Unraveling the Protracted Magmatic Evolution in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Northeast Saveh, Iran): Zircon U-Pb Dating, Lu-Hf Isotopes, and Geochemical Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
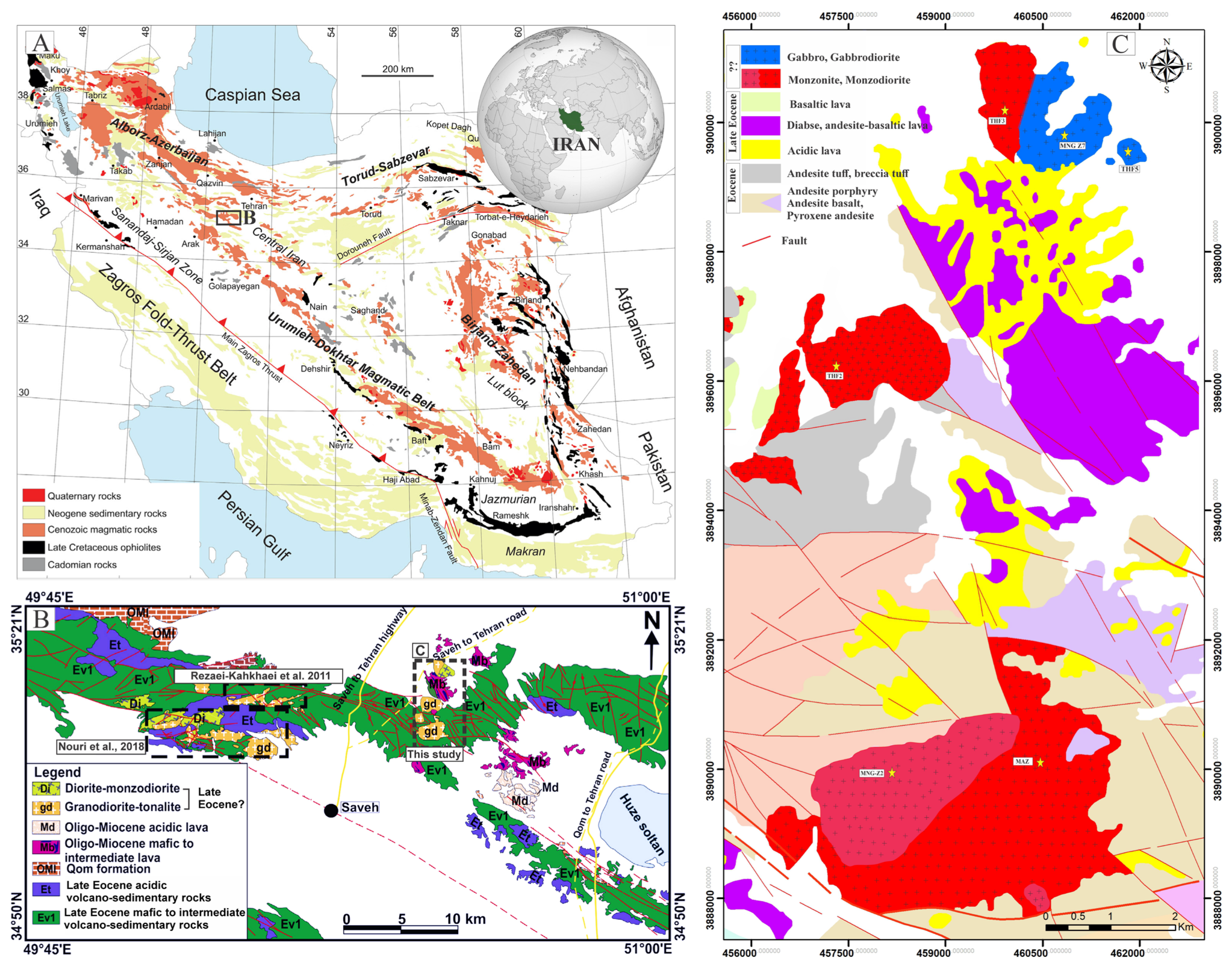
2. Geological Background
2.1. Regional Geology
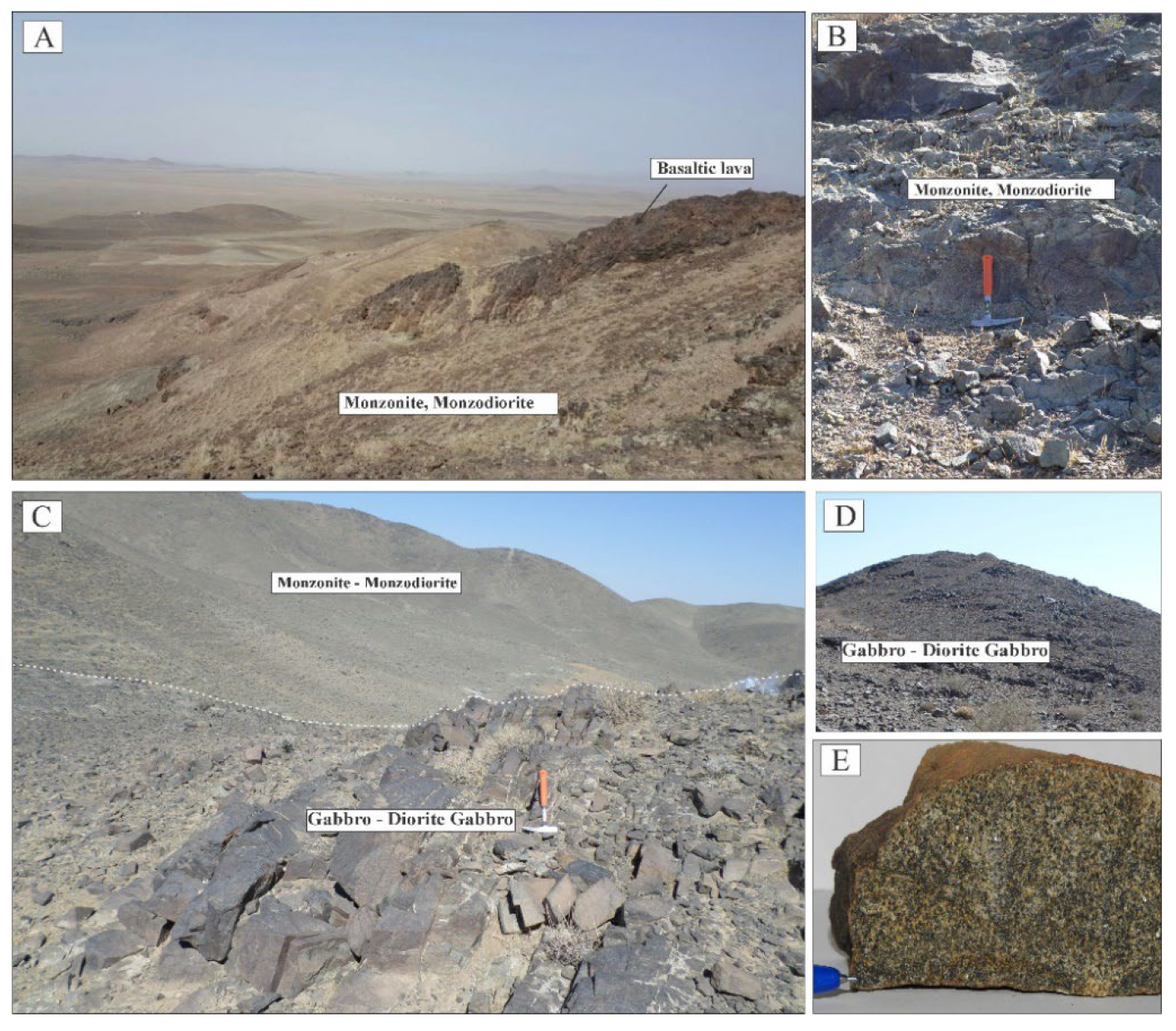
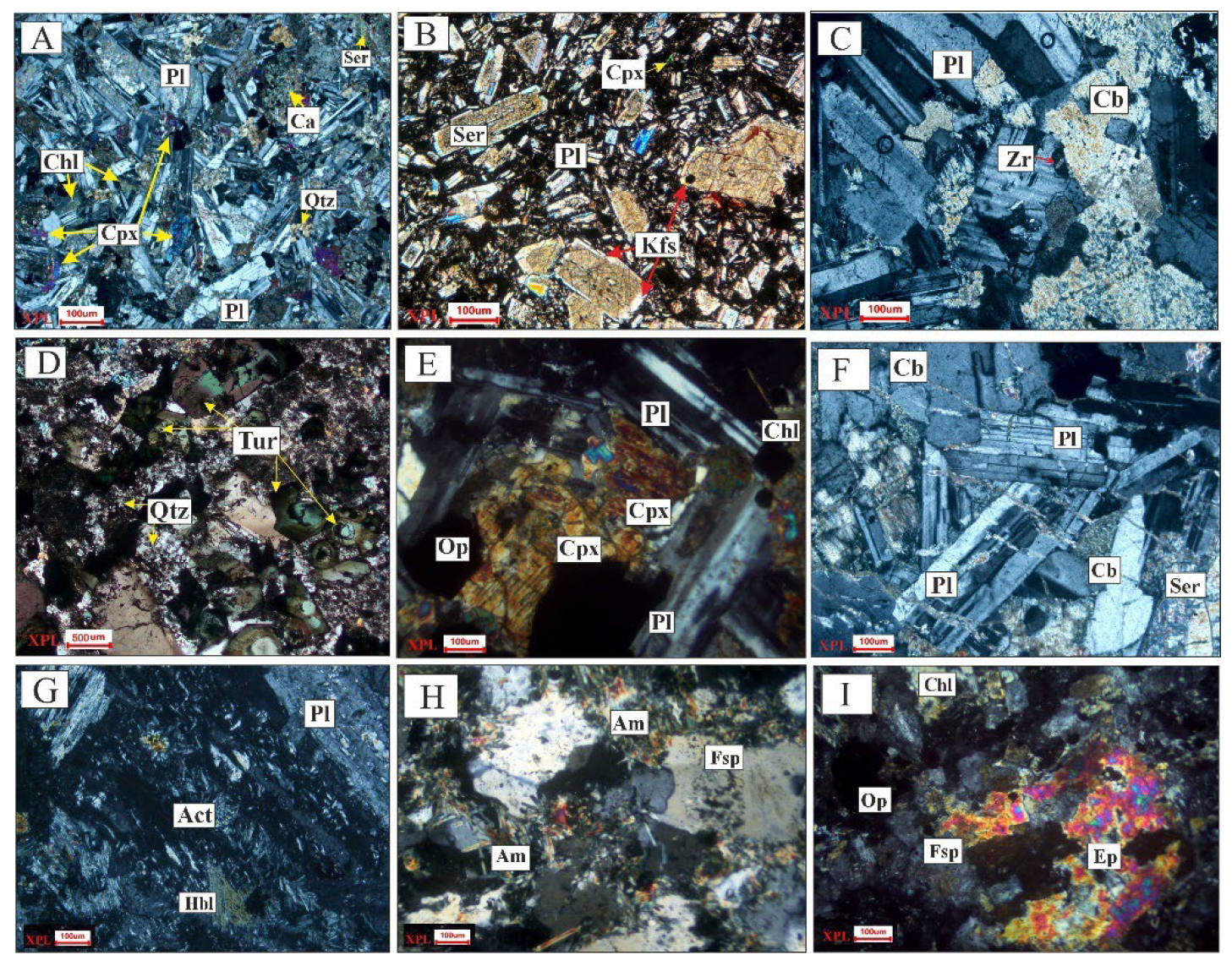
2.2. Geological Overview and Petrographic Observations of the Study Area
3. Analytical Methods
4. Results
4.1. Whole-Rock Geochemistry

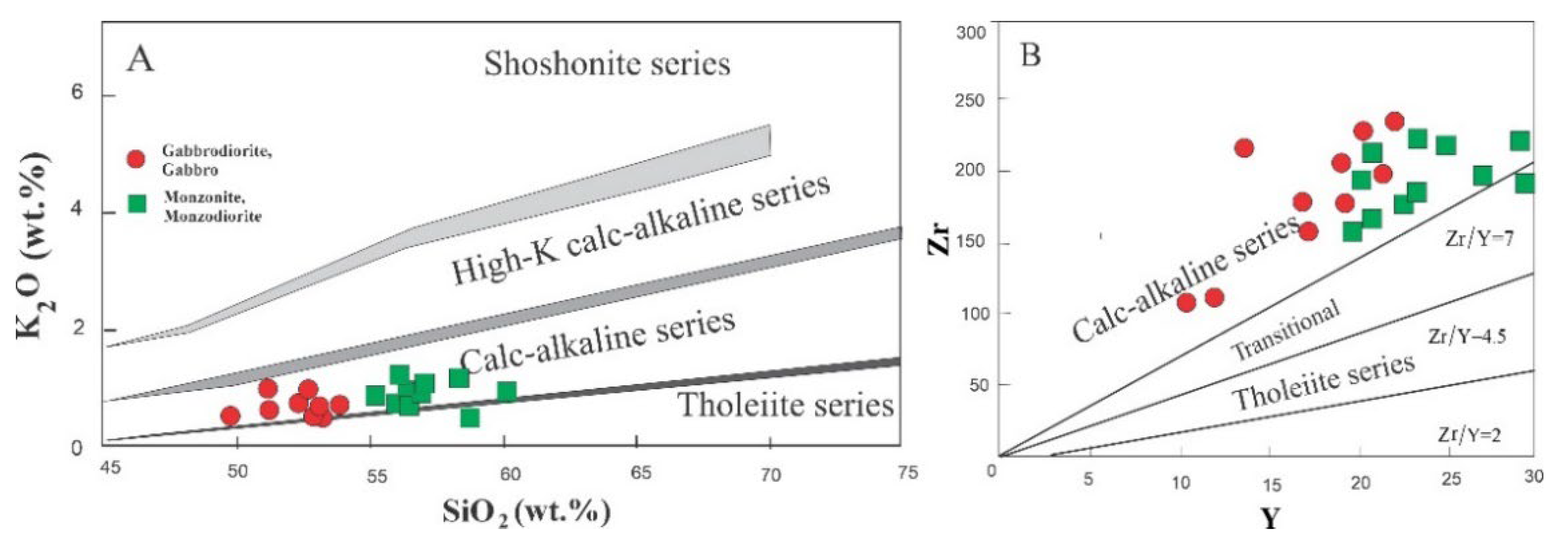


4.2. Mineral Chemistry

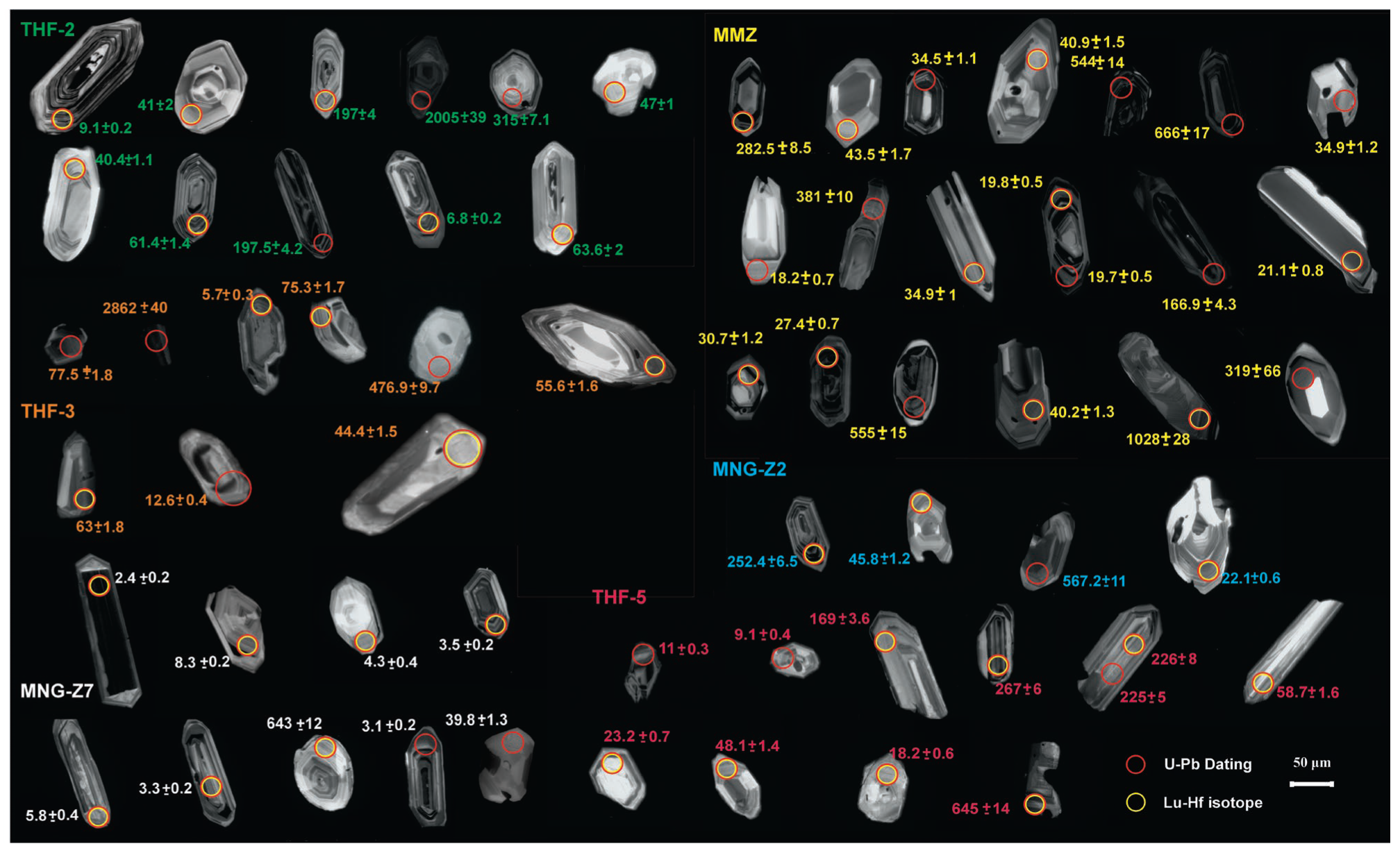
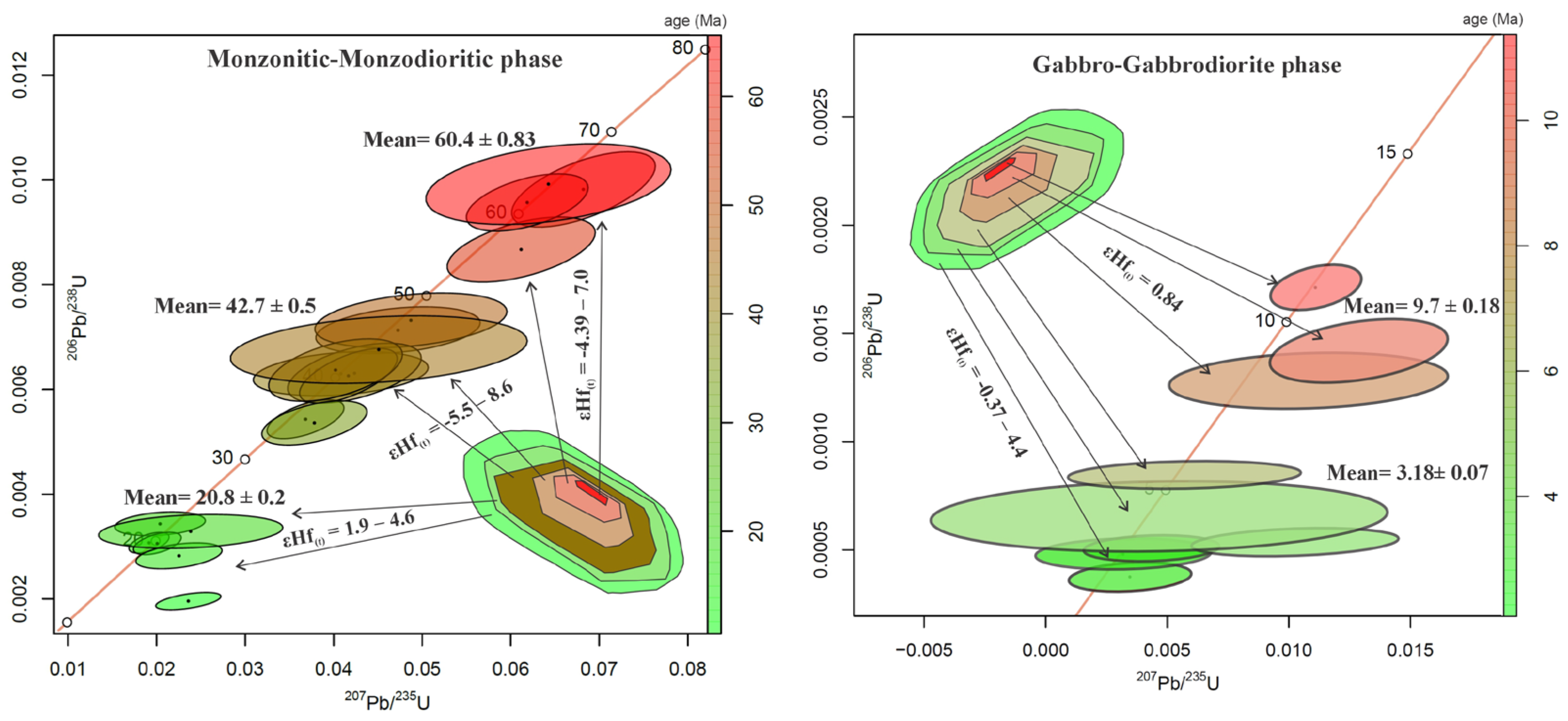
4.3. Zircon U-Pb Dating and Lu-Hf Isotopes
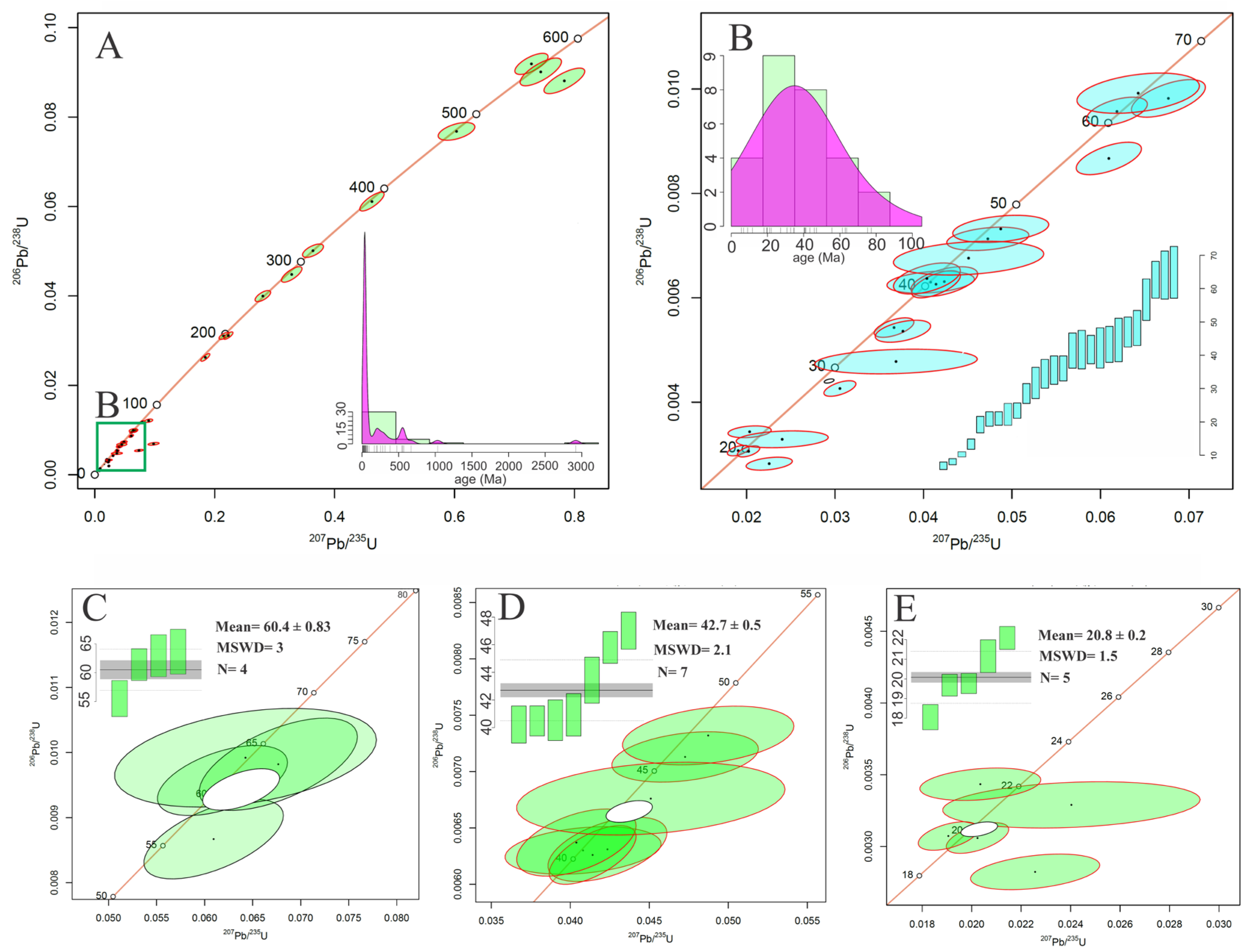
4.3.1. Zircon U-Pb Dating
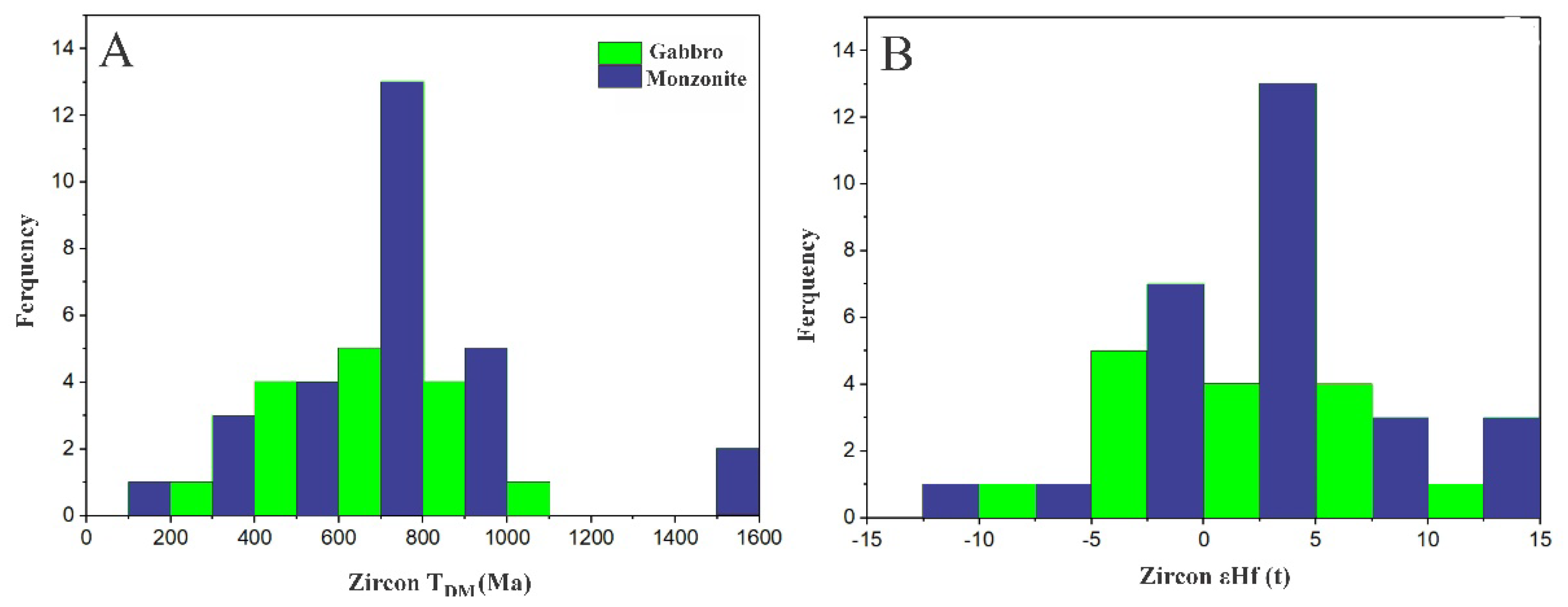
4.3.2. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotopes
5. Discussion
5.1. Tectonic Significance

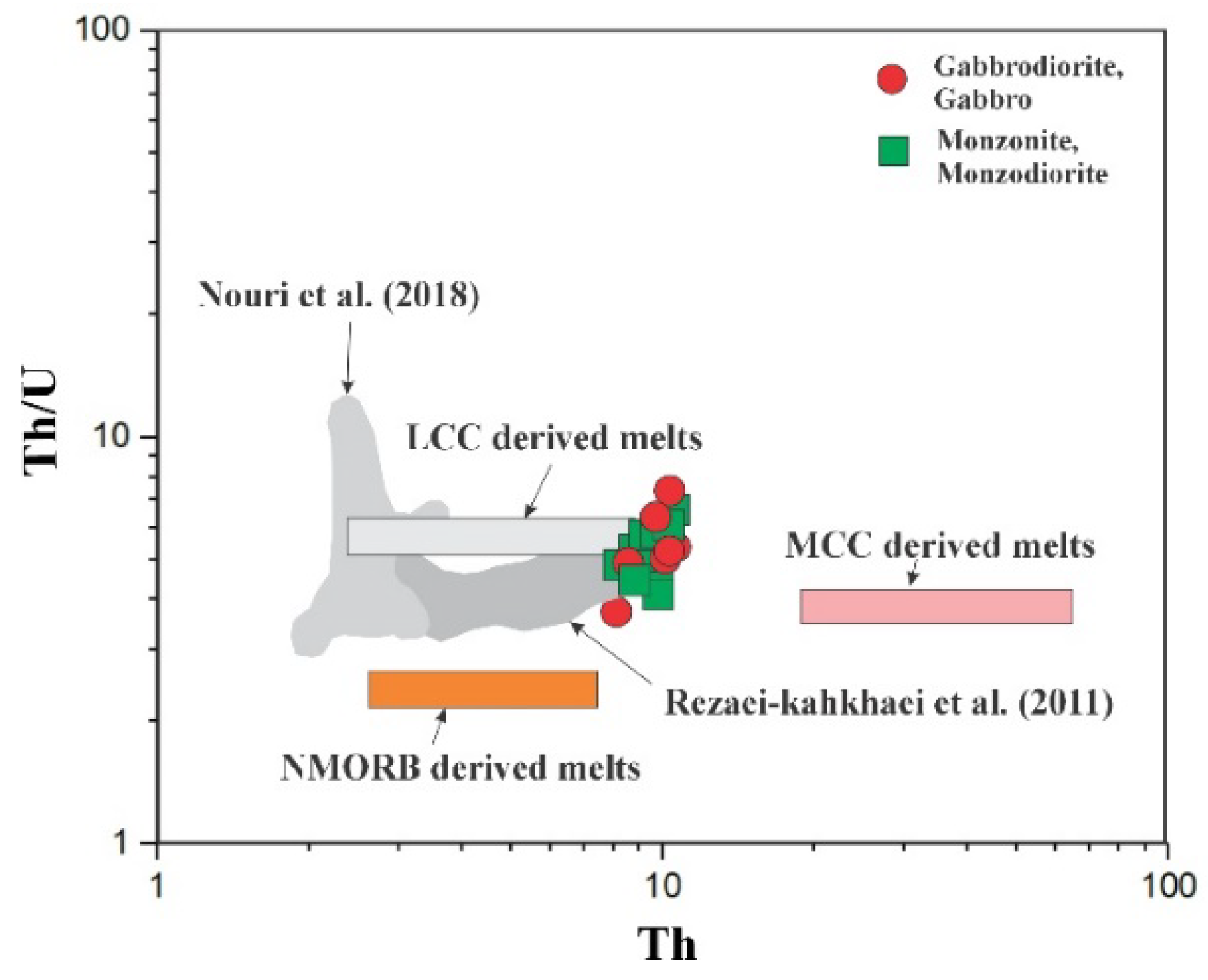
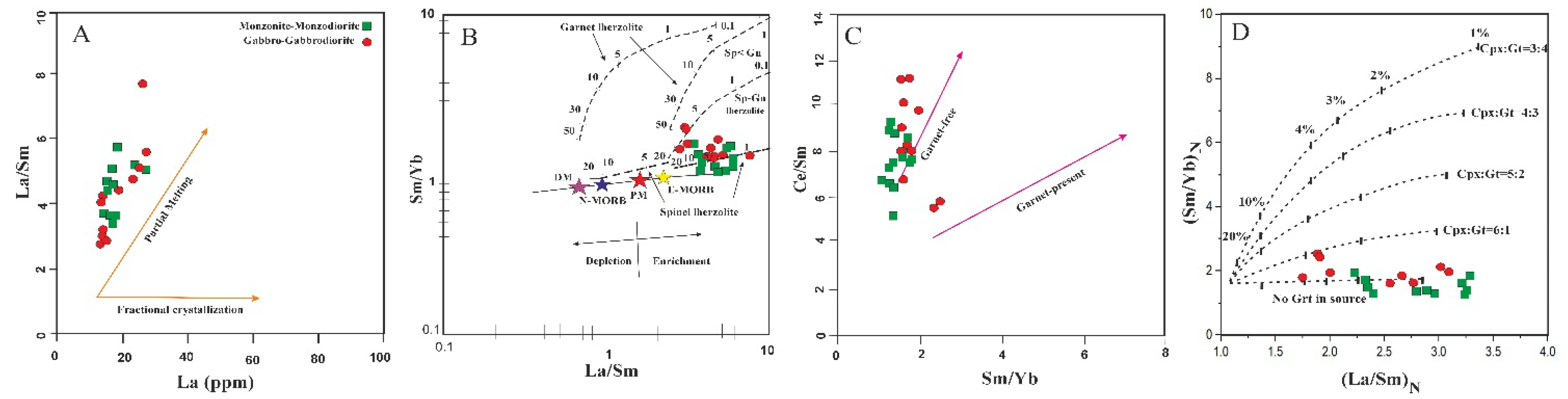
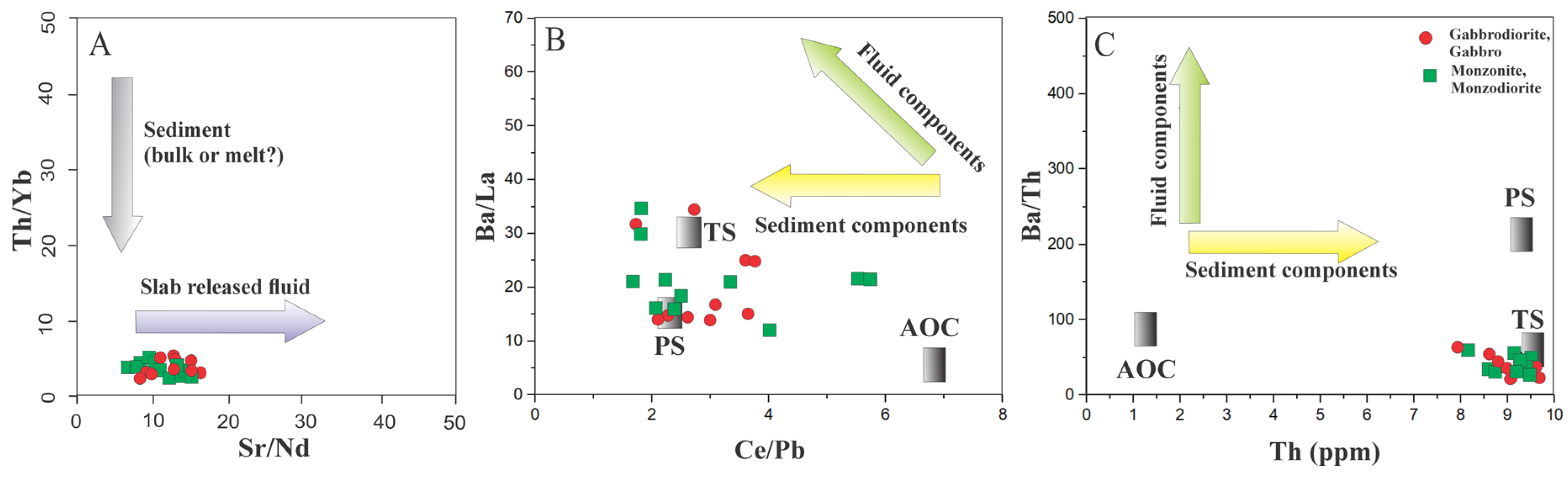
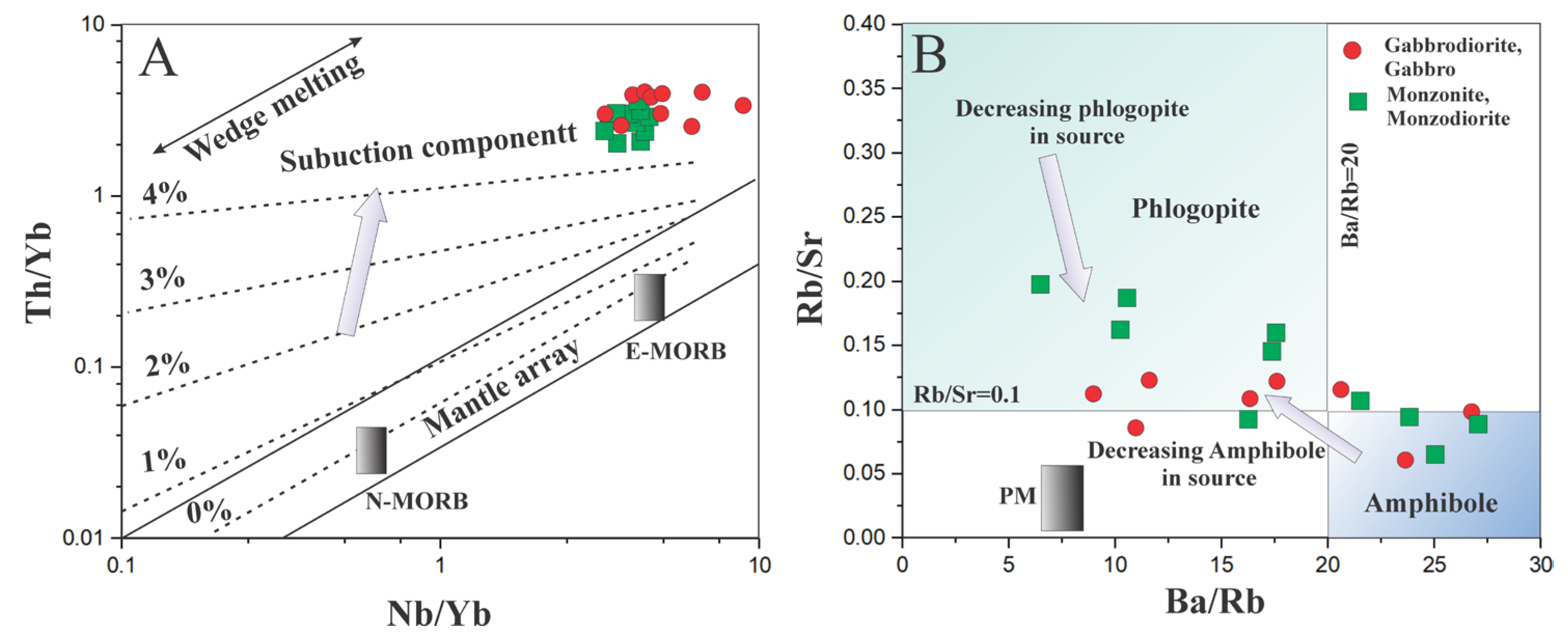
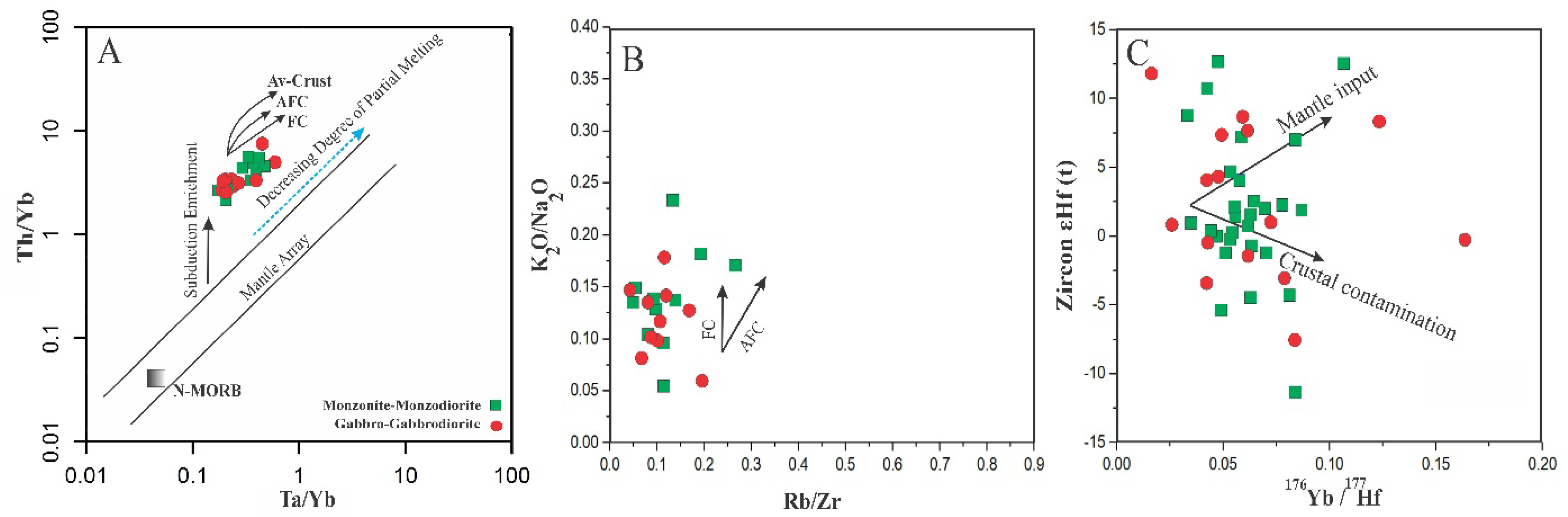
5.2. Characteristics of Mantle Source and Nature of Magma
5.3. Composition of Minerals
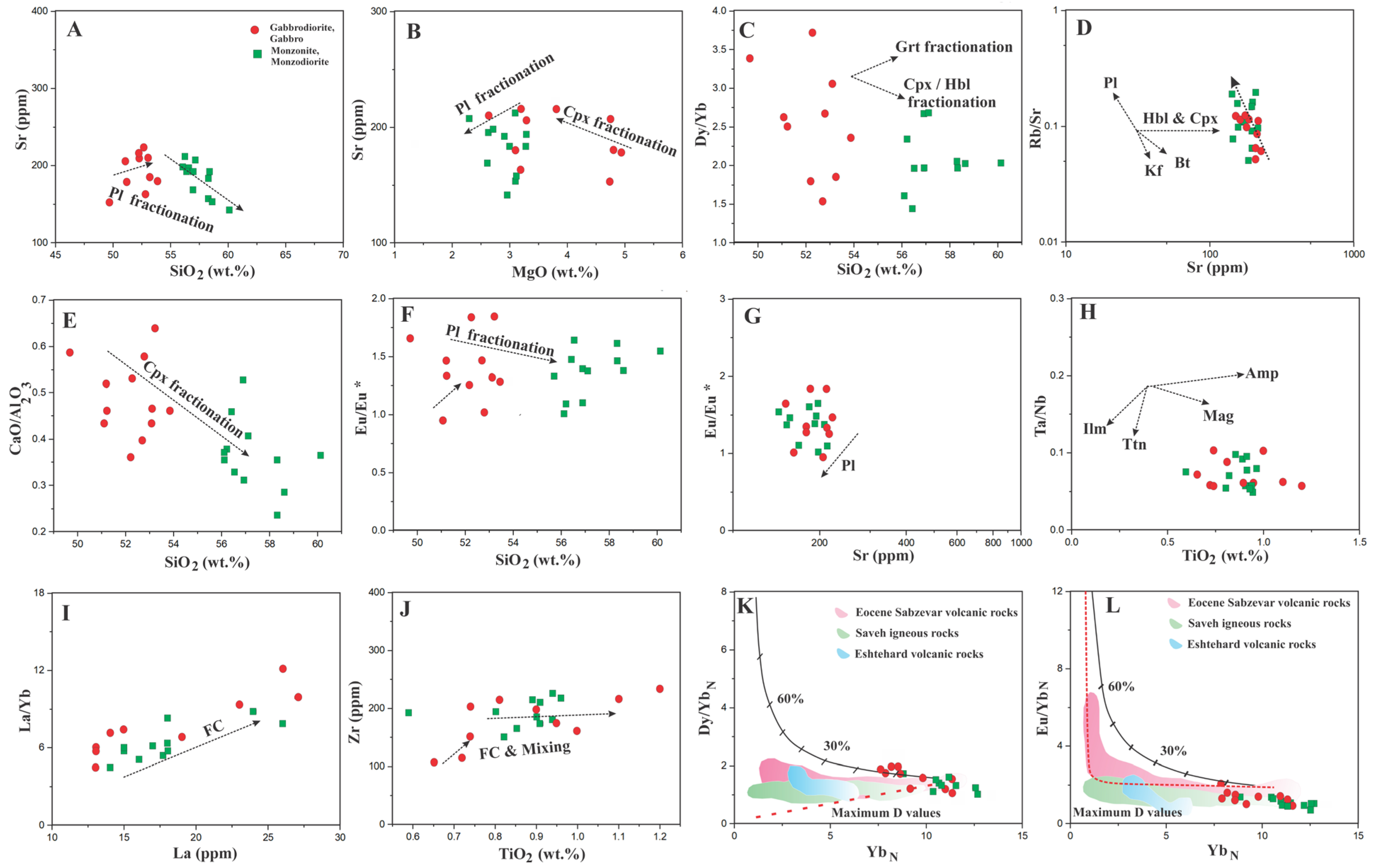
5.4. Crustal Contamination Signatures
5.5. Fractional Crystallization
5.6. Multi-Stage Tertiary Magmatism in Northeast Saveh
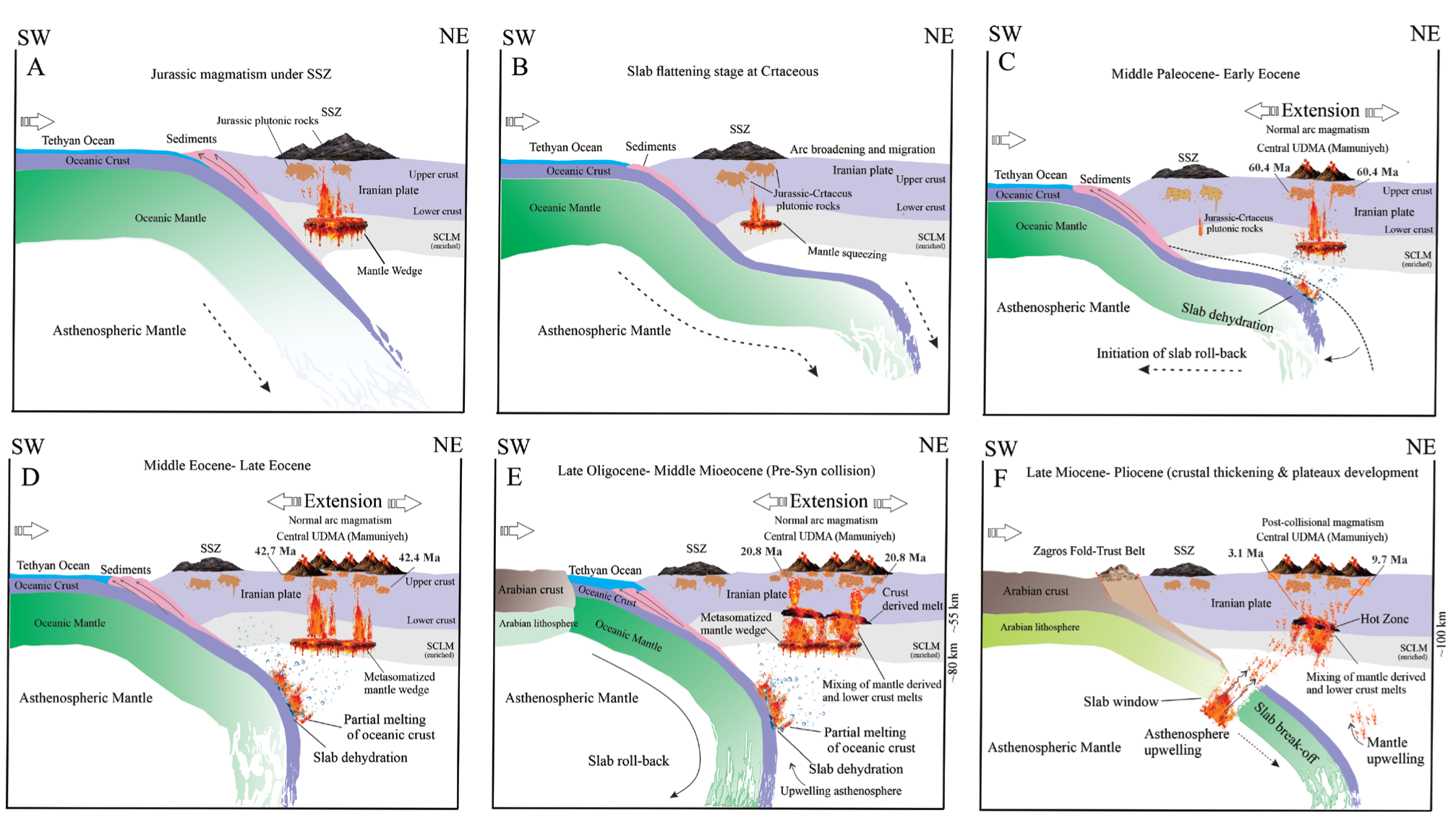
5.7. Geodynamic Evolution
6. Conclusions
- ∘
- The northeast Saveh magmatic rocks in the central UDMA comprise metaluminous, medium-K calc-alkaline monzonitic to gabbroic compositions;
- ∘
- The intermediate to mafic magma in northeast Saveh’s parental rocks originated from the partial melting of a shallow, metasomatized lithospheric mantle, likely triggered by extensional forces related to slab rollback and accompanied by localized compressional stresses. This tectonic interaction facilitated decompression melting at relatively low pressure. Additionally, while some geochemical trends suggest that magma evolution was influenced by the fractional crystallization of plagioclase, clinopyroxene, and hornblende, the scattered nature of the patterns suggests that other processes, such as magma mixing or crustal assimilation, may also have played a role;
- ∘
- The magmatic rocks formed under subduction-related, low-pressure conditions (<2 kb), with 1150–1200 °C crystallization temperatures. Geochemical data suggest a metasomatized mantle source with up to 10% partial melting in the spinel–lherzolite field and sedimentary subduction inputs (>4 wt.%) and melting depths below 80 km;
- ∘
- The studied zircon grains from northeast Saveh reveal a complex magmatic and tectonic history in Iran, encompassing contributions of magmatic rocks from the Mesoproterozoic to the Cenozoic. Negative εHf values indicate significant crustal contamination, while inherited zircon grains with ages ranging from the Archean to the Mesozoic suggest that these zircons may originate not only from primary magmatic sources but also from intermediate sedimentary reservoirs containing detrital zircon;
- ∘
- Although previous studies indicate a brief quiescence of ca. 15 Ma in the UDMA, spanning from around 72 to 57 Ma, the presence of zircons with ages ranging from ∼55 to 63 Ma in this study suggests a shorter quiescent period of approximately 10–12 My in the UDMA;
- ∘
- The dominant zircon populations in monzonitic rocks consist of crystals dated around 50 to 20 Ma. This age range corresponds to crystallization events that took place from the Early Eocene to the Early Miocene, which were probably sourced from a shared origin related to the subduction of the Neotethyan Plate beneath central Iran. The wide range of ages recorded suggests prolonged magmatic activity;
- ∘
- The zircon clusters dated ∼12 to 5 Ma from monzonitic rocks characterized by predominantly positive εHf(t) values, along with zircons from gabbroic rocks aged ∼11 to 2.5 Ma, are interpreted in this study as representing the most recent magmatic stages. These stages are nearly contemporaneous with post-collisional magmatic activity observed elsewhere in the Arabia–Eurasia collision zone, including the Zagros Orogen and surrounding regions;
- ∘
- The youngest and final magmatic pulses in the central UDMA, potentially extending across the entire UDMA, are dated between 5 and 2.5 Ma and identified in a cluster of zircons from gabbroic rocks.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navarrete, C.; Gianni, G.; Encinas, A.; Márquez, M.; Kamerbeek, Y.; Valle, M.; Folguera, A. Triassic to Middle Jurassic Geodynamic Evolution of Southwestern Gondwana: From a Large Flat-Slab to Mantle Plume Suction in a Rollback Subduction Setting. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 194, 125–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, P.T.; Usuki, T.; Hoang, N.; Usuki, M.; Minh, P.; Nong, A.T.Q.; Nguyen, Y.V.; Hieu, P.T. Emplacement Ages, Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf Isotopic Characteristics of Cenozoic Granites in the Phan Si Pan Uplift, Northwestern Vietnam: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implication for the Adjacent Structure of the Red River Shear Zone. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 112, 1475–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Santosh, M.; Tong, Y.; Luo, Z. Melt-Fluid Interaction in the Formation of Peralkaline Granite: Evidence from the Baiyinwula Intrusion, Inner Mongolia, China. Lithos 2023, 454–455, 107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Audétat, A.; Pettke, T. The Gold Content of Mafic to Felsic Potassic Magmas. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.P.; Tibaldi, A.M.; Cristofolini, E.A.; Barzola, M.G.; Schwartz, J.J.; Molina, J.F.; Escribano, F.A. Dioritic to Granodioritic Calc-Alkaline Magmatism in the Sierra de Comechingones Southern Tip, Córdoba, Argentina: Tracking the Famatinian Arc into the Pampean Belt. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2024, 113, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, C.; Gianni, G.; Tassara, S.; Zaffarana, C.; Likerman, J.; Márquez, M.; Wostbrock, J.; Planavsky, N.; Tardani, D.; Perez Frasette, M. Massive Jurassic Slab Break-off Revealed by a Multidisciplinary Reappraisal of the Chon Aike Silicic Large Igneous Province. Earth Sci. Rev. 2024, 249, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand, M.; Xiao, W.; Nabatian, G.; Blades, M.L.; Collins, A.S.; Ao, S. Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Bulk-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes from Late Neoproterozoic Basement in the Mahneshan Area, NW Iran: Implications for Ediacaran Active Continental Margin along Northern Gondwana and Constraints on the Late Oligocene Crustal Anatexis. Gondwana Res. 2018, 57, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; D’Antonio, M.; Cottle, J.M.; Ghalamghash, J.; Raeisi, D.; An, Y. Constraints from Geochemistry, Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Hf-Nd Isotopic Compositions on the Origin of Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks from Central Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. Gondwana Res. 2021, 90, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; Furman, T.; Santosh, M.; Raeisi, D.; Choi, S.H.; D’Antonio, M. Middle to Late Miocene K-Rich Magmatism in Central Iran: Geochemical Characterization of the Post-Collision Mantle beneath the Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc. Chem. Geol. 2024, 665, 122308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammaddoost, H.; Ghaderi, M.; Kumar, T.V.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Alirezaei, S.; Babu, E.V.S.S.K. Geology, Mineralization, Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Hf Isotopes of Serenu Porphyry Copper Prospect, Kerman Cenozoic Magmatic Arc, Southeastern Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 159, 105540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhang, H. Modification of Archean Lower Crust of the North China Craton by Magma Underplating during the Mesozoic: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb-Hf-O Isotopes of Granulite Xenoliths. Gondwana Res. 2024, 125, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, I.M.; Chauhan, H.; Ahmad, T.; Tanaka, T.; Bickle, M.; Asahara, Y.; Chapman, H.; Dar, R.A. Fate of an Oceanic Plate in the Neo-Tethys Intra-Oceanic Subduction System: Evidence from Elemental and Rb/Sr–Sm/Nd Isotopic Systematics. Gondwana Res. 2024, 125, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noudeh Shiva, A.; Yann, R.; Magali, R.; Olivier, B.; Mohammad, R. Eocene High-K Magmatic Flare-up in a Context of South Dipping Subduction and Strike-Slip Tectonics: Insights from the Talysh Massif, NW Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 264, 106045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Liotard, J.-M.; Dautria, J.-M. Geochemical Characteristics of an Intracontinental Shoshonitic Association: The Example of the Damavand Volcano, Iran. Comptes Rendus Géoscience 2002, 334, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbari Jafari, M.; Sepehr, H.; Mobasher, K. Tectonomagmatic Evolution of the South Dehshir Ophiolite, Central Iran. Geol. Mag. 2015, 153, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, I.; Meliksetian, K.; Allen, M.B.; Navarsardian, G.; Karapetyan, S. Pliocene-Quaternary Volcanic Rocks of NW Armenia: Magmatism and Lithospheric Dynamics within an Active Orogenic Plateau. Lithos 2013, 180–181, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E. Sequence Stratigraphy of the Qom Formation in the Sirjan-Abadeh Region. Stratigr. Sedimentol. Res. 2020, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunini, L.; Jiménez-Munt, I.; Fernández, M.; Vergés, J.; Villaseñor, A. Lithospheric Mantle Heterogeneities beneath the Zagros Mountains and the Iranian Plateau: A Petrological-Geophysical Study. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 200, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Ghorbani, M.R.; Jiang, S.Y.; Christiansen, E.H. Mafic to Intermediate Composition Intrusions from the Kahak Area, Central Urumieh-Dokhtar Arc of Iran: Transition from Eocene to Miocene Intra-Arc Extensional Magmatism. Miner. Pet. 2021, 115, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Jiang, S.Y.; Christiansen, E.; Ghorbani, M.R. Petrogenesis of Tertiary Granitoid Rocks from East of the Bidhand Fault, Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran: Implications for an Active Continental Margin Setting. Lithos 2021, 400–401, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, T.; Rashidnejad-Omran, N.; Chen, F.; Song, S.; Li, S.; Ghaderi, M. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Magmatic History of the Kashan Plutons in the Central Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran: Evidence for Neotethyan Subduction during the Paleogene-Neogene. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnia, T.; Saccani, E.; Torabi, G.; Chiari, M.; Goričan, Š.; Barbero, E. Cretaceous Tectonic Evolution of the Neo-Tethys in Central Iran: Evidence from Petrology and Age of the Nain-Ashin Ophiolitic Basalts. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.E.; Portner, D.E.; Beck, S.L.; Rocha, M.P.; Bianchi, M.B.; Assumpção, M.; Ruiz, M.; Alvarado, P.; Condori, C.; Lynner, C. Mantle Dynamics of the Andean Subduction Zone from Continent-Scale Teleseismic S-Wave Tomography. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 224, 1553–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttaqy, F.; Syuhada, S.; Nugraha, A.D.; Mori, J.; Puspito, N.T.; Supendi, P.; Rohadi, S. Lithospheric Mantle Dynamics in Central and East Java Region, Indonesia from Local Shear Wave Splitting Measurements. J. Geodyn. 2023, 158, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabayrol, F.; Hart, C.J.R.; Thorkelson, D.J. Temporal, Spatial and Geochemical Evolution of Late Cenozoic Post-Subduction Magmatism in Central and Eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Lithos 2019, 336–337, 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, M.; King, G.C.P. Towards a Paleogeography and Tectonic Evolution of Iran. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1981, 18, 210–265. [Google Scholar]
- Omrani, J.; Agard, P.; Whitechurch, H.; Benoit, M.; Prouteau, G.; Jolivet, L. Arc-Magmatism and Subduction History beneath the Zagros Mountains, Iran: A New Report of Adakites and Geodynamic Consequences. Lithos 2008, 106, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdel, C.; Wernicke, B.P.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Guest, B. A Paleogene Extensional Arc Flare-up in Iran. Tectonics 2011, 30, 3008–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, A.; Naudé, M.N.; Callegaro, S.; Monsef, I.; Rezaeian, M.; Niknam, A.; Cotton, L.J.; Roux, P.; Kriegsman, L.M.; Mason, P.R.D.; et al. Propagating Neotethys slab break-off beneath Iran following Arabia-Eurasia collision. Lithos 2024, 482–483, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganehfar, H.; Ghorbani, M.R.; Shinjo, R.; Ghaderi, M. Magmatic and Geodynamic Evolution of Urumieh-Dokhtar Basic Volcanism, Central Iran: Major, Trace Element, Isotopic and Geochronologic Implications. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Zarrinkoub, M.H.; Mohammadi, S.S.; Khatib, M.M.; Iizuka, Y. Zircon U–Pb Age Constraints from Iran on the Magmatic Evolution Related to Neotethyan Subduction and Zagros Orogeny. Lithos 2013, 162–163, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.R.; Graham, I.T.; Ghaderi, M. Oligocene-Miocene Geodynamic Evolution of the Central Part of Urumieh-Dokhtar Arc of Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaii Moghadam, H.; Khademi, M.; Hu, Z.; Stern, R.J.; Santos, J.F.; Wu, Y. Cadomian (Ediacaran–Cambrian) Arc Magmatism in the ChahJam–Biarjmand Metamorphic Complex (Iran): Magmatism along the Northern Active Margin of Gondwana. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjoughian, F.; Kananian, A. Zircon U–Pb Geochronology and Emplacement History of Intrusive Rocks in the Ardestan Section, Central Iran. Geol. Acta 2017, 15, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; Ghorbani, M.R.; Bröcker, M.; D’Antonio, M.; Cottle, J.M.; Gebbing, T.; Carmine Mazzeo, F.; Ahmadi, P. Late Oligocene–Miocene Mantle Upwelling and Interaction Inferred from Mantle Signatures in Gabbroic to Granitic Rocks from the Urumieh–Dokhtar Arc, South Ardestan, Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2017, 59, 1590–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, Y.; Liu, D.; Mo, X.; Cong, F. The Initial Slab Rollback of Neo-Tethys Ocean: Constrain from Gongga Adakitic Rocks and Enclaves in the Late Cretaceous. Lithos 2023, 440–441, 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; Ghorbani, M.R.; Cottle, J.M.; Bröcker, M. Multi-Stage Tectono-Magmatic Evolution of the Central Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, South Ardestan, Iran: Insights from Zircon Geochronology and Geochemistry. Geol. J. 2019, 54, 2447–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, S.M.; Shahrabi, M.; Navai, I. Geological Map of Zaviyeh; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 2004; Volume 6160. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Li, Q.L.; Li, X.H.; Chiaradia, M.; Karsli, O.; Hoernle, K.A.; Griffin, W.L. Mantle-Derived High-K Magmatic Fluxes in Northeast Iran Arc: Constraints from Zircon U–Pb–O–Hf and Bulk Rock Major-Trace Elements and Sr–Nd–Pb Isotopes. Gondwana Res. 2023, 119, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, N.; Azizi, H.; Stern, R.; Asahara, Y.; Khodaparast, S.; Madanipour, S.; Yamamoto, K. Zircon U-Pb Dating, Geochemistry and Evolution of the Late Eocene Saveh Magmatic Complex, Central Iran: Partial Melts of Sub-Continental Lithospheric Mantle and Magmatic Differentiation. Lithos 2018, 314–315, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Kahkhaei, M.; Esmaili, D.; Francisco, C.G. Geochemical and Isotopic (Nd and Sr) Constraints on Elucidating the Origin of Intrusions from Northwest Saveh, Central Iran. Geopersia 2014, 4, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, M.A.; Shahrabi, M.; Navaei, Y. 1:100,000 Geological Map of Zavieh; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, E.; Li, H.; Babazadeh, S.; Ma, C.; Förster, M.W. Late Eocene Slab Retreat, Extension, and Mantle Upwelling Inferred from Mantle Signatures in Potassium-Rich Magmatism in NE Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2023, 65, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; Haase, K.; Ghalamghash, J.; Regelous, M.; Poujol, M.; Raeisi, D.; Zhao, M. Magmatic Evolution of the Migrating Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Arc, Iran: Implications for Magma Production. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 112, 1577–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Ghorbani, G.; Khedr, M.Z.; Fazlnia, N.; Chiaradia, M.; Eyuboglu, Y.; Santosh, M.; Francisco, C.G.; Martinez, M.L.; Gourgaud, A.; et al. Late Miocene K-Rich Volcanism in the Eslamieh Peninsula (Saray), NW Iran: Implications for Geodynamic Evolution of the Turkish–Iranian High Plateau. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 1028–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Li, Q.L.; Li, X.H.; Stern, R.J.; Levresse, G.; Santos, J.F.; Lopez Martinez, M.; Ducea, M.N.; Ghorbani, G.; Hassannezhad, A. Neotethyan Subduction Ignited the Iran Arc and Back-Arc Differently. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaii Moghadam, H.; Li, Q.L.; Griffin, W.L.; Stern, R.J.; Chiaradia, M.; Karsli, O.; Ghorbani, G.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Pourmohsen, M. Zircon U-Pb, Geochemical and Isotopic Constraints on the Age and Origin of A- and I-Type Granites and Gabbro-Diorites from NW Iran. Lithos 2020, 374–375, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.J.; Moghadam, H.S.; Pirouz, M.; Mooey, W. The Geodynamic Evolution of Iran. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 49, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Griffin, W.L.; Santos, J.F.; Chen, R.X.; Karsli, O.; Lucci, F.; Sepidbar, F.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrology of the Oligocene Magmatism in the SE Segment of the UDMB. Iran. Lithos 2022, 416–417, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirkhah, M.; Neill, I.; Allen, M.B.; Emami, M.H.; Shahraki Ghadimi, A. Distinct Sources for High-K and Adakitic Magmatism in SE Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 196, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, G.; Altherr, R.; Siebel, W.; Schwarz, W.H.; Zack, T.; Hasozbek, A.; Barth, M.; Satır, M.; Cen, C. Carboniferous high-potassium I-type granitoid magmatism in the Eastern Pontides: The Gümüshane pluton (NE Turkey). Lithos 2010, 116, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, M.; Castro, A.; Omran, N.; Emami, M.; Moinvaziri, H.; Badrzadeh, Z. The gabbro (shoshonitic)–monzonite–granodiorite association of Khankandi pluton, Alborz Mountains, NW Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 38, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.N.; Chung, S.L.; Zarrinkoub, M.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Lo, C.H.; Khatib, M.M. Iranian Ultrapotassic Volcanism at 11 Ma Signifies the Initiation of Post-Collisional Magmatism in the Arabia–Eurasia Collision Zone. Terra Nova 2013, 25, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chung, S.L.; Feyzi Bingöl, A.; Yang, L.; Okrostsvaridze, A.; Pang, K.N.; Lee, H.Y.; Lin, T.H. Diachronous Initiation of Post-Collisional Magmatism in the Arabia-Eurasia Collision Zone. Lithos 2020, 356–357, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Daneshvar, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Asahara, Y.; Whattam, S.A.; Tsuboi, M.; Minami, M. Early Miocene Post-Collision Andesite in the Takab Area. NW Iran. J. Pet. 2021, 62, 022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Hoernle, K.A.; Hauff, F.; Chiaradia, M.; Garbe-Schönberg, D.; Orozco-Esquivel, T.; Bindeman, I.N.; Karsli, O.; Ghorbani, G.; Mousavi, N.; et al. Middle-Late Miocene to Pleistocene Post-Collisional Magmatism in the Arabia-Eurasia Collision Zone, an Example from Northwest Iran. J. Pet. 2023, 64, 081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, K.; Kananian, A.; Xiao, Y.; Sarjoughian, F. Petrogenesis of Middle-Eocene Granitoids and Their Mafic Microgranular Enclaves in Central Urmia-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Iran): Evidence for Interaction between Felsic and Mafic Magmas. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Rossetti, F.; Lucci, F.; Chiaradia, M.; Gerdes, A.; Martinez, M.L.; Ghorbani, G.; Nasrabady, M. The Calc-Alkaline and Adakitic Volcanism of the Sabzevar Structural Zone (NE Iran): Implications for the Eocene Magmatic Flare-up in Central Iran. Lithos 2016, 248, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, F.; Nasrabady, M.; Theye, T.; Gerdes, A.; Monie, P.; Lucci, F.; Vignaroli, G. Adakite Differentiation and Emplacement in a Subduction Channel: The Late Paleocene Sabzevar Magmatism (NE Iran). Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2014, 126, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, F.; Rossetti, F.; White, J.C.; Moghadam, H.S.; Shirzadi, A.; Nasrabady, M. Tschermak fractionation in calc-alkaline magmas: The Eocene Sabzevar volcanism (NE Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, D.; Babazadeh, S.; Long, L.E.; Zhao, M.; Cottle, J.M.; Nayebi, N.; Modabberi, S. Geochemical and Isotopic Signatures, and Zircon U–Pb Ages of the Oldest Known Intrusive Rocks Associated with Porphyry Cu Deposits in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 256, 107366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillat, C.; Dehlavi, P.; Martel Jantin, B. Géologie de la Région de Saveh (Iran): Contribution à L’étude du Volcanisme et du Plutonisme Tertiaires de la Zone de l’Iran Central. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Scientifique et Médicale de Grenoble, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, J.; Stockli, D.F.; Horton, B.K.; Axen, G.J.; Stockli, L.D.; Grove, M.; Schmitt, A.K.; Walker, J.D. U-Pb Zircon Geochronology of Late Neoproterozoic–Early Cambrian Granitoids in Iran: Implications for Paleogeography, Magmatism, and Exhumation History of Iranian Basement. Tectonophysics 2008, 451, 71–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, A.; Talbot, C.J. A new tectonic scenario for the Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone (Iran). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 26, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klotzli, U. Geochemistry and Tectono-Magmatic Setting of Hypabyssal Intrusive Rocks in the South of Mamouniyeh, Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2025, 35, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P.; Sholeh, A. The Tethyan Tectonic History and Cu-Au Metallogeny of Iran. Soc. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2016, 19, 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kretz, R. Symbols for rock-forming minerals. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.R.; Chappell, L.W. Granitoid Types and Their Distribution in the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeast Australia. Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 1983, 159, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.; Barnes, C.G.; Collins, W.J.; Arculus, R.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Frost, C.D. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, H.; Dolatshahi, S.; Yang, X.; Karimzadeh, S.A.; Meshkani, S.A. Geochemical, Fluid Inclusion and O-H-S Isotope Constraints on the Origin of the Rangraz Copper Deposit. Cent. Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 128, 103877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U.; Ullah, M. Evidence of Boiling in Ore Forming Process Based on Quartz Textures and Fluid Inclusions Studies, a Case Study in Mamouniyeh Cu Deposit, Iran. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U.; Lentz, D.; Ullah, M. Constraining Ore-Forming Processes Using Magnetite-Titanomagnetite Chemistry: A Case Study of the Mamuniyeh Cu Mineralization System, Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc. J. Econ. Geol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U.; Ullah, M. Chemical Composition of Hydrothermal Pyrite as an Indicator for Deciphering Ore-Forming Processes: A Case Study from the Mamuniyeh Copper Deposit, UDMA. J. Econ. Geol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U.; Lentz, D.; Ullah, M. Genesis of the Mamuniyeh Copper Deposit in the Central Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran: Constraints from Geology, Geochemistry, Fluid Inclusions, and H–O–S Isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 175, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U. Copper Mineralization Pattern Based on Mineralogy, Alteration, Geochemistry of Intrusive Rocks and Fluid Inclusion in the South of Mamuoniyeh, Middle Part of Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2024, 34, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of Some Modern Arc Magmas by Melting of Young Subducted Lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstron, J.M.; Zen, E.A. Aluminium in Hornblende: An Empirical Igneous Geobarometer. Am. Mineral. 1986, 71, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Rickwood, P.C. Boundary Lines within Petrologic Diagrams Which Use Oxides of Major and Minor Elements. Lithos 1989, 22, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.S.; Bédard, J.H. Magmatic Affinity of Modern and Ancient Subalkaline Volcanic Rocks Determined from Trace-Element Discriminant Diagrams. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 46, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M. Igneous Petrogenesis Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach; Unwin Hyman: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, E.H.; Keith, J.D. Trace Element Systematics in Silicic Magmas: A Metallogenic Perspective. In Trace Element Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks: Applications for Massive Sulphide Exploration; Wyman, D.A., Ed.; Short Course Notes; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 1996; pp. 115–151. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements, Meteorite Studies. In Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Developments in Geochemistry; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock Forming Minerals; Longman Scientific and Technical: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, N.; Fabries, J.; Ferguson, A.K.; Ginzburg, I.V.; Ross, M.; Seifert, F.A.; Zussman, J.; Aoki, K.; Gottardi, G. The Nomenclature of Pyroxenes. Mineral. Mag. 1988, 52, 535–550. [Google Scholar]
- Mojzsis, S.J.; Harrison, T.M. Establishment of a 3.83-Ga Magmatic Age for the Akilia Tonalite (Southern West Greenland). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 202, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, D.B.; Xue, F.; Tucker, R.D.; Peng, Z.X.; Baker, J.; Davis, A. Ages of Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism and Protolith Orthogneisses from the Eastern Dabie Shan: U/Pb Zircon Geochronology. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 151, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, C.L.; Smithies, R.H.; Taylor, R.J.M.; Evans, N.; McDonald, B. Zircon Th/U Ratios in Magmatic Environs. Lithos 2015, 212–215, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Zheng, Y.F. Study on the Genesis of Zircon and Its Restrictions on Explaining the U-Pb Age. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubatto, D. Zircon Trace Element Geochemistry; Partitioning with Garnet and the Link between U-Pb Ages and Metamorphism. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettke, T.; Audetat, A.; Schaltegger, U.; Heinrich, C.A. Magmatic-to-Hydrothermal Crystallization in the W-Sn Mineralized Mole Granite (NSW, Australia)—Part II: Evolving Zircon and Thorite Trace Element Chemistry. Chem. Geol. 2005, 220, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.R.; Sisson, T.W.; Mazdab, F.K. Young Cumulate Complex beneath Veniaminof Caldera, Aleutian Arc, Dated by Zircon in Erupted Plutonic Blocks. Geology 2007, 35, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Schaltegger, U. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Zircon. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Mensing, T.M. The U-Pb, Th-Pb, and Pb-Pb Methods. In Isotope Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 214–255. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Griffin, W.L.; Li, X.H.; Santos, J.F.; Karsli, O.; Stern, R.J.; Ghorbani, G.; Gain, S.; Murphy, R.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Crustal Evolution of NW Iran: Cadomian Arcs, Archean Fragments and the Cenozoic Magmatic Flare-Up. J. Pet. 2018, 58, 2143–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.E.; Flood, R.H. Zircon Hf Isotopic Evidence for Mixing of Crustal and Silicic Mantle-Derived Magmas in a Zoned Granite Pluton, Eastern Australia. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Zarrinkoub, M.H.; Melkonyan, R.; Pang, K.N.; Lee, H.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Mohammadi, S.S.; Khatib, M.M. Zircon Hf Isotopic Constraints on Magmatic and Tectonic Evolution in Iran: Implications for Crustal Growth in the Tethyan Orogenic Belt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 145, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaii Moghadam, H.; Corfu, F.; Chiaradia, M.; Stern, R.J.; Ghorbani, G. Sabzevar Ophiolite, NE Iran: Progress from Embryonic Oceanic Lithosphere into Magmatic Arc Constrained by New Isotopic and Geochemical Data. Lithos 2014, 210–211, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Groves, D.I. Potassic Igneous Rocks and Associated Gold–Copper Mineralization, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sarjoughian, F.; Kananian, A.; Ahmadian, J.; Murata, M. Chemical Composition of Biotite from the Kuh-e Dom Pluton, Central Iran: Implication for Granitoid Magmatism and Related Cu-Au Mineralization. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarasvandi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Lentz, D.; Adelpour, M.; Pourkaseb, H. Rare Earth Element Signatures of Economic and Sub-Economic Porphyry Copper Systems in Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (UDMA. Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, B.; Khalili, M.; Köksal, F.T.; Mansouri Esfahani, M.; Beavers, R. Petrological Constraints on the Origin of the Plutonic Massif of the Ghaleh Yaghmesh Area, Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 129, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, G.N. Chemical Subdivision of the A-Type Granitoids: Petrogenetic and Tectonic Implications. Geology 1992, 20, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.L. Influence of Slab Thermal Structure on Basalt Source Regions and Melting Conditions: REE and HFSE Constraints from Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, Northern Cascadia Subduction System. Lithos 2006, 87, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieblemont, D.; Tegyey, M. Une discrimination géochimique des roches différenciées témoin de la diversité origine et de situation tectonique des magmas calco-alcalins. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Sci. 1994, 319, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Morata, D.; Oliva, C.; Cruz, R.; Suarez, M. The Bandurrias gabbro; late Oligocene alkaline magmatism in the Patagonian Cordillera. J. Am. Earth Sci. 2005, 18, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sisson, T.W.; Grove, T.L. Temperatures and H2O Contents of Low-MgO High-Alumina Basalts. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 113, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Li, X.-H.; Ling, X.-X.; Santos, J.F.; Stern, R.J.; Li, Q.-L.; Ghorbani, G. Eocene Kashmar Granitoids (NE Iran): Petrogenetic Constraints from U–Pb Zircon Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry. Lithos 2015, 216–217, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A. Geochemical Fingerprinting of Oceanic Basalts with Applications to Ophiolite Classification and the Search for Archean Oceanic Crust. Lithos 2008, 100, 14–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schandl, E.S.; Gorton, M.P. Application of High Field Strength Elements to Discriminate Tectonic Settings in VMS Environments. Econ. Geol. 2002, 97, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.R. Origin of the Adakite-High-Nb Basalt Association and Its Implications for Post-Subduction Magmatism in Baja California, Mexico. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, P.A.; Hamada, M.; Arculus, R.J.; Johnson, K.; Marsaglia, K.M.; Savov, I.P.; Ishizuka, O.; Li, H. The Arc Arises: The Links between Volcanic Output, Arc Evolution, and Melt Composition. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 461, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, Y. Slab Melting: Its Role in Continental Crust Formation and Mantle Evolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3941–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchenbaur, M.; Münker, C.; Schuth, S.; Garbe-Schonberg, D.; Marchev, P. Tectonomagmatic Constraints on the Sources of Eastern Mediterranean K-Rich Lavas. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, J.; Eggins, S.; Johnson, R. Magma Genesis in the New Britain Island Arc: Further Insights into Melting and Mass Transfer Processes. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 1641–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Peate, D.W. Tectonic Implications of the Composition of Volcanic ARC Magmas. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1995, 23, 251–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, T.; Graham, D. Erosion of Lithospheric Mantle beneath the East African Rift System: Geochemical Evidence from the Kivu Volcanic Province. Lithos 1999, 48, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, D.A.; Hofmann, A.W. Nb-Ta-Rich Mantle Amphiboles and Micas: Implications for Subduction-Related Metasomatic Trace Element Fractionations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 131, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanmaz, E.; Pearce, J.A.; Thirlwall, M.F.; Mitchell, J.G. Petrogenetic Evolution of Late Cenozoic, Post-Collision Volcanism in Western Anatolia, Turkey. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2000, 102, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Qin, K.; Li, G.M.; Xiao, B.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.X. Post-Collisional Ore Bearing Adakitic Porphyries from Gangdese Porphyry Copper Belt, Southern Tibet: Melting of Thickened Juvenile Arc Lower Crust. Lithos 2011, 126, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.; O’Nions, R.K. Partial Melt Distributions from Inversion of Rare Earth Element Concentration. J. Petrol. 1991, 32, 1021–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlito, C. Bimodal Geochemical Evolution at Sheveluch Stratovolcano, Kamchatka, Russia: Consequence of a Complex Subduction at the Junction of the Kuril Kamchatka and Aleutian Island Arcs. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.M. Trace Element Fractionation during Anatexis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1970, 34, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesworth, C.J.; Gallager, K.; Hergt, J.M.; McDermott, F. Destructive plate margin magmatism: Geochemistry and melt generation. Lithos 1994, 33, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Agostini, S.; Innocenti, F.; Haller, M.J.; Manetti, P.; Mazzarini, F. Slab Window Related Magmatism from Southernmost South America: The Late Miocene Mafic Volcanics from the Estancia Glencross Area (52°S, Argentina–Chile). Lithos 2001, 57, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaluva, L.; Macciotta, G.; Piccardo, G.; Zeda, O. Clinopyroxene Composition of Ophiolite Basalts as Petrogenetic Indicator. Chem. Geol. 1989, 77, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, E.G.; Pearce, J.A. Clinopyroxene Composition of Mafic Lavas from Different Tectonic Settings. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1977, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, E.L.; Papike, J.J.; Bence, A.E. Statistical Analysis of Clinopyroxenes from Deep-Sea Basalts. Am. Mineral. 1979, 64, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, O.; Bağci, U.; Rizaoğlu, T.; Ionescu, C.; Onal, G.; Hock, V.; Kozlu, H. Petrology of Ultramafic to Mafic Cumulate Rocks from the Goksun (Kahramanmaraş) Ophiolite, Southeast Turkey. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBari, S.M.; Coleman, R.G. Examination of the Deep Levels of an Island Arc: Evidence from the Tonsina Ultramafic-Mafic Assemblage, Tonsina, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 1989, 94, 4373–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elthon, D. Petrology of Gabbroic Rocks from the Mid-Cayman Rise Spreading Center. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 1987, 92, 658–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soesoo, A. A Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Clinopyroxene Composition: Empirical Coordinates for the Crystallization PT-Estimations. Geol. Soc. Swed. Geol. Fören. 1997, 119, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arculus, R.J. Supra-Subduction Zone Pyroxenites from San Jorge and Santa Isabel (Solomon Islands). J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 1531–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, A. Relationship between Clinopyroxene Composition and the Formation Environment of Volcanic Host Rocks. IUP J. Earth Sci. 2010, 4, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, P.R.; Janney, P.E.; Solidum, R.U. Petrology and Geochemistry of Camiguin Island, Southern Philippines: Insights to the Source of Adakites and Other Lavas in a Complex Arc Setting. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1999, 134, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Wilde, S.A.; Li, Q.L.; Yang, Y.N. Continental Flood Basalts Derived from the Hydrous Mantle Transition Zone. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Longman Scientific and Technical: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Rudnick, R.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Michelfelder, G.S.; Feeley, T.C.; Wilder, A.D.; Klemetti, E.W. Modification of the Continental Crust by Subduction Zone Magmatism and Vice-Versa: Across-Strike Geochemical Variations of Silicic Lavas from Individual Eruptive Centers in the Andean Central Volcanic Zone. Geosciences 2013, 3, 633–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhai, S.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yin, X. Geochemical Characteristics of Major and Trace Elements in the Okinawa Trough Basaltic Glass. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Singh, S.K.; Samal, A.K. Geochemistry and Geodynamic Implications of the Mafic Magmatic Plumbing System of the ca. 1.98–1.97 Ga Jhansi Large Igneous Province in the Northern Indian Shield. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 131, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, A.; Gundogdu, A.; Gourgaud, M.N. Petrological and Geochemical Characteristics of Cenozoic High-K Calc-Alkaline Volcanism in Konya, Central Anatolia, Turkey. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 85, 327–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alici, P.; Temel, A.; Gourgaud, A.; Vidal, P.; Gündoğdu, M.N. Quaternary Tholeiitic to Alkaline Volcanism in the Karasu Valley, Dead Sea Rift Zone, Southeast Turkey: Sr-Nd-Pb-O Isotopic and Trace-Element Approaches to Crust-Mantle Interaction. Int. Geol. Rev. 2001, 43, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, G.; Jahangiri, A.; Lentz, D.; Mojtahedi, M. Petrogenesis of Plio-Quaternary Post-Collisional Ultrapotassic Volcanism in NW of Marand, NW Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Badrzadeh, Z.; Chichorro, M. Late Eocene–Oligocene Post-Collisional Monzonitic Intrusions from the Alborz Magmatic Belt, NW Iran. An Example of Monzonite Magma Generation from a Metasomatized Mantle Source. Lithos 2013, 180–181, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundy, J.; Wood, B. Partitioning of Trace Elements between Crystals and Melts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 210, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Turner, S.; Handley, H.; Macpherson, C.; Dosseto, A. Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust? Geology 2007, 35, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A.; Barberio, M.R.; Yirgu, G.; Ayalew, D.; Barbieri, M.; Wu, T.W. Relationships between Mafic and Peralkaline Silicic Magmatism in Continental Rift Settings: A Petrological, Geochemical, and Isotopic Study of the Gedemsa Volcano. Cent. Ethiop. Rift. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 2003–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchett, P.J.; Kouvo, O.; Hedge, C.E.; Tatsumoto, M. Evolution of Continental Crust and Mantle Heterogeneity: Evidence from Hf Isotopes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1981, 77, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfu, F.; Stott, G.M. Age and Petrogenesis of Two Late Archean Magmatic Suites, Northwestern Superior Province, Canada: Zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf Isotopic Relations. J. Petrol. 1993, 34, 817–883. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, A.I.S.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Foster, G.L.; Paterson, B.A.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hergt, J.M.; Gray, C.M.; Whitehouse, M.J. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf–O Isotopes in Zircon. Science 2007, 315, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutman, A.P.; Mohajjel, M.; Bennett, V.C.; Fergusson, C.L. Gondwanan Eoarchean-Neoproterozoic Ancient Crustal Material in Iran and Turkey: Zircon U–Pb–Hf Isotopic Evidence. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 51, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaömer, P.A.; Ustaömer, T.; Collins, A.S.; Robertson, A.H.F. Cadomian (Ediacaran–Cambrian) Arc Magmatism in the Bitlis Massif, SE Turkey: Magmatism along the Developing Northern Margin of Gondwana. Tectonophysics 2009, 473, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Şahin, S.; Aysal, N.; Güngör, Y.; Peytcheva, I.; Neubauer, F. Geochemistry and U–Pb zircon geochronology of metagranites in Istranca (Strandja) Zone, NW Pontides, Turkey: Implications for the geodynamic evolution of Cadomian orogeny. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 755–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.J.; Ali, K.A.; Ren, M.; Jarrar, G.H.; Romer, R.L.; Leybourne, M.I.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Ibrahim, K.M. Cadomian (560Ma) Crust Buried beneath the Northern Arabian Peninsula: Mineral, Chemical, Geochronological, and Isotopic Constraints from NE Jordan Xenoliths. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 436, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, L.; Timmerman, M.J.; Altenberger, U.; Moazzen, M.; Wilke, F.D.H.; Günter, C.; Sudo, M.; Sláma, J. Ediacaran to Jurassic Geodynamic Evolution of the Alborz Mountains, North Iran: Geochronological Data from the Gasht Metamorphic Complex. Swiss J. Geosci. 2024, 117, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, J.; Tucker, R.D. The Saghand Region, Central Iran: U-Pb Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Implications for Gondwana Tectonics. Am. J. Sci. 2003, 303, 622–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Whattam, S.A. Does Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic (570–530 Ma) Basement of Iran Belong to the Cadomian Orogeny? Precambrian Res. 2022, 368, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepidbar, F.; Homam, S.M.; Wu, G.; Moritz, R.; Hafezimoghadas, H. Early Paleozoic Mafic Intraplate Magmatism in the Binaloud Zone, NE Iran: Implications for the Long-Lived Mantle Plume Activity in the Northern Margin of Gondwana. Lithos 2023, 450–451, 107191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroozi, R.; Vaccaro, C.; Masoudi, F.; Petrini, R. Petrogenesis and Mantle Source Characteristics of Triassic Alkaline Basaltic Rocks of North Kamarbon, Northern Central Alborz, Iran. Solid. Earth Sci. 2018, 3, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghdour-Mashhour, R.; Hayes, B.; Pang, K.N.; Bolhar, R.; Tabbakh Shabani, A.A.; Elahi-Janatmakan, F. Episodic subduction initiation triggered Jurassic magmatism in the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone. Iran. Lithos 2021, 396–397, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdashtzadeh, N.; Dilek, Y.; Furnes, H.; Dantas, E.L. Early Jurassic and Late Cretaceous Plagiogranites in Nain–Baft Ophiolitic Mélange Zone in Iran: Remnants of Rift–Drift and SSZ Evolution of a Neotethyan Seaway. J. Geol. Soc. 2024, 181, 2023–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, F.; Mortazavi, M.; Asiabanha, A.; Santos, J. Late Cretaceous volcanism in the northern Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, central Iran. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Abh. 2024, 199, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Alirezaei, S.; Sun, W.; Li, C.Y. Age Revision of the Neotethyan Arc Migration into the Southeast Urumieh-Dokhtar Belt of Iran: Geochemistry and U–Pb Zircon Geochronology. Lithos 2017, 284–585, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Christiansen, E.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Ghorbani, M.R. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Cenozoic Mafic Volcanic Rocks in the Kahak Area of Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 239, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, D.; Mirnejad, H.; McFarlane, C.; Sheibi, M.; Babazadeh, S. Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Geochronology of Miocene Plutons in the Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, East Tafresh. Cent. Iran. Int. Geol. Rev. 2019, 62, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechmann, A.; Burg, J.-P.; Ulmer, P.; Guillong, M.; Faridi, M. Metasomatized Mantle as the Source of Mid-Miocene-Quaternary Volcanism in NW-Iranian Azerbaijan: Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence. Lithos 2018, 304, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalamghash, J.; Schmitt, A.K.; Chaharlang, R. Age and Compositional Evolution of Sahand Volcano in the Context of Post-Collisional Magmatism in Northwestern Iran: Evidence for Time Transgressive Magmatism Away from the Collisional Suture. Lithos 2019, 344–345, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, E.A.; Jimenez, J.M.G.; Graham, I.; Griffin, W.L.; OʼReilly, S.Y.; Pearson, N.; Martin, L.; Carven, S.; Talavera, C. The Enigma of Crustal Zircons in Upper-Mantle Rocks: Clues from the Tumut Ophiolite, Southeast Australia. Geology 2015, 43, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthereau, F.; Lacombe, O.; Vergés, J. Building the Zagros Collisional Orogen: Timing, Strain Distribution and the Dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia Plate Convergence. Tectonophysics 2012, 532–535, 27–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, S.; Raeisi, D.; Santosh, M.; Zhao, M.; D’Antonio, M. Recycled Mantle Source for Porphyry Mineralization: U−Pb and Re−Os Geochronology, and S–Pb–Cu Isotopic Constraints from the Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Central Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 268, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, D.; Zhao, M.; Babazadeh, S.; Long, L.E.; Hajsadeghi, S.; Modabberi, S. Synthesis on Productive, Sub Productive and Barren Intrusions in the Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc, Iran, Constrains on Geochronology and Geochemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 132, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, P.; Omrani, J.; Jolivet, L.; Whitechurch, H.; Vrielynck, B.; Spakman, W.; Monié, P.; Meyer, B.; Wortel, R. Zagros Orogeny: A Subduction-Dominated Process. Geol. Mag. 2011, 148, 692–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari Alavijeh, B.; Rashidnejad Omran, N.; Toksoy Kökçal, F.; Xu, W.; Ghalamghash, J. Oligocene Subduction-Related Plutonism in the Nodoushan Area, Urumieh-Dokhtar Magmatic Belt: Petrogenetic Constraints from U-Pb Zircon Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 725–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschke, M.R.; Scheuber, E.; Gunther, A.; Reutter, K.-J. Evolutionary Cycles during the Andean Orogeny: Repeated Slab Breakoff and Flat Subduction? Terra Nova 2002, 14, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, T.A.; Gans, P.B.; Foster, D.A.; Miller, E.L. Refrigeration of the Western Cordilleran Lithosphere during Laramide Shallow-Angle Subduction. Geology 1991, 19, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goudarzi, M.; Zamanian, H.; Klötzli, U.; Sláma, J.; Míková, J.; Burda, J.; Lentz, D.R.; Ullah, M.; Homnan, J. Unraveling the Protracted Magmatic Evolution in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Northeast Saveh, Iran): Zircon U-Pb Dating, Lu-Hf Isotopes, and Geochemical Constraints. Minerals 2025, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040375
Goudarzi M, Zamanian H, Klötzli U, Sláma J, Míková J, Burda J, Lentz DR, Ullah M, Homnan J. Unraveling the Protracted Magmatic Evolution in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Northeast Saveh, Iran): Zircon U-Pb Dating, Lu-Hf Isotopes, and Geochemical Constraints. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040375
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoudarzi, Mohammad, Hassan Zamanian, Urs Klötzli, Jiří Sláma, Jitka Míková, Jolanta Burda, David R. Lentz, Matee Ullah, and Jiranan Homnan. 2025. "Unraveling the Protracted Magmatic Evolution in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Northeast Saveh, Iran): Zircon U-Pb Dating, Lu-Hf Isotopes, and Geochemical Constraints" Minerals 15, no. 4: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040375
APA StyleGoudarzi, M., Zamanian, H., Klötzli, U., Sláma, J., Míková, J., Burda, J., Lentz, D. R., Ullah, M., & Homnan, J. (2025). Unraveling the Protracted Magmatic Evolution in the Central Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Northeast Saveh, Iran): Zircon U-Pb Dating, Lu-Hf Isotopes, and Geochemical Constraints. Minerals, 15(4), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040375








