Multiscale Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity in Deep Marine Qiongzhusi Shales from Southern Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
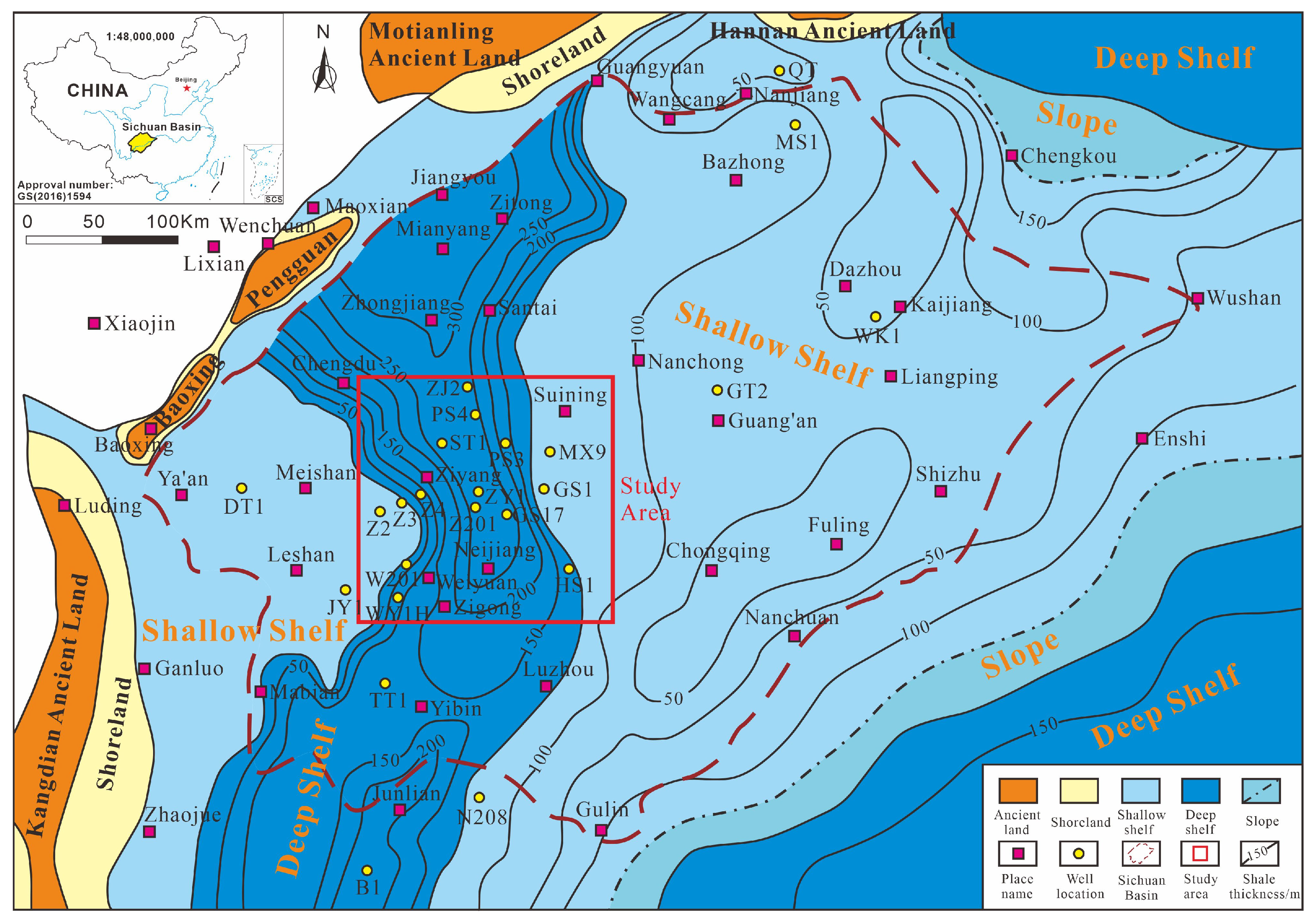
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. TOC and Mineralogical Experiments
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. CO2 Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
3.5. N2 Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
3.6. High-Pressure Mercury Injection Experiments
3.7. Fractal Dimension Calculation
4. Results
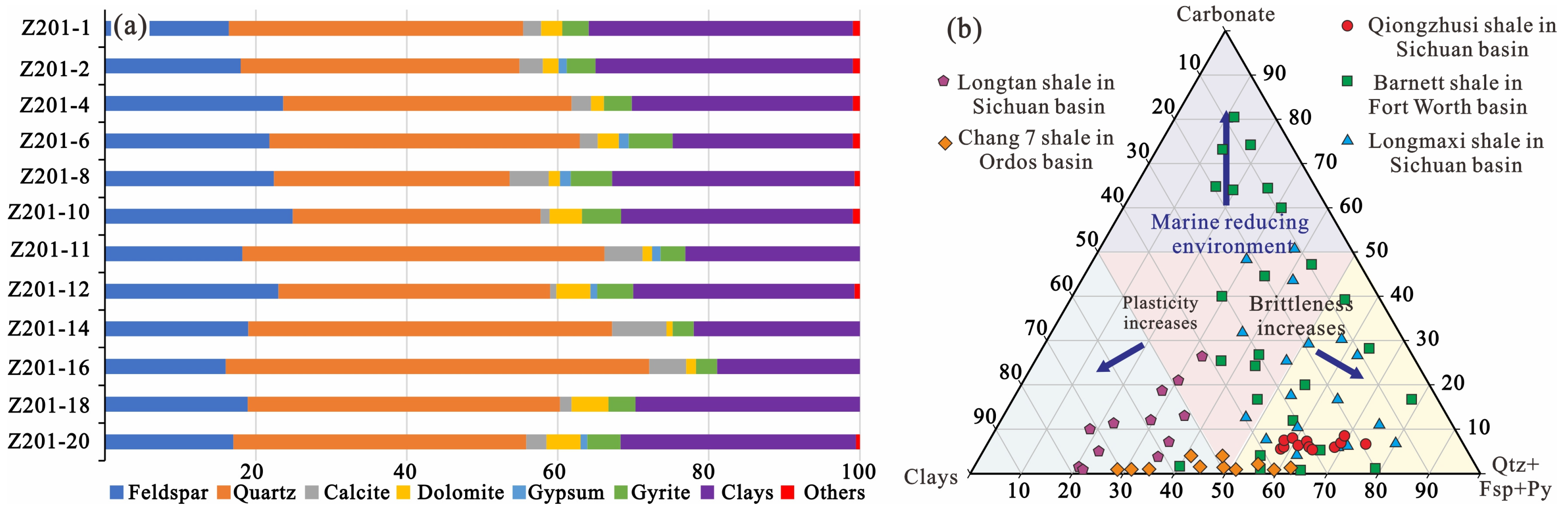
4.1. TOC and Mineralogy
4.2. Pore Types and Morphological Characteristics
4.3. Pore Structure and Pore Size Distribution
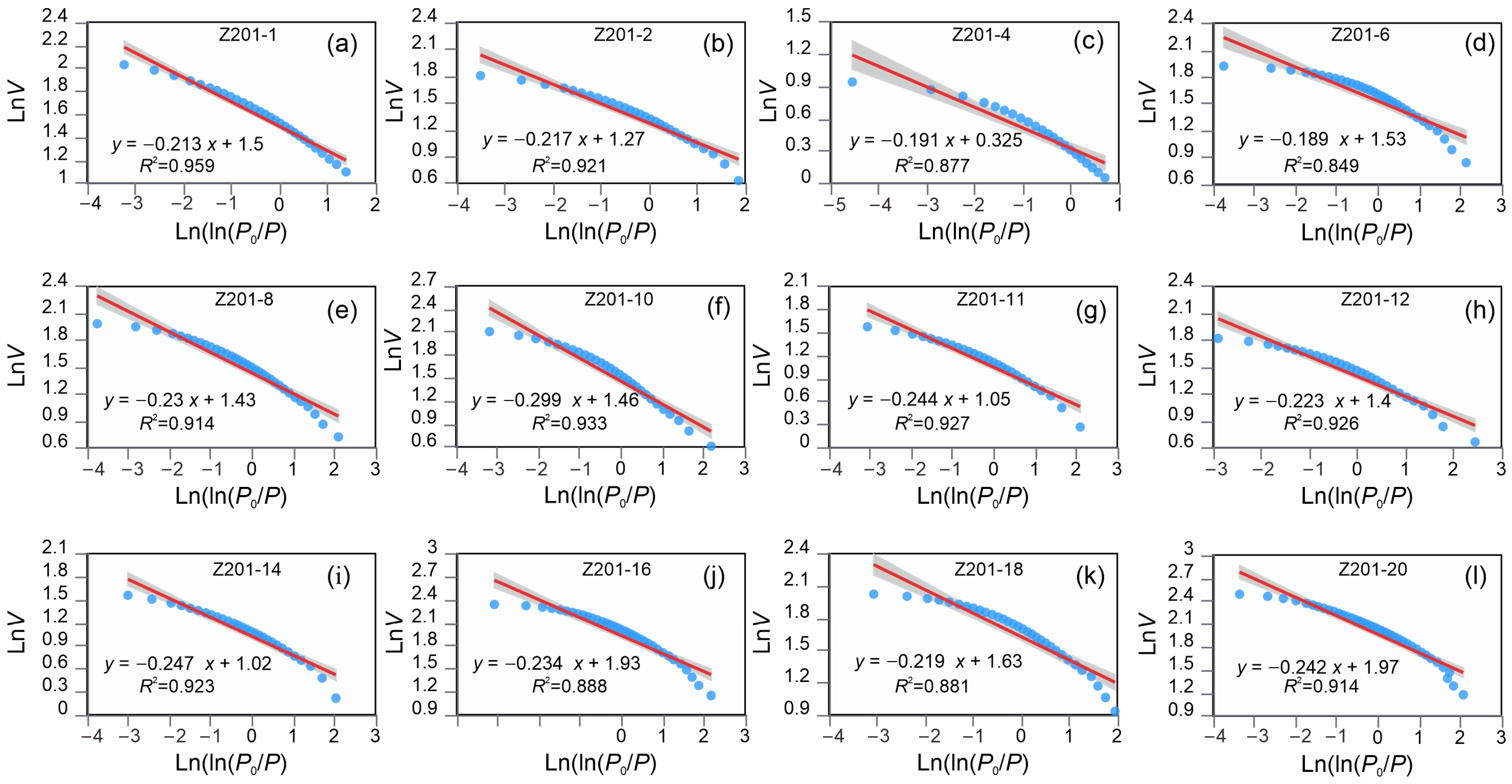
4.4. Fractal Dimensions
5. Discussion
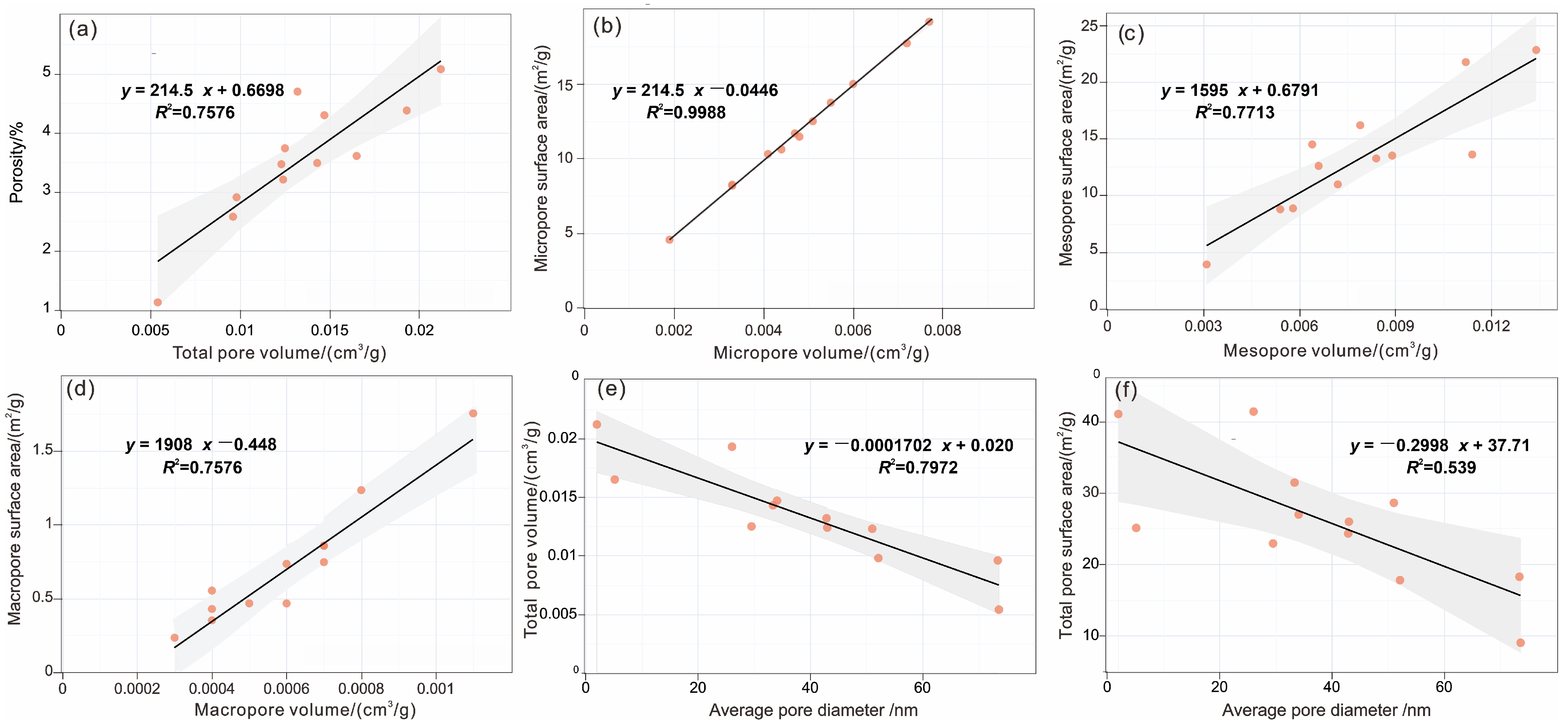
5.1. The Coupling Mechanism Between Pore Structure Parameters
5.2. The Influence of Heterogeneity on Pore Structure
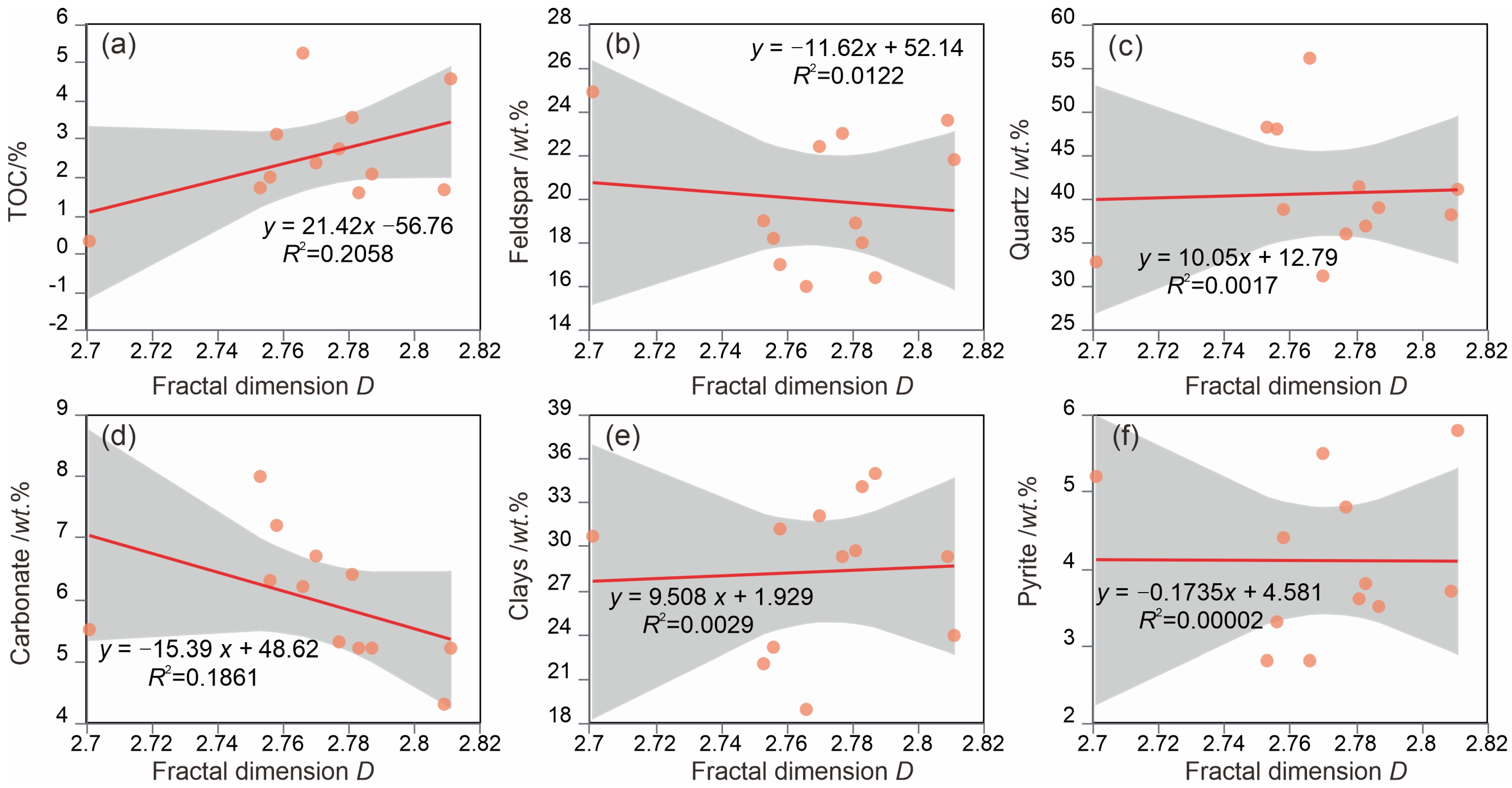
5.3. Compositional Controls on Pore Structure
5.4. Compositional Controls on Heterogeneity
6. Conclusions
- The pore size distribution of Qiongzhusi shale exhibits a complex, bimodal pattern in the <10 nm range, indicating that smaller pores significantly contribute to the total pore volume and specific surface area. The pore volume in the 10–100 nm range remained relatively stable, with minimal variation among samples.
- In comparison to Longmaxi shale (moderate maturity, Ro: 2.5–3.0%), Qiongzhusi shale has experienced excessive thermal evolution, leading to the collapse of organic pores and a reduction in micropore abundance and specific surface area. The pore system of Qiongzhusi shale is predominantly composed of inorganic pores.
- The fractal dimension of the Qiongzhusi shale samples is notably high (ranging from 2.701 to 2.811, with an average of 2.775), suggesting a highly complex and heterogeneous pore structure. This complexity may be attributed to multistage tectonic evolution, intricate mineral composition, diverse pore types, and a wide range of pore sizes, all of which enhance the heterogeneity and fractal characteristics of the pores.
- A strong linear correlation was observed between total porosity and total pore volume, as well as between specific surface area and pore volume of micropores, mesopores, and macropores. These relationships underscore the critical role of pore volume in influencing porosity and specific surface area. Conversely, a weak positive correlation between porosity and TOC content indicates that the contribution of organic matter to pore development is limited. Additionally, carbonate and clay minerals exhibit a significant negative correlation with porosity, reflecting their detrimental effects on pore preservation through processes of cementation and compaction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curtis, J.B. Fractured shale-gas systems. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1921–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Selley, R.C. UK shale gas: The story so far. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Boersma, T. Energy (in) security in Poland the case of shale gas. Energy Policy 2013, 53, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Nie, H.K.; Dang, W. Shale gas exploration and development in China: Current status, geological challenges and future directions. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6359–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Guo, Z.H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Wan, Y.J.; Luo, R.L.; Sun, Y.P.; Che, M.G. High-quality development of ultra-deep large gas fields in China: Challenges, strategies and proposals. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, E.; Hu, D.; Liu, R.; Li, G.; Lu, C. Restoration of sedimentary environment and geochemical features of deep marine Longmaxi shale and its significance for shale gas: A case study of the Dingshan area in the Sichuan Basin, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 151, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Hu, D.F.; Huang, R.C.; Wei, Z.H.; Duan, J.B.; Wei, X.F.; Fan, X.J.; Miao, Z.W. Deep and ultra-deep natural gas exploration in the Sichuan Basin: Progress and prospect. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wei, Z.; Jia, A.; He, S.; Hou, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, R. Fractal Characteristics of Pore Structure in Deep Overpressured Organic-Rich Shale in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Southeast Sichuan and Its Geological Significance. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Geng, C.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, Z.; Long, H.; Chang, Z.; Li, J.; Pang, H.; Yang, J. Application of the Hydrocarbon Generation Potential Method in Resource Potential Evaluation: A Case Study of the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin, China. Processes 2024, 12, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.E.; Zhao, Z.F.; Pan, S.Q.; Yin, J.; Lu, G.W.; Fu, F.L.; Yuan, M.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, G.S.; Luo, C.; et al. Unveiling the Oldest Industrial Shale Gas Reservoir: Insights for the Enrichment Pattern and Exploration Direction of Lower Cambrian Shale Gas in the Sichuan Basin. Engineering 2024, 42, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, R.; Shi, X.W.; Luo, C.; Zhong, K.S.; Wu, W.; Zheng, M.J.; Yang, Y.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.Q.; et al. Aulacogen-uplift enrichment pattern and exploration prospect of Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 1402–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Pang, H.; Zhang, B.J.; Jiang, F.J.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Ma, K.Y.; Huo, X.G. Application of shale TOC prediction model using the XGBoost machine learning algorithm: A case study of the Qiongzhusi Formation in central Sichuan Basin. Carb. Evap. 2025, 40, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.L.; Shen, J.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, D.M.; Tang, R.F.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.Y. Sedimentological and geochemical characteristics of lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi shale in the Sichuan Basin and its periphery, SW China: Implications for differences in organic matter enrichment. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 3774–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.R.; Bustin, R.M.; Power, I.M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses: Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig unit. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.R.L.; Ross, D.J.K.; Bustin, R.M. Geological controls on matrix permeability of Devonian Gas Shales in the Horn River and Liard basins, northeastern British Columbia, Canada. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, N.S.; Hackley, P.C.; Lowers, H.A.; Hill, R.J.; Egenhoff, S.O.; Eberl, D.D.; Blum, A.E. The nature of porosity in organic-rich mudstones of the Upper Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay Formation, North Sea, offshore United Kingdom. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Tao, G.L.; Bao, Y.J.; Lu, L.F.; Sun, Y.G.; Liu, W.X.; Shen, B.J.; Ne, H.K. Differential development and maintenance mechanismof reservoir space for marine shale gas in South China’s deep strata. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2022, 44, 845–865. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Jarvie, D.M. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale. J. Sedi. Res. 2009, 79, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, N.S.; Tao, N.; Xie, X.M.; Cheng, H.F.; Zuo, Z.X.; Ma, Z.L.; Shen, B.J.; Borjigin, T. Thermal maturity calibration of extremely high-mature pre-Devonian strata: A case study from the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin, South China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Li, X.Q.; Wei, Q.; Sun, K.X.; Zhang, G.W.; Wang, F.Y. Characterization of full-sized pore structure and fractal characteristics of marine−continental transitional Longtan formation shale of Sichuan Basin, South China. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10490–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.L.; Jiao, K.; Deng, B.; Hao, W.D.; Liu, S.G. Pore characteristics and preservation mechanism of over-6000-m ultra-deep shale reservoir in the Sichuan Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1059869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn, C.E. Fractal measurements of sandstone, shales and carbonates. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1988, 93, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1982; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Mendhe, V.A.; Varma, A.K.; Kamble, A.D.; Sharma, S.; Bannerjee, M.; Kalpanad, M.S. Influence of organic and inorganic content on fractal dimensions of Barakar and Barren Measures shale gas reservoirs of Raniganj basin, India. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 49, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, G.W.; Zou, X.Y.; Wang, F.Y.; Tang, Y.J. Microstructural investigation of different nanopore types in marine-continental transitional shales: Examples from the Longtan formation in Southern Sichuan Basin, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 110, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Tang, Y.J.; He, D.X.; Sun, P.; Zou, X.Y. Full-scale nanopore system and fractal characteristics of clay-rich lacustrine shale combining FE-SEM, nano-CT, gas adsorption and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 196, 105758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Li, X.Q.; Wei, Q.; Gao, W.J.; Liang, W.L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.Y. Quantitative characterization of pore-fracture system of organic-rich marine-continental shale reservoirs: A case study of the Upper Permian Longtan Formation, Southern Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2017, 200, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ding, W.D.; He, J.H.; Dai, P.; Yin, S.; Xie, F. Investigation of pore structure and fractal characteristics of organic–rich shale reservoirs: A case study of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi formation in Malong block of eastern Yunnan Province, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 70, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, S.I.; Rhee, C.K. An investigation of fractal characteristics of mesoporous carbon electrodes with various pore structures. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 4171–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Huang, S.P.; Sun, M.D.; Wen, Y.R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Luo, F.; Zhang, H. Palaeoenvironmental evolution based on elemental geochemistry of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Shales in Western Hubei, Middle Yangtze, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaver, J.; Hemes, S.; Houben, M.; Desbois, G.; Radi, Z.; Urai, J.L. The connectivity of pore space in mudstones: Insights from high-pressure Wood’s metal injection, BIB–SEM imaging, and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Geofluids 2015, 15, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslannejad, H.; Hassanizadeh, S.M.; Raoof, A.; de Winter, D.A.M.; Tomozeiu, N.; van Genuchten, M.T. Characterizing the hydraulic properties of a porous coating of paper using FIB-SEM tomography and 3D pore-scale modeling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 160, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Deng, Z.; Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, D. Study on pore structure and multifractal characteristics of middle- and high-rank coals based on gas adsorption method: A case study of Benxi Formation in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 4102–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Deng, Z.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Ding, R.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Z.; Hou, S.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Pore structure and fractal characteristics oftransitional shales with different lithofacies from the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin. Energy Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 3979–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, P. Nanopore structure characterization for organic-rich shale using the non-local-density functional theory by a combination of N2 and CO2 adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 227, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroniec, M. Evaluation of the fractal dimension from a single adsorption isotherm. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2316–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Hisham, B.M.; Ziad, B.; Raoof, G.; Mofazzal, H. The impact of supercritical CO2 on the pore structure and storage capacity of shales. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 98, 104394. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Pan, J.; Deng, Z. Effect of N2/CO2 injection and alternate injection on volume swelling/shrinkage strain of coal. Energy 2023, 275, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, S.; Tang, D.; Huang, W.; Pan, Z. Determining fractal dimensions of coal pores by FHH model: Problems and effects. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 21, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, Z.; Jin, Z.; Wen, X.; Geng, Y. Origin of authigenic quartz in organic-rich shales of the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin, South China: Implications for pore evolution. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 68, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.J.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Shang, F.H. Scale-Dependent Fractal Properties and Geological Factors for the Pore Structure in Shale: Insights from Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy and Fluid Intrusion. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 16519–16535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.F.; Zhang, J.J.; Khan, J. Influence of Pore Structure Particularity and Pore Water on the Occurrence of Deep Shale Gas: Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Luzhou Block, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Res. Res. 2022, 31, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.R.; Pang, X.Q.; Ma, X.H.; Wang, E.Z.; Hu, T.; Wu, Z.Y. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi shale in the Sichuan Basin, Central China: Implications for conventional and unconventional natural gas resource potential. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2021, 204, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yang, X.F.; Li, S.S.; Wang, Y.M.; Tan, G.C.; Yan, J.K.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.Z. Sedimentary characteristics and lithofacies paleogeography of the Cambrian in Sichuan basin, Southwest China. Petroleum 2024, 10, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, F.; Zeng, J.B.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, S.W.; Liu, W.; Kong, W.L. Paleoenvironment Comparison of the Longmaxi and Qiongzhusi Formations, Weiyuan Shale Gas Field, Sichuan Basin. Processes 2023, 11, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Tang, Z.L.; Zheng, W.Q. Micropore Structural Heterogeneity of Siliceous Shale Reservoir of the Longmaxi Formation in the Southern Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, P.; Avnir, D. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three. I. Fractal theory of heterogeneous surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3558–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, S.; Yi, J.Z. Nano-scale pore structure and fractal dimension of organic-rich wufeng-longmaxi shale from Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin: Investigations using FE-SEM, gas adsorption and helium pycnometry. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 70, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Lin, W.; Li, M.T.; Wang, J.G.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Y.C. Pore Structure and Heterogeneity Characteristics of Coal-Bearing Marine–Continental Transitional Shales from the Longtan Formation in the South Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Hao, F.; Lin, J.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q. Organic matter-hosted pore system in the Wufeng-Longmaxi (O3w-S11) shale, Jiaoshiba area, Eastern Sichuan Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 173, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.Z.; Dong, D.Z.; Wang, S.F.; Huang, J.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Lu, H.; Zhang, C.C. Preliminary study on shale gas micro-reservoir characteristics of the lower silurian Longmaxi formation in the southern Sichuan basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Zang, X.P.; Cui, W.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, Z.X. Organic matter pores structure and evolution in shales based on the he ion microscopy (HIM): A case study from the Triassic Yanchang, Lower Silurian Longmaxi and Lower Cambrian Niutitang shales in China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Zhu, Y.M.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.F.; Fu, C.Q.; Fang, J.H. Hydrocarbon generation and shale gas accumulation in the Longmaxi Formation, Southern Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2017, 86, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Zou, C.; Wang, H.; Dong, D.; Lu, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; He, J.; et al. Discussion on the characteristics and controlling factors of differential enrichment of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in south China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 5, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.Y.; Su, Y.L.; Lu, M.J.; Cai, M.Y.; Fu, J.K.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, K.Y.; Han, Q. Effect of surface type on the flow characteristics in shale nanopores. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6641922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.S.; Shan, B.C.; Wang, R.X.; Feng, G.; Guo, Z.L. Evaluation of different particle-actuation modes in molecular dynamics and their impact on nanoscale flow behaviors. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 072006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.Y.; Shen, L.M.; Maggi, F.; Chen, Z.W.; Pan, Z.J. Influence of surface roughness on methane flow in shale kerogen nano-slits. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 103, 104650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample ID | Depth/m | TOC/% | Feldspar | Quartz | Calcite | Dolomite | Gypsum | Pyrite | Clays | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z201-1 | 4573.41 | 2.08 | 16.4 | 39.0 | 2.4 | 2.8 | / | 3.5 | 35.0 | 0.9 |
| Z201-2 | 4579.10 | 1.59 | 18.0 | 36.9 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 3.8 | 34.1 | 0.9 |
| Z201-4 | 4589.70 | 1.67 | 23.6 | 38.2 | 2.6 | 1.7 | / | 3.7 | 29.3 | 0.9 |
| Z201-6 | 4604.00 | 4.57 | 21.8 | 41.1 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 23.9 | 0.9 |
| Z201-8 | 4610.94 | 2.37 | 22.4 | 31.2 | 5.2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 5.5 | 32.1 | 0.7 |
| Z201-10 | 4620.54 | 0.329 | 24.9 | 32.8 | 1.2 | 4.3 | / | 5.2 | 30.7 | 0.9 |
| Z201-11 | 4745.32 | 2.00 | 18.2 | 48.0 | 5.0 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 3.3 | 23.1 | 0.0 |
| Z201-12 | 4750.05 | 2.74 | 23.0 | 36.0 | 0.8 | 4.5 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 29.3 | 0.7 |
| Z201-14 | 4774.36 | 1.72 | 19.0 | 48.2 | 7.2 | 0.8 | / | 2.8 | 22.0 | 0.0 |
| Z201-16 | 4796.00 | 5.24 | 16.0 | 56.1 | 4.9 | 1.3 | / | 2.8 | 18.9 | 0.0 |
| Z201-18 | 4805.09 | 3.56 | 18.9 | 41.4 | 1.5 | 4.9 | / | 3.6 | 29.7 | 0.0 |
| Z201-20 | 4810.94 | 3.12 | 17.0 | 38.8 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 0.9 | 4.4 | 31.2 | 0.5 |
| Sample ID | Porosity | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Total Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micropore | Mesopore | Macropore | Micropore | Mesopore | Macropore | |||||
| Z201-1 | 4.30 | 0.0047 | 0.0089 | 0.0011 | 11.6913 | 13.5180 | 1.7545 | 0.0147 | 26.96 | 0.8116 |
| Z201-2 | 3.74 | 0.0048 | 0.0072 | 0.0006 | 11.4692 | 10.9810 | 0.4664 | 0.0125 | 22.92 | 1.0265 |
| Z201-4 | 3.61 | 0.0044 | 0.0114 | 0.0007 | 10.6194 | 13.6150 | 0.8580 | 0.0165 | 25.09 | 2.3071 |
| Z201-6 | 5.08 | 0.0072 | 0.0134 | 0.0005 | 17.7394 | 22.8170 | 0.4670 | 0.0212 | 41.02 | 1.1853 |
| Z201-8 | 4.70 | 0.0041 | 0.0084 | 0.0006 | 10.3071 | 13.2660 | 0.7346 | 0.0132 | 24.31 | 0.0004 |
| Z201-10 | 1.13 | 0.0019 | 0.0031 | 0.0004 | 4.5532 | 3.9290 | 0.5530 | 0.0054 | 9.04 | 0.5953 |
| Z201-11 | 2.91 | 0.0033 | 0.0058 | 0.0007 | 8.1804 | 8.8690 | 0.7460 | 0.0098 | 17.80 | 0.0003 |
| Z201-12 | 3.21 | 0.0051 | 0.0066 | 0.0007 | 12.5063 | 12.6080 | 0.8560 | 0.0124 | 25.97 | 1.0301 |
| Z201-14 | 2.58 | 0.0033 | 0.0054 | 0.0008 | 8.2447 | 8.7870 | 1.2340 | 0.0096 | 18.27 | 1.0886 |
| Z201-16 | 4.38 | 0.0077 | 0.0112 | 0.0004 | 19.1829 | 21.7570 | 0.4286 | 0.0193 | 41.37 | 0.0004 |
| Z201-18 | 3.49 | 0.0060 | 0.0079 | 0.0003 | 15.0056 | 16.1960 | 0.2340 | 0.0143 | 31.44 | 0.6588 |
| Z201-20 | 3.47 | 0.0055 | 0.0064 | 0.0004 | 13.7491 | 14.5040 | 0.3520 | 0.0123 | 28.61 | 2.0018 |
| Sample ID | Fractal Fitting Equation | D | R2 | Sample ID | Fractal Fitting Equation | D | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z201-1 | y = −0.213x + 1.50 | 2.787 | 0.959 | Z201-11 | y = −0.244x + 1.05 | 2.756 | 0.927 |
| Z201-2 | y = −0.217x + 1.27 | 2.783 | 0.921 | Z201-12 | y = −0.223x + 1.40 | 2.777 | 0.926 |
| Z201-4 | y = −0.191x + 0.325 | 2.809 | 0.877 | Z201-14 | y = −0.247x + 1.02 | 2.753 | 0.923 |
| Z201-6 | y = −0.189x + 1.53 | 2.811 | 0.849 | Z201-16 | y = −0.234x +1.93 | 2.766 | 0.888 |
| Z201-8 | y = −0.230x + 1.43 | 2.77 | 0.914 | Z201-18 | y = −0.219x + 1.63 | 2.781 | 0.881 |
| Z201-10 | y = −0.299x + 1.46 | 2.701 | 0.933 | Z201-20 | y = −0.242x + 1.97 | 2.758 | 0.914 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, M.; Chen, Y.; Tang, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, J. Multiscale Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity in Deep Marine Qiongzhusi Shales from Southern Basin, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050515
Zheng M, Chen Y, Tang T, Wu Y, Chen Y, Chen J, Peng S, Zhang J. Multiscale Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity in Deep Marine Qiongzhusi Shales from Southern Basin, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Majia, Yana Chen, Tingke Tang, Ya Wu, Ying Chen, Junyu Chen, Shixuan Peng, and Jizhen Zhang. 2025. "Multiscale Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity in Deep Marine Qiongzhusi Shales from Southern Basin, China" Minerals 15, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050515
APA StyleZheng, M., Chen, Y., Tang, T., Wu, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, J., Peng, S., & Zhang, J. (2025). Multiscale Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity in Deep Marine Qiongzhusi Shales from Southern Basin, China. Minerals, 15(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050515







