Petrogenesis of Jurassic Granite from the Shuitou Pluton in South Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Enrichment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background and Petrology
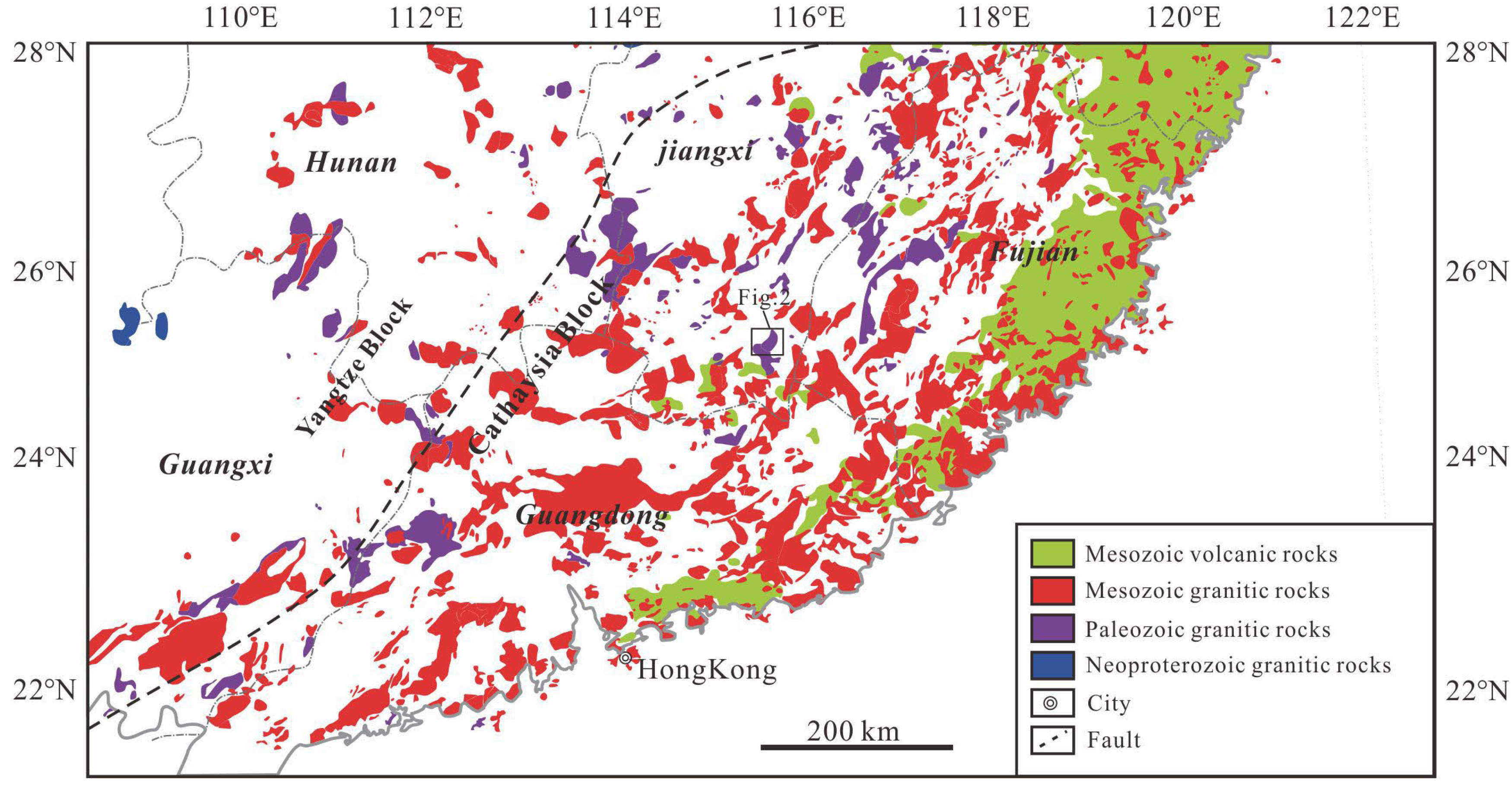
2.1. Geological Background

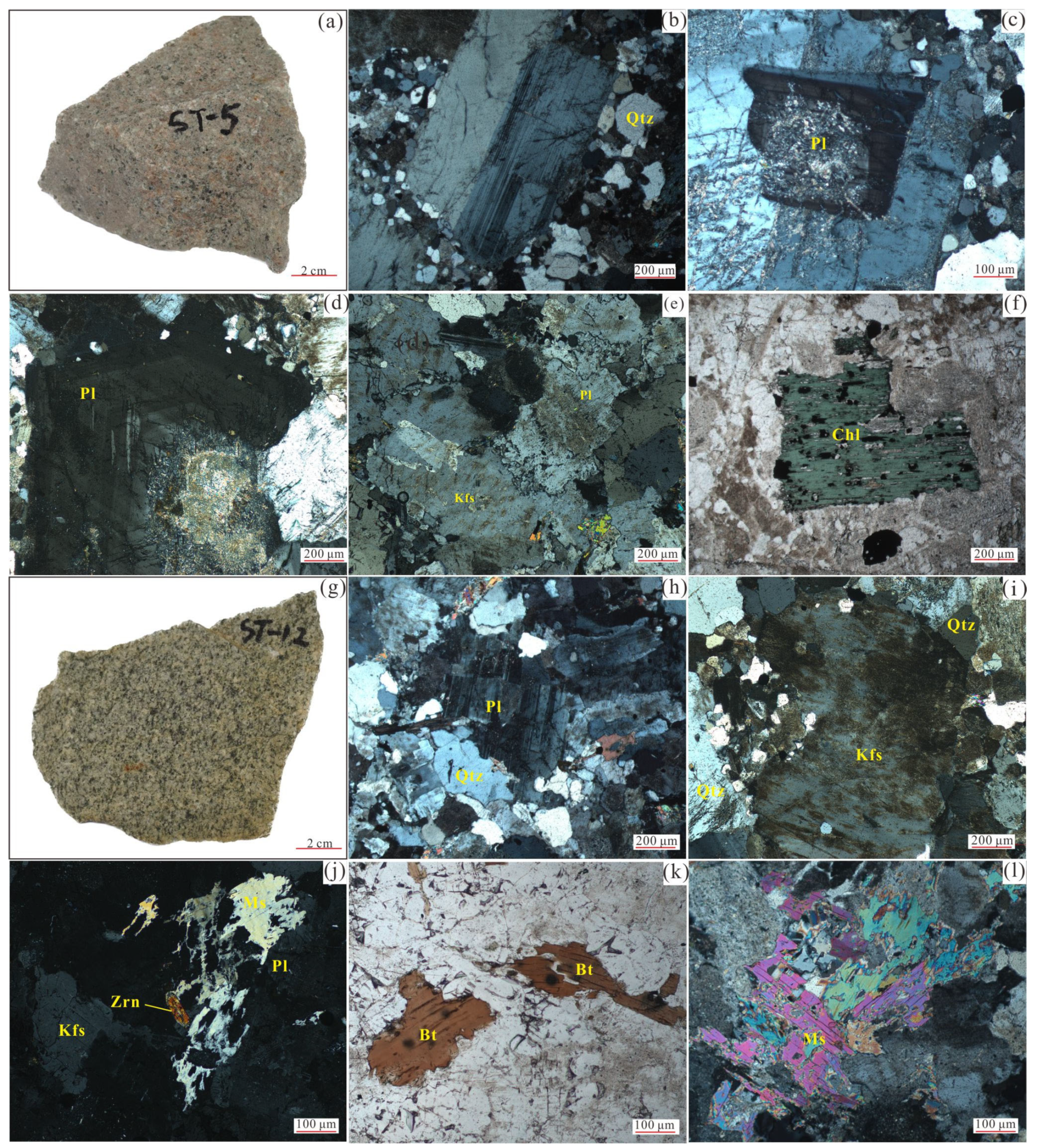
2.2. Petrology
3. Analytical Methods
3.1. Zircon and Monazite U–Pb Dating
3.2. Zircon Hf and Monazite Nd In Situ Analyses
3.3. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Element Analyses
4. Analysis Results
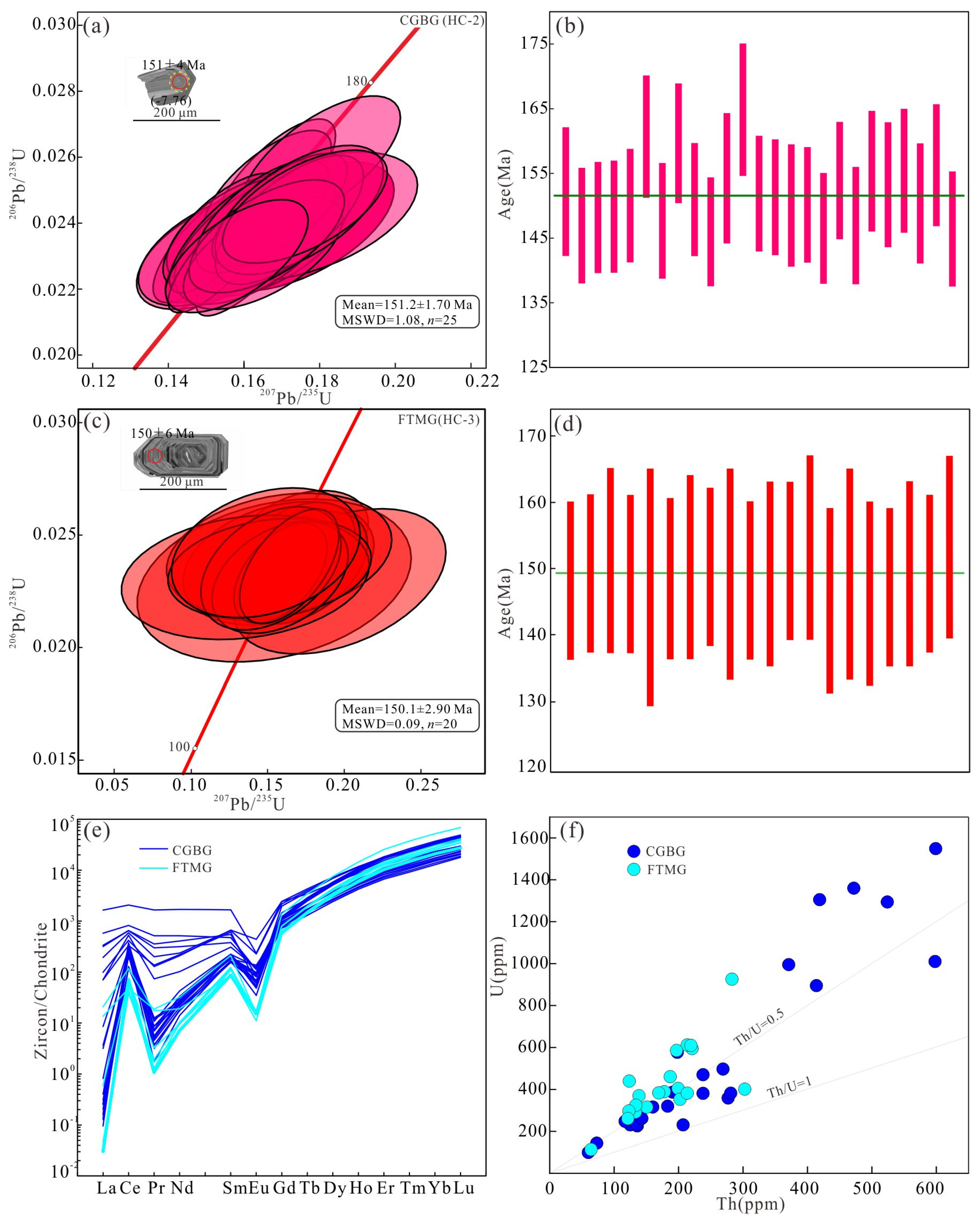
4.1. Zircon U–Pb Dating
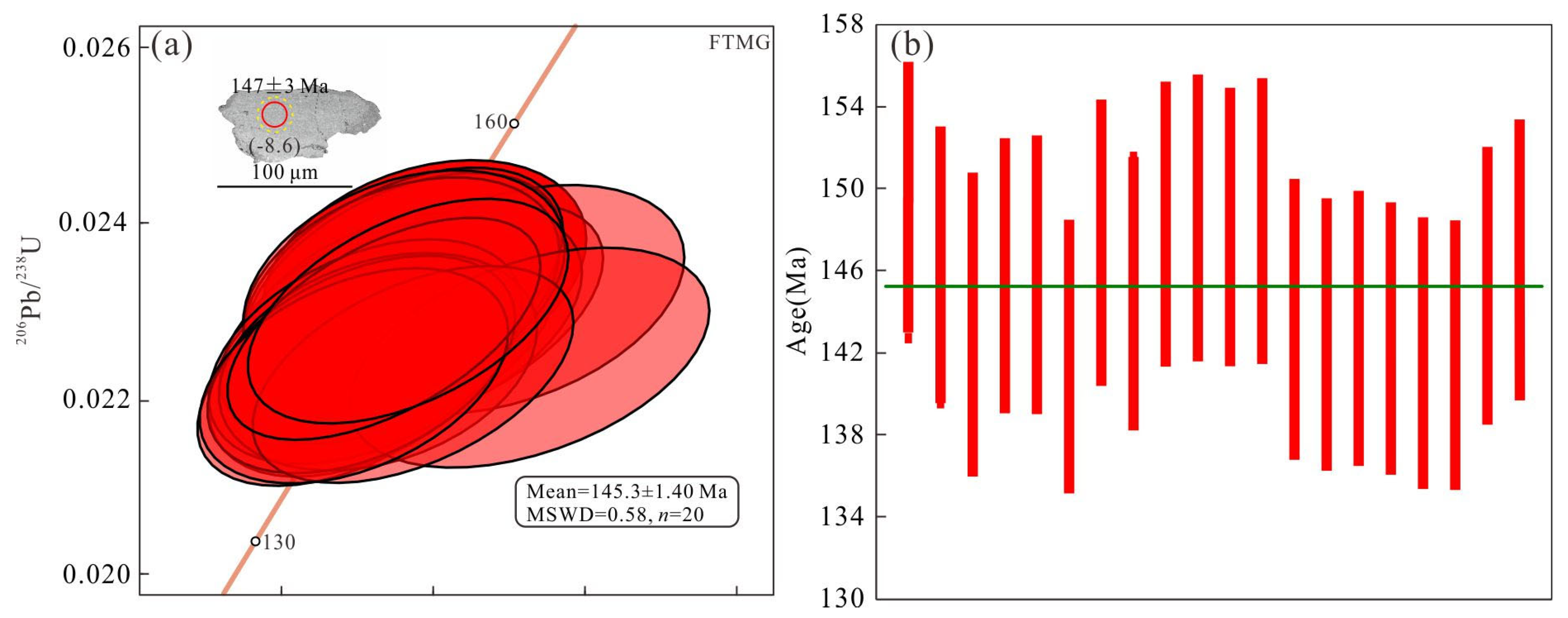
4.2. Monazite U–Pb Dating
4.3. Whole-Rock Geochemical Characteristics
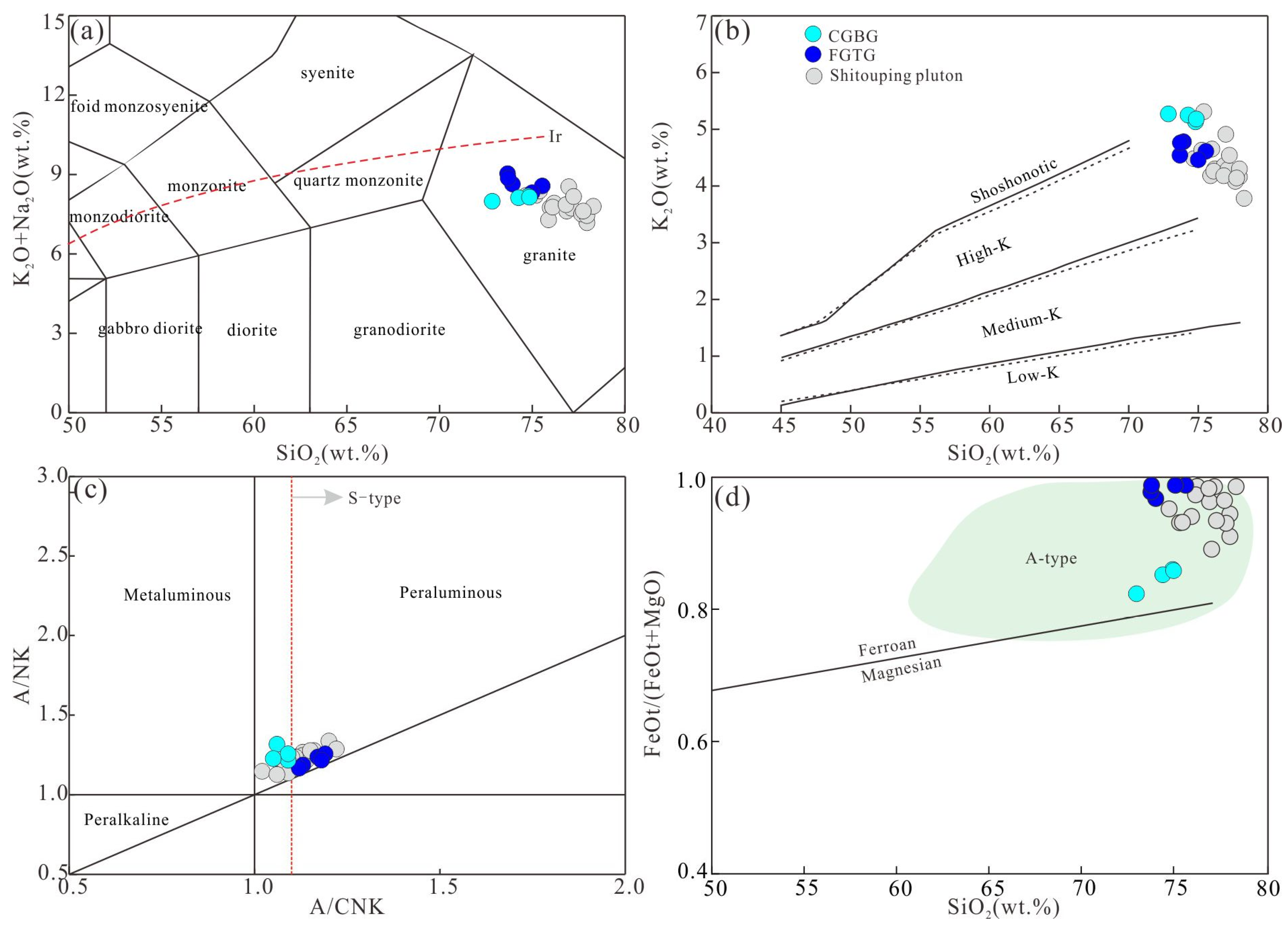
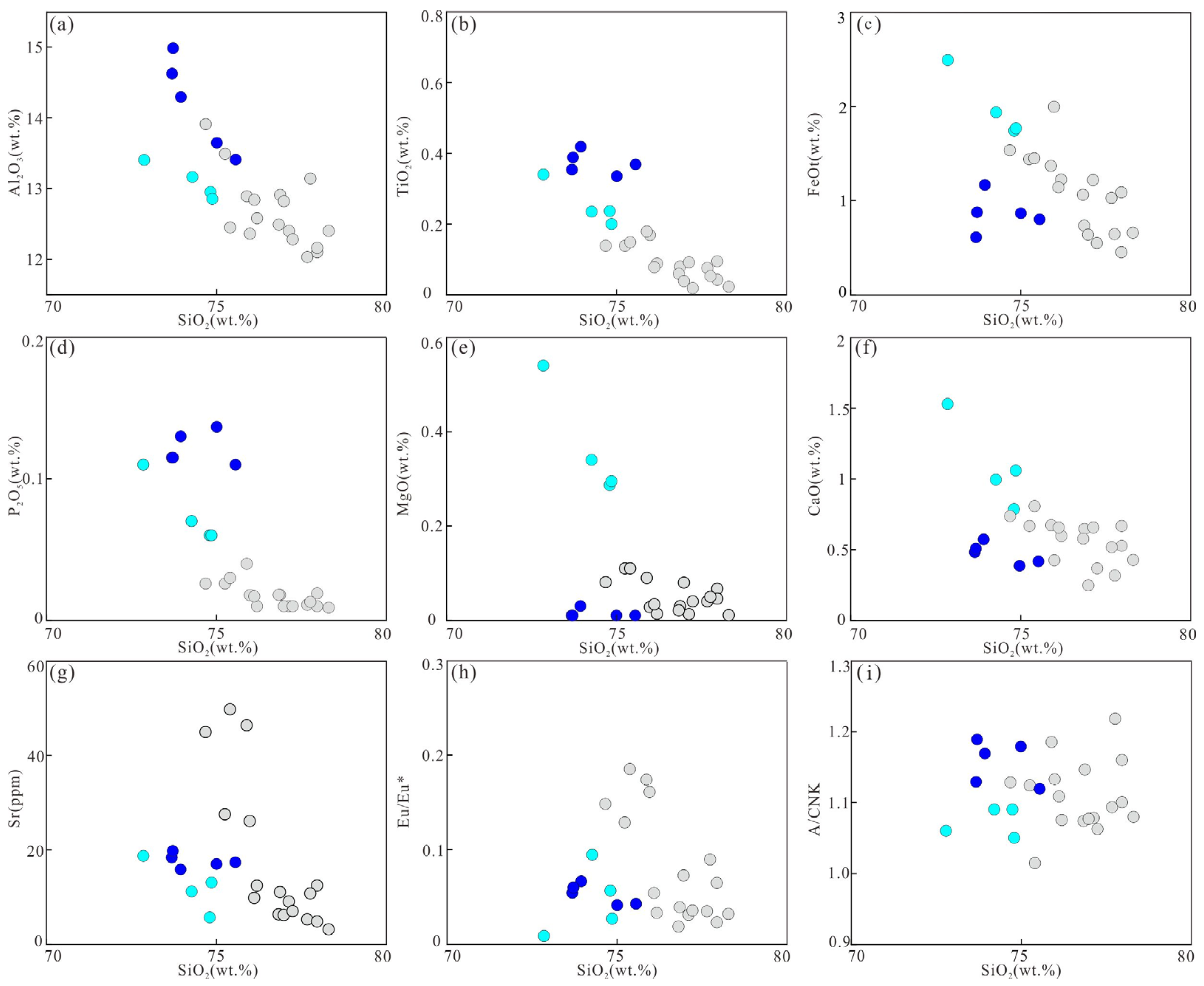
4.3.1. Major Elements
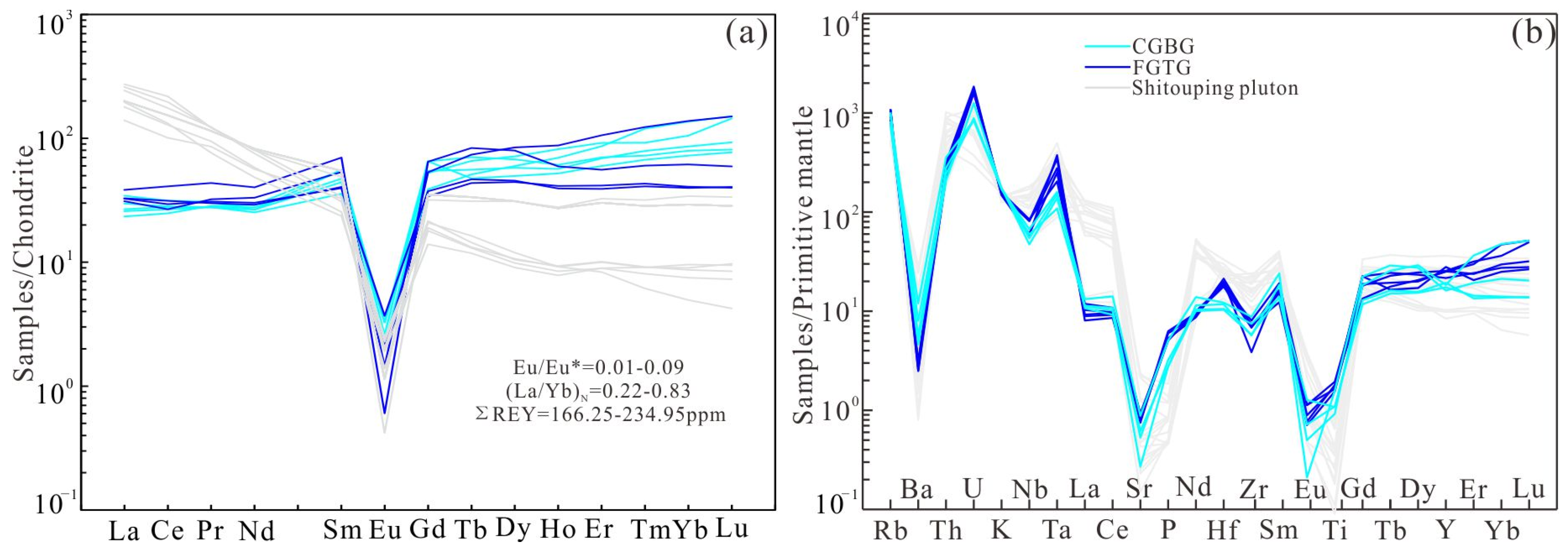
4.3.2. REE and Trace Elements
4.4. Zircon Hf Isotopic Results
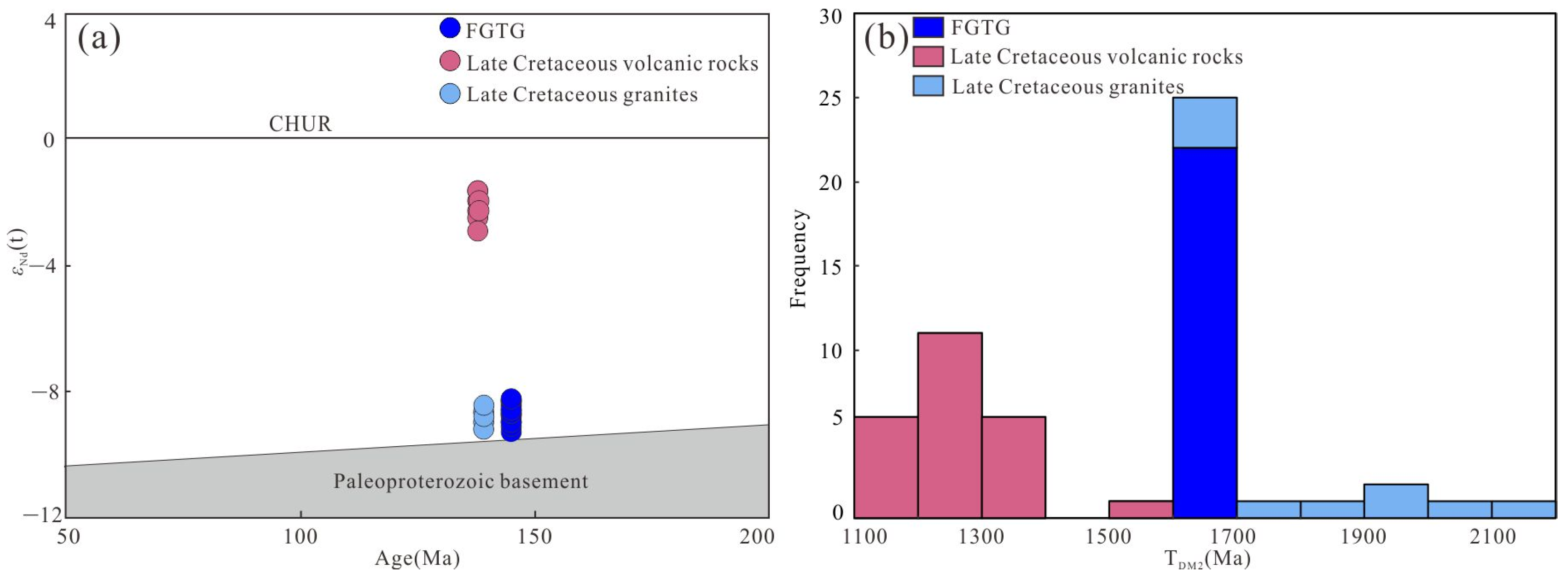
4.5. Monazite Nd Isotopic Results
5. Discussion
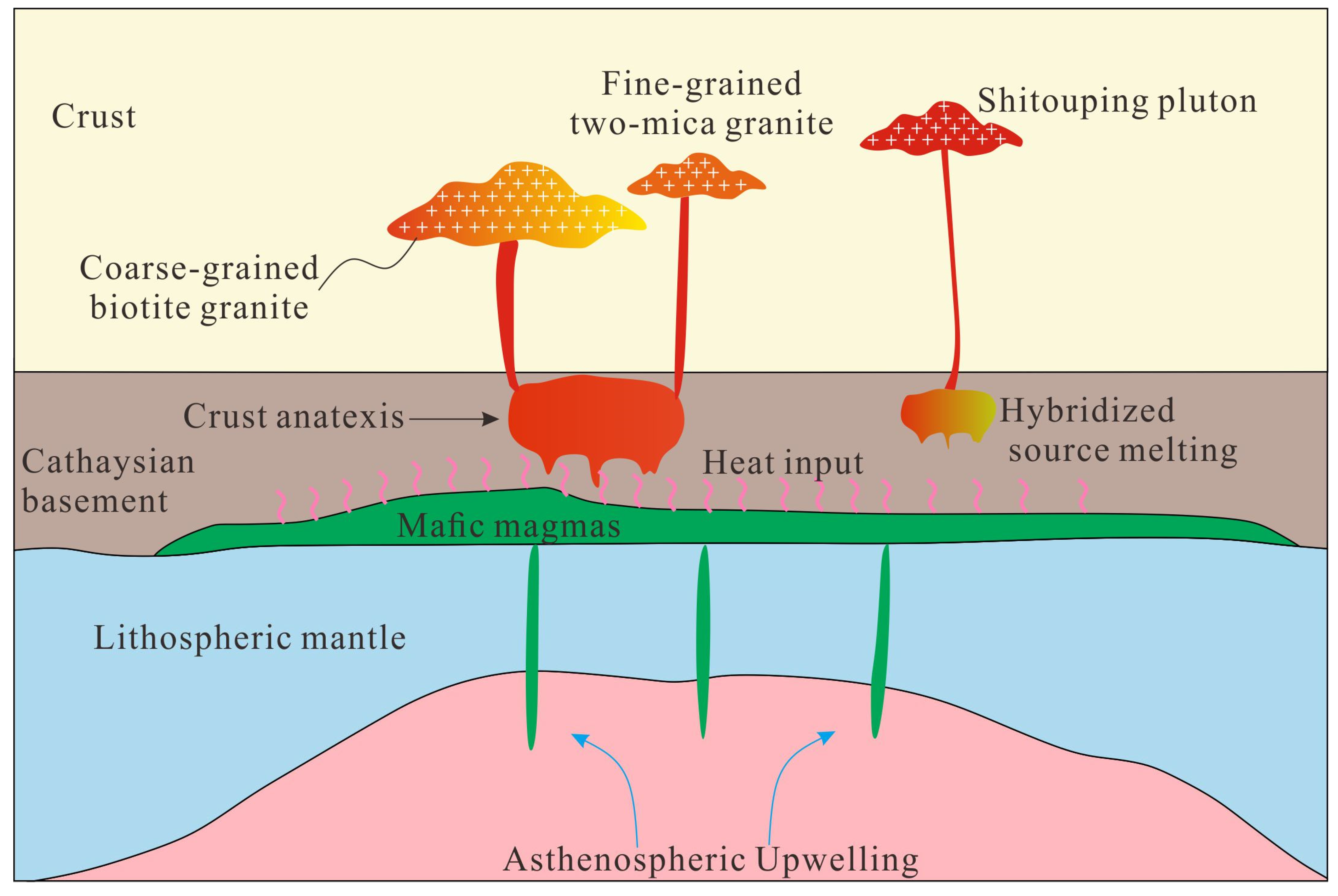
5.1. Petrogenesis of Shuitou Pluton
5.2. Magma Source
5.3. Geodynamic Setting
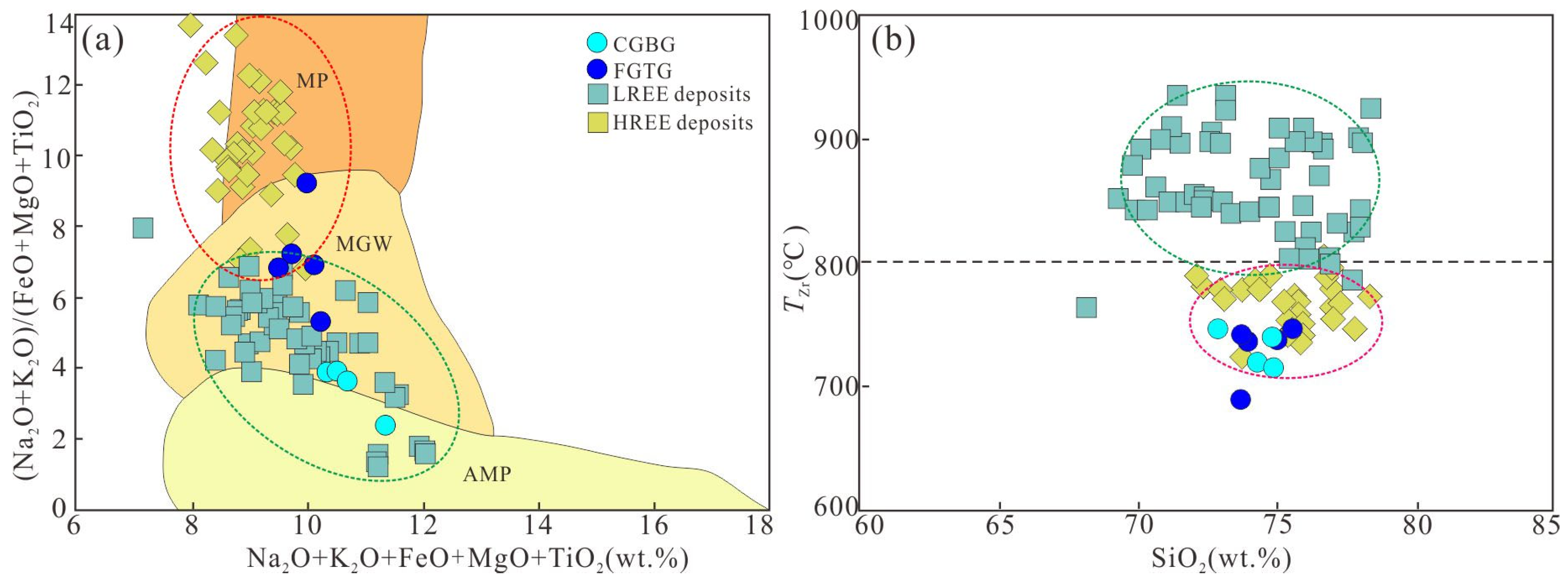
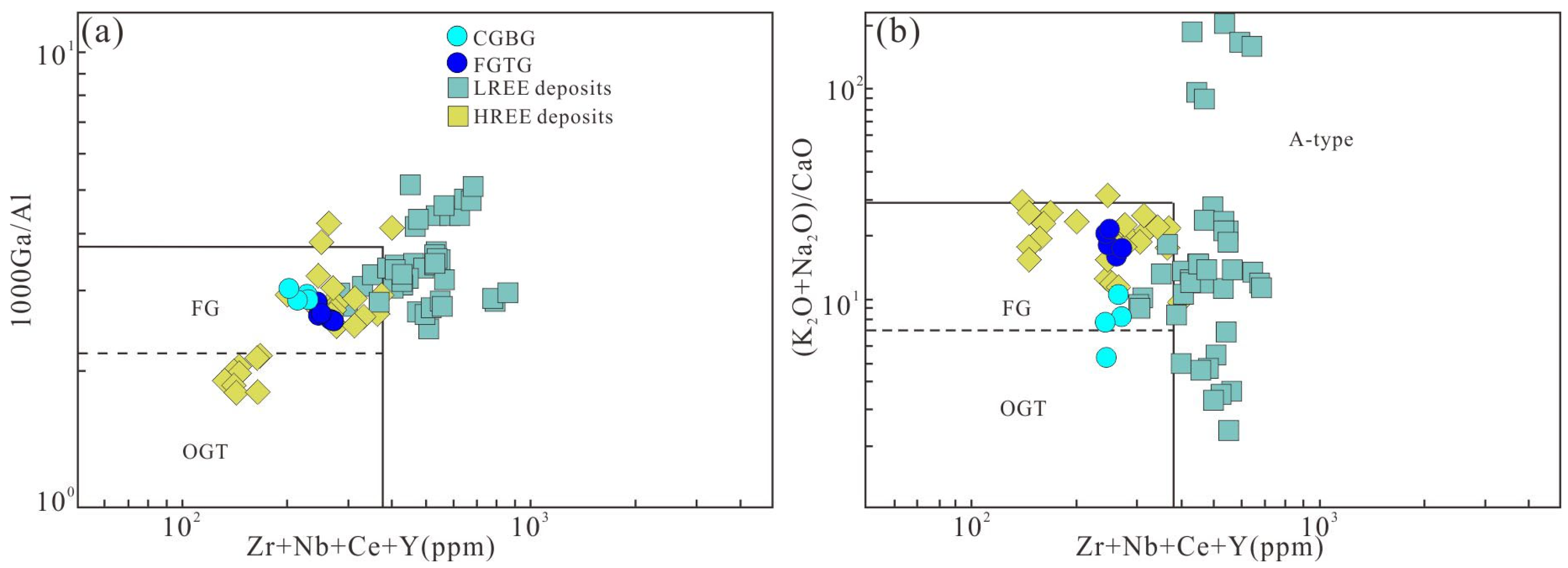
5.4. Implications for REE Enrichment
6. Conclusions
- The Shuitou pluton was formed at about 150 Ma and it contains Al-enriched minerals such as muscovite and garnet, has a high A/CNK value, and is classified as S-type granite.
- The εHf(t) values of zircon in the coarse-grained biotite syenogranite (CGBG) are −10.04 to −6.78, and the εHf(t) values of monazite in the fine-grained two-mica monzogranite (FGTG) are −9.27 to −8.26, indicating that the Shuitou pluton was derived from the partial melting of lower crustal sedimentary rocks.
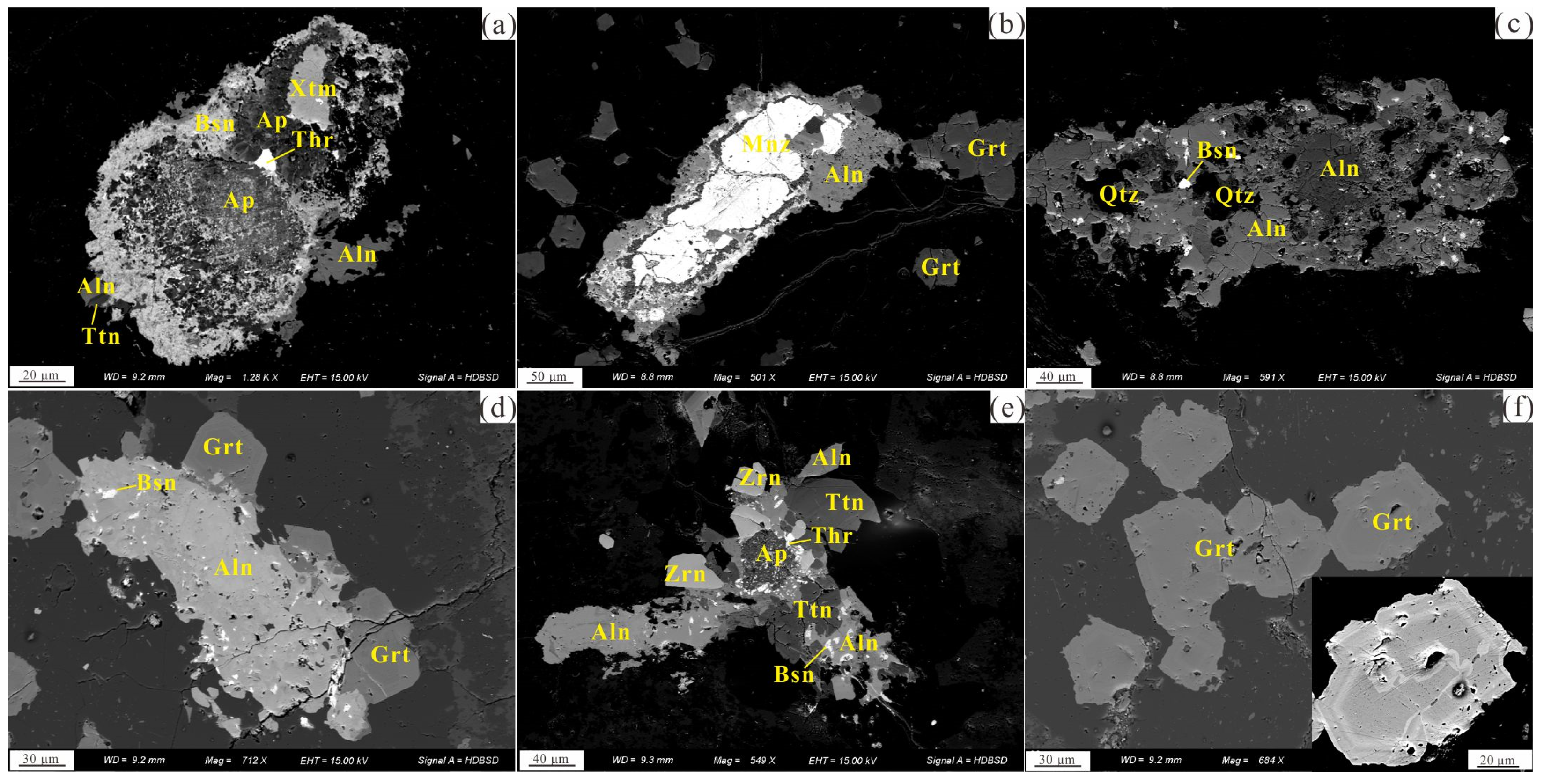
- The extensional tectonic setting is conducive to the initial enrichment of rare earth elements in the granite, and the higher content of F increases the solubility of REEs in the molten mass. Furthermore, REE-enriched minerals such as garnet, titanite, bastnaesite, and allanite in the Shuitou pluton also provide essential material conditions for the formation of the ion-adsorption REE deposit.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.Q.; Nie, L.S.; McKinley, J.M.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, B.M.; Han, Z.X. Geochemical background and dispersion pattern of the world’s largest REE deposit of Bayan Obo, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 215, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynicky, J.; Smith, M.P.; Xu, C. Diversity of rare earth deposits: The key example of China. Elements 2012, 8, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S.M.; Wong, V.N.L.; Wilson, S.; Gore, O. Critical metals in the critical zone: Controls, resources and future prospectivity of regolith-hosted rare earth elements. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 64, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulley, A.L.; Nassar, N.T.; Xun, S.A. China, the United States, and competition for resources that enable emerging technologies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4111–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Li, X.T.; Feng, Y.Y.; Feng, M.; Peng, Z.; Yu, H.X.; Lin, H.R. Chemical weathering of S-type granite and formation of rare earth element (REE)-rich regolith in South China: Critical control of lithology. Chem. Geol. 2019, 520, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.W.; Zhao, Z.H. Geochemistry of mineralization with exchangeable REY in the weathering crusts of granitic rocks in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 33, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F. The role of clay minerals in formation of the regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Liang, X.L.; He, H.P.; Li, J.T.; Ma, L.Y.; Tan, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Zhou, M.F.; Dong, H.L. Microorganisms accelerate REE mineralization in supergene environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e00632-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Tan, W.; Liang, X.L.; He, H.P.; Ma, L.Y.; Bao, Z.W.; Zhu, J.X. REE fractionation controlled by REE speciation during formation of the Renju regolith-hosted REE deposits in Guangdong Province, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.F. Nature of Parent Rocks, Mineralization Styles and Ore Genesis of Regolith-Hosted REE Deposits in South China: An Integrated Genetic Model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kynický, J.; Smith, M.P.; Kopriva, A.; Brtnický, M.; Urubek, T.; Song, W.L. Origin of heavy rare earth mineralization in South China. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Han, J.Z. REE geochemistry and mineralization characteristics of the Zudong and Guanxi granites, Jiangxi Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 1989, 2, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Hua, R.M.; Hoshino, M.; Murakami, H. REE abundance and REE minerals in granitic rocks in the Nanling range, Jiangxi Province, southern China, and generation of the REE-rich weathered crust deposits. Resour. Geol. 2008, 58, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. Characteristics and genesis of ion adsorption-type rare earth element deposits. Rev. Econ. Geol. 2016, 18, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.H.; Bagas, L.; Chen, Z.Y. Geochemical and REE mineralogical characteristics of the Zhaibei Granite in Jiangxi Province, southern China, and a model for the genesis of ion-adsorption REE deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, N.B.; Huizenga, J.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, W.B.; Niu, H.C. Granitic magma evolution to magmatic-hydrothermal processes vital to the generation of HREEs ion-adsorption deposits: Constraints from zircon texture, U–Pb geochronology, and geochemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 146, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.X.; Wang, X.G.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhong, W.; Cao, M.X. Zircon as a Monitoring Tool for the Magmatic-Hydrothermal Process in the Granitic Bedrock of Shitouping Ion-Adsorption Heavy Rare Earth Element Deposit, South China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.X.; Wang, X.G.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Gong, L.X.; Zhong, W. Petrogenesis and REE mineralogical characteristics of Shitouping granites in southern Jiangxi Province: Implication for HREE mineralization in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 168, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Kynicky, J.; Song, W.L.; Wang, L.Z. Petrogenesis and mineralization of REE-rich granites in Qingxi and Guanxi, Nanling region, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.X.; Xu, C.; Shi, A.G.; Smith, M.P.; Kynicky, J.; Wei, C.W. Origin of heavy rare earth elements in highly fractionated peraluminous granites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2023, 343, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.M.; Zhang, W.L.; Gu, S.Y.; Chen, P.R. Comparison between REE granite and W-Sn granite in the Nanling region, South China and their mineralizations. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.M.; Sun, T.; Shen, W.Z.; Shu, L.S.; Niu, Y.L. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 2006, 29, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Li, X.H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model. Geology 2007, 35, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, P.; Li, P.Q.; Lu, J.P.; Zhou, H.; Yi, Z.B.; Xu, C. Mineralization diversity of ion-adsorption type REE deposit in southern China and its critical influence by parent rocks. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3901–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.H.; Li, W.X.; Wyman, D.A.; Wang, A.D.; Xu, Z.T. Petrogenesis of Triassic Granite from the Jintan Pluton in Central Jiangxi Province, South China: Implication for Uranium Enrichment. Lithos 2018, 320, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, M.H.; Piraino, F. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Hao, X.L.; Li, Y.L.; Sun, W. The formation of the Dabaoshan porphyry molybdenum deposit induced by slab rollback. Lithos 2012, 150, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Li, X.H.; Collins, W.J.; Huang, H.Q. U–Pb age and Hf–O isotopes of detrital zircons from Hainan Island: Implications for Mesozoic subduction models. Lithos 2015, 239, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.S.; Zhao, K.; He, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Hong, W.T. Cretaceous volcanic-plutonic magmatism in SE China and a genetic model. Lithos 2021, 402, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F.; Williams-Jones, A.E. The genesis of regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits: Insights from the world-class Zudong deposit in Jiangxi Province, South China. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Lou, F.S.; Zhang, F.R.; Ding, P.X.; Cao, Y.B.; Xu, Z.; Sun, C.; Feng, Z.H.; Ling, L.H. Anatexis-ceremonies magmatism activity of the Qishan granitic pluton in Southern Jiangxi: Chronological study of zircon U–Pb precise dating. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Cao, M.X.; Gong, X.; Gong, L.X.; Zhong, W.; Qiu, W.J.; Wang, X.G. Geological characteristics of metallogenic host rock and their genetic significance of Shitouping heavy rare earth deposit in Southern Jiangxi Province. J. East China Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2024, 47, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, T.; Li, X.W.; Tao, J.H.; Zhao, X.L.; Xing, G.F. Geochronology, geochemistry and zircon Hf isotope for Banshi and Caifang volcanic rocks from southern Jiangxi province and their geological implications. Geotecton. Metallog. 2017, 41, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, K.D.; Palmer, M.R.; Chen, W.; Jiang, S.Y. Exploring volcanic-intrusive connections and chemical differentiation of high silica magmas in the Early Cretaceous Yanbei caldera complex hosting a giant tin deposit, Southeast China. Chem. Geol. 2021, 584, 120501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T. A new map showing the distribution of granites in South China and its explanatory notes. Geol. Bull. China. 2006, 25, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.C.; Wang, D.B. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U–Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00-A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol. Cent. Spec. Publ. 2003, 4, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Blichert-Toft, J.; Albarède, F. The Lu–Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 148, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Pearson, N.J.; Belousova, E.; Jackson, S.E.; Achterbergh, E.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Shee, S.R. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Wang, X.; Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Xu, X.S.; Zhou, X.M. Zircon geochemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous conplexes. Lithos 2002, 61, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.C.; Liu, Y.S. Iso-Compass: New freeware software for isotopic data reduction of LA-MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Luo, T.; Hu, S.H. In situ Nd isotope analyses in geological materials with signal enhancement and non-linear mass dependent fractionation reduction using laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, R.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks; Longman: London, UK, 1985; pp. 1–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniar, P.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 635–643. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/101/5/635/182281/Tectonic-discrimination-of-granitoids (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Frost, B.R.; Barnes, C.G.; Collins, W.J.; Arculus, R.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Frost, C.D. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, C.D.; Jin, W.J.; Jia, X.Q. A granite classification based on pressures. Geol. Bull. Geol. Surv. China. 2006, 25, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Gao, S. Lu–Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 185–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelin, Y.; Lee, D.C.; Halliday, A.N.; Pidgeon, R.T. Nature of the Earth’s earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature 1999, 399, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, J.D.; Patchett, P.J.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Albarède, F. Relationships between Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd isotopic systems in the global sedimentary system. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 168, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Yang, J.H.; Guo, H.F.; Xiong, X.L.; Ou, Q.; Zeng, J.P.; Gou, G.N.; et al. Early Cretaceous Sn-bearing granite porphyries, A-type granites, and rhyolites in the Mikengshan-Qingxixiang-Yanbei area, South China: Petrogenesis and implications for ore mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 235, 105274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. Two contrasting granite types. Pac. Geol. 1974, 8, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.M.; Tapia, M.D.M.; Schilling, J.G. The petrology and geochemistry of the Azores Islands. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1979, 69, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos 1999, 46, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, D.C.; Chappell, B.W. Petrogenesis of felsic I-type granites: An example from northern Queensland. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1992, 83, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.L.; Chappell, B.W.; Allen, C.M.; White, A.J.R. Are A-type granites the high-temperature felsic granites? Evidence from fractionated granites of the Wangrah Suite. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 48, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiselle, M.C.; Wones, D.R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1979, 11, 468. [Google Scholar]
- King, P.L.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W.; Allen, C.M. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan fold belt, Southeastern Australia. J. Petrol. 1997, 38, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Li, N.B.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhao, X. Geochemical differences of parent rocks for ion-adsorption LREE and HREE deposits: A case study of the Guanxi and Dabu granite plutons. Geotecton. Metallog. 2024, 48, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R.; Wyborne, D. The importance of residual source material (Restite) in granite petrogenesis. J. Petrol. 1987, 28, 1111–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 1998, 45, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Zhou, L.D. REE geochemistry of some alkali-rich intrusive rocks in China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 1997, 40, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mc Lennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle Recycling. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 891–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.C.; Mo, X.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H. Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I-type granites in the Zayu area of eastern Gangdese, Tibet: Constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Lv, T.T.; Wang, X.G.; Cao, M.X.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Gong, L.X. Petrogenesis of REE-rich two-mica granite from the Indosinian Xiekeng pluton in South China Block with implications for REE metallogenesis. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 12, 1493594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Wang, X.G.; He, T.; Cao, M.X.; Lv, T.T.; Gong, L.X.; Xu, J. Petrogenesis and geological significance of the Caledonian heavy rare earth ore parent rock in southern Jiangxi province. Geoscience 2024, 38, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño Douce, A.E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas? Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1999, 168, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1983, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsü, K.J.; Sun, S.; Li, J.L.; Chen, H.L.; Pen, H.P.; Sengor, A.M.C. Mesozoic overthrust tectonics in south China. Geology 1988, 16, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.R.; Troll, V.R.; Cailleau, B.; Belousov, A.; Schmincke, H.U.; Amelung, F.; Bogaard, P.V.D. Rift zone reorganization through flank instability in ocean island volcanoes: An example from Tenerife, Canary Islands. Bull. Volcanol. 2005, 67, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilder, S.A.; Gill, J.B.; Coe, R.S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Yuan, K.; Liu, W.; Kuang, G.; Wu, H. Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of south China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1996, 101, 16137–16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in southeast China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.R.; Tao, K.Y.; Xing, G.F.; Yang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y. Petrological records of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic mantle plume tectonics in epicontinental area of Southeast China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 1999, 20, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.Q.; Hu, R.Z.; Zhao, J.H.; Jiang, G.H. Mantle plume and the relationship between it and mesozoic large-scale metallogenesis in Southeastern China: A preliminary discussion. Geotecton. Metallog. 2001, 25, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.F.; Mo, X.X.; Zhao, H.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Luo, Z.H.; Su, S.G. A new model for the dynamic evolution of Chinese lithosphere: ‘continental roots-plume tectonics’. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 65, 223–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.R.; Xu, N.Z.; Hu, Q.; Xing, G.F.; Yang, Z.L. The Mesozoic rock-forming and ore-forming processes and tectonic environment evolution in Shanghang-Datian region, Fujian. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Dong, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhao, G.C.; Johnston, S.T.; Cui, J.J.; Xin, Y.J. New insights into Phanerozoic tectonics of south China: Part 1, polyphase deformation in the Jiuling and Lianyunshan domains of the central Jiangnan Orogen. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2016, 121, 3048–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjo, R.; Kato, Y. Geochemical constraints on the origin of bimodal magmatism at the Okinawa Trough, an incipient back-arc basin. Lithos 2000, 54, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, T.S.; Åhäll, K.I.; Menuge, J.F.; Storey, C.; Parrish, R. Mesoproterozoic bimodal volcanism in SW Norway, evidence for recurring pre-Sveconorwegian continental margin tectonism. Precambrian Res. 2004, 134, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, G.J.; Qi, C.S. U–Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I- and A- type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab? Lithos 2007, 96, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, Y.C. Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: Metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes. Sin. Acta Petrol. 2007, 23, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Shinjo, R. Was there Jurassic paleo-Pacific subduction in South China?: Constraints from 40Ar/39Ar dating, elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Mesozoic basalts. Lithos 2008, 106, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, C.Q.; Xing, G.F.; Zhou, H.W. The Early Cretaceous evolution of SE China; Insights from the Changle-Nan’ao Metamorphic Belt. Lithos 2015, 230, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Hou, Z.Q.; Lü, Q.T.; Zhang, X.W.; Pan, X.F.; Fan, X.K.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, C.G.; Lü, Y.J. Crustal architectural controls on critical metal ore systems in South China based on Hf isotopic mapping. Geology 2023, 51, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Cawood, P.A.; Li, S.Z. Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic constraints on multiple mantle domains for Mesozoic mafic rocks beneath the South China Block hinterland. Lithos 2008, 106, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.H.; Xing, G.F.; Zeng, Y.; Ge, W.Y. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Cretaceous A-type granites from the NE Jiangnan Orogen, SE China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 1359–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Xu, X.S. Petrogenesis of the Late Yanshanian mantle-derived intrusions in southeastern China; Response to geodynamics of paleo-Pacific plate subduction. Chem. Geol. 2012, 328, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. Treat. Geochem. 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, K.X.; Chen, L.K.; Zhu, P.; Ouyang, H. Metallogenic Features of Ion-adsorption Type REE Deposits in Southern Jiangxi Province. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths. 2015, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Wu, C.Y.; Ding, X.S.; Yuan, Z.X.; Huang, D.H.; Wang, P.H. Genesis and Spatial Distribution of Ion-Adsorption Type Ree Deposit in Nanling Region; Institute of Ore Deposit Geology: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Luo, P.; Hu, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.Y.; Peng, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.B.; Feng, M.; Yu, H.X.; Zhou, Y.Z. Enrichment of ion-exchangeable rare earth elements by felsic volcanic rock weathering in South China: Genetic mechanism and formation preference. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, N.B.; Huizenga, J.M.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Niu, H.C. Rare earth element enrichment in the ion-adsorption deposits associated granites at Mesozoic extensional tectonic setting in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 137, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.B.; Ding, X.; Ling, M.X.; Li, C.Y.; Harlov, D.E.; Sun, W.D. Three late-Mesozoic fluorite deposit belts in southeast China and links to subduction of the (paleo-) Pacific plate. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 129, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Beams, S.D.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 80, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjerlie, K.P.; Johnston, A.D. Fluid-absent melting behavior of an F-rich tonalitic gneiss at mid-crustal pressures: Implications for the generation of anorogenmic granites. J. Petrol. 1993, 34, 785–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.R.; Gysi, A.P.; Hurtig, N.C. Hydrothermal fluorite solubility experiments and mobility of REE in acidic to alkaline solutions from 100 to 250 °C. Chem. Geol. 2023, 67, 121256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Tang, M.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Petrogenesis of Jurassic Granite from the Shuitou Pluton in South Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Enrichment. Minerals 2025, 15, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050476
You S, Zhang D, Liu H, Tang M, Pang X, Wang Y, Zhang Z. Petrogenesis of Jurassic Granite from the Shuitou Pluton in South Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Enrichment. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050476
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Shuifeng, Defu Zhang, Hanfeng Liu, Meihua Tang, Xinlong Pang, Yufei Wang, and Zhiwei Zhang. 2025. "Petrogenesis of Jurassic Granite from the Shuitou Pluton in South Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Enrichment" Minerals 15, no. 5: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050476
APA StyleYou, S., Zhang, D., Liu, H., Tang, M., Pang, X., Wang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Petrogenesis of Jurassic Granite from the Shuitou Pluton in South Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Enrichment. Minerals, 15(5), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050476