The Effects of Amino Acids on the Polymorphs and Magnesium Content of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Properties of Amino Acids
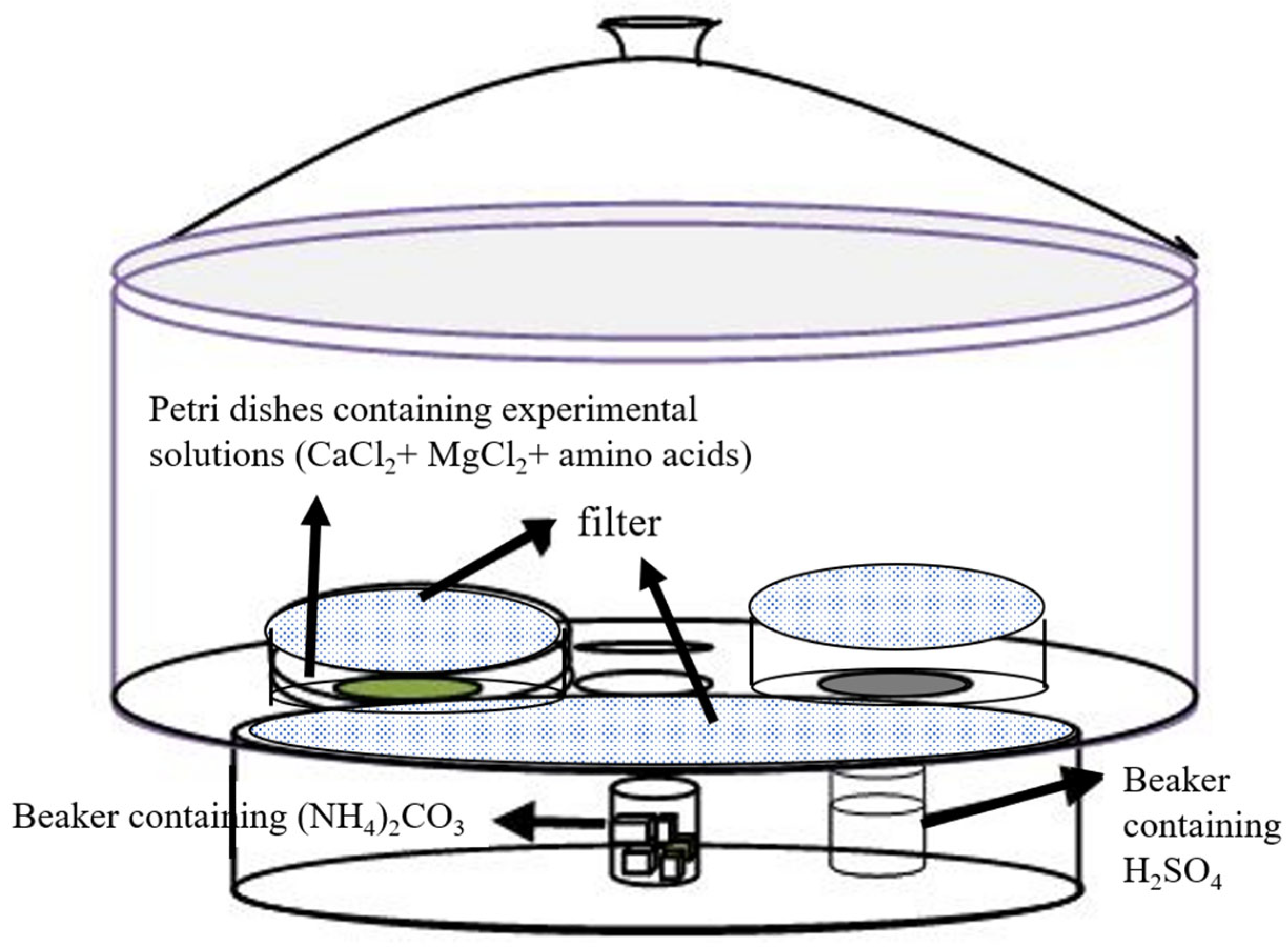
2.2. Biomimetic Mineralization Experiments of Ca–Mg Carbonates
2.3. Observation and Analysis
3. Results
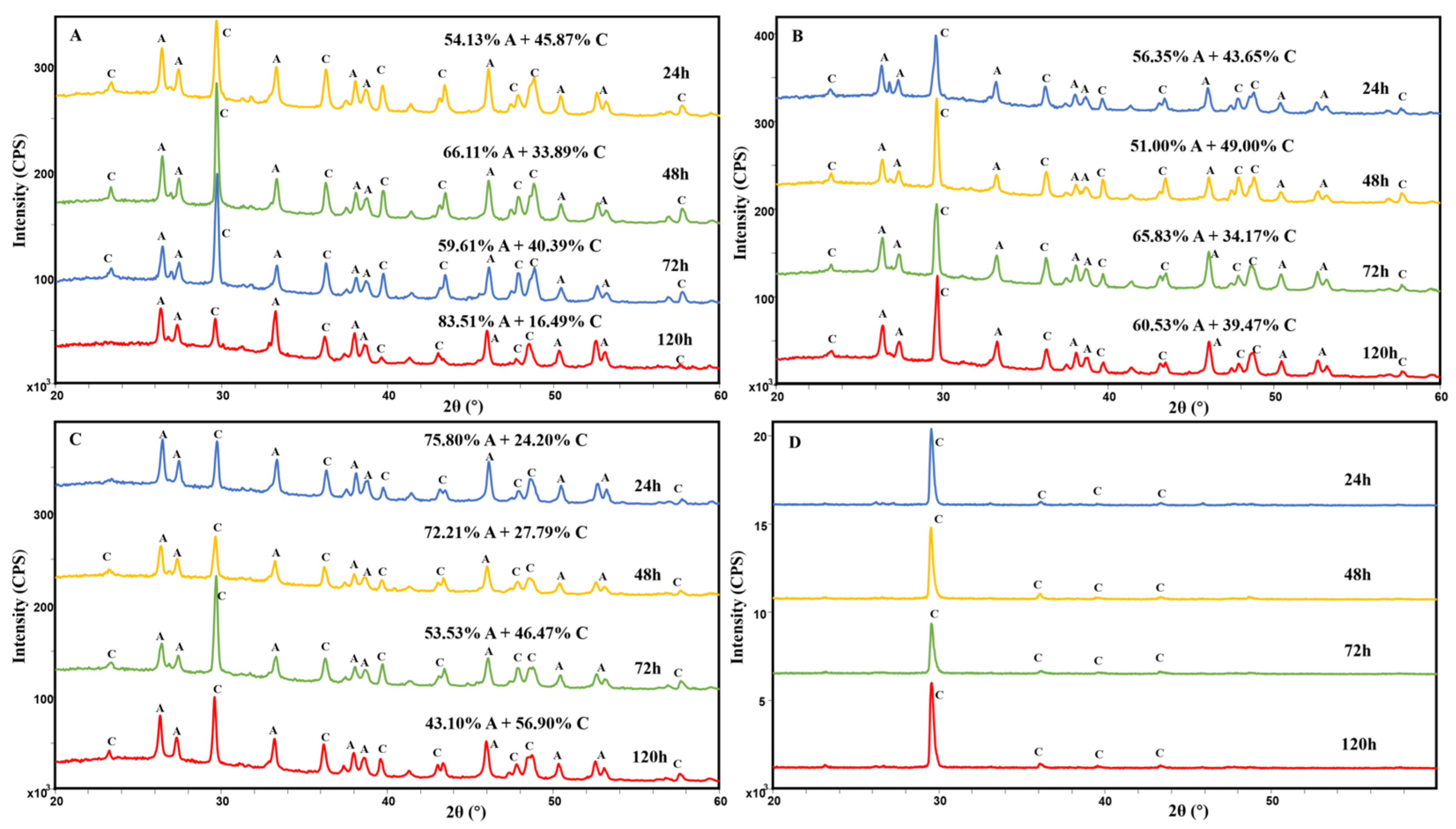
3.1. XRD and FT-IR Analyses of Ca-Mg Carbonate
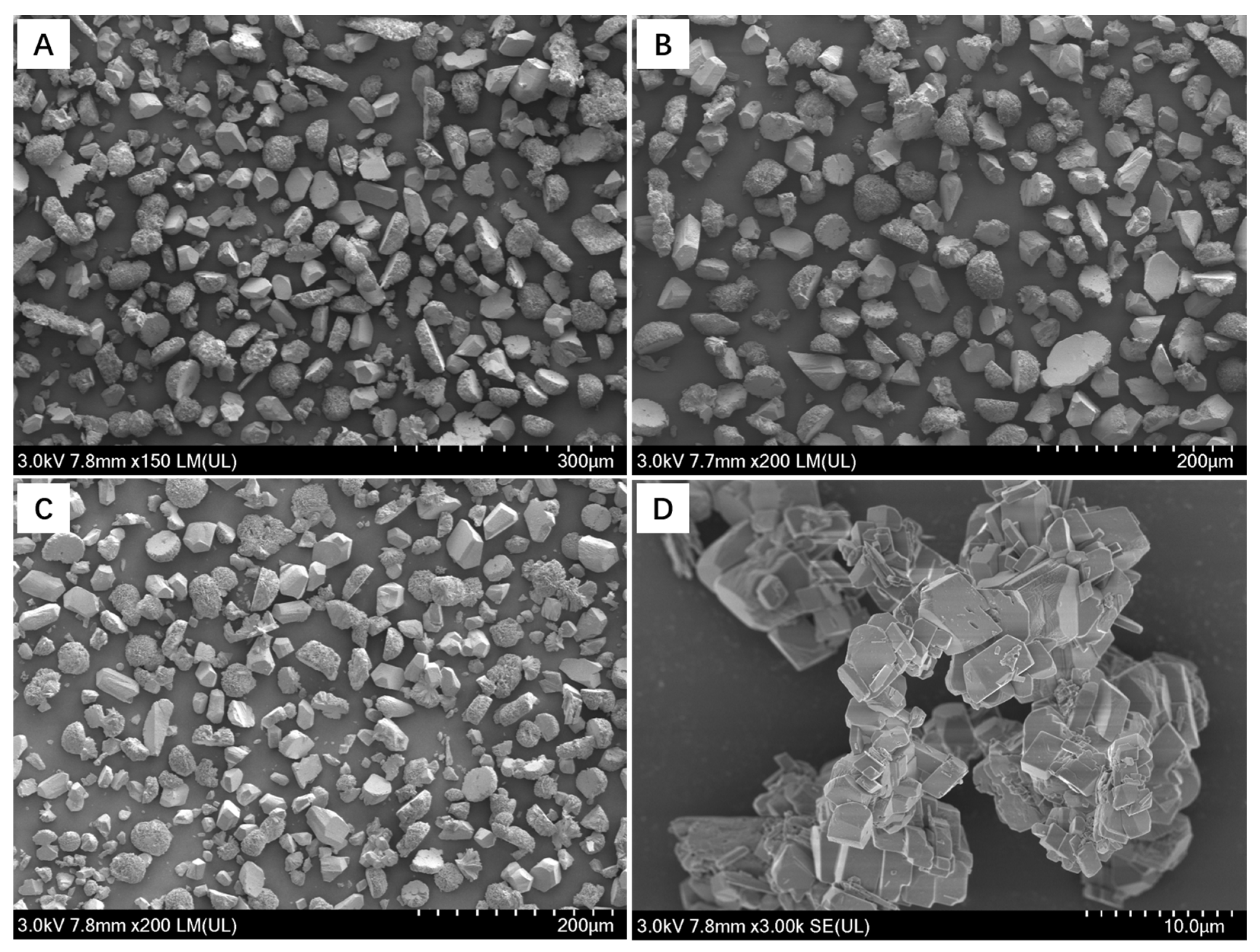
3.2. Morphological Changes of Ca-Mg Carbonate
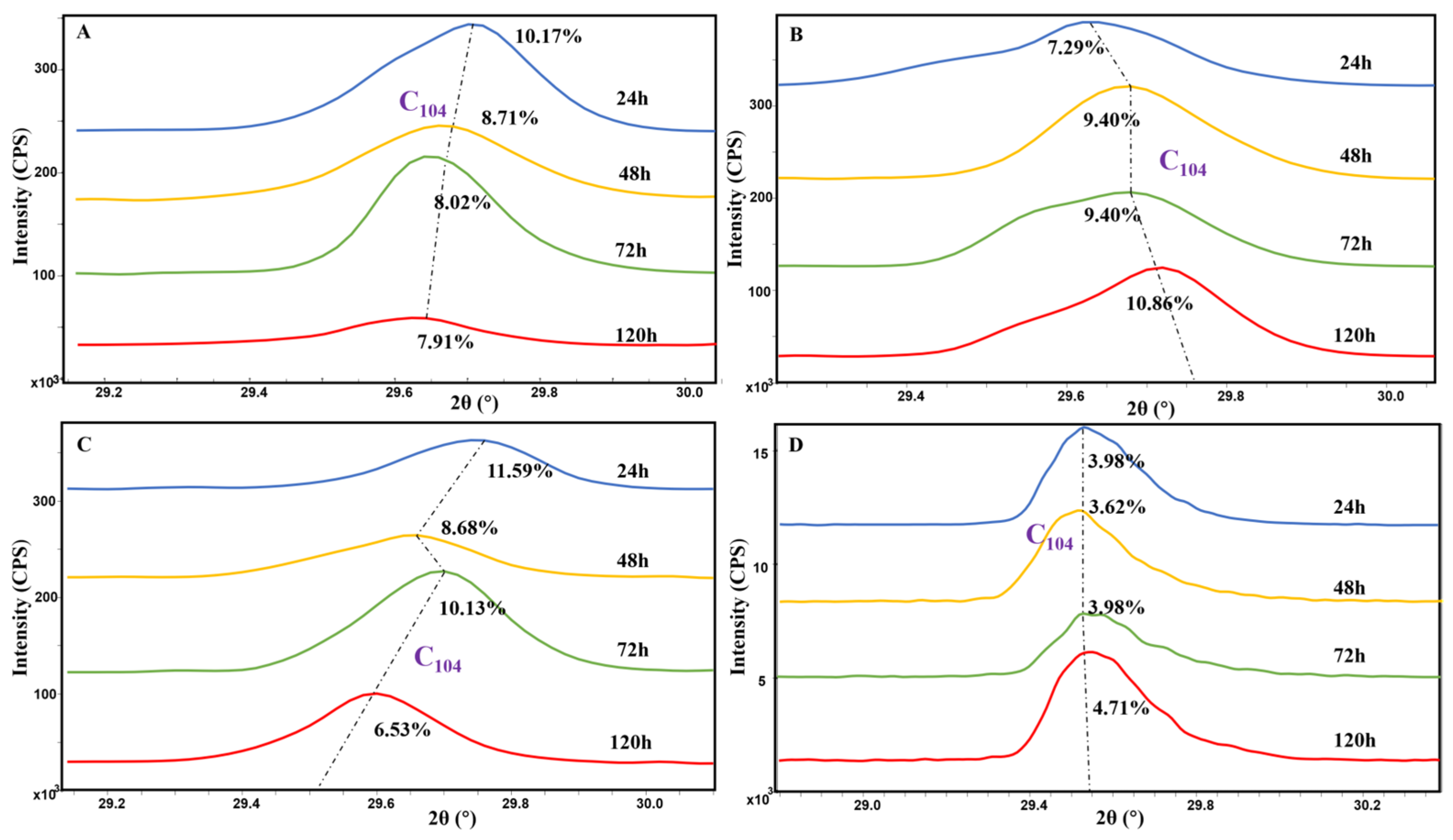
3.3. Magnesium Content in Calcite
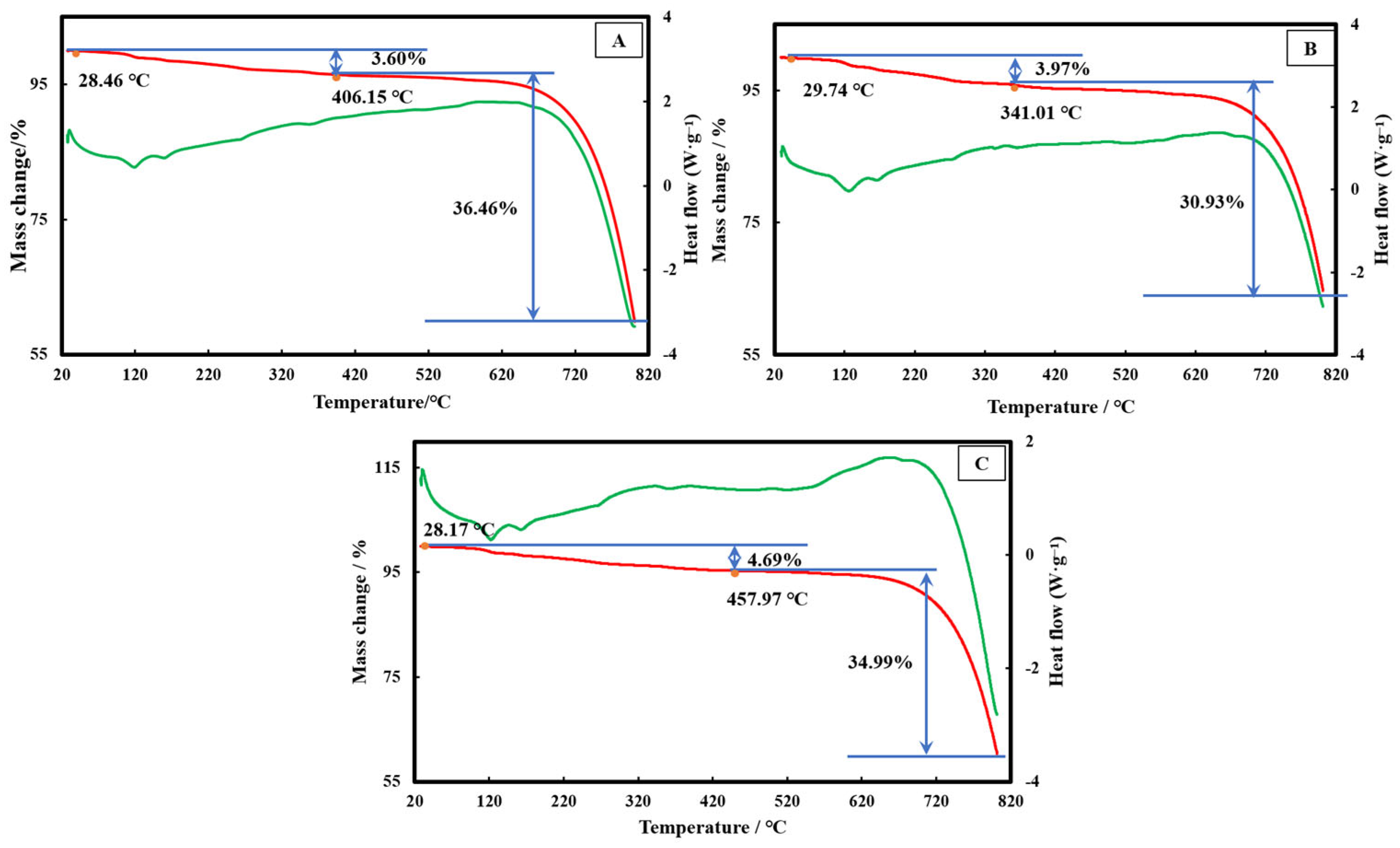
3.4. Thermal Decomposition Characteristics of the Different Precipitates
4. Discussion
4.1. Control of Reaction Liquid and Mineral Precipitation
4.2. The Effect of Amino Acids on Polymorphs of Ca–Mg Carbonates
4.3. The Effect of Amino Acids on Mg Content in Calcite
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morse, J.W.; Arvidson, R.S.; Lüttge, A. Calcium carbonate formation and dissolution. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 342–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Guo, Q. Mineral transformation, element transport and hydrological impact in weathering at the Bingling Temple Grottoes: Implications for weathering in alkaline environments in NW China. Catena 2024, 239, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanken, N.M.; Bjørlykke, K.; Nielsen, J.K. Carbonate sediments. In Petroleum Geoscience: From Sedimentary Environments to Rock Physics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 151–216. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.S.; Nguyen, H.; Venâncio, F.; Ramteke, D.; Zevenhoven, R.; Kinnunen, P. Mechanisms of Mg carbonates precipitation and implications for CO2 capture and utilization/storage. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 2507–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Shen, M.J.; Li, J.; Jiao, K.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L.N. Microbe-mediated extracellular and intracellular mineralization: Environmental, industrial, and biotechnological applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, R. The mineralization of molluscan shells: Some unsolved problems and special considerations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 874534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Sánchez-Román, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y. Nucleation and stabilization of Eocene dolomite in evaporative lacustrine deposits from central Tibetan plateau. Sedimentology 2020, 67, 3333–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanienda-Pilecki, K.J. Crystals structures of carbonate phases with Mg in Triassic rocks, mineral formation and transitions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhimova, N. Calcium and/or magnesium carbonate and carbonate-bearing rocks in the development of alkali-activated cements—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, A.; Kassa, Y.; Lemma, B.; Bhaskarwar, A.N.; Mullu, T.; Tibebe, D. Optimised phosphate adsorption using a synergistic calcite-dolomite mix: A novel approach for water treatment. Chem. Ecol. 2025, 41, 668–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, P.; Kang, C.H.; Shin, Y.J.; So, J.S. Formations of calcium carbonate minerals by bacteria and its multiple applications. Springerplus 2016, 5, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Roles of bacteria and extracellular polymeric substance in calcium carbonate formation: Insights from the effects of calcium source and deposition rate on nucleation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 202, 109160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Lyu, J.; Yao, Y. Biomimetic mineralization of Ca-Mg carbonates: Relevance to microbial cells and extracellular polymeric substances. Microsc. Microanal. 2023, 29, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Fernández, A.; Areias, C.; Daffonchio, D.; Vahrenkamp, V.C.; Sánchez-Román, M. The role of microorganisms in the nucleation of carbonates, environmental implications and applications. Minerals 2022, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, M.; Bourg, I.C.; Coward, E.K.; Hansel, C.M.; Myneni, S.C.; Nunan, N. Dynamic interactions at the mineral–organic matter interface. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Berg, J.K.; Kellermeier, M.; Gebauer, D. Sweet on biomineralization: Effects of carbohydrates on the early stages of calcium carbonate crystallization. Eur. J. Mineral. 2014, 26, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Kenward, P.A.; Fowle, D.A.; Goldstein, R.H.; González, L.A.; Moore, D.S. Surface chemistry allows for abiotic precipitation of dolomite at low temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14540–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenward, P.A.; Fowle, D.A.; Goldstein, R.H.; Ueshima, M.; González, L.A.; Roberts, J.A. Ordered low-temperature dolomite mediated by carboxyl-group density of microbial cell walls. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 2113–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, B.; Hu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ji, J.; Teng, H.H. Carbonate biomineralization induced by soil bacterium Bacillus megaterium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 5522–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyannis, C.G.; Vagenas, N.V. Calcium carbonate phase analysis using XRD and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2000, 125, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, D.N. Discrepancy between thin-section and X-ray estimates of dolomite in limestone. J. Sediment. Res. 1979, 49, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Štajner, L.; Kontrec, J.; Džakula, B.N.; Maltar-Strmečki, N.; Plodinec, M.; Lyons, D.M.; Kralj, D. The effect of different amino acids on spontaneous precipitation of calcium carbonate polymorphs. J. Cryst. Growth 2018, 486, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Gower, L.; Wasman, S.; Sun, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Gu, L.; Tang, X.; et al. From the inside out: Elemental compositions and mineral phases provide insights into bacterial calcification. Chem. Geol. 2021, 559, 119974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Gómez-Morales, J.; Jiménez-López, C.; Nys, Y.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Influence of model globular proteins with different isoelectric points on the precipitation of calcium carbonate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, X.; Fang, Q.; Ma, X. Biomimetic synthesis of calcium carbonate with different morphologies under the direction of different amino acids. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Luu, N.H.; Luong, H.V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen-Thi, B.T.; Pham, D.T.; Pham, N.C.; Ho, M.H. Curcumin-Loaded Co-Axial Electrospun Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Calcium Chloride Nanofibrous Membranes for Wound Healing Enhancement. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202402644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Aymonier, C.; Fermani, S.; Kralj, D.; Falini, G.; Zhou, C.H. Calcium carbonate: Controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7883–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardella, G.; Castillo Alvarez, M.C.; Presslee, S.; Finch, A.A.; Penkman, K.; Kroger, R.; Clog, M.; Allison, N. Contrasting the Effects of Aspartic Acid and Glycine in Free Amino Acid and Peptide Forms on the Growth Rate, Morphology, Composition, and Structure of Synthetic Aragonites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 9379–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Qiu, S.R.; Orme, C.A.; Morse, D.E.; De Yoreo, J.J. Acceleration of calcite kinetics by abalone nacre proteins. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.; Kim, H.; Lim, M.; You, K.; Ahn, J. Comparison of dissolution and surface reactions between calcite and aragonite in L-glutamic and L-aspartic acid solutions. Molecules 2010, 15, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borukhin, S.; Bloch, L.; Radlauer, T.; Hill, A.H.; Fitch, A.N.; Pokroy, B. Screening the incorporation of amino acids into an inorganic crystalline host: The case of calcite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4216–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerdijk, N.A.; With, G.D. Biomimetic CaCO3 mineralization using designer molecules and interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4499–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, S.; He, Y.; Yang, X.; Duan, L.; Cai, J. Effects of L-glutamic acid, N, N-diacetic acid as chelating agent on acidification of carbonate reservoirs in acidic environments. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 82, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. The Formation of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals Induced by Curvibacter sp. HJ-1 under Different Mg/Ca Molar Ratios. Minerals 2024, 14, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purgstaller, B.; Mavromatis, V.; Immenhauser, A.; Dietzel, M. Transformation of Mg-bearing amorphous calcium carbonate to Mg-calcite–In situ monitoring. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 174, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astilleros, J.M.; Fernández-Díaz, L.; Putnis, A. The role of magnesium in the growth of calcite: An AFM study. Chem. Geol. 2010, 271, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Ma, Y.; Qi, L. Biogenic and synthetic high magnesium calcite—A review. J. Struct. Biol. 2014, 185, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| L-Glycine | L-Lysine | L-Glutamic Acid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isoelectric Point (pl) | 5.97 | 9.74 | 3.22 |
| Charge state (Physiological pH) | Neutral | Positively charged (basic) | Negatively charged (acidic) |
| Side Chain Structure | -H | -(CH2)4NH2 | -(CH2)2COOH |
| R+/R− | 0.155–0.225 | 0.225–0.414 | 0.414–0.732 | 0.732–1 | ≥1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordination number | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, S. The Effects of Amino Acids on the Polymorphs and Magnesium Content of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals. Minerals 2025, 15, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070763
Zhang C, Jiang Y, Qian S. The Effects of Amino Acids on the Polymorphs and Magnesium Content of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals. Minerals. 2025; 15(7):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070763
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chonghong, Yuyang Jiang, and Shuhao Qian. 2025. "The Effects of Amino Acids on the Polymorphs and Magnesium Content of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals" Minerals 15, no. 7: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070763
APA StyleZhang, C., Jiang, Y., & Qian, S. (2025). The Effects of Amino Acids on the Polymorphs and Magnesium Content of Calcium–Magnesium Carbonate Minerals. Minerals, 15(7), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070763






