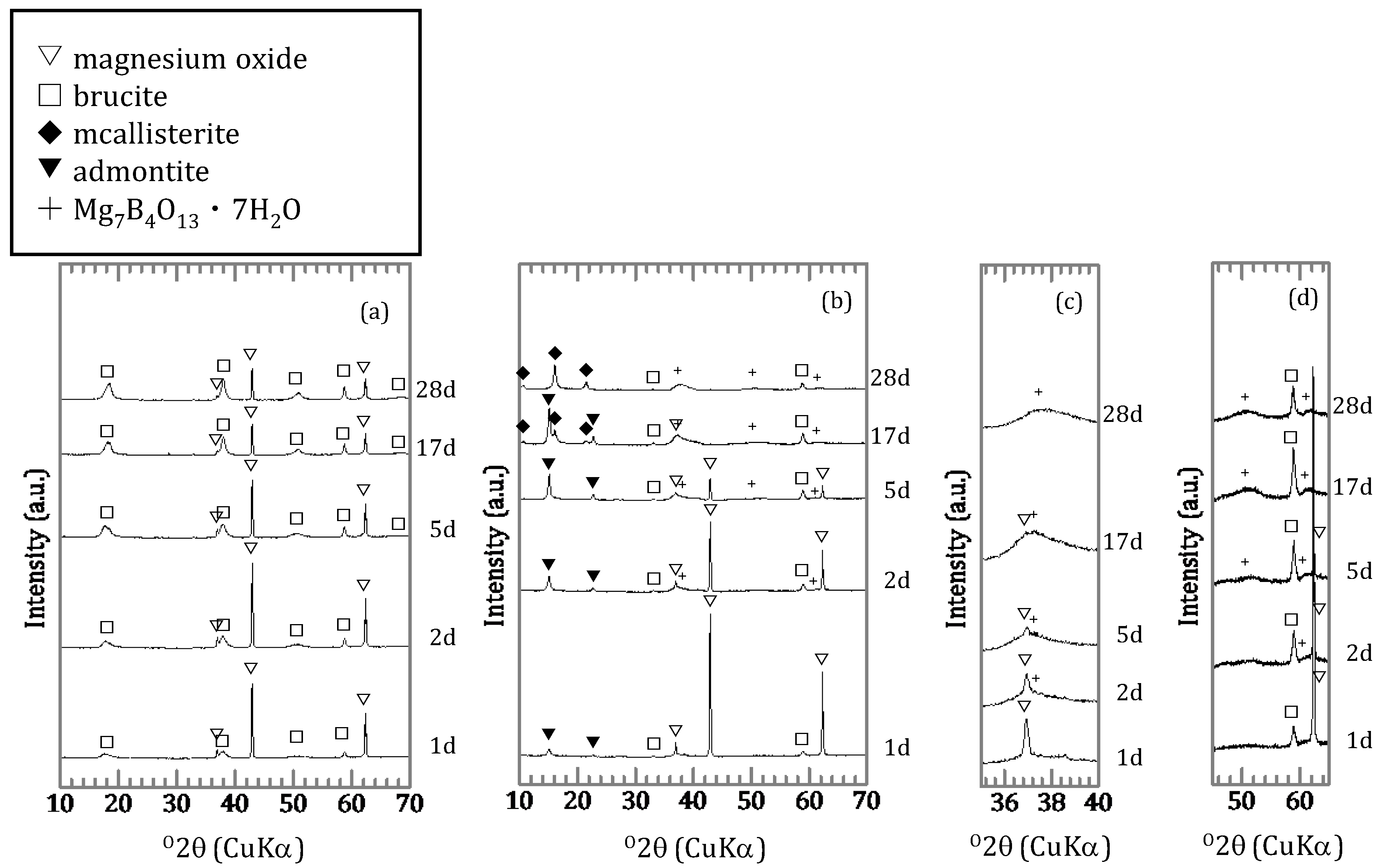
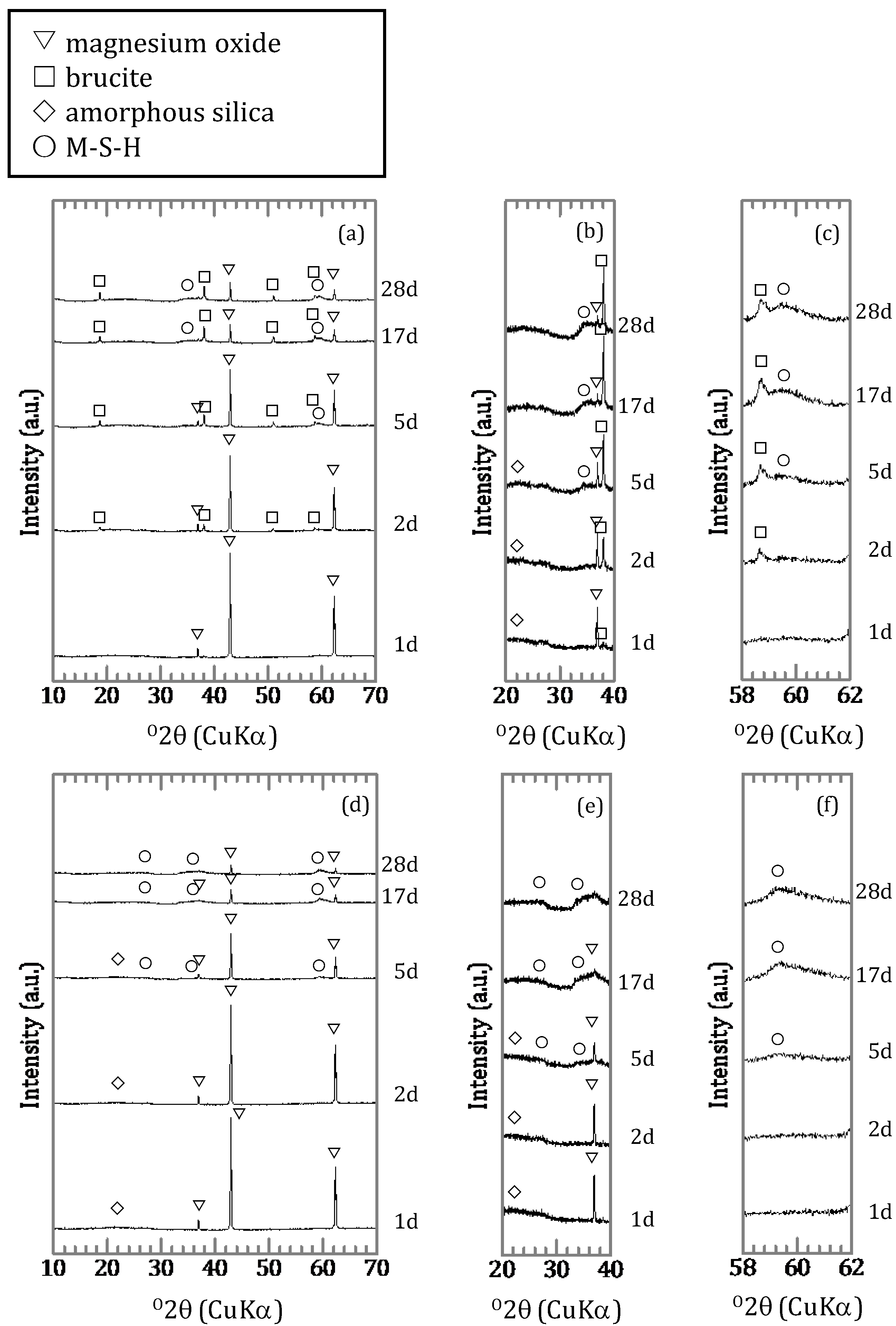
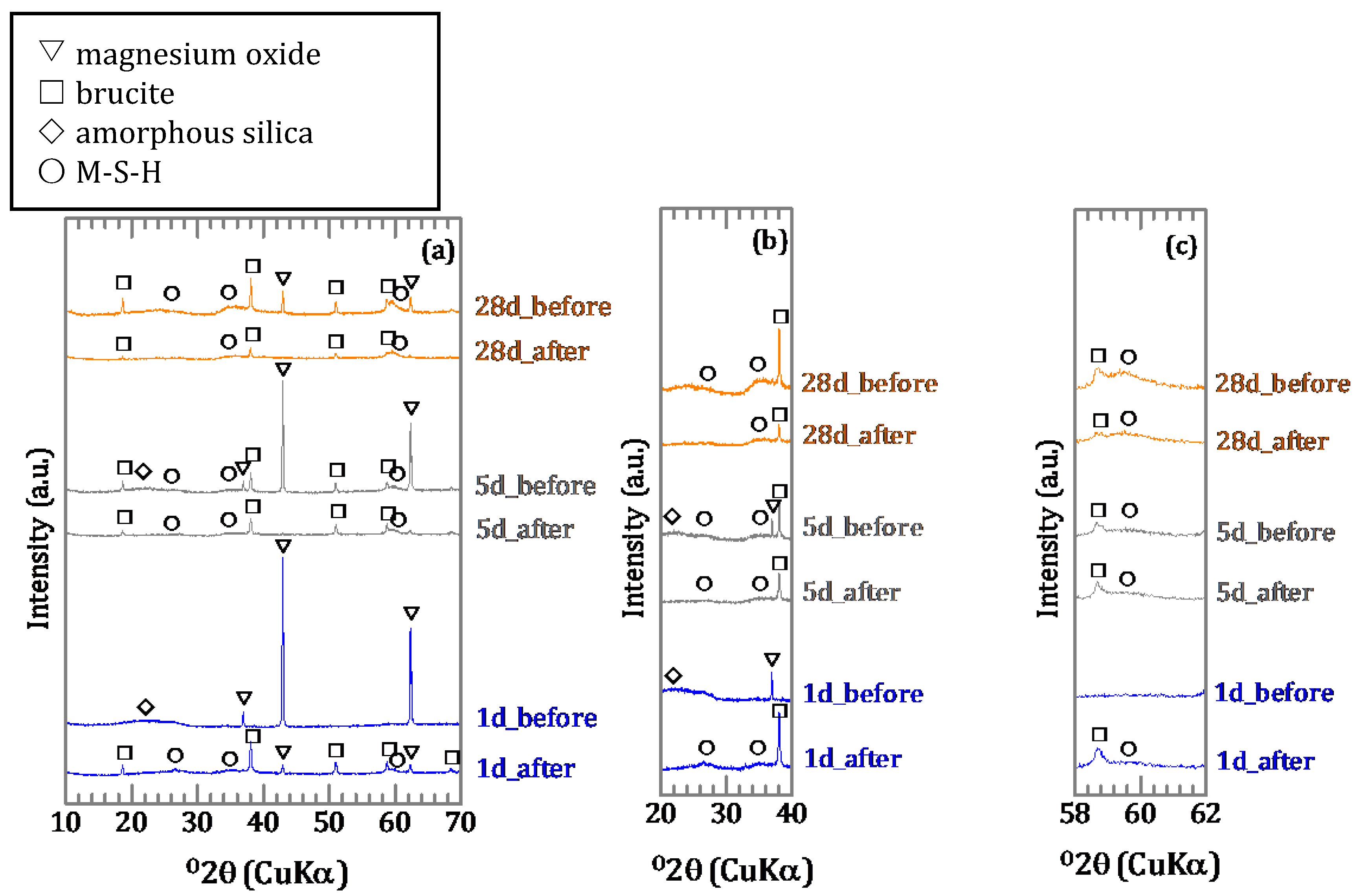
For the solids of the silica free samples with an initial concentration of 0.46 mmol/L, brucite was formed as a secondary mineral (Figure 4a) with the shapes of the peaks broader than those of hydrated magnesium oxide. For the solids with an initial concentration of 9.25 mmol/L, admontite (MgB6O7(OH)6) was formed after 1 day (Figure 4b) and Mg7B4O13∙7H2O after 2 days (Figure 4c,d). After 17 days, a different magnesium borate, mcallisterite (Mg2(B6O7(OH)6)2), had started to form. The peaks of admontite had disappeared after 28 days. For samples obtained in the presence of silica, the peaks of magnesium oxide and signal of amorphous silica disappeared gradually (Figure 5a,b,d,e) and the peak intensity of the magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H) increased (Figure 5b,c,e,f). In the [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L condition, brucite formed as the reaction period lengthened (Figure 5a,c).
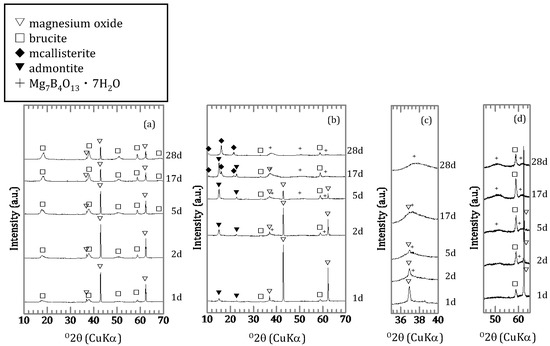
Figure 4.
X-ray diffractometry (XRD) spectra of samples without amorphous silica; (a) [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L and (b) [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L with magnified (b) spectra for (c) 35–40° and (d) 45–65° in 2θ.
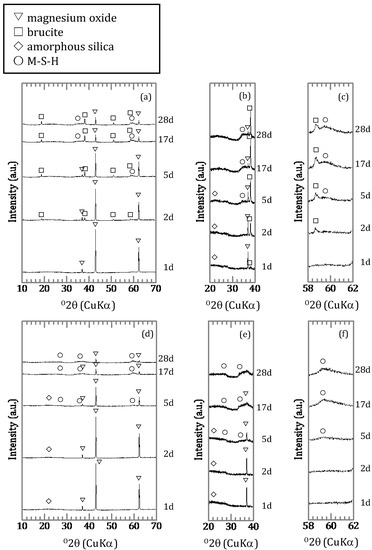
Figure 5.
XRD spectra of samples with amorphous silica; (a) [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L and (d) [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L with magnified spectra of (a) and (d) for (b and e) 35–40° and (c and f) 45–65° in 2θ.
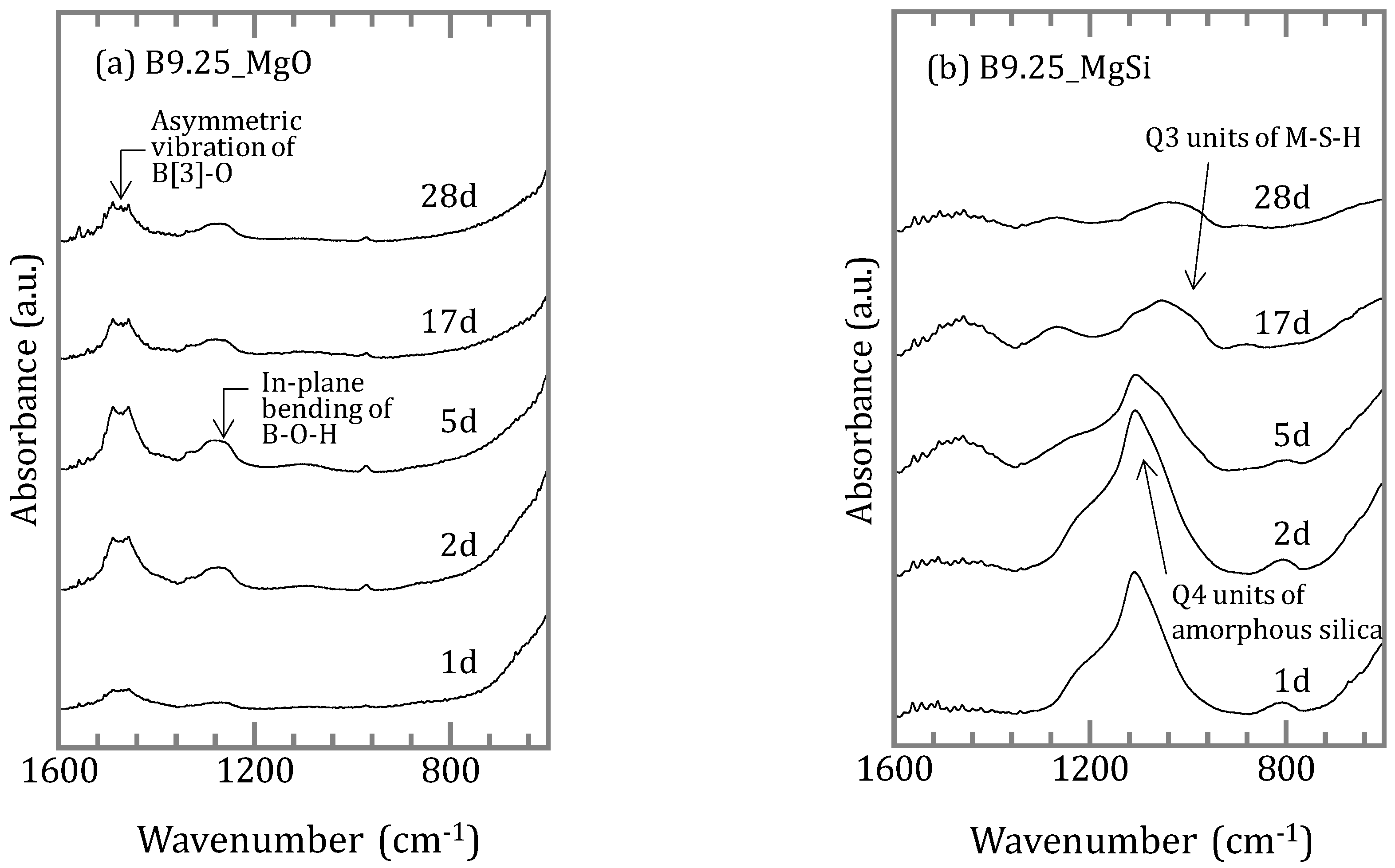
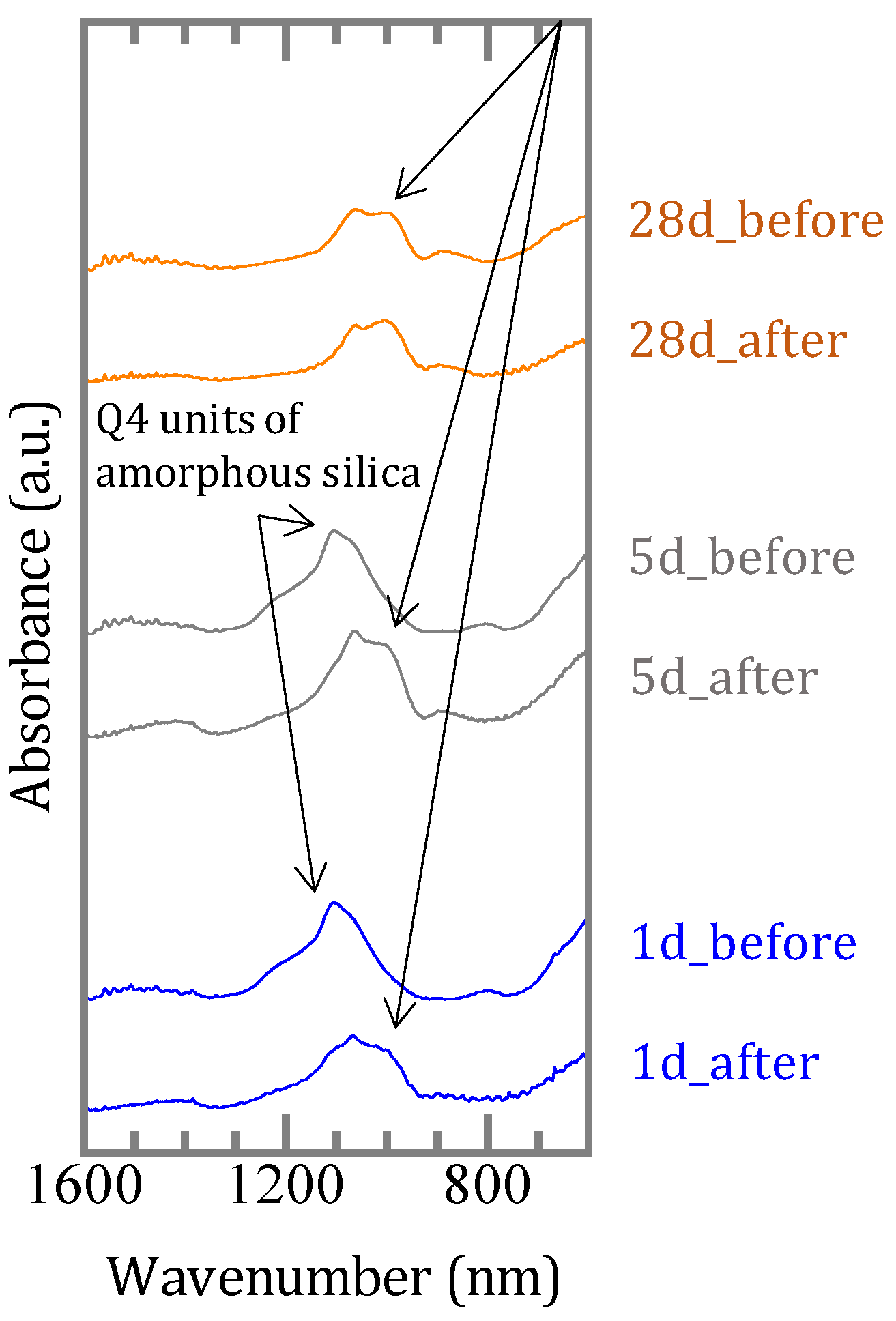
The FT-IR spectra of solid samples were assigned referring to the literature [11,14,15,16,17]. Silica free samples exhibit four absorption bands at 1490–1460, 1340, 1270 and 976 cm−1. All of these bands are assigned as asymmetric vibrations of BO3 units, symmetric vibration of BO3 units, in-plane bending of B–O–H linkage, and asymmetric vibration of BO4 units (Figure 6a). For the samples with silica, there are bands at 1460, 1270, 1000–1180, 960, 880 and 800 cm−1. In addition to the B–O bands noted above, other bands are assigned as asymmetric stretching of Si–O–Si (1000–1180 cm−1), asymmetric vibration of B–O–Si (880 cm−1) and symmetric stretching of Si–O–Si (800 cm−1) (Figure 6b).
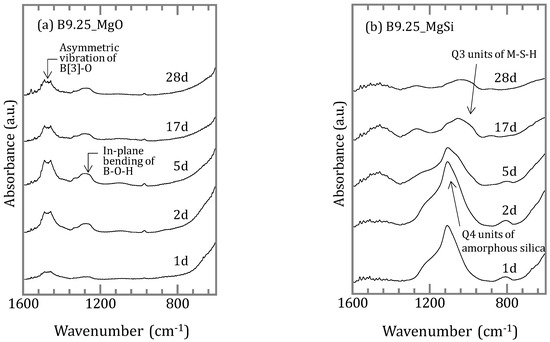
Figure 6.
Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) spectra of samples (a) without amorphous silica and (b) with amorphous silica.
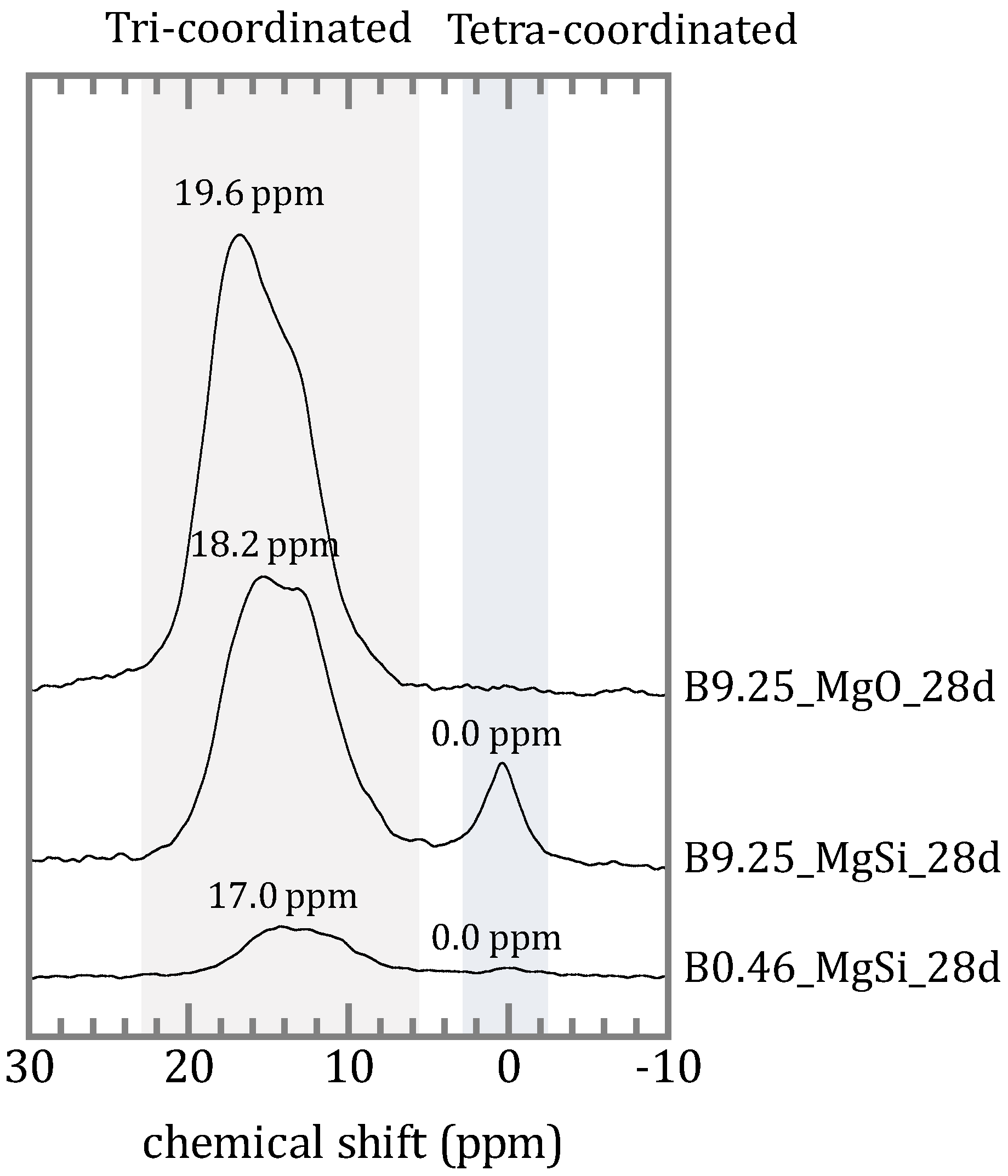
The 11B MAS-NMR spectra of both the silica free sample and the samples with silica are shown in Figure 7. In the sample without silica, resonance from tri-coordinated boron was observed at 19.6 ppm. For the samples containing silica, the spectra contain two types of 11B resonance, a broad peak between 5 and 20 ppm due to tri-coordinated boron and a relatively narrow resonance near 0 ppm from tetrahedral boron. The peak position of tri-coordinated boron of the sample with an initial concentration of 0.46 mmol/L was 17.0 ppm and of 9.25 mmol/L was 18.2 ppm.
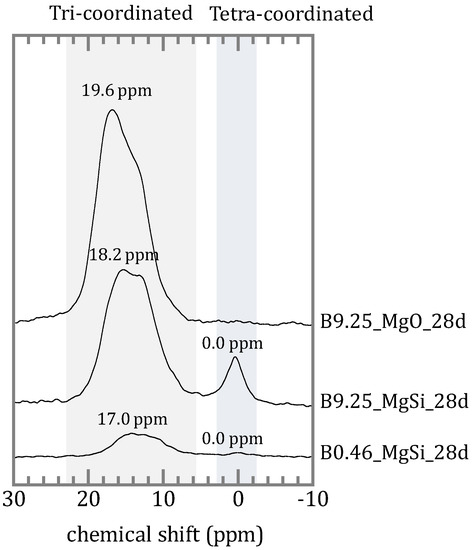
Figure 7.
11B magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR) spectra of 28-day aged samples with [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L and silica (bottom spectrum), and with [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L with (mid) and without silica (top) all aged for 28 days.
3.2. Sorption Experiments with Boron Added after Reaction of Magnesium Oxide and Amorphous Silica
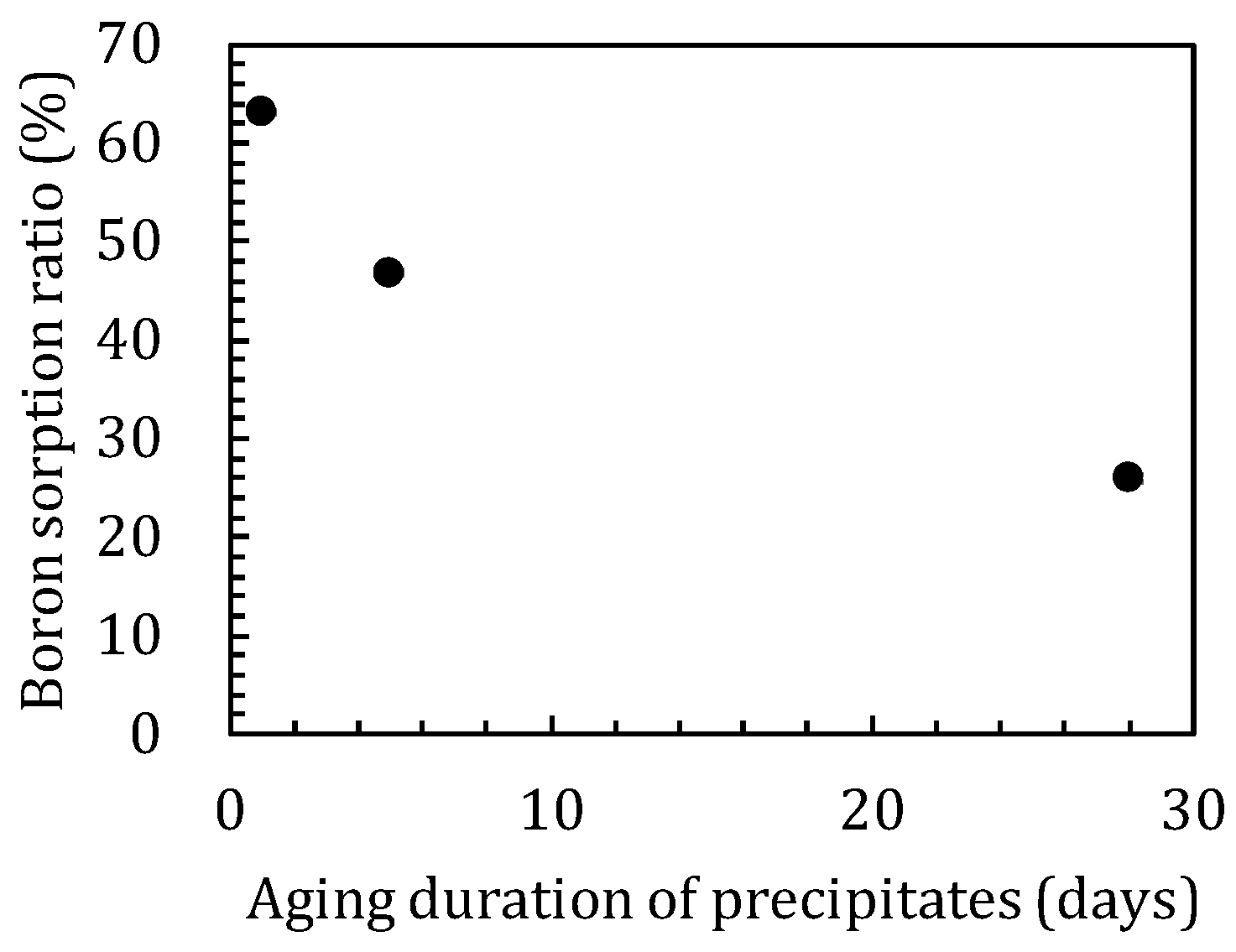
In the sorption experiments where boron was added after the reaction of magnesium oxide and amorphous silica, shorter precipitate synthesis times show higher sorption ratios of boron, with sorption ratios of 63.2, 46.9, and 26.0% for the precipitates synthesized for 1, 5, and 28 days, respectively (Figure 8).
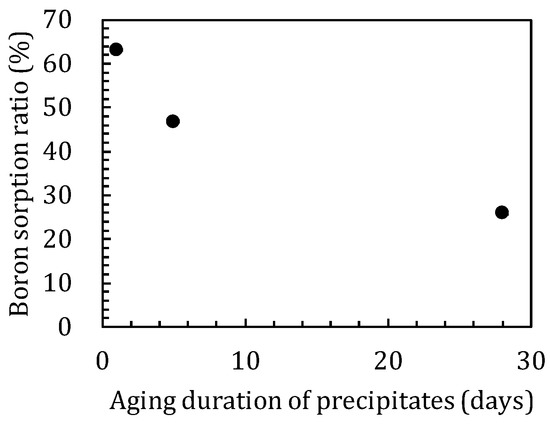
Figure 8.
Differences in boron sorption ratios with aging of precipitates.
Before the sorption, there was amorphous silica and magnesium oxide in the precipitate synthesized for one day, and with five days of synthesis there was also brucite and M-S-H in the precipitate (Figure 9a–c). Brucite and M-S-H were also identified in the precipitate synthesized for 28 days. After the sorption, magnesium oxide and amorphous silica was absent in the precipitate synthesized for one day and there were spectra for brucite and M-S-H (Figure 9a–c). Peaks of magnesium oxide and signal of amorphous silica were absent in the precipitate synthesized for five days (Figure 9a,b). The mineral phases were also present in the precipitate synthesized for 28 days, with decreased intensity of all peaks (Figure 9a).
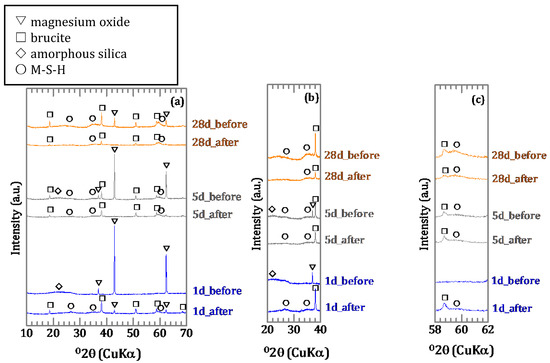
Figure 9.
XRD spectra of precipitates (a) before and after sorption with magnified spectra shown in (a) for (b) 20–40° and (c) 58–62° in 2θ.
The Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) spectra showed that the band at 1100 cm−1 was strong in the precipitates synthesized for one and five days before the sorption, and that this band shifted to ~1050 cm−1 after the sorption (Figure 10). In the precipitates synthesized for 28 days the band was present at ~1050 cm−¹ before the sorption experiment, and there was no significant change after the sorption.
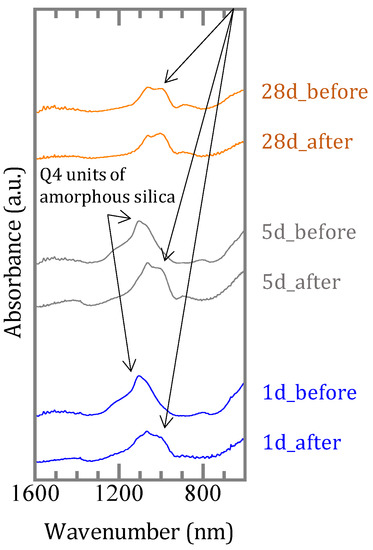
Figure 10.
FT-IR spectra of precipitates before and after boron sorption.
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Silica on Boron Sorption Reactions
Sorption experiments of boron using magnesium oxide in the absence and presence of silica were conducted. The change of components in the liquid phase and compositions of precipitates were investigated over time. The results obtained here showed differences in terms of the initial concentration of boron and the presence or absence of silica. Significant differences were observed both in solutions and solids in the [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L experiments, also in the absence of silica. At [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L, magnesium oxide and brucite were the only minerals identified by XRD in the solids after 28 days (Figure 4a). With [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L, magnesium borate minerals, such as admontite and Mg7B4O13∙7H2O were present after 1 day (Figure 4b). However, maximum boron sorption ratios were similar, 45% and 37% at [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L (Figure 1a), indicating that some boron was removed from the solutions under both conditions. In the case of [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L, it was clear that boron was removed from the solutions as magnesium borates due to the high boron concentrations. The boron sorption ratio decreased slightly after 5 days, likely due to transformation of magnesium borate mineral into a more stable phase. The magnesium concentration increased slightly during the transformation and was likely controlled by the solubility of magnesium borates. In the case of [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L, boron was likely removed together with the brucite which was formed during the experiments. This is supported by the broadened peaks for brucite in the XRD spectra (Figure 4a). Sasaki et al. [11] reported that peak shapes of borate-incorporating brucite are broad except for the (hk0) plane because boric acid interferes with the c-axis stacking of brucite by coordinating Mg atoms in parallel to the layer plane. The magnesium concentrations were controlled by the solubility of brucite [18].
When silica was introduced to the experimental solutions, boron was removed more efficiently both in the [B]ini = 0.46 and 9.25 mmol/L solutions, but it took longer to reach the steady states than in the absence of silica (Figure 1b). In both cases, no borates were detected in the solids by XRD, the peaks and signals in the XRD spectra were in agreement with those for M-S-H [19,20,21] and brucite (Figure 5a,d). Therefore, the higher boron sorption ratios in the solutions with silica were the result of formation of M-S-H. Recent investigations [22,23,24] have suggested that M-S-H, formed at the interface between cement with natural rock, can be expressed as (MgO)x-(SiO2)y-(H2O)z with variable stoichiometric ratios of Mg:Si:H. The magnesium concentrations were controlled by the solubility of brucite [18] for the case of [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L. In the case of [B]ini = 9.25 mmol/L, the liquid phase did not reach the equilibrium in 28 days therefore the magnesium concentrations were higher than reported value of M-S-H [20]. The IR spectra of the solid samples from the solutions with silica after 17 days (Figure 6b) are consistent with those of synthesized M-S-H phases [19,20,21,25,26,27] though there is a band at 665 cm−1, corresponding to Si–O–Si bending vibrations [20,28], which was not observed in our samples. This is likely due to the fact that the reaction times in the experiments here were shorter (only up to 28 days) than those of the previous studies (3 months–2 years), causing the Si–O–Si units to be too little developed to be detected by FT-IR. The IR spectra of the solid samples in the solutions with silica after 1, 2, and 5 days (Figure 6b) show a large broad band at ~1100 cm−1, suggesting the presence of amorphous silica as the band at ~1100 cm−1 was assigned to the Si–O stretching of Q4 units [17]. After 17 days, the band weakened and shifted to ~1050 cm−1, corresponding to Q3 units with one non-binding oxygen (Si–O–NBO) [17], indicating the transformation of amorphous silica into layer structured M-S-H. This means that the formation of M-S-H would have completed between 5 and 17 days, and this is the reason it took ~17 days for the boron sorption ratio to reach the steady state.
4.2. Chemical Form of Boron in the Precipitates
The presence of silica also affected the chemical form of boron in the precipitates. The peak position and the peak shape of the tri-coordinated boron observed at 5–20 ppm were different, and the samples containing silica showed a peak of tetra-coordinated boron at 0.0 ppm (Figure 7). The IR spectra of the silica free samples (Figure 6a) were in agreement with the study of Sasaki et al. as the sample containing silica formed M-S-H and was involved in boron sorption, specifically in the tetra-coordinated boron substitute with tetra-coordinated silicon. In general, the chemical shift for the tetra-coordinated boron resonance reflects the distribution of the second-nearest neighbor cation (B or Si). Negative chemical shifts occur only for B(4)–O–Si linkage, and positive chemical shifts indicate predominantly B(4)–O–B linkages. The peak positions of tetra-coordinated boron of Inderite (MgB3O3(OH)5∙5H2O) [29], borosilicate glass [30] and tourmaline [31] have been reported as 1.29, 0.0, and −0.1 ppm, respectively. Angeli et al. [30] and Lin-Shu et al. [32] have been reported that tetra-coordinated boron in borosilicate glass has a chemical shift near 0 ppm and a structure of BO–B*–(OSi)3. The peaks at 0.0 ppm in silica containing sample in this study, possibly showing that the tetra-coordinated boron in the precipitates has the same structure as that of boron in borosilicate and that it is isomorphically substituted in the silica lattice of M-S-H. As silicates containing boron in the tetrahedral position, sillimanite in which tetra-coordinated silicon is substituted with boron has been reported [33]. Stubican et al. [34] reported that the lattice of saponite, muscovite and phlogopite synthesized under hydrothermal synthesis conditions were substituted with tetra-coordinated boron. Therefore, tetra-coordinate silicon in the silicate lattice can be replaced by boron. Tri-coordinated boron is more common than the boron incorporated in the solid phase, but details remain unclear.
Compared to the peak of tri-coordinated boron in magnesium borate, the peak positions of the silica containing samples showed at the higher magnetic field side (Figure 7). This would be the result of a shielding effect of silica [35], however the peak would be expected to shift more if the second nearest atom is silicon. According to Hwang et al. [36], the chemical shifts of non-framework tri-coordinated boron (B–(OB)3), main boron (B–(OSi)3) and other boron (HO–B–(OSi)2) in borosilicate zeolites were observed at 18.0, 10.1, and 14.6 ppm respectively. The chemical shift of boron in the samples here is 17.0 ppm for the [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L. Compared to the boron in borosilicate zeolites, the chemical shift of the sample here is close to that of B–(OB)3, and it is unlikely that boron is in the silicate framework. Since M-S-H has a layered structure [20,21,37], there is a possibility that in-plane boron such as in boric acid or boroxol rings are present in the layer because the IR spectra showed absorption bands of in-plane bending of B(3)–O at 1270 cm−1 (Figure 6b). Tourmaline also has a layered structure where in-plane BO3 units are present in the layer [38]. The three boron atoms are each surrounded by three oxygen atoms in plane triangular coordination. The chemical shift of tri-coordinated boron in tourmaline has been reported at 18.1 ppm [31]. There is also the possibility that undetected silica glass was formed, and that boron was incorporated here. The chemical shift of tri-coordinated boron in borosilicate glass is reported to be 17.0–17.8 ppm [30,32,39], which is close to that of the samples here.
4.3. The Mechanism of Boron Incorporation in Precipitates
The sorption ratio of boron showed different values depending on the duration of the synthesis of the precipitates (Figure 8). For the precipitates before sorption, there was a broad peak at 20–25° in the XRD spectra (Figure 9b) and a band at ~1100 cm−1 in the IR spectra (Figure 10) for the precipitates synthesized for 1 and 5 days, which indicated the presence of amorphous silica. However, in the precipitate synthesized for 28 days no amorphous silica was detected by XRD. The band at 1100 cm−1 specific to amorphous silica was not appeared also by FT-IR and the development of the Q3 unit had already occurred (Figure 10). The precipitates synthesized for 1 and 5 days may be seen to be in the process of M-S-H formation, and the precipitate synthesized for 28 days was the precipitate in which M-S-H formation was complete, because in the first series of sorption experiments (Chapter 3.1) in which boron and magnesium oxide were both added, the formation of M-S-H was completed between 5 and 17 days (Figure 1b and Figure 6b). After the sorption, peaks of brucite and signals of M-S-H were detected by XRD in all solids (Figure 9b,c), and the IR spectra of the precipitates synthesized for 1 and 5 days showed a band of the Q3 unit indicating the layered structure (Figure 10). This suggests that M-S-H was formed during the experiment. There were no significant changes observed in the IR spectra of the precipitate synthesized for up to 28 days. As the time for synthesis of the precipitates was shorter, the boron sorption ratios were higher, suggesting that the sorption of boron was mainly based on the formation of M-S-H.
4.4. Implications for Immobilization of Boron in Contaminated Soils
In this study, high boron sorption ratios were observed in boron sorption experiments. The boron concentration decreased to 0.25 mmol/L at [B]ini = 0.46 mmol/L in the experiments with no silica present, with coexisting silica it decreased to 0.02 mmol/L in 28 days, satisfying the standard for drinking water mandated by the World Health Organization (WHO) [5].
There are several reports about immobilization of boron using magnesium oxide. Garcia-Soto et al. [12] proposed a mechanism of the boron adsorption process into magnesium oxide: First, the hydration reaction of magnesium oxide yielded brucite gel, with the pH of the solution increasing followed by a stereospecific chemical reaction between borate ions and active sites on the brucite surface. Sasaki et al. [11] indicated that molecular B(OH)3 preferentially reacts with the surface of magnesium oxide to form surface complexes. The surface complexes dissociate into [MgB(OH)4]+ and precipitate as magnesium borate and brucite. However, it is difficult to apply these proposed mechanisms to reactions in soil in general, because brucite and magnesium borates can rarely be expected to be present in soil when dissolved silica is contained in the pore water. Magnesium reacts with silica to form M-S-H and boron is immobilized in there.
Although the immobilization reactions have been discussed mainly in a simple system, soil is complicated. Therefore, as shown in this study, it is important to investigate immobilization in the presence of silica, which can be thought closer to the soil environment. It will lead us a more appropriate evaluation of immobilization.
5. Conclusions
Depending on the presence or absence of silica, the sorption reaction of boron with magnesium oxide determined here showed significant differences in both the sorption ratios and the sorption mechanism of boron. Boron was removed from the reaction solution by co-precipitation with brucite and the formation of multiple magnesium borates in solutions without silica. Despite low initial concentrations of boron, as low as as 0.46 mmol/L, it decreased only to 0.25 mmol/L. In the solutions with coexisting silica, M-S-H was formed, and some boron was incorporated into this structure, resulting in the boron concentration decreasing to 0.02 mmol/L. The results of the 11B NMR and FT-IR determinations showed that tetra-coordinated boron incorporated into the silica lattice of M-S-H and that tri-coordinated boron is present in some form. Stable immobilization can be expected for boron in such a structure, though it is necessary to pay attention to the elution behavior of the tri-coordinated boron that is not substituted in the lattice.
It is also important to consider the composition of the soil water where these processes take place, as there may be changes in the soil pH by the addition of different components and other factors when considering the immobilization reactions in the soils. If the supposed phases where hazardous substances are immobilized become different as a result of the immobilization reactions, it may not be possible to assess the risks of elution correctly.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Y. Kumaki of the High-Resolution NMR Laboratory, Hokkaido University for technical support on the 11B MAS NMR analysis, and F. Chikanda for valuable comments on an early version of the manuscript. The authors also thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author contributions
Shoko Nozawa conducted the experiments, the analysis, and the writing of the paper. Tsutomu Sato is the chief supervisor of Shoko Nozawa in the doctoral course. Tsutomu Sato proposed the idea for this research and provided helpful suggestions. Tsubasa Otake helped in the data interpretation and the development of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. Isrn Ecol. 2011, 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, S.I.; Morishita, T. Stabilization of Heavy Metals Contaminated Soils by Magnesium Oxide and Related Chemical and Mineralogical Reactions. Nendo Kagaku 2013, 51, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, K.; Sato, T.; Yoneda, T. Complexation Reactions of Oxyanions on Brucite Surfaces. Nendo Kagaku 2009, 48, 9. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.A.; Chimenos, J.M.; Fernández, A.I.; Miralles, L.; Segarra, M.; Espiell, F. Low-grade MgO used to stabilize heavy metals in highly contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorchev, H.G.; Ozolins, G. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. WHO Guidel. Drink. Qual. 2011, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, N. The Essence of Problems on Groundwater and Soil Pollutions Caused by Naturally Occurring Heavy Metals and Harmful Elements: Boron. Oyo Tech. Rep. 2013, 32, 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Remy, P.; Muhr, H.; Plasari, E.; Ouerdiane, I. Removal of boron from wastewater by precipitation of a sparingly soluble salt. Environ. Prog. 2005, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, N.; Sarp, S.; Yuksel, M.; Arar, Ö.; Bryjak, M. Removal of boron from seawater by selective ion exchange resins. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicak, N.; Gazi, M.; Bulutcu, N. N,N-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) octadecylamine for liquid-liquid extraction of boric acid. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengü, L.; Taştan, B.E.; Dönmez, G. Detection of boron removal capacities of different microorganisms in wastewater and effective removal process. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Qiu, X.; Moriyama, S.; Tokoro, C.; Ideta, K.; Miyawaki, J. Characteristic Sorption of H3BO3/B(OH)4− on Magnesium Oxide. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente García-Soto, M.M.; Muñoz Camacho, E. Boron removal by means of adsorption processes with magnesium oxide—Modelization and mechanism. Desalination 2009, 249, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Martens, D.C.; Zelazny, L.W. Distribution and Plant Availability of Soil Boron Fractions1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipcak, A.S.; Gurses, P.; Kunt, K.; Derun, E.M.; Piskin, S. Magnesium borate synthesis by microwave energy: A new method. J. Chem. Mol. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2013, 7, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Zeng, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Single-Crystal Szaibelyite MgBO2(OH) Nanobelt as a New Host Material for Red-Emitting Rare-Earth Ions. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.G.V.M.; Rupesh Kumar, A.; Neeraja, K.; Veeraiah, N.; Rami Reddy, M. Optical and structural investigation of Dy3+-Nd3+ co-doped in magnesium lead borosilicate glasses. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, M.E.; Sonderby, C.; Li, Z.; Sogaard, E.G. XPS and FT-IR investigation of silicate polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y. Thermodynamic properties of brucite determined by solubility studies and their significance to nuclear waste isolation. Aquat. Geochem. 2008, 14, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Rentsch, D.; Pochard, I.; Dauzères, A. Formation of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H). Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 99, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nied, D.; Enemark-Rasmussen, K.; L’Hopital, E.; Skibsted, J.; Lothenbach, B. Properties of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosz, C.; Grangeon, S.; Blanc, P.; Montouillout, V.; Lothenbach, B.; Henocq, P.; Giffaut, E.; Vieillard, P.; Gaboreau, S. Crystal structure of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H): The relation with 2:1 Mg-Si phyllosilicates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauzeres, A.; Achiedo, G.; Nied, D.; Bernard, E.; Alahrache, S.; Lothenbach, B. Magnesium perturbation in low-pH concretes placed in clayey environment—Solid characterizations and modeling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Calvo, J.L.; Hidalgo, A.; Alonso, C.; Fernández Luco, L. Development of low-pH cementitious materials for HLRW repositories. Resistance against ground waters aggression. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenni, A.; Mäder, U.; Lerouge, C.; Gaboreau, S.; Schwyn, B. In situ interaction between different concretes and Opalinus Clay. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 70–71, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, D.R.M.; Glasser, F.P. Synthesis and characterisation of magnesium silicate hydrate gels. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Nied, D.; L’Hôpital, E.; Achiedo, G.; Dauzères, A. Magnesium and calcium silicate hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 77, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sang, S.; Jin, S. Enhanced formation of magnesium silica hydrates (M-S-H) using sodium metasilicate and caustic magnesia in magnesia castables. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9110–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, Mid-, and Far-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Michaelis, V.K.; Pan, Y.; Yao, Y.; Tait, K.T.; Hyde, B.C.; Wren, J.E.C.; Sherriff, B.L.; Kroeker, S. Crystal structure refinements of borate dimorphs inderite and kurnakovite using 11B and 25Mg nuclear magnetic resonance and DFT calculations. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, F.; Charpentier, T.; De Ligny, D.; Cailleteau, C. Boron speciation in soda-lime borosilicate glasses containing zirconium. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, A.J.; Aguiar, P.M.; Michaelis, V.K.; Kroeker, S.; Hawthorne, F.C. The occurrence of tetrahedrally coordinated Al and B in tourmaline: An 11B and 27Al MAS NMR study. Am. Mineral. 2009, 94, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Stebbins, J.F. Nature of Silicon-Boron Mixing in Sodium Borosilicate Glasses: A High-Resolution 11B and 17O NMR Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 10063–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grew, E.S.; Rossman, G.R. Coordination of Boron in Sillimanite. Mineral. Mag. 1985, 49, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stubican, V.; Roy, R. Boron substitution in synthetic micas and clays. Am. Mineral. 1962, 47, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. 11B NMR investigation of boron interaction with mineral surfaces: Results for boehmite, silica gel and illite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3231–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Zones, S.I. Boron sites in borosilicate zeolites at various stages of hydration studied by solid state NMR spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 18535–18546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Le Goff, F.; Pochard, I.; Dauzères, A. Effect of magnesium on calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 97, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, G.E.; Buerger, M.J. The Structure of Tourmaline. Am. Mineral. 1948, 33, 532–540. [Google Scholar]
- Quintas, A.; Charpentier, T.; Majérus, O.; Caurant, D.; Dussossoy, J.L.; Vermaut, P. NMR study of a rare-earth aluminoborosilicate glass with varying CaMo-Na2O ratio. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2007, 32, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).