Extraction of Copper from Printed Circuit Boards in an Alkaline Solution Using EDTA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grinding, Classification, and Characterization of WPCBs
2.2. Copper Extraction Process with H2O2/EDTA
2.3. Determination of Extracted Copper Amount by UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
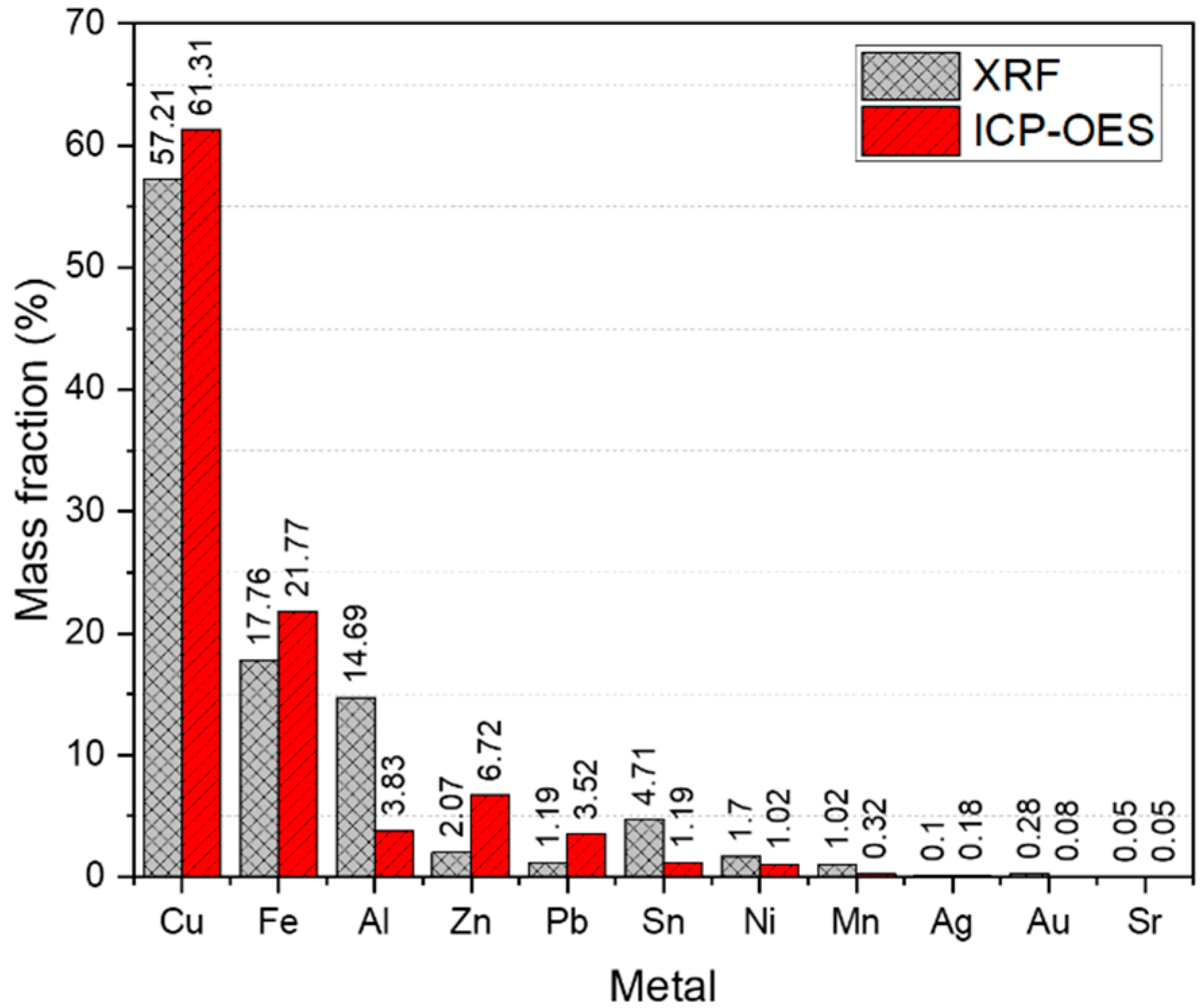
3.1. XRF Analysis of WPCB Samples
3.2. ICP-OES Analysis of WPCB Samples
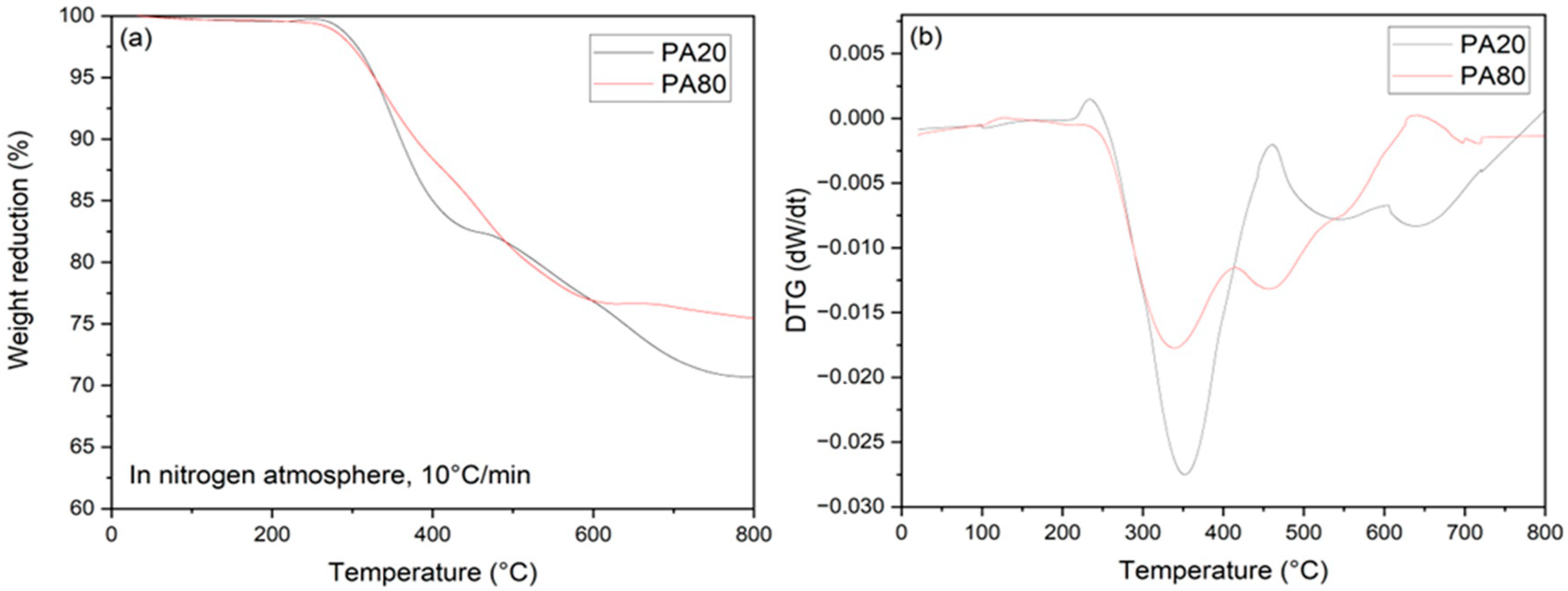
3.3. Determination of the Polymeric Fraction
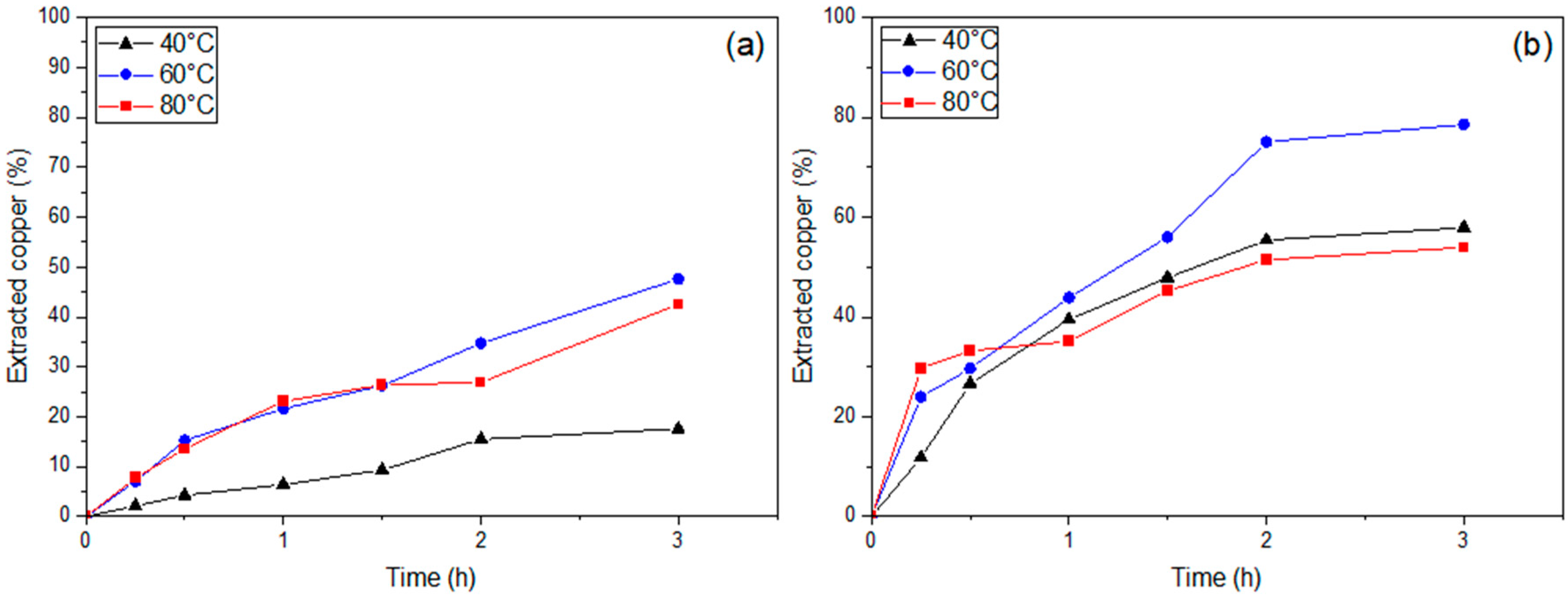
3.4. Copper Extraction from WPCBs with H2O2/EDTA
3.5. Kinetics of Copper Extraction from WPCBs with H2O2/EDTA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shittu, O.S.; Williams, I.D.; Shaw, P.J. Global E-Waste Management: Can WEEE Make a Difference? A Review of e-Waste Trends, Legislation, Contemporary Issues and Future Challenges. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Awasthi, A.K.; Qin, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, C. Recycling Value Materials from Waste PCBs Focus on Electronic Components: Technologies, Obstruction and Prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R. E-Waste Statistics: Guidelines on Classifications, Reporting and Indicators, 2nd ed.; United Nations University, ViE–SCYCLE: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Yamamoto, T.; McDonald, R.; Althaf, S.; Bel, G.; Deubzer, O.; Fernandez-Cubillo, E.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; et al. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2024; Genebra: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Charitopoulou, M.A.; Stefanidis, S.D.; Lappas, A.A.; Achilias, D.S. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Polymers with Brominated Flame-Retardants Originating in Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Using Various Catalysts. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 26, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, N.R.; Arias, S.F.R.; Rivera, L.A.M.; Oliveros, M.E.M. Recovery of Copper through Concentration Processes from Ashes Produced by WEEE Pyrolysis. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2021, 19, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumbergs, E.; Serga, V.; Shishkin, A.; Goljandin, D.; Shishko, A.; Zemcenkovs, V.; Markus, K.; Baronins, J.; Pankratov, V. Selective Disintegration–Milling to Obtain Metal-Rich Particle Fractions from E-Waste. Metals 2022, 12, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Eksteen, J.; Oraby, E. Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Metals from Waste Printed Circuit Boards (WPCBs): Current Status and Perspectives–A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, M.; Gurumurthy, K. Characterization of End-of-Life Mobile Phone Printed Circuit Boards for Its Elemental Composition and Beneficiation Analysis. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2021, 71, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekar, S.; Stella, T.J.; Thenmozhi, A.; Bharathi, N.D.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Singh, P.; Reddy, Y.S.; Srinivas, G.; Jayakumar, M. Study of Polymer Matrix Composites for Electronics Applications. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 8605099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, F. Metal Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards: A Review for Current Status and Perspectives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Pickles, C.A. Potential and Current Practices of Recycling Waste Printed Circuit Boards: A Review of the Recent Progress in Pyrometallurgy. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei, R.K.; Pahlevani, F.; Rajarao, R.; Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Two-Step Pre-Processing Enrichment of Waste Printed Circuit Boards: Mechanical Milling and Physical Separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, C.; Soni, R.K. Milling and Classification of Printed Circuit Boards for Material Recycling. Part. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubau, A.; Chagnes, A.; Minier, M.; Touzé, S.; Chapron, S.; Guezennec, A.G. Recycling-Oriented Methodology to Sample and Characterize the Metal Composition of Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Waste Manag. 2019, 91, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touzé, S.; Laperche, V.; Hubau, A.; Moreau, P. PXRF on Printed Circuit Boards: Methodology, Applications, and Challenges. Waste Manag. 2022, 146, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Holuszko, M.E.; Janke, T. Determination of loss on ignition test conditions for nonmetal fraction from processed waste printed circuit boards. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsawa, T.; Traiwongsa, N.; Pancharoen, U.; Nootong, K. A Review of the Recovery of Precious Metals Using Ionic Liquid Extractants in Hydrometallurgical Processes. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, S.; Nie, C.; Zhu, X.; Jiao, T. Review on the Gentle Hydrometallurgical Treatment of WPCBs: Sustainable and Selective Gradient Process for Multiple Valuable Metals Recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. The Twelve Principles of Circular Hydrometallurgy. J. Sust. Metall. 2023, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, R.; Sivasankari, C.; Thirunavukkarasu, A. Electronic Waste Generation, Regulation and Metal Recovery: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1347–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirola, K. Chelating Adsorbents in Purification of Hydrometallurgical Solutions; Lappeenrannan Teknillinen Yliopisto: Lappeenranta, Finland, 2009; ISBN 978-952-214-843-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, G.; Jadhao, P.R.; Pant, K.K.; Nigam, K.D.P. Novel Technologies and Conventional Processes for Recovery of Metals from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment: Challenges & Opportunities–A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1288–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Deng, C.; Liu, T.; Xue, D.; Gong, J.; Tan, R.; Mi, X.; Gong, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; et al. Selective Recovery of Copper from Electroplating Sludge by Integrated EDTA Mixed with Citric Acid Leaching and Electrodeposition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhao, P.; Chauhan, G.; Pant, K.K.; Nigam, K.D.P. Greener Approach for the Extraction of Copper Metal from Electronic Waste. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefzadeh, S.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S.; Alavi, N.; Nabizadeh, R. Comparative Analysis of Hydrometallurgical Methods for the Recovery of Cu from Circuit Boards: Optimization Using Response Surface and Selection of the Best Technique by Two-Step Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzyk, B.; Martyak, N.M.; Berger, P. Complexation Equilibria for the Copper—EDTA—Cyanide System. Trans. IMF 1995, 73, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.K.; Oh, W.Z.; Woo, S.I. Dissolution Behaviors of Copper Metal in Alkaline H2O2-EDTA Solutions. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1993, 30, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torres, R.; Lapidus, G.T. Copper Leaching from Electronic Waste for the Improvement of Gold Recycling. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.R.H. The Kinetics and Mechanisms of Catalytic Reactions. In Heterogeneous Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwadasi, B.S.; Goverapet Srinivasan, S.; Rai, B. Interfacial Structure in the Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Rare Earth Elements by Phosphoric Acid Ligands: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4177–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlík, T. Kinetics of Heterogeneous Reactions of Leaching Processes. In Hydrometallurgy; Havlík, T., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 184–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. Kinetics and Behavior of Cobalt Extraction from Low Nickel Matte Converter Slag by Pressure Oxidative Leaching with Sulfuric Acid. CIESC J. 2015, 66, 3971–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzayanha, S.U.; Yudha, C.S.; Hasanah, L.M.; Gupita, L.T.; Widiyandari, H.; Purwanto, A. Comparative Study of Various Kinetic Models on Leaching of Nca Cathode Material. Indo J. Chem. 2020, 20, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, F. Optimizing the Leaching Parameters and Studying the Kinetics of Copper Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3689–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Kinetics of Vanadium Leaching from a Spent Industrial V2O5/TiO2 Catalyst by Sulfuric Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Garciano, L.O.; Tran, T.; Wainwrigh, M.S. Structure and Kinetics of Leaching for the Formation of Skeletal (Raney) Cobalt Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Rashchi, F.; Mostoufi, N. Kinetics of Leaching: A Review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, N.; Løvik, A.N.; Figi, R.; Schreiner, C.; Kuntz, C.; Mählitz, P.M.; Rösslein, M.; Wäger, P.; Rotter, V.S. Multi-Element Chemical Analysis of Printed Circuit Boards: Challenges and Pitfalls. Waste Manag. 2019, 92, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canassa, T. Utilização Da Lei de Lambert-Beer Para Determinação Da Concentração de Soluções. J. Exp. Tech. Instrum. 2018, 1, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, S.B.; Saraswati, T.E.; Masykur, A.; Finantrena, N.N.F.; Syaima, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Tetrakis (2-Amino-3-Methylpyridine) Copper (II) Sulfate Tetrahydrate. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 349, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chang, F.; Ashraf, U.; Peng, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, L. Application of Corrected Methods for High-Resolution XRF Core Scanning Elements in Lake Sediments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suponik, T.; Franke, D.M.; Nuckowski, P.M.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D.; Tora, B. Impact of Grinding of Printed Circuit Boards on the Efficiency of Metal Recovery by Means of Electrostatic Separation. Minerals 2021, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, L.H.; de Moraes, V.T.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Tenório, J.A.S. Recycling of WEEE: Characterization of Spent Printed Circuit Boards from Mobile Phones and Computers. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Selective Copper Recovery by Acid Leaching from Printed Circuit Board Waste Sludge. Metals 2020, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Metal | PA20 | PA80 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | RSD (%) | Mean (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Bal | 45.39 | 1.16 | 41.99 | 1.28 |
| Cu | 26.85 | 1.02 | 13.21 | 1.22 |
| Al | 6.27 | 2.77 | 5.33 | 2.98 |
| Fe | 2.36 | 1.15 | 18.33 | 0.86 |
| Sn | 1.94 | 1.66 | 2.21 | 1.62 |
| Zn | 0.79 | 1.68 | 0.34 | 2.93 |
| Ni | 0.57 | 2.08 | 0.30 | 3.84 |
| Pb | 0.51 | 2.31 | 0.58 | 2.20 |
| Bi | 0.37 | 2.47 | 0.27 | 2.81 |
| Ti | 0.29 | 6.81 | 0.25 | 7.87 |
| Au | 0.13 | 4.97 | 0.09 | 6.15 |
| Ag | 0.07 | 3.07 | 0.04 | 3.67 |
| Mn | 0.04 | 17.53 | 0.18 | 7.31 |
| Sr | 0.03 | 3.54 | 0.03 | 3.36 |
| Metal | PA20 | PA80 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | RSD (%) | Mean (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Cu | 36.63 | 0.24 | 7.09 | 2.26 |
| Zn | 5.28 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| Fe | 4.52 | 0.23 | 19.73 | 0.3 |
| Pb | 1.77 | 4.57 | 0.77 | 5.79 |
| Al | 0.93 | 1.03 | 2.17 | 0.82 |
| Sn | 0.46 | 14.94 | 0.45 | 11.92 |
| Ni | 0.66 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 3.42 |
| Mn | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0.11 | 0.86 |
| Ag | 0.09 | 3.94 | 0.05 | 0.74 |
| Au | 0.03 | 5.64 | 0.03 | 16.64 |
| Sr | 0.01 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.14 |
| ME | 50.53 | 0.57 | 30.90 | 1.13 |
| Sample | Materials | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Polymer | Ceramic | ||||
| Mean (%) | SD (%) | Mean (%) | SD (%) | Mean (%) | SD (%) | |
| PA20 | 50.5 | 0.3 | 28.9 | 3.1 | 20.5 | 3.1 |
| PA80 | 30.9 | 0.4 | 24.1 | 3.4 | 44.9 | 3.4 |
| Time | PA20 | PA80 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Cu (%) | RSD (%) | Extraction Cu (%) | RSD (%) | |
| 40 °C | ||||
| T1 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 11.8 | 0.5 |
| T2 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 26.6 | 0.7 |
| T3 | 6.4 | 2.1 | 39.5 | 1.7 |
| T4 | 9.3 | 0.6 | 47.9 | 2.1 |
| T5 | 15.5 | 2.4 | 55.4 | 2.7 |
| T6 | 17.6 | 2.2 | 57.9 | 2.5 |
| 60 °C | ||||
| T1 | 7.0 | 0.6 | 24.0 | 6.3 |
| T2 | 15.3 | 2.2 | 29.7 | 1.7 |
| T3 | 21.6 | 2.0 | 43.8 | 0.5 |
| T4 | 26.2 | 0.1 | 56.0 | 10.8 |
| T5 | 34.7 | 0.8 | 75.0 | 0.7 |
| T6 | 47.6 | 0.9 | 78.6 | 1.4 |
| 80 °C | ||||
| T1 | 7.8 | 0.6 | 29.7 | 1.0 |
| T2 | 13.6 | 1.2 | 33.2 | 0.9 |
| T3 | 23.1 | 1.5 | 35.1 | 0.8 |
| T4 | 26.4 | 1.8 | 45.2 | 1.5 |
| T5 | 26.9 | 2.1 | 51.4 | 0.8 |
| T6 | 42.6 | 2.4 | 54.4 | 0.8 |
| Step | PA20 | PA80 |
|---|---|---|
| Initial feed (WPCBs) | 10.0 g | 10.0 g |
| Copper mass in WPCBs | 3.66 g | 0.71 g |
| Mass of copper extracted at 60 °C | 1.74 g | 0.56 g |
| Mass of Copper remaining in WPCBs | 1.86 g | 0.13 g |
| Copper present in the rates of solution collected over time | 0.06 g | 0.02 g |
| Accountability factor | 100% | 100% |
| Temperature (°C) | Chemical Reaction | Diffusion | Mixed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA20 | ||||||
| 40 | 0.00035 | 0.95172 | 0.00002 | 0.92462 | 0.00072 | 0.95184 |
| 60 | 0.00098 | 0.98976 | 0.00019 | 0.94608 | 0.00208 | 0.98958 |
| 80 | 0.00078 | 0.94952 | 0.00014 | 0.90692 | 0.00165 | 0.94570 |
| PA80 | ||||||
| 40 | 0.00124 | 0.87439 | 0.000322 | 0.93774 | 0.0027 | 0.88417 |
| 60 | 0.00209 | 0.94157 | 0.000749 | 0.93140 | 0.0049 | 0.94272 |
| 80 | 0.00071 | 0.92859 | 0.000217 | 0.93677 | 0.0017 | 0.93035 |
| Reaction | |
|---|---|
| Zeroth order | |
| First order | |
| Second order | |
| Three-halves-order kinetics (reaction control) | |
| One-half-order kinetics (reaction control) | |
| Two-thirds-order kinetics (reaction control) | |
| One-thirds-order kinetics (diffusion control) |
| Model | Temperature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 °C | 60 °C | 80 °C | ||||
| PA20 | ||||||
| Zeroth order | 0.00035 | 0.95172 | 0.00098 | 0.98976 | 0.00078 | 0.94952 |
| First order | 0.00002 | 0.92462 | 0.00019 | 0.94608 | 0.00014 | 0.90692 |
| Second order | 0.00072 | 0.95184 | 0.00208 | 0.98958 | 0.00165 | 0.94570 |
| Three-halves-order | 0.00058 | 0.95210 | 0.00079 | 0.98435 | 0.00153 | 0.94604 |
| One-half-order | 0.00052 | 0.95159 | 0.00070 | 0.98942 | 0.00112 | 0.94907 |
| Two-thirds-order | 0.00068 | 0.95144 | 0.00092 | 0.98859 | 0.00141 | 0.94824 |
| One-thirds-order | 0.00035 | 0.95172 | 0.00048 | 0.98976 | 0.00078 | 0.94952 |
| PA80 | ||||||
| Zeroth order | 0.00124 | 0.87439 | 0.00209 | 0.94157 | 0.00071 | 0.92859 |
| First order | 0.000322 | 0.93774 | 0.000749 | 0.93140 | 0.0049 | 0.94272 |
| Second order | 0.00071 | 0.92859 | 0.000217 | 0.93677 | 0.0017 | 0.93035 |
| Three-halves-order | 0.00291 | 0.91508 | 0.00348 | 0.93783 | 0.00186 | 0.93585 |
| One-half-order | 0.00171 | 0.86496 | 0.00271 | 0.93965 | 0.00105 | 0.92692 |
| Two-thirds-order | 0.00210 | 0.85515 | 0.00228 | 0.93676 | 0.00128 | 0.92519 |
| One-thirds-order | 0.00124 | 0.87439 | 0.00139 | 0.94157 | 0.00077 | 0.92859 |
| Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PA20 | |||
| 40 | 0.0019 | 0.9012 | 0.9803 |
| 60 | 0.0086 | 0.8204 | 0.9812 |
| 80 | 0.0122 | 0.7189 | 0.9709 |
| PA80 | |||
| 40 | 0.0186 | 0.7765 | 0.9537 |
| 60 | 0.0312 | 0.7490 | 0.9548 |
| 80 | 0.1300 | 0.3388 | 0.9067 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goulart, A.O.; Veloso, T.C.; Veit, H.M.; Benvenuti, T. Extraction of Copper from Printed Circuit Boards in an Alkaline Solution Using EDTA. Minerals 2025, 15, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040409
Goulart AO, Veloso TC, Veit HM, Benvenuti T. Extraction of Copper from Printed Circuit Boards in an Alkaline Solution Using EDTA. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040409
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoulart, Alan Oliveira, Tácia Costa Veloso, Hugo Marcelo Veit, and Tatiane Benvenuti. 2025. "Extraction of Copper from Printed Circuit Boards in an Alkaline Solution Using EDTA" Minerals 15, no. 4: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040409
APA StyleGoulart, A. O., Veloso, T. C., Veit, H. M., & Benvenuti, T. (2025). Extraction of Copper from Printed Circuit Boards in an Alkaline Solution Using EDTA. Minerals, 15(4), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040409








