Petrogenesis of Mafic–Ultramafic Cumulates in the Mayudia Ophiolite Complex, NE Himalaya: Evidence of an Island Arc Root in Eastern Neo-Tethys
Abstract
1. Introduction
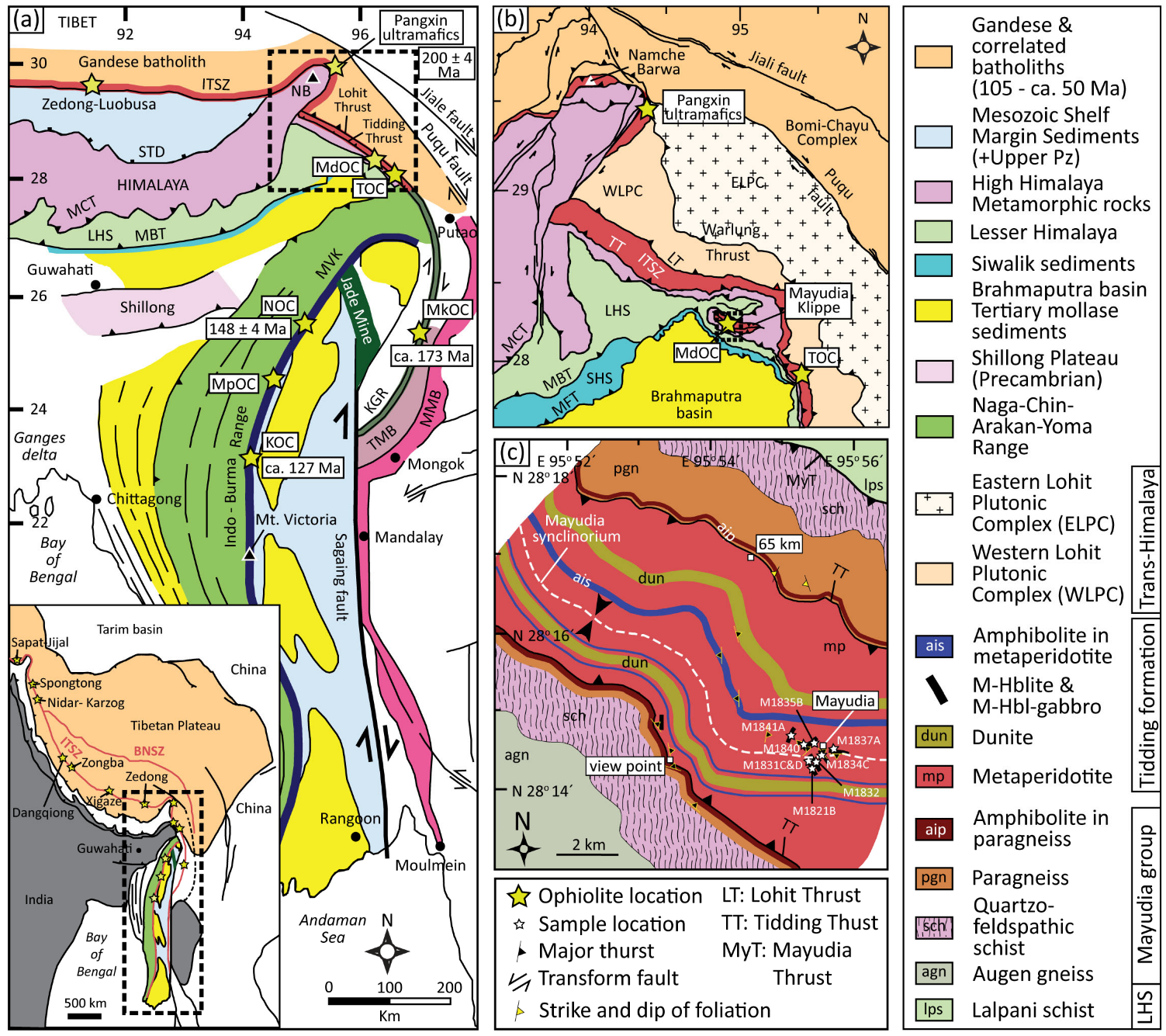
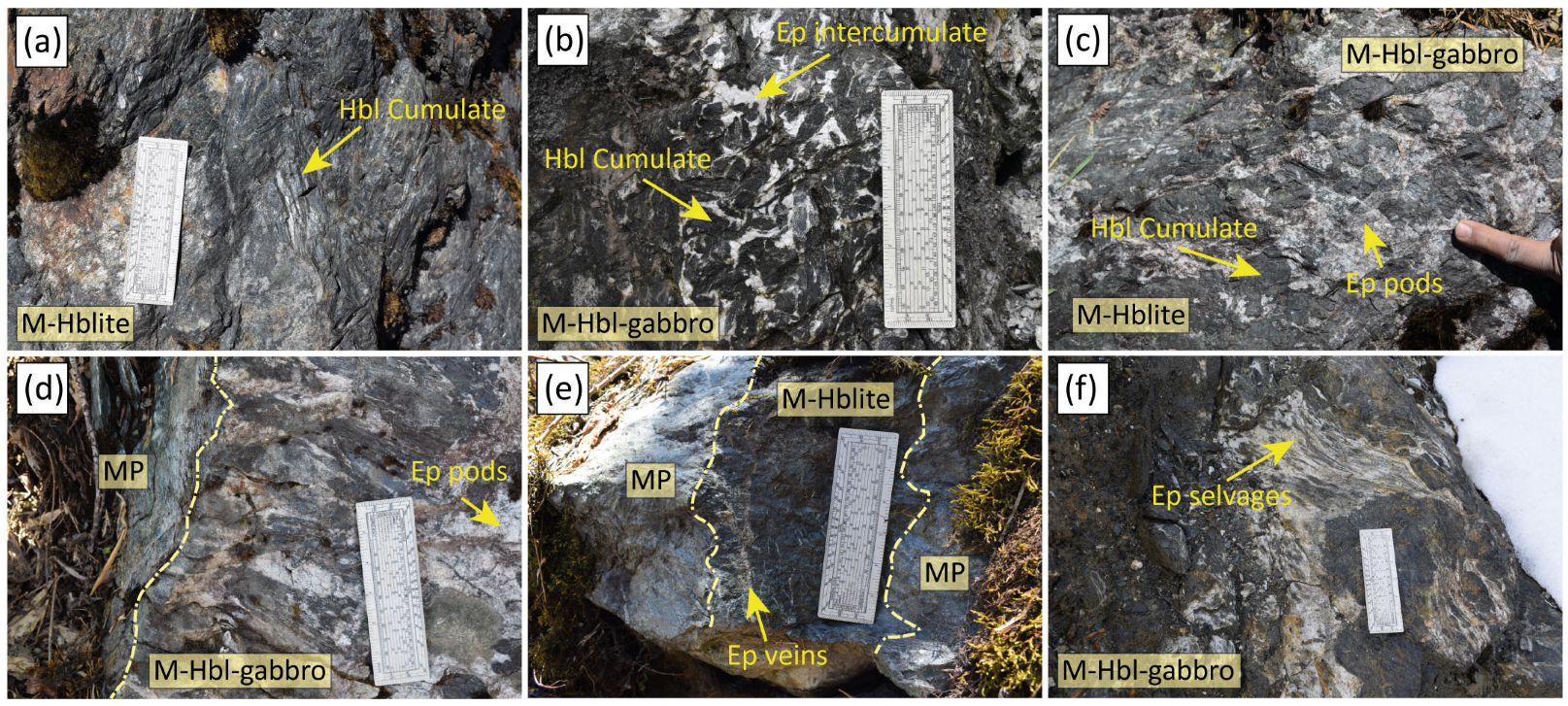
2. Geological Background and Field Relationships
3. Analytical Techniques
4. Results
4.1. Petrography and Mineral Chemistry
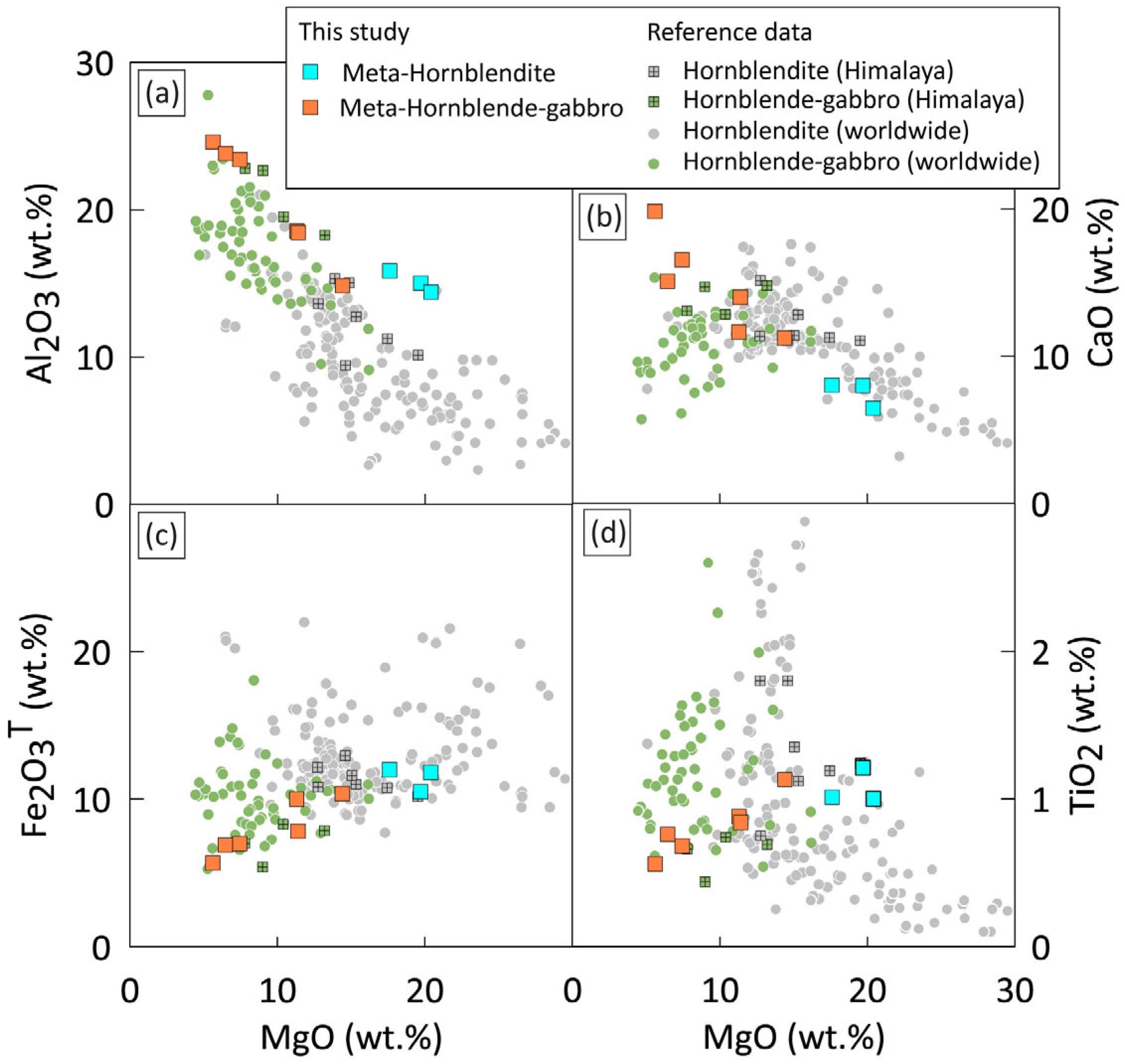
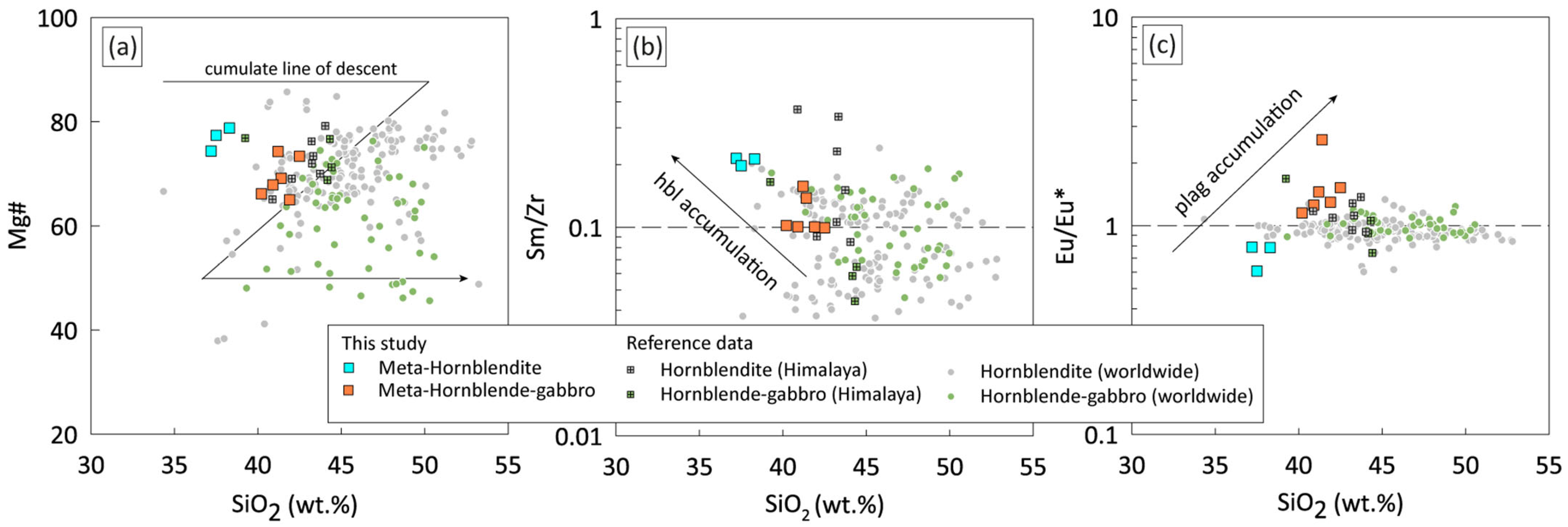
4.2. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
4.3. Sr-Nd Isotope Signatures
5. Discussion
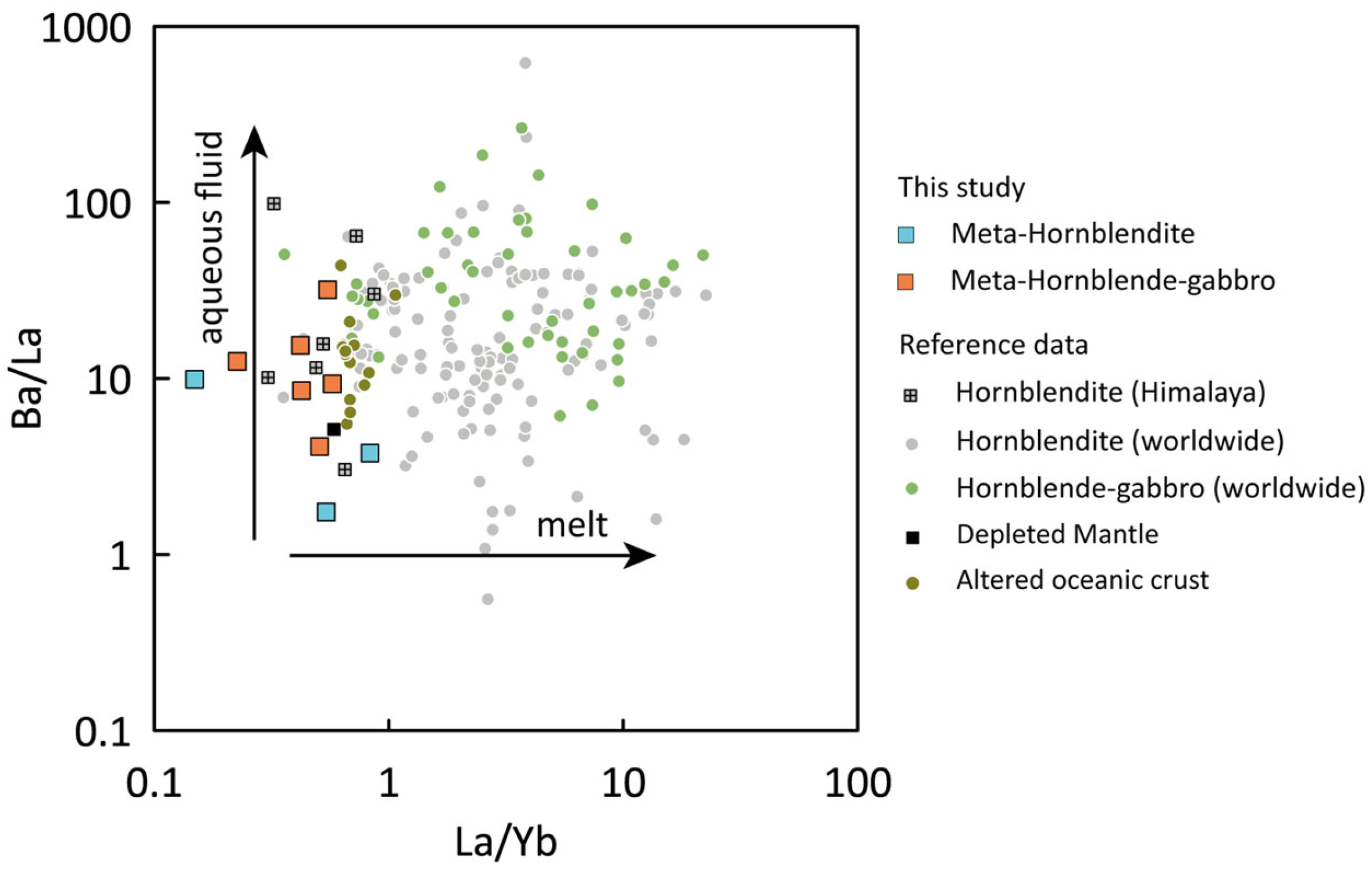
5.1. Protolith Signatures
5.2. Physico-Chemical Conditions
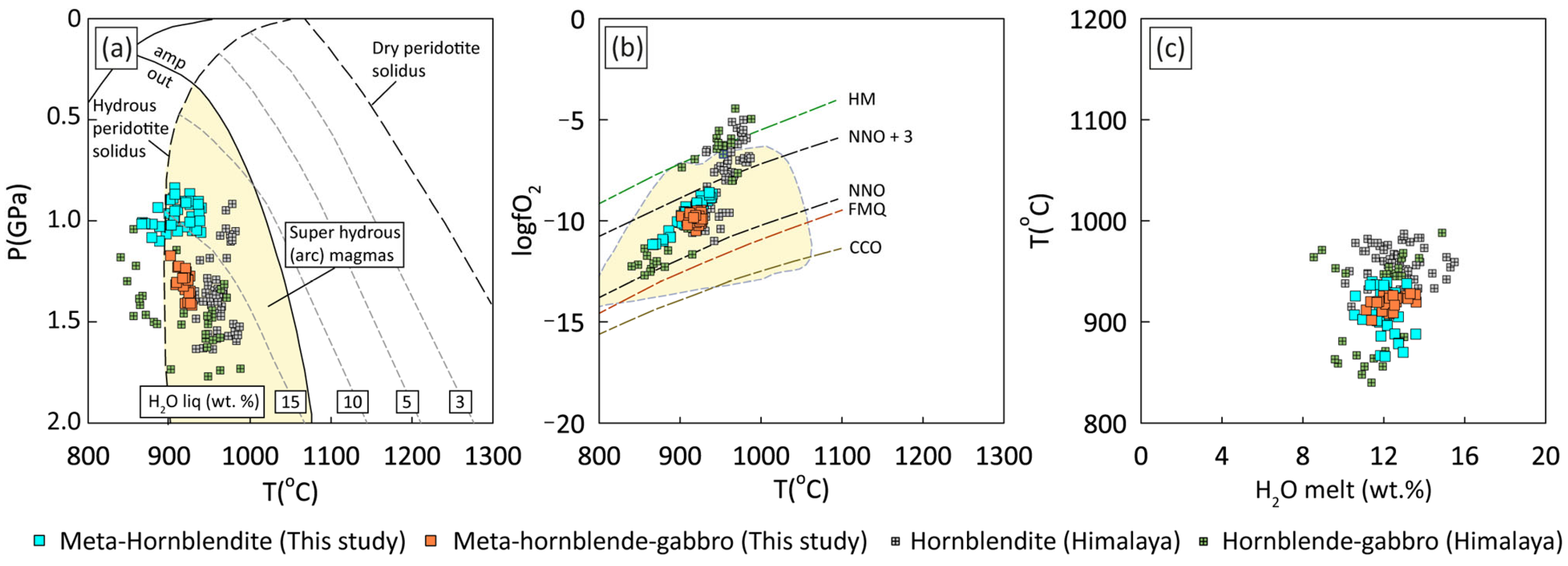
5.3. Parental Magma Characteristics
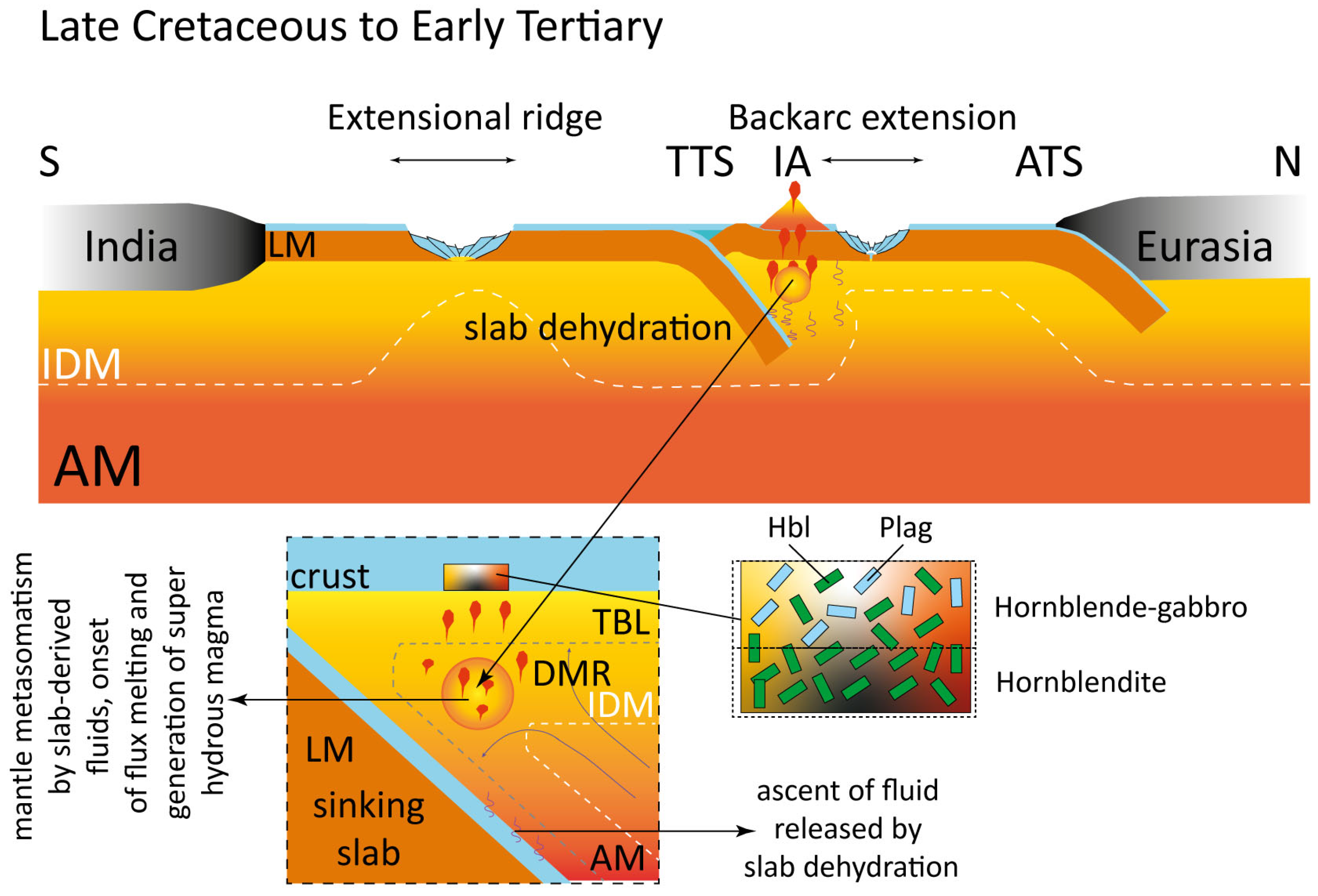
5.4. Geodynamic Implications
6. Conclusions
- The cumulate lithologies in the MdOC complex varies from hornblendite to hornblende-gabbro, where hornblendite originated prior to hornblende-gabbro due to earlier crystallization of amphibole than plagioclase.
- Constituent amphiboles have crystallized in a stable physico-chemical condition (T: 865–940 °C, P: 0.8–1.4 GPa, logfO2: −8.59–−11.19 unit) at a lower crustal depth (30–38 km) from a super hydrous (H2O in melt: 10.56–13.61 wt.%) parental magma, which was, in turn, produced due to the flux melting of sub-arc mantle with aqueous inputs from the dehydrating subducting slab.
- The MdOC cumulates preserve the root of an island arc complex and signify the presence of super hydrous sub-arc mantle reservoirs in the eastern Neo-Tethys Ocean, which have potentially controlled the composition of arc magmas and crust during intraoceanic subduction.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhuime, B.; Bosch, D.; Bodinier, J.-L.; Garrido, C.; Bruguier, O.; Hussain, S.S.; Dawood, H. Multistage Evolution of the Jijal Ultramafic–Mafic Complex (Kohistan, N Pakistan): Implications for Building the Roots of Island Arcs. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 261, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Fryer, B.J.; Samson, I.M.; Weisener, C.; Appel, P.W.; Frei, R.; Windley, B.F. Geochemistry of Ultramafic Rocks and Hornblendite Veins in the Fiskenæsset Layered Anorthosite Complex, SW Greenland: Evidence for Hydrous Upper Mantle in the Archean. Precambrian Res. 2012, 214, 124–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Turner, S.; Handley, H.; Macpherson, C.; Dosseto, A. Amphibole “Sponge” in Arc Crust? Geology 2007, 35, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Furnes, H. Ophiolite Genesis and Global Tectonics: Geochemical and Tectonic Fingerprinting of Ancient Oceanic Lithosphere. Bulletin 2011, 123, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batanova, V.; Pertsev, A.; Kamenetsky, V.; Ariskin, A.; Mochalov, A.; Sobolev, A. Crustal Evolution of Island-Arc Ultramafic Magma: Galmoenan Pyroxenite–Dunite Plutonic Complex, Koryak Highland (Far East Russia). J. Petrol. 2005, 46, 1345–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, B.; Namur, O.; Latypov, R.; Tegner, C. Layered Intrusions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 94-017-9652-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkesworth, C.; Turner, S.; McDermott, F.; Peate, D.; Van Calsteren, P. U-Th Isotopes in Arc Magmas: Implications for Element Transfer from the Subducted Crust. Science 1997, 276, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, M.J.; Grove, T.L.; Behrens, H. Amphibole Stability in Primitive Arc Magmas: Effects of Temperature, H2O Content, and Oxygen Fugacity. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 164, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, T.O.; Nelson, W.R.; Ayalew, D.; Hanan, B.; Yirgu, G.; Kappelman, J. Melting the Lithosphere: Metasomes as a Source for Mantle-Derived Magmas. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 461, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, K.; Morishita, T.; Nishio, I.; Guotana, J.M.; Ogusu, Y.; Ishizuka, O.; Tamura, A. Petrogenesis of Amphibole-Rich Ultramafic Rocks in the Hida Metamorphic Complex, Japan: Its Role in Arc Crust Differentiation. Lithos 2021, 404, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daczko, N.R.; Piazolo, S.; Meek, U.; Stuart, C.A.; Elliott, V. Hornblendite Delineates Zones of Mass Transfer through the Lower Crust. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, M.M.; Abd El-Wahed, M.A.; El Dien, H.G.; Morishita, T. Garnet Hornblendite in the Meatiq Core Complex, Central Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implications for Crustal Thickening Preceding The ~600 Ma Extensional Regime in the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Precambrian Res. 2017, 298, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.T.; Calderón, M.; de Arellano, C.R.; Hervé, F.; Opitz, J.; Theye, T.; Fanning, C.M.; Pankhurst, R.J.; González-Guillot, M.; Fuentes, F. Trace Element Composition of Amphibole and Petrogenesis of Hornblendites and Plutonic Suites of Cretaceous Magmatic Arcs Developed in the Fuegian Andes, Southernmost South America. Lithos 2020, 372, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Jagoutz, O.; Upadhyay, R.; Royden, L.H.; Eddy, M.P.; Bailey, E.; Nichols, C.I.; Weiss, B.P. Paleocene Latitude of the Kohistan–Ladakh Arc Indicates Multistage India–Eurasia Collision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29487–29494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoutz, O.; Royden, L.; Holt, A.; Becker, T. Anamolously Fast Convergence of India and Eurasia caused by double subduction. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. The Ancient Tethys Oceans of Asia: How Many? How Old? How Deep? How Wide? UNAEC Asia Pap. 1999, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, R.; Bezard, R.; Guilmette, C.; Dostal, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. The Indus–Yarlung Zangbo Ophiolites from Nanga Parbat to Namche Barwa Syntaxes, Southern Tibet: First Synthesis of Petrology, Geochemistry, and Geochronology with Incidences on Geodynamic Reconstructions of Neo-Tethys. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, R.V.; Shervais, J.W. Suprasubduction-Zone Ophiolites: Is There Really an Ophiolite Conundrum? Spec. Pap.-Geol. Soc. Am. 2008, 438, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Dutt, A.; Shukla, A.D.; Singh, A.K.; Narayanan, A. A Hydrous Sub-Arc Mantle Domain within the Northeastern Neo-Tethyan Ophiolites: Insights from Cumulate Hornblendites. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Hong, J.; Tang, M.; Zhu, D.-C. Nb-Ta Systematics of Kohistan and Gangdese Arc Lower Crust: Implications for Continental Crust Formation. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ghosh, B.; Chattopadhaya, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Dhar, A.; Koley, M.; Morishita, T.; Tripathi, S.K. Mayodia Ophiolitic Complex of Arunachal Pradesh, India: A Multistage Evolutionary Record during the Tethyan Closure. Int. Geol. Rev. 2024, 66, 3017–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, M.; Noble, S.; Cottle, J.; Waters, D.; Mitchell, A.; Hlaing, T.; Horstwood, M. Tectonic Evolution of the Mogok Metamorphic Belt, Burma (Myanmar) Constrained by U-Th-Pb Dating of Metamorphic and Magmatic Rocks. Tectonics 2007, 26, TC3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haproff, P.J. Tectonic Evolution of the Easternmost Himalayan Collisional System; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Morishita, T.; Dhar, A.; Koley, M.; Chattopadhaya, S.; Karmakar, A.; Ghosh, B. Microtextural Evolution of Chrome Spinels in Dunites from Mayodia Ophiolite Complex, Arunachal Pradesh, India: Implications for a Missing Link in the “Two-Stage” Alteration Mechanism. Lithos 2022, 420, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Z.; Chung, S.-L.; Wu, F.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.-G.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S. Tethyan Suturing in Southeast Asia: Zircon U-Pb and Hf-O Isotopic Constraints from Myanmar Ophiolites. Geology 2016, 44, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, N.; Choudhuri, B. Geology and Tectonic History of the Lohit Valley, Eastern Arunachal Pradesh, India. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003, 21, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Guitang, P.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Fisher, R.D.; Sun, Z.; Ou, C.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S. The Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis: Major Tectonic Domains, Ophiolitic Mélanges and Geologic Evolution. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 27, 265–285. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-Z.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.-G.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.; Wu, F.-Y.; Sein, K. Petrology and Geochemistry of Mantle Peridotites from the Kalaymyo and Myitkyina Ophiolites (Myanmar): Implications for Tectonic Settings. Lithos 2016, 264, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chung, S.; Somerville, I.D. Petrogenesis of Mantle Peridotites in Neo-Tethyan Ophiolites from the Eastern Himalaya and Indo-Myanmar Orogenic Belt in the Geo-tectonic Framework of Southeast Asia. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 4886–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovung, N.T.; Ghosh, B.; Ray, J. Petrogenesis of Neo-Tethyan Ophiolites from the Indo-Myanmar Ranges: A Review. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 63, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Ray, J. Mineral Chemistry of Ophiolitic Rocks of Mayodia-Hunli Area of Dibang Valley District, Arunachal Pradesh, North Eastern India. In Milestone in Petrology and Future Perspectives; Geological Society of India: Bangalore, India, 2003; pp. 447–471. [Google Scholar]
- Dutt, A.; Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Oinam, G. Evidence of Melt–and Fluid–Rock Interactions in the Refractory Forearc Peridotites and Associated Mafic Intrusives from the Tuting–Tidding Ophiolites, Eastern Himalaya, India: Petrogenetic and Tectonic Implications. Geol. J. 2020, 56, 2082–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, D.; Mathew, G.; Kohn, B.; Pande, K.; Borgohain, B. Thermochronological Insights into the Thermotectonic Evolution of Mishmi Hills across the Dibang Valley, NE Himalayan Syntaxis. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 190, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, B.; Gururajan, N.; Singh, R. Geology and Sructural Evolution of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. Himal. Geol. 2009, 30, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dutt, A.; Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Oinam, G.; Bikramaditya, R. Geochemical and Metamorphic Record of the Amphibolites from the Tuting–Tidding Suture Zone Ophiolites, Eastern Himalaya, India: Implications for the Presence of a Dismembered Metamorphic Sole. Geol. Mag. 2020, 158, 787–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeoReM—Database on Geochemical, Environmental and Biological Reference Materials Homepage. Available online: https://georem.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Fuenlabrada, J.M. High-precision Sr and Nd Isotope Characterization of BHVO-2 Reference Material by Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Togashi, S.; Kamioka, H.; Amakawa, H.; Kagami, H.; Hamamoto, T.; Yuhara, M.; Orihashi, Y.; Yoneda, S.; Shimizu, H. JNdi-1: A Neodymium Isotopic Reference in Consistency with LaJolla Neodymium. Chem. Geol. 2000, 168, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.L.; Evans, B.W. Abbreviations for Names of Rock-Forming Minerals. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, F.C.; Oberti, R.; Harlow, G.E.; Maresch, W.V.; Martin, R.F.; Schumacher, J.C.; Welch, M.D. Nomenclature of the Amphibole Supergroup. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeditse, M.; Rajesh, H.; Belyanin, G.; Fukuyama, M.; Tsunogae, T. Primary Magmatic Amphibole in Archaean Meta-Pyroxenite from the Central Zone of the Limpopo Complex, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2016, 119, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leake, B.E. On Aluminous and Edenitic Hornblendes. Mineral. Mag. 1971, 38, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.-Z.; Smith, D.J.; Wang, F.; Qin, J.-F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, S.-C. Hornblendites as a Record of Differentiation, Metasomatism and Magma Fertility in Arc Crust. Chem. Geol. 2024, 650, 121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.; Schenk, V.; Haase, K.; Scherer, E.; Tembo, F. Evidence for a Neoproterozoic Ocean in South-Central Africa from Mid-Oceanic-Ridge–Type Geochemical Signatures and Pressure-Temperature Estimates of Zambian Eclogites. Geology 2003, 31, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.S. Characteristic Mineralogy of Arc-Related Cumulate Gabbros: Implications for the Tectonic Setting of Gabbroic Plutons and for Andesite Genesis. Geology 1986, 14, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Mahoney, J.; Ray, J. Mayodia Ophiolites of Arunachal Pradesh, Northeastern Himalaya. J. Geol. Soc. India 2007, 70, 595–604. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Polat, A.; Fryer, B.J.; Appel, P.W.; Windley, B.F. Geochemistry of the Mesoarchean Fiskenæsset Complex at Majorqap Qâva, SW Greenland: Evidence for Two Different Magma Compositions. Chem. Geol. 2012, 314, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.F.; Blundy, J.D.; Macpherson, C.G.; Humphreys, M.C.; Davidson, J.P. Evidence from Plutonic Xenoliths for Magma Differentiation, Mixing and Storage in a Volatile-Rich Crystal Mush beneath St. Eustatius, Lesser Antilles. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 174, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salters, V.J.; Stracke, A. Composition of the Depleted Mantle. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2004, 5, Q05B07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, A.; Hart, S. Chemical Geodynamics. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1986, 14, 493–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arculus, R.J.; Powell, R. Source Component Mixing in the Regions of Arc Magma Generation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 5913–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudigel, H.; Plank, T.; White, B.; Schmincke, H. Geochemical Fluxes during Seafloor Alteration of the Basaltic Upper Oceanic Crust: DSDP Sites 417 and 418. Subduction Top Bottom 1996, 96, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdy, N.M.; Abd El-Rahman, Y.; Frische, M.; Ondrejka, M.; Mira, H.I.; Iizuka, T.; Skublov, S.G.; Saleh, G.M.; Ghoniem, M.M.; Mitwally, M. A Remnant Root of a Neoproterozoic Island Arc in the Northern Eastern Desert of Egypt: Evidence from the Whole-Rock and Amphibole Chemistry of the Gattar Gabbro. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Audétat, A.; Li, J.-W. In Situ Reaction-Replacement Origin of Hornblendites in the Early Cretaceous Laiyuan Complex, North China Craton, and Implications for Its Tectono-Magmatic Evolution. J. Petrol. 2021, 62, egab030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.C. Metamorphic Amphiboles: Composition and Coexistence. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2007, 67, 359–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J. Clinopyroxene Precursors to Amphibole Sponge in Arc Crust. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.F.; Scarrow, J.H.; Montero, P.G.; Bea, F. High-Ti Amphibole as a Petrogenetic Indicator of Magma Chemistry: Evidence for Mildly Alkalic-Hybrid Melts during Evolution of Variscan Basic–Ultrabasic Magmatism of Central Iberia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 158, 69–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, T. Terminology for Layered Intrusions. J. Petrol. 1982, 23, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.V.; McLeod, C.; Blakemore, D.; Shaulis, B.; Hill, T. Bolivian Hornblendite Cumulates: Insights into the Depths of Central Andean Arc Magmatic Systems. Lithos 2020, 370, 105618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe-Piper, G. Mineralogy of an Appinitic Hornblende Gabbro and Its Significance for the Evolution of Rising Calc-Alkaline Magmas. Minerals 2020, 10, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enami, M.; Liou, J.; Mattinson, C. Epidote Minerals in High P/T Metamorphic Terranes: Subduction Zone and High-to Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2004, 56, 347–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrow, E.; Baginski, B. Chloritisation of Hornblende and Biotite: A HRTEM Study. Acta Geol. Pol. 1998, 48, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps, F.; Godard, M.; Guillot, S.; Hattori, K. Geochemistry of Subduction Zone Serpentinites: A Review. Lithos 2013, 178, 96–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Diamond, L.W.; Alt-Epping, P.; Brett-Adams, A.C. Reaction Mechanism and Water/Rock Ratios Involved in Epidosite Alteration of the Oceanic Crust. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoutz, O.; Müntener, O.; Schmidt, M.W.; Burg, J.-P. The Roles of Flux-and Decompression Melting and Their Respective Fractionation Lines for Continental Crust Formation: Evidence from the Kohistan Arc. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 303, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müntener, O.; Ulmer, P. Arc Crust Formation and Differentiation Constrained by Experimental Petrology. Am. J. Sci. 2018, 318, 64–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessimoz, M.; Müntener, O.; Ulmer, P. A Case for Hornblende Dominated Fractionation of Arc Magmas: The Chelan Complex (Washington Cascades). Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 163, 567–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Hong, J. Amphibole Fractionation and Its Potential Redox Effect on Arc Crust: Evidence from the Kohistan Arc Cumulates. Am. Mineral. 2022, 107, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.M. Geochemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 1-119-43810-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shane, P.; Smith, V.C. Using Amphibole Crystals to Reconstruct Magma Storage Temperatures and Pressures for the Post-Caldera Collapse Volcanism at Okataina Volcano. Lithos 2013, 156, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O.; Dungan, M.A. Temperature-Induced Al-Zoning in Hornblendes of the Fish Canyon Magma, Colorado. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, M.; Zhang, C.-L.; Jing, Y.; Hussain, Z.; Song, Z.-H.; Wang, H.-R.; Liu, X.-Q.; Ye, X.-T. Reconstructing Mantle–Crust Boundary Magmatism through Cimmerian Orogenic Events: Evidence from Deep Crustal Cumulates in Northeastern Pamir. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2025, 180, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Lin, S.; Bédard, J.H.; Santos, G.S.; He, W.; Yin, C.; Xiao, W. Late Tonian (ca. 785 Ma) Subduction-Related Mafic-Ultramafic Cumulates in the West Cathaysia Terrane, South China. Precambrian Res. 2023, 387, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, B.; Harangi, S.; Ntaflos, T.; Mason, P.R.; Pál-Molnár, E. Amphibole Perspective to Unravel Pre-Eruptive Processes and Conditions in Volcanic Plumbing Systems beneath Intermediate Arc Volcanoes: A Case Study from Ciomadul Volcano (SE Carpathians). Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 167, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F.; Renzulli, A. Calcic Amphiboles in Calc-Alkaline and Alkaline Magmas: Thermobarometric and Chemometric Empirical Equations Valid up to 1130 °C and 2.2 GPa. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 163, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F.; Renzulli, A.; Perugini, D.; Cesare, B.; Braga, R.; Del Moro, S. Unravelling the Complex Interaction between Mantle and Crustal Magmas Encoded in the Lavas of San Vincenzo (Tuscany, Italy). Part II: Geochemical Overview and Modelling. Lithos 2016, 244, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, A.; Ridolfi, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Taussi, M.; Renzulli, A. Application and Reliability of Calcic Amphibole Thermobarometry as Inferred from Calc-Alkaline Products of Active Geothermal Areas in the Andes. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 358, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Blundy, J. Non-Ideal Interactions in Calcic Amphiboles and Their Bearing on Amphibole-Plagioclase Thermometry. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1994, 116, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstrom, J.M.; Zen, E. Aluminum in Hornblende: An Empirical Igneous Geobarometer. Am. Mineral. 1986, 71, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.C.; Rutherford, M.J. Experimental Calibration of the Aluminum-in-Hornblende Geobarometer with Application to Long Valley Caldera (California) Volcanic Rocks. Geology 1989, 17, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Moreno, J.; Castro, A.; Rodríguez, C.; Fershtater, G. Calcic Amphibole Thermobarometry in Metamorphic and Igneous Rocks: New Calibrations Based on Plagioclase/Amphibole Al-Si Partitioning and Amphibole/Liquid Mg Partitioning. Lithos 2015, 232, 286–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K. Amphibole Thermometers and Barometers for Igneous Systems and Some Implications for Eruption Mechanisms of Felsic Magmas at Arc Volcanoes. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F. Amp-TB2: An Updated Model for Calcic Amphibole Thermobarometry. Minerals 2021, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocque, J.; Canil, D. The Role of Amphibole in the Evolution of Arc Magmas and Crust: The Case from the Jurassic Bonanza Arc Section, Vancouver Island, Canada. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 159, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.L. Theory of the Earth; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; ISBN 0-86542-335-0. [Google Scholar]
- Urann, B.; Le Roux, V.; Jagoutz, O.; Müntener, O.; Behn, M.; Chin, E. High Water Content of Arc Magmas Recorded in Cumulates from Subduction Zone Lower Crust. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoutz, O. Arc Crustal Differentiation Mechanisms. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 396, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-X. Continental versus Oceanic Subduction Zones. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 495–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müntener, O.; Kelemen, P.B.; Grove, T.L. The Role of H 2 O during Crystallization of Primitive Arc Magmas under Uppermost Mantle Conditions and Genesis of Igneous Pyroxenites: An Experimental Study. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 141, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, G.A.; Grove, T.L.; Bryan, W.B. The Influence of Water on the Petrogenesis of Subduction related Igneous Rocks. Nature 1993, 365, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müntener, O.; Ulmer, P.; Blundy, J.D. Super hydrous Arc Magmas in the Alpine Context. Elements 2021, 17, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Campbell, I.H.; Park, J.-W. Nd-Hf Isotopic Systematics of the Arc Mantle and Their Implication for Continental Crust Growth. Chem. Geol. 2022, 602, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Castillo, P.R.; Hawkins, J.W.; Hilton, D.R.; Hanan, B.B.; Pietruszka, A.J. Major and Trace Element and Sr–Nd Isotope Signatures of Lavas from the Central Lau Basin: Implications for the Nature and Influence of Subduction Components in the Back-Arc Mantle. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 178, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, M.K.; Ishizuka, O.; Stern, R.J.; Kelley, K.A.; Ohara, Y.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Bloomer, S.H.; Cash, J.; Fryer, P.; Hanan, B.B. Fore-arc Basalts and Subduction Initiation in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana System. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, Q03X12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Jagoutz, O. The Global Systematics of Primitive Arc Melts. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 2817–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiepolo, M.; Oberti, R.; Zanetti, A.; Vannucci, R.; Foley, S.F. Trace-Element Partitioning between Amphibole and Silicate Melt. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2007, 67, 417–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.B.; Scoggin, S.H.; Kapp, P.; Carrapa, B.; Ducea, M.N.; Worthington, J.; Oimahmadov, I.; Gadoev, M. Mesozoic to Cenozoic Magmatic History of the Pamir. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 482, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, M.; Hacker, B. Structural and Metamorphic Evolution of the Karakoram and Pamir Following India–Kohistan–Asia Collision. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 483, 555–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Chung, S.-L.; Cawood, P.A.; Zhao, Z.-D. Gangdese Magmatism in Southern Tibet and India–Asia Convergence since 120 Ma. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 483, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Weinberg, R.F.; Cawood, P.A.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Mo, X.-X. Continental Crustal Growth Processes Recorded in the Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibet. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2023, 51, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, S.; Aitchison, J.C.; Nutman, A.P.; Bennett, V.C.; Saktura, W.M.; Walsh, J.M.; Kachovich, S.; Hidaka, H. The Spongtang Massif in Ladakh, NW Himalaya: An Early Cretaceous Record of Spontaneous, Intra-Oceanic Subduction Initiation in the Neotethys. Gondwana Res. 2018, 63, 226–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Liu, C.-Z.; Wu, F.-Y.; Ji, W.-Q.; Wang, J.-G. Zedong Terrane Revisited: An Intra-Oceanic Arc within Neo-Tethys or a Part of the Asian Active Continental Margin? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 80, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; An, W.; Palin, R.M.; Ding, H.; Dong, X.; Tian, Z. Intraoceanic Subduction System Within the Neo-Tethys: Evidence From Late Cretaceous Arc Magmatic Rocks of the Eastern Himalaya. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2023, 24, e2023GC011214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.M.; Buckman, S.; Nutman, A.P.; Zhou, R. Age and Provenance of the Nindam Formation, Ladakh, NW Himalaya: Evolution of the Intraoceanic Dras Arc before Collision with India. Tectonics 2019, 38, 3070–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, M.P. Timing of Subduction Initiation, Arc Formation, Ophiolite Obduction and India–Asia Collision in the Himalaya. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 483, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Misra, S.; Ghosh, B. Melt-Rock Interaction and Fractional Crystallization in the Moho Transition Zone: Evidence from the Cretaceous Naga Hills Ophiolite, North-East India. Lithos 2018, 322, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, J.; Carmichael, I. A Hornblende Basalt from Western Mexico: Water-Saturated Phase Relations Constrain a Pressure–Temperature Window of Eruptibility. J. Petrol. 2004, 45, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Murphy, J.B.; Johnson, T.E.; Huang, H.-Q. Critical Role of Water in the Formation of Continental Crust. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikramaditya, R.; Chung, S.-L.; Singh, A.K.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-H.; Iizuka, Y. Age and Isotope Geochemistry of Magmatic Rocks of the Lohit Plutonic Complex, Eastern Himalaya: Implications for the Evolution of Transhimalayan Arc Magmatism. J. Geol. Soc. 2020, 177, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Yang, Z.-M.; Hou, Z.-Q. Fluid Flux Melting Generated Postcollisional High Sr/Y Copper Ore–Forming Water-Rich Magmas in Tibet. Geology 2015, 43, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouteau, G.; Scaillet, B. Experimental Constraints on the Origin of the 1991 Pinatubo Dacite. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 2203–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, I.S. The Andesite Aqueduct: Perspectives on the Evolution of Intermediate Magmatism in West-Central (105–99 W) Mexico. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 143, 641–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, G.; Bourdon, B. Non-Chondritic Sm/Nd Ratio in the Terrestrial Planets: Consequences for the Geochemical Evolution of the Mantle–Crust System. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3333–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Wasserburg, G. Sm-Nd Isotopic Evolution of Chondrites and Achondrites, II. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 67, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugmair, G.; Shimamura, T.; Lewis, R.; Anders, E. Samarium-146 in the Early Solar System: Evidence from Neodymium in the Allende Meteorite. Science 1983, 222, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, R.H.; Jäger, E. Subcommission on Geochronology: Convention on the Use of Decay Constants in Geo-and Cosmochronology. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 36, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villares, F.; Blanco-Quintero, I.F.; Reyes, P.S.; Proenza, J.A.; Cartagena, R.; Lázaro, C.; Garcia-Casco, A. Petrogenesis of the Tampanchi Ultramafic–Mafic Complex (Ecuador): Geodynamic Implications for the Northwestern Margin of South America during the Late Cretaceous. Gondwana Res. 2022, 105, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlnia, A.; Alizade, A. Petrology and Geochemistry of the Mamakan Gabbroic Intrusions, Urumieh (Urmia), Iran: Magmatic Development of an Intra-Oceanic Arc. Period. Mineral. 2013, 82, 263–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kettanah, Y.A.; Ismail, S.A.; Karo, N.M. Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and 40Ar/39Ar Dating of Hornblendite/Amphibolite Pods in Penjween Ophiolite of Northeastern Iraq: Implications for Petrogenesis and Tectonics. J. Afr. Earth Sc. 2022, 193, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jagoutz, O.; Shinevar, W.J.; Zhang, H.-F. Formation and Composition of the Late Cretaceous Gangdese Arc Lower Crust in Southern Tibet. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 175, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Baele, J.; Bruguier, O.; Diot, H.; Ennih, N.; Monnier, C.; Plissart, G.; Vandycke, S.; Watlet, A. Intra-Oceanic Arc Growth Driven by Magmatic and Tectonic Processes Recorded in the Neoproterozoic Bougmane Arc Complex (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2018, 304, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Weinberg, R.F.; Wang, R.; Li, S.-M.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhao, Z.-D. Constructing the Early Mesozoic Gangdese Crust in Southern Tibet by Hornblende-Dominated Magmatic Differentiation. J. Petrol. 2019, 60, 515–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Suzuki, K.; Tian, W.; Jahn, B.; Ireland, T. Geochemistry and Os–Nd–Sr Isotopes of the Gaositai Alaskan-Type Ultramafic Complex from the Northern North China Craton: Implications for Mantle–Crust Interaction. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 158, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Santosh, M.; Hou, Z.; Wei, R.; Ma, G.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. High Sr/Y Magmas Generated through Crystal Fractionation: Evidence from Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in the Northern Taihang Orogen, North China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Shen, Z. Lower-Crustal Magmatic Hornblendite in North China Craton: Insight into the Genesis of Porphyry Cu Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1879–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, J.; Seidel, E.; Kreuzer, H. Ophiolites on the Southern Aegean Islands Crete, Karpathos and Rhodes: Composition, Geochronology and Position within the Ophiolite Belts of the Eastern Mediterranean. Lithos 2002, 65, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, N.T.; Hattori, K.H. The Quetico Intrusions of Western Superior Province: Neo-Archean Examples of Alaskan/Ural-Type Mafic–Ultramafic Intrusions. Precambrian Res. 2006, 149, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daczko, N.; Emami, S.; Allibone, A.; Turnbull, I. Petrogenesis and Geochemical Characterisation of Ultramafic Cumulate Rocks from Hawes Head, Fiordland, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 2012, 55, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.-X.; Wyman, D.A.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Yang, J.-H.; Gou, G.-N.; Guo, H.-F. Early Late Cretaceous (ca. 93 Ma) Norites and Hornblendites in the Milin Area, Eastern Gangdese: Lithosphere–Asthenosphere Interaction during Slab Roll-Back and an Insight into Early Late Cretaceous (ca. 100–80 Ma) Magmatic “Flare-up” in Southern Lhasa (Tibet). Lithos 2013, 172, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Fan, H.-R.; Santosh, M.; Guo, J. Petrology and Geochemistry of the Guyang Hornblendite Complex in the Yinshan Block, North China Craton: Implications for the Melting of Subduction-Modified Mantle. Precambrian Res. 2016, 273, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, M.; Teng, X.-M.; He, X.-F.; Tang, L.; Yang, Q.-Y. Discovery of Neoarchean Suprasubduction Zone Ophiolite Suite from Yishui Complex in the North China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2016, 38, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, P.; Kontinen, A.; Huhma, H. Petrogenesis of the Mantle Sequence of the Jormua Ophiolite (Finland): Melt Migration in the Upper Mantle during Palaeoproterozoic Continental Break-Up. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 297–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-K.; Chen, B.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, L. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic Zijinguan Mafic Pluton from the Taihang Mountains, North China Craton: Petrological and Os–Nd–Sr Isotopic Constraints. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Tectonic Domain | Tectonostratigraphic Unit and Subunit | Lithology with Mineralogical Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Trans-Himalayan Granitoids | Eastern Lohit Plutonic Complex | Leucogranite, quartz diorite, granodiorite, tourmaline-bearing pegmatites |
| Warlung Thrust (WT) | ||
| Western Lohit Plutonic Complex | Gabbro, intrusive leucogranite, aplite dyke, trondhjemite, mylonite gneiss, hornblende granite, tonalite, meta-diorite, dacite, pegmatite | |
| Lohit Thrust (LT) | ||
| Mayudia Ophiolite Complex (MdOC) | Tidding formation | Metacarbonate (Dolomite + muscovite + quartz) |
| Metapelite grading into metachert (Quartz + biotite + muscovite + plagioclase + epidote ± titanite ± carbonate ± garnet ± chlorite) | ||
| Metabasalt (Actinolititc amphibole + plagioclase + chlorite) | ||
| Amphibolite (Hornblende + plagioclase + opaque (mostly magnetite) ± epidote ± titanite) | ||
| Metaperidotite (olivine + clinopyroxene + serpentine + spinel) with hornblendite–hornblende–zoisite schist (pargasitic amphibole ± plagioclase ± zoisite) intrusives | ||
| Tidding Thrust (TT) | ||
| Mayudia Gneiss | Mayudia Group | Garnet–biotite schist and gneiss, quartzite, and amphibolite |
| Mayudia Thrust (MyT) | ||
| Lalpani Group | Lesser Himalayan Sequence (LHS) | Garnet–biotite schist, and paragneiss, micaceous quartzite, marble, carbonaceous schist, carbon-bearing calcareous schist, amphibolite |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahoo, S.; Majumdar, A.S.; Anand, R.; Ray, D.; Fuenlabrada, J.M. Petrogenesis of Mafic–Ultramafic Cumulates in the Mayudia Ophiolite Complex, NE Himalaya: Evidence of an Island Arc Root in Eastern Neo-Tethys. Minerals 2025, 15, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060572
Sahoo S, Majumdar AS, Anand R, Ray D, Fuenlabrada JM. Petrogenesis of Mafic–Ultramafic Cumulates in the Mayudia Ophiolite Complex, NE Himalaya: Evidence of an Island Arc Root in Eastern Neo-Tethys. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahoo, Sapneswar, Alik S. Majumdar, Rajagopal Anand, Dwijesh Ray, and José M. Fuenlabrada. 2025. "Petrogenesis of Mafic–Ultramafic Cumulates in the Mayudia Ophiolite Complex, NE Himalaya: Evidence of an Island Arc Root in Eastern Neo-Tethys" Minerals 15, no. 6: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060572
APA StyleSahoo, S., Majumdar, A. S., Anand, R., Ray, D., & Fuenlabrada, J. M. (2025). Petrogenesis of Mafic–Ultramafic Cumulates in the Mayudia Ophiolite Complex, NE Himalaya: Evidence of an Island Arc Root in Eastern Neo-Tethys. Minerals, 15(6), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060572







