Abstract
The Dehbid region, located in the southern part of the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone (SSZ), is a significant iron oxide mining district with over 20 iron oxide deposits (IODs) and reserves of up to 50 million tons of iron oxide ores. The region features a NW–SE oriented ductile shear zone, parallel to the Zagros thrust zone, experienced significant deformation. Detailed structural studies indicate that the iron mineralization is primarily stratiform to stratabound and hosted in late Triassic to early Jurassic silicified dolomites and schists. These ore deposits consist of lenticular iron oxide orebodies and exhibit various structures and textures, including banded, laminated, folded, disseminated, and massive forms of magnetite and hematite. The Fe2O3 content in the mineralized layers varies from 30 to 91 wt%, whereas MnO has an average of 3.9 wt%. The trace elements are generally low, except for elevated concentrations of Cu (up to 4350 ppm) and Zn (up to 3270 ppm). Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analysis of magnetite reveals high concentrations of Mg, Al, Si, Mn, Ti, Cu, and Zn, with significant depletion of elements such as Ga, Ge, As, and Nb. This study refutes the hypothesis of vein-like or hydrothermal genesis, providing evidence for a sedimentary origin based on the trace element geochemistry of magnetite and LA-ICP-MS geochemical data. The Dehbid banded iron ores (BIOs) are thought to have formed under geodynamic conditions similar to those of BIOs in back-arc tectonic settings. The combination of anoxic conditions, submarine hydrothermal iron fluxes, and redox fluctuations is essential for the formation of these deposits, suggesting that similar iron–manganese deposits can form during the Phanerozoic under specific geodynamic and oceanographic conditions, particularly in tectonically active back-arc environments.
1. Introduction
Iran is a significant global iron producer, with over 200 iron oxide deposits (IODs [1]). In 2023, the country produced approximately 78 Mt of iron ore. Iran has reserves of 4.2 Gt of iron oxide ore, representing about 1.7% of global reserves in 2024 [2,3]. Most of this production is derived from Iron oxide-apatite (IOA) or Kiruna-type deposits (e.g., Chadormalu, Chahgaz, Gazestan, Esfordi, Sechahun, Choghart, and Sorkhedizaj), skarn deposits (e.g., Incheh, Bashkand, Sangan, Alamkandi, and Bisheh), sedimentary and volcano-sedimentary banded iron ore (BIO; e.g., Halab, Golcheshme, and Gol-e-Gohar), iron oxide copper-gold (IOCG, e.g., Panjkuh, Tanourche, and Kuhe Zar), sideritic Fe-Mn (Cu-Zn-Pb-Ba) Irish-type deposits (e.g., Ahangaran, Sarchal, and Shamsabad), laterites (e.g., Koupan and Koree), exhalative Fe-Mn deposits (e.g., Narigan, Rabiei, and Halalan), and placer deposits (e.g., Khaf).
Iron oxide deposits in Iran are distributed across several regions, including the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone (SSZ), Central Iran, Alborz, Sabzevar zone, Hormozgan, and northeastern and northwestern Iran. Economically significant Kiruna-type and skarn deposits are spatially and temporally related to magmatism throughout the Iranian Plate. Major iron oxide mineralization occurred during the late Precambrian–Cambrian, early Ordovician, late Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic [1].
Although various vein-type, epithermal, stratiform, and karst-related Fe-Mn deposits have been extensively studied worldwide [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15], the investigation of these deposits in Iran has not been as extensively addressed as that of iron ore deposits [16]. The Dehbid region, located in the southern SSZ (Figure 1), is a significant iron oxide mining district that contains numerous Fe (-Mn) oxide deposits and prospects [17] (Figure 1). In this district, over 20 IODs, with reserves of up to 50 Mt Fe oxide ores, are hosted in late Triassic-early Jurassic carbonates and schists. The most significant active mines in the Dehbid district include Goushti, Heneshk, Goli, Cheshme Esi, Faryadan, Cheshme Sorkh, Moazam, and Kuh Sorkh (Figure 1C and Figure 2).
The origin of Dehbid’s IODs has been widely debated since their discovery, with significant uncertainty remaining despite numerous studies [17,18,19,20]. Rajabzadeh and Rasti [20,21] proposed a hydrothermal origin based on geochemical data and fluid inclusion studies. Conversely, Kazemirad et al. [19] suggested a syngenetic, volcano-sedimentary model informed by the geology of the Heneshk, Madkansar, Goushti, and Cheshme Esi deposits.
This paper presents new geological, mineralogical, petrological, and geochemical data from Fe (-Mn) oxide ores at four key Dehbid region sites: Heneshk, Cheshme Esi, Goli, and Cheshme Sorkh deposits. Ore textures, structures, and geochemical data were analyzed to evaluate the genetic characteristics of these mineralizations.
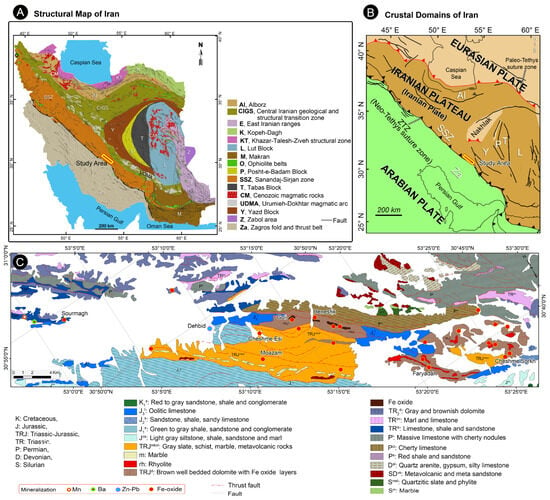
Figure 1.
(A) Tectonic map of Iran [22,23] showing the Dehbid region. (B) Terrane map of the western Tethysides [22]. (C) Geological map of the Dehbid region within the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone (SSZ).
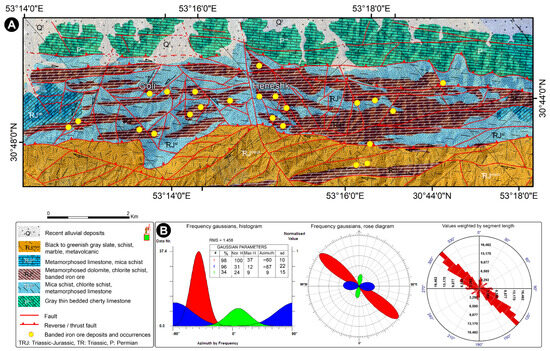
Figure 2.
(A) Geological map of the northeastern Dehbid region and the distribution of banded iron ores in Triassic–Jurassic dolomites and schists. (B) Frequency Gaussians histogram, rose diagram, and weighted segment length values of faults.
2. Tectonic and Geological Setting
The Dehbid district, located 175 km northeast of Shiraz, lies on the southern margin of the Sanandaj–Sirjan metamorphic zone and is known for its complex deformation. This zone is a key part of the Zagros orogenic system within the Alpine–Himalayan belt. The SSZ extends from eastern Turkey to the Minab Fault in southern Iran and includes Paleozoic to Jurassic high-grade metamorphic rocks, which are overlain by Mesozoic metasedimentary strata.
The SSZ contains part of the Precambrian continental basement of Iran, formed through orogenic events during Gondwana’s assembly [24,25]. Recent studies indicate that early Cambrian magmatism in the SSZ represents a magmatic arc formed along the Proto-Tethyan margin of the Gondwana supercontinent [26,27].
The entire Iranian Plate was a stable continental platform before the early Silurian opening of the Paleo-Tethys. In the Permian and Triassic, the northern margin evolved into a passive continental margin with extensive carbonate platforms [25,28]. A significant rifting event in the south during the middle to late Permian caused the Iranian Plate, including the SSZ, to separate from Gondwana, leading to the opening of the Neo-Tethys Ocean. This was accompanied by a north-dipping subduction system along the Paleo-Tethys margin, resulting in its closure due to subduction beneath Eurasia in the Late Triassic [28].
The final closure of the Paleo-Tethys led to the transformation of the boundary between the Arabian and Iranian plates from passive to convergent during the late Triassic [28,29]. This convergence initiated subduction beneath the Iranian plate, driving late Triassic to Cretaceous arc magmatism in the SSZ. Subsequent uplift and erosion have removed volcanic arc remnants from various areas. Convergence and magmatism also caused contact and regional metamorphism in older SSZ sequences [28,30]. The Zagros thrust zone (Figure 1B), between the Zagros ranges and the SSZ, delineates the suture between the Arabian and Iranian plates. The northern margin of the SSZ is a complex back-arc basin that formed from the Jurassic to the Cretaceous. Convergence between the Arabian and Iranian plates in the southwest of the SSZ likely began in the late Eocene [15,16,17,18]. Madanipour et al. [24] proposed that the Neo-Tethys closure occurred in two phases: a soft collision in the early Oligocene, followed by a hard collision in the middle Miocene.
The collision of the Arabian and Iranian plates has caused several phases of deformation and thrust faulting, resulting in regional deformation characterized by lineation, foliation, folding, and faulting, along with ongoing crustal shortening in the SSZ.
3. Geology of the Dehbid Region
The Dehbid region is characterized by a prominent NW–SE ductile shear zone [20], aligned with the Zagros thrust zone (Figure 1 and Figure 2). This area is primarily composed of metamorphosed sedimentary and igneous rocks and has experienced significant deformation, which led to the development of mylonitic foliation and lineation. The oldest rock units in the region range from the Silurian to early Devonian, and include quartzite, metamorphosed sandstones, phyllite, and marble, along with thin chert and limestone beds, which are predominantly exposed in the northeastern part of the region (Figure 2). Overlying these units are the Permian strata, consisting of shale, sandstone, and crystalline limestone, trending NW–SE. These units are succeeded by Triassic–Jurassic brown, well-bedded silicified dolomite and schist, which host iron ore deposits [19,20].
The late Triassic units mark the onset of volcanic activity following a period of sedimentation hiatus. Alkaline rhyolitic and andesitic rocks signify the development of an extensional environment during the late Triassic-early Jurassic in this region [31]. The early Jurassic is characterized by shallow marine sediments including shales, sandstones, and conglomerates, while oolitic limestones mark the late Jurassic. Cretaceous sandstones, shales, and limestones overlie these units [19,20].
The Dehbid region (Figure 1C and Figure 2) is located within the Henshk shear zone [32] and is associated with the main oblique-slip thrust fault of the Zagros Mountains. Evidence of ductile deformation in the Henshk area is demonstrated by various deformational fabrics, including foliation, crenulation, kink bands, grain size reduction, elongation, C/S fabrics, and fish-scale structures, some of which provide insights into the SE–NW shear direction [19]. Brittle deformation is also widespread, characterized by extensive faulting and geological contacts that display fault displacement (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Outcrops of faulted dolomite and schist units, as well as iron oxide ore lenses, are found in the Madkansar (A) and Cheshmeh Esi (B) deposits, Dehbid region.
Upon initial observation, the study area exhibits a folded penetrative foliation. The predominant strike of the significant foliation is approximately NW–SE, with moderate to steep dips toward the NE and SW. The folding is characterized by open to closed folds, with a shallow plunge of the fold axis toward the NW and SE (Figure 4A). The relict bedding is parallel to the folded major foliation (Figure 4A), indicating the presence of an older foliation that predates the penetrative one [33]. Microscopic analysis and investigation of the preserved microstructures in the mictolitons have revealed evidence of an earlier foliation (S1, Figure 4B). Based on field and microscopic observations, the study area contains at least three generations of foliation: S1 and S2, which are penetrative foliations, and the younger S3. The remnant of the earlier foliation (S1) appears as spaced foliation, while S2 is continuous to space-disjunctive, and S3 typically exhibits crenulation to zonal crenulation (Figure 4B–G).
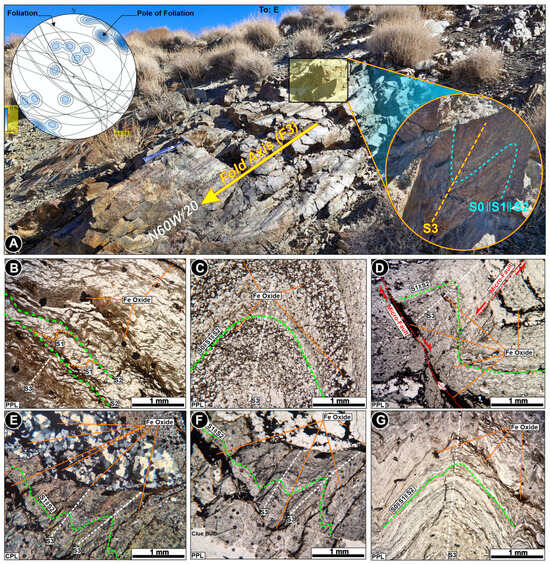
Figure 4.
Field and microscopic evidence of polyfolding of metasediments (mica schist) in the study area and its geometric relation to Fe oxide mineralization. (A) Field view of folding of penetrative foliation (S2) in the study area. Structural measurements of foliation planes are represented in the equal area lower hemisphere projection at the top and left corners, with a close-up image of folded foliation (S0, S1, and S2) at the bottom right corner of the field image, respectively. (B) Microscopic view of three types of foliations (S1, S2, and S3) and the relic of iron oxide minerals. (C) Parallelism of iron oxide mineralization with respect to early (S0 = bedding) and metamorphic foliations (S1, S2, and S3). (D) Younger generation of iron oxide within the micro-fault crush zones. (E,F) Cross and plain polarized images of iron oxide veinlets parallel to penetrative foliation and S3 subparallel younger fractures. (G) Concordant folding of iron oxide lamina parallel to S0, S1, and S2. (PPL: Plain polarized light and CPL: Cross polarized light).
4. Mineralization, Ore Geology, and Mineralogy
The metamorphism and deformation of the orebodies have hindered geological research in the Dehbid region. While some studies [20,21] have suggested a vein geometry for the iron mineralization in these deposits, detailed geological and structural investigations [17,19] reveal that a significant portion of the iron mineralization is stratiform to stratabound, consistently hosted in late Triassic-early Jurassic silicified dolomites and schists (Figure 5). However, in certain deposits, tectonic processes have also led to the concentration of Fe ores along more recent fault zones within carbonate rocks. The Madkansar deposit, also called Goushti-Heneshk, is the most significant iron mineralization in this district. Iron oxide mineralization occurs in lenticular orebodies, ranging from 100 to 700 m in length and 10 to 15 m in thickness. These orebodies exhibit a northwest–southeast trend, with a dip of approximately 40 to 50 degrees toward the northeast (Figure 3A). The mineralized dolomites and schists are thrust over the metamorphosed volcanic-sedimentary sequences of the late Triassic-early Jurassic, by a northwestern–southeastern trending reverse fault that dips towards the northeast.
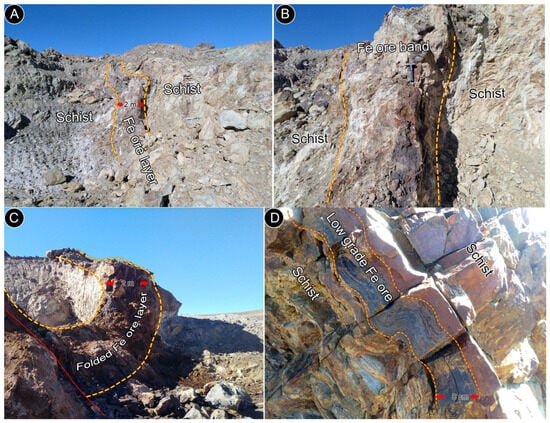
Figure 5.
(A,B) Stratiform Fe oxide ore lenses in the Cheshme Sorkh deposit, hosted within Late Triassic to Early Jurassic chlorite and mica schists. (C) Folded Fe oxide ore layer in the Cheshme Sorkh deposit. (D) Folded stratiform Fe oxide bands in chlorite schists, east of the Heneshk deposit.
At the Cheshmeh Esi deposit, a small mine located in the east–northeast of the Madkansar area, iron oxide mineralization occurs in the form of small lenses and layers in Triassic–Jurassic dolomites and schists, ranging from 10 to 50 m in length and 2 to 4 m in thickness (Figure 3B). The ore body outcrops with a northeast–southwest trend and a dip of approximately 40 degrees towards the northwest, which appears to be associated with local folding within the deposit. Given the presence of the shear zone in this area, the mineralized horizon and the host rocks have been repeated four times, as the hanging wall and footwall of the orebodies comprise late Triassic-early Jurassic volcanic-sedimentary rocks, including mylonitized metavolcanic and sericite–quartz schist. The orebody exhibits a lenticular geometry, aligned with the bedding, with dimensions varying from several meters to less than half a meter.
The Goli deposit, located northeast of the Madkansar mine, exhibits iron oxide mineralization in the form of lenticular orebodies aligned with the bedding of the host rock. These orebodies display a northwest trend, with angles ranging from 50 to 70 degrees and a northeast dip of 20 to 30 degrees. The iron oxide mineralization occurs as thin layers within Triassic–Jurassic strata, with lengths ranging from 8 to 40 m and thickness from 2 to 5 m.
These orebodies in all deposits consist of stratiform layers parallel to the host rock (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The ore minerals exhibit a variety of textures and structures, including banded, laminated, folded, disseminated, and massive forms (Figure 5). Furthermore, magnetite grains within the massive Fe oxide bands display lumpy microtextures, characterized by irregular, often rounded, non-uniform or smooth aggregates of magnetite (Figure 7). In certain fault zones, Fe oxide ores are characterized by veins, open space filling, and symmetrical banding, which exhibit cockade structures.
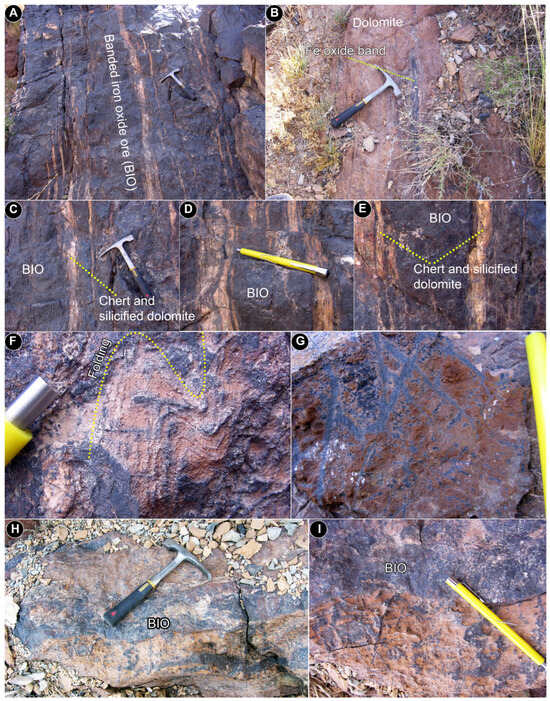

Figure 6.
(A–E) Outcrop of stratiform BIO associated with chert and silicified dolomite. (F) Folding of iron oxide laminae within silicified dolomite. (G) Iron oxide veinlets in host rock fractures. (H,I) Iron oxide (magnetite and hematite) bands parallel to the host rock foliation.
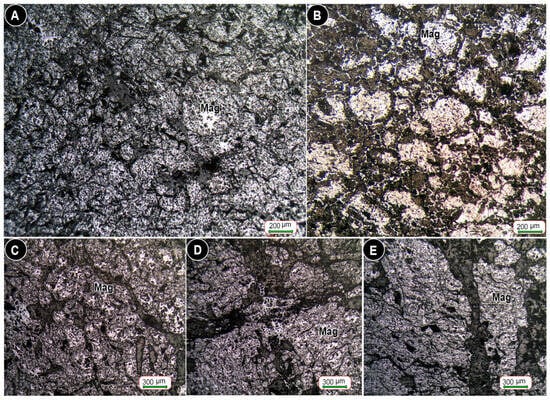
Figure 7.
Reflected light photomicrographs of magnetite (Mag) in massive banded iron ores. Magnetite exhibits lumpy microtextures (A–C) and is progressively replaced by hematite through martitization (D,E).
Magnetite and hematite are the principal ore minerals in all iron oxide deposits (Figure 7), and pyrite, cryptomelane, psilomelane, and ramsdellite are present in trace amounts in the mineralized layers. Magnetite predominantly occurs in massive, granular, banded, and lumpy forms within the orebodies. Also, some samples’ coarse magnetite crystals exhibit secondary growth, indicating recrystallization during metamorphism. Hematite typically replaces magnetite, particularly in the upper portions of the orebodies, along grain boundaries and fractures. Goethite also replaces both hematite and magnetite, often forming colloform textures, particularly in near-surface zones. The weathering process has induced martitization of magnetite, transforming it into hematite (Figure 8).
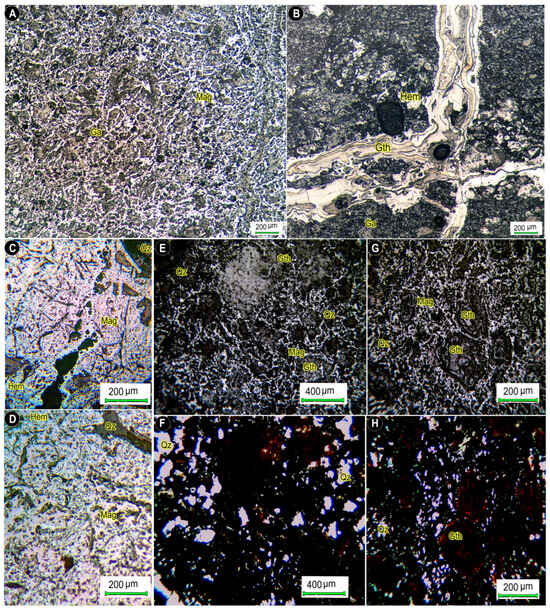
Figure 8.
Reflected light (A–E,G) and transmitted light (F,H) photomicrographs of massive magnetite (Mag) with dendritic and massive lumpy microtextures (A,E,G), and hematite (Hem) and goethite (Gth) veinlets (B). Magnetite is replaced by hematite during martitization (C,D).
In surface exposures of the ore bodies, goethite and hematite are more prevalent, while deeper sections predominantly contain magnetite. Goethite forms vein-like, colloform, and sometimes dendritic structures within fractures and void spaces affected by weathering. Although the manganese content in the mineralized layers is relatively low (less than 2%), manganese-bearing minerals, most likely high-manganese magnetite, undergo weathering. This leads to the formation of secondary manganese minerals such as pyrolusite, psilomelane, and goethite, which accumulate in weathered zones, fractures, and veinlets.
Despite the negligible manganese oxide content in the Dehbid Fe oxide deposit, SEM analyses revealed the presence of manganese oxide phases (cryptomelane and psilomelane) and iron-bearing carbonates (ankerite) associated with iron oxide layers (Figure 9).
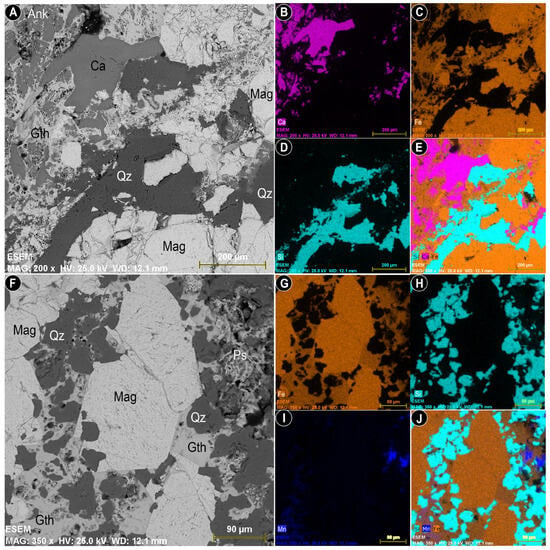
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and elemental mapping of the polished section of Fe oxide ore, Heneshk deposit. The backscattered electron images (A,F) highlight the mineralogical diversity, including calcite (Ca), quartz (Qz), magnetite (Mag), goethite (Gth), psilomelane (Ps), and ankerite (Ank). Elemental maps (B–E,G–J) display the distribution of calcium, silicon, iron, and manganese across the sample, illustrating textural relationships and mineral associations within the iron ore matrix.
The primary gangue minerals associated with the mineralization in the Dehbid iron deposits are quartz and dolomite, especially within the banded ores, where quartz forms chert bands within the ore lenses. In addition, regional metamorphism has led to the formation of secondary quartz veins, some of which are associated with iron mineralization. These secondary quartz veins can be distinguished from the primary mineralization by their coarser grain size. Furthermore, the host dolomite and schists have undergone silicification as a result of subsequent metamorphism, further altering the original mineral composition of the host rocks.
5. Sampling and Methods
Seventy-five rock samples were collected from surface outcrops at the Madkansar, Cheshme Esi, Goli, and Cheshme Sorkh deposits. Mineralogical, textural, and paragenetic investigations were conducted at the University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran, employing reflected and transmitted light microscopy. Electron microscopy studies (ESEM) were undertaken at the Queen’s Facility for Isotope Research (QFIR), Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Whole-rock major and trace element analyses of 11 samples were performed using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS; PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at the Zarazma laboratory in Tehran, Iran. Additionally, data from previous geochemical studies (Supplementary Materials Table S1; [17,18,19,20,21]) were included for comparative analysis.
The trace element analysis of magnetite was carried out using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (LA–ICP–MS) at the University of Concepción, Chile. The analysis utilized a Resonetics S-155-LR 193 mm Eximer Laser Ablation system (Resonetics, Nashua, NH, USA) coupled to an Agilent 7700x Quadrupole ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The laser’s spot size and frequency were set to 32 μm and 5 Hz, respectively. Each analysis commenced with approximately 20 s of background acquisition, followed by 40 s of data collection from the sample. Sylvester has provided an in-depth discussion on the principles, techniques, and applications of LA-ICP-MS. For LA-ICP-MS preparation, polished thin Sections (12) were mapped using Energy Dispersive Spectrometry (EDS) with a Bruker M4 Tornado micro-XRF (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA). In subsequent analysis, the polished magnetite thin sections were placed inside an airtight cell where a high-energy laser beam converted a small portion of the magnetite into an aerosol of particles. This aerosol was directed to the ICP, where it underwent vaporization, atomization, and ionization via plasma generated from helium and argon at high temperatures. The ions created within the ICP were then directed into the mass spectrometer, which sorted them based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The samples were analyzed using NIST610 (National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and BCR-2G (U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA, USA) glass as primary standards, with 56Fe as the internal standard in both cases. Results were reported in ppm, along with 2σ internal standard deviation and level of detection (LOD). The analyses incorporated a 33 μm crater, a repetition rate of 4 Hz, 30 s of ablation, 30 s of background acquisition, and a fluence of 3 J/cm2.
6. Results
Geochemistry of Iron Ores
The chemical composition of all studied samples is summarized in Supplementary Materials Table S1. As illustrated in Figure 10A, the Fe2O3 content of ore bodies varies widely from 30 to 91 wt% for magnetite–hematite ores. The MnO content of Fe ores ranges from 3.9 wt% to 57% (av. 3.9%), while P2O5 is typically low at 0.1 wt%. MgO and CaO contents in the Fe ores are also high, averaging 1.6 wt% (up to 7%) and 8% (up to 46%), respectively. The K2O and Na2O values for the iron ore samples range from 0.0 to 2.0 wt% and 0.1–3.0 wt%, respectively (Figure 10A).
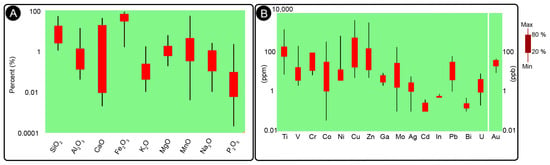
Figure 10.
Box plot illustrating the major (A) and trace (B) element concentrations in the Dehbid banded iron ore deposits, highlighting maximum, minimum, and median values across the samples.
The analyzed Fe oxide ores exhibit low concentrations of trace elements, including Cr (av. 70 ppm), Co (av. 25 ppm), Ni (av. 42 ppm), Ag (av. 2 ppm), Mo (av. 28 ppm), and Pb (av. 18 ppm). In contrast, Cu (av. 519 ppm, reaching up to 4350 ppm) and Zn (av. 194 ppm, peaking at 3270 ppm) display significantly higher concentrations (Figure 10B). Additionally, Au shows a very low concentration, with a maximum of 48 ppb in the ore deposits [20].
Supplementary Materials Table S2 presents the trace element and REE data derived from LA-ICP-MS analyses of magnetite sourced from the Madkansar mine. The findings indicate a broad spectrum of trace element concentrations (Figure 11). Although magnetite is primarily deficient in several trace elements (such as Ga, Ge, As, Nb, Mo, Ag, Sn, Pb, Bi, Zr, and W), it exhibits significantly elevated levels of Mg, Al, Si, Mn, Ti, Cu, and Zn, typically ranging from hundreds to over 10,000 ppm.
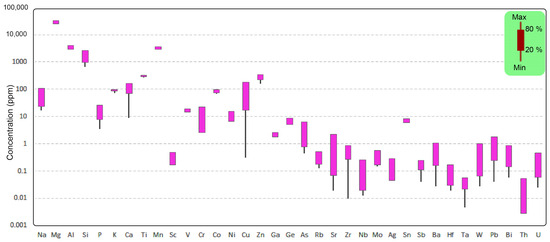
Figure 11.
A box plot illustrating the concentrations of elements in magnetite from the banded iron ore deposits in the Dehbid region.
7. Discussion
7.1. Origin and Type of Mineralization
Iron oxide (-Mn) mineralization in the Dehbid region of the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone (e.g., Heneshk, Cheshme Esi, Goli, Cheshmeh Sorkh, and Moazam deposits) is hosted in late Triassic-early Jurassic carbonates and schists, and in some areas, it is closely associated with metamorphosed rhyolitic rocks. The iron mineralization includes stratiform to stratabound orebodies, which are represented by banded, massive, laminated, as well as minor veins and veinlets (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). These orebodies are composed of magnetite, hematite, goethite, along with minor amounts of cryptomelane, psilomelane, ramsdellite, and pyrite. Both the mineralization and host rocks have undergone regional metamorphism [17,19]. However, metasomatic calc-silicates typical of skarns, such as wollastonite and diopside, are absent [17,18,20].
Previous studies of the Fe-oxide deposits in the Dehbid region have proposed both volcanic-sedimentary [17,19] and hydrothermal vein-type [20,21] origins. Considering the geometry of the mineralizations and the presence of Fe oxide-silica bands, laminated textures, and folded ore bands and laminae (Figure 5 and Figure 6) across all orebodies, vein-type, magmatic, and skarn models are ruled out for the primary mineralization. Despite the influence of deformation and metamorphic events, the consistent presence of stratiform and layered structures, along with lumpy, intermittently laminated, and banded textures, provides strong evidence for a primary sedimentary origin of the iron mineralization, characteristic of BIOs. However, metamorphic processes may account for certain aspects of the observed vein mineralization in this region.
Despite extensive research on Phanerozoic ooidal ironstone deposits (e.g., Bakchar [34] and Clinton [35]), there is a lack of information about Phanerozoic banded iron ores, particularly in Western Asia. Banded iron ores undergoing metamorphism typically exhibit complex textures due to recrystallization and compaction. Moreover, metasomatic processes and hydrothermal alteration can partially or entirely replace primary minerals [36], resulting in dense, irregular, and intricate veins [37]. Furthermore, prolonged exposure of BIOs to varying climatic conditions over geological time has facilitated both congruent and incongruent dissolution, leading to textural modifications and the development of secondary minerals and textures [36,37]. Despite these post-depositional alterations, the Dehbid iron oxide deposits retain stratiform and layered structures, as well as lumpy, and occasionally laminated and banded micro-textures. These characteristics unequivocally indicate a chemical–sedimentary origin for the iron mineralization, consistent with deposition under conditions typical of banded iron ore systems.
Although the primary textures and structures of the Dehbid banded iron ores have been overprinted by metamorphic and deformational processes, microstructural analyses of the low-grade ore bands offer valuable insights into the relationships among iron mineralization, foliation, and folding. Detailed structural analyses demonstrate that the geometric relationship of Fe oxide mineralization in relation to metamorphic foliation can be classified into three categories (Figure 4): (1) laminae that are parallel to the bedding (S0), which have become parallel to the first and second foliation (S1 and S2) due to superposition during poly folding and metamorphism (Figure 4B–G); (2) Fe oxide veinlets that are injected into or situated along oblique micro-faults, suggesting late-tectonic remobilization or fluid migration along fracture zones (Figure 4D); and (3) Fe oxide veinlets are subparallel to the S3 fracture system, indicating that mineralization locally conformed to late-stage deformation fabrics.
7.2. Geochemistry of Fe-Oxide Ores
While the whole-rock geochemistry of iron ore is not commonly employed to determine the origins of mineralization, the assessment of trace element concentrations in the Dehbid iron ores suggests a sedimentary source for the mineralization. Plots of the geochemical data for the iron ore on Mg vs. V/Ni and Ba vs. Fe diagrams reveal that the samples fall within the sedimentary iron ore field (Figure 12). Similarly, the data are situated within the sedimentary iron ore domain on the V vs. Ti vs. Ni, V vs. Ni + Co, and V/Fe vs. Ti/Fe diagrams (Figure 13).
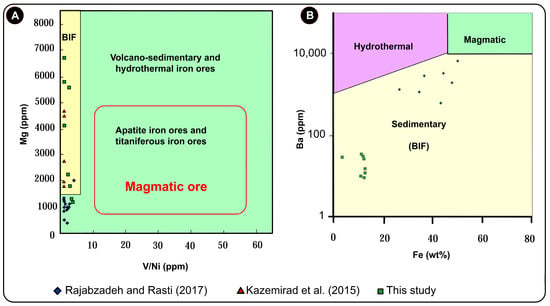
Figure 12.
The plots of whole-rock geochemistry data of iron ores from the Dehbid BIO deposits [19,20] on (A) Mg vs. V/Ni [38], and (B) Ba-Fe (after [39]) diagrams.
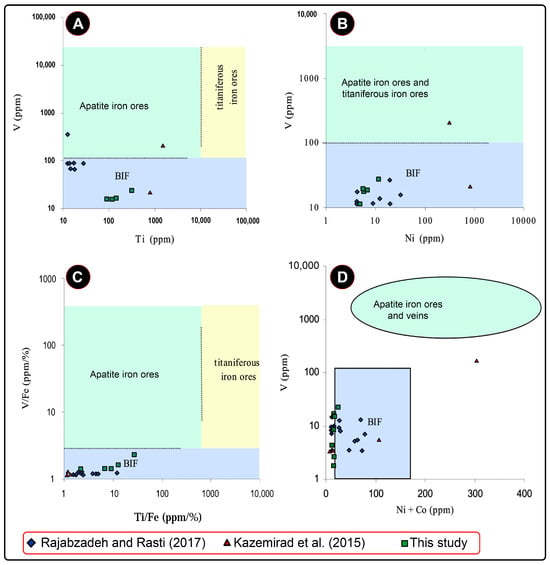
Figure 13.
The plots of whole-rock geochemistry data of iron ores from the Dehbid BIO deposits [19,20] on V vs. Ti (A), V vs. Ni (B), V/Fe vs. Ti/Fe (C), and Ba vs. Fe (D) diagrams [40].
Magnetite from hydrothermal ore deposits (including skarns) typically exhibits low concentrations of Ti (<2.3 ppm), V (<4 ppm), Ga (0.1–0.28 ppm) [39], and Sc (mean = 12 ppb) [40]. In contrast, magnetite from the Dehbid BIO deposits shows higher concentrations of Ti, ranging from 270 to 316 ppm; V, ranging from 14 to 17.5 ppm; Ga, ranging from 1.7 to 2.3 ppm; and Sc, ranging from 0.17 to 0.46 ppm. Despite the elevated Mn values of magnetite in BIO deposits (~0.3%), other geochemical values fall outside the typical range for hydrothermal magnetite, suggesting a sedimentary iron ore origin rather than a magmatic–hydrothermal genesis in the Dehbid deposits.
Comparing trace element concentrations among different ore deposit types, it is noted that magnetite from Fe-skarn deposits displays significantly lower Cu and Zn concentrations, averaging approximately 20 and 185 ppm, respectively [41,42]. In the Dehbid BIO deposits, the Cu concentration in the magnetite ranges from 0.3 to 178 ppm (av. 73 ppm), and the Zn concentration in magnetite ranges from 160 to 333 ppm (av. 258 ppm). However, these values resemble the magnetite geochemistry of Cu and Zn-rich skarn deposits; they are higher than those of Fe-skarn and other hydrothermal Fe oxide deposits, and correlate strongly with concentrations of Cu and Zn found in volcanic-sedimentary sequences [41].
Various classification diagrams have been developed to distinguish the genesis of magnetite based on its characteristic trace element composition [43,44,45]. Although each of these diagrams has inherent limitations, they remain highly informative for interpreting the origin of magnetite [45,46]. In the V vs. Ti, V vs. Ni, V vs. Ni+Co, and V/Fe vs. Ti/Fe diagrams (Figure 14), all magnetite samples from the study area consistently plot within the sedimentary field.
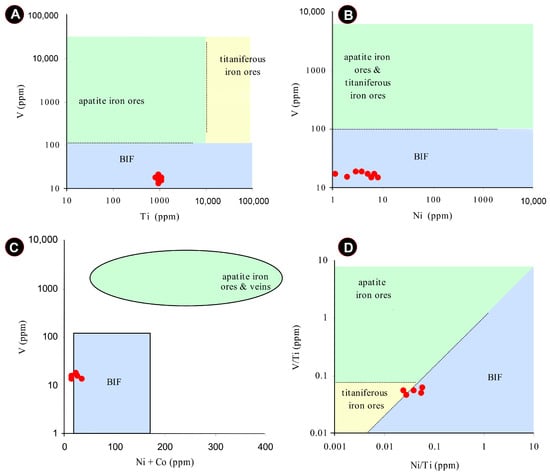
Figure 14.
The plots of whole-rock geochemistry data of iron ores from the Dehbid BIO deposits on V vs. Ti (A), V vs. Ni (B), V vs. Ni+Co (C), and V/Ti vs. Ni/Ti (D) diagrams [40].
Magnetite from banded iron formations (BIFs) typically exhibits low and consistent trace element levels, reflecting its sedimentary origin and limited post-depositional changes [37]. LA-ICP-MS analysis shows that the magnetite in Dehbid banded iron ores maintains low and uniform trace element levels, aside from unusual amounts of Mg, Al, and Mn, suggesting the influence of terrigenous or volcaniclastic impurities. Generally, trace element levels remain stable from greenschist to granulite facies [47]; however, high-grade and retrogressive metamorphism can alter the overall elemental composition of Fe oxide ore and magnetite [48]. Elements such as Fe, Al, K, Mg, and Mn can undergo modifications during diagenetic or subsequent metamorphic processes, particularly when the orebodies are linked to clastic and volcanic components [47].
Hydrothermal processes can also modify the trace element composition of magnetite in BIOs. For example, in the Beebyn deposit of the Yilgarn Craton [49], Western Australia, hypogene fluids led to the replacement of silica-rich bands in BIO by siderite and magnetite, followed by ferroan dolomite. This process resulted in carbonate-altered BIOs markedly depleted in SiO2 and enriched in CaO, MgO, P2O5, and Fe2O3 (total) compared to the least-altered BIO. Dehbid’s BIOs represent a low content of P2O5 (0.1 wt%), but the MgO and CaO contents in the mineralized rocks are high (av. 1.6 wt%, up to 7%, and av. 8%, up to 46%), respectively. The significant increase in CaO and MgO suggests that the Dehbid BIOs have experienced considerable hydrothermal/metamorphic alteration, likely due to the influx of carbonate-rich fluids, similar to what is observed in the Beebyn system. Nevertheless, the relatively low P2O5 levels in Dehbid samples might indicate either a lower phosphate mobility during the alteration or a variation in fluid composition. The elevated carbonate levels, along with iron enrichment and the retention of stratiform and banded textures, imply that the original sedimentary characteristics of the BIO were altered by later metasomatic processes, leading to a partial substitution by hydrothermal magnetite and carbonate minerals. This interpretation is consistent with the geochemical characteristics identified in other hydrothermally altered BIO-hosted iron systems.
In summary, the trace element composition of magnetite significantly differs from that of magnetite associated with magmatic–hydrothermal genesis, aligning with the banded iron ore deposits of the Dehbid iron deposits.
7.3. Metallotectonic Setting and Formation of Banded Iron Ores
Despite their metallogenic significance, the BIOs in Iran have received limited detailed investigation. The most notable BIO occurrences have been reported from Central Iran [50,51], the Takab area [52], southeastern Gol Gohar, Hormuz Island, the Bandar Abbas region [53], and northern Posht-e-Badam. These deposits are predominantly hosted within late Precambrian to early Cambrian volcano-sedimentary sequences. In addition to BIOs, stratiform exhalative iron–manganese deposits have been documented from various geological periods, including the early Cambrian (e.g., Narigan), Jurassic (e.g., Dom Siyah and Halalan), early Cretaceous (e.g., Sorkhvand and Nasirabad), Paleogene (e.g., Menamin and Sardar), and Neogene (e.g., Garab and Zarashlou) [16]. These deposits are distinct from classic BIOs, primarily due to their higher manganese content and genetic affinity with volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS)-type systems. Notably, all of these iron-bearing deposits exhibit a strong genetic association with submarine volcanic activity and appear to have developed within back-arc extensional basins, characterized by a volcano-sedimentary sequence [1,16,54].
The host basins are associated with rift-fill sequences that commonly contain VMS-type mineralization, indicating that iron deposition was closely linked to hydrothermal processes associated with active submarine volcanism in extensional tectonic environments. This close spatial and temporal relationship between BIOs, iron–manganese exhalative deposits, and VMS systems in Iran underscores the shared tectono-magmatic controls on their formation. It suggests that iron deposition in these settings was primarily driven by hydrothermal activity at or near the seafloor, superimposed on a volcanogenic sedimentary environment.
The Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone (SSZ) is one of Iran’s most important tectono-metallogenic belts, reflecting a complex geodynamic history shaped by the convergence and collision of the Arabian and Iranian plates [6,55]. Initially, the SSZ was influenced by the northward subduction of the Neo-Tethys oceanic lithosphere beneath the Iranian plate following the closure of the Paleo-Tethys in the late Triassic, north of the Iranian plate (Figure 1B, [29,55,56]). This subduction triggered substantial arc magmatism and back-arc extension from the late Triassic to early Cretaceous, as corroborated by the presence of tholeiitic and calc-alkaline magmatic rocks, extensional sedimentary basins, and geochemical signatures indicative of a subduction-related environment [55,57,58,59,60,61]. Several studies confirm the existence of a back-arc extensional environment between the SSZ and the Central Iranian Microcontinent during this period [30,55,60,62]. For instance, the geodynamic models, paleogeographic and paleotectonic reconstructions, integrated with geological mapping efforts [63,64,65,66], and tectonostratigraphic and structural syntheses [6,24,55,66], suggest the development of a back-arc extensional basin between the SSZ and Central Iran during the Jurassic period, leading to the formation of the Naein-Baft extensional basin.
Recent studies by Mousivand et al. [67,68] focused on the Bavanat region southeast of the Dehbid area, further corroborate this model. Their research documents the formation of volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits, characterized by felsic-siliciclastic and pelitic-mafic affinities, within a Jurassic volcano-sedimentary succession. U–Pb geochronology from the region provides age constraints for the meta-rhyodacites at 175.7 ± 1.7 Ma and for the metasandstones at 191 ± 12 Ma, likely representing the depositional ages of bimodal volcanic rocks associated with Jurassic back-arc rifting.
Analogous to Algoma-type banded iron formations, which are commonly interpreted to have formed in back-arc tectonic settings [69], the Dehbid BIOs are similarly considered to have developed under comparable geodynamic conditions. A critical distinction, however, lies in the redox state of the depositional environment. Whereas modern oceans are predominantly oxic, the late Triassic–Jurassic back-arc basin in which the Dehbid BIOs formed likely sustained anoxic and ferruginous water column conditions. These environmental factors, coupled with elevated submarine hydrothermal iron fluxes, were crucial in iron precipitation and the formation of the Dehbid BIO-type deposits. While BIF deposits are typically associated with the Precambrian and early Phanerozoic strata [70], some banded Fe-Mn ores have also been reported in later geological periods, including the Mesozoic. Notably, late Permian and Jurassic manganese–iron oxide deposits have been documented in the Um Irna Formation, NW Jordan [7], and in Central Europe [9]. The presence of manganese carbonates in shallow marine environments during the Early Jurassic has been recognized in Central Europe, particularly in regions such as Germany and Hungary, where similar anoxic conditions are believed to have facilitated manganese mineralization. These deposits are generally found in anoxic or semi-anoxic environments, particularly in areas associated with active submarine volcanism and low-oxygen depositional settings. In these regions, changes in chemical conditions and temperature likely resulted in the deposition of manganese–iron ores in stratiform layers, with manganese carbonates and iron minerals forming within sedimentary layers [7,9,70]. These deposits are typically found in sedimentary basins characterized by active volcanic activity and semi-enclosed or restricted marine environments, where redox fluctuations have been documented [7,9,70]. Localized reducing environments may have developed within rift-related back-arc basins. Fe-Mn mineralization evolved from cooler hydrothermal fluids distal from active vents in the basin. In such settings, submarine volcanism could introduce substantial hydrothermal iron into the basin waters. The subsequent oxidation of these iron-rich fluids, driven by intermittent oxygenation of the water column or basin ventilation, could result in the precipitation of iron oxides and Fe-Mn rich sediments, leading to the formation of banded iron ore deposits. For the precipitation of iron in oxide form, the depositional environment must be devoid of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), as its presence would favor the formation of iron sulfides instead, thereby preventing the accumulation of iron oxides. These processes suggest that BIO-type iron deposits can form during the Phanerozoic under specific geodynamic and oceanographic conditions, particularly in tectonically active back-arc environments characterized by episodic redox fluctuations.
The subduction of the Neo-Tethyan oceanic lithosphere beneath the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone from the Triassic to the Eocene, along with the post-late Cretaceous closure of back-arc basins, triggered multiple compressional phases in this structural zone. These events led to successive deformation and metamorphism of the SSZ sequences, reflecting a complex tectono-metamorphic evolution shaped by arc magmatism, crustal shortening, and back-arc basin closure [24,32,55,71]. As outlined by some researchers [72,73], the SSZ underwent at least three significant compressional phases. The initial phase, spanning from the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene, featured tight folding, regional metamorphism, and the formation of slaty cleavage alongside axial-plane foliation. The second phase, occurring during the Eocene to Oligocene, is associated with a soft collision, which introduced crenulation cleavage and extensive transpressional tectonics. The concluding phase, the hard collision in the Miocene, led to considerable crustal shortening, high-angle faulting, and the alteration of earlier ductile fabrics by brittle structures.
The dual evolution—spanning extensional arc and back-arc environments during the late Triassic to early Cretaceous and transitioning to compressional regimes from the Late Cretaceous onward—has made the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone a structurally intricate and metallogenically rich area. This tectonic history offers essential insights into the broader processes of Tethyan oceanic development, continental collision, and crustal reworking within the Alpine–Himalayan orogenic belt.
8. Conclusions
This study provides important insights into the origin of the iron oxide deposits from the Dehbid region, refuting the hypothesis of vein-like or hydrothermal genesis. Extensive fieldwork and detailed structural studies reveal these deposits’ stratiform and sedimentary nature, supported by complex stratigraphy and distinct layering, contrasting with previous interpretations pointing to an epigenetic origin. In this district, the BIO developed in stratiform layers and bands, parallel to the late Triassic-early Jurassic silicified dolomites and schists. These deposits have been subjected to thrusting and deformation processes associated with subsequent tectonic events.
The whole-rock element composition of iron ores (ICP-MS) and LA-ICP-MS of magnetite provides a robust proxy to assert a synsedimentary origin. The trace element signatures in the orebodies and magnetite reflect influences and conditions typically associated with marine sedimentary environments.
This research highlights the need for robust, integrated geological field studies with advanced analytical techniques, to revise existing models of deposit formation. Future work should focus on detailed geological mapping and geochemical analysis to enhance understanding of sedimentary processes in ore deposition, which could inform mineral exploration strategies in similar geological settings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15060590/s1, Table S1: Summary of geochemical analyses (ICP-MS and XRF) conducted on iron oxide ore samples from the Dehbid mining district. This includes data from the present study and comparative results from previous works [19,20]. Table S2: Trace element concentrations (in ppm) in magnetite were determined by LA-ICP-MS analysis on selected samples from the Dahbid iron oxide deposits. Detailed analytical procedures, including instrument settings and calibration standards, are described in the Section 5.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization A.R., R.N., S.M., S.N. and S.R. (Shahrokh Rajabpour); investigation, A.R., R.N., S.M., S.N., A.K.M., M.K., M.A., P.M. and O.L.F.; data curation, A.R., S.R. (Shahrokh Rajabpour), C.C., P.A., S.R. (Somaye Rezaei), P.M. and R.N.; provided reagents/materials/data, A.R., S.M., S.R. (Shahrokh Rajabpour) and O.L.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R., R.N. and S.R. (Somaye Rezaei); writing—review and editing, A.R, R.N, C.C., P.A., S.R. (Shahrokh Rajabpour) and A.M.; project administration, A.R. and R.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a research grant from the University of Tehran, Iran, under grant number 99/10204.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article, and the analytical data supporting the findings of this study are provided in the Supplementary Materials available online.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank IMPASCO and Parsi Kankav companies for granting access to information and facilitating fieldwork. The authors sincerely thank Matthew Leybourne and Agatha Dobosz for their invaluable support and assistance in conducting the SEM analyses in QFIR, Queen’s University.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Ahmad Kazemi Mehrnia was employed by the Parsi Kankav company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Nabatian, G.; Rastad, E.; Neubauer, F.; Honarmand, M.; Ghaderi, M. Iron and Fe–Mn mineralisation in Iran: Implications for Tethyan metallogeny. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 62, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2024. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/publication/mcs2024 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- NGDIR. Statistical Report of Iron Status in Iran; National Geoscience Database of Iran (NGDIR): Tehran, Iran, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baturin, G.N. Manganese and Molybdenum in Phosphorites from the Ocean. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2002, 37, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H. Terrestrial ferromanganese ore concentrations from mid-european basement blocks and their implication concerning the environment of formation during the late cenozoic (northern Bavaria, F.R.G.). Sediment. Geol. 1985, 45, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G.; Pöllmann, H.; Techmer, A. 500Million years of rift- and unconformity-related Mn mineralization in the Middle East: A geodynamic and sequence stratigraphical approach to the recycling of Mn. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 53, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G.; Bechtel, A.; Kus, J.; Gratzer, R.; Abu Hamad, A.M.B. Deposition and alteration of carbonaceous series within a Neotethyan rift at the western boundary of the Arabian Plate: The Late Permian Um Irna Formation, NW Jordan, a petroleum system. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 81, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzmer, J. Cretaceous Karstic Cave-Fill Manganese-Lead-Barium Deposits of Imini, Morocco. Econ. Geol. 2006, 101, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkyns, H.C.; Géczy, B.; Marshall, J.D. Jurassic Manganese Carbonates of Central Europe and the Early Toarcian Anoxic Event. J. Geol. 1991, 99, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, P.R. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of an Epithermal Manganese District, Sierras Pampeanas, Argentina. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzmer, J.; Beukes, N.J. Fault-controlled metasomatic alteration of early Proterozoic sedimentary manganese ores in the Kalahari manganese field, South Africa. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 823–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzmer, J.; Beukes, N.J. Mineral paragenesis of the Kalahari managanese field, South Africa. Ore Geol. Rev. 1996, 11, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikos, H.; Beukes, N.J.; Moore, J.M.; Harris, C. Deposition, Diagenesis, and Secondary Enrichment of Metals inthe Paleoproterozoic Hotazel Iron Formation, Kalahari Manganese Field, South Africa. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, V.N. A superlarge deposit—Kalahari manganese ore field (Northern Cape, South Africa): Geochemistry of isotopes (δ13C and δ18O) and genesis. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2012, 47, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madondo, J.; Canet, C.; González-Partida, E.; Rodríguez-Díaz, A.A.; Núñez-Useche, F.; Alfonso, P.; Rajabi, A.; Pi, T.; Blignaut, L.; Vafeas, N. Geochemical constraints on the genesis of the ‘Montaña de Manganeso’ vein-type Mn deposit, Mexican Plateau. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghfouri, S.; Rastad, E.; Movahednia, M.; Lentz, D.R.; Reza Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ye, L.; Mousivand, F. Metallogeny and temporal–spatial distribution of manganese mineralizations in Iran: Implications for future exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Niroomand, S.; Nozaem, R. Investigation of Metallogeny and Mineralization Potential of the Northern Fars Region, Southwest of the Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone and Northwest Zagros; IMPASCO (Iran Minerals Production and Supply Company): Tehran, Iran, 2023; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabzadeh, M.A.; Rasti, S. Mineralization of Iron Deposits from Dehbid Area, Fars Province, South Iran: Geochemical and Mineralogical Data. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress for Applied Mineralogy (ICAM); Broekmans, M.A.T.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 567–574. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-642-27682-8_67 (accessed on 1 January 2012).
- Kazemirad, M.; Rastad, E.; Mohajjel, M. Fe-Mn Mineralization in Dolomites Equivalent to Shotori Formation in NE of Dehbid, Southern Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone, Fars Province. Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2015, 24, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, M.A.; Rasti, S. Investigation on mineralogy, geochemistry and fluid inclusions of the Goushti hydrothermal magnetite deposit, Fars Province, SW Iran: A comparison with IOCGs. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 82, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, M.A.; Rasti, S. Mineralization study on Dehbid magnetite deposit, Fars; using mineralogical and geochemical data. J. Econ. Geol. 2012, 3, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Canet, C.; Alfonso, P.; Mahmoodi, P.; Yarmohammadi, A.; Sharifi, S.; Mahdavi, A.; Rezaei, S. Mineralization and Structural Controls of the AB-Bid Carbonate-Hosted Pb-Zn (±Cu) Deposit, Tabas-Posht e Badam Metallogenic Belt, Iran. Minerals 2022, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanabati, A. Major Sedimentary and Structural Units of Iran (Map). Geosciences 1998, 7, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Madanipour, S.; Najafi, M.; Nozaem, R.; Vergés, J.; Yassaghi, A.; Heydari, I.; Khodaparast, S.; Soudmand, Z.; Aghajari, L. The Arabia–Eurasia collision zone in Iran: Tectonostratigraphic and structural synthesis. J. Pet. Geol. 2024, 47, 123–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, M.; King, G.C.P. Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1981, 18, 210–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, A. Evidences for formation of the Precambrian crust in the Takab complex, northwest Iran (review). Petrol. J. 2018, 9, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarzadeh, E.; Masoudi, F.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Pourmoafi, S.M. The presence of Precambrian basement in Gole Gohar of Sirjan (south of Iran). Petrol. J. 2016, 7, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Talbot, C.J. A new tectonic scenario for the Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone (Iran). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 26, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Stampfli, G.M. The Anarak, Jandaq and Posht-e-Badam metamorphic complexes in central Iran: New geological data, relationships and tectonic implications. Tectonophysics 2008, 451, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Jahangiri, A. Cretaceous subduction-related volcanism in the northern Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone, Iran. J. Geodyn. 2008, 45, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, A.; Taraz, H.; Zamani Pedram, M.; Alavi, M. Geological Map of the Dehbid Area, Scale. 1:100,000; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkarinejad, K.; Azizi, A. Slip partitioning and inclined dextral transpression along the Zagros Thrust System, Iran. J. Struct. Geol. 2008, 30, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passchier, C.W.; Trouw, R.A.J. Microtectonics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudmin, M.; Banerjee, S.; Maximov, P.; Novoselov, A.; Trubin, Y.; Smirnov, P.; Abersteiner, A.; Tang, D.; Mazurov, A. Origin of ooids, peloids and micro-oncoids of marine ironstone deposits in Western Siberia (Russia). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 237, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, E.J.; Pufahl, P.K. Clinton ironstone revisited and implications for Silurian Earth system evolution. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 215, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varajao, C.A.C.; Bruand, A.; Ramanaidou, E.R.; Gilkes, R.J. Microporosity of BIF hosted massive hematite ore, Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Ann. Braz. Acad. Sci. 2002, 74, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Slack, J.F.; Planavsky, N.; Krapez, B.; Hofmann, A.; Konhauser, K.O.; Rouxel, O.J. Iron Formation: The Sedimentary Product of a Complex Interplay among Mantle, Tectonic, Oceanic, and Biospheric Processes. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystroem, J.O.; Henriquez, F. Magmatic features of iron ores of the Kiruna type in Chile and Sweden; ore textures and magnetite geochemistry. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 820–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.J.; Solomon, M.; Walshe, J.L. The genesis of sediment-hosted, exhalative zinc + lead deposits. Miner. Depos. 1981, 16, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loberg, B.E.H.; Horndahl, A.-K. Ferride geochemistry of Swedish precambrian iron ores. Miner. Depos. 1983, 18, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Shi, X.; Ji, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Deng, H. The Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the Magnetite and Fe Isotope Geochemistry of the Makeng Iron Deposit in Southwest Fujian and Their Significance in Ore Genesis. Minerals 2024, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.F.; Shao, J.L. Typomorphic Characteristics and Practical Significance of Magnetite. Geochem. Explor. 1979, 23, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nadoll, P.; Angerer, T.; Mauk, J.L.; French, D.; Walshe, J. The chemistry of hydrothermal magnetite: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 61, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Konhauser, K.O.; Robbins, L.J. Geology and geochemistry of the high-grade Zankan magnetite ore, Western Kunlun Mountains, NW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 150, 105129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lentz, D.; Li, J.; Hall, D. Re-equilibration Processes of Magnetite from Iron Skarn Deposits. In Proceedings of the Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, the 14th Quadrennial International Association on the Genesis of Ore Deposits Symposium, Kunming, China, 19–22 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nadoll, P. Geochemistry of Magnetite from Hydrothermal Ore Deposits and Host Rocks: Case Studies from the Proterozoic Belt Supergroup, Cu-Mo-Porphyry + Skarn and Climax-Mo Deposits in the Western United States. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Manikyamba, C. Petrology and Geochemistry of Mixed Oxide-Silicate Facies Banded Iron Formations from Sandur Schist Belt, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 1998, 52, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, C.; Bagas, L.; Duan, H. Modified magnetite and hydrothermal apatite in banded iron-formations and implications for high-grade Fe mineralization during retrogressive metamorphism. Am. Mineral. 2024, 109, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duuring, P.; Hagemann, S. Leaching of silica bands and concentration of magnetite in Archean BIF by hypogene fluids: Beebyn Fe ore deposit, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabi, A.; Atapour, H.; Mohseni, S.; Babaki, A. Geochemical discrimination among different types of banded iron formations (BIFs): A comparative review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.; Aftabi, A. Structural, textural, geochemical and isotopic signatures of synglaciogenic Neoproterozoic banded iron formations (BIFs) at Bafq mining district (BMD), Central Iran: The possible Ediacaran missing link of BIFs in Tethyan metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Boudouma, O.; Rividi, N.; Orberger, B.; Nabatian, G.; Honarmand, M.; Monsef, I. Magnetite Texture and Geochemistry in the Takab Ore Deposit (NW Iran): Implications for a Complex Hydrothermal Evolution. Minerals 2025, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, F.; Atapour, H.; Ranjbar, H. The Ediacaran metamorphosed banded iron formation (BIF) at Gohar Zamin mine (Gol-e-Gohar #3 anomaly), Sirjan (southeastern Iran): Perspective from ore structures, bulk ore-rock geochemistry and O-S-Pb isotopic signatures. Precambrian Res. 2023, 394, 107124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Canet, C.; Rastad, E.; Alfonso, P. Basin evolution and stratigraphic correlation of sedimentary-exhalative Zn–Pb deposits of the Early Cambrian Zarigan–Chahmir Basin, Central Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 328–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajjel, M.; Fergusson, C.L. Jurassic to Cenozoic tectonics of the Zagros Orogen in northwestern Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Nouri, F.; Stern, R.J.; Azizi, M.; Lucci, F.; Asahara, Y.; Zarinkoub, M.H.; Chung, S.L. New evidence for Jurassic continental rifting in the northern Sanandaj Sirjan Zone, western Iran: The Ghalaylan seamount, southwest Ghorveh. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 62, 1635–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemei, M.; Arvin, M.; Dargahi, S. Geochemistry and source characteristics of Dehsard mafic volcanic rocks in the southeast of the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, Iran: Implications for the evolution of the Neo-Tethys Ocean. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 27, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomali, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Ghassemi, M.R.; Moosavi, E.; Slama, J. Petrography, U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Varcheh intrusions: Insight into younging trend of mid-Cretaceous subduction in the northern Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone, western Iran. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 2156–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.A.; Tadayon, M. Early Cretaceous sedimentary provenance and structural evolution of the central Sanandaj–Sirjan Zone, Iran: Implications for palaeogeographic reconstructions of the northern Neo-Tethyan margin. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 62, 1359–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Rastad, E.; Niroomand, S.; Canet, C.; Alfonso, P.; Shabani, A.A.T.; Yarmohammadi, A. Comments on “Dehydration of hot oceanic slab at depth 30–50 km: Key to formation of Irankuh-Emarat Pb-Zn MVT belt, Central Iran” by Mohammad Hassan Karimpour and Martiya Sadeghi. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.; Rastad, E.; Canet, C. Metallogeny of Cretaceous carbonate-hosted Zn–Pb deposits of Iran: Geotectonic setting and data integration for future mineral exploration. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 54, 1649–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larvet, T.; Le Pourhiet, L.; Agard, P. Evolution of Strain Patterns in Deforming Upper Plates in Subduction Zones: The Case Study of Cretaceous Extension in the Iranian Plateau. 2021. Available online: https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU21/EGU21-11949.html (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Stern, R.J.; Moghadam, H.S.; Pirouz, M.; Mooney, W. The Geodynamic Evolution of Iran. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 49, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotese, C.R. An Atlas of Phanerozoic Paleogeographic Maps: The Seas Come In and the Seas Go Out. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 49, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, P.; Omrani, J.; Jolivet, L.; Whitechurch, H.; Vrielynck, B.; Spakman, W.; Monié, P.; Meyer, B.; Wortel, R. Zagros orogeny: A subduction-dominated process. Geol. Mag. 2011, 148, 692–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrier, E.; Vrielynck, B. Paleotectonic Maps of the Middle East Basin Evolution (MEBE) Program, Scale 1: 18,500,000: Paris; CNRS-Université Pierre et Marie Curie: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mousivand, F.; Rastad, E.; Meffre, S.; Peter, J.M.; Mohajjel, M.; Zaw, K.; Emami, M.H. Age and tectonic setting of the Bavanat Cu–Zn–Ag Besshi-type volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, southern Iran. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 911–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousivand, F.; Rastad, E.; Meffre, S.; Peter, J.M.; Solomon, M.; Zaw, K. U–Pb geochronology and Pb isotope characteristics of the Chahgaz volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit, southern Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 1239–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Planavsky, N.J.; Krapež, B.; Rasmussen, B.; Hofmann, A.; Slack, J.F.; Rouxel, O.J.; Konhauser, K.O. Iron Formations: Their Origins and Implications for Ancient Seawater Chemistry. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 561–628. [Google Scholar]
- Mücke, A. The Nigerian manganese-rich iron-formations and their host rocks—From sedimentation to metamorphism. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005, 41, 407–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, J.M.; Moazzen, M.; Rahghoshay, M.; Moghadam, H.S. The Geodynamic setting of the Nain ophiolites; Central Iran: Evidence from chromian spinels in the chromitites and associated rocks. Ofioliti 2011, 36, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikholeslami, M.R. Tectono-stratigraphic evidence for the opening and closure of the Neotethys Ocean in the southern Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, Iran. In Tectonic Evolution, Collision, and Seismicity of Southwest Asia; Smith, S.A.F., Handy, M.R., Horton, B.K., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikholeslami, M.R.; Ghassemi, M.R.; Hassanzadeh, J. Tectonic evolution of the hinterland of the Zagros Orogen revealed from the deformation of the Golpaygan Metamorphic Complex, Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 182, 103929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).