Rare Earth Element Concentrations as a Novel Proxy for Lateral Continuity: An Initial Case Study in the Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming
Abstract
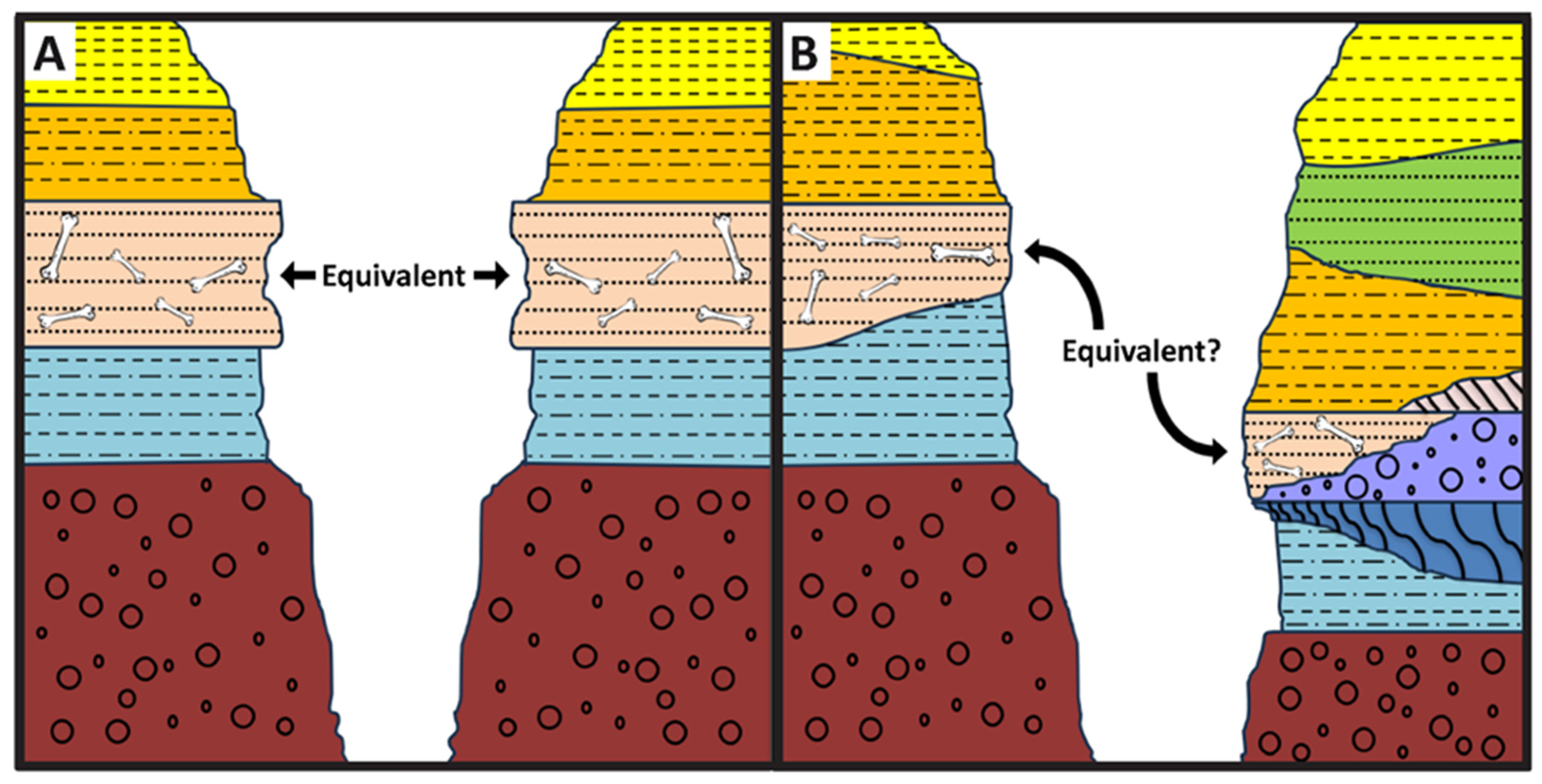
1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- (4)
- (5)
- Inferring the mode of formation of a vertebrate fossil assemblage (i.e., mass death vs. attritional accumulation) independent of traditional taphonomic observations [18];
- (6)
- (7)
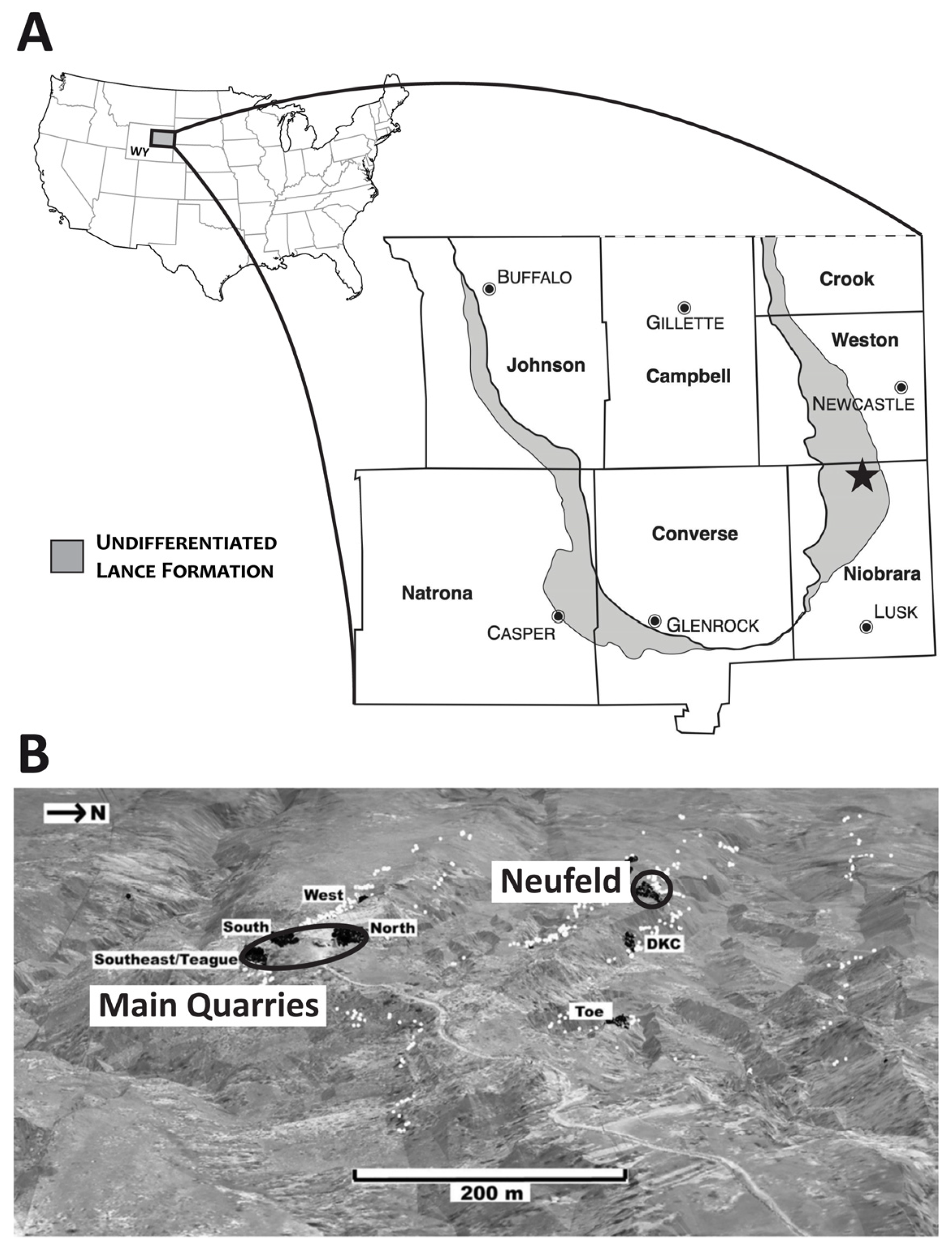
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
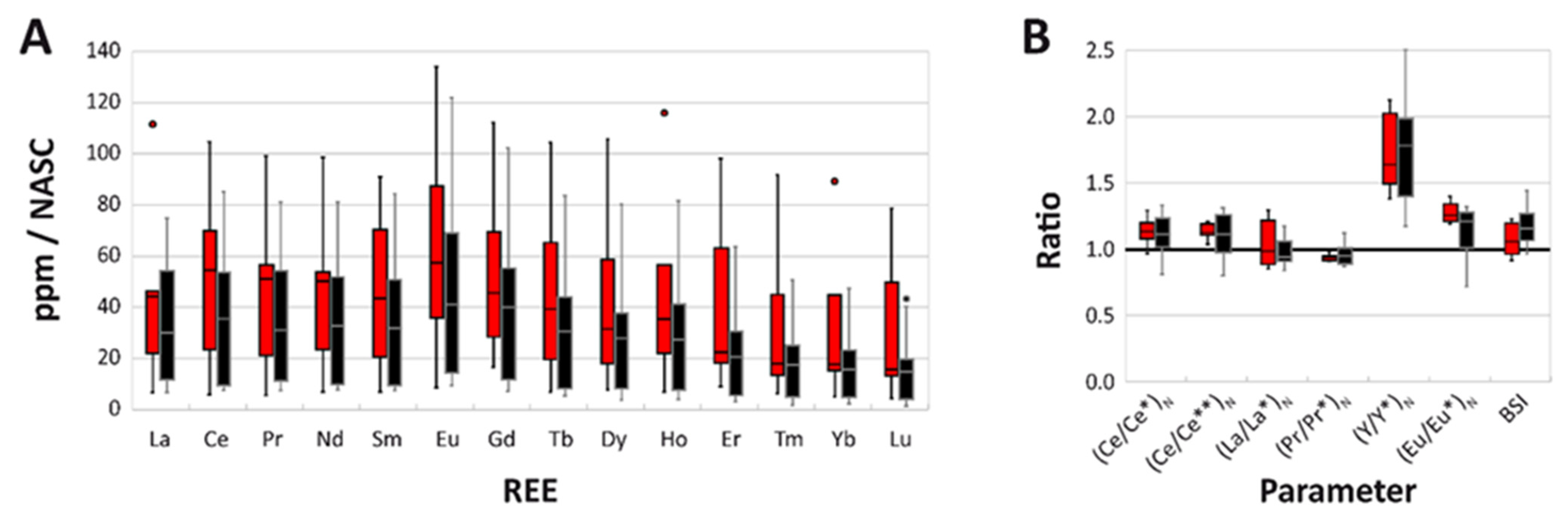
3.1. Overall REE Composition
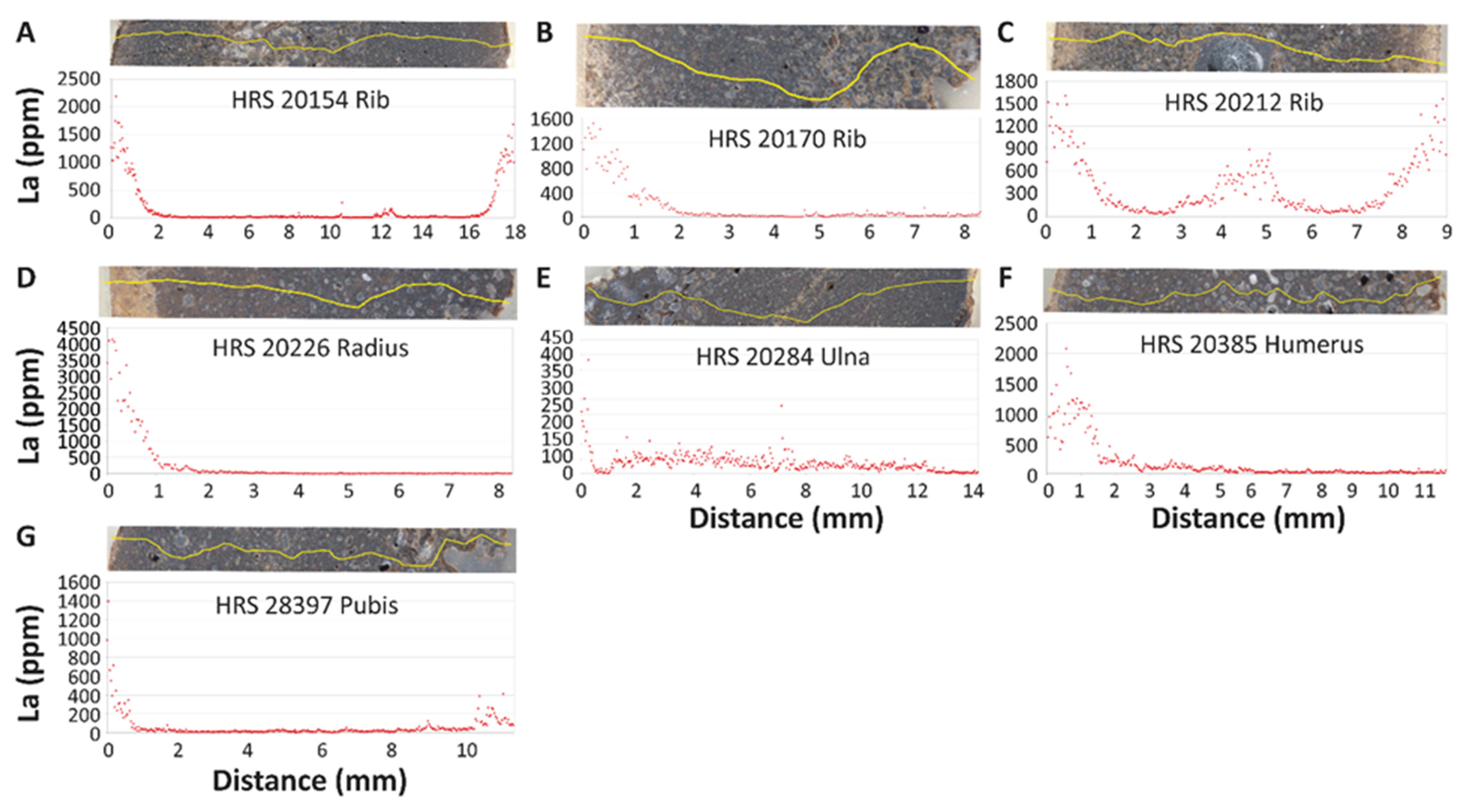
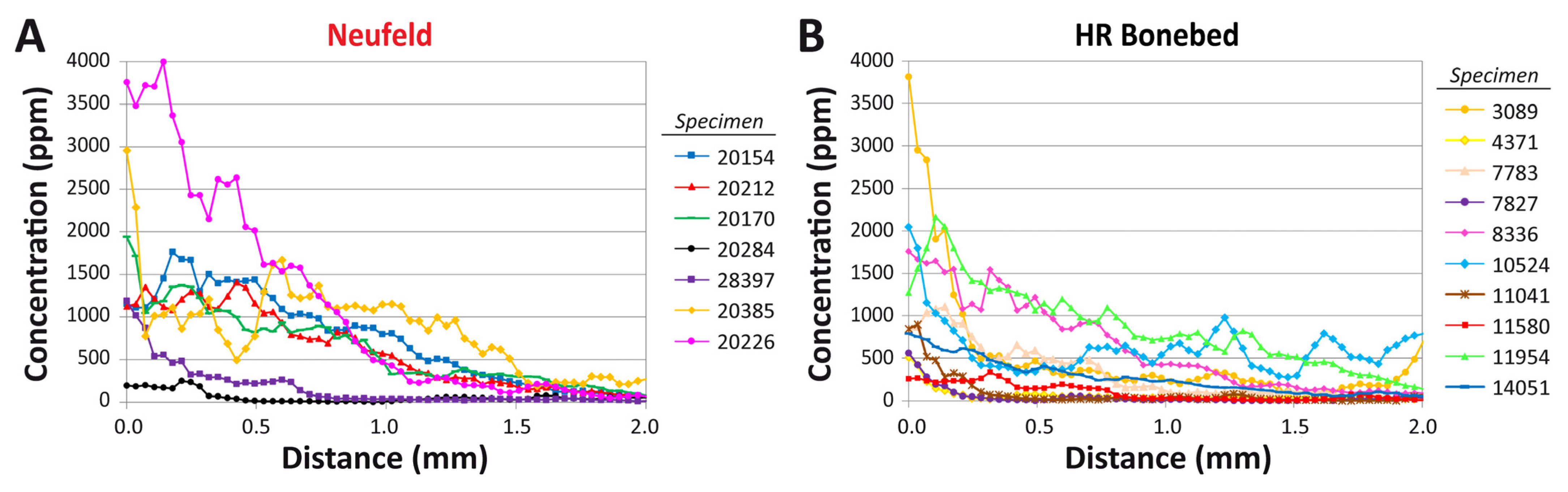
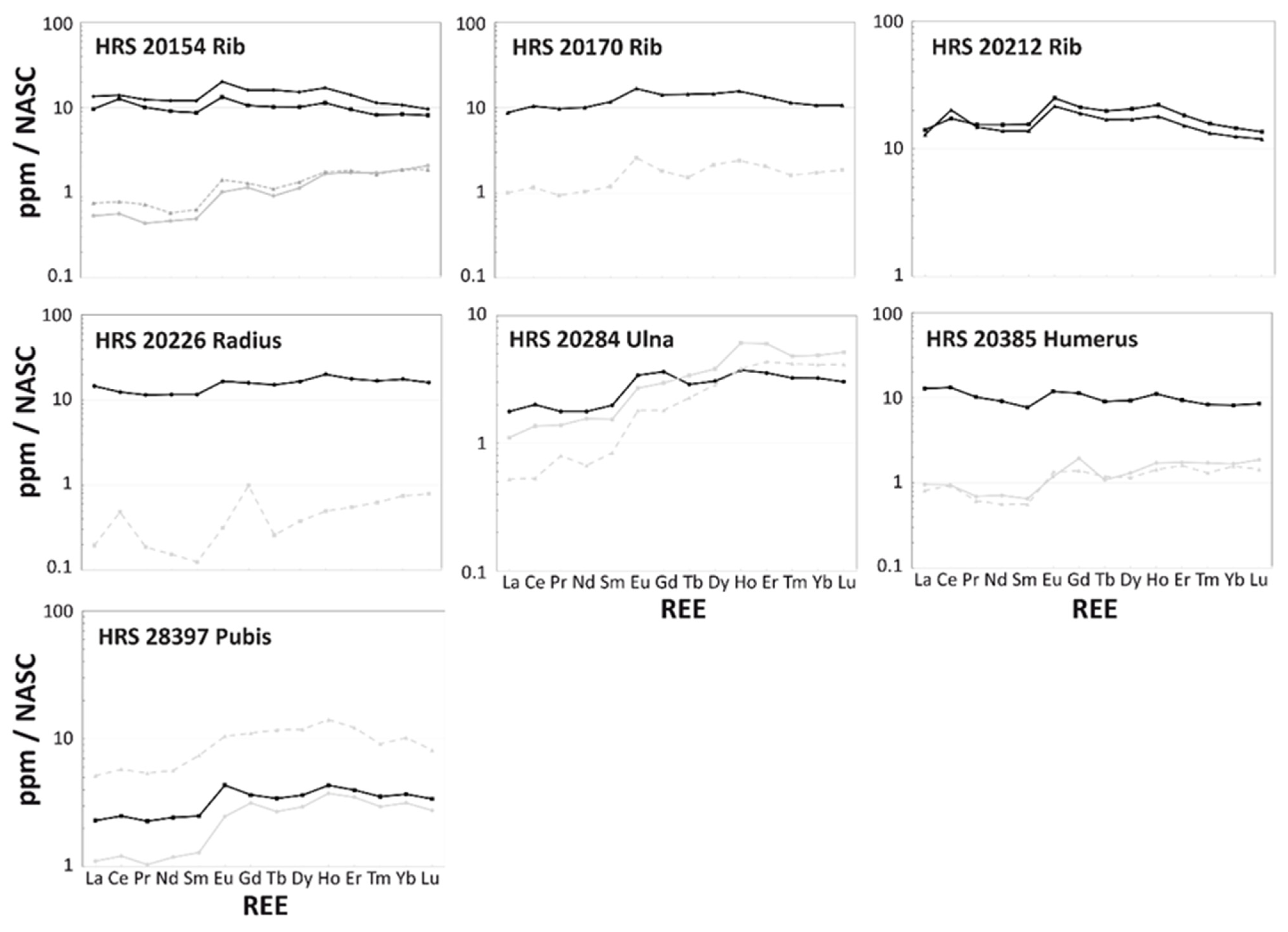
3.2. Intra-Bone REE Depth Profiles
3.3. NASC-Normalized REE Patterns
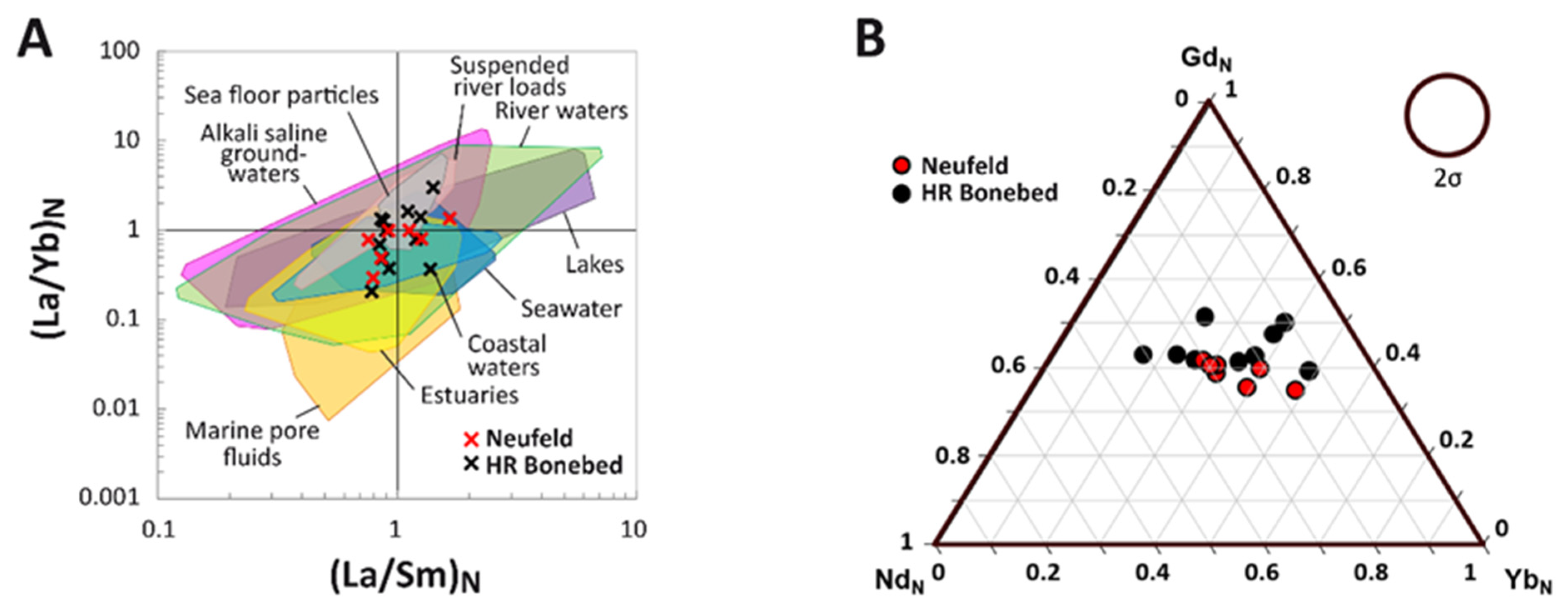
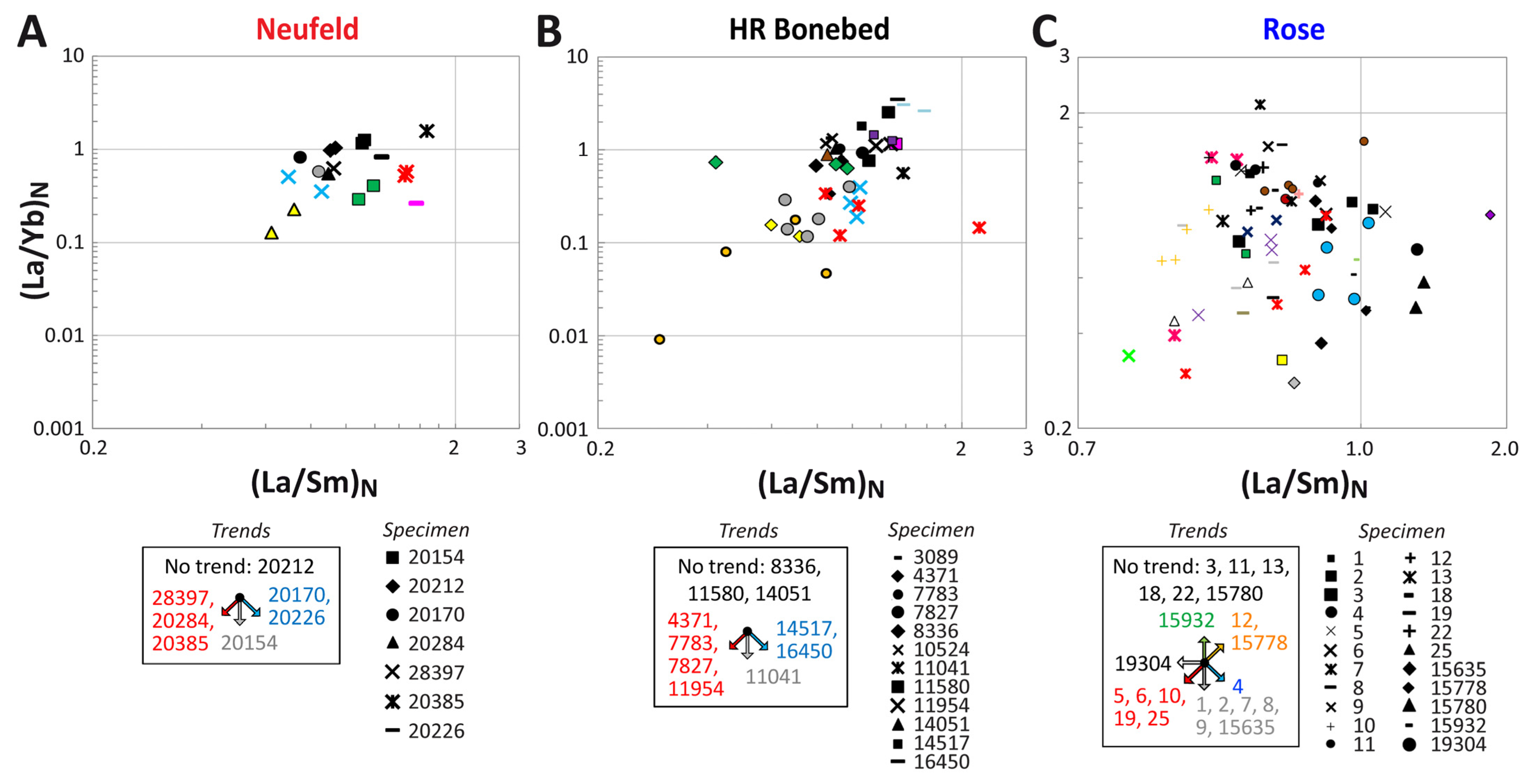
3.4. (La/Yb)N vs. (La/Sm)N Ratio Patterns
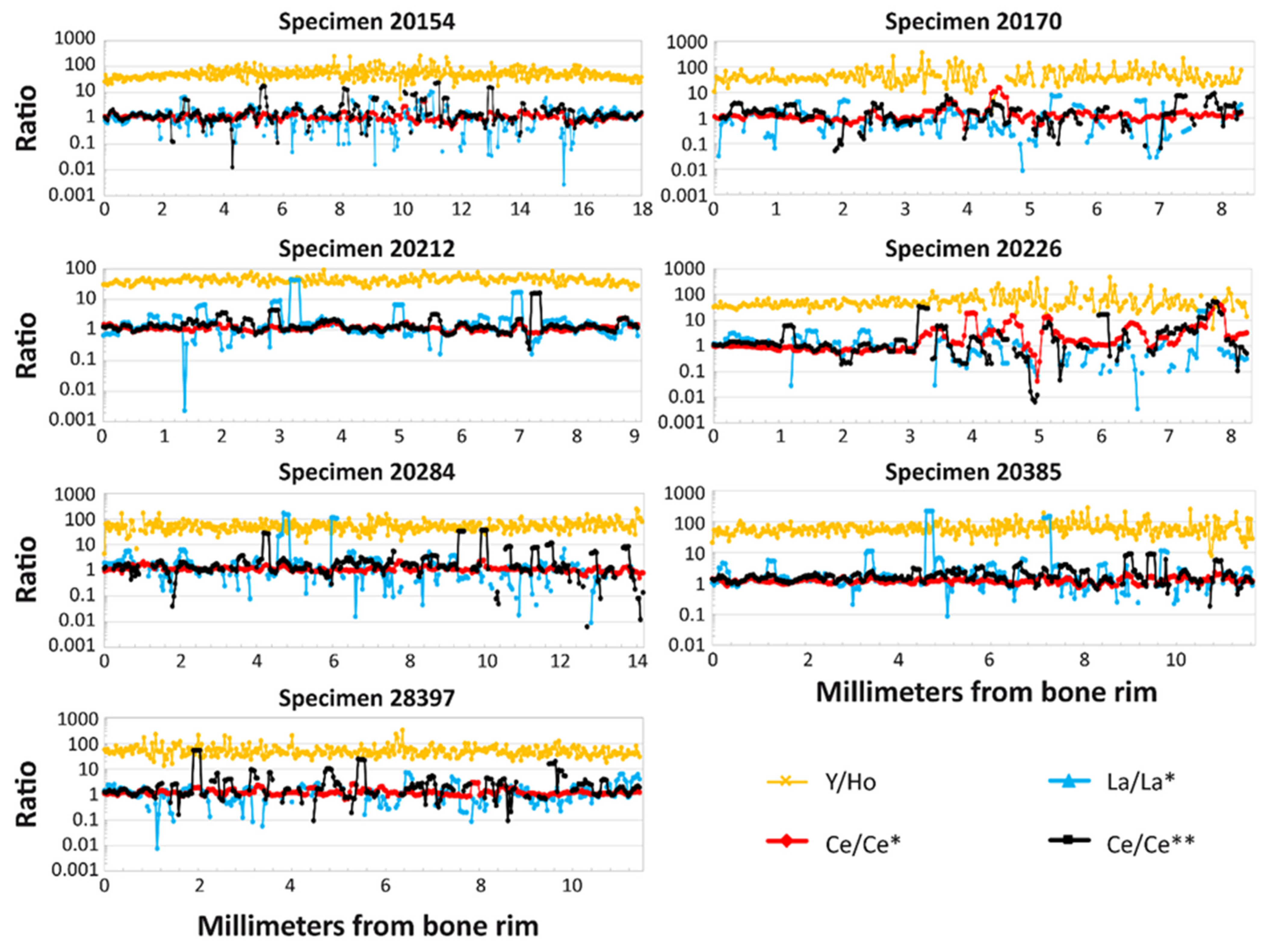
3.5. REE Anomalies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trueman, C.N. Rare earth element geochemistry and taphonomy of terrestrial vertebrate assemblages. Palaios 1999, 14, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N. Trace element geochemistry of bonebeds. In Bonebeds: Genesis, Analysis, and Paleobiological Significance; Rogers, R.R., Eberth, D.A., Fiorillo, A.R., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007; pp. 397–435. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, S.W. From bone to fossil: A review of the diagenesis of bioapatite. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.A.; Morschhauser, E.M.; Suarez, M.B.; You, H.; Li, D.; Dodson, P. Rare earth element geochemistry of bone beds from the Lower Cretaceous Zhonggou Formation of Gansu Province, China. J. Vertebr. Vertebr. Paleontol. 2018, 38, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, P.V.; Voegele, K.K.; Grandstaff, D.E.; Ash, R.D.; Zheng, W.; Schroeter, E.R.; Schweitzer, M.H.; Lacovara, K.J. Molecular tests support the viability of rare earth elements as proxies for fossil biomolecule preservation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwartz, D.; Tütken, T.; Jochum, K.P.; Sander, P.M. Rare earth element systematics of fossil bone revealed by LA-ICPMS analysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 103, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.T.; Henderson, P.; Marlow, C.A.; Molleson, T.I. The environment of deposition indicated by the distribution of rare earth elements in fossil bones from Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. Appl. Geochem. 1997, 12, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueriau, P.; Bertrand, L. Deciphering exceptional preservation of fossils through trace elemental imaging. Microsc. Today 2015, 23, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, C.A.; Terry, D.O.; Grandstaff, D.E. Effect of paleosol formation on rare earth element signatures in fossil bone. Geology 2004, 32, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandstaff, D.E.; Terry, D.O. Rare earth element composition of Paleogene vertebrate fossils from Toadstool Geologic Park, Nebraska, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, J.; Amiot, R.; Arnaud-Godet, F.; Cuny, G.; Fourel, F.; Hernandez, J.-A.; Pedreira-Segade, U.; Lécuyer, C. Miocene (Burdigalian) seawater and air temperatures estimated from the geochemistry of fossil remains from the Aquitaine Basin, France. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 481, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrée, S.; Herwartz, D.; Mercadier, J.; Miján, I.; de Buffrénil, V.; Leduc, T.; Lambert, O. The post-mortem history of a bone revealed by its trace element signature: The case of a fossil whale rostrum. Chem. Geol. 2018, 477, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, P.V.; Ash, R.D.; Scannella, J.B. Taphonomic and diagenetic pathways to protein preservation, part II: The case of Brachylophosaurus canadensis specimen MOR 2598. Biology 2022, 11, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N.; Palmer, M.R.; Field, J.; Privat, K.; Ludgate, N.; Chavagnac, V.; Eberth, D.A.; Cifelli, R.; Rogers, R.R. Comparing rates of recrystallisation and the potential for preservation of biomolecules from the distribution of trace elements in fossil bones. Comptes Rendus Palevol 2008, 7, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, P.V.; Grandstaff, D.E.; Ash, R.D.; Lacovara, K.J. Geochemical taphonomy of the Standing Rock Hadrosaur Site: Exploring links between rare earth elements and cellular and soft tissue preservation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 269, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, P.V.; Macauley, K.; Ash, R.D.; Shoup, B.; Scannella, J.B. Taphonomic and diagenetic pathways to protein preservation, part I: The case of Tyrannosaurus rex specimen MOR 1125. Biology 2021, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueman, C.N.; Benton, M.J. A Geochemical method to trace the taphonomic history of reworked bones in sedimentary settings. Geology 1997, 25, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLain, M.A.; Ullmann, P.V.; Ash, R.D.; Bohnstedt, K.; Nelsen, D.; Clark, R.O.; Brand, L.R.; Chadwick, A.V. Independent confirmation of fluvial reworking at a Lance Formation (Maastrichtian) bonebed by traditional and chemical taphonomic analyses. Palaios 2021, 36, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N.; Behrensmeyer, A.K.; Potts, R.; Tuross, N. High-resolution records of location and stratigraphic provenance from the rare earth element composition of fossil bones. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4343–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.V.; Nikolskiy, P.A.; Basilyan, A.E. Stratigraphic interpretation of rare earth element signatures in Pleistocene mammal bones: A case study from Kharabai Site, east Siberia. Quatern. Int. 2017, 445, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, L.; Ulianov, A.; Mouflih, M.; Khaldoune, F.; Gheerbrant, E. Geochemical investigation of the taphonomy, stratigraphy, and palaeoecology of the mammals from the Ouled Abdoun Basin (Paleocene-Eocene of Morocco). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeocl. 2021, 577, 110523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, L.; Botfalvai, G.; Qamarina, Q.; Razak, H.; Király, E.; Lugli, F.; Wings, O.; Lambertz, M.; Raven, H.; Briguglio, A.; et al. Geochemical analyses suggest stratigraphic origin and Late Miocene age of reworked vertebrate remains from Penanjong Beach in Brunei Darussalam (Borneo). Hist. Biol. 2021, 33, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N. Chemical taphonomy of biomineralized tissues. Palaeontology 2013, 56, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, J.M.; Bahr, A.; Gerdes, A.; Tütken, T.; Prinz-Grimm, P. Preservation of successive diagenetic stages in Middle Triassic bonebeds: Evidence from in situ trace element and strontium isotope analysis of vertebrate fossils. Chem. Geol. 2015, 410, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, S.; Heaman, L.M.; DuFrane, S.A.; Williamson, T.; Currie, P.J. Introducing a geochemical screen to identify geologically meaningful U-Pb dates in fossil teeth. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimstead, D.N.; Clark, A.E.; Rezac, A. Uranium and vanadium concentrations as a trace element method for identifying diagenetically altered bone in the inorganic phase. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2018, 25, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicoff, S. Essentials of Geology; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kocsis, L.; Trueman, C.N.; Palmer, M.R. Protracted diagenetic alteration of REE contents in fossil bioapatites: Direct evidence from Lu-Hf isotope systematics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6077–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.; McLain, M.; Wood, J.; Chadwick, A. Over 13,000 elements from a single bonebed help elucidate disarticulation and transport of an Edmontosaurus thanatocoenosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, P.V.; Caputo, C.; Snyder, K.; Chadwick, A.; Ash, R.D. Trace element taphonomy of the Hanson Ranch Edmontosaurus bonebed supports its origin via transportation of a mass death assemblage. Chem. Geol. 2025, 672, 122501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromet, L.P.; Haskin, L.A.; Korotev, R.L.; Dymek, R.F. The “North American Shale Composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskin, L.A.; Haskin, M.A.; Frey, F.A.; Wildeman, T.R. Relative and absolute terrestrial abundances of the rare earths. In Origin and Distribution of the Elements; Ahrens, L.H., Ed.; International Series of Monographs in Earth Sciences; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1968; pp. 889–912. [Google Scholar]
- Lumiste, K.; Lang, L.; Paiste, P.; Lepland, A.; Kirsimäe, K. Heterogeneous REE + Y distribution in early Paleozoic shelly phosphorites: Implications for enrichment mechanisms. Chem. Geol. 2021, 586, 120590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Shields, G.A.; Tarbuck, G.M.; He, T.; Clarkson, M.O.; Wood, R.A. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings. Chem. Geol. 2016, 438, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, T.; Kempe, U.; Monecke, J.; Sala, M.; Wolf, D. Tetrad effect in rare earth element distribution patterns: A method of quantification with application to rock and mineral samples from granite-related rare metal deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J. Models of diffusion-limited uptake of trace elements in fossils and rates of fossilization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 3758–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, C.; Cavin, L.; Vennemann, T.; Martini, R. Histology and geochemistry of Allosaurus (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry (Late Jurassic, Utah): Paleobiological implications. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 641060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, E.R.; Ullmann, P.V.; Macauley, K.; Ash, R.D.; Zheng, W.; Schweitzer, M.H.; Lacovara, K.J. Soft-tissue, rare earth element, and molecular analyses of Dreadnoughtus schrani, an exceptionally complete titanosaur from Argentina. Biology 2022, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.N.; Haley, B.A.; McManus, J.; Reimers, C.E. The sedimentary flux of dissolved rare earth elements to the ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 154, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, M.; Corin, N. Distribution of rare earth elements in anionic, cationic and particulate fractions in boreal humus-rich streams affected by acid sulphate soils. Water Res. 2003, 37, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroux, G.; Sonke, J.E.; Boaventura, G.; Viers, J.; Godderis, Y.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Sondag, F.; Gardoll, S.; Lagane, C.; Seyler, P. Seasonal dissolved rare earth element dynamics of the Amazon River main stem, its tributaries, and the Curuaí floodplain. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 143, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Knappe, A.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a micropollutant in river waters in Pennsylvania and in Lake Erie, northeastern United States. Geochemistry 2006, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayon, G.; Birot, D.; Ruffine, L.; Caprais, J.-C.; Ponzevera, E.; Bollinger, C.; Donval, J.-P.; Charlou, J.-L.; Voisset, M.; Grimaud, S. Evidence for intense REE scavenging at cold seeps from the Niger Delta margin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 312, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddau, R.; Cidu, R.; Frau, F. Rare earth elements in waters from the albitite-bearing granodiorites of Central Sardinia, Italy. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwire Ojiambo, S.; Lyons, W.B.; Welch, K.A.; Poreda, R.J.; Johannesson, K.H. Strontium isotopes and rare earth elements as tracers of groundwater-lake water interactions, Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1789–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Sposito, F.; Inguaggiato, C.; Zuddas, P.; Inguaggiato, S.; Venturi, M. Zr, Hf and REE distribution in river water under different ionic strength conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeno, L.M.; Faure, G.; Lee, G.; Talnagi, J. Fractionation of chemical elements including the REEs and 226Ra in stream contaminated with coal-mine effluent. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevis, D.A.; Johannesson, K.H.; Burdige, D.J.; Tang, J.; Moran, S.B.; Kelly, R.P. Submarine groundwater discharge of rare earth elements to a tidally-mixed estuary in Southern Rhode Island. Chem. Geol. 2015, 397, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baar, H.J.W.; Bacon, M.P.; Brewer, P.G. Rare-earth distributions with a positive Ce anomaly in the Western North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 1983, 301, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baar, H.J.W.; Bruland, K.W.; Schijf, J.; van Heuven, S.M.A.C.; Behrens, M.K. Low cerium among the dissolved rare earth elements in the central North Pacific Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 236, 5–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carlo, E.H.; Green, W.J. Rare earth elements in the water column of Lake Vanda, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. The rare earth elements in seawater. Nature 1982, 296, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Rare earth elements in the pore waters of reducing nearshore sediments. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 1987, 82, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili-Vardanjani, M.; Shamsipour-Dehkordi, R.; Eslami, A.; Moosaei, F.; Pazand, K. A study of differentiation pattern and rare earth elements migration in geochemical and hydrogeochemical environments of Airekan and Cheshmeh Shotori areas (Central Iran). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Wood, S.A.; Pedrozo, F.; Varekamp, J.C.; Nelson, B.J.; Shope, C.L.; Baffico, G. Hydrogeochemistry and rare earth element behavior in a volcanically acidified watershed in Patagonia, Argentina. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Wood, S.A.; Nimick, D.A. Diel behavior of rare earth elements in a mountain stream with acidic to neutral pH. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Solsona, E.; Jeandel, C.; Labatut, M.; Lacan, F.; Vance, D.; Chavagnac, V.; Pradoux, C. Rare earth elements and Nd isotopes tracing water mass mixing and particle-seawater interactions in the SE Atlantic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 125, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Holliday, B.P.; Elderfield, H. Redox cycling of rare earth elements in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Masuzawa, T.; Greaves, M.J.; Elderfield, H.; Edmond, J.M. Dissolved rare earth elements in the Southern Ocean: Cerium oxidation and the influence of hydrography. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. Rare earth elements in river waters. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 1988, 89, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Jeandel, C.; Lacan, F.; Vance, D.; Venchiarutti, C.; Cros, A.; Cravatte, S. From the subtropics to the central equatorial Pacific Ocean: Neodymium isotopic composition and rare earth element concentration variations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 592–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.A.; Klinkhammer, G.P.; McManus, J. Rare earth elements in pore waters of marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathorne, E.C.; Stichel, T.; Brück, B.; Frank, M. Rare earth element distribution in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean: The balance between particle scavenging and vertical supply. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, Y.; Obata, H.; Alibo, D.S.; Nozaki, Y. Spatial variations of rare earth elements in North Pacific surface water. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 62, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, J.; Elderfield, H.; Gledhill, A.; Greaves, M. The behaviour of the rare earth elements during mixing of river and sea waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandel, C.; Delattre, H.; Grenier, M.; Pradoux, C.; Lacan, F. Rare earth element concentrations and Nd isotopes in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B. Rare-earth element geochemistry of Colour Lake, an acidic freshwater lake on Axel Heiberg Island, Northwest Territories, Canada. Chem. Geol. 1995, 119, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Byrne, R.H. The solubility control of rare earth elements in natural terrestrial waters and the significance of PO43- and CO32- in limiting dissolved rare earth concentrations: A review of recent information. Aquat. Geochem. 1995, 1, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Hodge, V.F. Rare earth elements as geochemical tracers of regional groundwater mixing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3605–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Farnham, I.M.; Guo, C.; Stetzenbach, K.J. Rare earth element fractionation and concentration variations along a groundwater flow path within a shallow, basin-fill aquifer, southern Nevada, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Tang, J.; Daniels, J.M.; Bounds, W.J.; Burdige, D.J. Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in organic-rich blackwaters of the Great Dismal Swamp, Virginia, USA. Chem. Geol. 2004, 209, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Palmore, C.D.; Fackrell, J.; Prouty, N.G.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Chevis, D.A.; Telfeyan, K.; White, C.D.; Burdige, D.J. Rare earth element behavior during groundwater-seawater mixing along the Kona Coast of Hawaii. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 198, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalender, L.; Aytimur, G. REE geochemistry of Euphrates River, Turkey. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Torres, M.E.; Haley, B.A.; Kastner, M.; Pohlman, J.W.; Riedel, M.; Lee, Y.J. The effect of diagenesis and fluid migration on rare earth element distribution in fluids of the northern Cascadia accretionary margin. Chem. Geol. 2011, 291, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Contrasting behaviour of anthropogenic gadolinium and natural rare earth elements in estuaries and the gadolinium input into the North Sea. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 2007, 260, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements in the Rhine River, Germany: First case of anthropogenic lanthanum as a dissolved microcontaminant in the hydrosphere. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a microcontaminant in tap water used as drinking water in urban areas and megacities. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybourne, M.I.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare earth elements (REE) and yttrium in stream waters, stream sediments, and Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides: Fractionation, speciation, and controls over REE + Y patterns in the surface environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5962–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybourne, M.I.; Goodfellow, W.D.; Boyle, D.R.; Hall, G.M. Rapid development of negative Ce anomalies in surface waters and contrasting REE patterns in groundwaters associated with Zn-Pb massive sulphide deposits. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 695–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Xing, L.; Zhan, Y.; Li, F.; Shao, J.; Niu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, C. Geochemical behaviors of rare earth elements in groundwater along a flow path in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 117, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merschel, G.; Bau, M.; Schmidt, K.; Münker, C.; Dantas, E.L. Hafnium and neodymium isotopes and REY distribution in the truly dissolved, nanoparticulate/colloidal and suspended loads of rivers in the Amazon Basin, Brazil. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 213, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Lerche, D.; Alibo, D.S.; Tsutsumi, M. Dissolved indium and rare earth elements in three Japanese rivers and Tokyo Bay: Evidence for anthropogenic Gd and In. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 3975–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.H.; Hathorne, E.C.; Schijf, J.; Plancherel, Y.; Böning, P.; Frank, M. The potential of sedimentary foraminiferal rare earth element patterns to trace water masses in the past. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 1550–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepgras, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. The behavior of rare earth elements in seawater: Precise determination of variations in the North Pacific water column. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.S.; Viers, J.; Shirokova, L.S.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Filipov, A.S.; Dupré, B. Dissolved, suspended, and colloidal fluxes of organic carbon, major and trace elements in the Severnaya Dvina River and its tributary. Chem. Geol. 2010, 273, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, T.C.C.; Sonke, J.E.; Chmeleff, J.; van Beek, P.; Souhat, M.; Boaventura, G.; Seyler, P.; Jeandel, C. Rapid neodymium release to marine waters from lithogenic sediments in the Amazon estuary. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The geochemistry of rare earth elements in the Amazon River estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Landing, W.M.; Lewis, B.L. Ocean particle chemistry: The fractionation of rare earth elements between suspended particles and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L. The geochemistry of rare earth elements in groundwater from the Carnmenellis area, southwest England. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 2767–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Liu, X.-M. Spatial and temporal distribution of rare earth elements in the Neuse River, North Carolina. Chem. Geol. 2018, 488, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Johannesson, K.H. Speciation of rare earth elements in natural terrestrial waters: Assessing the role of dissolved organic matter from the modeling approach. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2321–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Johannesson, K.H. Controls on the geochemistry of rare earth elements along a groundwater flow path in the Carrizo Sand aquifer, Texas, USA. Chem. Geol. 2006, 225, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Flierdt, T.; Pahnke, K.; Amakawa, H.; Andersson, P.; Basak, C.; Coles, B.; Colin, C.; Crocket, K.; Frank, M.; Frank, N.; et al. GEOTRACES intercalibration of neodymium isotopes and rare earth element concentrations in seawater and suspended particles. Part 1: Reproducibility of results for the international intercomparison. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Yamada, M. Geochemistry of dissolved rare earth elements in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nozaki, Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji basins of the western South Pacific Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-Y.; Plancherel, Y.; Saito, M.A.; Scott, P.M.; Henderson, G.M. Rare earth elements (REEs) in the tropical South Atlantic and quantitative deconvolution of their non-conservative behavior. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 177, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, R.A.; Trueman, C.N. Rare earth elements in Solnhofen biogenic apatite: Geochemical clues to the palaeoenvironment. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 155, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, E.V.; Mysovskaya, I.N.; Lozhkin, V.I.; Sandimirova, G.P.; Pakhomova, N.N.; Smagunova, A.A. Spectral interferences from polyatomic barium ions in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 73, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, A.; Russell, S.S.; Shelley, J.M.G.; van Zuilen, M. Geo- and cosmochemistry of the twin elements yttrium and holmium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 4592–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal-Linka, M.; Jochum, K.P.; Surmik, D. LA-ICP-MS analysis of rare earth elements in marine reptile bones from the Middle Triassic bonebed (Upper Silesia, S Poland): Impact of long-lasting diagenesis, and factors controlling the uptake. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal-Linka, M.; Jochum, K.P. Variability of trace element uptake in marine reptile bones from three Triassic sites (S Poland): Influence of diagenetic processes on the host rock and significance of the applied methodology. Chem. Geol. 2015, 397, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J.; Moses, R.J. Trace element diffusivities in bone rule out simple diffusive uptake during fossilization but explain in vivo uptake and release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwartz, D.; Münker, C.; Tütken, T.; Hoffmann, J.E.; Wittke, A.; Barbier, B. Lu–Hf isotope systematics of fossil biogenic apatite and their effects on geochronology. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 101, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, A.; Zigaite, Z.; Blom, H.; Perez-Huerta, A.; Jeffries, T.; Maersse, T.; Ahlberg, P.E. Palaeoenvironmental signatures revealed from rare earth element (REE) compositions of vertebrate microremains of the Vesiku Bone Bed (Homerian, Wenlock), Saaremaa Island, Estonia. Est. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 64, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarre-Sitchler, A.; Brantley, S.L.; Rother, G. How porosity increases during incipient weathering of crystalline silicate rocks. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2015, 80, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.F.; Panish, P.T.; Chure, D.J.; Prostak, K.S. Chemistry, microstructure, petrology, and diagenetic model of Jurassic dinosaur bones, Dinosaur National Monument, Utah. J. Sediment. Res. 1996, 66, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfretzschner, H.-U. Pyrite in fossil bone. Neues Jahrb. Geol. P.-A. 2001, 220, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wings, O. Authigenic minerals in fossil bones from the Mesozoic of England: Poor correlation with depositional environments. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2004, 204, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.A.; Macpherson, G.L.; González, L.A.; Grandstaff, D.E. Heterogeneous rare earth element (REE) patterns and concentrations in a fossil bone: Implications for the use of REE in vertebrate taphonomy and fossilization history. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 2970–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwartz, D.; Tütken, T.; Münker, C.; Jochum, K.P.; Stoll, B.; Sander, P.M. Timescales and mechanisms of REE and Hf uptake in fossil bones. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N.; Behrensmeyer, A.K.; Tuross, N.; Weiner, S. Mineralogical and compositional changes in bones exposed on soil surfaces in Amboseli National Park, Kenya: Diagenetic mechanisms and the role of sediment pore fluids. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.H. Hell Creek Formation and the early picking of the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in the Williston Basin. In The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary Boundary in the Northern Great Plains: An Integrated Continental Record of the End of the Cretaceous; Hartman, J.H., Johnson, K.R., Nichols, D.J., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Paper 361; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, J.H.; Butler, R.D.; Weiler, M.W.; Schumaker, K.K. Through the End of the Cretaceous in the Type Locality of the Hell Creek Formation in Montana and Adjacent Areas; Wilson, G.P., Clemens, W.A., Horner, J.R., Hartman, J.H., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Paper 503; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014; pp. 89–122. [Google Scholar]



| Trace Element Metric | Utility | Interpretation of Values | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Ce/Ce*)N | Redox indicator | >1 = reducing <1 = oxidizing | [6] |
| (Ce/Ce**)N | Redox indicator | >1 = oxidizing <1 = reducing | [6] |
| (La/La*)N | Indicator of fractionation among REE during uptake | 1 = no fractionation; values of >1 and <1 indicate fractionation | [6] |
| (Pr/Pr*)N | Indicator of fractionation among REE during uptake | 1 = no fractionation; values of >1 and <1 indicate fractionation | [6] |
| (Y/Y*)N | Indicator of fractionation among trace elements during uptake | 1 = no fractionation; values of >1 and <1 indicate fractionation | [33] |
| (Eu/Eu*)N | Redox indicator | >1 = oxidizing <1 = reducing | [34] |
| BSI (Bell Shaped Index) | Indicator of fractionation among REE during uptake | >1 = MREE enrichment <1 = MREE depletion | [34] |
| T3 (Third Tetrad Effect) | Track severity of tetrad effects on REE uptake | 0 = no tetrad effects; the more + or − the value, the greater the influence of tetrad effects | [35] |
| Element/Ratio | HRS Specimen Number | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20154 | 20170 | 20212 | 20226 | 20284 | 20385 | 28397 | |
| Sc | 22 | 19 | 57 | 33 | 11 | 18 | 13 |
| Mn | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.32 |
| Fe | 3.19 | 1.32 | 2.31 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.84 |
| Sr | 4206 | 4537 | 4650 | 3381 | 4397 | 4281 | 3895 |
| Y | 270 | 372 | 793 | 509 | 217 | 314 | 221 |
| Ba | 3717 | 4801 | 4609 | 3970 | 4463 | 4131 | 4316 |
| La | 157 | 177 | 392 | 285 | 38 | 198 | 60 |
| Ce | 402 | 450 | 1131 | 527 | 93 | 436 | 142 |
| Pr | 39 | 49 | 109 | 57 | 10 | 40 | 15 |
| Nd | 127 | 177 | 372 | 200 | 39 | 124 | 57 |
| Sm | 25 | 42 | 77 | 41 | 9 | 22 | 13 |
| Eu | 9 | 13 | 26 | 12 | 3 | 7 | 5 |
| Gd | 31 | 48 | 100 | 53 | 15 | 32 | 20 |
| Tb | 5 | 8 | 15 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Dy | 32 | 53 | 101 | 57 | 18 | 27 | 21 |
| Ho | 7 | 11 | 21 | 13 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Er | 20 | 30 | 56 | 38 | 16 | 18 | 15 |
| Tm | 2 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Yb | 15 | 22 | 41 | 34 | 12 | 14 | 12 |
| Lu | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Th | 2 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| U | 13 | 10 | 20 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 5 |
| ∑REE | 874 | 1087 | 2454 | 1336 | 265 | 932 | 371 |
| Y/Ho | 39 | 51 | 39 | 61 | 56 | 63 | 55 |
| (Ce/Ce*)N | 1.20 | 1.13 | 1.29 | 0.97 | 1.08 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| (Ce/Ce**)N | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.19 | 1.10 | 1.03 | 1.18 | 1.21 |
| (La/La*)N | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 1.29 | 0.92 | 1.06 | 1.22 |
| (Pr/Pr*)N | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| (Y/Y*)N | 1.61 | 1.38 | 1.49 | 1.64 | 2.02 | 2.13 | 1.90 |
| (Eu/Eu*)N | 1.40 | 1.32 | 1.34 | 1.19 | 1.23 | 1.21 | 1.26 |
| BSI | 1.06 | 1.23 | 1.19 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 1.12 |
| T3 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.13 |
| HRS Specimen Number | Profile Type(s) in External Cortex | Clear DMD Kink for LREEs? | Relative Noise in Outer Cortex for La | REE Suggest Flow in Medullary Cavity? | Relative ∑REE Content (Whole Bone) | Relative Porosity of the Cortex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20154 | Simple diffusion, leached | No | Low | No | Moderate | Low |
| 20170 | Oversteepened, leached | No | Low | No | High | Low |
| 20212 | Simple diffusion, leached | No | Low | Yes | High | Moderate |
| 20226 | Simple diffusion | No | Moderate | No | High | Moderate |
| 20284 | Simple diffusion | No | Moderate | No | Low | Moderate |
| 20385 | Oversteepened, leached | No | Moderate | No | Moderate | High |
| 28397 | DMD | Yes | Low | Yes | Low | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Booth, S.; Snyder, K.; Chadwick, A.; Ash, R.D.; Voegele, K.K.; Ullmann, P.V. Rare Earth Element Concentrations as a Novel Proxy for Lateral Continuity: An Initial Case Study in the Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming. Minerals 2025, 15, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090919
Booth S, Snyder K, Chadwick A, Ash RD, Voegele KK, Ullmann PV. Rare Earth Element Concentrations as a Novel Proxy for Lateral Continuity: An Initial Case Study in the Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090919
Chicago/Turabian StyleBooth, Skylor, Keith Snyder, Arthur Chadwick, Richard D. Ash, Kristyn K. Voegele, and Paul V. Ullmann. 2025. "Rare Earth Element Concentrations as a Novel Proxy for Lateral Continuity: An Initial Case Study in the Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming" Minerals 15, no. 9: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090919
APA StyleBooth, S., Snyder, K., Chadwick, A., Ash, R. D., Voegele, K. K., & Ullmann, P. V. (2025). Rare Earth Element Concentrations as a Novel Proxy for Lateral Continuity: An Initial Case Study in the Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming. Minerals, 15(9), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090919







