Tectonic Setting of the Neoproterozoic Gabbroic Intrusions in the Luanchuan Area, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from Ilmenite and Biotite Mineralogy
Abstract
1. Introduction
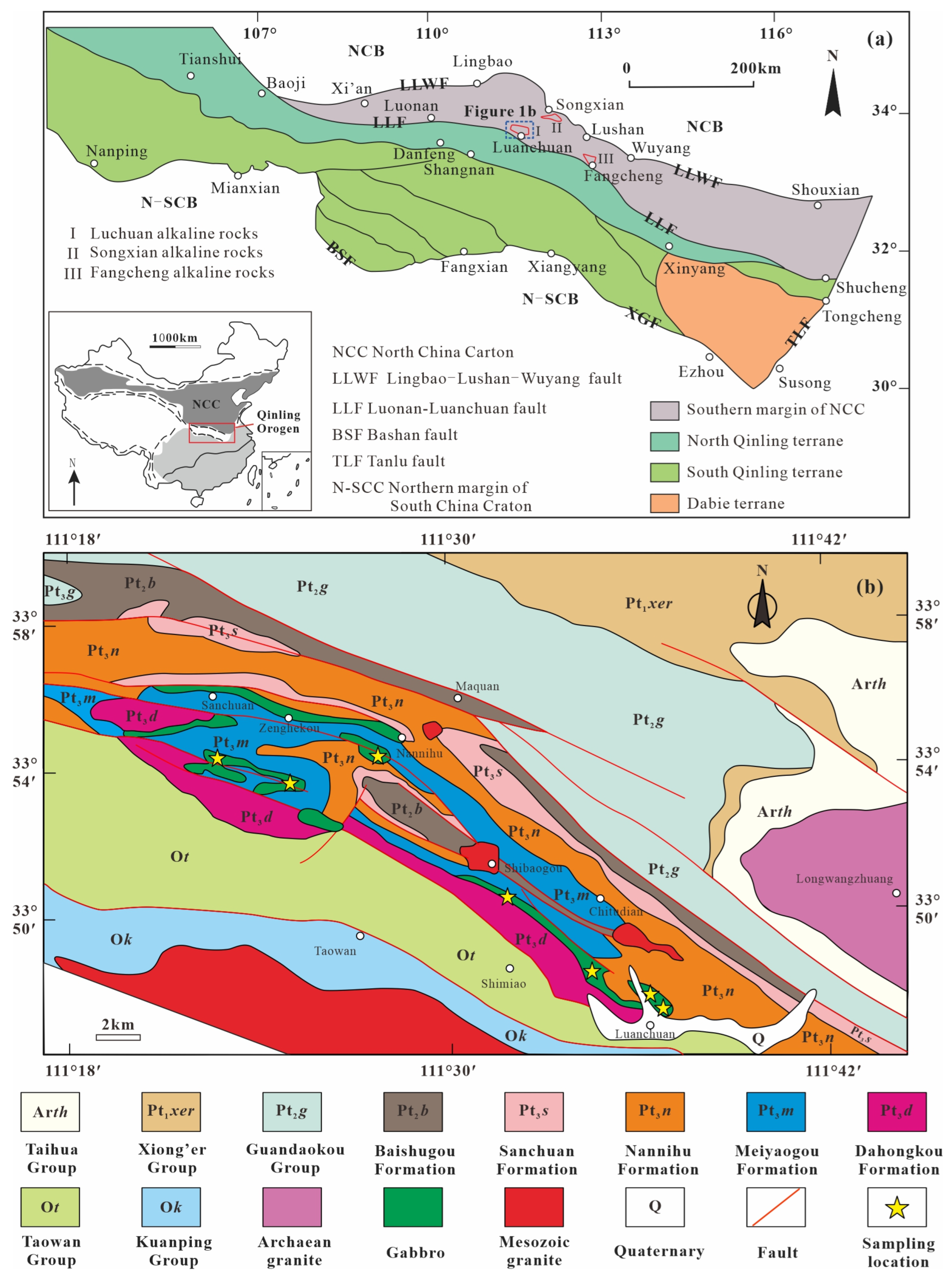
2. Geological Background
3. Petrography and Analytical Methods
3.1. Petrography
3.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4. Results
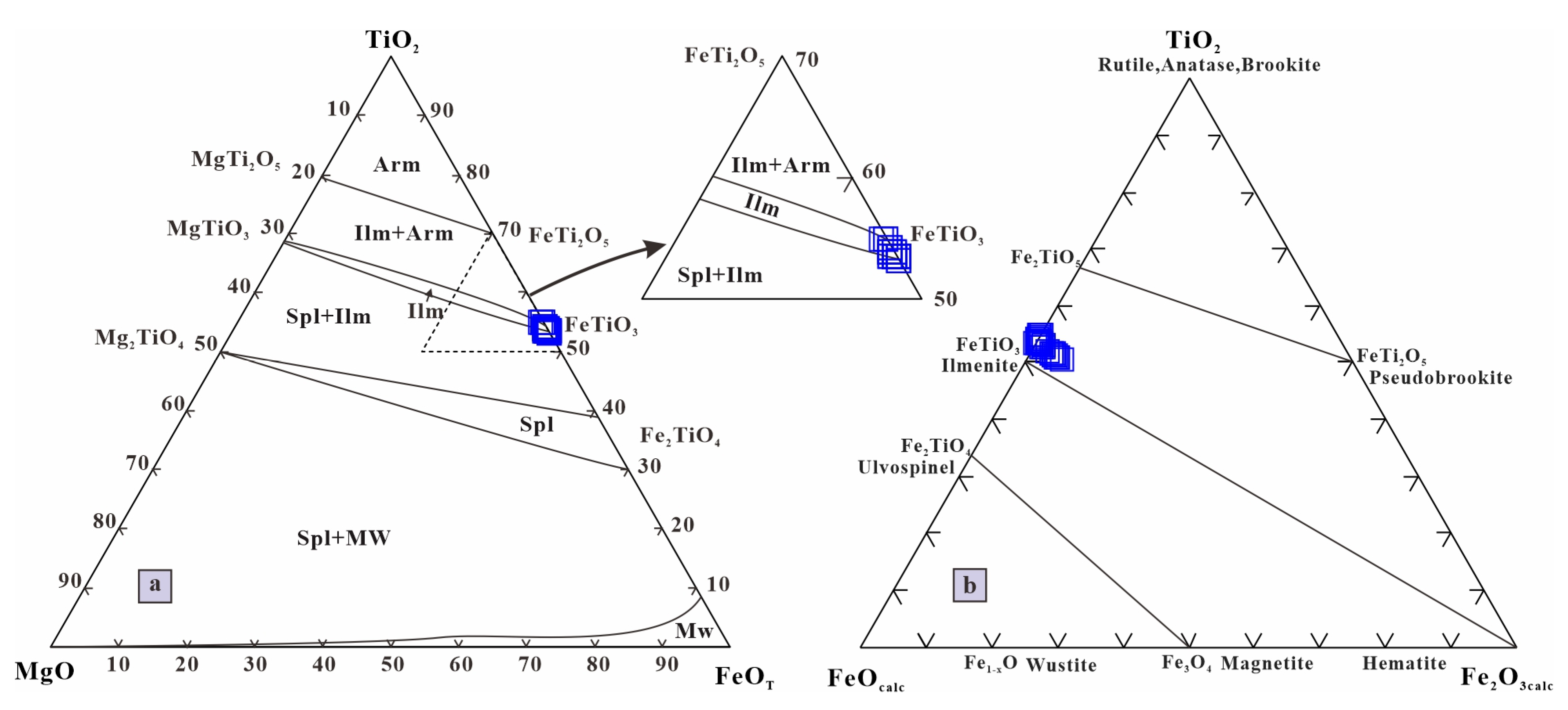
4.1. Ilmenite
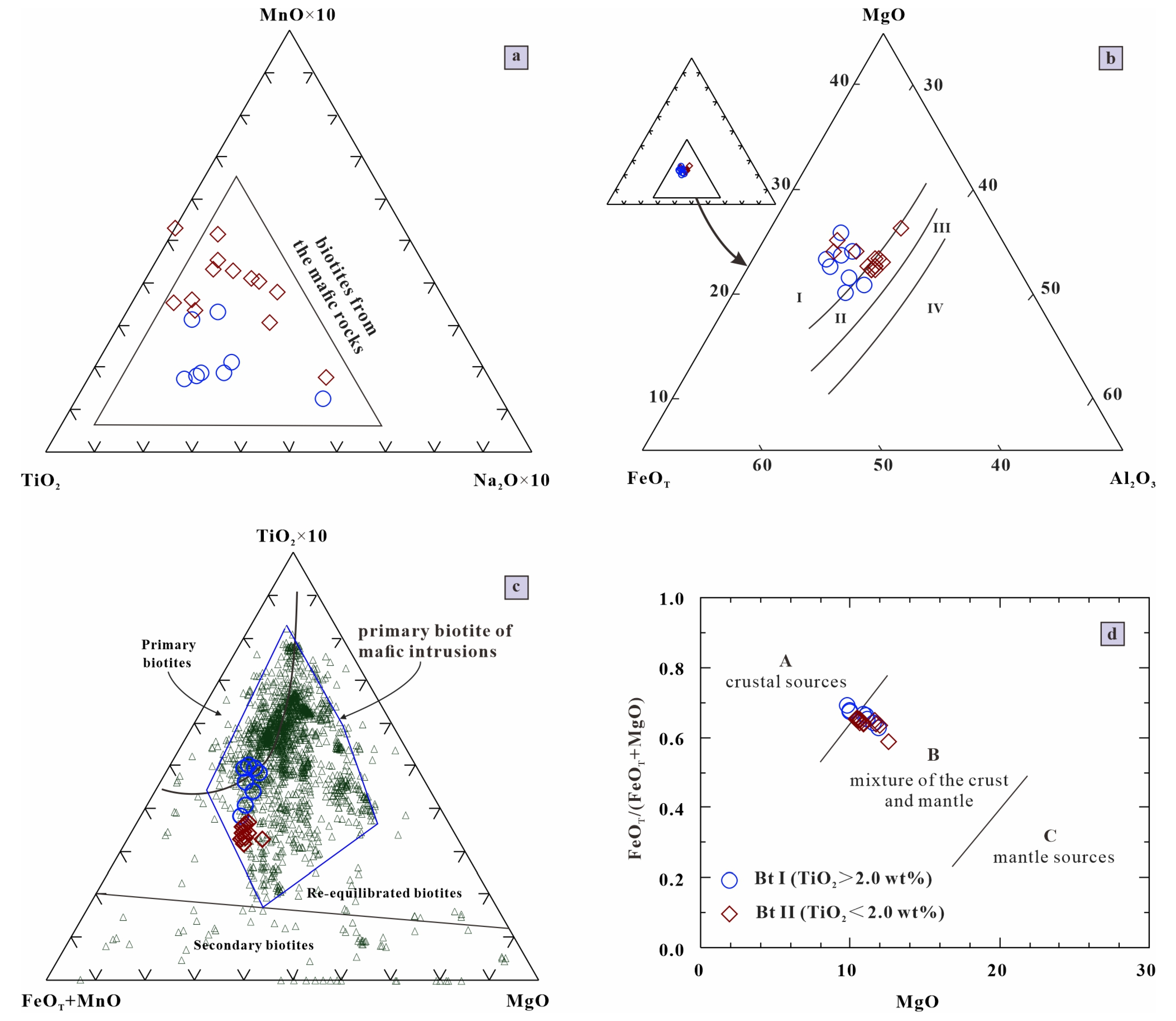
4.2. Biotite

| No. | 49 | 50 | 53 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 92 | 93 | 71 | 79 | 80 | 101 | 114 | 117 | 119 | 120 | 123 | 124 | 128 | 130 | 131 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | SBG22-4-1 | MYG22-3-5 | SHC22-3-8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Shibaogou (111°34′54″, 33°50′01″) | Meiyaogou (111°38′18″, 33°47′54″) | Shuanghecun (111°24′02″, 33°53′51″) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rock | coarse-grained gabbro | ilmenite-bearing medium-grained gabbro | ilmenite-bearing fine-grained gabbro | ||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Biotite I (TiO2 > 2.00 wt%) | Biotite II (TiO2 < 2.00 wt%) | |||||||||||||||||||
| SiO2 | 34.49 | 34.63 | 35.73 | 35.63 | 37.04 | 35.33 | 35.81 | 36.15 | 35.18 | 36.57 | 35.61 | 36.42 | 37.52 | 37.20 | 37.01 | 37.44 | 37.18 | 37.15 | 37.15 | 36.83 | 37.16 |
| TiO2 | 3.15 | 3.14 | 2.66 | 2.55 | 2.99 | 3.12 | 2.25 | 2.03 | 1.88 | 1.72 | 1.90 | 1.51 | 1.50 | 1.40 | 1.41 | 1.66 | 1.71 | 1.58 | 1.59 | 1.52 | 1.50 |
| Al2O3 | 16.45 | 16.79 | 15.83 | 15.79 | 14.20 | 14.98 | 14.80 | 15.12 | 15.84 | 14.69 | 14.85 | 16.89 | 16.53 | 16.73 | 16.39 | 16.54 | 16.49 | 16.47 | 16.46 | 16.48 | 16.27 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.09 | b.d.l | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02 | b.d.l | 0.02 | b.d.l |
| FeOT | 22.08 | 20.93 | 20.80 | 20.65 | 19.94 | 20.73 | 21.65 | 21.74 | 20.64 | 20.88 | 21.42 | 18.03 | 19.26 | 19.22 | 19.49 | 19.57 | 19.79 | 19.73 | 19.46 | 19.64 | 20.03 |
| Fe2O3calc | 5.16 | 5.50 | 10.60 | 11.48 | 9.10 | 11.02 | 9.45 | 6.22 | 9.55 | 9.16 | 8.89 | 7.26 | 4.29 | 3.62 | 5.85 | 3.93 | 3.82 | 3.63 | 3.46 | 6.43 | 4.82 |
| FeOcalc | 17.44 | 15.98 | 11.26 | 10.32 | 11.75 | 10.82 | 13.15 | 16.14 | 12.05 | 12.64 | 13.41 | 11.49 | 15.40 | 15.96 | 14.23 | 16.04 | 16.35 | 16.47 | 16.35 | 13.85 | 15.69 |
| MnO | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| MgO | 9.80 | 9.94 | 9.99 | 11.55 | 11.87 | 11.11 | 11.08 | 10.85 | 11.71 | 12.00 | 11.62 | 12.57 | 10.87 | 10.67 | 10.90 | 10.37 | 10.45 | 10.50 | 10.60 | 10.59 | 10.61 |
| NiO | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | b.d.l | b.d.l |
| CaO | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.85 | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | b.d.l | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| Na2O | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | b.d.l | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| K2O | 9.23 | 8.97 | 7.61 | 7.56 | 8.39 | 7.74 | 8.41 | 9.32 | 8.28 | 8.60 | 8.69 | 8.61 | 9.41 | 9.62 | 9.05 | 9.50 | 9.58 | 9.67 | 9.73 | 8.85 | 9.37 |
| H2Ocalc | 3.12 | 3.09 | 2.95 | 3.23 | 3.08 | 3.02 | 3.26 | 3.35 | 3.39 | 3.42 | 3.38 | 3.42 | 3.44 | 3.48 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 3.43 | 3.46 | 3.48 | 3.40 | 3.43 |
| Total | 99.21 | 98.36 | 99.00 | 98.84 | 99.09 | 98.01 | 98.60 | 99.53 | 98.25 | 99.11 | 98.64 | 98.86 | 99.25 | 98.97 | 98.85 | 99.23 | 99.29 | 99.23 | 99.04 | 98.48 | 99.19 |
| Site assignment of biotite (A1M3T4O10W2) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| T.Si | 2.68 | 2.68 | 2.74 | 2.68 | 2.80 | 2.70 | 2.74 | 2.77 | 2.68 | 2.76 | 2.72 | 2.73 | 2.83 | 2.82 | 2.80 | 2.83 | 2.82 | 2.82 | 2.82 | 2.79 | 2.82 |
| T.Al | 1.21 | 1.22 | 1.06 | 1.10 | 0.97 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.12 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 1.14 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.02 |
| T.Fe3+ | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| sum. T | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| M.Al | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
| M.Mg | 1.14 | 1.15 | 1.14 | 1.28 | 1.33 | 1.27 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 1.32 | 1.34 | 1.32 | 1.39 | 1.20 | 1.19 | 1.22 | 1.15 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.19 | 1.18 |
| M.Fe2+ | 1.13 | 1.03 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.90 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 0.99 |
| M.Fe3+ | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.11 |
| M.Ti | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| M.Cr | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| M.Mn | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Sum. M | 2.95 | 2.92 | 2.81 | 2.82 | 2.83 | 2.84 | 2.86 | 2.89 | 2.86 | 2.84 | 2.87 | 2.84 | 2.81 | 2.82 | 2.82 | 2.81 | 2.83 | 2.83 | 2.83 | 2.80 | 2.82 |
| Vacancy. M | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.18 |
| A.K | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| A.Na | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| A.Ca | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| Sum. A | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.93 |
| Vacancy. A | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| W.OH | 1.61 | 1.60 | 1.51 | 1.62 | 1.55 | 1.54 | 1.66 | 1.71 | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.71 | 1.73 | 1.76 | 1.73 | 1.73 | 1.74 | 1.75 | 1.76 | 1.72 | 1.74 |
| W.O2− | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.26 |
| Fe3+/FeTot | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 0.22 |
| T.°C | 793 | 790 | 792 | 790 | 766 | 767 | 785 | 807 | 801 | 796 | 799 | 818 | 813 | 815 | 812 | 807 | 812 | 811 | 815 | 807 | 810 |
| P.kbar | 8.80 | 8.19 | 5.75 | 7.03 | 5.30 | 5.82 | 6.21 | 8.02 | 7.38 | 6.46 | 6.58 | 7.78 | 8.39 | 8.33 | 8.04 | 8.55 | 8.66 | 8.05 | 8.31 | 8.71 | 8.31 |
| log fO2 | −12.86 | −13.02 | −13.29 | −13.17 | −14.06 | −13.96 | −13.42 | −12.60 | −12.84 | −13.09 | −13.00 | −12.35 | −12.40 | −12.36 | −12.47 | −12.53 | −12.39 | −12.50 | −12.36 | −12.51 | −12.49 |
5. Discussion
5.1. Genesis of Ilmenite

5.2. Genesis of Biotite
5.3. Physicochemical Conditions
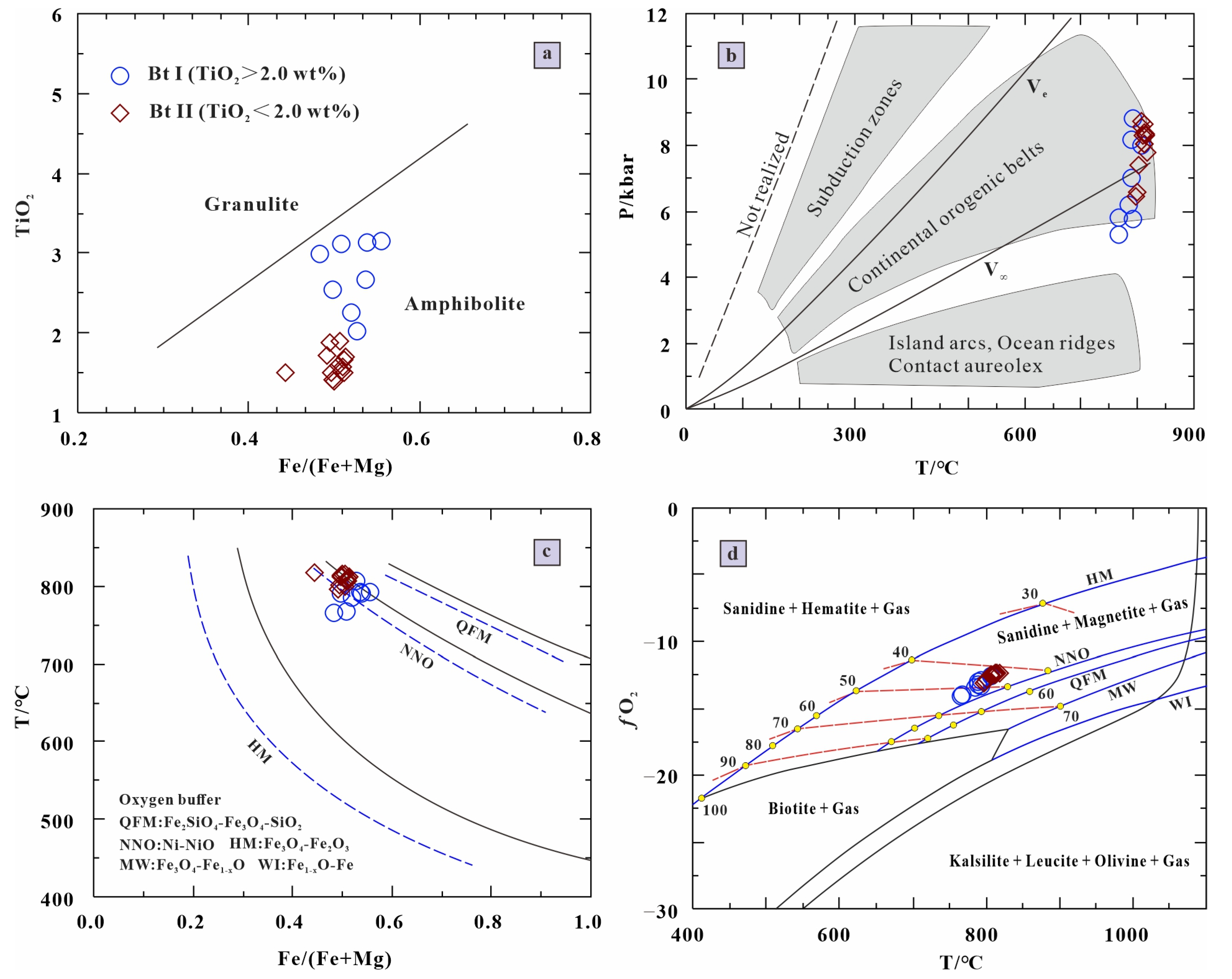
5.4. Implications for Tectonic Setting
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The ilmenite in the Luanchuan gabbroic intrusions is characterized by low MgO and Fe2O3 content and high FeO and MnO content, showing compositional similarities to ilmenite from the Skaergaard intrusion and the Panzhihua layered intrusion;
- (2)
- The biotite in the Luanchuan gabbroic intrusions is of magmatic origin, with total Al contents ranging from 1.26 to 1.53 and Fe/(Fe+Mg) ratios varying from 0.44 to 0.56;
- (3)
- The estimated temperature and pressure for both types of biotite are broadly consistent (766 °C–818 °C and 5.75 kbar–8.80 kbar, respectively), comparable to values reported for the Fanshan complex and the Falcon Island intrusion;
- (4)
- Integrated regional geology, geochronology, and geochemical evidence indicates that the Luanchuan gabbroic intrusions formed in a continental rift setting, potentially related to the breakup of the Rodinia supercontinent.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.P.; Zhou, M.F.; Zhai, M.G.; Xia, B. Paleoproterozoic rift-related volcanism of the Xiong’er Group, North China Craton: Implications for the breakup of Columbia. Int. Geol. Rev. 2002, 44, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.C.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S.A.; Sanzhong, L. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Res. 2005, 136, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.C.; Cawood, P.A.; Li, S.Z.; Wilde, S.A.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.H.; Yin, C.Q. Amalgamation of the North China Craton: Key issues and discussion. Precambrian Res. 2012, 222, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Zhai, M.; Guo, J.; Kusky, T.; Zhao, T. Nature of mantle source contributions and crystal differentiation in the petrogenesis of the 1.78 Ga mafic dykes in the central North China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2007, 12, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Zhai, M.G.; Ernst, R.E.; Guo, J.H.; Liu, F.; Hu, B. A 1.78 Ga large igneous province in the North China Craton: The Xiong’er Volcanic Province and the North China dyke swarm. Lithos 2008, 101, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Xu, H.R.; Wang, C.; Su, X.D.; Sun, F.B.; Wang, X.P. Spatiotemporal evolution of large igneous provinces and their related rifts in the North China craton: Role in craton breakup and destruction. In Large Igneous Provinces and Their Plumbing Systems; Srivastava, R.K., Ernst, R.E., Buchan, K.L., de Kock, M., Eds.; Geological Society, London, Special Publications; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2022; Volume 518, pp. 129–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.G.; Hu, B.; Peng, P.; Zhao, T.P. Meso-Neoproterozoic magmatic events and multistage rifting in the NCC. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 100–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.G.; Peng, P.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhao, L. Early Continent Evolution of the North China Craton; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–300. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.A.; Zhang, L.Q.; Li, D.M. Three Proterozoic extensional events in North China Craton. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2002, 18, 152–160, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Henan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Geology and Mineral Records of Henan Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1989; pp. 1–689, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Henan Institute of Geological Sciences. Studies on the Luanchuan Group in the Henan Province: Internal Communication Reports; Henan Institute of Geological Sciences: Zhengzhou, China, 1990; pp. 1–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.H.; Cai, J.H.; Ren, K.X.; He, G.Q.; Mu, B.L.; Xu, B.L.; Li, F.T.; Yang, B. Intraplate Extensional Magmatism of North China Craton and Break-up of Three Supercontinents and Their Deep Dynamics. Geol. J. China Univ. 2007, 13, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.W.; Wang, Q.; Bai, G.D.; Zhao, Z.H.; Song, Y.W.; Liu, X.M. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Fangcheng Neoproterozoic alkali-syenites in East Qinling orogen and its geodynamic implications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.W.; Wang, Q.H. Impact of hydrothermal alteration on the U-Pb isotopic system of zircons from the Fangcheng syenites in the Qinling orogen, Henan Province, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2009, 28, 163–171, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yan, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiang, Z.J.; Jiang, C.F.; Gao, L.D. Timing of the Transformation from Seafloor Spreading on the South Margin of the North China Block to Subduction within the North Qinling Orogenic Belt. Acta Geol. Sin. 2009, 83, 1565–1583, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F. Preliminary Researching on the Volcanic Rock of Dahongkou Formation, Luanchuan Group. Henan Geol. 2000, 18, 181–189, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.Q. Geochemistry and Tectonic Evolution of Alkaline Rocks in the Southern Margin of the North China Craton. Master’s Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2016; pp. 1–77, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.P.; Santosh, M. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Res. 2016, 29, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Dai, B.Z.; Griffin, W.L.; Dai, M.N.; Yang, Y.H. Age, geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Neoproterozoic (ca 830 Ma) gabbros on the southern margin of the North China Craton. Precambrian Res. 2011, 190, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L. Analysis on the hydrogeological and engineering geological characteristics of Ti-Fe deposit. Mod. Min. 2014, 6, 68–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, X.X.; Schmädicke, E.; Li, Q.L.; Gose, J.; Wu, R.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, G.Q.; Li, X.H. Age determination of nephrite by in-situ SIMS U–Pb dating syngenetic titanite: A case study of the nephrite deposit from Luanchuan, Henan, China. Lithos 2015, 220, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.J. Neoproterozoic Evolution of the Southern Passive Continental Margin of the North China Block. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–66, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.S.; Jia, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Huo, J.J.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, J.D. Depositional age and provenance analysis of the Luanchuan Group in the southern margin of North China Craton and its significance for regional tectonic evolution: Constraints from zircon U- Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1046–1066, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wones, D.R.; Eugster, H.P. Stability of biotite: Experiment, theory, and application. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1965, 50, 1228–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Wones, D.R. Significance of the assemblage titanite+ magnetite+ quartz in granitic rocks. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde, A.E.; Bernard, P. Composition and color of biotite from granites; two useful properties in characterization of plutonic suites from the Hepburn internal zone of Wopmay Orogen, Northwest Territories. Can. Mineral. 1993, 31, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.Q. Compositional characteristics and petrological significance of Mg-Fe micas in alkalic rocks of the Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang rift system. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1995, 15, 82–87, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.W.; Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. Petrogenic implication of the characteristics of micas in shoshonitic rocks in eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2002, 18, 205–211, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ayer, J.A. The mafic minerals of the Falcon Island ultrapotassic pluton, Lake of the Woods, Ontario: Progressive reduction during fractionation. Can. Mineral. 1998, 36, 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein, S.N.; Lange, R.A. Pliocene potassic magmas from the Kings River region, Sierra Nevada, California: Evidence for melting of a subduction-modified mantle. J. Petrol. 1999, 40, 1301–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, F. LIMICA: A program for estimating Li from electron-microprobe mica analyses and classifying trioctahedral micas in terms of composition and octahedral site occupancy. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broska, I.; Harlov, D.; Tropper, P.; Siman, P. Formation of magmatic titanite and titanite–ilmenite phase relations during granite alteration in the Tribeč Mountains, Western Carpathians, Slovakia. Lithos 2007, 95, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiboust, S.; Harlov, D. Ilmenite breakdown and rutile-titanite stability in metagranitoids: Natural observations and experimental results. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 2017, 102, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, R.; Torabi, G.; Kawabata, H.; Miller, N.R. Biotite as a petrogenetic discriminator: Chemical insights from igneous, meta-igneous and meta-sedimentary rocks in Iran. Lithos 2021, 386, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, H.; Pandit, D.; Ahmad, T.; Giri, R.K.; Pandey, A.C. Formation of manganoan ilmenite in Archean tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) gneisses inferred from re-equilibration of biotite and Fe-Ti oxide assemblage: A case study from the Aravalli Craton, northwest India. Neues Jahrb. Für Mineral.-Abh. 2023, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.Z.; Ren, S.L.; Li, J.H.; Chen, Z.C.; Lian, Y.; Cao, Z.C. The strain partition in the southern margin of the North China plate: A study of Luonan-Luanchuan fault belt and the strong deformation belt in the northern margin of the Qinling orogenic belt. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 181–189, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Hu, G.H.; Qiu, Y.F.; Su, W.B.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhao, T.P. Advances in the study of Meso-Neoproterozoic stratigraphic chronology and sedimentary evolution in the southern margin of the North China Craton. J. Stratigr. 2021, 45, 180–195, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wang, Z.; Ding, L. Discovery and preliminary study of Shuang shan jade in Fangcheng, Henan. Northwestern Geol. 2020, 53, 243–251, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhong, J.W.; Ji, Q.H.; Gui, X.X.; Wu, H.Z. Geological characteristics and genetic analysis of diopside–tremolite deposit in Laozhuang, Nanzhao County, Henan Province. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 56, 203–212, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, S.Y. New geochronological constraints on the Dahongkou Formation of the Luanchuan Group and its implications on the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the southern margin of the North China Craton. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 2503–2517, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.Q. Characteristics of the Dahongkou Formation and the Yuku Formation and their tectonic environment in Luanchuan area, Henan Province. Geoscience 1993, 7, 138–144, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.Q.; Zhou, H.R.; Wang, Z.Q. Stratigraphic sequence, sedimentary environment and its tectono-paleogeographic significance of the Luanchuan Group, Luanchuan area, Henan province. Geoscience 1994, 8, 430–440, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.E.; Woermann, E.; Muan, A. Equilibrium studies in the system MgO-FeO-TiO2. Am. J. Sci. 1971, 271, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddington, A.F.; Lindsley, D.H. Iron-titanium oxide minerals and synthetic equivalents. J. Petrol. 1964, 5, 310–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.D. Interpretation of the Composition of Trioctahedral Micas; United States Geological Survey Professional Paper; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1960; Volume 354-B, pp. 11–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf, G.; Förster, H.J.; Gottesmann, B. Minor-and trace-element composition of trioctahedral micas: A review. Mineral. Mag. 2001, 65, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.L.; Yang, J.S.; Feng, G.Y.; Liu, F. Mineral chemistry of biotites from the Fanshan ultramafic syenitic complex and its petrogenetic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1108–1119, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, C.; Behrens, H.; Holtz, F. On the improvement of calculating biotite formula from EPMA data: Reexamination of the methods of, and reply to the discussion of Baidya and Das. Lithos 2022, 412, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, C. Machine learning thermobarometry for biotite-bearing magmas. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischendorf, G.; Forster, H.J.; Gottesmann, B.; Rieder, M. True and brittle micas: Composition and solid-solution series. Mineral. Mag. 2007, 71, 285–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, M.; Cavazzini, G.; D’yakonov, Y.S.; Frank-Kamenetskii, V.A.; Gottardi, G.; Guggenheim, S.; Koval, P.W.; Mueller, G.; Neiva, A.M.R.; Radoslovich, E.W. Nomenclature of the micas. Clays Clay Miner. 1998, 46, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Q.; Deng, Y.F.; Song, X.Y.; Chen, L.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Zhou, G.F.; Liu, S.R.; Xiang, J.X. Composition and genetic significance of the ilmenite of the Panzhihua intrusion. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1432–1442, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Charlier, B.; Duchesne, J.C.; Vander Auwera, J. Magma chamber processes in the Tellnes ilmenite deposit (Rogaland Anorthosite Province, SW Norway) and the formation of Fe–Ti ores in massif-type anorthosites. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 264–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, B.; Skår, Ø.; Korneliussen, A.; Duchesne, J.C.; Vander Auwera, J. Ilmenite composition in the Tellnes Fe–Ti deposit, SW Norway: Fractional crystallization, postcumulus evolution and ilmenite–zircon relation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegner, C.; Duncan, R.A.; Bernstein, S.; Brooks, C.K.; Bird, D.K.; Storey, M. 40Ar39Ar geochronology of Tertiary mafic intrusions along the East Greenland rifted margin: Relation to flood basalts and the Iceland hotspot track. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 156, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Qi, H.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, L.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.F. Formation of thick stratiform Fe-Ti oxide layers in layered intrusion and frequent replenishment of fractionated mafic magma: Evidence from the Panzhihua intrusion, SW China. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2013, 14, 712–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhou, M.F.; Hou, Z.Q.; Cao, Z.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Y.G. Geochemical constraints on the mantle source of the upper Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts, southwestern China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2001, 43, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G.; He, B.; Chung, S.-L.; Menzies, M.A.; Frey, F.A. Geologic, geochemical, and geophysical consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood-basalt province. Geology 2004, 32, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G.; Chung, S.L.; Jahn, B.M.; Wu, G.Y. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian–Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China. Lithos 2001, 58, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.H.; Sparks, R.S.J. The differentiation of the Skaergaard intrusion. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.D.; Naslund, H.R.; McBirney, A.R. The differentiation trend of the Skaergaard intrusion and the timing of magnetite crystallization: Iron enrichment revisited. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 189, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.D.; Naslund, H.R. Major and trace element variation in ilmenite in the Skaergaard Intrusion: Petrologic implications. Chem. Geol. 2003, 193, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockolds, S.R. The relation between chemical composition and paragenesis in the biotite micas of igneous rocks. Am. J. Sci. 1947, 245, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Albuquerque, C.A.R. Geochemistry of biotites from granitic rocks, northern Portugal. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachit, H.; Ibhi, A.; Ohoud, M.B. Discrimination between primary magmatic biotites, reequilibrated biotites and neoformed biotites. Comptes Rendus. Géoscience 2005, 337, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsapoor, A.; Khalili, M.; Tepley, F.; Maghami, M. Mineral chemistry and isotopic composition of magmatic, re-equilibrated and hydrothermal biotites from Darreh-Zar porphyry copper deposit, Kerman (Southeast of Iran). Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 66, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.; Exley, C.S.; George, M.C. Compositions of trioctahedral micas in the Cornubian batholith. Mineral. Mag. 1988, 52, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Q.; Yang, K.G.; Tang, Z.H.; Li, Z.T. Magma-Dynamics of Granitoids—Theory, Method and a Case Study of the Eastern Hubei Granitoids; Press of China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 1994; pp. 1–260, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M. Petrogenetic implications from biotite compositional variations in the Cornubian granite batholith. Mineral. Mag. 2000, 64, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X. Chemical characteristics of mafic mica in intrusive rocks and its geological meaning. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1988, 4, 63–73, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.F.M. Nature of biotites from alkaline, calc-alkaline, and peraluminous magmas. J. Petrol. 1994, 35, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, D.J.; Guidotti, C.V.; Thomson, J.A. The Ti-saturation surface for low-to-medium pressure metapelitic biotites: Implications for geothermometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, C.; Behrens, H.; Holtz, F. Calculating biotite formula from electron microprobe analysis data using a machine learning method based on principal components regression. Lithos 2020, 356, 105371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Cong, B.L. Mineral Thermometer and Manometer; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1983; pp. 164–179. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ague, J.J. Thermodynamic calculation of emplacement pressures for batholithic rocks, California: Implications for the aluminum-in-hornblende barometer. Geology 1997, 25, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino Douce, A.E.; Johnston, A.D.; Rice, J.M. Octahedral excess mixing properties in biotite: A working model with applications to geobarometry and geothermometry. Am. Mineral. 1993, 78, 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaka, T.; Akitou, T.; Abe, N.; Tribuzio, R. Biotite in olivine gabbros from Atlantis Bank: Evidence for amphibolite-facies metasomatic alteration of the lower oceanic crust. Lithos 2019, 348, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, S.Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.G.; Yang, J.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.M. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of biotite in magma type ore deposit: A case study of Fanshan phosphate deposit in Zhuolu County, Hebei Province. Glob. Geol. 2021, 40, 288–297, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cesare, B.; Satish-Kumar, M.; Cruciani, G.; Pocker, S.; Nodari, L. Mineral chemistry of Ti-rich biotite from pegmatite and metapelitic granulites of the Kerala Khondalite Belt (southeast India): Petrology and further insight into titanium substitutions. Am. Mineral. 2008, 93, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, Z.; Lentz, D.R.; McFarlane, C.R.M.; Whalen, J.B. Using magmatic biotite chemistry to differentiate barren and mineralized Silurian–Devonian granitoids of New Brunswick, Canada. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 175, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, E.; Endo, S.; Makino, M. Relationship between solidification depth of granitic rocks and formation of hydrothermal ore deposits. Resour. Geol. 2007, 57, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skublov, S.G.; Drugova, G.M. REE geochemistry of metamorphic biotite. Geochem. Int. 2004, 42, 280–284. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cruciani, G.; Franceschelli, M.; Massonne, H.J. Low-temperature metamorphic evolution of a pre-Variscan gabbro: A case study from the Paleozoic basement of northwest Sardinia, Italy. Mineral. Mag. 2011, 75, 2793–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.B.; England, P.C. Pressure—Temperature—Time paths of regional metamorphism II. Their inference and interpretation using mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 929–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R. Introduction to oxygen fugacity and its petrologic importance. In Oxide Minerals; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.P.; Pang, L.Y.; Qiu, Y.F.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Geng, Y.S. The Paleo-Mesoproterozoic boundary: 1.8Ga. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 2281–2298, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhang, G.W.; Hauzenberger, C.; Neubauer, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.M. Palaeozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the Qinling orogen: Evidence from geochemistry and geochronology of ophiolite and related volcanic rocks. Lithos 2011, 122, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, M. Alkaline rocks and their inclusions: A window on the Earth’s interior. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1987, 30, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampunzu, A.; Tembo, F.; Matheis, G.; Kapenda, D.; Huntsman-Mapila, P. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of mafic igneous units in the Neoproterozoic Katangan Basin, Central Africa: Implications for Rodinia break-up. Gondwana Res. 2000, 3, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, L.; Famin, V.; Quidelleur, X. Evolution of the East African Rift System from trap-scale to plate-scale rifting. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 231, 104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Uribe, A.M.; Marschall, H.R.; Gaetani, G.A.; Le Roux, V. Generation of alkaline magmas in subduction zones by partial melting of mélange diapirs-An experimental study. Geology 2018, 46, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Cann, J.R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1973, 19, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.N.; Chen, Z.H.; Li, H.K.; Hao, G.J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xiang, Z.Q. Late Mesoproterozoic-early Neoproterozoic evolution of the Qinling orogen. Geol. Bull. China 2004, 23, 107–112, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Bagas, L.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yao, J.M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, P. Isotope (S–Sr–Nd–Pb) constraints on the genesis of the ca. 850 Ma Tumen Mo–F deposit in the Qinling Orogen, China. Precambrian Res. 2015, 266, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 14 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 31 | 37 | 38 | 41 | 46 | 55 | 56 | 66 | 67 | 73 | 74 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 95 | 98 | 100 | 105 | 106 | 111 | 113 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | SBG22-4-4 | SBG22-4-1 | MYG22-3-5 | MYG22-3-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Shibaogou (111°34′54″, 33°50′01″) | Meiyaogou (111°38′18″, 33°47′54″) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rock | coarse-grained gabbro | ilmenite-bearing medium-grained gabbro | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TiO2 | 50.46 | 49.92 | 50.54 | 49.94 | 50.71 | 50.42 | 50.88 | 50.81 | 51.44 | 50.74 | 52.56 | 52.95 | 51.46 | 53.34 | 53.53 | 52.78 | 52.36 | 51.07 | 52.05 | 52.42 | 51.79 | 52.49 | 52.60 | 52.58 | 52.79 | 52.35 | 52.85 | 52.78 | 52.35 | 53.75 | 52.81 | 53.17 | 53.20 | 52.92 | 52.49 |
| FeOT | 48.18 | 48.46 | 47.43 | 47.83 | 47.31 | 48.13 | 47.56 | 47.80 | 46.97 | 47.18 | 45.39 | 44.47 | 46.14 | 43.95 | 44.08 | 45.73 | 45.56 | 45.80 | 46.07 | 45.58 | 45.73 | 45.27 | 45.78 | 45.39 | 45.61 | 45.74 | 45.49 | 45.61 | 45.58 | 43.87 | 45.17 | 45.00 | 45.17 | 45.80 | 45.34 |
| Fe2O3calc | 44.29 | 43.50 | 44.06 | 43.54 | 44.30 | 44.02 | 44.28 | 44.25 | 44.67 | 44.21 | 45.39 | 44.47 | 44.69 | 43.95 | 44.08 | 45.73 | 45.44 | 44.76 | 44.88 | 45.17 | 44.63 | 44.95 | 45.35 | 44.92 | 45.31 | 45.25 | 45.49 | 45.52 | 45.00 | 43.87 | 45.07 | 45.00 | 45.17 | 45.21 | 44.94 |
| FeOcalc | 4.33 | 5.52 | 3.74 | 4.76 | 3.34 | 4.56 | 3.65 | 3.94 | 2.55 | 3.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.61 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 1.16 | 1.33 | 0.46 | 1.22 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.44 |
| MnO | 1.25 | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 1.12 | 1.17 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.37 | 1.24 | 1.34 | 1.47 | 1.33 | 1.29 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 1.53 | 1.68 | 1.46 | 1.47 | 1.45 | 1.80 | 1.65 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.84 | 1.85 | 1.61 | 1.76 | 1.62 | 1.53 |
| MgO | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.41 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.02 | b.d.l | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | b.d.l | 0.03 | 0.03 | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | b.d.l | 0.04 | b.d.l | 0.04 | 0.02 | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.02 | b.d.l | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
| NiO | 0.01 | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.01 | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.01 | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.01 | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.03 | b.d.l | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | b.d.l | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.04 | 0.02 | b.d.l | b.d.l |
| V2O3 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.06 | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.06 | 0.01 | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | b.d.l | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| Total | 100.49 | 100.28 | 99.73 | 99.66 | 99.61 | 100.30 | 100.25 | 100.40 | 100.20 | 99.64 | 99.51 | 99.07 | 99.24 | 98.92 | 99.06 | 99.97 | 99.44 | 98.38 | 100.04 | 99.94 | 99.42 | 99.68 | 100.54 | 100.14 | 100.37 | 99.79 | 100.05 | 100.19 | 99.87 | 99.91 | 100.24 | 100.33 | 100.64 | 100.87 | 99.92 |
| Site assignment of ilmenite (FeTiO3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ti | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Fe2+ | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| Fe3+ | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Mn | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Mg | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Cr | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ni | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| V | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sum | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.99 | 2.00 | 1.99 | 1.98 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.99 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, K.; Huang, X.; Ren, M.; Fan, Y. Tectonic Setting of the Neoproterozoic Gabbroic Intrusions in the Luanchuan Area, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from Ilmenite and Biotite Mineralogy. Minerals 2025, 15, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060602
Huang J, Huang Z, Chen D, Li K, Huang X, Ren M, Fan Y. Tectonic Setting of the Neoproterozoic Gabbroic Intrusions in the Luanchuan Area, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from Ilmenite and Biotite Mineralogy. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jianhan, Zhenzhen Huang, Danli Chen, Kekun Li, Xiaoxiao Huang, Minghao Ren, and Yazhou Fan. 2025. "Tectonic Setting of the Neoproterozoic Gabbroic Intrusions in the Luanchuan Area, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from Ilmenite and Biotite Mineralogy" Minerals 15, no. 6: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060602
APA StyleHuang, J., Huang, Z., Chen, D., Li, K., Huang, X., Ren, M., & Fan, Y. (2025). Tectonic Setting of the Neoproterozoic Gabbroic Intrusions in the Luanchuan Area, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from Ilmenite and Biotite Mineralogy. Minerals, 15(6), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060602