Optimising Nature-Based Treatment Systems for Management of Mine Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Configuration
2.2. Bioreactor Operation
2.3. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Substrate Sampling and Analysis
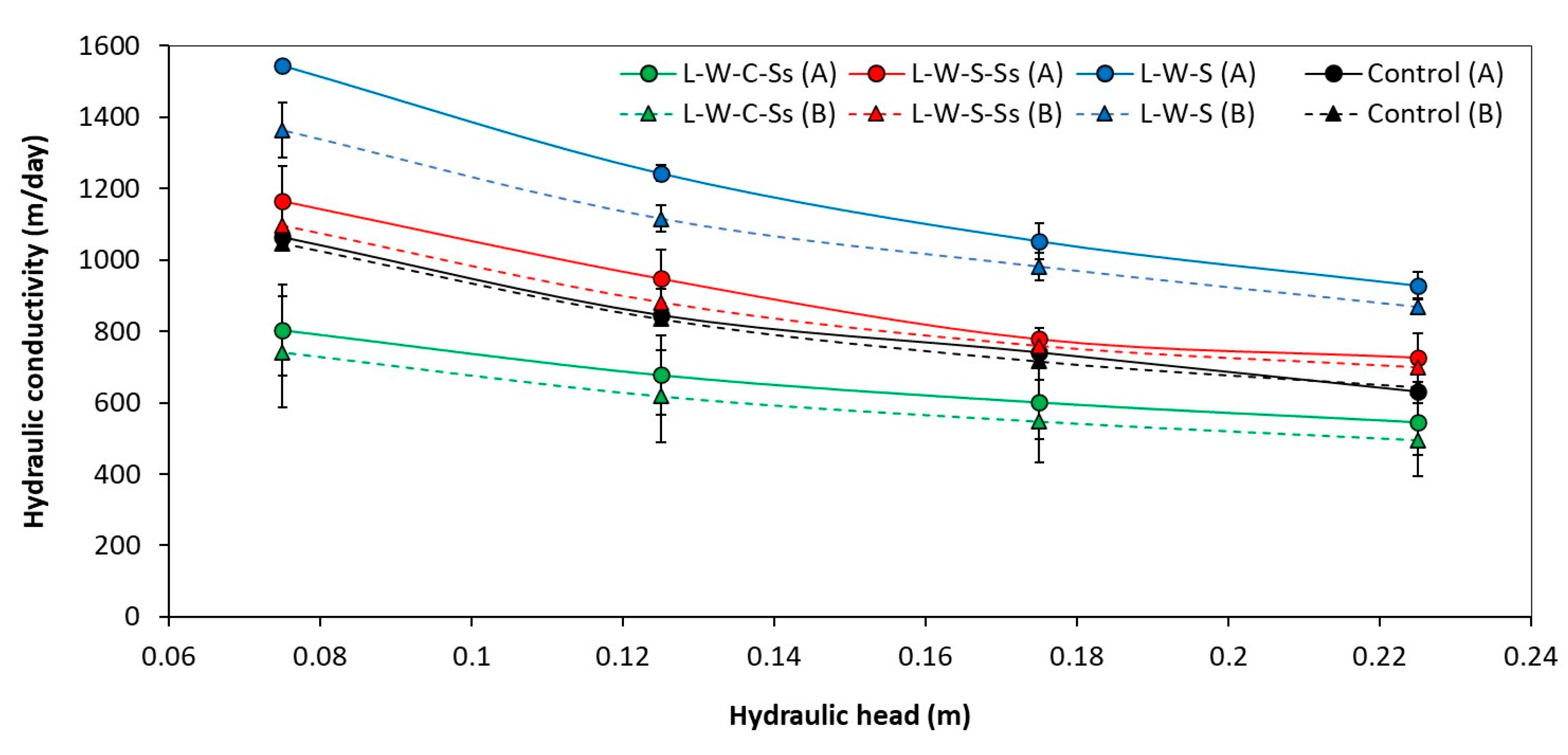
2.5. Hydraulics Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
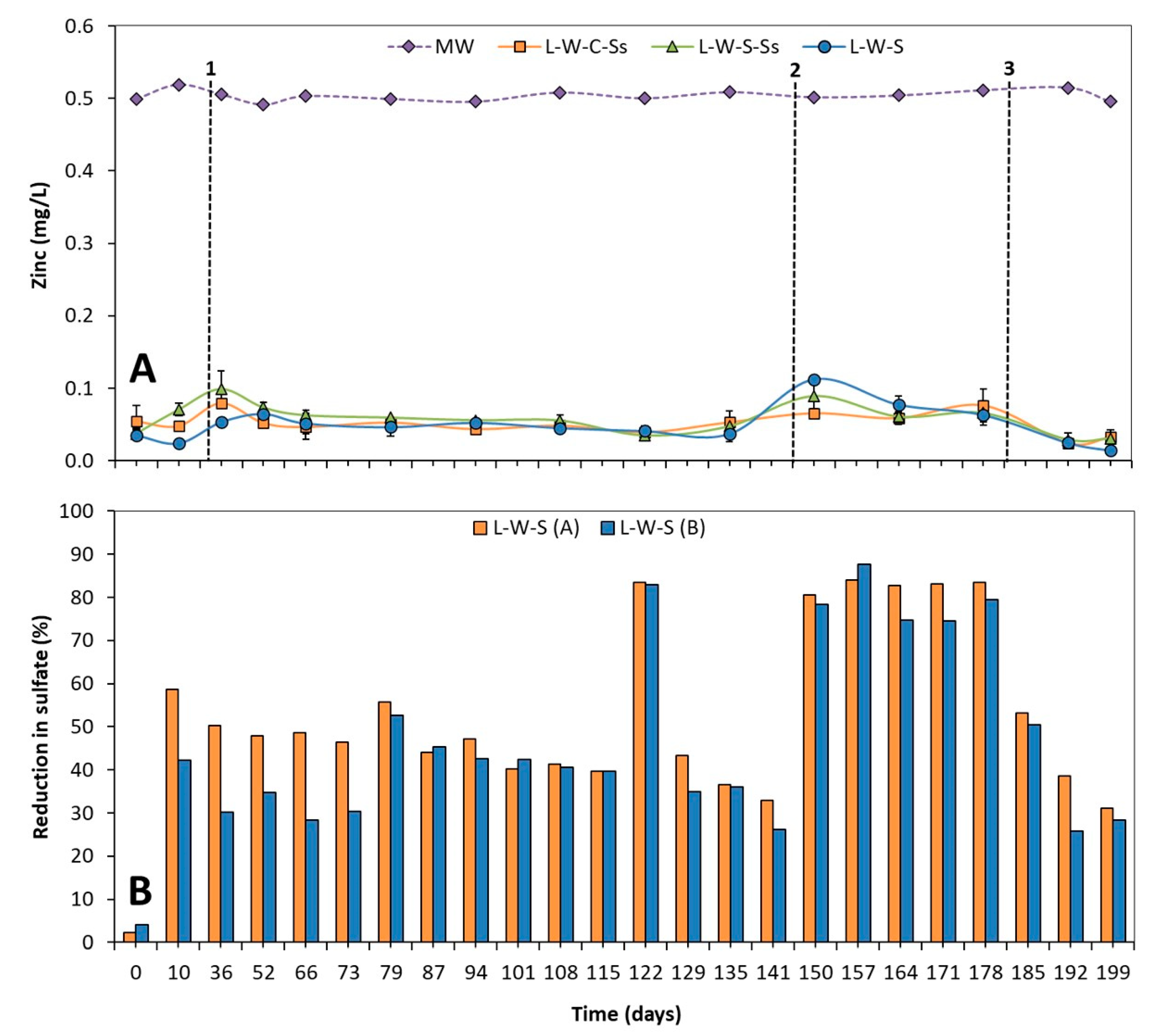
3.1. Effectiveness of Different Substrate Mixes
3.1.1. Zinc and Sulfate Removal
3.1.2. Hydraulic Performance
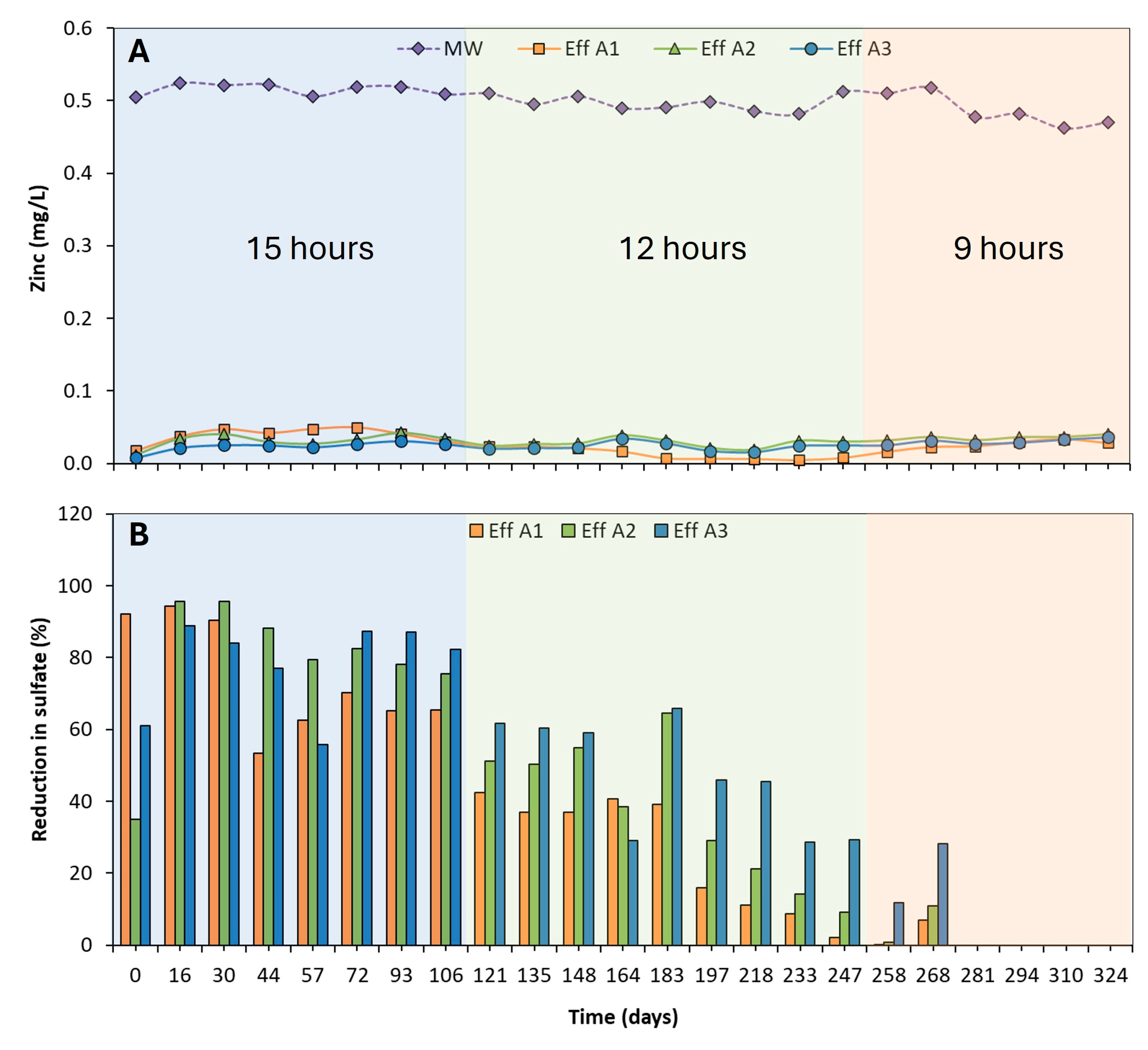
3.2. Effectiveness of Zinc and Sulfate Removal at Reduced Hydraulic Residence Time
3.2.1. Zinc and Sulfate Removal
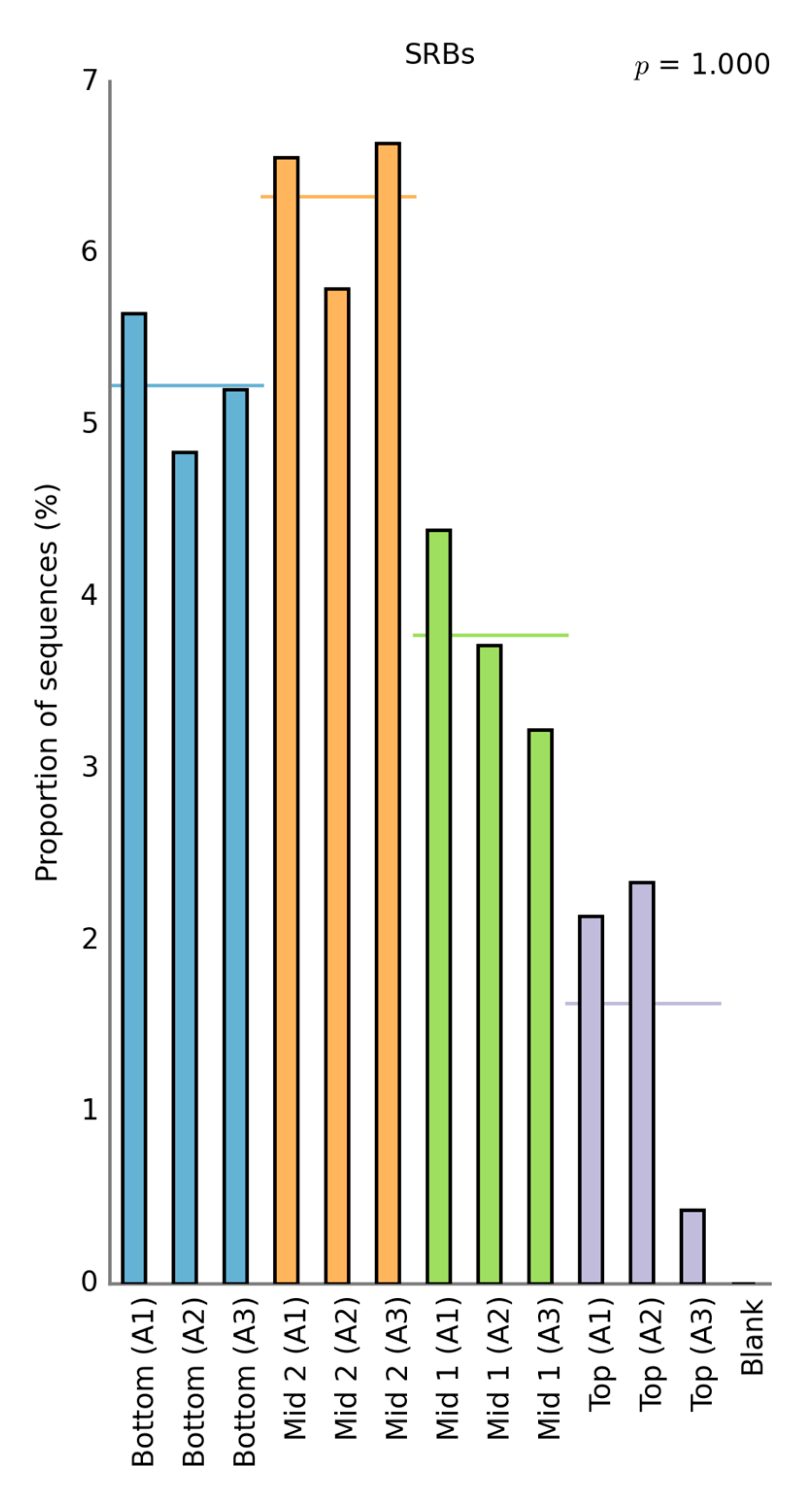
3.2.2. Zinc Removal Mechanisms
3.2.3. Hydraulic Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R.; Macías, F.; Basallote, M.D.; Nieto, J.M. The evolution of pollutant concentrations in a river severely affected by acid mine drainage: Río Tinto (SW Spain). Minerals 2020, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Ziper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of passive systems for acid mine drainage. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.E.; Antweiler, R.C.; Roth, D.A.; Alpers, C.N.; Dileanis, P. Selected trace elements in the Sacramento River, California: Occurrence and distribution. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 62, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, W.M.; Potter, H.A.B.; Jarvis, A.P. Inventory of aquatic contaminant flux arising from historical metal mining in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, W.M.; Potter, H.A.B.; Jarvis, A.P. Riverine flux of metals from historically mined orefields in England and Wales. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, A.S.; Sheoran, V. Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.P.; Gandy, C.J.; Webb, J.A. Controls on the generation and geochemistry of neutral mine drainage: Evidence from Force Crag mine, Cumbria, UK. Minerals 2023, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency. Abandoned Metal Mines in England: Baseline Length of Rivers and Estuaries Polluted by Harmful Metals; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.C.; Sadykova, D.; Qu, Y.; Keller, V.D.J.; Bachiller-Jareno, N.; Jürgens, M.D.; Eastman, M.; Edwards, F.; Rizzo, C.; Scarlett, P.M.; et al. Zinc and copper have the greatest relative importance for river macroinvertebrate richness at a national scale. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 4068–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandy, C.J.; Davis, J.E.; Orme, P.H.A.; Potter, H.A.B.; Jarvis, A.P. Metal removal mechanisms in a short hydraulic residence time subsurface flow compost wetland for mine drainage treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandy, C.J.; Gray, N.D.; Mejeha, O.K.; Sherry, A.; Jarvis, A.P. Use of propionic acid to enhance zinc removal from mine drainage in short residence time, flow-through sulfate-reducing bioreactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.S.; Park, H.S.; Ji, W.H.; Kim, D.-M.; Jo, H.Y. Removal of Cu and Zn from mine water using bench-scale bioreactors with spent mushroom compost: A case study in an abandoned mine region, South Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, Y.; Escobar, M.C.; Neculita, C.M.; Arbeli, Z.; Roldan, F. Biochemical passive reactors for treatment of acid mine drainage: Effect of hydraulic retention time on changes in efficiency, composition of reactive mixture, and microbial activity. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.-M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Passive treatment of acid mine drainage in bioreactors using sulfate-reducing bacteria: Critical review and research needs. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.-M.; Zagury, G.J. Biological treatment of highly contaminated acid mine drainage in batch reactors: Long-term treatment and reactive mixture characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, W.M.; Davis, J.; Silva, V.; Jarvis, A.P. Treatment of zinc-rich acid mine water in low residence time bioreactors incorporating waste shells and methanol dosing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 19, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.-M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Effectiveness of sulfate-reducing passive bioreactors for treating highly contaminated acid mine drainage: I Effect of hydraulic retention time. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.E.B.; Neculita, C.-M.; Molson, J.W.; Maqsoud, A.; Zagury, G.J. Salinity and low temperature effects on the performance of column biochemical reactors for the treatment of acidic and neutral mine drainage. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, T.; Hamai, T.; Hori, T.; Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sato, Y.; Inaba, T.; Ogata, A.; Habe, H.; Sakata, T. Hydraulic retention time and pH affect the performance and microbial communities of passive bioreactors for treatment of acid mine drainage. AMB Express 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, W.M.; Perks, M.T.; Large, A.R.G.; Davis, J.E.; Gandy, C.J.; Orme, P.A.H.; Jarvis, A.P. Effect of an extreme flood event on solute transport and resilience of a mine water treatment system in a mineralised catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, D.; Cyr, J. Evaluation of biofilter performance to remove dissolved arsenic: Wood Cadillac. In Proceedings of the Sudbury 2003—Mining and the Environment, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 25–28 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Botes, A.; James, C.; Sheridan, C.M. Assessing the clogging and permeability of degrading packed bed reactors. Water SA 2018, 44, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, P.W.; Younger, P.L. Substrate characterisation for a subsurface reactive barrier to treat colliery spoil leachate. Water Res. 2003, 37, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, A.; Gandy, C. Review of substrate compositions for passive metal mine drainage treatment systems. 2018; unpublished report. [Google Scholar]
- BS 7755-3.9:1995; Soil Quality—Part 3: Chemical Methods—Section 3.9 Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1995.
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of highthroughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-N.; Chen, Y. Advances in heavy metal removal by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1797–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, G.; Coudert, L.; Janin, A.; Blais, J.F.; Mercier, G. Influence of organic carbon sources on metal removal from mine impacted water using sulfate-reducing bacteria bioreactors in cold climates. Mine Water Environ. 2019, 38, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oporto, C.; Baya, G.; Vandecasteele, C. Efficiencies of available organic mixtures for the biological treatment of highly acidic-sulphate rich drainage of the San Jose mine, Bolivia. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.-M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Effectiveness of sulfate-reducing passive bioreactors for treating highly contaminated acid mine drainage: II Metal removal mechanisms and potential mobility. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3545–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, O.; de Pablo, J.; Cortina, J.L.; Ayora, C. Chemical characterisation of natural organic substrates for biological mitigation of acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4186–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Fitch, M.; Burken, J.; Nass, L.; Chilukiri, S.; Gale, N.; Ross, C. Lead and zinc removal by laboratory-scale constructed wetlands. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijp, J.J.; Metselaar, K.; Limpens, J.; Gooren, H.P.A.; van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. A modification of the constant-head permeameter to measure saturated hydraulic conductivity of highly permeable media. MethodsX 2017, 4, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, A.P.; Davis, J.E.; Orme, P.H.A.; Potter, H.A.B.; Gandy, C.J. Predicting the benefits of mine water treatment under varying hydrological conditions using a synoptic mass balance approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Biogeochemistry of the compost bioreactor components of a composite acid mine drainage passive remediation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hem, J.D. Chemistry and occurrence of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s Guide to PHREEQC—A Computer Program for Speciation, BATCH-reaction, ONE-dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; U.S. Geological Survey: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1999.
- Drennan, D.M.; Almstrand, R.; Ladderud, J.; Lee, I.; Landkamer, L.; Figueroa, L.; Sharp, J.O. Spatial impacts of inorganic ligand availability and localized microbial community structure on mitigation of zinc laden mine water in sulfate-reducing bioreactors. Water Res. 2017, 115, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz Viggi, C.; Pagnanelli, F.; Cibati, A.; Uccelletti, D.; Palleschi, C.; Toro, L. Biotreatment and bioassessment of heavy metal removal by sulphate reducing bacteria in fixed bed reactors. Water Res. 2010, 44, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Substrate | Limestone Gravel | Wood Chips | Straw | PAS 100 Compost | Municipal Sewage Sludge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-W-C-SS | 50% | 25% | 0% | 15% | 10% |
| L-W-S-SS | 50% | 25% | 15% | 0% | 10% |
| L-W-S | 50% | 25% | 25% | 0% | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandy, C.J.; Christgen, B.; Jarvis, A.P. Optimising Nature-Based Treatment Systems for Management of Mine Water. Minerals 2025, 15, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070765
Gandy CJ, Christgen B, Jarvis AP. Optimising Nature-Based Treatment Systems for Management of Mine Water. Minerals. 2025; 15(7):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070765
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandy, Catherine J., Beate Christgen, and Adam P. Jarvis. 2025. "Optimising Nature-Based Treatment Systems for Management of Mine Water" Minerals 15, no. 7: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070765
APA StyleGandy, C. J., Christgen, B., & Jarvis, A. P. (2025). Optimising Nature-Based Treatment Systems for Management of Mine Water. Minerals, 15(7), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070765







