Assessing Jarosite Kinetic Dissolution Rates at Acidic Conditions and Different Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solvents
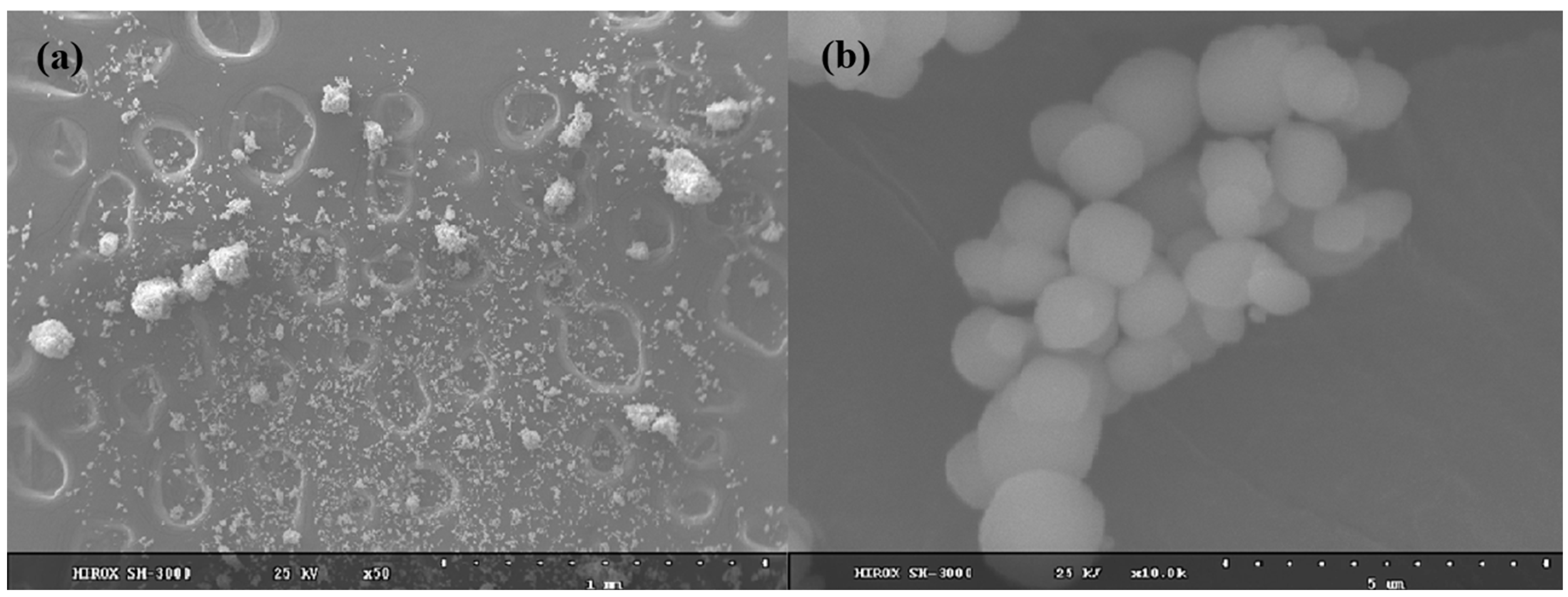
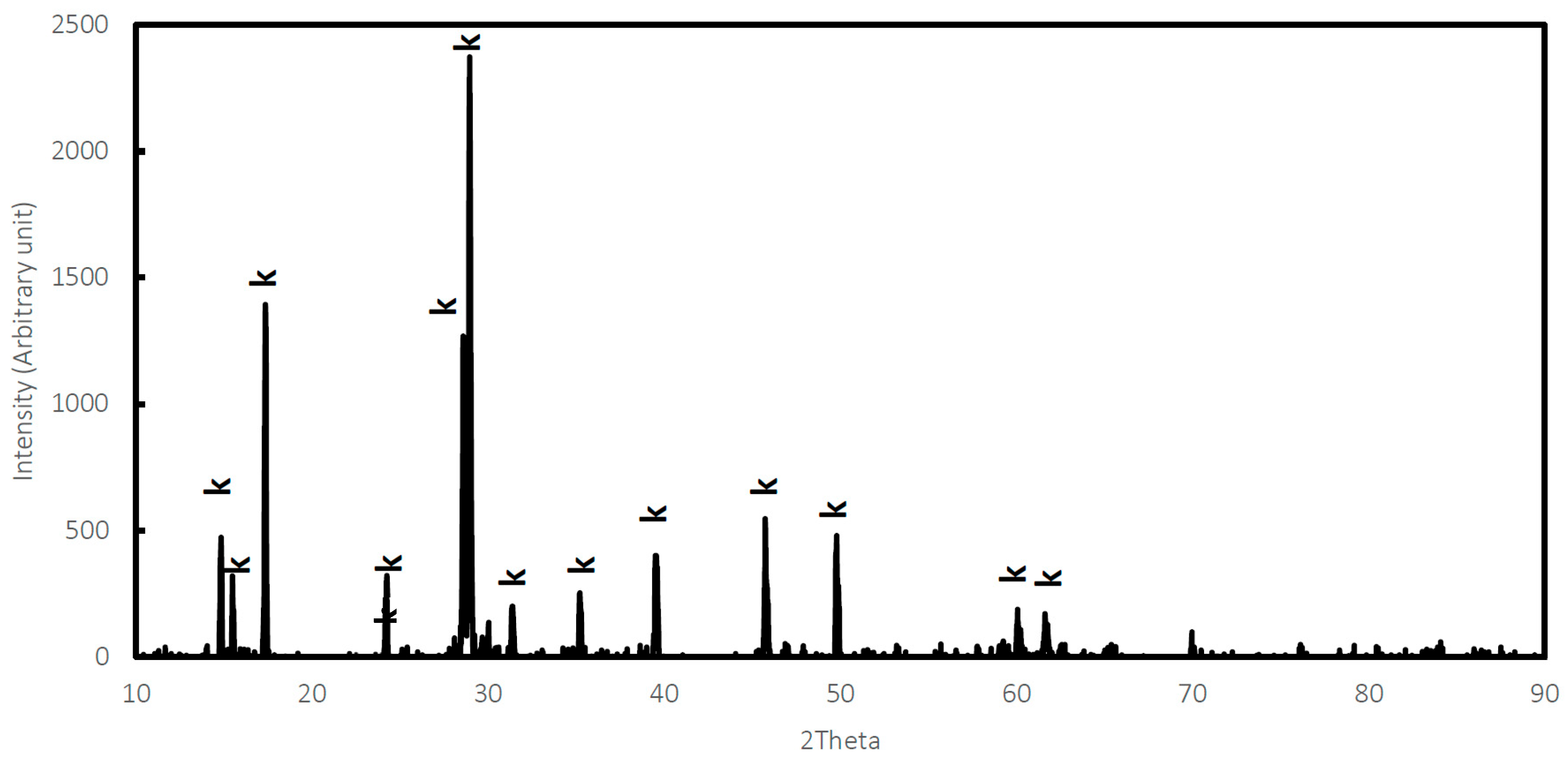
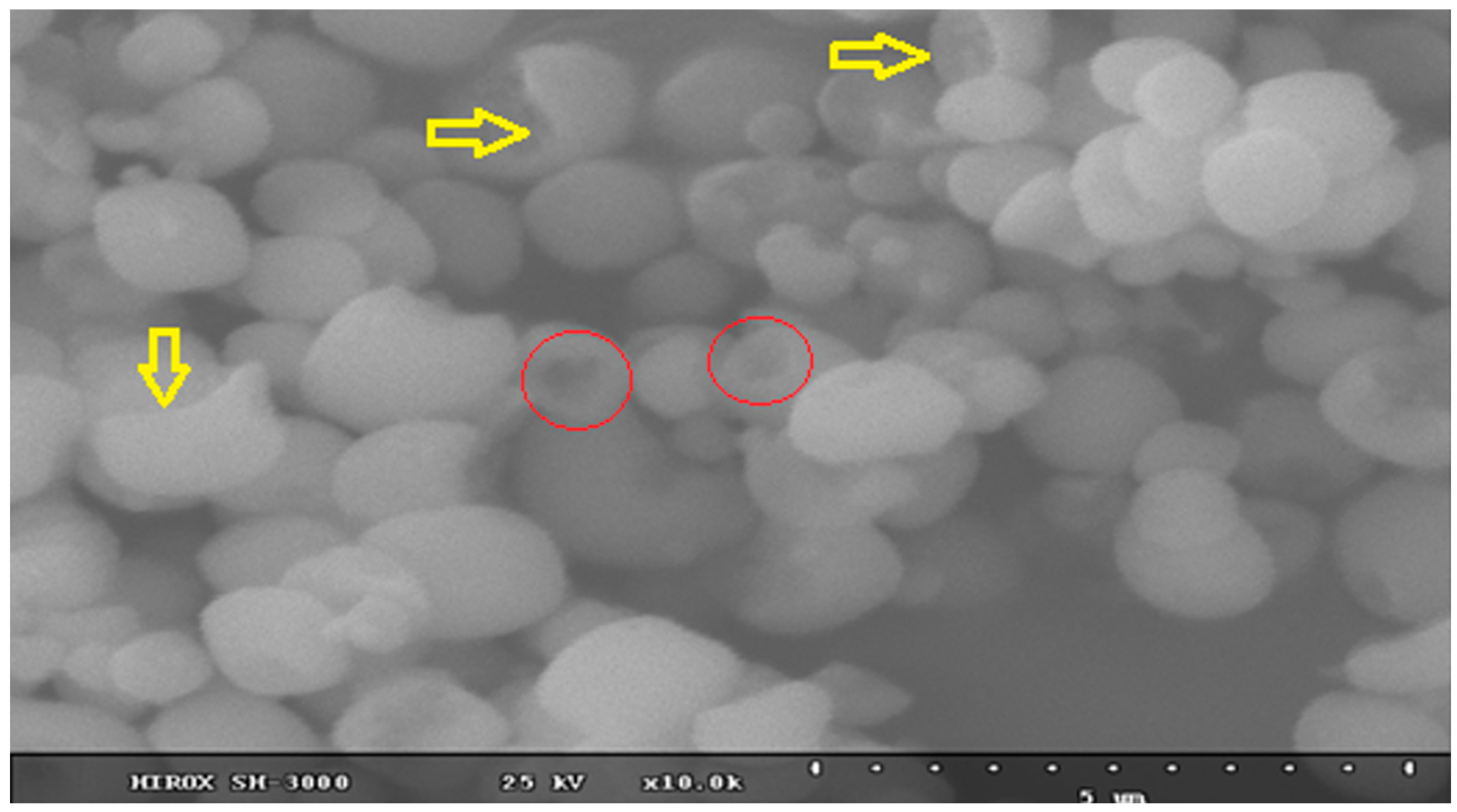
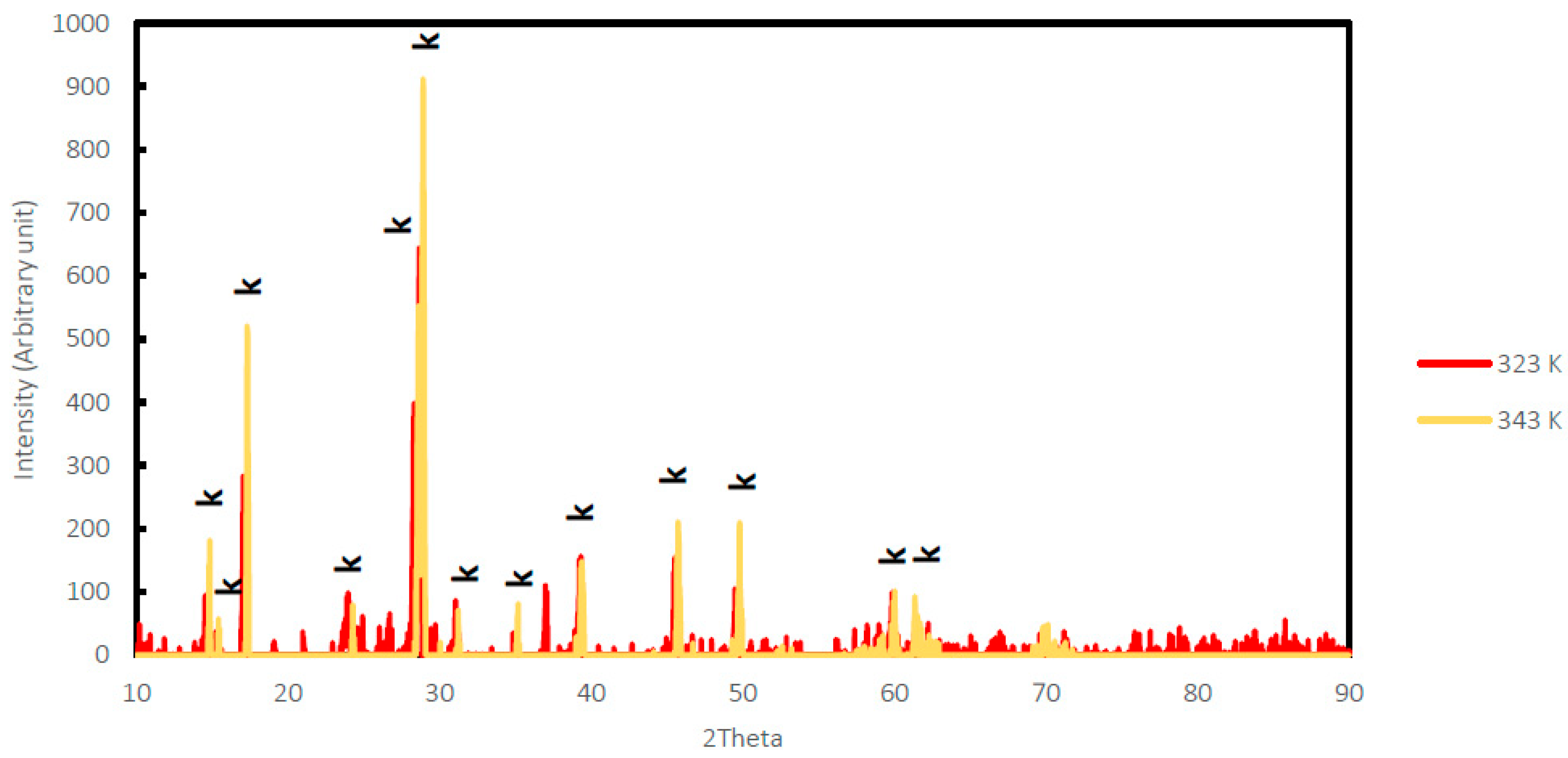
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of K-Jarosite
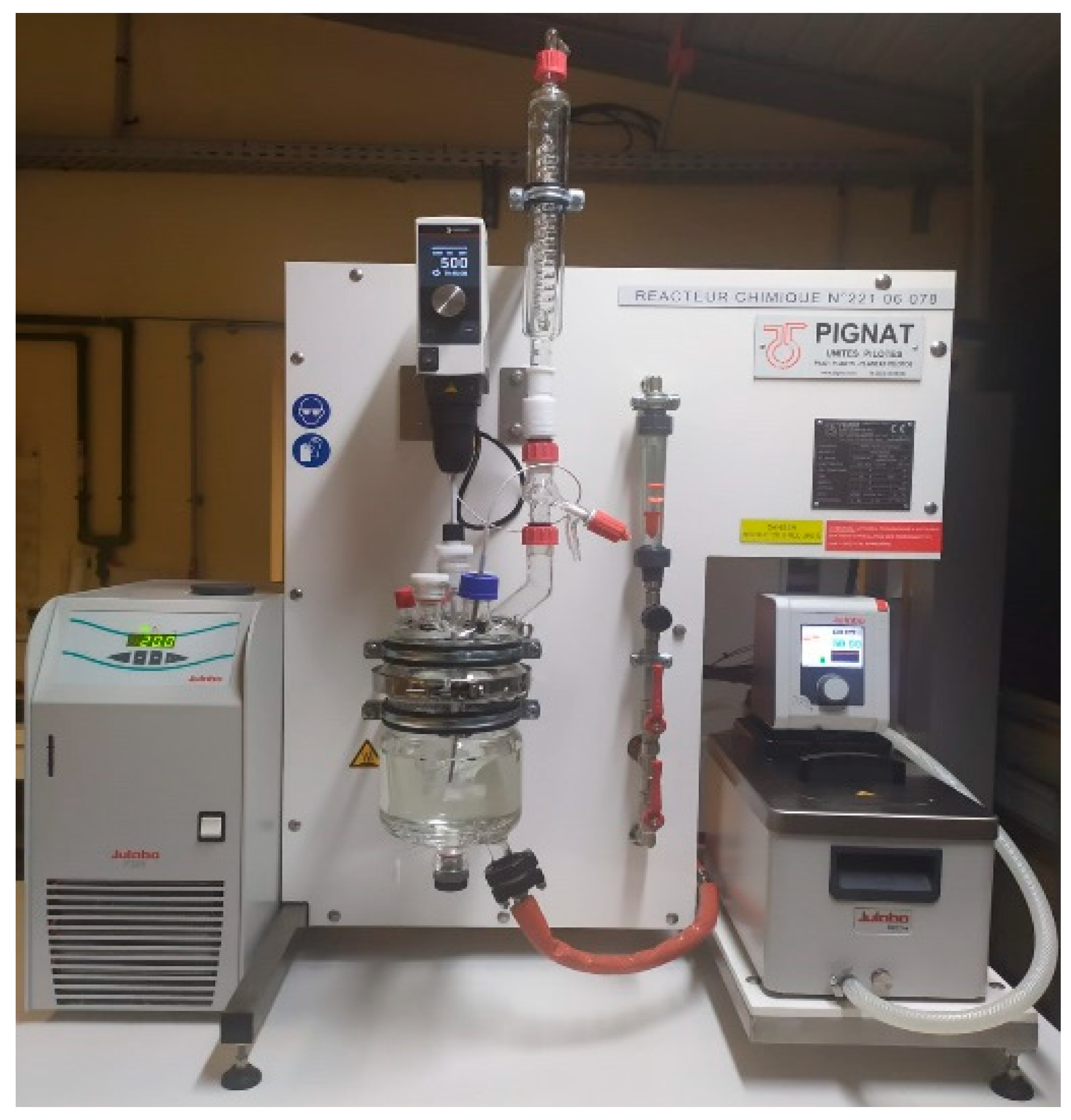
2.3. Dissolution Apparatus
2.4. Dissolution Experiments
2.5. Kinetic Modelling
2.5.1. Derivative Kinetic Model (DVKM)
2.5.2. Noyes–Whitney Kinetic Model (NWKM)
2.5.3. Shrinking Core Kinetic Model (SCKM)
3. Results and Discussion
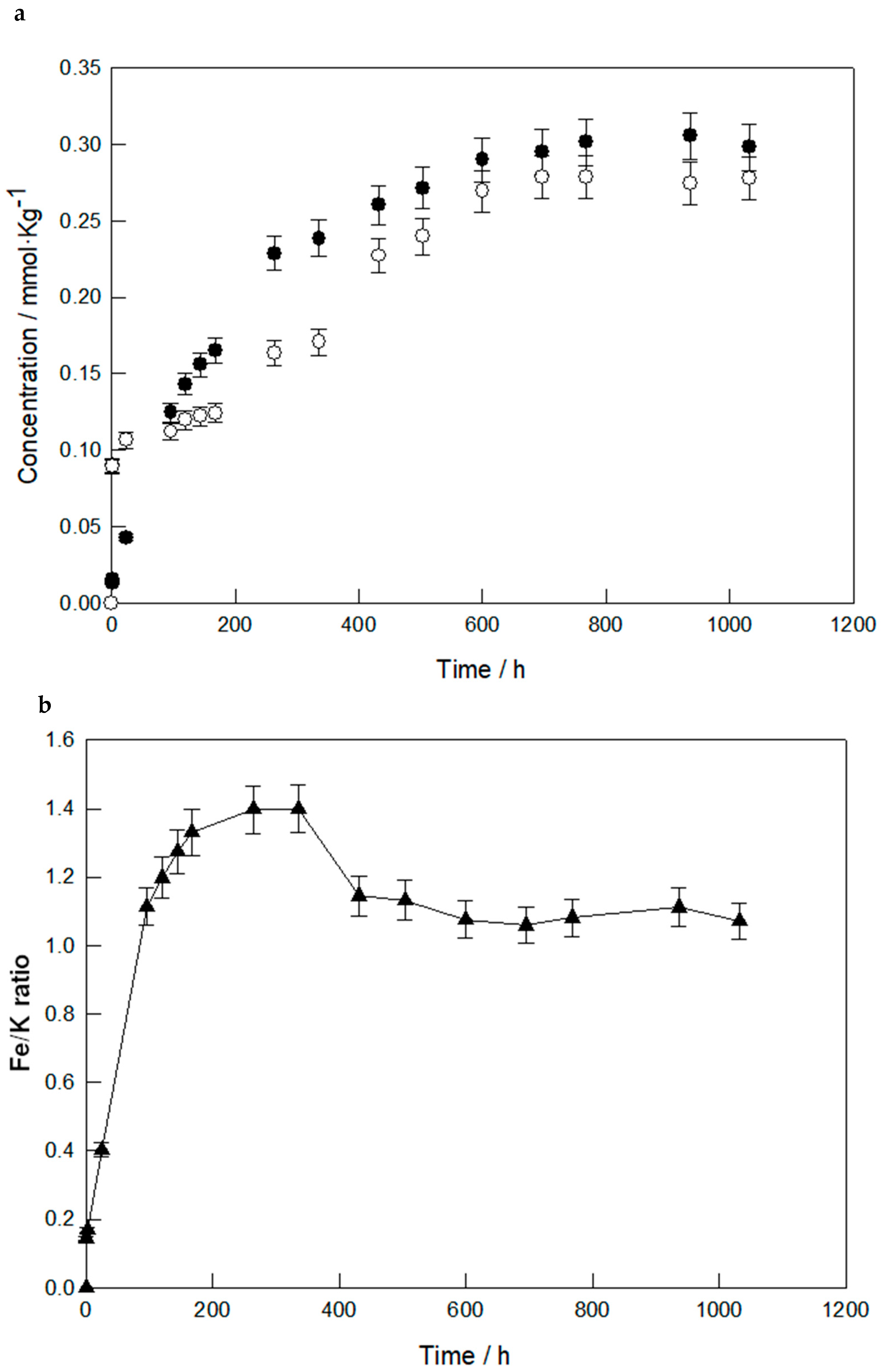
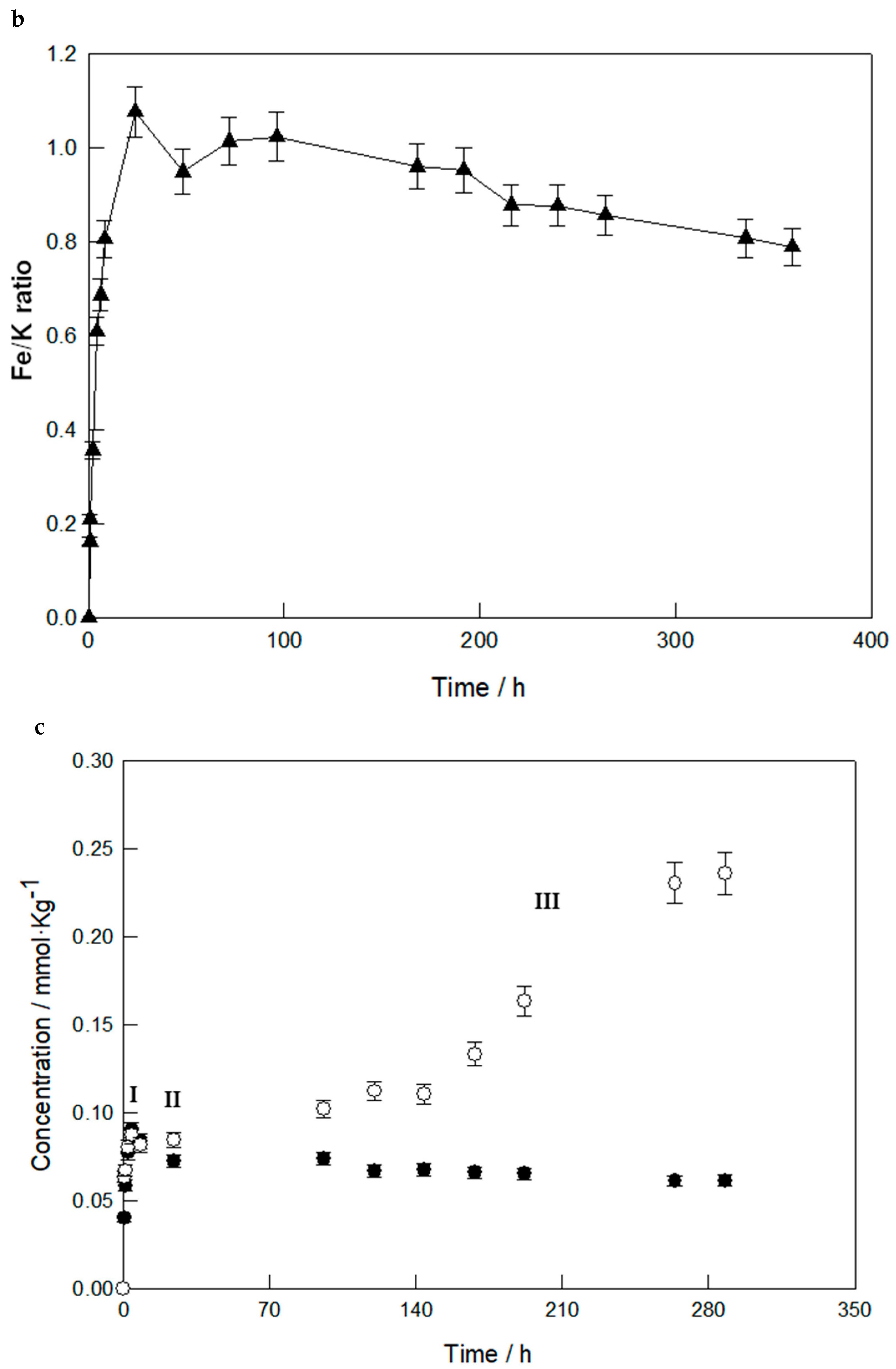
3.1. Dissolution Behavior at Room Temperature
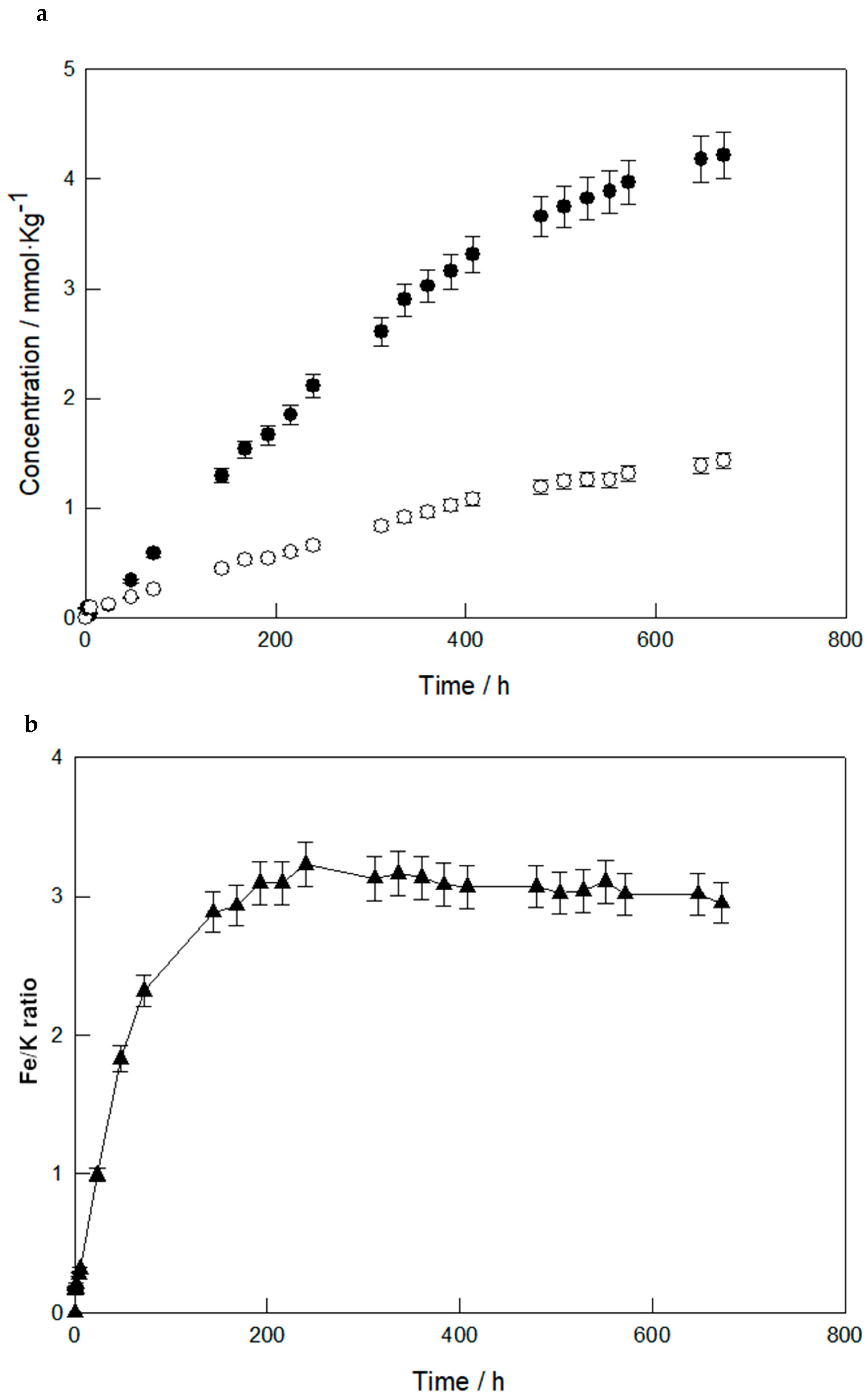
3.2. Dissolution Behavior at Higher Temperatures
3.3. Modeling of Dissolution Kinetics
3.3.1. Derivative Kinetic Model (DVKM)
3.3.2. Noyes–Whitney Kinetic Model (NWKM)
3.3.3. Shrinking Core Kinetic Model (SCKM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eftekhari, N.; Kargar, M.; Zamin, F.; Rastakhiz, N.; Manafi, Z. A review on various aspects of jarosite and its utilization potentials. Ann. Chim. Sci. Matériaux 2020, 44, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, C.N.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Ball, J.W. Solubility of jarosite solid solutions precipitated from acid mine waters, Iron Mountain, California, USA. Sci. Géologiques Bull. 1989, 42, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, B.B.; Benison, K.C. Geochemical characteristics of naturally acid and alkaline saline lakes in southern Western Australia. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood Madden, M.E.; Bodnar, R.J.; Rimstidt, J.D. Jarosite as an indicator of water-limited chemical weathering on Mars. Nature 2004, 431, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, G.; Morris, R.V.; Bernhardt, B.; Schröder, C.; Rodionov, D.S.; De Souza, P.A.; Yen, A.; Gellert, R.; Evlanov, E.N.; Zubkov, B. Jarosite and hematite at meridiani planum from opportunity’s Mössbauer spectrometer. Science 2004, 306, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squyres, S.W.; Arvidson, R.E.; Bollen, D.; Bell, J.F.; Brückner, J.; Cabrol, N.A.; Calvin, W.M.; Carr, M.H.; Christensen, P.R.; Clark, B.C. Overview of the opportunity Mars exploration rover mission to meridiani planum: Eagle crater to purgatory ripple. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2006, 111, 2006JE002771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriti, M.S.; Cézac, P.; Casás, L. Dissolution and precipitation of jarosite-type compounds: State of the art and future perspectives. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2024, 27, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, D.; Palmer, C.D. Solubility of jarosite at 4–35 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasharova, B.; Göttlicher, J.; Becker, U. Dissolution at the surface of jarosite: An in situ AFM study. Chem. Geol. 2005, 215, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.L.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Dubbin, W.E.; Wright, K. Dissolution of jarosite [KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6] at pH 2 and 8: Insights from batch experiments and computational modelling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, S.A.; Kirste, D.; Christy, A.G.; Beavis, F.R.; Beavis, S.G. Jarosite dissolution II—Reaction kinetics, stoichiometry and acid flux. Chem. Geol. 2008, 254, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood Madden, M.E.; Madden, A.S.; Rimstidt, J.D.; Zahrai, S.; Kendall, M.R.; Miller, M.A. Jarosite dissolution rates and nanoscale mineralogy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 91, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, B.N.; Elwood Madden, M.E.; Madden, A.S. Jarosite dissolution rates and maximum lifetimes in high salinity brines: Implications for Earth and Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 357–358, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahrai, S.K.; Elwood Madden, M.E.; Madden, A.S.; Rimstidt, J.D. Na-jarosite dissolution rates: The effect of mineral composition on jarosite lifetimes. Icarus 2013, 223, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legett, C.; Pritchett, B.N.; Elwood Madden, A.S.; Phillips-Lander, C.M.; Elwood Madden, M.E. Jarosite dissolution rates in perchlorate brine. Icarus 2018, 301, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.R.; Madden, A.S.; Elwood Madden, M.E.; Hu, Q. Effects of arsenic incorporation on jarosite dissolution rates and reaction products. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 112, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steefel, C.; Depaolo, D.; Lichtner, P. Reactive transport modeling: An essential tool and a new research approach for the Earth sciences. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 240, 539–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, E.M.; Elwood Madden, A.S.; Hausrath, E.M.; Elwood Madden, M.E. Assessing hydrodynamic effects on jarosite dissolution rates, reaction products, and preservation on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Fan, R.; Short, M.D.; Schumann, R.C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Smart, R.S.C.; Gerson, A.R. Evaluation of the rate of dissolution of secondary sulfate minerals for effective acid and metalliferous drainage mitigation. Chem. Geol. 2019, 504, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, A.M.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Mosley, L.M.; Fitzpatrick, R.W. Composition and dissolution kinetics of jarosite-rich segregations extracted from an acid sulfate soil with sulfuric material. Chem. Geol. 2020, 543, 119606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkhoshk, E.; Jorjani, E.; Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Rashchi, F.; Naazeri, M. Review of the hydrometallurgical processing of non-sulfide zinc ores. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 149, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, I.A.; Patiño, F.; Flores, M.U.; Pandiyan, T.; Cruz, R.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Reyes, M.; Flores, V.H. Dissolution rates of jarosite-type compounds in H2SO4 medium: A kinetic analysis and its importance on the recovery of metal values from hydrometallurgical wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Labra, M.; Romero-Serrano, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, E.; Avila-Davila, E.O.; Reyes-Perez, M. Synthesis, thermodynamic, and kinetics of rubidium jarosite decomposition in calcium hydroxide solutions. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2012, 43, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, I.J.E.; Flores, D.M.U.; Patiño, D.F.; Reyes, D.M.; Juárez, J.C.; Reyes, D.I.A.; Palacios, D.E.G. Synthesis and nature of the reaction of a solid solution of ammonium-potassium arsenojarosite in NaOH medium. In Proceedings of the EMC 2015–European Metallurgical Conference, Düsseldorf, Germany, 14–17 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, I.A.; Mireles, I.; Patiño, F.; Pandiyan, T.; Flores, M.U.; Palacios, E.G.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Reyes, M. A study on the dissolution rates of K-Cr(VI)-jarosites: Kinetic analysis and implications. Geochem. Trans. 2016, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordoñez, S.; Flores, M.U.; Patiño, F.; Reyes, I.A.; Islas, H.; Reyes, M.; Méndez, E.; Palacios, E.G. Kinetic analysis of the decomposition reaction of the mercury jarosite in NaOH medium: Kinetic analysis of the decomposition reaction of the mercury jarosite. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2017, 49, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, H.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, I.A.; Juárez, J.C.; Reyes, M.; Teja, A.M.; Palacios, E.G.; Pandiyan, T.; Aguilar-Carrillo, J. Determination of the dissolution rate of hazardous jarosites in different conditions using the shrinking core kinetic model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calla-Choque, D.; Lapidus, G.T. Jarosite dissolution kinetics in the presence of acidic thiourea and oxalate media. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 200, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisz, J. Studies on synthetic alkali-hydronium jarosite. I. Synthesis of jarosite and natrojarosite. Mineral. Pol. 1970, 1, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Härtig, C.; Brand, P.; Bohmhammel, K. Fe-Al-Isomorphism and Structural Water in Crystals of Jarosite-Alunite-Type. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1984, 508, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripmeester, J.A.; Ratcliffe, C.A.; Dutrizac, J.E.; Jambor, J.L. Hydronium in the alunite-jarosite group. Can. Mineral. 1986, 24, 773–784. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, R.; Leinze, R. Methods for Synthesis of Some Jarosites; Techniques and Methods 05-D1; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2005.
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königsberger, E. Editorial: Guidelines for the measurement of solid–liquid solubility data at atmospheric pressure. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriti, M.S.; Poulain, M.; Cézac, P.; Casás, L. K-jarosite precipitation kinetics at low-moderate temperatures: Factors affecting mechanism, formation rates, solid morphology and crystallinity. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 235, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, A.A.; Whitney, W.R. The rate of solution of solid substances in their own solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1897, 19, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, G.; Fraile, S.; Torrado, S.; Torrado, S. Process-induced crystallite size and dissolution changes elucidated by a variety of analytical methods. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 166, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff-Boenisch, D.; Gislason, S.R.; Oelkers, E.H. The effect of crystallinity on dissolution rates and CO2 consumption capacity of silicates. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Casas, J.M.; Paipa, C.; Godoy, I.; Vargas, T. Solubility of sodium-jarosite and solution speciation in the system Fe(III)–Na–H2SO4–H2O at 70 °C. J. Geochem. Explor. 2007, 92, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapieszko, R.S.; Patel, R.C.; Matijevic, E. Ferric hydrous oxide sols. 2. Thermodynamics of aqueous hydroxo and sulfato ferric complexes. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nolasco, M.C.; Flores, L.F.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Aguilar, J.; Palacios, E.G.; Flores, M.U.; Rodríguez, I.; Reyes, I.A. Acid dissolution of jarosite-type compounds: Effect of the incorporation of divalent cations into the structure on the reaction rate. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 212, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, G. Principles of Chemical Kinetics, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]







| Sample | Formula of Bulk Solid Based on SO4 = 2 | Ratio Fe/K |
|---|---|---|
| K-Jarosite | (H3O)0.17K0.83Fe2.54(SO4)2(OH)4.62(H2O)1.38 | 3.06 |
| Initial Solution pH | T (K) | C0 (g K-Jarosite/kg Solution) | Solution Medium | Time Duration | log r—K (mol/m2·s) | log r—Fe (mol/m2·s) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.00 | 25 | 0.2 a | HCl | 40 days | −8.51 (0.03) | N. D. | Baron and Palmer (1996) [8] |
| 2.00 | 25 | 0.2 a | HCl | 85 days | −8.80 | N. D. | Smith et al., 2006 [10] |
| 2.00 | 23 | 1.0 a | H2SO4 | 2 h | −8.55 (0.06) | N. D. | Elwood Madden et al., 2012 [12] |
| 2.00 | 23 | 1.0 a | H2SO4 | 2 h | −8.42 (0.03) | N. D. | Kendall et al., 2013 [16] |
| 1.97 | 23 | 1.0 a | H2SO4 | 16 days | −11.18 | −11.19 | Dixon et al., 2015 [18] |
| 2.00 | 23 | 1.0 | H2SO4 | 45 days | −10.26 (0.01) | −9.95 (0.01) | This study |
| 2.00 | 23 | 0.4 | H2SO4 | 40 days | −9.89 | −9.54 | This study |
| 0.90 | 23 | 1.0 a | H2SO4 | 2 h | −7.18 (0.06) | N. D. | Elwood Madden et al., 2012 [12] |
| 1.00 | 23 | 1.0 | H2SO4 | 27 days | −9.39 | −8.83 | This study |
| 1.00 | 23 | 0.4 | H2SO4 | 21 days | −9.23 | −8.66 | This study |
| 1.00 | 50 | 0.4 | H2SO4 | 1 day | −7.90 (0.03) | −7.37 (0.03) | This study |
| 1.00 | 70 | 0.4 | H2SO4 | 4 h | −7.06 (0.01) | −6.62 (0.01) | This study |
| Solid/Liquid Ratio | Intersection | Order (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | Fe3+ | K+ | Fe3+ | |
| 0.4 | −8.44 | −7.62 | 0.71 | 0.95 |
| 1 | −8.34 | −7.50 | 0.95 | 1.21 |
| 1st Order Dissolution | 2nd Order Dissolution | |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated rate equation | ln [Ceq − C] = −k + ln [Ceq] | [1/[Ceq − C]] = k + [1/[Ceq]] |
| Linear data fit | ln [Ceq − C] versus time | 1/[Ceq − C] versus time |
| Slope of linear fit | −k | k |
| Source | Parameters | NWKM log (k) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T (K) | Agitation (rpm) | do (µm) | Co (g K-Jarosite/kg Solution) | Fe | K | |
| Baron and Palmer (1996) [8] | 2.0 | 298 | 50 | 10–150 | 0.2 | N. D. | −6.01 |
| This study | 2.0 | 296 | 600 | <100 | 1.0 | −5.96 ± 0.10 | −6.06 ± 0.16 |
| This study | 2.0 | 296 | 600 | <100 | 1.0 | ||
| This study | 1.0 | 296 | 600 | <100 | 1.0 | −5.91 | −5.93 |
| This study | 2.0 | 296 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | −5.88 | −6.13 |
| This study | 1.0 | 296 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | −5.86 | −5.90 |
| This study | 1.0 | 323 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | −4.42 ± 0.01 | −4.44 ± 0.00 |
| This study | 1.0 | 323 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | ||
| This study | 1.0 | 343 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | −3.84 ± 0.01 | −3.78 ± 0.08 |
| This study | 1.0 | 343 | 600 | <100 | 0.4 | ||
| Experimental Conditions | Controlling Mechanism a | k (min−1) | tind (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T | C0 (g K-Jarosite/kg Solution) | Fe | ||
| 2 | 296 | 1.0 | MT SP/LP | 2.04 10−5 | 1564.99 |
| 0.4 | MT SP | 2.03 10−5 | 36.75 | ||
| 1 | 1.0 | MT LP | 2.53 10−5 | 54.94 | |
| 0.4 | MT LP | 3.43 10−5 | 404.19 | ||
| 323 | CR | 4.42 10−4 | 36.60 | ||
| CR | |||||
| 343 | CR | 2.46 10−3 | 0.63 | ||
| CR | |||||
| H2SO4 mol/L | pH | T/K | [H3O+] | k | tind | Source | Jarosite-Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.07 | 0.91 | 323 | 0.123 | 0.00114 | 78.0 | Reyes et al., 2017 [22] | (K·NH4·Na)-As-Jarosites |
| 0.07 a | 1.00 | 323 | 0.079 | 0.00044 | 36.6 | This study | K-Jarosite |
| 0.07 | 0.90 | 323 | 0.126 | 0.00130 | 40.5 | Nolasco et al., 2022 [43] | Na/Cu-J |
| 0.07 | 1.02 | 303 | 0.095 | 0.00013 | 408.0 | Reyes et al., 2017 [22] | (K·NH4·Na)-As-Jarosites |
| 0.07 a | 1.00 | 296 | 0.079 | 0.00003 | 404.2 | This study | K-Jarosite |
| 0.01 | 1.90 | 323 | 0.013 | 0.00008 | 638.0 | Reyes et al., 2017 [22] | (K·NH4·Na)-As-Jarosites |
| 0.01 | 1.29 | 323 | 0.051 | 0.00130 | 111.0 | Nolasco et al., 2022 [43] | Na/Cu-J |
| 0.006 a | 2.00 | 296 | 0.009 | 0.00002 | 36.75 | This study | K-Jarosite |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buriti, M.D.S.; Poulain, M.; Cézac, P.; Casás, L. Assessing Jarosite Kinetic Dissolution Rates at Acidic Conditions and Different Temperatures. Minerals 2025, 15, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090965
Buriti MDS, Poulain M, Cézac P, Casás L. Assessing Jarosite Kinetic Dissolution Rates at Acidic Conditions and Different Temperatures. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090965
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuriti, Mateus De Souza, Marie Poulain, Pierre Cézac, and Lidia Casás. 2025. "Assessing Jarosite Kinetic Dissolution Rates at Acidic Conditions and Different Temperatures" Minerals 15, no. 9: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090965
APA StyleBuriti, M. D. S., Poulain, M., Cézac, P., & Casás, L. (2025). Assessing Jarosite Kinetic Dissolution Rates at Acidic Conditions and Different Temperatures. Minerals, 15(9), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090965






