Barite Deposits of Türkiye: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
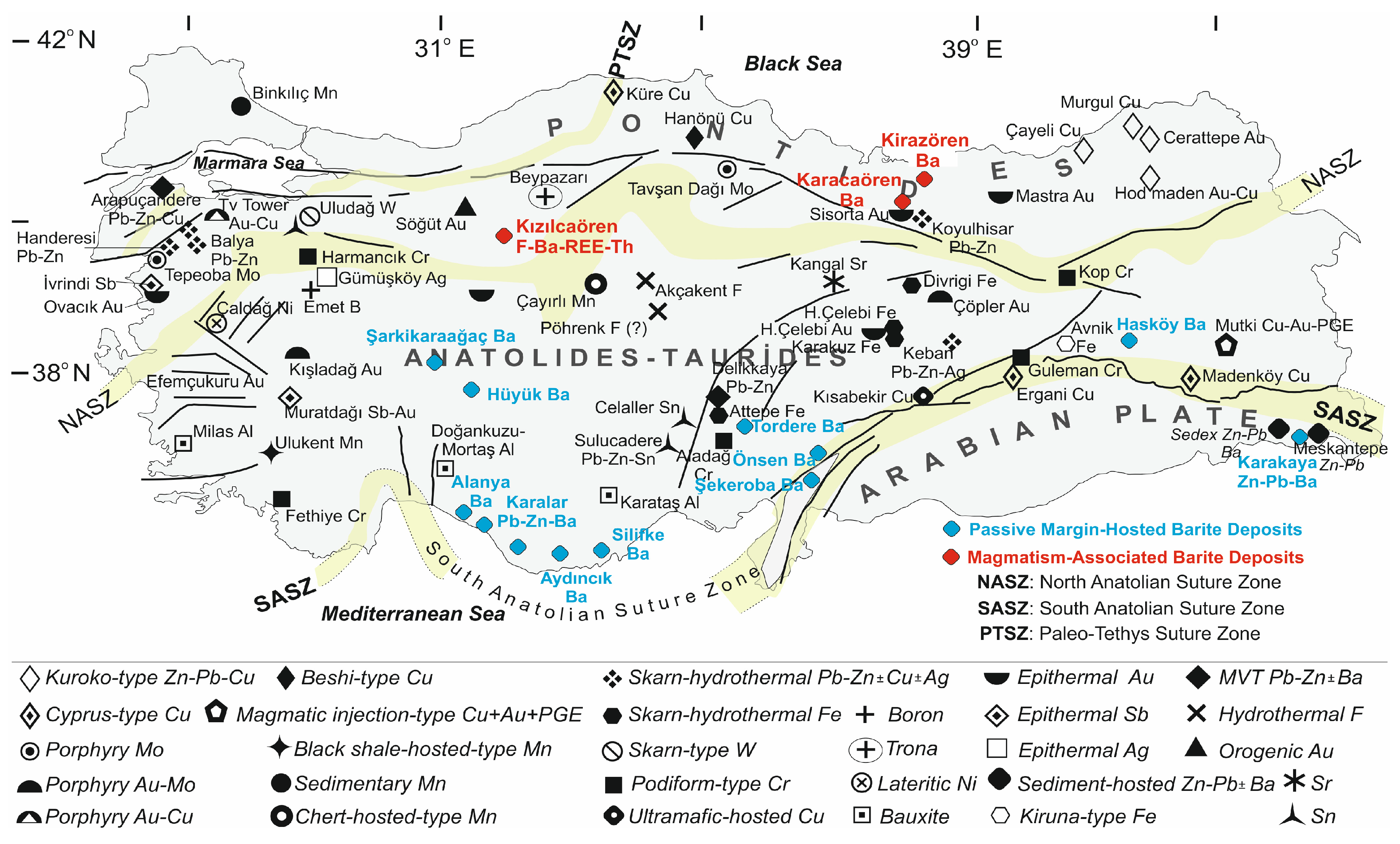
3. Barite Deposits
3.1. Magmatism-Associated Barite Deposits
3.1.1. The Kirazören (Bulancak/Giresun) Deposit
3.1.2. The Karacaören (Mesudiye/Ordu) Deposit
3.1.3. The Kızılcaören (Beylikova/Eskişehir) F + Ba + REE + Th Deposit
The Ore Geometry and Types
3.2. Passive Margin Deposits (PMH) (From Sedimentary to Vein Type)
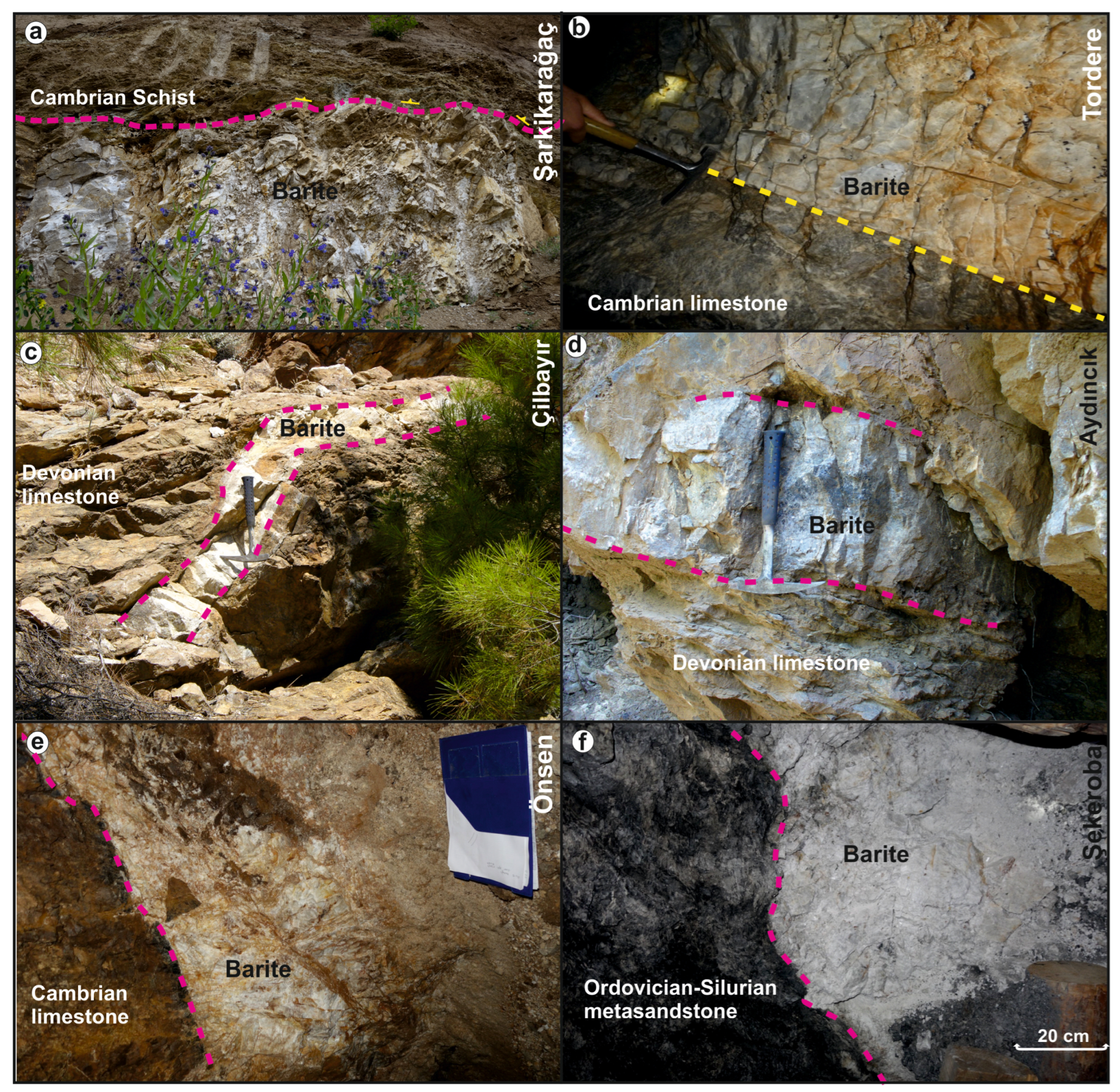
3.2.1. The Şarkikarağaç (Isparta) and Hüyük (Konya) Deposit
3.2.2. The Tordere (Feke/Adana) Region Deposits
3.2.3. The Karalar (Gazipaşa/Antalya) Deposit
3.2.4. The Aydıncık–Silifke Region (Mersin) Deposits
3.2.5. The Önsen Region (Kahramanmaraş) Deposit
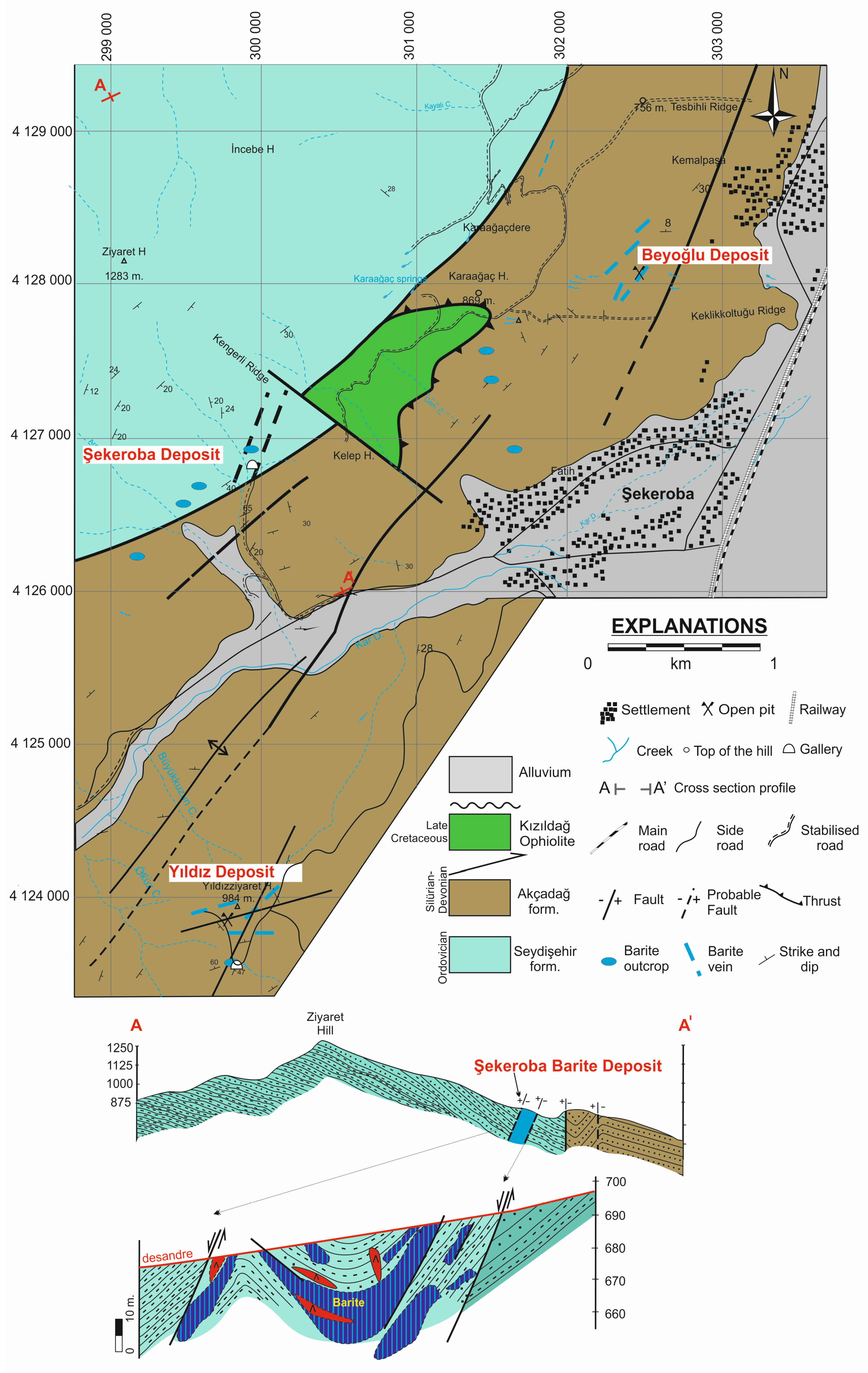
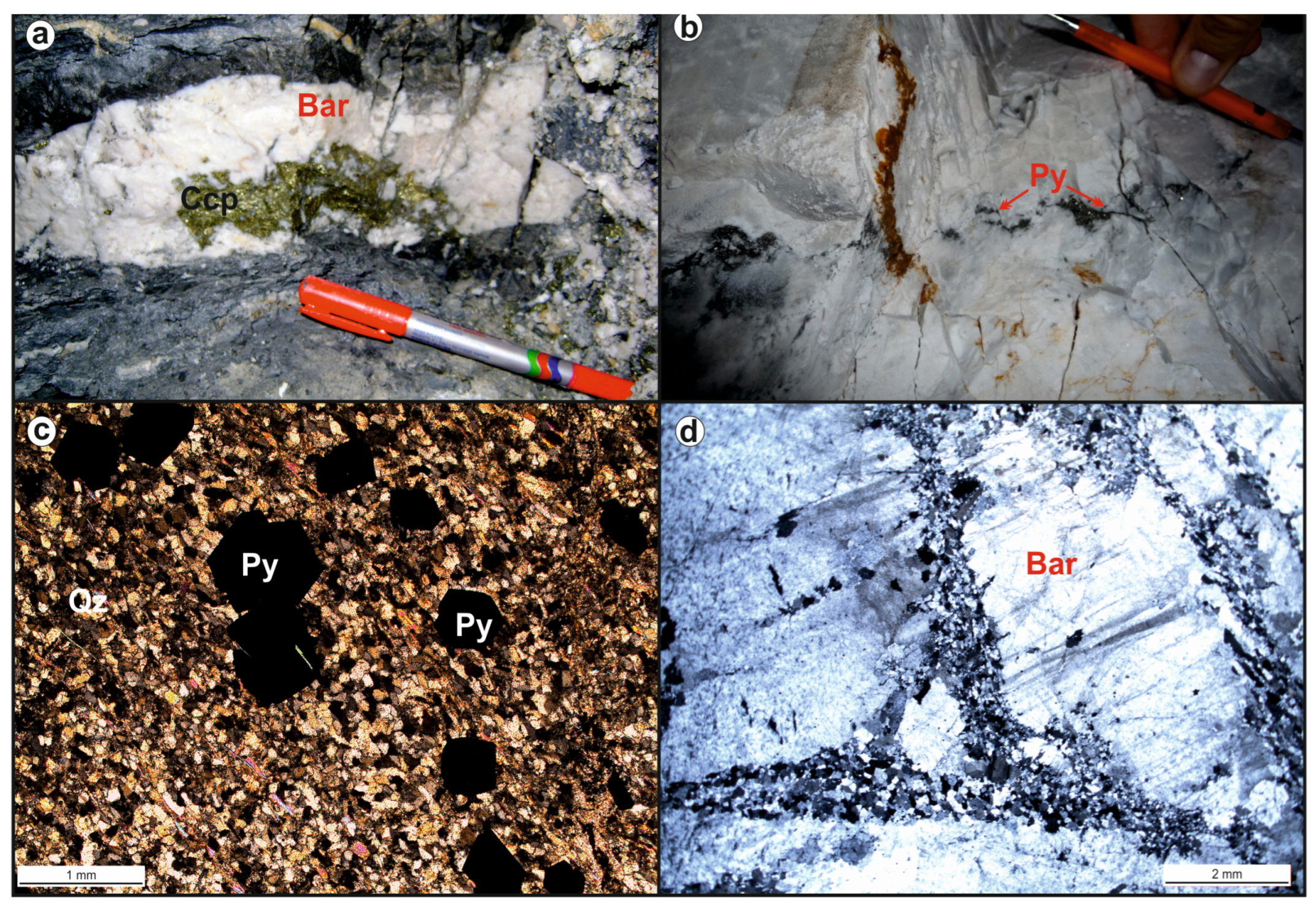
3.2.6. The Şekeroba Region (Kahramanmaraş) Deposit
3.2.7. The Hasköy (Muş) Deposit
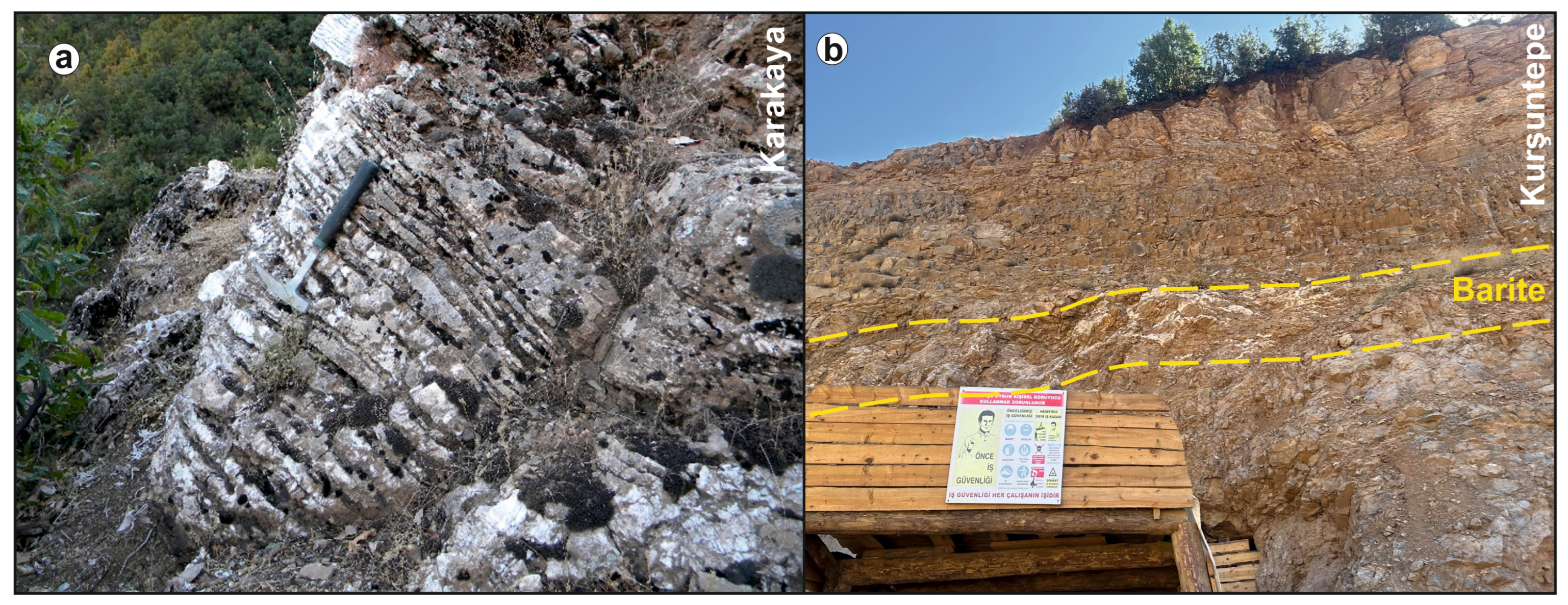
3.2.8. The Karakaya (Hakkari) Deposit
4. Analytical Methods
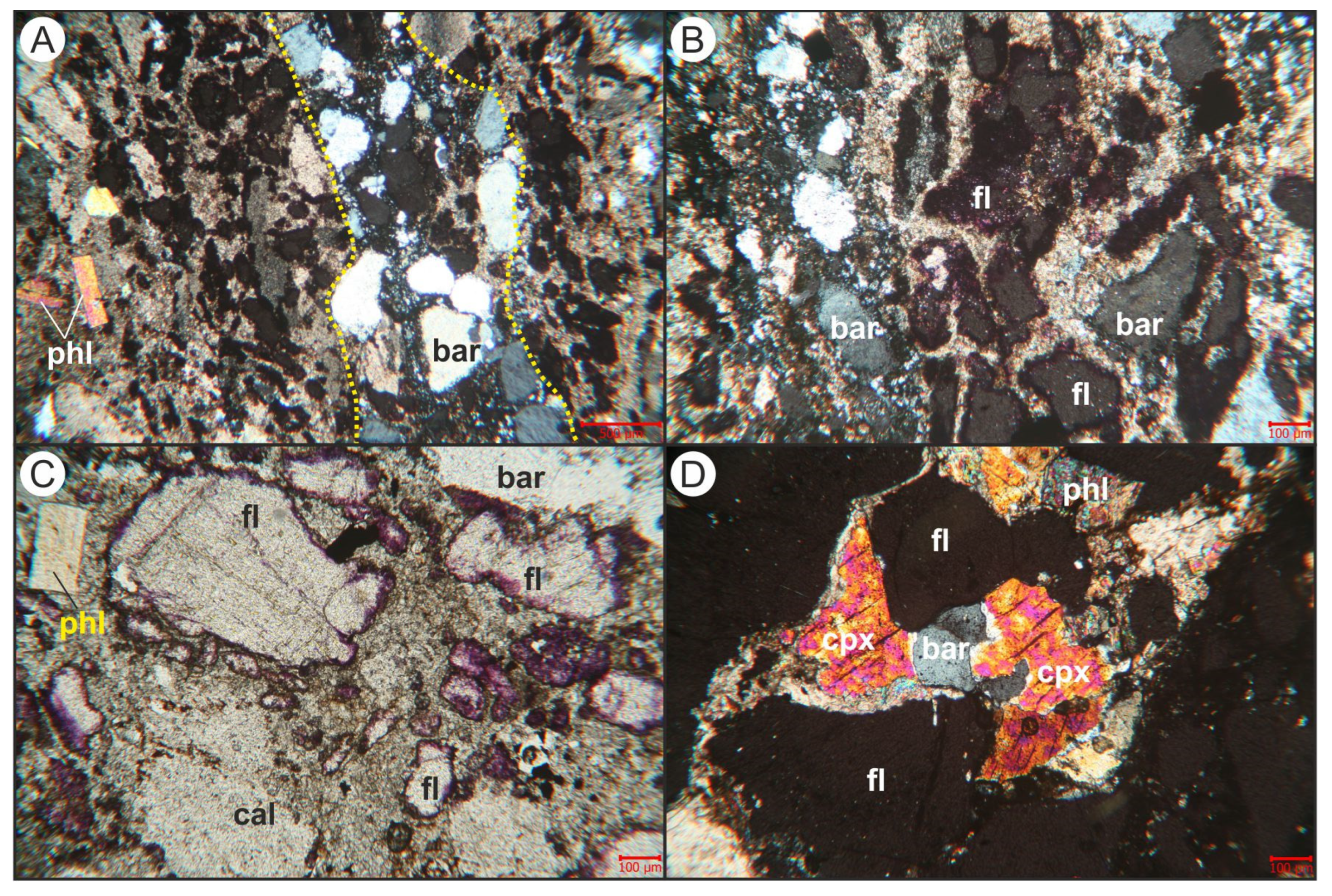
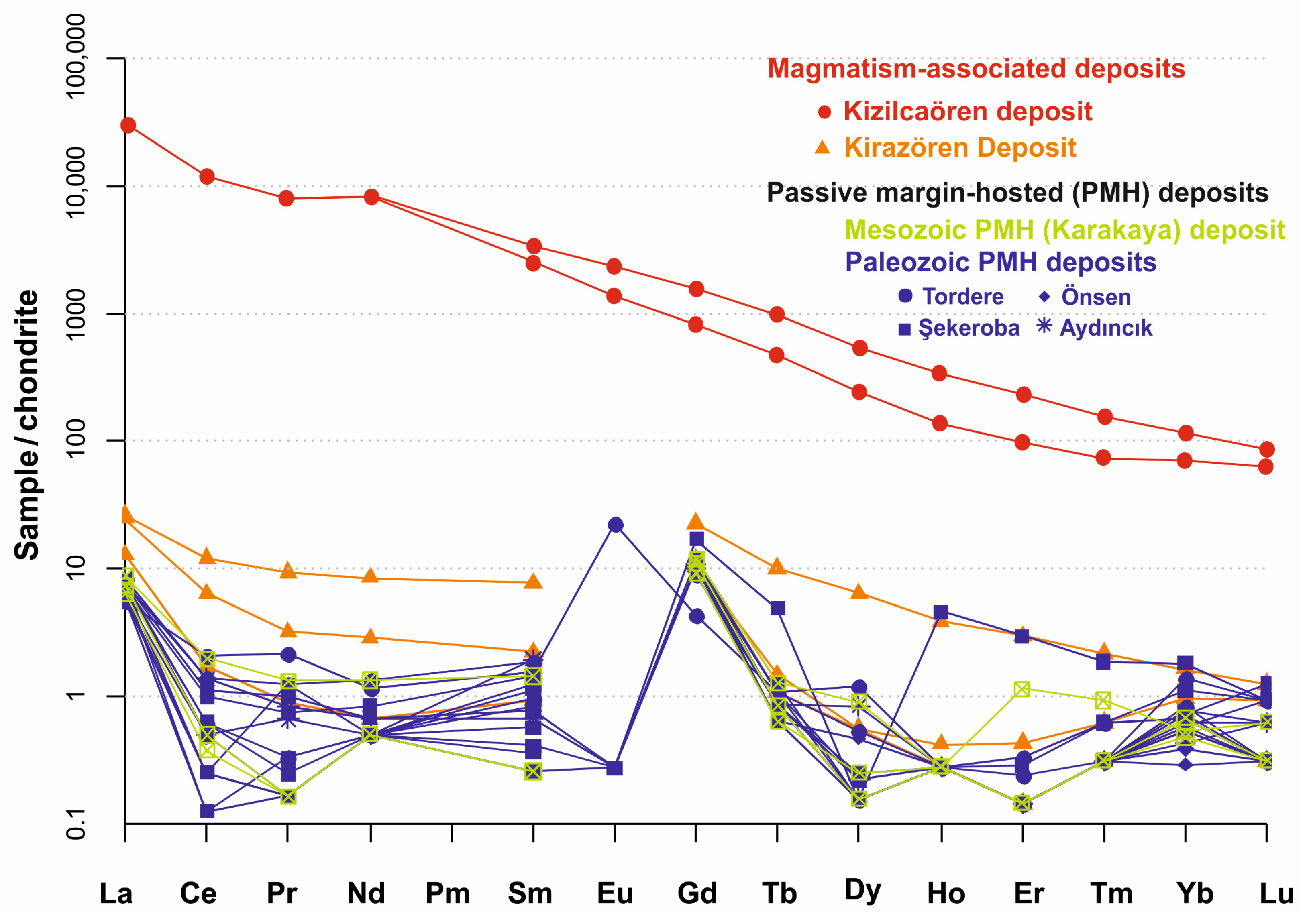
5. Ore Geochemistry
5.1. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry
| Deposit | Sr | Hf | Zr | Y | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | As | Cd | Sb | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirazören (n:3) | 8793.4 | 2.4 | 17 | 3.9 | 82.3 | 980.8 | 34.3 | <20 | 995 | 0.4 | 1300 | 0.62 |
| Kızılcaören (n:2) | 5515 | 0.6 | 42.5 | 549 | 2 | 633 | 212.5 | 77 | 122.5 | 0.9 | 10 | 0.07 |
| Şarkikaraağaç (n:18) | >10,000 | - | - | - | 27.3 | 20.9 | 343.7 | <20 | <5 | - | 6.9 | - |
| Hüyük (n:21) | >10,000 | - | - | - | <10 | <5 | 353.8 | <20 | <5 | - | 2.35 | - |
| Aydıncık (n:2) | 16,292.5 | 2.05 | 2.85 | 1.8 | 2.65 | 0.75 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.6 | <0.1 | 0.7 | 0.065 |
| Tordere (n:3) | 13,756.5 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.63 | 39.23 | 29.87 | 4.00 | 1.33 | 12.00 | <0.1 | 17.20 | 4.19 |
| Önsen (n:3) | 15,205.2 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 25.2 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 0.1 | <0.5 | <0.1 | 0.8 | 0.3 |
| Şekeroba (n:7) | 10,923.6 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 22.8 | 0.8 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | <0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| Karakaya(n:3) | 24,448.1 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 5.9 | 1334.2 | 13.5 | 10.4 | 2.6 | 241.4 | 0.4 | 0.637 |
| Deposit | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirazören (n:3) | 6.57 | 5.47 | 0.55 | 2.40 | 0.7 | * | 3.87 | 0.20 | 0.81 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.03 |
| Kızılcaören (n:2) | >10,000 | >10,000 | >1000 | 5140 | 599.5 | 140 | 317.5 | 34.8 | 128.9 | 17.52 | 35.05 | 3.75 | 19.95 | 2.49 |
| Şarkikaraağaç (n:18) | 0.36 | <0.1 | 0.08 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.98 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.05 | <0.1 | <0.04 |
| Hüyük (n:21) | 0.16 | <0.1 | 0.16 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 1.8 | 0.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.05 | <0.1 | <0.04 |
| Aydıncık (n:2) | 2.55 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.26 | * | 2.71 | 0.04 | 0.17 | <0.02 | <0.03 | <0.01 | 0.10 | 0.015 |
| Tordere (n:3) | 2.17 | 1.10 | 0.15 | 0.75 | 0.28 | 1.68 | 2.16 | 0.05 | 0.28 | <0.02 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
| Önsen (n:3) | 1.8 | 0.2 | <0.02 | <0.3 | 0.2 | <0.02 | 2.7 | 0.03 | 0.2 | <0.02 | <0.03 | <0.01 | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| Şekeroba (n:7) | 2.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | <0.02 | 3.0 | 0.04 | 0.1 | <0.03 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.03 |
| Karakaya (n:3) | 2.3 | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.06 | * | 2.46 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
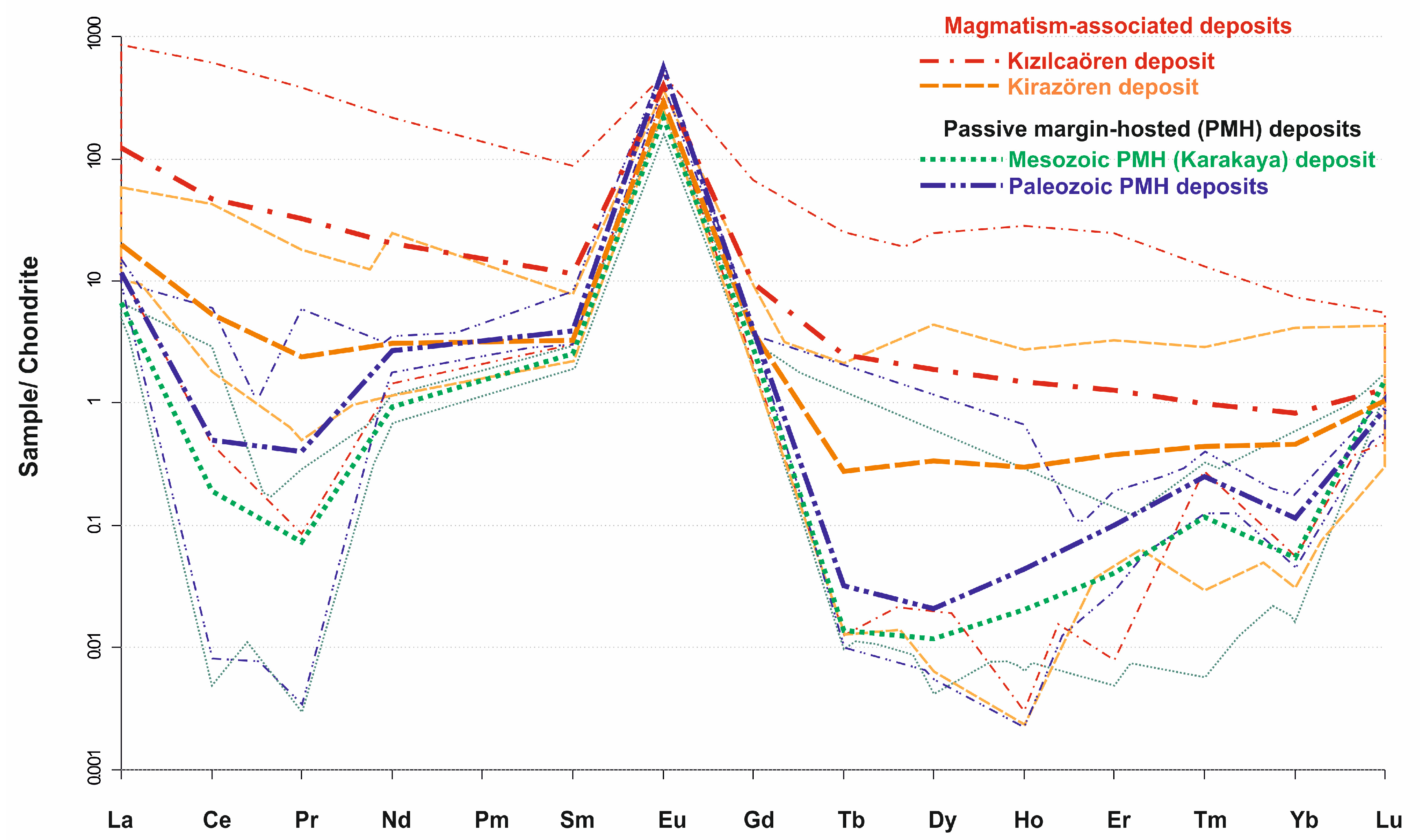
5.2. Rare Earth Element (REE) Geochemistry
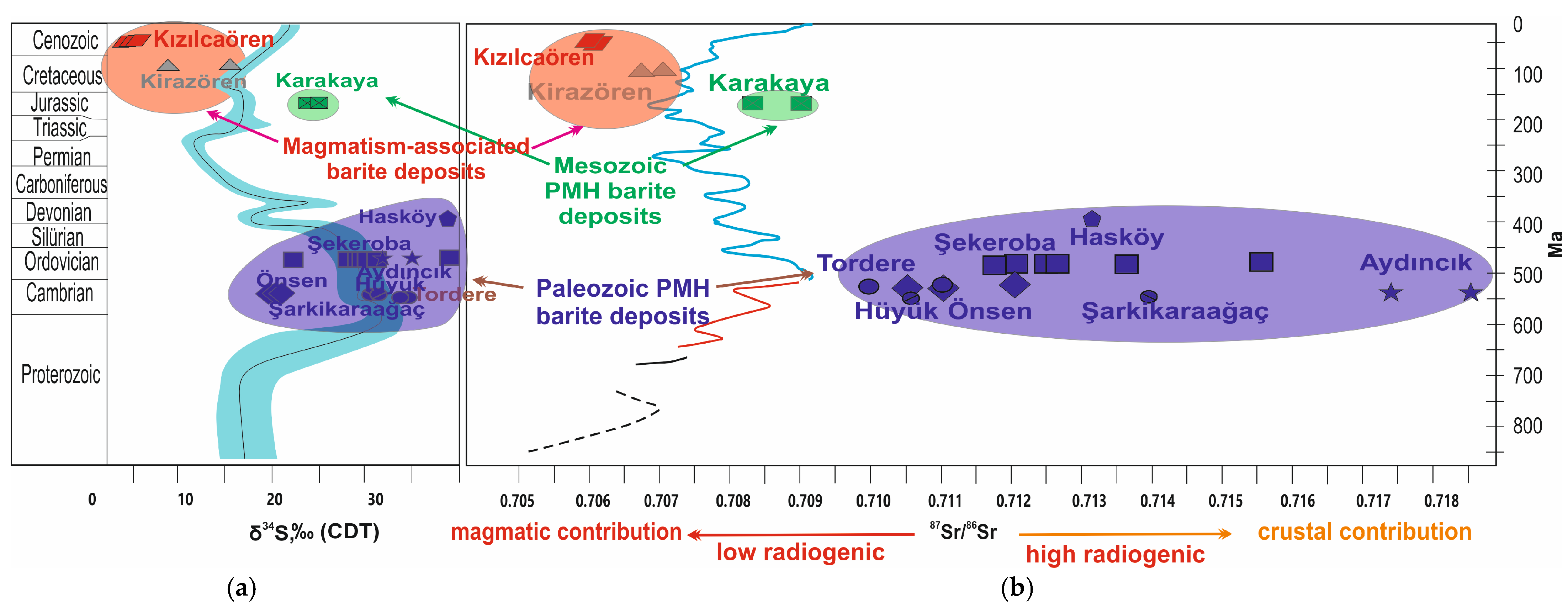
5.3. Isotope Geochemistry (S, O, D, Sr)
6. Discussion
6.1. Geological Environment
6.2. Trace Element Geochemistry
6.3. Isotopic Signatures
7. Conclusions
- Primarily found within passive continental margin deposits of Lower Paleozoic age (e.g., Şarkikaraağaç, Tordere, Aydıncık, Hasköy), exhibiting either stratiform or vein geometries.
- Characterized by a relatively low abundance of trace elements, but high radiogenic 87Sr/86Sr and δ34S values.
- Barite-forming solutions represent a mixture of seawater, diagenetic waters, or deep-circulating continental crustal waters.
- Share similarities in age and origin with the Atlas Mountains barite deposits (Moroccan deposits).
- Hosted in arc volcanics within the Pontides or in post-collisional Oligocene-aged carbonatites in NW Anatolia.
- Display higher concentrations of trace elements (e.g., Zn, Pb, As, Ag, Au, and REEs) compared to passive continental margin deposits.
- Exhibit low radiogenic Sr isotope values (7Sr/86Sr) and moderate δ34S values relative to passive continental margin deposits, clearly indicating an igneous (magmatic) source.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brobst, D.A. Barite: World Production, Reserves, and Future Prospects; No. 1321-1325; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Fortier, S.M.; Nassar, N.T.; Graham, G.E.; Hammarstrom, J.M.; Day, W.C.; Mauk, J.L.; Seal, R.R. Mınıng engıneerıng Annual Review 2021: Critical Minerals USGS critical minerals review. Min. Eng. 2022, 74, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2023; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2023; 210p. [CrossRef]
- Griffith, E.M.; Paytan, A. Barite in the ocean-occurrence, geochemistry, and palaeoceanographic applications. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanor, J.S. Barite-celestine Geochemistry and Environments of Formation. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2000, 40, 193–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmond, J.M.; Measures, C.; McDuff, R.E.; Chan, L.H.; Collier, R.; Grant, B.; Gordon, L.I.; Corliss, J.B. Ridge crest hydrothermal activity and the balances of the major and minor elements in the ocean: The Galapagos data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 46, 1–18, ISSN 0012-821X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Damm, K.L.; Oosting, S.E.; Kozlowski, R.; Buttermore, L.G.; Colodner, D.; Edmonds, H.N.; Edmond, J.M.; Grebmeir, J.M. Evolution of East Pacific Rise hydrothermal vent fluids following a volcanic eruption. Nature 1995, 375, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Brumsack, H.J.; Bohrmann, G.; Emeis, K.C. Barite fronts in continental margin sediments: A new look at barium remobilization in the zone of sulfate reduction and formation of heavy barites in diagenetic fronts. Chem. Geol. 1996, 127, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvelin, P. Baryum et strontium. Notes Mémoires Serv. Géologique Maroc. 1980, 276, 271–308. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, S.H.B.; Gallagher, M.J.; Poole, F.G. World barite resources—A review of recent production patterns and a genetic classification. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall.-Sect. B-Appl. Earth Sci. 1990, 99, B125–B132. [Google Scholar]
- Jewell, P.W. Bedded barite in the geologic record. In Marine Authigenesis: From Global to Microbial; Glenn, C.R., Prévôt-Lucas, L., Lucas, J., Eds.; Society for Sedimentary Geology Special Publication: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2000; Volume 66, pp. 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bonel, K.A. Barytes; British Geological Survey, Mineral Profile: Edinburgh, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, J.B.; Okita, P.M. Bedded barite deposits in the United States, Canada, Germany, and China; two major types based on tectonic setting. Econ. Geol. 1991, 86, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G. The “chessboard” classification scheme of mineral deposits: Mineralogy and geology from aluminum to zirconium. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 100, 1–420. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, N.A.; Gleeson, S.S.; Magnall, J.M.; Creaser, R.A.; Martel, E.; Fischer, B.J.; Sharp, R. The origin of Late Devonian (Frasnian) stratiform and stratabound mudstone-hosted barite in the Selwyn Basin, Northwest Territories, Canada. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 85, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A.; Nadine, M.P.; Miller, M.M. Critical Mineral Resources of the United States—Barite (Barium); USGS Professional Paper 1802–D; Klaus, J.S., John, H.D., Jr., Robert, R.S., II, Dwight, C.B., Eds.; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- Göncüoğlu, M.C.; Kozlu, H.; Dirik, K. Pre-Alpine and Alpine terranes in Türkiye: Explanatory notes to the terrane map of Türkiye. Ann. Geol. Pays Hell. 1997, 37, 515–536. [Google Scholar]
- Göncüoğlu, M.C.; Kozlu, H. Early Paleozoic evolution of the NW Gondwanaland: Data from southern Türkiye and surrounding areas. Gondwana Res. 2000, 3, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göncüoğlu, M.C. Introduction to the Geology of Türkiye: Geodynamic Evolution of the Pre-Alpine and Alpine Terranes 5; sayı/Monography series; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 2010; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Yılmaz, Y. Tethyan evolution of Türkiye, a plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 181–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I. Geology of Türkiye: A Synopsis. Anschnitt 2008, 21, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, A.H.F.; Parlak, O.; Ustaömer, T. Late Palaeozoic–Early Cenozoic tectonic development of Southern Turkey and the easternmost Mediterranean region: Evidence from the inter-relations of continental and oceanic units. In Geological Development of Anatolia and the Easternmost Mediterranean Region; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göncüoğlu, M.C.; Göncüoğlu, Y.; Kozur, H.W.; Kozlu, H. Geological evolution of the Taurides during the Infra-Cambrian to Carboniferous period: A Gondwanan perspective based on new biostratigraphic findings. Geol. Carpat. 2004, 55, 433–447. [Google Scholar]
- Gürsu, S.; Möller, A.; Göncüoglu, M.C.; Köksal, S.; Demircan, H.; Köksal, F.T.; Kozlu, H.; Sunal, G. Neoproterozoic continental arc volcanism at the northern edge of the Arabian Plate, SE Türkiye. Precambr. Res. 2015, 258, 208–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çopuroğlu, İ. Mineralogical—Petrographical and genetic exploration of Karalar—Gazipaşa (Antalya) galenite—Barite deposit. Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 1994, 116, 29–36. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, O.; Kuşçu, M. Geochemical Properties and the source of barite deposits between Şarkikaraağaç (Isparta) and Hüyük (Konya). Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 2002, 123–124, 67–89. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Bozkaya, G.; Gökçe, A. Trace- and Rare-Earth Element Geochemistry of the Karalar (Gazipaşa-Antalya) Barite-Galena Deposits, Southern Türkiye. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2004, 13, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkaya, G.; Gökçe, A. Lead and sulfur isotopic studies of the barite–galena deposits in the Karalar area (Gazipaşa–Antalya), Southern Türkiye. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 30, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Alan, İ.; Şahin, Ş.; Elibol, H.; Altun, İ.; Keskin, H.; Bakırhan, B.; Balcı, V.; Böke, N.; Esirtgen, T.; Kop, A.; et al. Orta Toroslar’ın Jeodinamik Evrimi Bozyazı—Aydıncık—Gülnar—Silifke (Mersin) Yöresi. [Geodynamic Evolution of Central Taurus, Bozyazı- Aydıncık-Gülnar-Silifke (İçel) regions]. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration Report no 11462. (In Turkish, unpublished).
- Cansu, Z.; Öztürk, H. Formation and genesis of Paleozoic sediment-hosted barite deposits in Turkey. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125, 103700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumral, M. Mineralogical, Geochemical and Isotopic (Sr, O, S) Evidence for Multiple Sources for the Hasköy Barite Deposits, SE, Anatolia, Türkiye. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 208–220. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçın, N. Lithological characteristics of the Amanos mountain range and its significance on the tectonic evolution of the southeast Türkiye. Bull. Geol. Soc. Türkiye 1980, 23, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hanilçi, N.; Öztürk, H.; Banks, D. Geological, geochemical and microthermometric characteristics of the Hakkari region Zn-Pb deposits, SE Turkey. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125, 103667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Tüysüz, O.; Yiğitbaş, E.; Genç, Ş.C.; Şengor, A.M.C. Geology and Tectonic Evolution of the Pontides. In Regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region; Robinson, A.G., Ed.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housh, T.B.; Çiftçi, E. Cu isotope geochemistry of volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits of the eastern Pontides, Türkiye. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2008; Volume 2, p. 012025. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, H.; Hanilci, N. Metallogenic Evaluation of Türkiye: Implications for Tin Sources of Bronze Age in Anatolia. Tuba-Ar-Turk. Acad. Sci. J. Archaeol. 2009, 12, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Revan, M.K.; Genç, Y.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.V. Mineralogy and trace-element geochemistry of sulfide minerals in hydrothermal chimneys from the Upper-Cretaceous VMS deposits of the eastern Pontide orogenic belt (NE Türkiye). Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçi, E. Volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits of Türkiye. Miner. Resour. Türkiye 2019, 16, 427–495. [Google Scholar]
- Tüysüz, N.; Özdoğan, K.; Er, M.; Yılmaz, Z.; Ağan, A. A Carlin type gold occurence in the Pontide island arc: The Kaletaş Gold Occurence (Gümüşhane, NE-Turkey). Geol. Bull. Turk. 1994, 37, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tüysüz, N.; Sadıklar, B.; Er, M.; Yılmaz, Z. An epithermal gold-silver deposit in the Pontide island arc, Mastra, Gumushane, northeast Turkey. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H. Manganese deposits in Türkiye: Distributions, types and tectonic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 1997, 12, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, Ö. Mineral Deposits of Türkiye in relation to Tethyan Metallogeny: Implications for Future Mineral Exploration. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, A.V.; Ozturk, H.; Altuncu, S.; Lebedev, V.A. Kızılcaören ore-bearing complex with carbonatites (northwestern Anatolia, Türkiye): Formation time and mineralogy of rocks. Geol. Ore Depos. 2014, 56, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, K.M.; Deady, E.A.; Beard, C.D.; Broom-Fendley, S.; Elliott, H.A.L.; Berg, F.; Öztürk, H. Carbonatites and Alkaline Igneous Rocks in Post-Collisional Settings: Storehouses of Rare Earth Elements. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 1332–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, A.H.; Örgün, Y.; Suner, F. Geology, mineralogy and fluid inclusion data of the Kızılcaören fluorite barite REE deposit, Eskisehir, Türkiye. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003, 21, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H. Rare earth element and torium complex ore deposit at southern edge of Eskişehir-Sivrihisar-Kızılcaören village. J. Geol. Eng. 1977, 2, 29–34. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Sarıfakıoğlu, E.; Özen, H.; Hall, C. Petrogenesis of extensionrelated alkaline volcanism in Karaburhan (Sivrihisar–Eskisehir), NW Anatolia, Türkiye. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgenç, I. Geology and ree geochemistry of carbothermal bastnaesite -fluorite—Barite deposit of Kızılcaören (Sivrihisar—Eskişehir). Geol. Bull. Türkiye 1993, 36, 1–11, (In Turkish with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hatzl, T. Die Genese Der Karbonatit—Und Alkalivulkanit—Assoziierten FluoritBaryt-Bastnasit—Vererzung Bei Kızılcaören (Turkei); Münchner Geol. Hefte; Technischen Universitat München: Munich, Germany, 1992; 271p. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, F. Kızılcaören Fluorite-Barite-Bastnäsite Carbothermal Ore Deposits: Rare Earth Elements in a Post-Collisional Setting. Master’s Thesis, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK, 2017; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpel, E.F.; Kırıkoğlu, M.S. Fluorite-barite-rare earths deposits at Kızılcaören, Türkiye, Mitt. Österr. Geol. Ges. 1985, 78, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, H.; Altuncu, S.; Hanilçi, N.; Kasapçı, C.; Goodenough, K.M. Rare earth element-bearing fluorite deposits of Türkiye: An overview. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 105, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.; Hein, J.R.; NHanilçi, N. Genesis of the Doğankuzu and Mortaş Bauxite Deposits, Taurides, Turkey: Separation of Al, Fe and Mn and Implications for Passive Margin Metallogeny. Econ. Geol. 2002, 97, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, O.; Uçurum, A.; Muchez, P. Determination of the source of Sarkikaraagaç (Isparta), Hüyük, Beysehir (Konya) ve Gazipasa (Antalya) barite deposits by fluid inclusion and S, O, C, Sr ve Pb isotope studies. Final. Rep. TUBITAK Proj. 2008, 211, 104Y032, (In Turkish With English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ayhan, A. Characteristics of Low-Mid Cambrian hosted Barit Mineralizations in Hüyük (Beysehir) region. Selçuk Univ. J. Enginnering-Archit. Fac. 1986, 1, 1–17, (In Turkish With English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ayhan, A. Stratiform Barite Deposits Between Sarkikaraagaç (Isparta) and Hüyük (Konya) in Sultandag Region, Türkiye. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2001, 61, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Elmas, N.; Suner, F. Barite mineralizations in Dinek (Şarkikaraağaç-Isparta) and its surroundings. İTÜ J. 2006, 5, 267–277. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Elmas, N.; Kumral, M.; Suner, F.; Taşdelen, S. Stratiform barite deposits hosted in metamorphic assemblages of Dinek and surrounding regions, Isparta, Turkey. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 48, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özüş, A.S.; Yaman, S. Fluorite-Barite mineralization of Akkaya (Feke-Adana) and genetical problema. Bull. Geol. Soc. Türkiye 1986, 29, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gökçe, A.; Bozkaya, G. Geology and Fluid Inclusion Characteristics of the Karalar (Gazipaşa, Antalya) Barite–Galena Deposits. Geol. Bull. Türkiye 2003, 46, 1–16, (In Turkish with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Striebel, H. Die Bleierz-Baryt-Lagerstaette Von Karalar-Gazipaşa (Turkei) Und Ihr -Geoiogischer Rahmen. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Ayhan, A. Geologie und Mineralogie der blei-zink- Baryt-Lagerstaetten Zwischen Burhan Mah. und Yuları bei Gazipaşa-Antalya. Ph.D. Thesis, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Gökçe, A.; Bozkaya, G. Fluid inclusion and stable isotope characteristics of the Karalar (Gazipaşa, Antalya) barite-galena deposits, Southern Turkey. Geol. Ore Depos. 2008, 50, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, V.; Oner, F.; Yalcin, C.; Uras, Y.; Yalcin, M.G. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and stable isotope characteristics of Paleozoic carbonate-hosted vein-type barite deposits from Silifke–Mersin, Southern Türkiye. Carbonates Evaporites 2024, 39, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumral, M.; Çoban, H.; Taşdelen, S.; İmamoğlu, Ş.; Kargı, H.; Baran, H.A.; Kepekli, A.; Kıran, D.; Elmas, N. Formation Conditions of Barite Deposits in Muş Region and Investigation of Industrial Properties. Final. Rep. TUBITAK Proj. 2008, 117, 104Y315, (In Turkish With English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Baran, H.A. Geological and Petrographical Features of Toprakkale (Muş) Barite Mineralization. E-J. New World Sci. Acad. Nat. Sci. 2010, 4A0029, 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Hanilçi, N.; Öztürk, H.; Koral, H. Metallogenic Evolution of Hakkari Region Zn-Pb Deposits in Light of the Stable Sulphur Isotope and Fluid Inclusion Geochemistry. Final. Rep. TUBITAK Proj. 2018, 105, 114Y554, (Unpublished Final Report). [Google Scholar]
- Jochum, K.P.; Willbold, M.; Raczek, I.; Stoll, B.; Herwig, K. Chemical Characterisation of the USGS Reference Glasses GSA-1G, GSC-1G, GSD-1G, GSE-1G, BCR-2G, BHVO-2G and BIR-1G Using EPMA, ID-TIMS, ID-ICP-MS and LA-ICP-MS. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2005, 29, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z. Calibration and correction of LA-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS analyses for element contents and isotopic ratios. Solid Earth Sci. 2016, 1, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Rare Earth Element Geochemistry; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. The rare earth elements in seawater. Nature 1982, 296, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Rare earth elements in the pore waters of reducing near-shore sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 82, 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R.W.; Buchholtz ten Brink, M.R.; Jones, D.L.; Gerlach, D.C.; Russ, G.P., III. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments in chert and shale. Geology 1990, 18, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarasvandi, Z.; Zaheri, N.; Houshang, P.; Chrachi, A.; Bagheri, H. Geochemistry and fluid-inclusion microthermometry of the Farsesh barite deposit, Iran. Geologos 2014, 20, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurković, I.; Garašić, V.; Hrvatović, H. Geochemical characteristics of barite occurrences in the Palaeozoic complex of south-eastern Bosnia and their relationship to the barite deposits of the mid-Bosnian Schist Mountain. Geol. Croat. 2010, 63, 241–258. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, F.; Church, T.M.; Treuil, M.; Jaffrezic, H. Rare earths in barites: Distribution and effects on aqueous partitioning. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, A.; Banerjee, D.M.; Schidlowski, M.; Balaram, V. Rare-earth elements and stable isotope geochemistry of early Cambrian chert-phosphorite assemblages from the lower Tal Formation of the Krol Belt (Lesser Himalaya, India). Chem. Geol. 1999, 156, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.; Albarede, F.; Michard, G.; Minster, J.F.; Charlou, J.L. Rare-earth elements and uranium in high-temperature solutions from East Pacific Rise hydrothermal vent field (13 N). Nature 1983, 303, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.M.; Olivarez, A.M. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in Pacific hydrothermal sediments. Mar. Chem. 1988, 25, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douville, E.; Bienvenu, P.; Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Fouquet, Y.; Appriou, P.; Gamo, T. Yttrium and rare earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverjensky, D.A. Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 67, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derry, L.A.; Jacobsen, S.B. The chemical evolution of Precambrian seawater: Evidence from REEs in banded iron formations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2965–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Planavsky, N.; Krapez, B.; Rasmussen, B.; Hofmann, A.; Slack, J.F.; Rouxel, O.; Konhouser, K. Iron Formations: Their Origins and Implications for Ancient Seawater Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 561–628. [Google Scholar]
- Elderfield, H. Strontium isotope stratigraphy. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1986, 57, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Longman Scientific and Technical: London, UK, 1993; ISBN 0 582 06701 4. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, H.P. The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal Alteration and Ore Deposition. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 843–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.J.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Fallick, A.E.; Foster, R.P. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic evolution of Variscan crustal fluids, south Cornwall, U.K. Chem. Geol. 1995, 123, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paytan, A.; Mearon, S.; Cobb, K.; Kastner, M. Origin of marine barite deposits: Sr and S isotope characterization. Geol. Geol. Soc. Am. 2002, 30, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, E.M.; Paytan, A.; Wortmann, U.G.; Eisenhauer, A.; Scher, H.D. Combining metal and nonmetal isotopic measurements in barite to identify mode of formation. Chem. Geol. 2018, 500, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina, L.; Dia, A.N.; Boulegue, J.; Bourgois, J.; Fouillac, A.M. Massive barite deposits in the convergent margin off Peru: Implications for fluid circulation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinert, J.; Bollwerk, S.M.; Derkachev, A.; Bohrmann, G.; Suess, E. Massive barite deposits and carbonate mineralization in the Derugin Basin, Sea of Okhotsk: Precipitation processes at cold seep sites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 203, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Roberts, H. Geochemical characteristics of the barite deposits at cold seeps from the northern Gulf of Mexico. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 309, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, E.W.N.; Bailey, J.V.; Flood, B.E.; Jones, D.S.; Gilhooly, W.P., III; Joye, S.B.; Teske, A.; Mason, O.U. Barite encrustation of benthic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at a marine cold seep. Geobiology 2015, 13, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, I.; Lee, K.-Y. S, Sr, and Pb isotopic systematics of hydrothermalm chimney precipitates from the Eastern Manus Basin, western Pacific: Evaluation of magmatic contribution to hydrothermal system. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, B12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickmann, B.; Thorseth, I.H.; Peters, M.; Strauss, H.; Brocker, M.; Pedersen, R.B. Barite in hydrothermal environments as a recorder of subseafloor processes: A multiple-isotope study from the Loki’s Castle vent field. Geobiology 2014, 12, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, S.; Paytan, A.; Li, H.; Wortmann, U.G. A revised seawater sulfate oxygen isotope record for the last 4 Myr. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 175, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.T.; Gill, B.C.; Masterson, A.; Beirne, E.; Casciotti, K.L.; Knapp, A.N.; Berelson, W. Placing an upper limit on cryptic marine sulphur cycling. Nature 2014, 514, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paytan, A.; Kastner, M.; Martin, E.E.; Macdougall, J.D.; Herbert, T. Marine barite as a monitor of seawater strontium isotope composition. Nature 1993, 366, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Bohrmann, G.; Dube, T.E.; Poole, F.G. Formation of modern and Paleozoic stratiform barite at cold methane seeps on continental margins. Geology 2003, 912, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, G.; Wallmann, K.; Bollwerk, S.M.; Derkachev, A.; Bohrmann, G.; Suess, E. The effect of dissolved barium on biogeochemical processes at cold seeps. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, C.; Anadón, P.; González-Partida, E.; Alfonso, P.; Rajabi, A.; Pérez-Segura, E.; AlbaAldave, L.A. Paleozoic bedded barite deposits from Sonora (NW Mexico): Evidence for a hydrocarbon seep environment of formation. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Böttcher, M.E.; Lüschen, H.; Neretin, L.N.; Volkov, I.I. Anaerobic methane oxidation and a deep H2S sink generate isotopically heavy sulfides in Black Sea sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2095–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnall, J.M.; Gleeson, S.A.; Stern, R.A.; Newton, R.J.; Poulton, S.W.; Paradis, S. Open system sulphate reduction in a diagenetic environment–Isotopic analysis of barite (δ34S and δ18O) and pyrite (δ34S) from the Tom and Jason Late Devonian Zn–Pb–Ba deposits, Selwyn Basin, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 180, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, D.F. The role of dense brines in the formation of vent-distal sedimentary-exhalative (SEDEX) lead-zinc deposits: Field and laboratory evidence. Miner. Depos. 2002, 37, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, D.F. Toward an integrated genetic model for vent-distal SEDEX deposits. Miner. Depos. 2018, 53, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Canet, C.; Rastad, E.; Alfonso, P. Basin evolution and stratigraphic correlation of sedimentary-exhalative Zn–Pb deposits of the Early Cambrian ZariganChahmir Basin, Central Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 328–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Rastad, E.; Canet, C.; Alfonso, P. The early Cambrian Chahmir shalehosted Zn–Pb deposit, Central Iran: An example of vent-proximal SEDEX mineralization. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnall, J.M.; Gleeson, S.A.; Blamey, N.J.F.; Paradis, S.; Luo, Y. The thermal and chemical evolution of hydrothermal vent fluids in shale hosted massive sulphide (SHMS) systems from the MacMillan Pass district (Yukon, Canada). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 193, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnall, J.M.; Gleeson, S.A.; Paradis, S. A new subseafloor replacement model for the macmillan pass clastic-dominant Zn-Pb ± Ba deposits (Yukon, Canada). Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnall, J.M.; Wirth, R.; Hayward, N.; Gleeson, S.A.; Schreiber, A. Stratiform host-rock replacement via self-sustaining reactions in a clastic-dominated (CD-type) Zn deposit. Econ. Geol. 2023, 118, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Alfonso, P.; Canet, C.; Rastad, E.; Niroomand, S.; Modabberi, S.; Mahmoodi, P. The world-class Koushk Zn-Pb deposit, Central Iran: A genetic model for vent-proximal shale-hosted massive sulfide (SHMS) deposits–Based on paragenesis and stable isotope geochemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 124, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Alfonso, P.; Canet, C.; Andrew, C.; Azhdari, S.; Rezaei, S.; Alaminia, Z.; Tamarzadeh, S.; Yarmohammadi, A.; et al. Barite Replacement as a Key Factor in the Genesis of Sediment-Hosted Zn-Pb±Ba and Barite-Sulfide Deposits: Ore Fluids and Isotope (S and Sr) Signatures from Sediment-Hosted Zn-Pb±Ba Deposits of Iran. Minerals 2024, 14, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claypool, G.E.; Holser, W.T.; Kaplan, I.R.; Sakai, H.; Zak, I. The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem. Geol. 1980, 28, 199–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M.; Howarth, R.J.; Shields, G.A. Strontium Isotope Stratigraphy; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Honma, H.; Shuto, K. On strontium isotopic ratio of barite from Kuroko-type ore deposits, Japan. J. Japan. Assoc. Min. Petr. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, J.W.; Hannington, M.D.; Tivey, M.K.; Hansteen, T.; Williamson, N.M.B.; Stewart, M.; Fietzke, J.; Butterfield, D.; Frische, M.; Allen, L.; et al. Precipitation and Growth of Barite within Hydrothermal Vent Deposits from the Endeavour Segment, Juan de Fuca Ridge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 173, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, K.; Moritz, R.; Mouttaqi, A.; Fontignie, D.; Sharp, Z. Vein and karst barite deposits in the Western Jebilet of Morocco: Fluid inclusion and isotope (S, O, Sr) evidence for regional fluid mixing related to Central Atlantic rifting. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jébrak, M.; Wartiti, M.; Marcoux, E.; Zaharoui, M. The Bouznika Cambrian barite deposit (Morocco), an early mineralization on the Iapetus margin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2011, 60, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Deposit (City) | Mineralogy | Shape of Deposit | Host Rock | Tectonic Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magmatism-associated deposits | Kirazören (Giresun) | Barite ± pyrite | Vein | Cretaceous limestone and arc volcanoclastics (this study) | Pontides |
| Karacaören (Ordu) | Barite ± galena ± sphalerite ± hematite | Vein | Eocene andesites (this study) | Pontides | |
| Kızılcaören (Eskişehir) | Fluorite + barite + bastnaesite | Banded and disseminated ore | Late Paleozoic–Triassic accretionary complex (sandstone, shale, conglomerate, spilite, lithic tuff) [43,44] | Tavşanlı Zone, Anatolides | |
| Passive margin-hosted deposits | Şarkikaraağaç (Isparta) | Barite ± galena ± sphalerite ± chalcopyrite ± pyrite ± bornite | Stratiform-stratabound and vein | Cambrian–Devonian schist and limestone [25] | Central Taurides |
| Hüyük (Konya) | Barite ± pyrite | Vein | Cambrian–Devonian schist and limestone [26] | Central Taurides | |
| Tordere (Adana) | Barite ± chalcopyrite ± pyrite ± galena ± malachite ± fluorite | Vein | Cambrian limestone [30] | Eastern Taurides | |
| Karalar (Antalya) | Barite + galena + sphalerite + chalcopyrite + pyrite + bornite | Vein | Permian–Triassic limestones and schist [27,28] | Central Taurides | |
| Koçaşlı, Aydıncık, Gökbelen, Çilbayır (Mersin) | Barite ± galena | Vein | Cambrian–Devonian limestone [29] | Central Taurides | |
| Önsen (Kahramanmaraş) | Barite ± pyrite | Vein | Cambrian limestone [30] | Arabian Plate | |
| Şekeroba, Kahramanmaraş | Barite ± chalcopyrite ± galena | Vein | Ordovician–Devonian meta-sandstone and shale [30] | Arabian Plate | |
| Kızılağaç-Hasköy (Muş) | Barite ± chalcopyrite ± pyrite ± sphalerite galena± malachite | Stratiform and vein | Devonian dolomitic limestone [31] | Eastern Taurides | |
| Karakaya (Hakkari) | Barite | Stratiform | Jurassic limestone [33] | Arabian Plate |
| Deposit | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | MnO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | BaSO4 | References for Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirazören (n:3) | 6.33 | 1.78 | 3.78 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 80.99 | this study |
| Kızılcaören (n:2) * | 4.38 | 1.04 | 1.985 | 0.465 | 1.54 | 30.35 | 0.075 | 0.84 | 38.28 | |
| Şarkikaraağaç (n:18) | 2.36 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.77 | 0.251 | 1.82 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 94 | [54] |
| Hüyük (n:21) | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 94 | |
| Aydıncık (n:2) | 2.94 | 0.12 | 0.09 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 95.45 | this study |
| Tordere (n:3) | 0.77 | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.07 | <0.01 | 1.95 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 96.51 | [30] |
| Önsen (n:3) | 1.42 | <0.01 | <0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 97.04 | |
| Şekeroba (n:7) | 0.28 | <0.01 | 0.07 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 97.68 | |
| Hasköy (n:13) | 3.71 | 0.16 | 0.89 | 3.39 | 0.07 | 4.53 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 43.5 | [65] |
| Karakaya (n:3) | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | <0.01 | 2.27 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 93.79 | this study |
| Deposit | Kızılcaören (n:44) | Kirazören (n:26) | Cenozoic PMH (Karakaya) (n:31) | Paleozoic PMH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tordere (n:9) | Önsen (n:12) | Hasköy (n:12) | Mean PMH (n:33) | ||||
| Sc | 0.15 | 2.53 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| V | 2.78 | 12.06 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.28 |
| Cr | 4.18 | 20.79 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Co | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| Ni | 0.49 | 1.21 | 0.69 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 2.14 | 0.92 |
| Ga | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Ge | 1.03 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.59 |
| Rb | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Sr | 9123.38 | 14,587.19 | 44,720.26 | 30,874.79 | 19,722.82 | 26,640.41 | 25,294.30 |
| Y | 18.81 | 14.00 | 16.71 | 13.52 | 14.55 | 13.59 | 13.92 |
| Zr | 0.69 | 12.20 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Nb | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.00 |
| Cs | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| La | 37.90 | 6.17 | 2.05 | 3.63 | 3.18 | 4.14 | 3.65 |
| Ce | 38.15 | 4.34 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.40 |
| Pr | 3.92 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.004 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| Nd | 12.14 | 1.86 | 0.56 | 1.64 | 1.32 | 1.85 | 1.60 |
| Sm | 2.24 | 0.64 | 0.49 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.76 |
| Eu | 29.22 | 21.39 | 16.06 | 40.69 | 36.17 | 46.78 | 41.26 |
| Gd | 2.48 | 0.98 | 0.74 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 1.12 | 1.06 |
| Tb | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.002 | 0.0004 | 0.002 | 0.00 |
| Dy | 0.61 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.0013 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ho | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.002 | 0.0047 | 0.002 | 0.00 |
| Er | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Tm | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Yb | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Lu | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Hf | 1.04 | 1.15 | 2.00 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 1.14 | 1.10 |
| Ta | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.00 |
| Pb | 0.34 | 76.86 | 6.18 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.56 | 0.40 |
| Th | 15.02 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| U | 1.20 | 1.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Zn | 1291.45 | 1336.82 | 1680.12 | 1024.76 | 1202.43 | 1053.34 | 1099.76 |
| Deposit | 87Sr/86Sr | δ18O (‰) | δ34S (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kirazören1 | 0.70717 | 6.3 | 17.08 |
| Kirazören 2 | 0.70688 | 7.0 | 7.73 |
| Kızılcaören1 | 0.70598 | 8.6 | 5.90 |
| Kızılcaören3 | 0.70605 | 9.6 | 5.61 |
| Kızılcaören5 | 0.70608 | 7.5 | 5.78 |
| Şarkikaraağaç * | 0.714 | 13.6 | 27.9 |
| Hüyük * | 0.7105 | 13,2 | 28.5 |
| Aydıncık | 0.71884 | 13.1 | 35.48 |
| Aydıncık 2 | 0.71761 | 12.7 | 32.10 |
| Tordere Feke | 0.71283 | 16.6 | 31.46 |
| Tordere Feke2 | 0.71109 | 15.8 | 32.01 |
| Önsen | 0.71213 | 11.5 | 20.70 |
| Önsen Dadağlı | 0.71111 | 11.1 | 21.14 |
| Önsen Çınaraltı | 0.71052 | 11.3 | 19.98 |
| Şekeroba | 0.71183 | 11.6 | 28.93 |
| Şekeroba | 0.71213 | 9.1 | 40.44 |
| Şekeroba | 0.71259 | 10.2 | 34.59 |
| Sekeroba Beyoğlu | 0.71273 | 10.8 | 29.46 |
| Şekeroba Yıldız | 0.7157 | 10.3 | 32.68 |
| Şekeroba Yıldız | 0.71373 | 12.8 | 31.80 |
| Hasköy * | 0.71311 | 14.04 | 38.18 |
| Karakaya 2 | 0.70831 | 14.3 | 24.19 |
| Karakaya 3 | 0.709 | 13.9 | 23.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cansu, Z.; Öztürk, H.; Hanilçi, N. Barite Deposits of Türkiye: A Review. Minerals 2025, 15, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070692
Cansu Z, Öztürk H, Hanilçi N. Barite Deposits of Türkiye: A Review. Minerals. 2025; 15(7):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070692
Chicago/Turabian StyleCansu, Zeynep, Hüseyin Öztürk, and Nurullah Hanilçi. 2025. "Barite Deposits of Türkiye: A Review" Minerals 15, no. 7: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070692
APA StyleCansu, Z., Öztürk, H., & Hanilçi, N. (2025). Barite Deposits of Türkiye: A Review. Minerals, 15(7), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070692