Study on the Flotation Behavior of CMS-Na for Talc with Different Particle Sizes: Based on the Hydrophobicity Difference of Fracture Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Minerals and Reagents
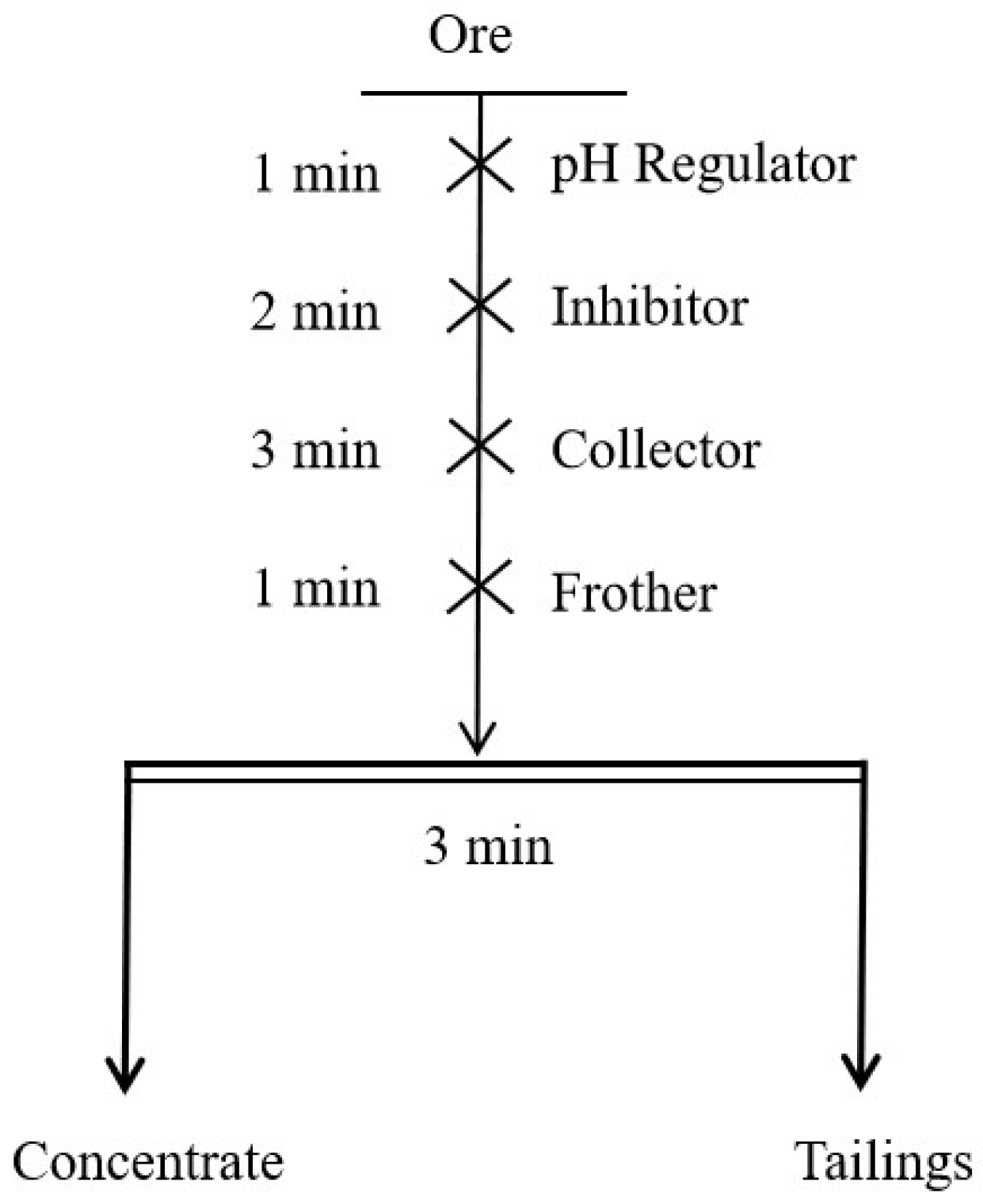
2.2. Flotation Experiments
2.3. FTIR Spectral Measurements
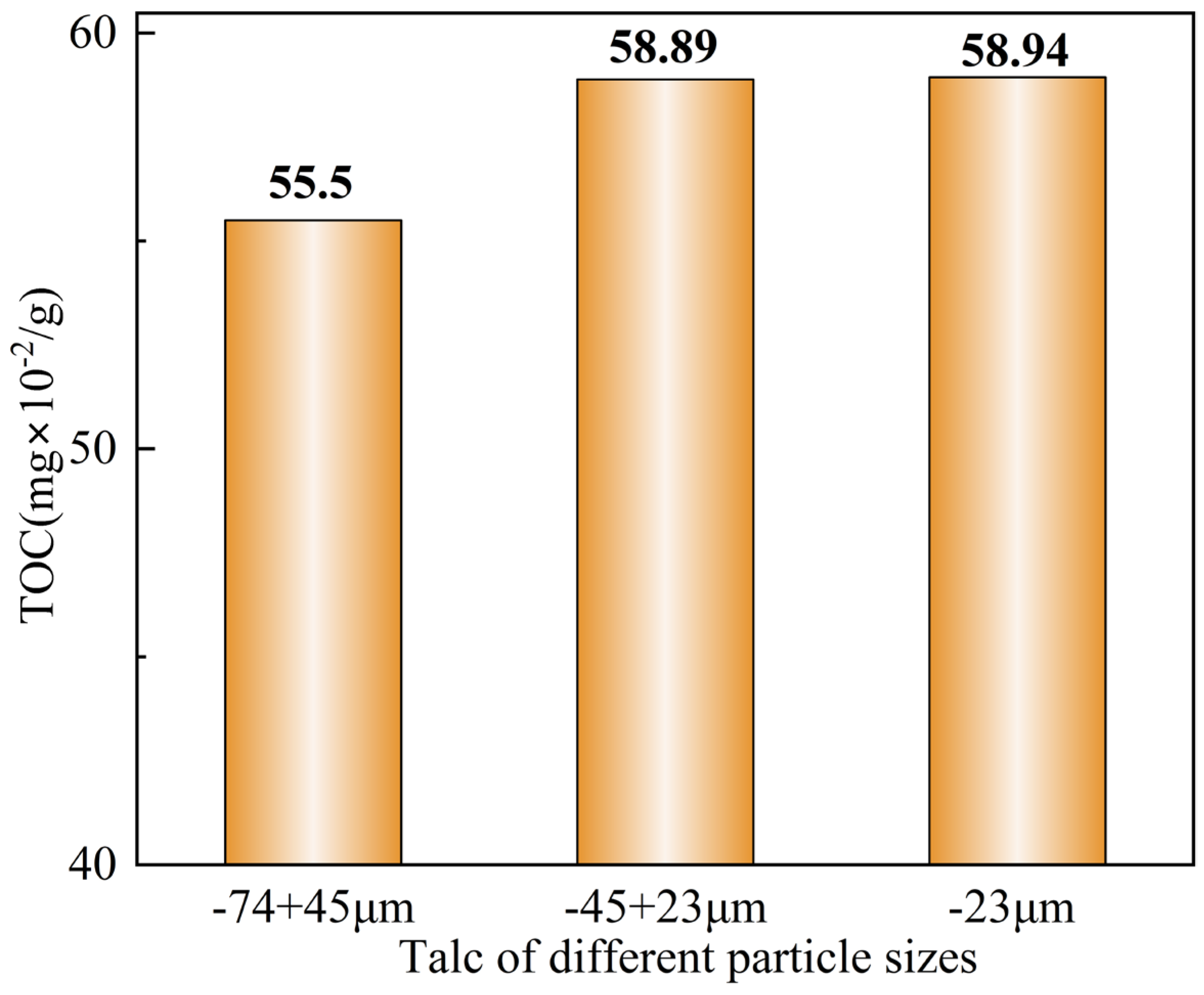
2.4. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Content Measurements
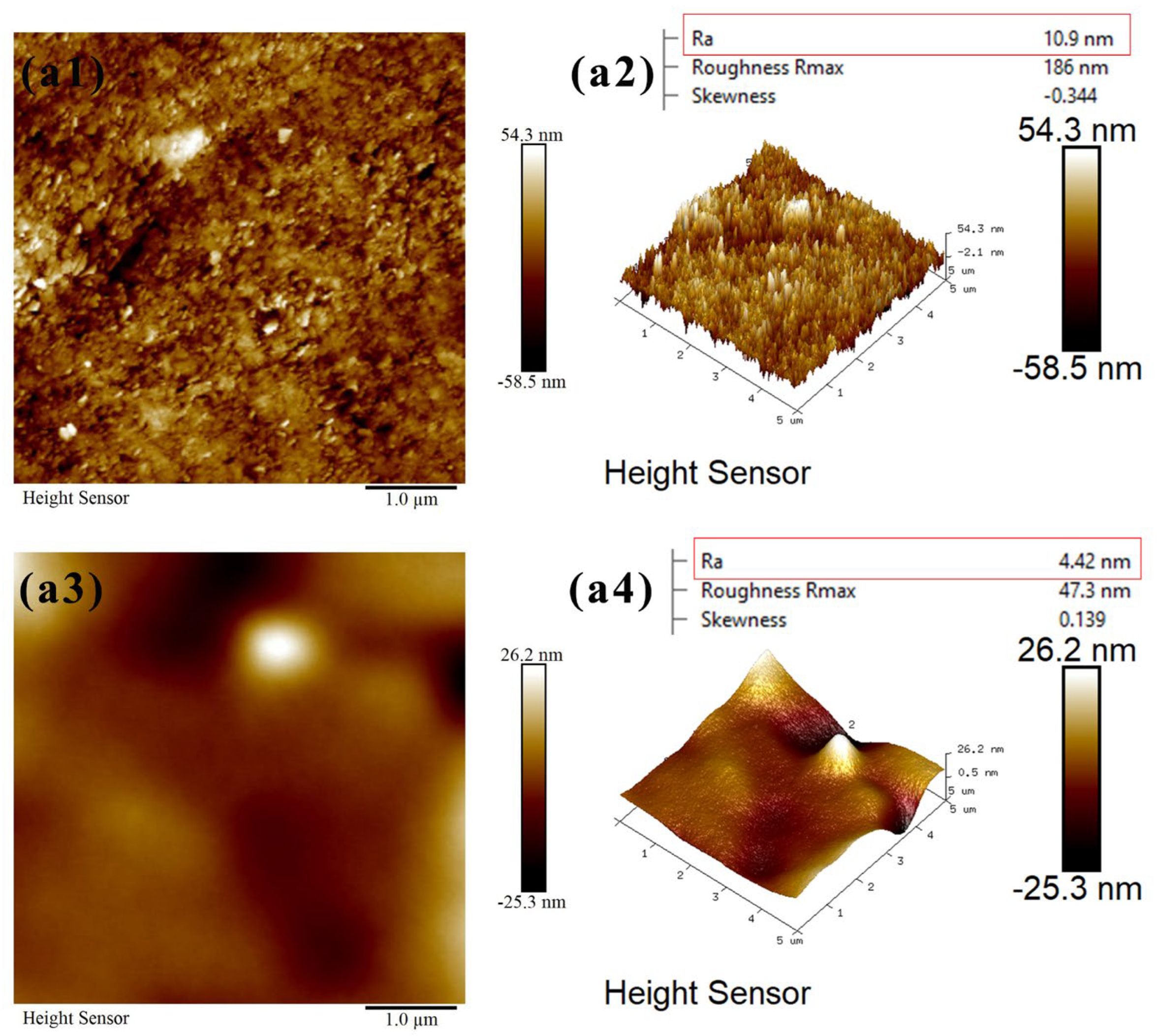
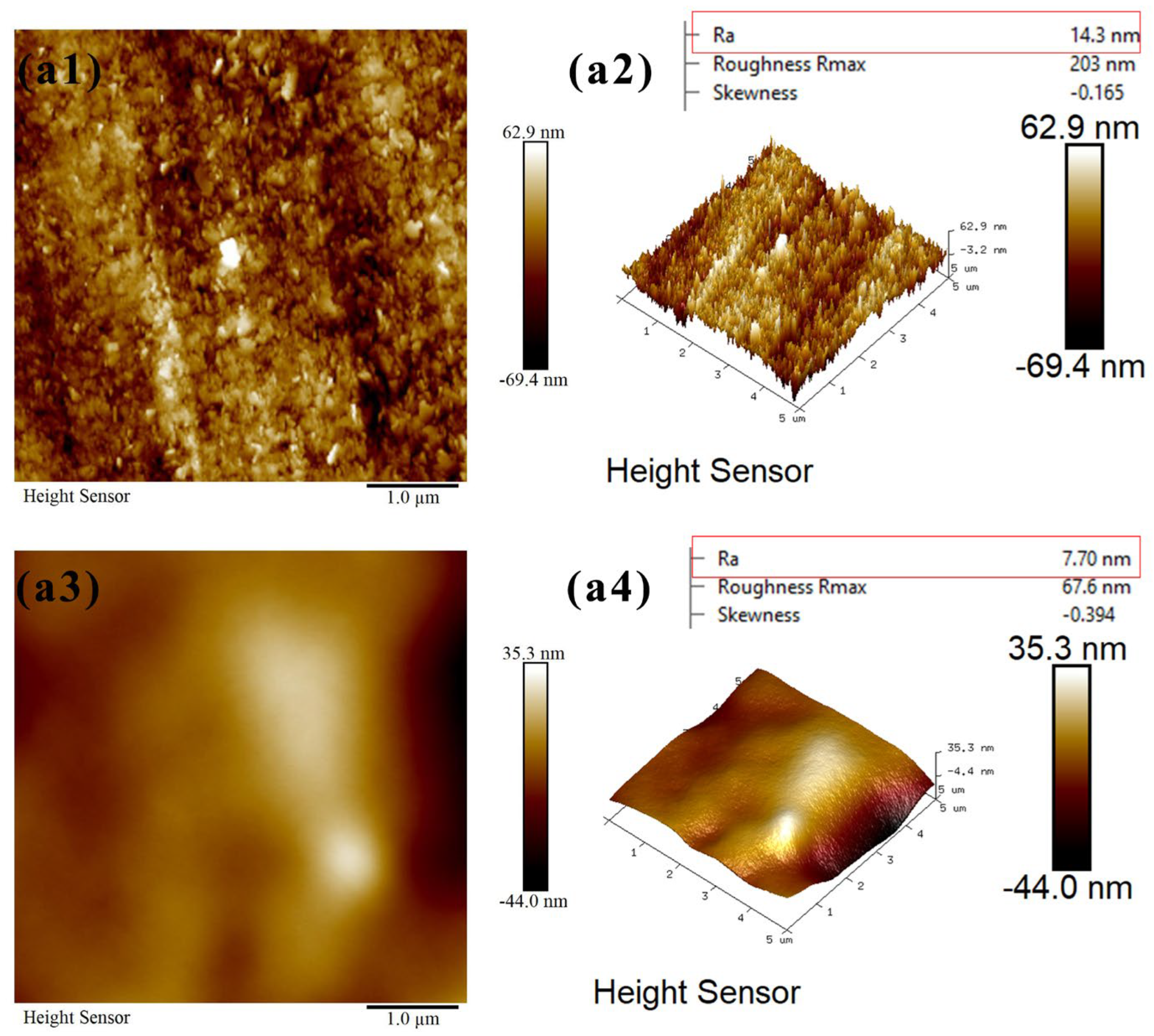
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Measurements
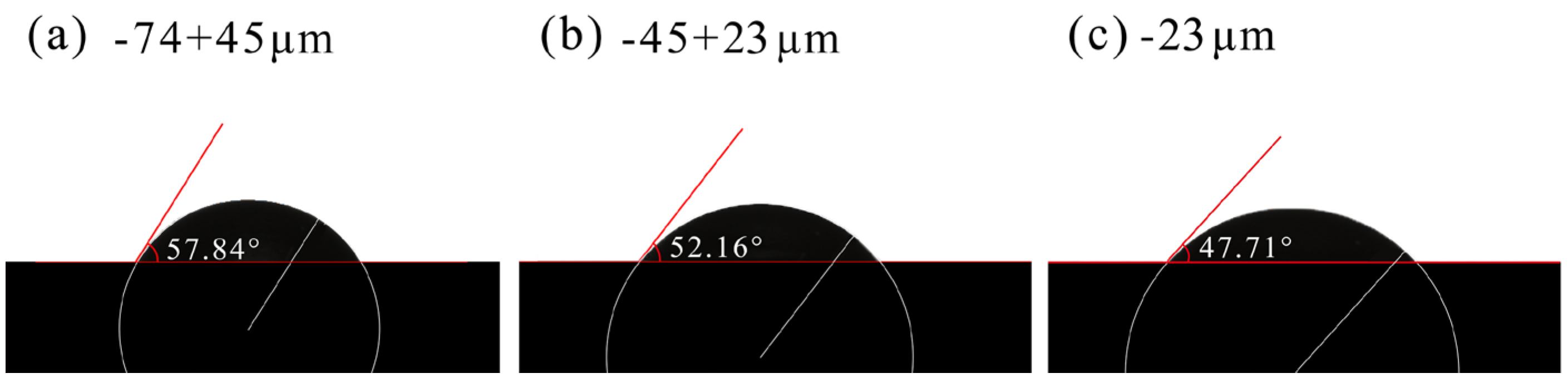
2.6. Contact Angle Measurements
3. Results
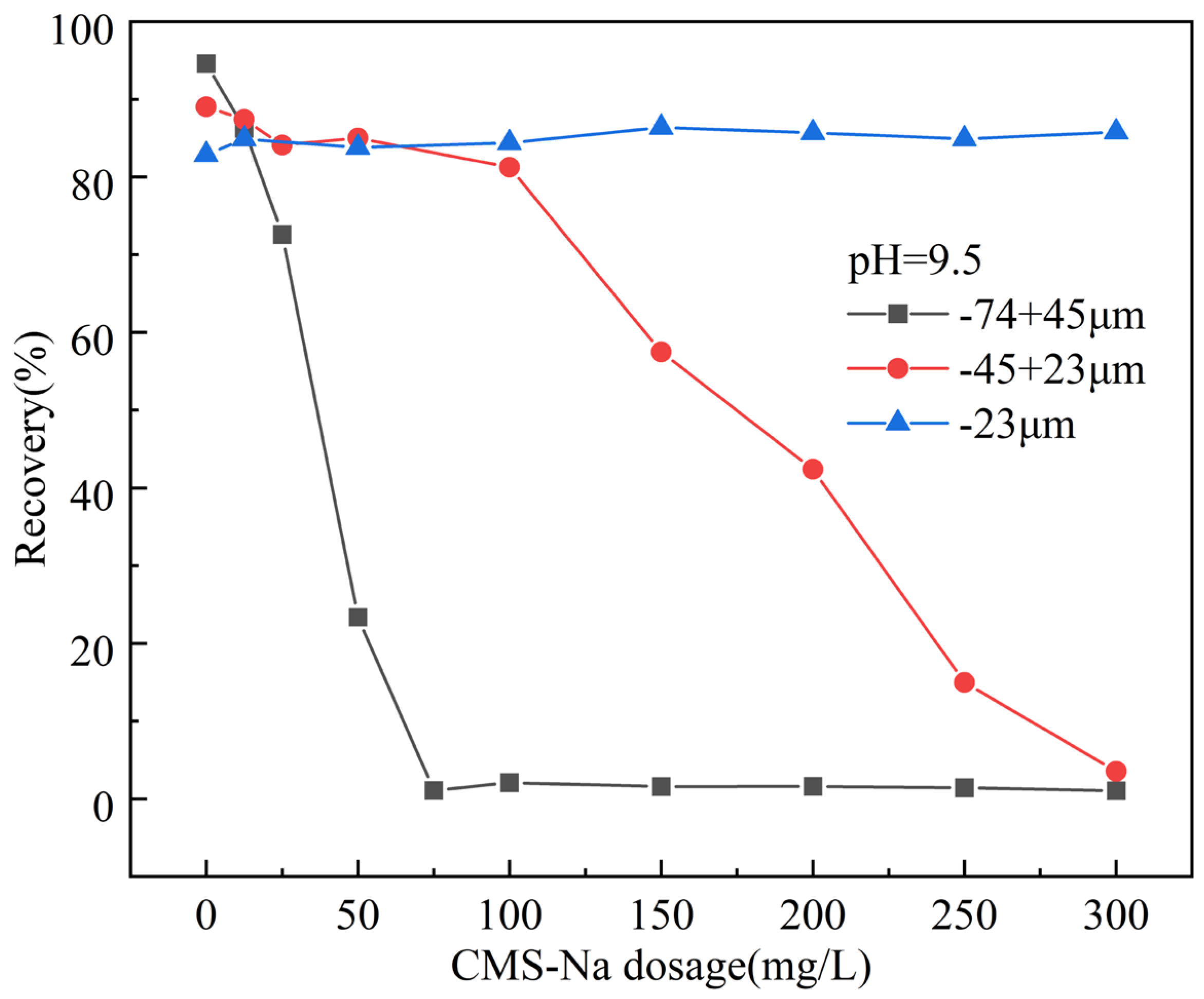
3.1. Flotation Experiments
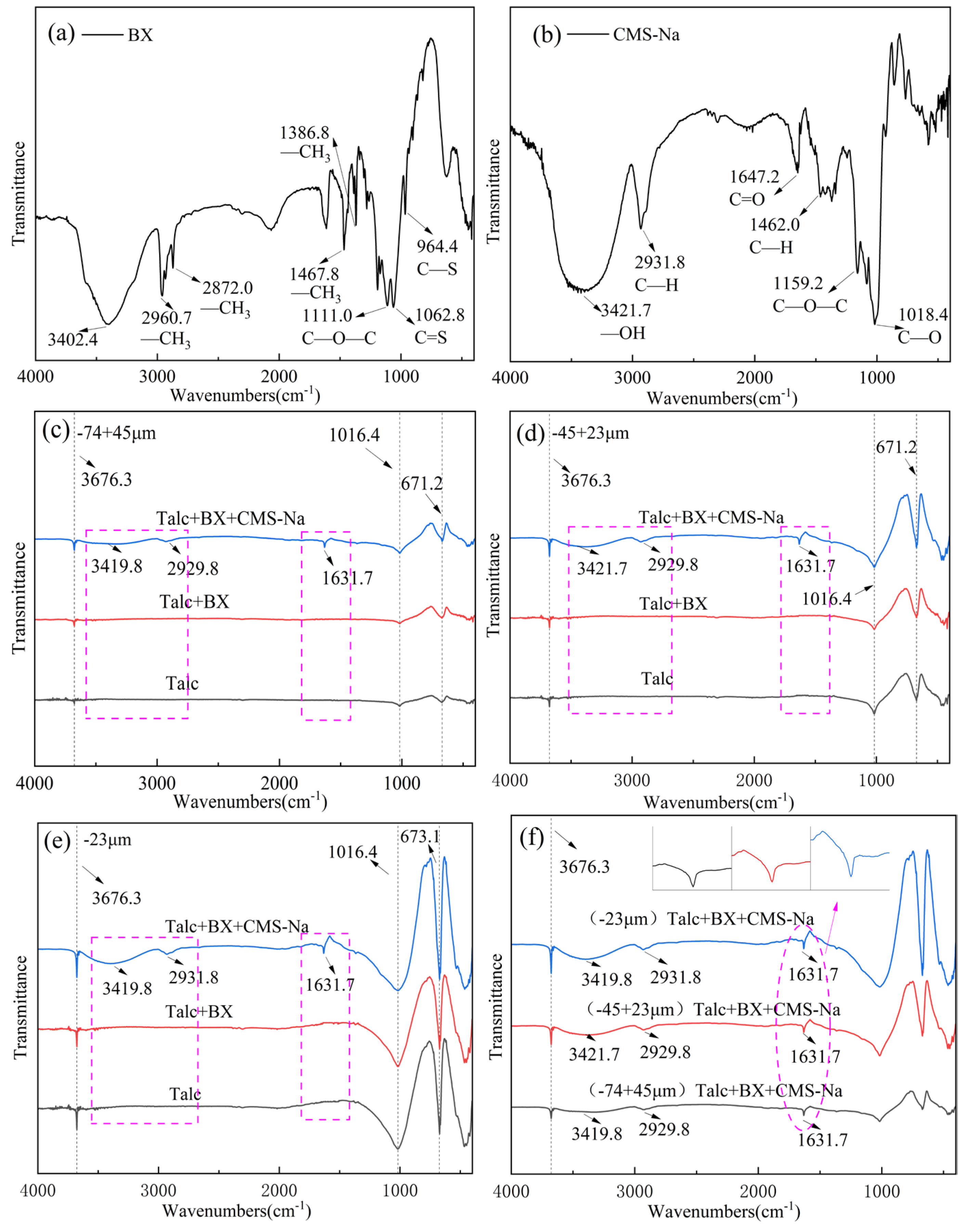
3.2. FTIR Spectral Measurements
3.3. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Content Measurements
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Measurements
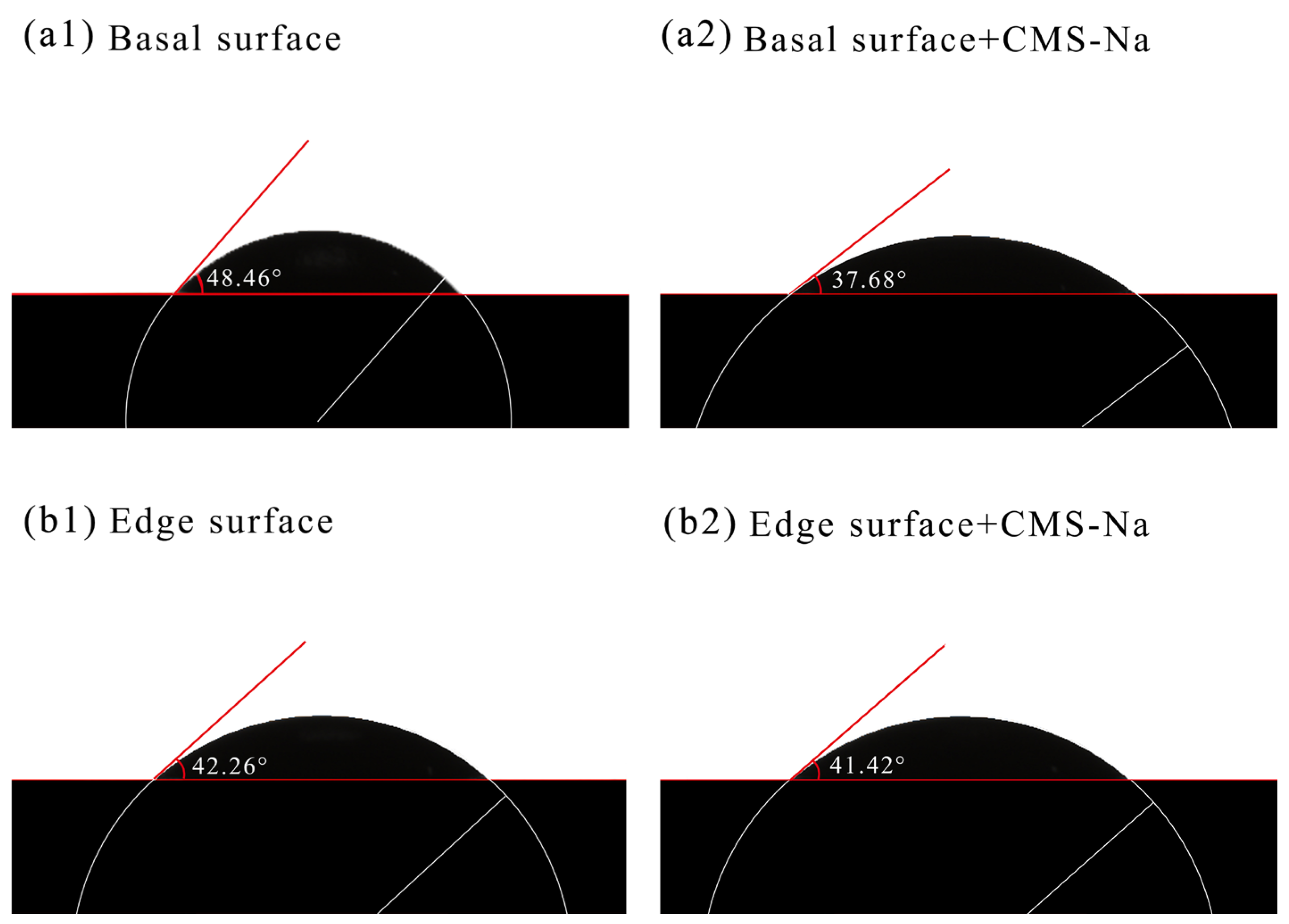
3.5. Contact Angle Measurements
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- CMS-Na demonstrated a strong inhibtion influence on talc in an alkaline pulp environment. At a pH of 11.5 and a CMS-Na dosage of 200 mg/L, the recovery of talc in the −74 + 45 μm fraction was 1.27%, while in the −45 + 23 μm fraction, it was 10.5%, and in the −23 μm fraction, it was 70.3%, indicating that CMS-Na is more effective at depressing coarse-grained talc. With an increasing CMS-Na dosage, talc recovery decreased.
- (2)
- FTIR analysis confirmed that CMS-Na was adsorbed on talc through both chemical and physical adsorption, with stronger interactions observed with fine-grained talc. The AFM results indicate that the edge surfaces of talc exhibited a higher adsorption capacity for CMS-Na. Contact angle measurements revealed that with the particle size decreasing, a higher proportion of edge surfaces were exposed, and the effect of CMS-Na on modifying the wettability of the basal surface was significantly greater than its effect on the edge surface.
- (3)
- Under the same CMS-Na dosage and pH conditions, the increased proportion of exposed edge surfaces in fine-grained talc, combined with their stronger adsorption capacity for CMS-Na, led to the adsorption of a large amount of reagent on the edge surfaces. Consequently, the adsorption of CMS-Na on the basal plane was reduced, allowing the talc surface to maintain relatively strong hydrophobicity. This is a key factor contributing to the poor depression effect of fine-grained talc.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, S. Research on crystal chemistry of talc and review and application of talc flotation in mineral processing of nonferrous sulphide ores. Min. Metall. 2010, 19, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L. Study on Flotation Kinetics and Separation Mechanism of Talcose Chalcopyrite Ore. Ph.D. Thesis, Mineral Processing Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Ma, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, C.; Qi, C. Research situation of development and utilization of talc in china. Refract. Lime 2023, 48, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhpay, S.; Ndlovu, B.; Bradshaw, D. Behavior of talc and mica in copper ore flotation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, P.; Ou, L. Study on the depression mechanism of zinc sulfate on talc in chalcopyrite flotation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Rao, F.; Song, S. Hydrophobic agglomeration of talc fines in aqueous suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C. Hydrophilic modification of macroscopically hydrophobic mineral talc and its specific application in flotation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 25988–25996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Qi, C. Depressing of polysaccharides in floating separation of talc from molybdenite of non-polar surface minerals. Met. Mine 2015, 5, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Shi, Q. Effect of carboxylation chitosan on flotation behaviors of talc in presence of calcium ions. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2018, 28, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Feng, B.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Ning, X.; Wang, H. Effects of three organic depressants on flotation separation of molybdenite and talc. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2022, 32, 3843–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kong, L.; Lv, J.; Wei, M. Reaction mechanism and research progress of organic depressants on talc in flotation of sulfide ores. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2023, 43, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Peng, J.; Ning, X.; Wang, H. Synergistic effect of acidified water glass and locust bean gum in the flotation of a refractory copper sulfide ore. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Ning, S.; Pei, B.; Lang, B.; Liu, R.; Liu, D. Depression mechanism of ZnSO4 and Na2CO3 on talc flotation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Peng, J.; Zhang, W.; Ning, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W. Use of locust bean gum in flotation separation of chalcopyrite and talc. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, T.; Shao, Y.; Ye, G.; Xiong, T. The flotation separation of molybdenite from talc using zinc sulfate in sodium silicate system and related mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, G.; Huang, G. Selective depression of talc in chalcopyrite flotation by xanthan gum: Flotation response and adsorption mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, G. Understanding the role of calcium lignosulphonate in flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2024, 45, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Pawlik, M. The effect of lignosulfonates on the floatability of talc. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 83, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortridge, P.G.; Harris, P.J.; Bradshaw, D.J.; Koopal, L.K. The effect of chemical composition and molecular weight of polysaccharide depressants on the flotation of talc. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 59, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y. Research on new beneficiation technology for refractory molybdenum ore with high talc content. Nonferrous Met. Miner. Process. Sect. 2024, 7, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, F.; Zhu, G.; Cao, Y.; Cao, S. Flotation separation of molybdenite from talc using carrageenan as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2025, 222, 109122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Feng, B. Flotation separation of molybdenite and talc by xanthan gum. Powder Technol. 2021, 388, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ou, L.; Mai, Q. Flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc using a new depressant carrageenan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 125274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Gu, G.; Wang, C.; Rao, X.; Wang, X.; Xiong, X. The effect of a new polysaccharide on the depression of talc and the flotation of a nickel–copper sulfide ore. Miner. Eng. 2015, 77, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Yin, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Sun, H.; Jin, Y. Selective depression of talc in azurite sulfidization flotation by tamarind polysaccharide gum: Flotation response and adsorption mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2022, 178, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Ning, S.; Zuo, Q.; Fang, J.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. Welan gum as a new depressant for the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc. Chem. Phys. 2024, 578, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, Z.; Ren, L.; Yang, S. The selective adsorption mechanism of calcium ions/pullulan in the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, X.; Pan, C.; Hu, X.; Luo, Y.; Xu, P. Selective flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc by a novel depressant: N-methylene phosphonic chitosan. Miner. Eng. 2022, 177, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, R.; Cheng, C. Selective depression of biodegradable talc depressant sodium carboxymethyl starch on molybdenite flotation with sodium diethyldithiocarbamate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 352, 127950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Song, S.; Li, H. A novel method to improve carboxymethyl cellulose performance in the flotation of talc. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Long, T. Effect of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose on flotability and dispersion of talc. Met. Mine 2010, 39, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Liang, Y. Study on the foam stability and flotation behavior of talc. Non-Met. Miner. 1994, 04, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, W.; Lei, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Tian, J. Inhibition mechanism of lead ions synergized with malic acid on talc. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2023, 43, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Feng, Q.; Ou, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, G. Adsorption of polysaccharide onto talc. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Yang, S.; Bao, S.; Ren, L.; Liu, C. A novel insight of interaction mechanism of carboxymethyl cellulose with talc surface: A combined molecular dynamic simulation and DFT investigation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 247, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Tu, H.; Shi, J.; An, Y.; Wan, H.; Bu, X. Enhanced inhibition of talc flotation using acidified sodium silicate and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as the combined inhibitor. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, W.; Yao, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, J.; Xue, F.; Tian, D. Flotation behavior and surface adsorption mechanism of a novel selective inhibitor HDP in the separation of chalcopyrite and talc flotation. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 398, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann Bazar, J.; Rahimi, M.; Fathinia, S.; Jafari, M.; Chipakwe, V.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. Talc flotation—An overview. Minerals 2021, 11, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ren, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J. Process mineralogical study of comprehensive tailings from nanfen concentrator. Mod. Min. 2024, 40, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Peng, Z.; Gao, Z.; Cao, X. Flotation test study on low-grade sulfide copper-nickel ore with high slime and high magnesium content. Min. Metall. Eng. 2023, 43, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | SiO2 | Fe | CaO | Other | |
| Talc | 31.06 | 61.51 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 6.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Man, W.; Dong, W.; Wu, Y.; Huangfu, Z. Study on the Flotation Behavior of CMS-Na for Talc with Different Particle Sizes: Based on the Hydrophobicity Difference of Fracture Surfaces. Minerals 2025, 15, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040402
Liu R, Man W, Dong W, Wu Y, Huangfu Z. Study on the Flotation Behavior of CMS-Na for Talc with Different Particle Sizes: Based on the Hydrophobicity Difference of Fracture Surfaces. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040402
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Runqing, Wenye Man, Wenchao Dong, Yacong Wu, and Zechao Huangfu. 2025. "Study on the Flotation Behavior of CMS-Na for Talc with Different Particle Sizes: Based on the Hydrophobicity Difference of Fracture Surfaces" Minerals 15, no. 4: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040402
APA StyleLiu, R., Man, W., Dong, W., Wu, Y., & Huangfu, Z. (2025). Study on the Flotation Behavior of CMS-Na for Talc with Different Particle Sizes: Based on the Hydrophobicity Difference of Fracture Surfaces. Minerals, 15(4), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040402






