Experimental Investigation of Kaolinite–Zeolite Transformation: Insights from Al-Habala Area Saprolite, Abha, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geologic Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bulk X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
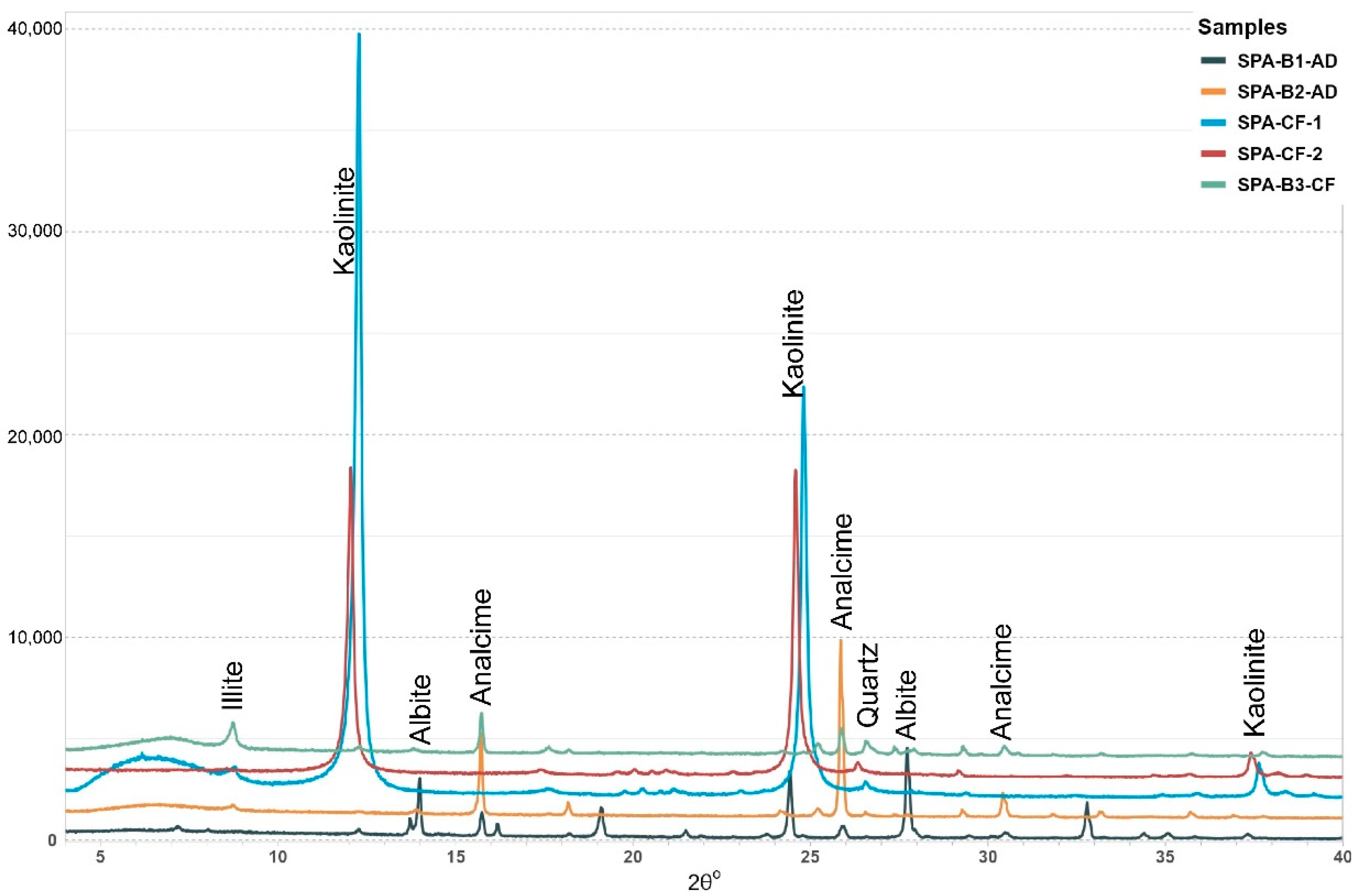
3.2. Clay Fraction X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
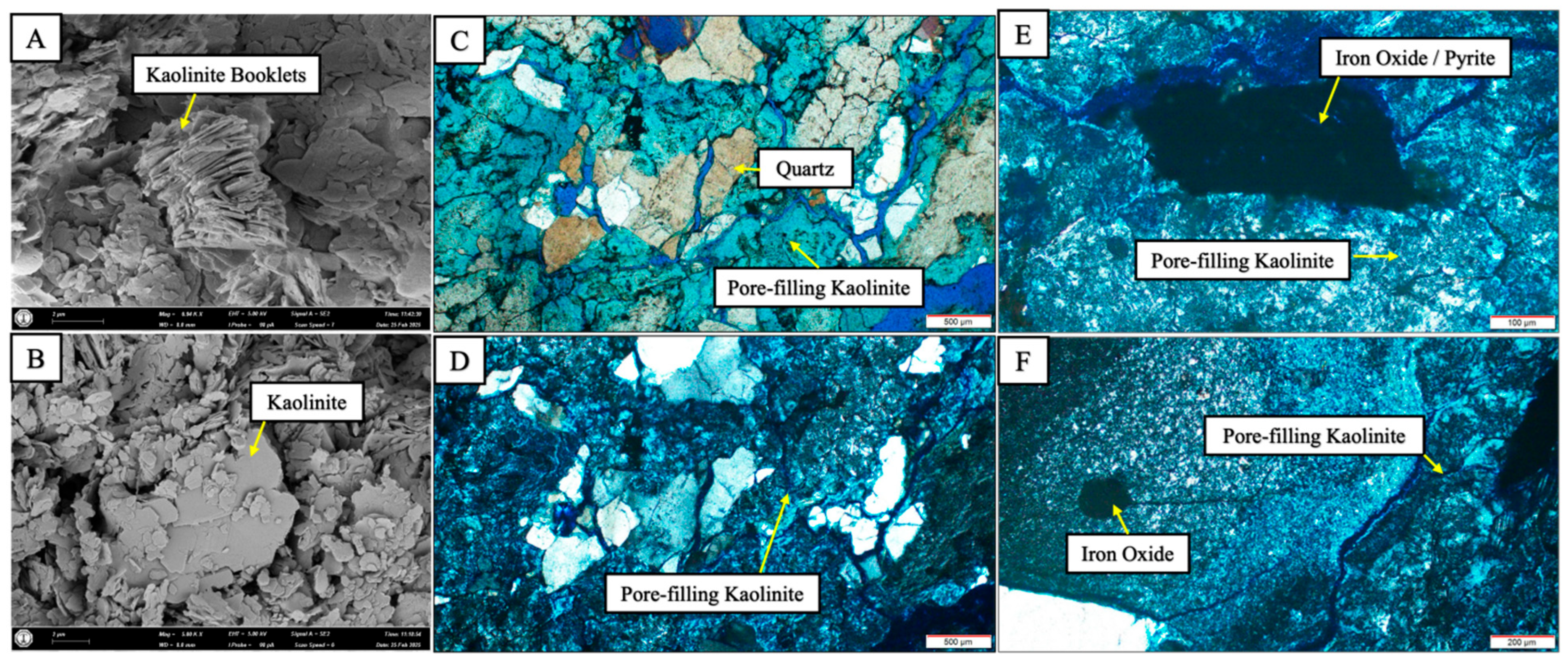
3.3. Thin Section Microscopy
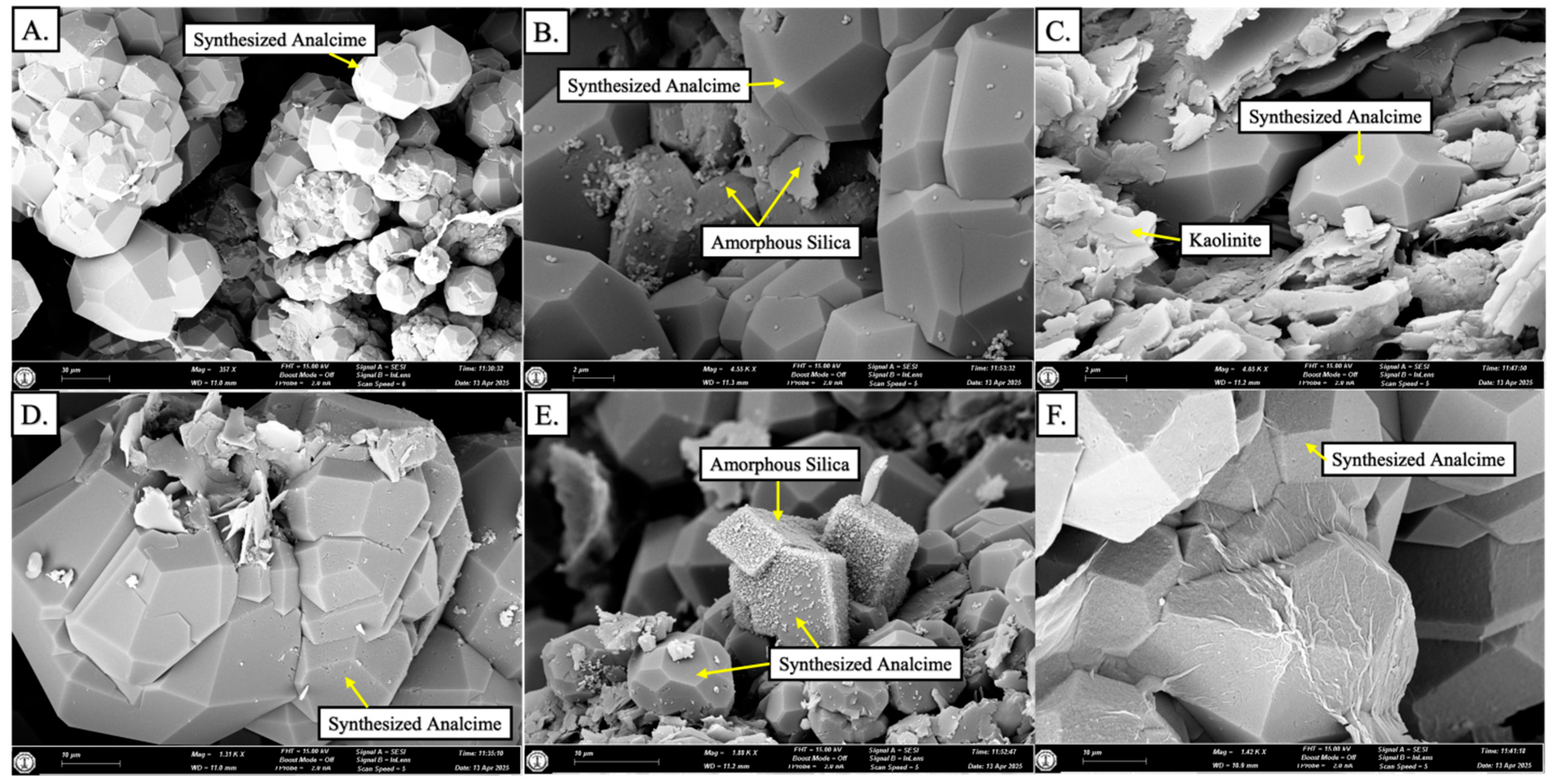
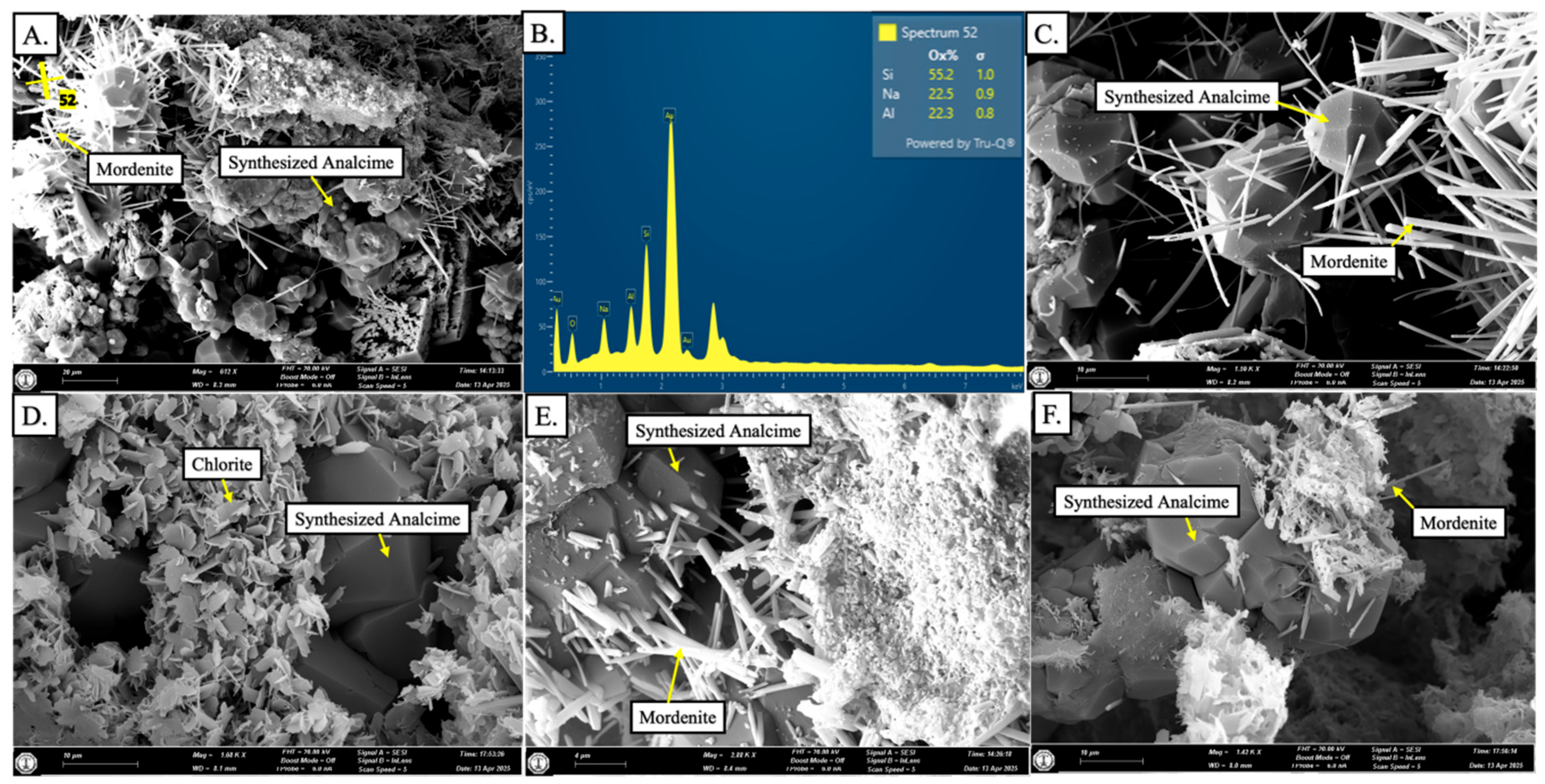
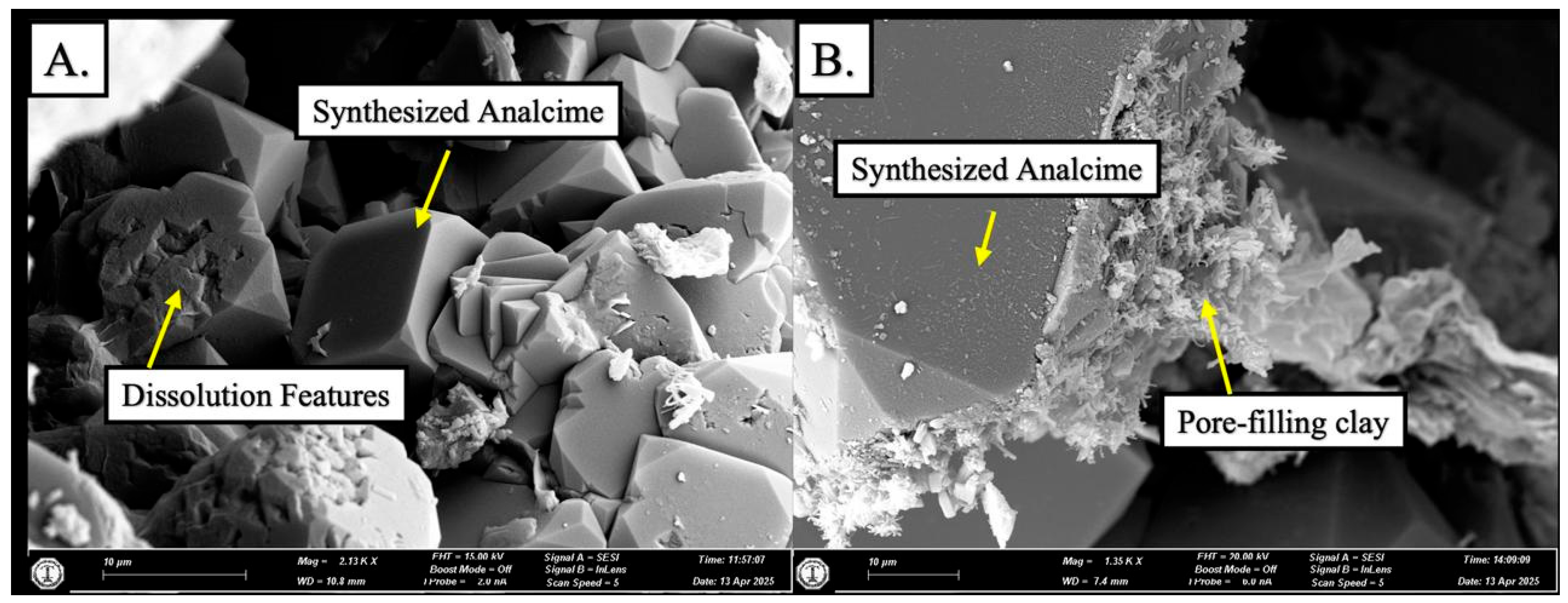
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
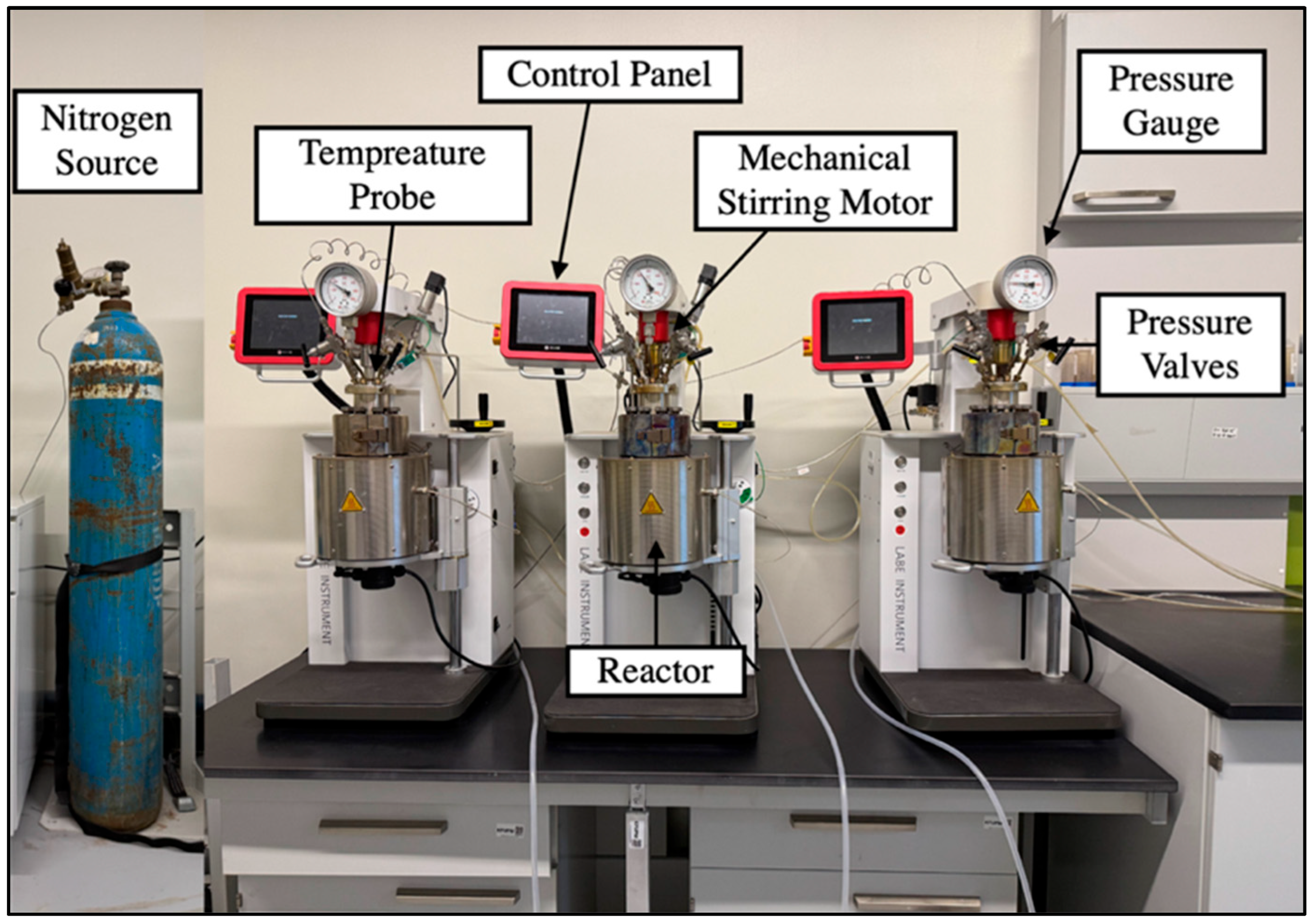
3.5. Hydrothermal Reactors
3.6. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
3.7. Post-Synthesizing Analysis
4. Results
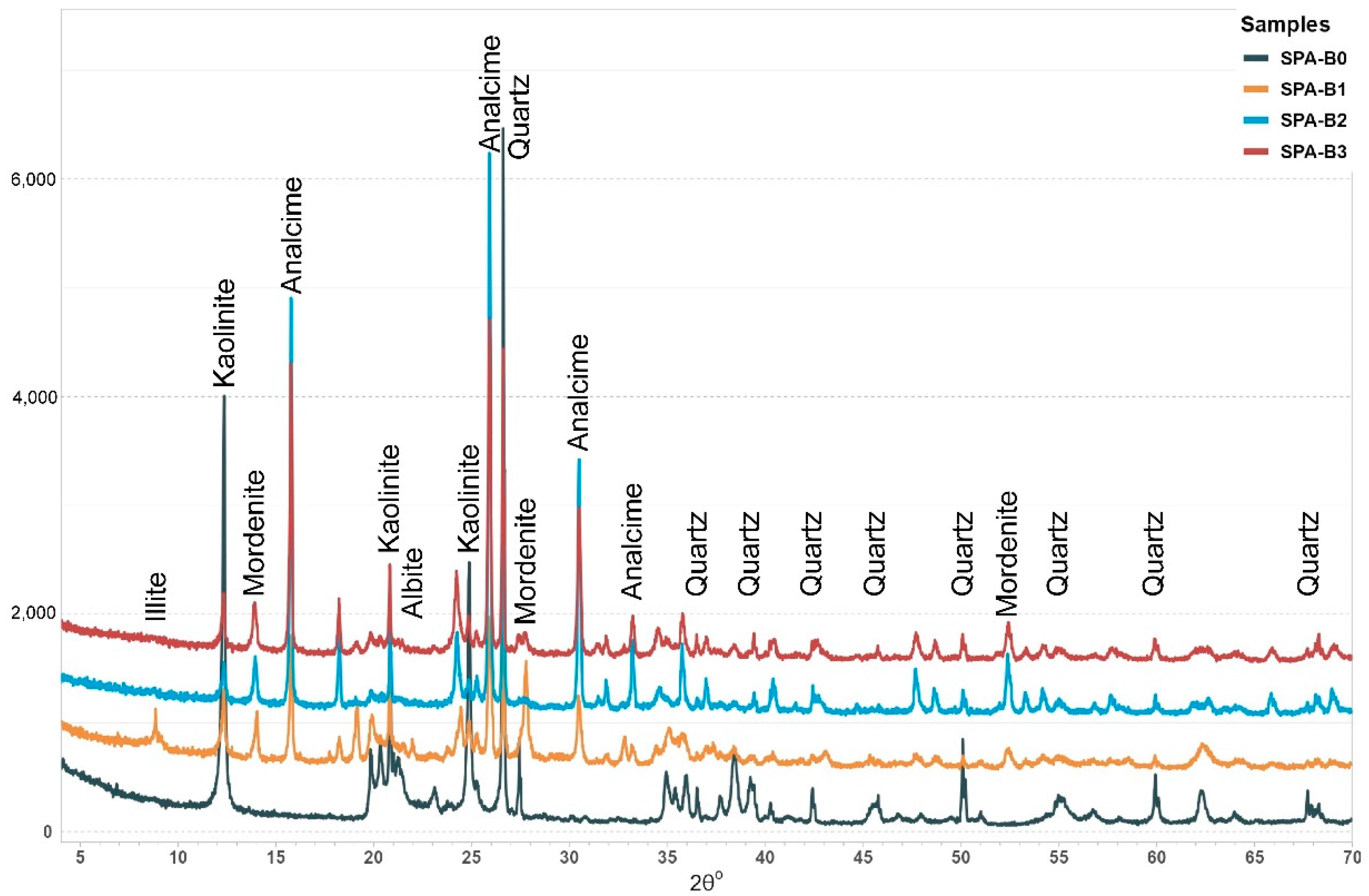
4.1. Mineralogical Composition of Starting Material
4.2. Reacted Samples’ Mineralogical Composition
4.2.1. Experiment 1—SPA-B1 (150 °C)
4.2.2. Experiment 2—SPA-B2 (200 °C)
4.2.3. Experiment 3—SPA-B3 (250 °C)
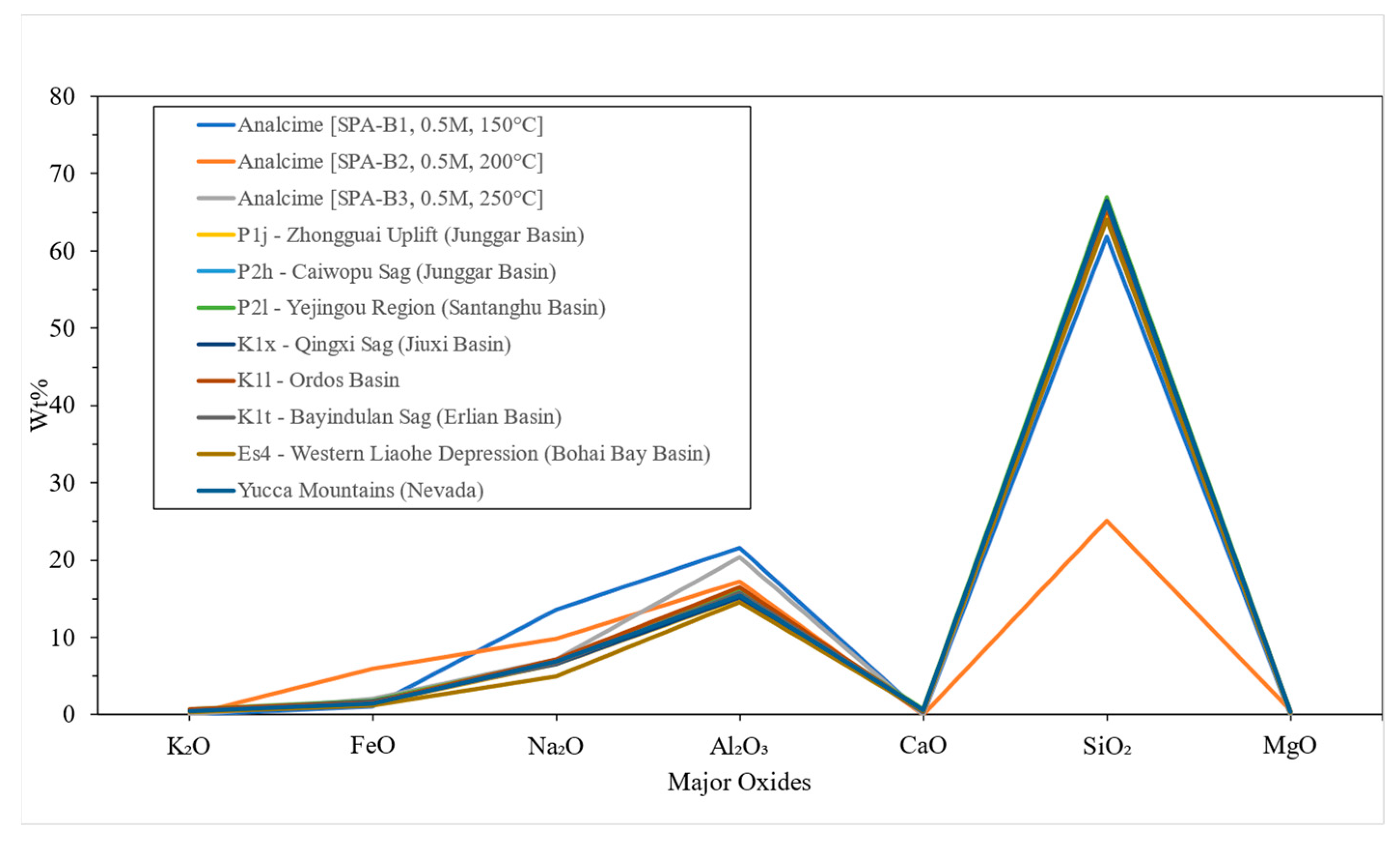
4.3. ICP-OES
4.4. Structural Formula
5. Discussion
5.1. Synthesized Zeolite Formation
5.2. Mechanism of Zeolite Formation
5.3. Limitations of Study and Future Work
6. Conclusions
- This study aims to convert kaolinite into zeolite and investigate the transformation within zeolite phases. A series of hydrothermal reactor experiments were conducted utilizing saprolite from the Al-Habala Area (NW Saudi Arabia) as the starting material. Analcime was synthesized at temperatures ranging from 150 °C to 250 °C over a duration of 336 h (14 days), using a synthetic solution. The dissolution of kaolinite initially occurred at 150 °C, resulting in the formation of synthesized analcime crystals. These crystals exhibited a continued development of trapezohedron faces at temperatures of 150 °C and 200 °C, transitioning to aggregate formations at the higher temperature of 250 °C.
- Zeolite demonstrated two mineral phases, including mordenite and analcime, showing an unusual transformation pathway, identified through SEM and SEM-EDX.
- Amorphous silica formed through the dissolution of the clay and feldspar grains, which supplied the Si and Al.
- Mordenite formed from the amorphous silica, with a sufficient Na+ supply from the synthetic solution used in this study.
- Analcime was synthesized under alkaline conditions of a pH = 11 in a sodium carbonate solution, forming crystals that are similar in composition to naturally occurring analcime.
- SPA-B3 represents the final product of the experiments, exhibiting several phases, specifically analcime, mordenite, amorphous silica, and minor kaolinite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chipera, S.J.; Apps, J.A. Geochemical Stability of Natural Zeolites. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2001, 45, 117–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Y.T.; Lee, J.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.S. Natural zeolite and its application in concrete composite production. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 165, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, E.; Salvi, L.; Paoli, F.; Fucile, M.; Masciandaro, G.; Manzi, D.; Masini, C.M.; Mattii, G.B. Application of Zeolites in Agriculture and Other Potential Uses: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovo, A.S.; Holmes, S.M.; Rios, C.A.; Otaru, A.J.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Eluwa, V.C. Synthesis of zeolites from different kaolin deposits worldwide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2025, 269, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zeolites; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, R.F.; Zones, S.I.; Davis, M.E. Structure-direction in zeolite synthesis. J. Incl. Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem. 1995, 21, 47–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic Zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, A. Zeolites in Petroleum and Natural Gas Reservoirs. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 45, 347–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Cui, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tong, H.; Ma, L. Occurrence, composition, and origin of analcime in sedimentary rocks of non-marine petroliferous basins in China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novembre, D.; Gimeno, D. Synthesis and characterization of analcime (ANA) zeolite using a kaolinitic rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaifan, M.; Al Daboubi, F.; Hourani, M.K. Preparation of Mesoporous Analcime/Sodalite Composite from Natural Jordanian Kaolin. Materials 2024, 17, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, T.S.; Youssef, H.F. Microwave Synthesis of Zeolites from Egyptian Kaolin: Evaluation of Heavy Metals Removal. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 2876–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.Y.; Jibril, B.Y.; Aderemi, B.O.; Adefila, S.S. Preparation of analcime from local kaolin and rice husk ash. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 61, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.G.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Angelica, R.S.; Macedo, E.N.; Neves, R.F. Analcime zeolite production from amazon kaolin. Ceramica 2013, 59, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godang, S.; Idrus, A.; Fadlin, B.P.; Basuki, N.I. Saprolitization’s Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in Volcanic Regolith on Drill Core #65 in Western Sulawesi, Indonesia. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 7, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.F.; Nasr, R.A.; El-Anwar, E.A.A.; Mekky, H.S.; El Rahim, S.H.A. Preparation and characterization of different zeolites from andesite rock: Product evaluation for efficient dye removal. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 328, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Tamizhdurai, P.; Mangesh, V.L.; Ragupathi, C.; Krishnan, P.S.; Ramesh, A. Recent advances in the synthesis and applications of mordenite zeolite—Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 11, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.M.; Charlaftis, D.; Jones, S.J.; Gluyas, J.; Acikalin, S.; Cartigny, M.; Al-Ramadan, K. Experimental diagenesis using present-day submarine turbidite sands. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 952690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.M.; Salisu, A.M.; Amao, A.O.; Umar, M.; Al-Ramadan, K. Experimental development of chlorite: Insights from a kaolinite precursor. J. Sediment. Res. 2025, 95, 462–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, W. A Geological and Geochemical Reconnaissance of the Tathlith One-Degree Quadrangle, Sheet 19/43 Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1978; pp. 78–1072.
- Yoldi, M.; Fuentes-Ordoñez, E.; Korili, S.; Gil, A. Zeolite synthesis from industrial wastes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 287, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencía, R.V.d.l.V.; Goiti, E.; Ocejo, M.; Giménez, R.G. Synthesis of zeolite type analcime from industrial wastes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 293, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchagina, T.A.; Kutikhina, E.A.; Solovyov, L.A.; Vereshchagin, S.N.; Mazurova, E.V.; Chernykh, Y.Y.; Anshits, A.G. Synthesis and structure of analcime and analcime-zirconia composite derived from coal fly ash cenospheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 258, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Lin, I.; Lo, H.; Song, S.; Chen, Y. The Kinetics of Analcime Synthesis in Alkaline Solution. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2004, 51, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wang, D.; Ye, S. Synthesis of micro-mesoporous glass-analcime composite structure with soda–lime–silica glass as raw material. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2019, 12, 1950021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.N.; Kumar, R. Synthesis of zeolite beta using silica gel as a source of SiO2. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1990, 48, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Ma, H.; Chuan, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite A from K-feldspar and its crystallization mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, D.; Tan, J.; Chen, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, H.; Shen, B.; Wu, D.; et al. In Situ Hydrothermal Conversion of Silica Gel Precursors to Binderless Zeolite X Pellets for Enhanced Olefin Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 9997–10009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, C.; Cao, Y.; Tian, Y. Occurrence, Genesis, and Significance of Analcime in Fine-Grained Sedimentary Rocks. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 3633047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincapie, B.O.; Garces, L.J.; Zhang, Q.; Sacco, A.; Suib, S.L. Synthesis of mordenite nanocrystals. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 67, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gili, M.; Conato, M. Synthesis and characterization of mordenite-type zeolites via hydrothermal method using amorphous silica and sodium aluminate as Si and Al sources at varying temperature. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1191, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | Sample ID | Solution (M) | Temperature (°C) | Duration (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SPA-B1 | 200 mL of 0.5 M Na2CO3 | 150 | 14 |
| 2 | SPA-B2 | 200 | 14 | |
| 3 | SPA-B3 | 250 | 14 |
| Oxide | Analcime [SPA-B1, 0.5 M, 150 °C] | Analcime [SPA-B2, 0.5 M, 200 °C] | Analcime [SPA-B3, 0.5 M, 250 °C] | Mordenite [SPA-B1, 0.5 M, 150 °C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 62.93 | 42.42 | 68.79 | 54.37 |
| TiO2 | 0.15 | 0.76 | 0 | 0 |
| Al2O3 | 21.96 | 29.25 | 21.49 | 22.62 |
| FeO Total | 1.13 | 10.07 | 2.11 | 0 |
| MnO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MgO | 0 | 0.93 | 0 | 0 |
| CaO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Na2O | 13.83 | 16.56 | 7.62 | 23.01 |
| K2O | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cr2O3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| V2O3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Structural Formula | ||||
| Element | Analcime [SPA-B1, 0.5 M, 150 °C] | Analcime [SPA-B2, 0.5 M, 200 °C] | Analcime [SPA-B3, 0.5 M, 250 °C] | Mordenite [SPA-B1, 0.5 M, 150 °C] |
| Si | 33.44 | 23.70 | 34.51 | 22.86 |
| Ti | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Al | 13.76 | 11.02 | 12.90 | 11.24 |
| Fe2 + all ferrous | 0.51 | 4.93 | 1.07 | 0.00 |
| Mn | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Mg | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ca | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Na | 14.27 | 10.31 | 7.92 | 18.84 |
| K | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cr | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| V | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| P | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| F | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cl | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Si/Al | 2.43 | 2.15 | 2.67 | 2.03 |
| (Ca + Mg)/(Na + K) | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| (K + Na)/(K + Na + Ca) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| (Na + K + Ca + Mg) | 14.27 | 10.73 | 7.92 | 18.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoshnaw, A.S.; Alismail, D.N.; Bello, A.M.; Al-Ramadan, K. Experimental Investigation of Kaolinite–Zeolite Transformation: Insights from Al-Habala Area Saprolite, Abha, Saudi Arabia. Minerals 2025, 15, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090920
Khoshnaw AS, Alismail DN, Bello AM, Al-Ramadan K. Experimental Investigation of Kaolinite–Zeolite Transformation: Insights from Al-Habala Area Saprolite, Abha, Saudi Arabia. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090920
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoshnaw, Ali Sarbast, Dana Nader Alismail, Abdulwahab Muhammad Bello, and Khalid Al-Ramadan. 2025. "Experimental Investigation of Kaolinite–Zeolite Transformation: Insights from Al-Habala Area Saprolite, Abha, Saudi Arabia" Minerals 15, no. 9: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090920
APA StyleKhoshnaw, A. S., Alismail, D. N., Bello, A. M., & Al-Ramadan, K. (2025). Experimental Investigation of Kaolinite–Zeolite Transformation: Insights from Al-Habala Area Saprolite, Abha, Saudi Arabia. Minerals, 15(9), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090920






