Investigation of the Coloration Mechanisms of Yellow-Green Nephrite from Ruoqiang (Xinjiang), China
Abstract
1. Introduction
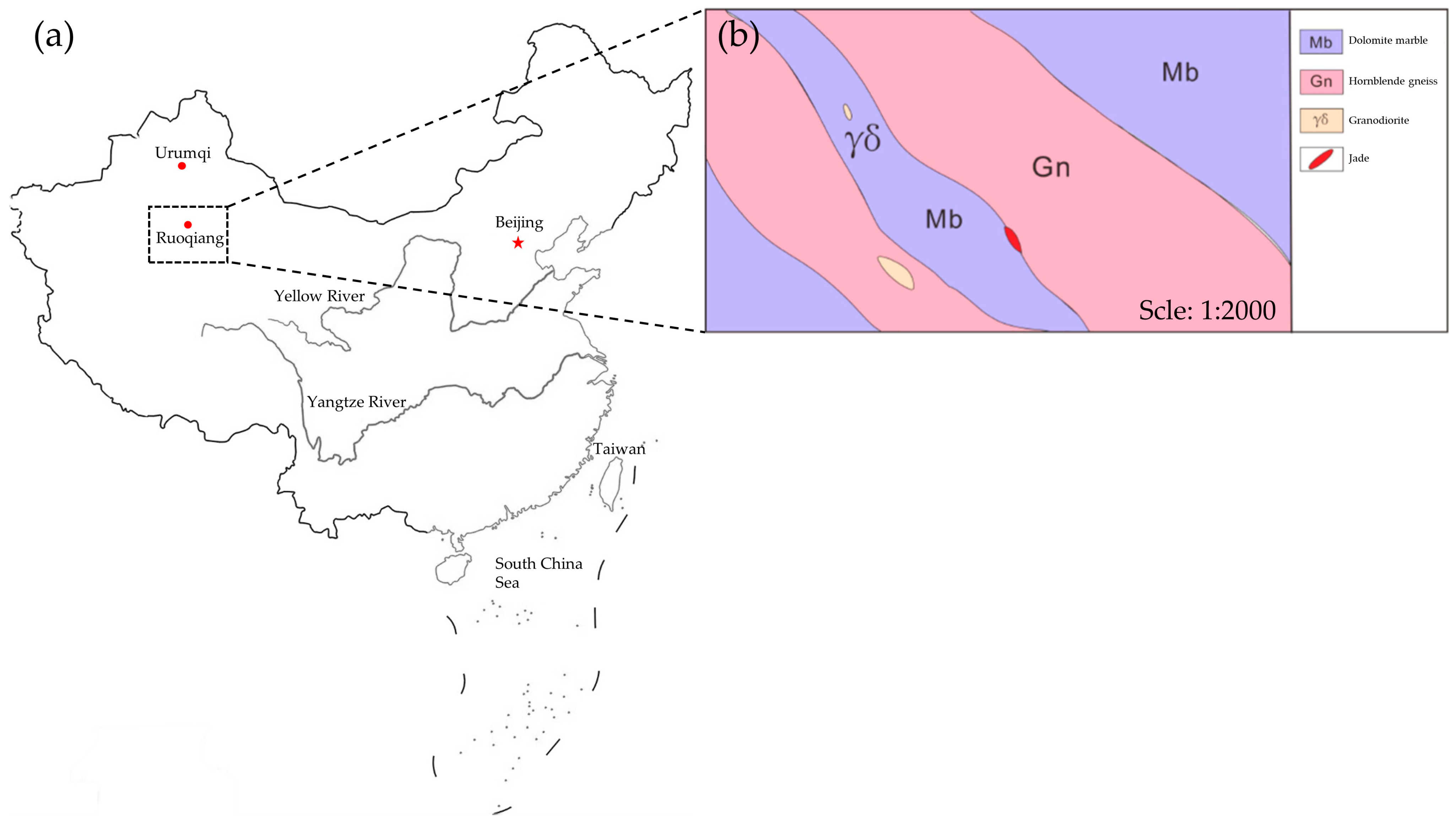
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
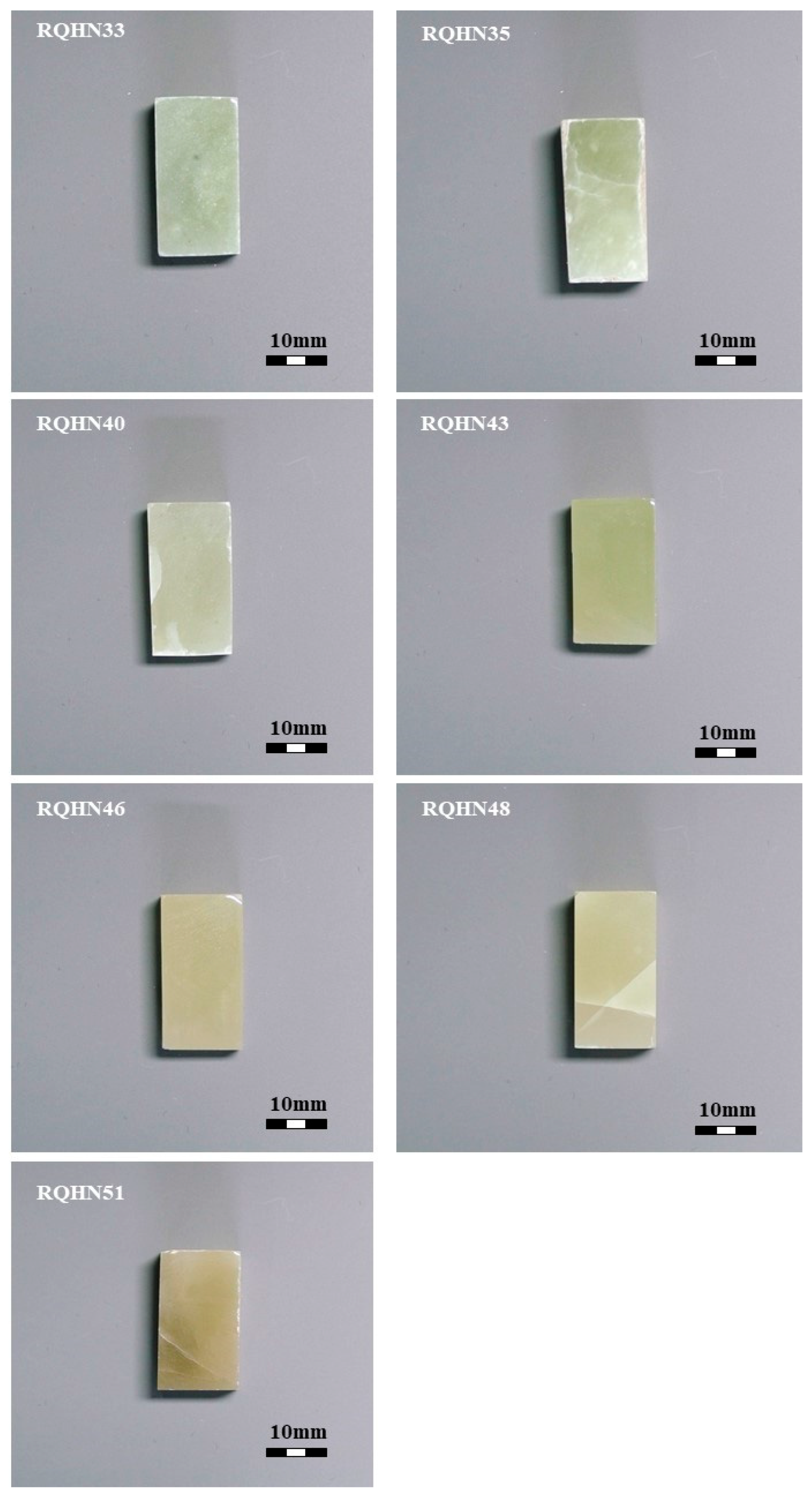
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Chromatometric Analysis
3.2.2. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.2.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.2.4. Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)
3.2.5. X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF) and Titrimetric Analysis
4. Results
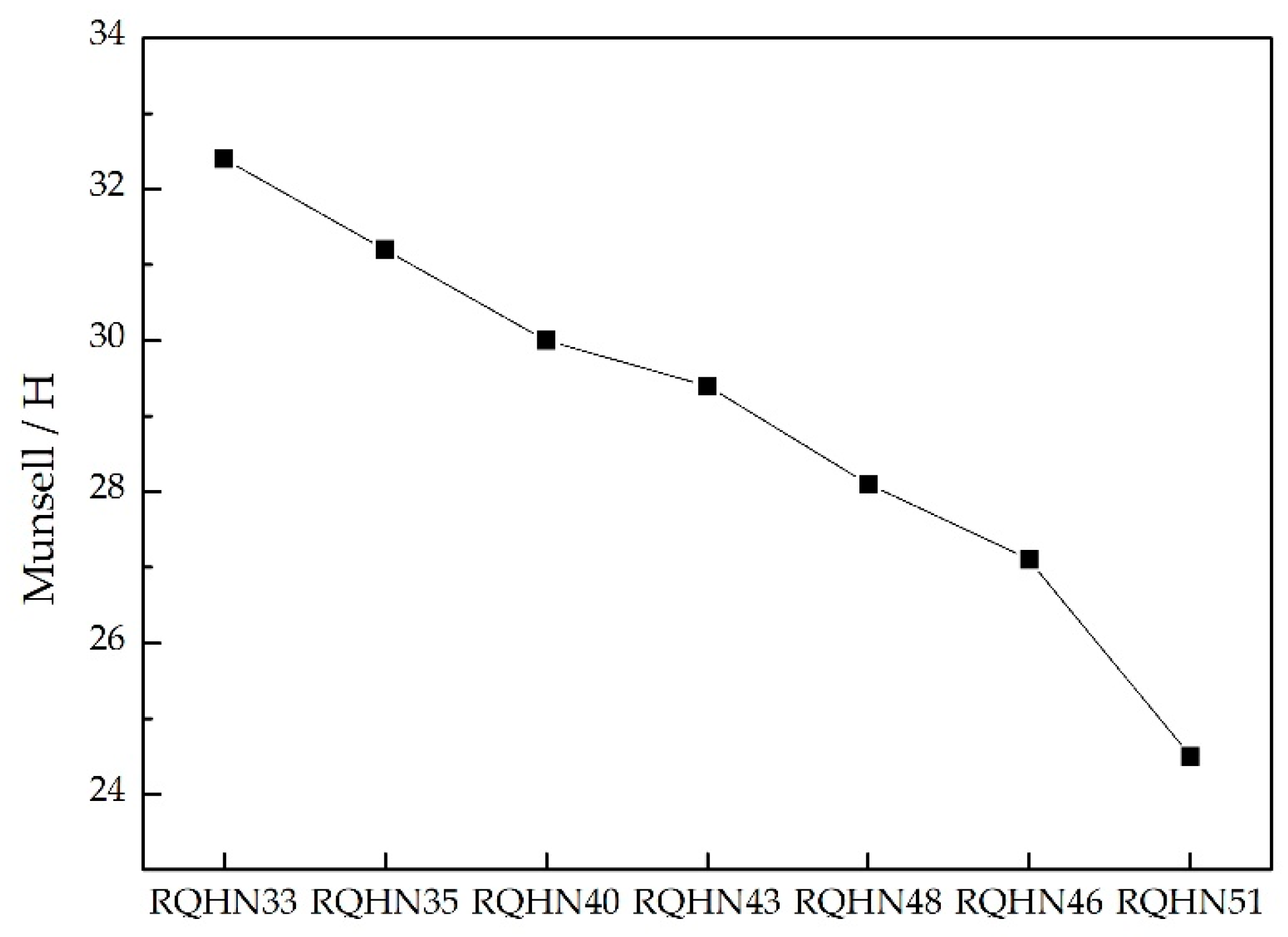
4.1. Chromaticity of Yellow-Green Nephrite
4.2. Spectroscopic Characteristics of Yellow-Green Nephrite
4.3. Bulk Composition and Trace Element Analysis of Yellow-Green Nephrite
4.3.1. Bulk Composition Analysis

| Value | Standard Error | Adj. R-Square | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.651 | 0.0489 | 0.942 |
| Slope | −0.017 | 0.0017 |
4.3.2. Trace Element Analysis
- Low ΣREE content (<10 μg/g);
- LREE-enriched patterns with negative Eu anomalies;
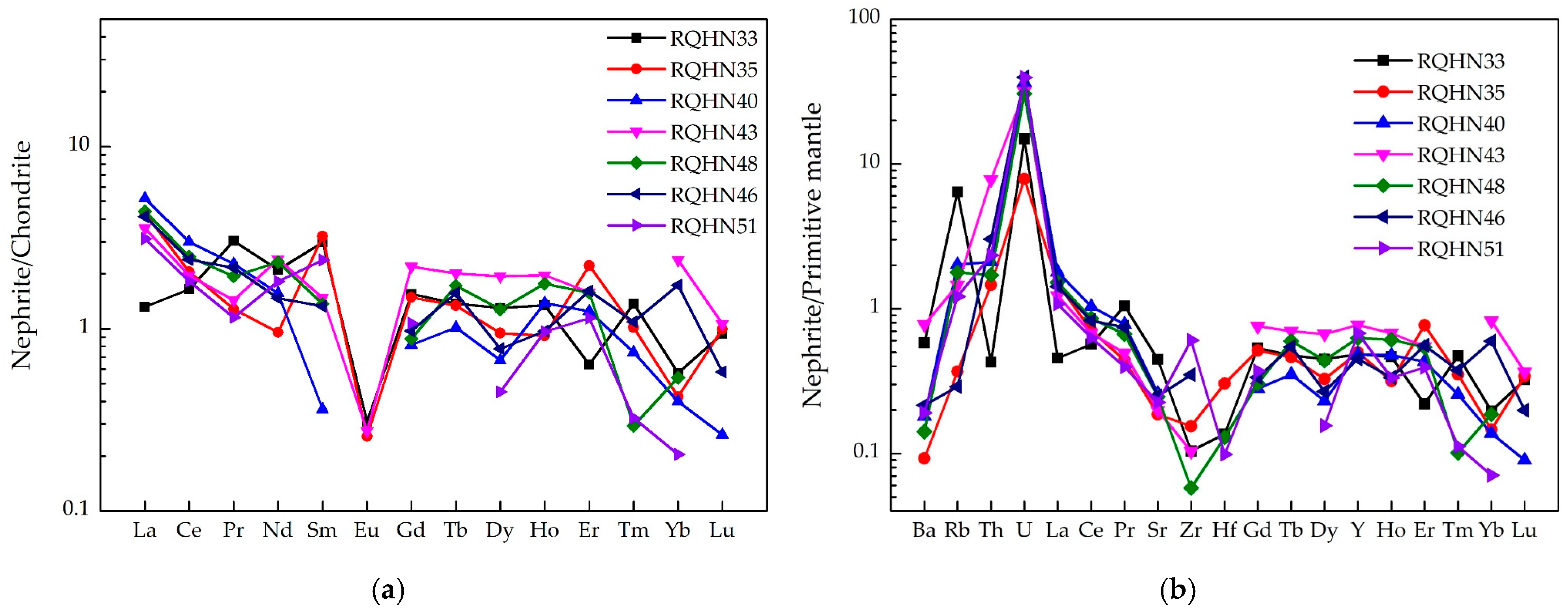
5. Discussion
5.1. Coloration Mechanism Analysis
5.2. Relationship Between Ore-Forming Environment and Color Genesis
- Oxidation-reduction conditions: The ore-forming fluid in Ruoqiang, Xinjiang, has a high oxygen fugacity, which favors the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, thereby increasing the proportion of this ion. The oxidation may result from regional metamorphism or magma-fluid interaction; under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, Fe2+ and Fe3+ distribution is controlled by oxygen fugacity and fluid composition, and Fe3+ is more stable and color-determining under high oxygen fugacity conditions.
- Fluid composition and temperature-pressure conditions: High SiO2 activity in ore-forming fluid may affect Fe site selection during tremolite crystallization. In Si-rich conditions, Fe3+ prefers the M1 site, altering M-OH vibration modes. Regional metamorphism may change crystal field splitting energy, affecting Fe3+ d-d transition energy. Higher temperatures may enhance Fe3+ charge transfer intensity, deepening the yellow hue.
- Influence of country rock properties: The country rock of Ruoqiang in Xinjiang is mainly composed of magnesian marble with high MgO content, which can inhibit the entry of Fe2+ and promote Fe3+ enrichment. This interaction between the properties of the country rocks and the ore-forming fluid is a key factor in yellow-green hue formation. Additionally, intermediate-acidic igneous rocks in the contact zone can provide additional Fe inputs into the ore-forming system through hydrothermal activity.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Abuduwayiti, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Chonghui, S.; Zhang, Z.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. SHRIMP U–Pb Zircon Ages, Mineral Compositions and Geochemistry of Placer Nephrite in the Yurungkash and Karakash River Deposits, West Kunlun, Xinjiang, Northwest China: Implication for a Magnesium Skarn. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 72, 699–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Shen, M.; Ke, J.; Zhang, J. GB/T 16552-2017; Gems-Nomenclature. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Harlow, G.; Sorensen, S.S. Jade: Occurrence and Metasomatic Origin. In Proceedings of the 31st International Geologic Congress, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 6–17 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harlow, G.E.; Sorensen, A.S.S. Jade (Nephrite and Jadeitite) and Serpentinite: Metasomatic Connections. Int. Geol. Rev. 2005, 47, 113–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhor, S. The Genesis of Nephrite and Emplacement of the Nephrite-Bearing Ultramafic Complexes of East Sayan. Int. Geol. Rev. 1991, 33, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J. A Mineralogical and Gemological Characterization of the Korean Jade from Chuncheon Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 1986, 22, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Yui, T.-F.; Kwon, S.-T. Origin of a Dolomite-Related Jade Deposit at Chuncheon, Korea. Econ. Geol. 2002, 97, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Maituohuti, A. Characterization of Yellow—Green Hetian Jade in Qiemo-Ruoqiang, Xinjiang. Rock Miner. Anal. 2022, 41, 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Q.; Abuduwayiti, M.; Liu, J. Mineral Inclusions and SHRIMP U–Pb Dating of Zircons from the Alamas Nephrite and Granodiorite: Implications for the Genesis of a Magnesian Skarn Deposit. Lithos 2014, 212–215, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Yang, M.; Feng, X.; Su, J. Gemmological Characteristics and Cause of Colour of Huangkouliao Nephrite. J. Gems Gemmol. 2017, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xifeng, L.; Gil, G.; Yan, L.; Xuemei, H.; Xiaochao, S. Timing of Formation and Cause of Coloration of Brown Nephrite from the Tiantai Deposit, South Altyn Tagh, Northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 131, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Bai, F.; Heide, G. Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Nephrite from Tieli, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Li, G.; Lei, J.; Sun, J. Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Petrogenesis of Nephrite from Panshi, Jilin, Northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, B. Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Petrogenesis of Green Nephrite from Dahua, Guangxi, Southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 118, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Geological Survey Report on the Fuguo Ridge Jade Mine in the Milan River, Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang; The Third Geological Brigade of the Xinjiang Geological and Mineral Bureau: Urumqi, China, 2002.
- Xu, F.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y. A New Conversion Algorithm between Munsell Color Order System and CIE1931 Standard Colorimetric System. Acta Photonica Sin. 2007, 36, 650–6545. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q. Mechanized Conversation of Munsell Notation to CIE Coordinates. J. Guangxi Univ. 1988, 2, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D1535-14(2023); Standard Practice for Specifying Color by the Munsell System. ASTM International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023.
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Yang, T. T/CAQI 134-2020; Gems-Determination of Trace Element-Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Hill, B.; Fw, V.; Roger, T. Comparative analysis of the quantization of color spaces on the basis of the CIELAB color-difference formula. Acm Trans. Graph. 1997, 16, 109–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, N.T.; Monika Koch-Muller Klaus, L. Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy of Natural (Fe2+, Fe3+)-Bearing Spinels of Spinel s.s.-Hercynite and Gahnite-Hercynite Solid Solutions at Different Temperatures and High-Pressures. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2005, 32, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislov, E.V.; Erokhin, Y.V.; Popov, M.P.; Nikolayev, A.G. Nephrite of Bazhenovskoye Chrysotile–Asbestos Deposit, Middle Urals: Localization, Mineral Composition and Color. Minerals 2021, 11, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. The Color Causes and Spectroscopy Characteristics of Sapphire from Shandong ChangLe. J. Grad. Sun Yat-Sen Univ. 2015, 13, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Huang, W.; Shao, T.; Shen, C.; Li, Z.; Shen, X. The Study on UV-Vis Spectrum of a Special Color-Changed Sapphire. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 2470–2473. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Han, J. The IR Analyses of M1 and M3 Cation Occupation of Hetian Jade, Manasi Green Jude and Xiuyan Old Jade. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2002, 21, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, N.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y. Study on the Color Classification of Hetian Jade by Colorimetry Test and Raman Spectroscopy. J. Hebei Geo Univ. 2023, 46, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, R.I.; Protochristov, C.; Stoyanov, C. Micro-PIXE Geochemical Fingerprinting of Nephrite Neolithic Artifacts from Southwest Bulgaria. Geoarchaeology 2012, 27, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Chang, Y.; Yang, M. Nephrite from Xinjiang Qiemo Margou Deposit: Gemological and Geochemical Insights. Minerals 2024, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapes, R.; Yun, S.-T. Geochemistry of a New Zealand Nephrite Weathering Rind. New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 2010, 53, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Shi, G.; Yui, tzen-fu; Zhang, G.-B.; Abuduwayiti, M.; Yang, L.; Sun, X. Geochemistry and Petrology of Nephrite from Alamas, Xinjiang, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqin, B.; Qian, R.; Zhuo, S.; Gan, F.; Dong, M.; Hua, Y. Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry Studies on Nephrite Minerals Formed by Different Metallogenic Mechanisms and Geological Environments. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 309, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Qi, L.; Liu, Y. Multiple Solutions of Ore-Forming Fluids of Carbonate Rock-Related Nephrite Deposits Constrained by Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. Minerals 2025, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

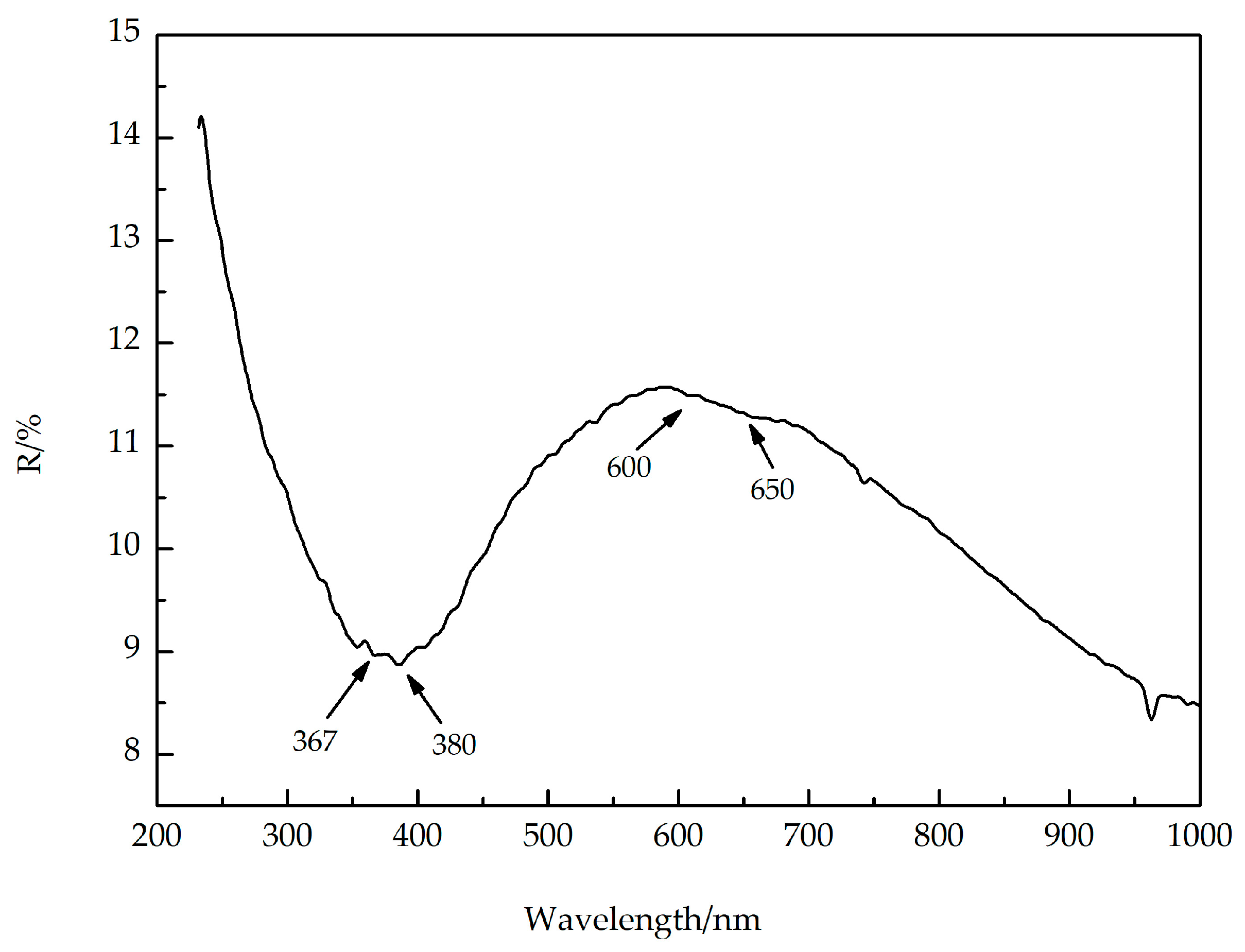
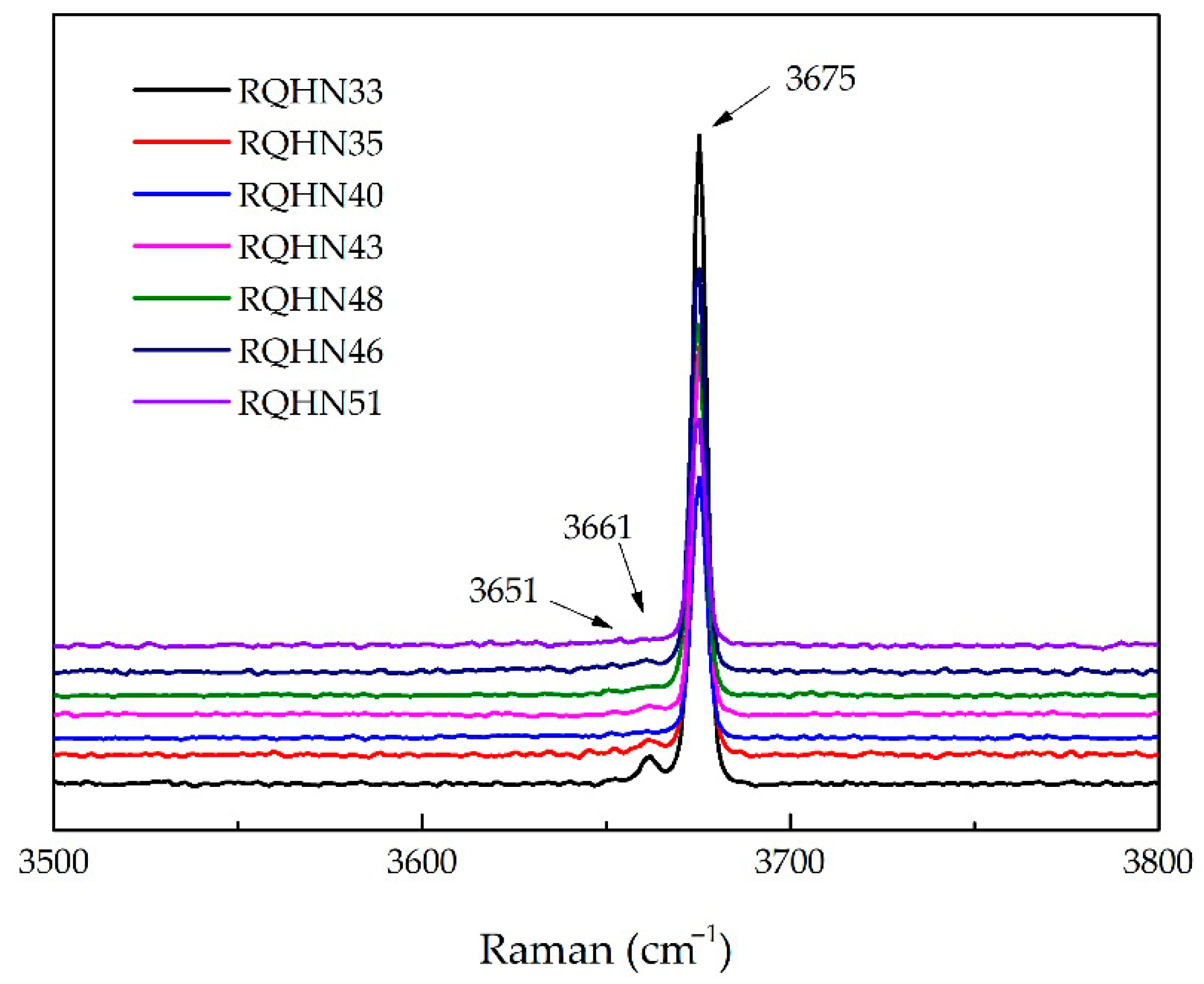
| N.O | X | Y | Z | H | V | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RQHN33 | 29.22 | 32.63 | 19.11 | 2.4 GY | 6.36 | 3.71 |
| RQHN35 | 24.72 | 27.48 | 13.26 | 1.2 GY | 5.92 | 4.42 |
| RQHN40 | 29.21 | 31.79 | 18.58 | 10.0 Y | 6.29 | 3.53 |
| RQHN43 | 25.59 | 27.79 | 14.22 | 9.4 Y | 5.95 | 4.05 |
| RQHN46 | 30.98 | 32.90 | 15.71 | 7.1 Y | 6.41 | 4.62 |
| RQHN48 | 29.92 | 32.09 | 15.10 | 8.1 Y | 6.33 | 4.65 |
| RQHN51 | 21.73 | 22.29 | 10.03 | 4.5 Y | 5.42 | 4.43 |
| N.O | Munsell/H | sRGB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sR | sG | sB | Fitted Colors | |||
| RQHN33 | 2.4 GY | 32.4 | 160 | 157 | 109 | |
| RQHN35 | 1.2 GY | 31.2 | 152 | 145 | 88 | |
| RQHN40 | 10.0 Y | 30.0 | 163 | 154 | 107 | |
| RQHN43 | 9.4 Y | 29.4 | 156 | 144 | 92 | |
| RQHN48 | 8.1 Y | 28.1 | 173 | 154 | 96 | |
| RQHN46 | 7.1 Y | 27.1 | 170 | 153 | 94 | |
| RQHN51 | 4.5 Y | 24.5 | 151 | 127 | 76 | |
| Raman Shift | M-OH |
|---|---|
| 3675 cm−1 | Mg2+, Mg2+, Mg2+ |
| 3661 cm−1 | Mg2+, Mg2+, Fe2+ |
| 3651 cm−1 | Mg2+, Mg2+, Fe3+ |
| N.O | 3651 cm−1 | 3661 cm−1 | 3651 cm−1/(3661 cm−1 + 3651 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RQHN33 | 450 | 2500 | 0.15 |
| RQHN35 | 322 | 1415 | 0.19 |
| RQHN40 | 213 | 550 | 0.28 |
| RQHN43 | 285 | 620 | 0.31 |
| RQHN48 | 500 | 833 | 0.38 |
| RQHN46 | 764 | 1100 | 0.41 |
| RQHN51 | 540 | 632 | 0.46 |
| N.O | RQHN33 | RQHN35 | RQHN40 | RQHN43 | RQHN48 | RQHN46 | RQHN51 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 58.29 | 52.51 | 58.35 | 58.39 | 57.81 | 58.34 | 57.31 |
| TiO2 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 |
| Al2O3 | 0.75 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| TFe | 0.57 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| MnO | 0.031 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.018 |
| MgO | 24.67 | 20.62 | 24.59 | 24.65 | 24.75 | 24.72 | 23.13 |
| CaO | 13.46 | 21.03 | 13.65 | 13.70 | 13.70 | 13.48 | 16.48 |
| Na2O | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.19 |
| K2O | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.05 |
| P2O5 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| LOI | 2.03 | 5.21 | 2.51 | 2.53 | 2.68 | 2.88 | 2.05 |
| SUM | 100.18 | 100.62 | 100.43 | 100.52 | 100.67 | 100.37 | 100.32 |
| FeO | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Fe2O3/TFe | 0.117 | 0.122 | 0.139 | 0.158 | 0.190 | 0.213 | 0.233 |
| Rare Element | Content (μg/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RQHN33 | RQHN35 | RQHN40 | RQHN43 | RQHN48 | RQHN46 | RQHN51 | |
| Li | 2.784 | 5.504 | 2.061 | 3.352 | 0.871 | 2.646 | 1.988 |
| Be | 1.643 | 2.613 | 10.154 | 5.995 | 7.454 | 11.167 | 4.467 |
| Sc | 5.025 | 6.347 | 7.968 | 4.054 | 6.509 | 8.218 | 9.571 |
| Ti | 32.559 | 12.316 | 47.775 | 63.387 | 48.387 | 35.234 | 39.577 |
| V | 5.898 | 1.242 | <0.335 | 12.704 | 5.837 | 8.085 | 8.558 |
| Cr | 5.461 | <0.100 | 7.159 | <0.100 | 0.293 | 56.676 | 9.588 |
| Mn | 242.816 | 118.559 | 106.807 | 153.171 | 120.949 | 122.369 | 121.918 |
| Co | 1.975 | 1.128 | 0.636 | 0.667 | 0.503 | 0.513 | 1.339 |
| Ni | 1.520 | 4.548 | 0.905 | 3.866 | 2.417 | 1.736 | 1.557 |
| Cu | 0.771 | <0.230 | <0.230 | 2.904 | <0.230 | 2.623 | 4.127 |
| Zn | 93.609 | 76.790 | 38.488 | 47.299 | 49.106 | 54.954 | 25.779 |
| Ga | 0.624 | 0.625 | 0.769 | 0.781 | 0.995 | 0.989 | 1.515 |
| Rb | 4.077 | 0.233 | 1.282 | 0.921 | 1.129 | 0.184 | 0.773 |
| Sr | 9.401 | 3.925 | 5.488 | 4.195 | 5.203 | 5.252 | 4.761 |
| Y | 2.202 | 2.262 | 2.205 | 3.507 | 2.847 | 2.057 | 3.071 |
| Zr | 1.162 | 1.727 | <0.001 | 1.156 | 0.649 | 3.918 | 6.791 |
| Nb | 0.377 | 0.047 | 0.282 | 0.202 | 0.321 | 0.164 | 0.470 |
| Mo | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.227 |
| Ag | 0.128 | <0.027 | 0.104 | 0.156 | 0.079 | 0.079 | 0.259 |
| Cd | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.196 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.250 |
| Sn | 0.560 | 0.948 | 3.451 | 1.980 | 1.072 | 3.105 | 3.874 |
| Sb | 0.022 | 0.256 | 0.236 | 0.294 | 0.229 | 0.278 | 0.384 |
| Cs | 0.176 | 0.066 | 0.233 | 0.082 | 0.150 | 0.079 | 0.140 |
| Ba | 4.061 | 0.646 | 1.264 | 5.424 | 0.988 | 1.505 | 1.333 |
| La | 0.313 | 1.022 | 1.232 | 0.844 | 1.045 | 0.979 | 0.740 |
| Ce | 1.009 | 1.260 | 1.837 | 1.201 | 1.522 | 1.465 | 1.116 |
| Pr | 0.289 | 0.122 | 0.215 | 0.136 | 0.185 | 0.206 | 0.109 |
| Nd | 0.982 | 0.446 | 0.731 | 1.125 | 1.086 | 0.686 | 0.850 |
| Sm | 0.456 | 0.493 | 0.055 | 0.226 | 0.210 | 0.203 | 0.365 |
| Eu | 0.018 | 0.015 | <0.001 | 0.016 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Gd | 0.319 | 0.306 | 0.167 | 0.451 | 0.181 | 0.200 | 0.221 |
| Tb | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.038 | 0.075 | 0.064 | 0.059 | <0.001 |
| Dy | 0.330 | 0.241 | 0.170 | 0.493 | 0.325 | 0.198 | 0.114 |
| Ho | 0.076 | 0.052 | 0.078 | 0.111 | 0.100 | 0.055 | 0.055 |
| Er | 0.105 | 0.368 | 0.207 | 0.262 | 0.261 | 0.267 | 0.189 |
| Tm | 0.035 | 0.026 | 0.019 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.008 |
| Yb | 0.097 | 0.072 | 0.068 | 0.406 | 0.092 | 0.294 | 0.035 |
| Lu | 0.024 | 0.025 | 0.007 | 0.027 | <0.001 | 0.015 | <0.001 |
| Hf | 0.042 | 0.094 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.040 | <0.001 | 0.030 |
| Ta | 0.059 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.052 | 0.055 | 0.009 | 0.046 |
| W | 0.043 | <0.001 | 0.662 | 0.361 | 0.645 | 0.881 | 0.435 |
| Tl | 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.017 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.009 | <0.001 |
| Bi | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.073 | 0.035 | 0.009 | 0.040 | 0.052 |
| Pb | 0.345 | 0.509 | 19.514 | 1.830 | 1.216 | 1.298 | 0.940 |
| Th | 0.036 | 0.124 | 0.179 | 0.664 | 0.145 | 0.258 | 0.198 |
| U | 0.314 | 0.165 | 0.772 | 0.667 | 0.641 | 0.834 | 0.832 |
| LREE | 3.049 | 3.342 | 4.071 | 3.532 | 4.047 | 3.538 | 3.180 |
| HREE | 1.038 | 1.140 | 0.754 | 1.827 | 1.030 | 1.115 | 0.622 |
| ΣREE | 4.105 | 4.497 | 4.825 | 5.375 | 5.077 | 4.653 | 3.802 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Han, H.; Wang, S. Investigation of the Coloration Mechanisms of Yellow-Green Nephrite from Ruoqiang (Xinjiang), China. Minerals 2025, 15, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090961
Huang B, Yang M, Yang X, Wang X, Fang T, Han H, Wang S. Investigation of the Coloration Mechanisms of Yellow-Green Nephrite from Ruoqiang (Xinjiang), China. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090961
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Boling, Mingxing Yang, Xihan Yang, Xuan Wang, Ting Fang, Hongwei Han, and Shoucheng Wang. 2025. "Investigation of the Coloration Mechanisms of Yellow-Green Nephrite from Ruoqiang (Xinjiang), China" Minerals 15, no. 9: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090961
APA StyleHuang, B., Yang, M., Yang, X., Wang, X., Fang, T., Han, H., & Wang, S. (2025). Investigation of the Coloration Mechanisms of Yellow-Green Nephrite from Ruoqiang (Xinjiang), China. Minerals, 15(9), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090961






