Diagenetic Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Middle to High-Porosity and Ultralow-Permeability Tuff Reservoirs in the Huoshiling Formation of the Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
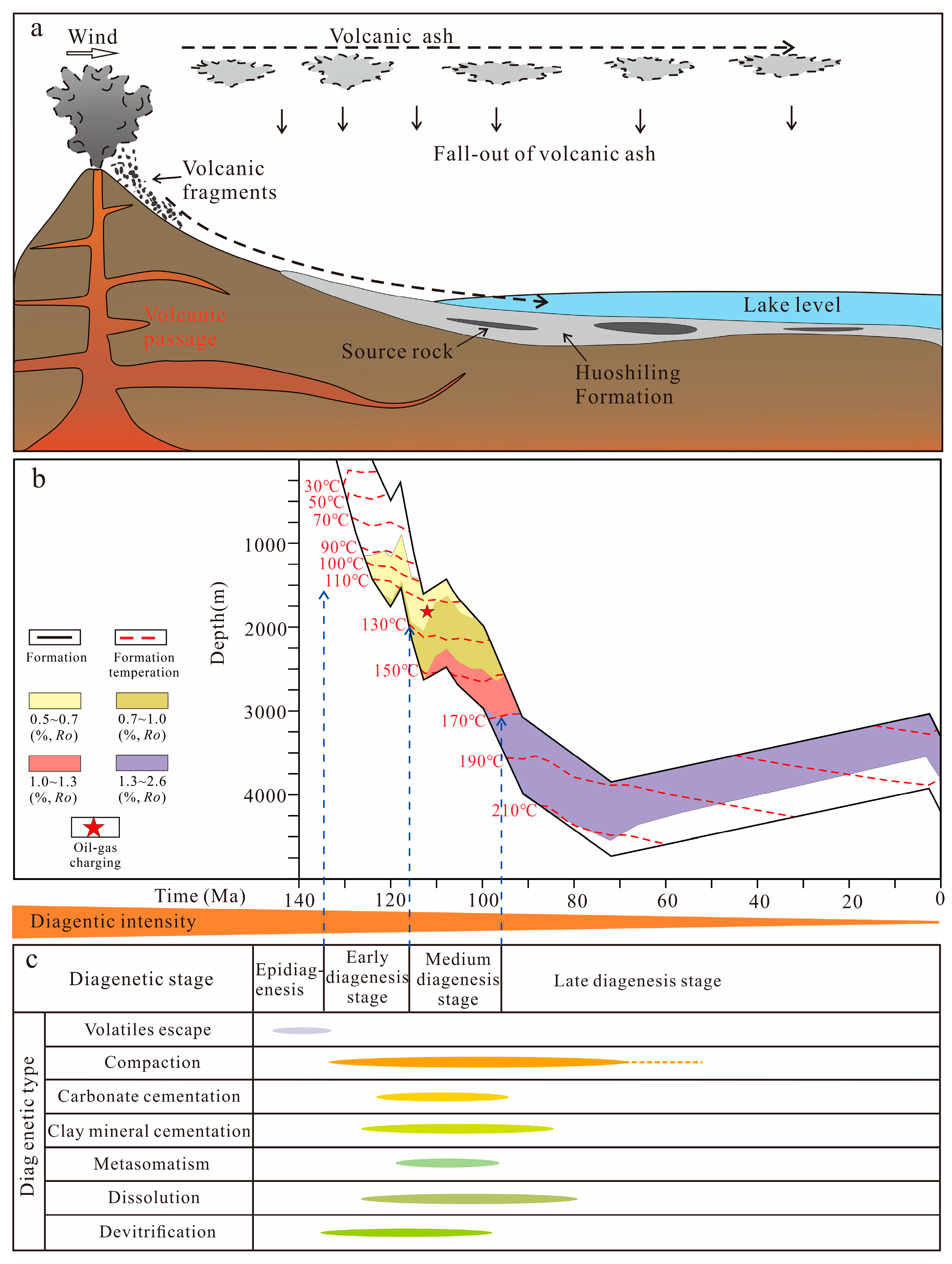
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
3.2. Electron Probes
3.3. Cathodoluminescence
3.4. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Microanalysis
3.5. Fluid Inclusions
4. Results
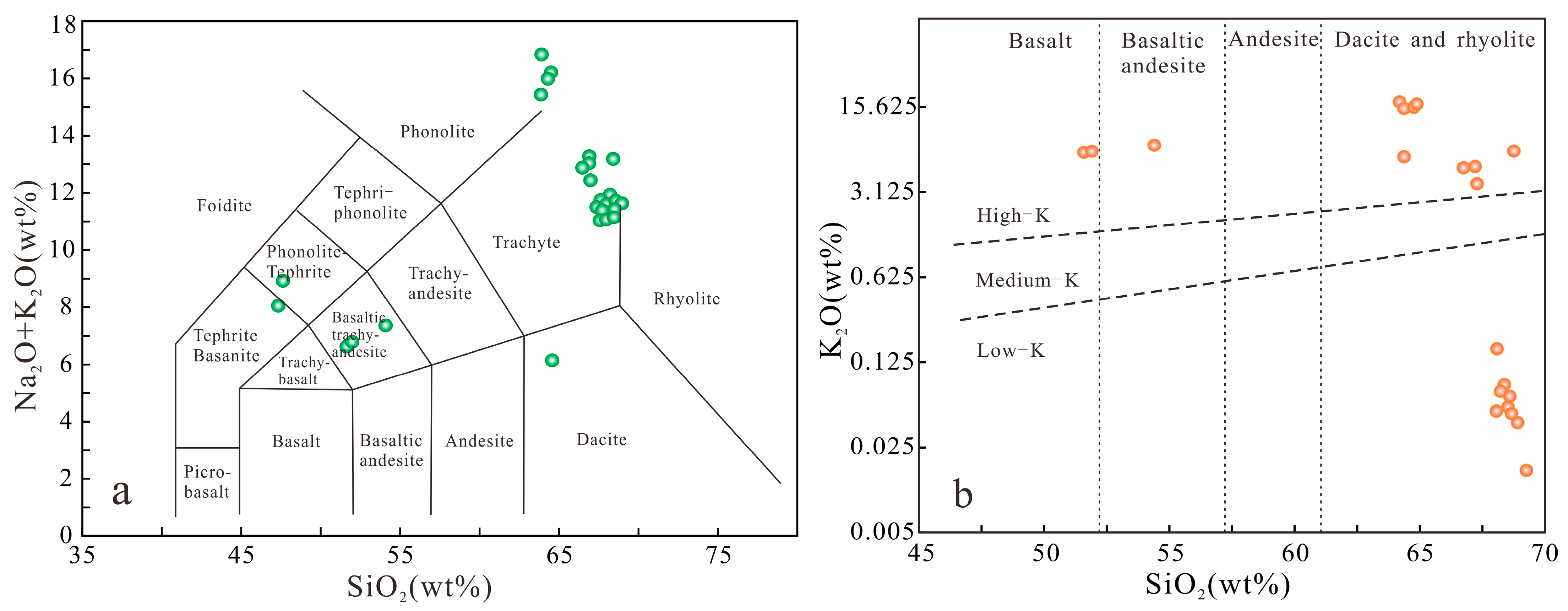
4.1. Reservoir Characteristics
4.1.1. Petrological Characteristics
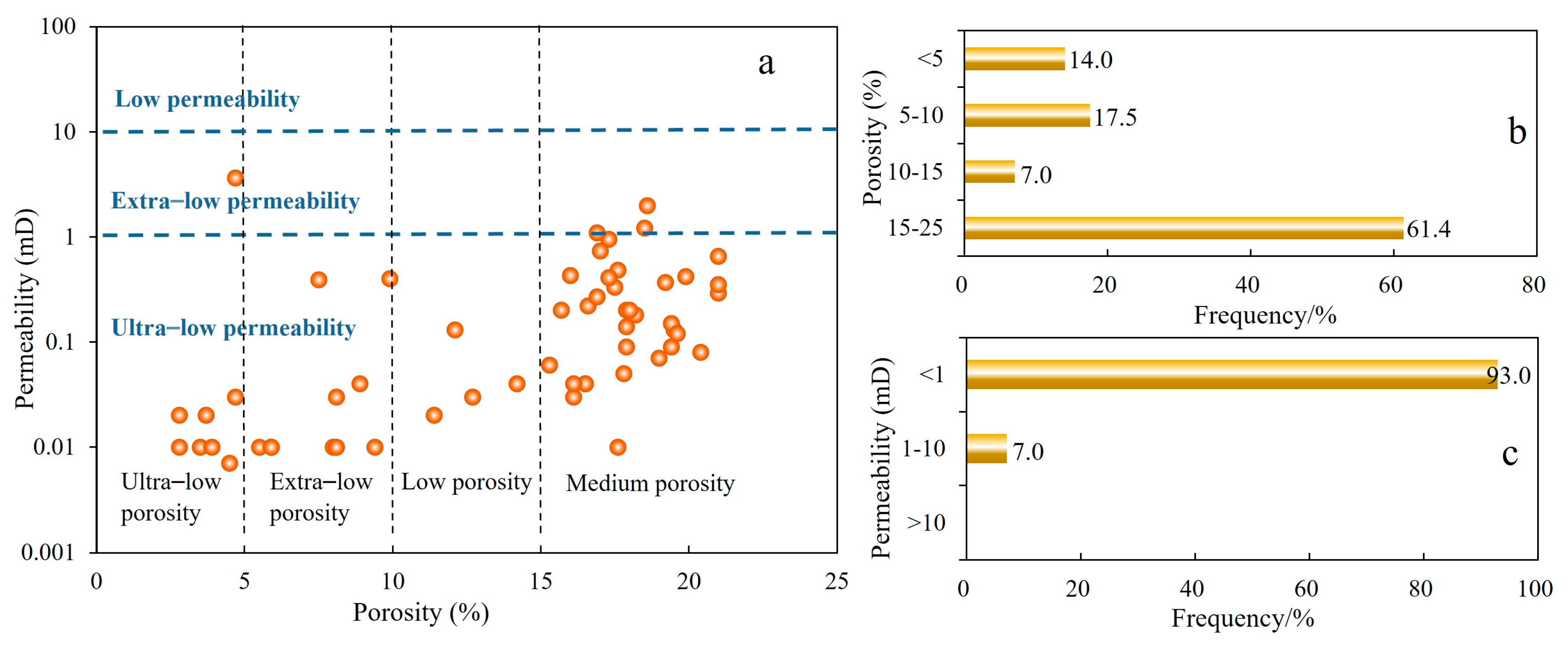
4.1.2. Reservoir Porosity and Permeability
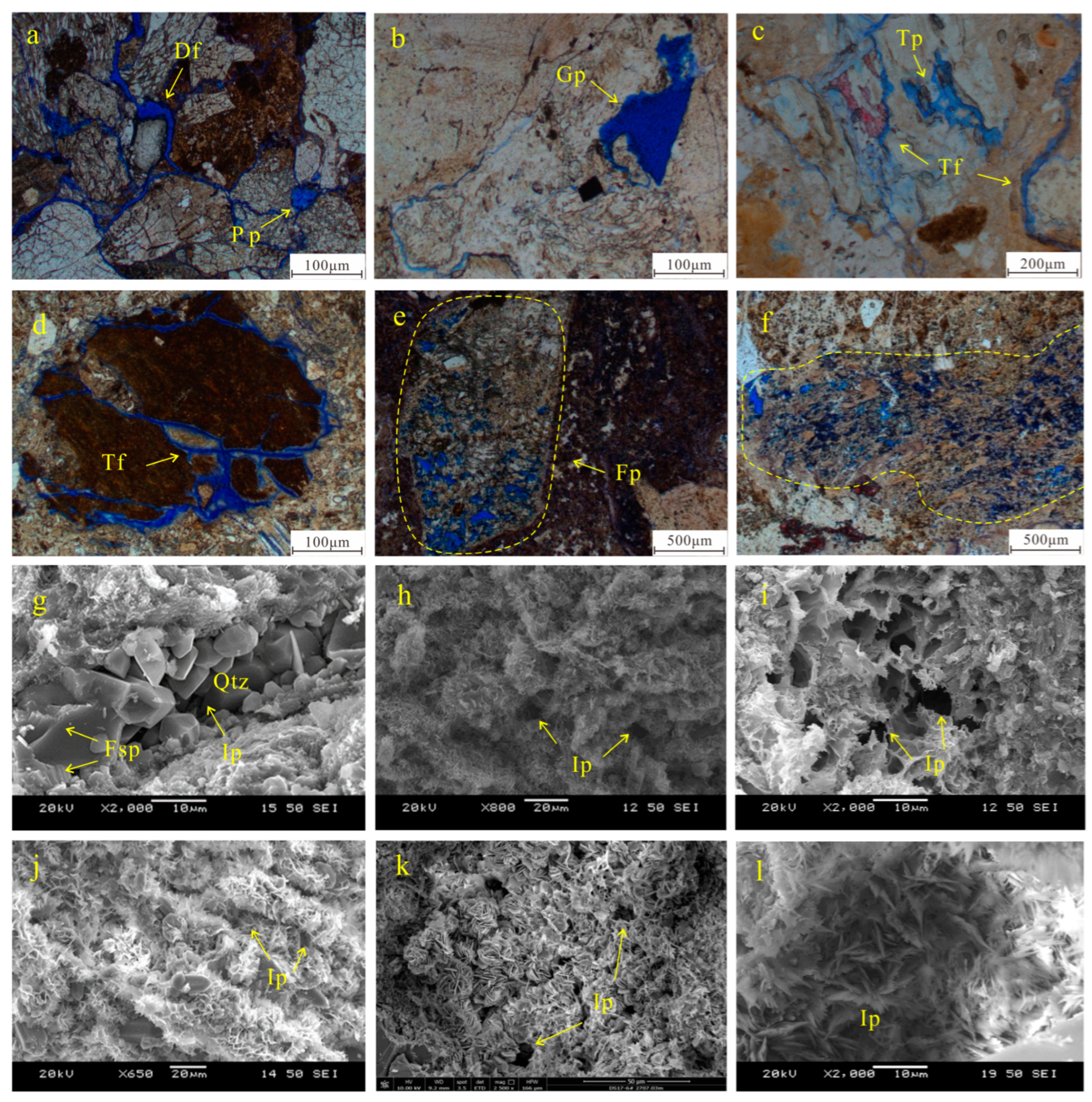
4.1.3. Pore Types
4.2. Diagenetic Types
4.2.1. Mechanical Compaction
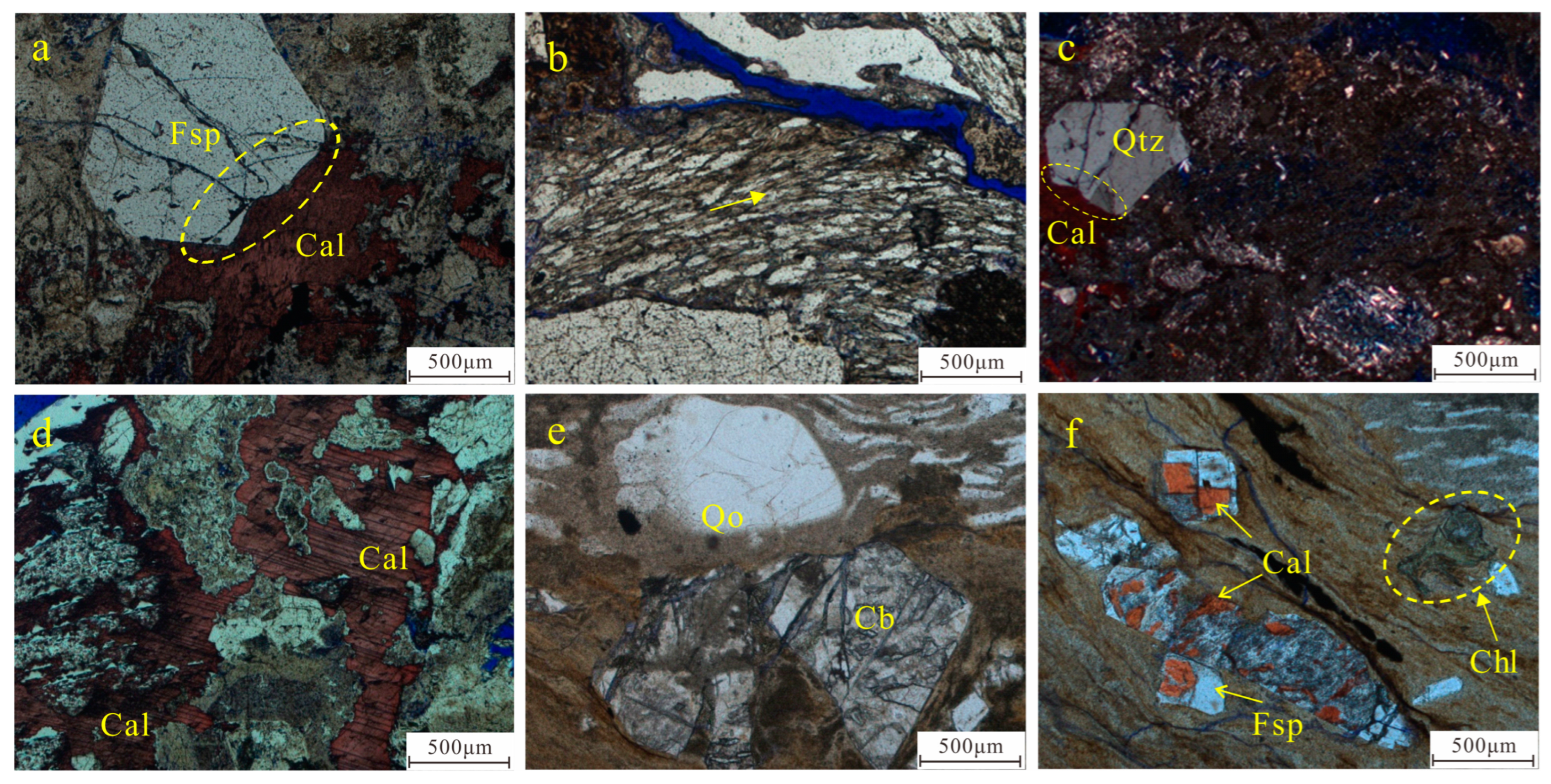
4.2.2. Cementation and Metasomatism
Carbonate Cementation
Siliceous Cementation
Clay Mineral Cementation
Metasomatism
4.2.3. Dissolution
4.2.4. Devitrification
5. Discussion
5.1. Mechanism of Diagenetic Fluid Action
5.2. Diagenetic Fluid Properties
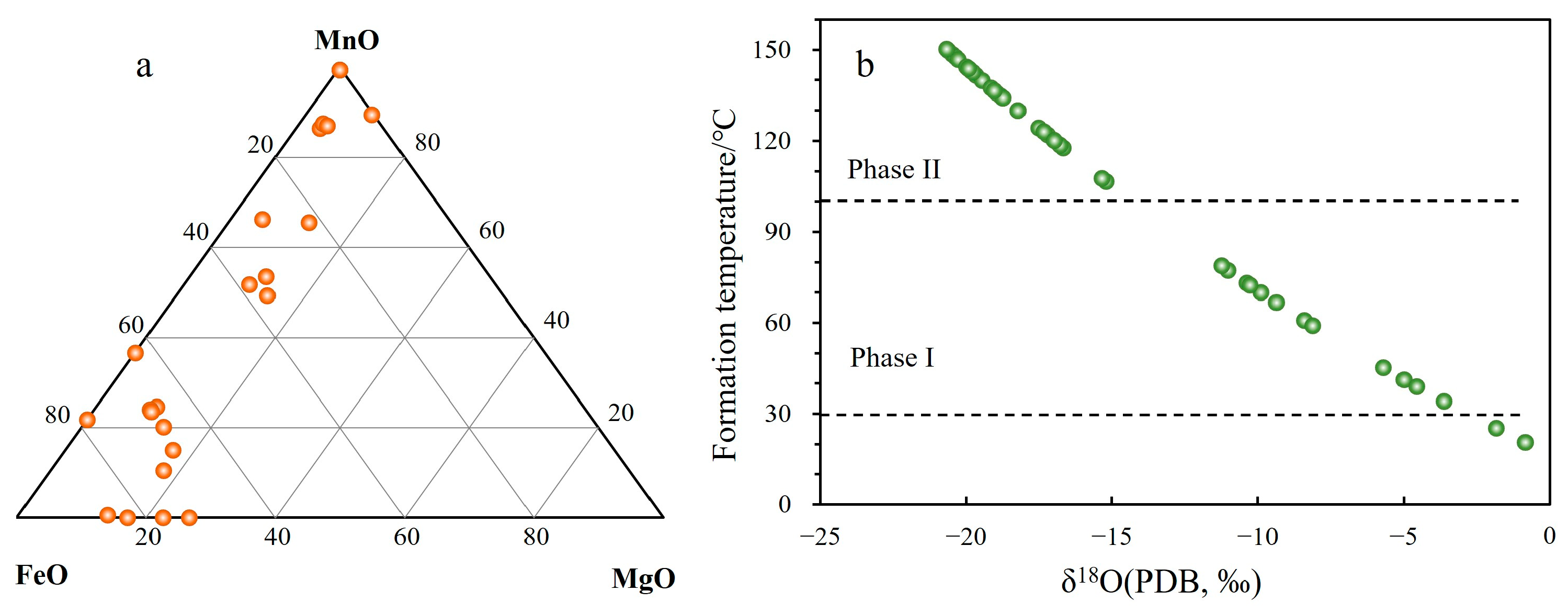
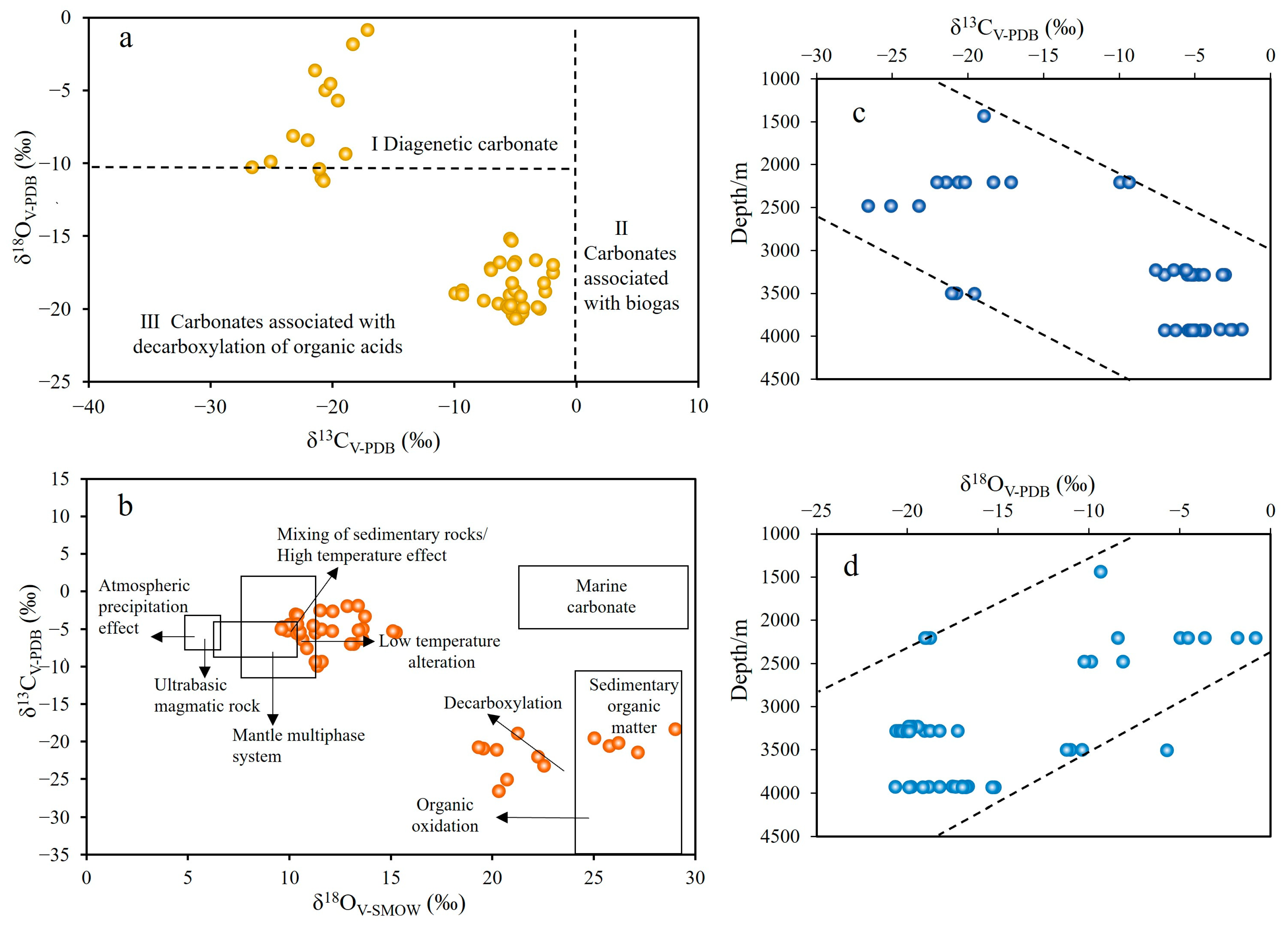
5.2.1. C-O Isotope Characteristics
5.2.2. Fluid Related to Source Rock Thermal Evolution
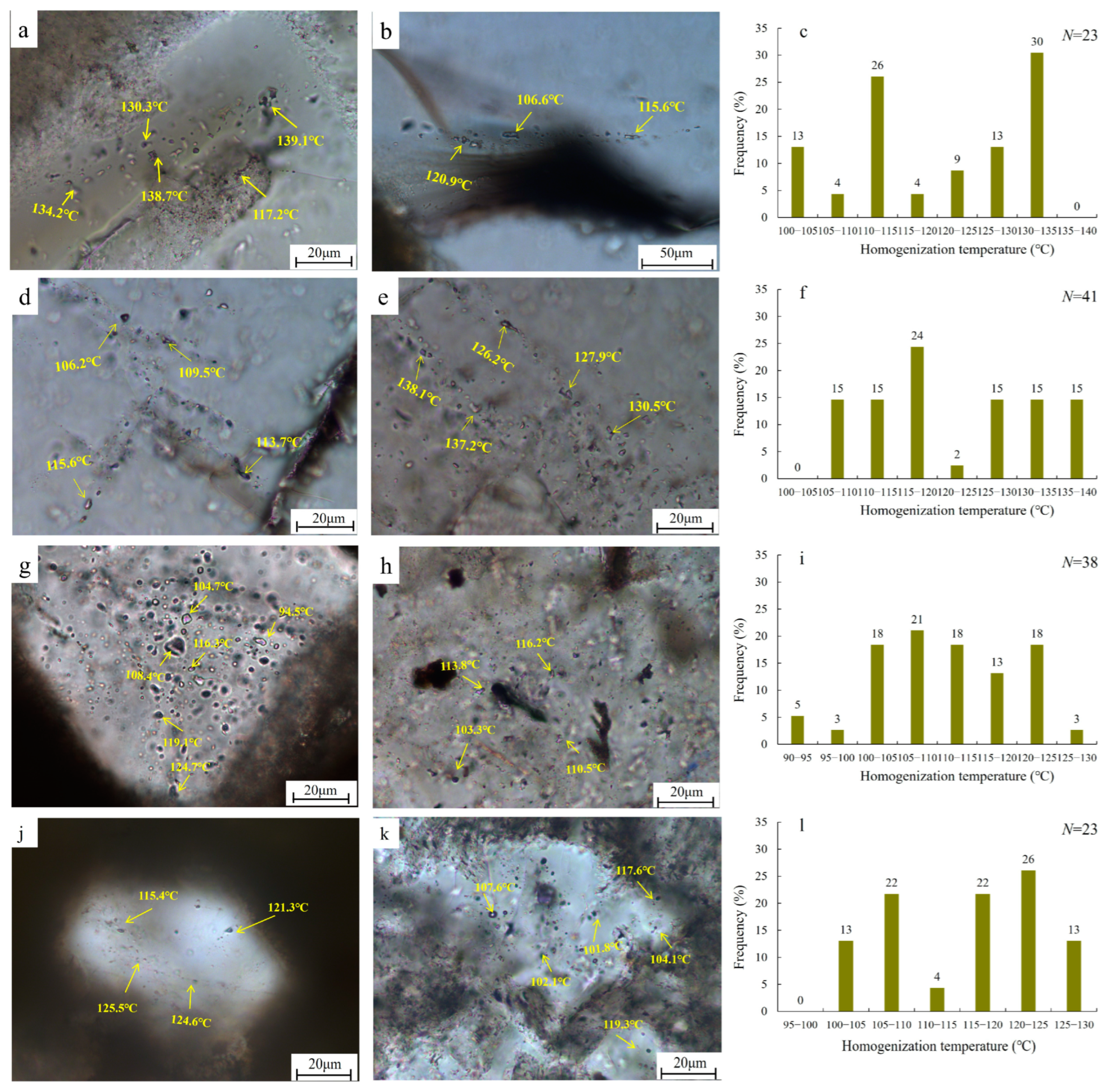
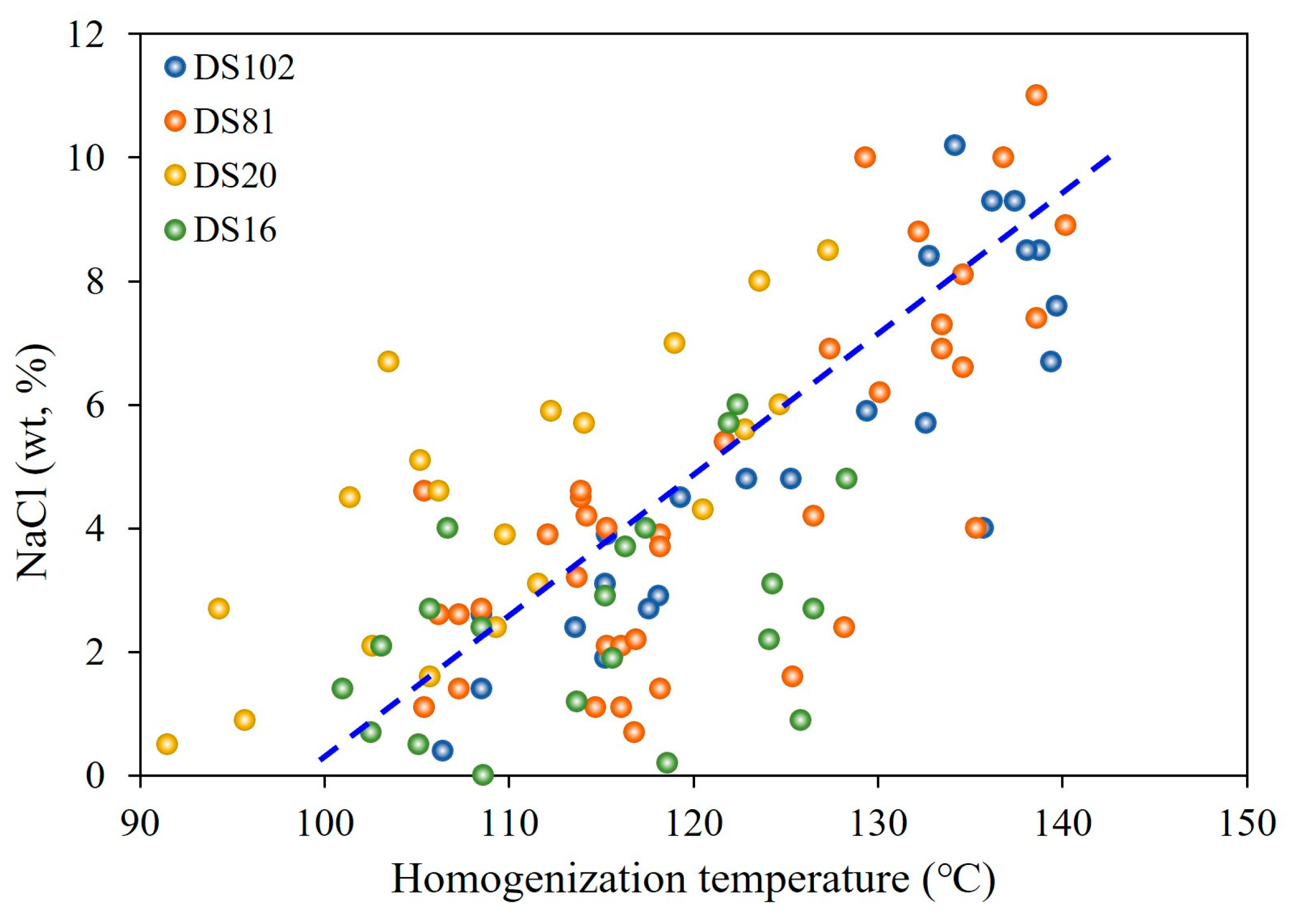
5.2.3. Indicative Significance of Hydrocarbon Associated Saline Inclusions
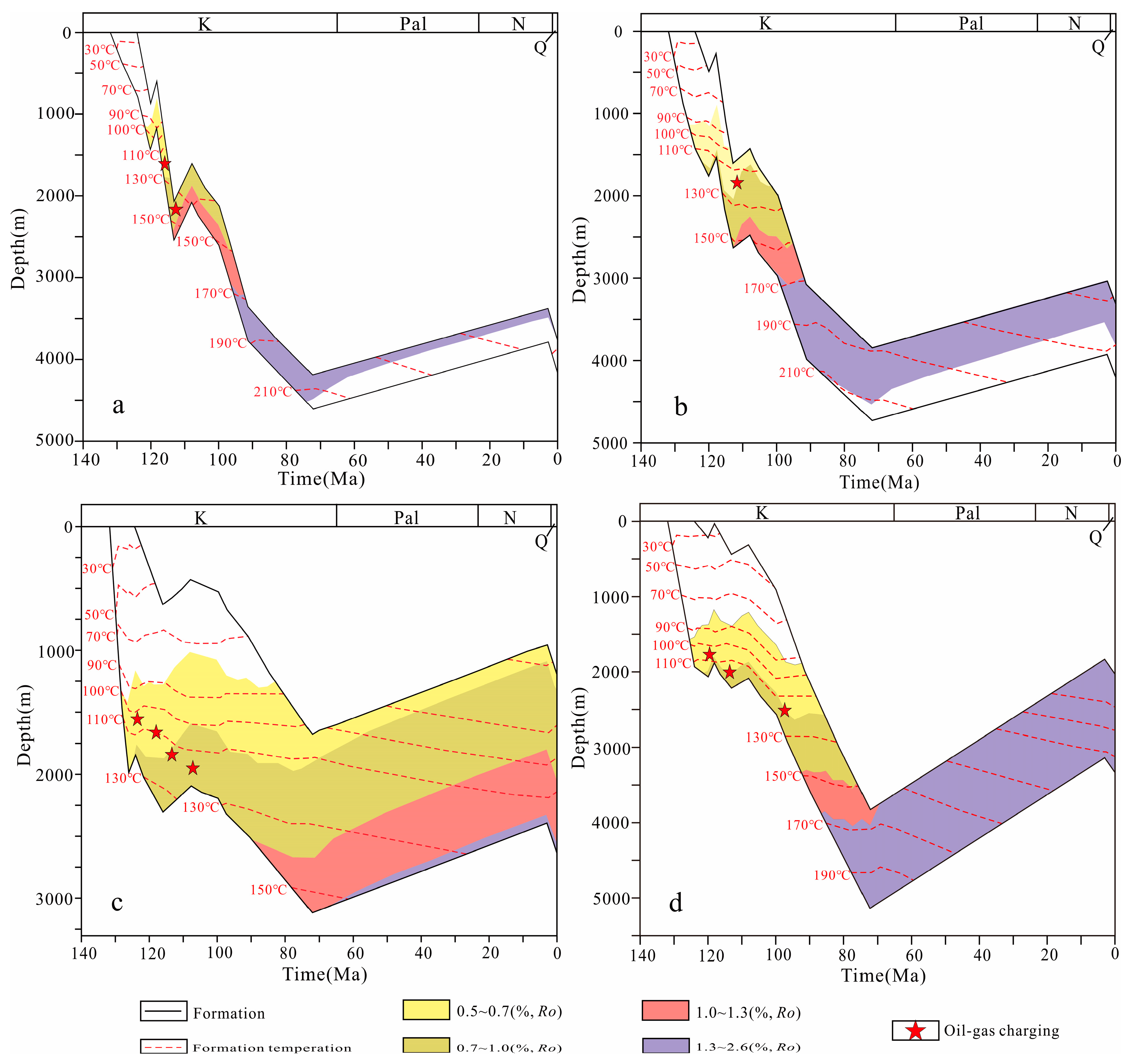
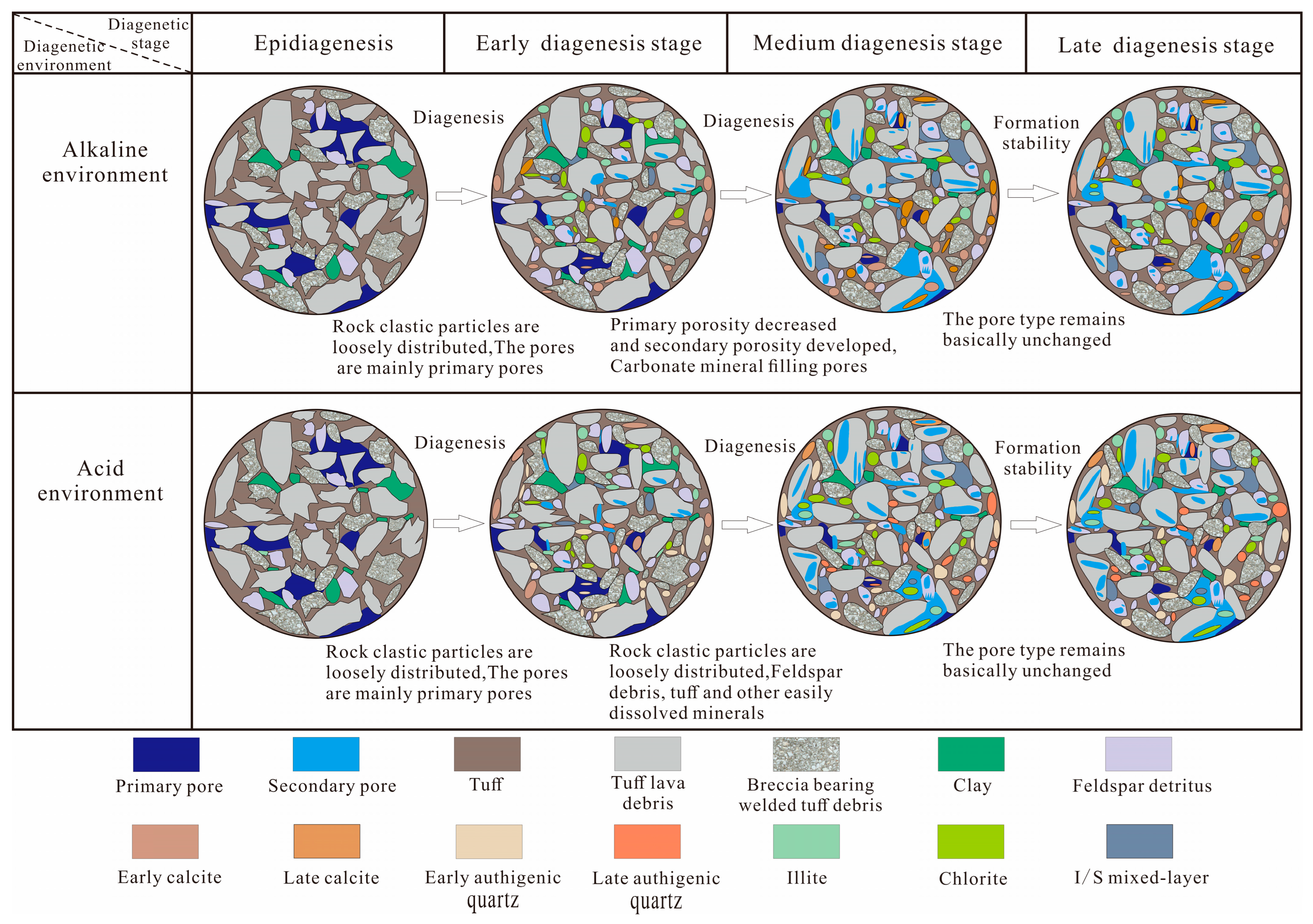
5.3. Diagenetic Evolution Stage Division
5.4. Formation of Reservoir Pores
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huff, W.D.; Bergström, S.M.; Kolata, D.R. Gigantic Ordovician volcanic ash fall in North America and Europe: Biological, tectonomagmatic, and event stratigraphic significance. Geology 1992, 20, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Mao, G.Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, F.F.; Wang, J.Q. Late Triassic tuff intervals in the Ordos basin, Central China: Their depositional, petrographic, geochemical characteristics and regional implications. Asian J. Earth Sci. 2014, 80, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.; Nan, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.J.; Kou, J.Y.; Zhou, N.C. Characteristics and origin of tuff-type tight oil in Jimusar Depression, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaland, H.J.; Furnes, H.; Martinsen, O.J. Paleogene tuffaceous intervals, Grane Field (Block 25/11), Norwegian North Sea: Their depositional, petrographical, geochemical character and regional implications. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunggen, S.; Olgun, N.; Croot, P. The role of airborne volcanic ash for the surface ocean biogeochemical iron-cycle: A review. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynberg, M.E.; Papava, D.; Shengelia, M.; Takaishvili, A.; Nanadze, A.; Patton, D.K. Petrophysical characteristics of the middle eocene laumontite tuff reservoir, Samgori Field, Republic of Georgia. J. Pet. Geol. 1993, 16, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.S.; Ni, G.H.; Lu, S.P. Genesis and reservoir features of tuffaceous rocks in Wuerhe oilfield of the Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2010, 31, 481–485. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.Q.; Fan, T.L.; Wang, H.Y. Characteristics and diagenesis of the volcaniclastic rock reservoirs from the Nantun Formation within the Sudert structural zone in the Buir depression. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2011, 31, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.L.; Liu, J.T.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, K.C. Tight reservoir characteristics and formation conditions of tuff in Santanghu Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2014, 25, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Aliou Mahamidou, M.H.; Koral, H. Sedimentology of the Paleogene Volcaniclastic Gravity Flow Deposit of the Ulukışla Formation, South Central Türkiye. Rud.-Geološko-Naft. Zb. 2024, 39, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, W.; Permana, H.; Ernowo; Swamidharma; Pinahalan, I.; Cahyadi, A.; Krisnanto, Y. An Update to the Geology of Sebuku Island, South Kalimantan, Indonesia: Constraints from Petrological Studies. Rud.-Geološko-Naft. Zb. 2024, 39, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.M.; Liu, H.N.; LU, Z.X.; Wang, P. Mechanism of water–rock interaction of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the middle part of western Sichuan depression. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.K.; Gong, L.; Schott, J.; Lu, P.; Chen, K.Y.; Yuan, H.L.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.A.; Apps, J.; Zhu, C. Coupled feldspar dissolution and secondary mineral precipitation in batch systems: 6. Labradorite dissolution, calcite growth, and clay precipitation at 60 °C and pH 8.2–8.4. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2025, 390, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Jin, J.; Wu, H.G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Selective dissolution of alkali feldspars and its effect on Lower Triassic sandy conglomerate reservoirs in the Junggar Basin, northwestern China. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.B.; Cao, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.I.; Eriksson, K.A. Role of CO2-water-rock interactions and implications for CO2 sequestration in Eocene deeply buried sandstones in the Bonan Sag, eastern Bohai Bay Basin, China. Chem. Geol. 2022, 541, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.C.; Yuan, G.H.; Wang, Y.Z.; Jiu, N.M.; Jin, Z.H.; Liu, K.Y.; Xi, K.L.; Wei, Y.H.; Sun, P.P. Successive formation of secondary pores via feldspar dissolution in deeply buried feldspar-rich clastic reservoirs in typical petroliferous basins and its petroleum geological significance. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1673–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonova, I.V.; Gorichev, I.G.; Godunov, E.B. Kinetics of Manganese Oxides Dissolution in Sulphuric Acid Solutions Containing Oxalic Acid. Engineering 2013, 05, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.X.; Kang, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Fu, B.; Wu, H.G. Thermochemical oxidation of methane induced by high-valence metal oxides in a sedimentary basin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Worden, R.H.; Fisher, Q.J. Diagenesis and reservoir quality of the Sherwood Sandstone (Triassic), Corrib field, Slyne basin, west of Ireland. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Zhu, F.; Tang, Q.S.; Gao, W.L. Fluid-rock interaction and its effects on the Upper Triassic tight sandstones in the Sichuan Basin, China: Insights from petrographic and geochemical study of carbonate cements. Sediment. Geol. 2019, 383, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Li, X.N.; Ma, Q.; Xiang, H.; Luo, Q.S.; Chen, X.; Bai, G.J.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Y.L. Geological features and exploration potential of permian Tiaohu formation tight oil, Santanghu Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.M.; Zhou, Q.M. Characterizations of pore, mineral and petrographic properties of marine shale using multiple techniques and their implications on gas storage capability for Sichuan Longmaxi gas shale field in China. Fuel 2018, 241, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, G.H.; Huang, Z.L.; Ou, G.X.; Li, T.J.; Guo, X.B. Tight tuff reservoir characteristics and its controlling factors: A comparative study of the Permian Tiaohu Formation and Carboniferous Haerjiawu Formation in the Santanghu Basin, NW China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 187, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, X.T.; Ding, L.; Li, X.P.; Zhou, F.J.; Jin, Z.H.; Yuan, G.H. Reservoir characteristics and differential evolution of low permeability tuffaceous sandstone in Wenchang Formation, Lufeng sag, Pearl River Mouth basin. China Offshore Oil Gas. 2023, 35, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.M.; Wei, Y.S.; Zhu, H.Q.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, S.Q.; Cheng, M.H. Pore structure characteristics and reservoir classification and evaluation of tight tuffaceous sandstone gas reservoir: Taking the tight tuffaceous sandstone of Yingcheng Formation in southern Songliao Basin as an example. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.H.; Yuan, G.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Cao, Y.C.; Ding, L.; Li, X.Y.; Bo, X.H. Differences of tuffaceous components dissolution and their impact on physical properties in sandstone reservoirs: A case study on Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Huizhou-Lufeng area, Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Han, D.L.; Ma, B.Y.; Zeng, X.Y.; Lin, Y.P. Diagenetic differentiation of tuffaceous interstitial materials in sandy conglomerate and their effect on reservoir properties. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 157, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Fan, T.L.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Chen, J.; Nie, W.B. Effect of tuffaceous components on physical property of sandstone reservoir. Acta Pet. Sin. 2010, 31, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.F.; Wen, C.J.; Li, Y.P.; Ren, Z.Y.; Xiao, D.S.; Feng, Y.Q. Characteristics and formation conditions of tight tuff reservoir of Tiaohu Formation in Malang Depression. Lithol. Reserv. 2017, 29, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.J.; Xie, X.A.; Frank, M.; Ren, Y.G.; Zhu, D.F.; Sun, X.M. The The Cretaceous Songliao Basin: Volcanogenic succession, sedimentary sequence and tectonic evolution, NE China. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2007, 81, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, R.F.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, L.S.; Xie, G.A.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.Y. Tectonic Evolution of Songliao Basin and the Prominent Tectonic Regime Transition in Eastern China. Geol. Rev. 2010, 56, 180–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, W.L. Exploration Prospect of Deep Gas in Jilin Oilfield. China Pet. Explor. 2003, 8, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.F.; Li, Z.C.; Guo, X.T.; Bai, L.H.; Li, Z.L. Characteristics and classification evaluation of tight gas reservoirs in the 1st member of Quantou Formation of Helong-Lanjia inversion zone in Dehui Fault Depression. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 31, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T 5163-2018; X-Ray Diffraction Analysis Method for Clay Minerals and Common Non-Clay Minerals in Sedimentary Rocks. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Machel, H.G. Cathodoluminescence in calcite and dolomite and its chemical interpretation. Geosci. Can. 1985, 12, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Habermann, D.; Neuser, R.D.; Richter, D.K. Low limit of Mn²+-activated cathodoluminescence of calcite: State of the art. Sediment. Geol. 1996, 101, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, D.K.; Götte, T.; Götze, J.; Neuser, R.D. Progress in application of cathodoluminescence (CL) in sedimentary petrology. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 79, 127–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, S.; Krinsley, D. Application of Cathodoluminescence Imaging to the Study of Sedimentary Rocks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.G.; Song, Y.G. Mineral Composition and Their Weathering Significance of Zhaosu Loess—Paleosol Sequence in the Ili Basin, Xinjiang. Geol. Rev. 2013, 59, 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.Z.; Zhao, Y.T.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.S. Geological Characteristics of Tuff Reservoir of Yingcheng Formation in Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2022, 52, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.J.; Huang, K.K.; Feng, W.L.; Tong, H.P.; Liu, L.H.; Zhang, X.H. Mass exchanges among feldspar, kaolinite and illite and their influences on secondary porosity formation in clasticdiagenesis: A case study on the Upper Paleozoic, Ordos basin and Xujiahe formation, western Sichuan depression. Geochimica 2009, 38, 498–506. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.R.; He, S.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Q.L. A study on abnormal transformation of smectite clay minerals—Taking Junggar Basin as an example. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2006, 13, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bas, M.J.; Le Maitre, R.W.; Streckeisen, A.; Zanettin, B. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram. J. Petrol. 1986, 27, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maitre, R.W. Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms: Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks; Appendices; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 36–225. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Peng, J.; Ge, H.; Ji, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Rock Fabric of Lacustrine Shale and Its Influence on Residual Oil Distribution in the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 7151–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Ge, H.; Shen, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, Z. Insight into Water Occurrence and Pore Size Distribution by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Marine Shale Reservoirs, Southern China. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, L. Effect of initial water saturation and water film on imbibition behavior in tight reservoirs using nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 056603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Meng, X.G.; Shen, Z.Z.; Yang, R.G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, F.L. Discovery and geochemical characteristics of Chang 7 source rocks from the eastern margin of a Triassic lacustrine basin in the Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 991–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, D.K. Micro-petrology, pore throat characteristics and genetic mechanism of tight oil reservoirs—A case from the 6th and 7th members of Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin. Oll Gas Geol. 2017, 38, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.T.; Cui, B.Q.; Huang, S.J.; Shan, Y.M. The theoreyical approach and the case application of the control of reservoir evaluation for the clastic reservoir means of clay minerals. J. Chengdu Coll. Geol. 1991, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.T.; Mu, W.W.; Yan, C.C. Influences of clay minerals on physical properties of Chang 6 tight sandstone reservoir in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2017, 28, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.X.; Yang, T.; Tian, J.C.; Yi, J.Z.; Ren, Q.Q. Advances in Studies of Development and Growth Mechanisms of Clay Minerals in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2023, 41, 1859–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Lei, H.Y.; Xian, B.Z.; Wang, J.; Luo, Z.J.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Niu, J.; Pu, Q.; Tian, R.H. Influence of Source Rock Properties on the Development of Authigenic Chlorite in Conglomerate Reservoirs and Its Significance for Oil and Gas Reservoirs: A case study from the Lower Urhe Formation in the Mahu Depression, Junggar Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2020, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Duan, D.P.; Liu, B.B.; Li, B.Y.; Ding, F.; Wang, W.; Lou, M. Origin Mechanism of Chlorite and Its Impact on Reservoir Properties in Huagang Formation, Xihu Depression. J. Jilin Univ. (Ear Sci. Ed.) 2021, 51, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Peng, G.R.; Ding, L.; Yuan, G.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.L.; Jin, Z.H. Physical simulation experiment of tuffaceous dissolution effect in sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Huizhou and Lufeng area, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2024, 46, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.F.; Cheng, R.H.; Zhao, X.Q.; Shun, F.X. Types and Succession of Pyroclastic Rocks Diagenesis in Lower Cretaceous of Wuerxun and Bei’er Depression in Hailaer Basin. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37, 851–859. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.H.; Shen, Y.J.; Yan, J.B.; Li, Q.F.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, F.; Xv, Z.J. Diagenesis of volcaniclastic rocks in Hailaer Basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q.; Yao, M.D.; Feng, Y.Q.; Fan, T.G. Influencing Factor Analysis of Devitrification Pore and Its Relationship with Hydrocarbon in Tiaohu Formation of Malang Depression. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2018, 25, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wei, P.S.; Shi, L.T.; Chen, G.P.; Peng, W.; Sun, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Xie, M.X.; Hong, L. Fluid interaction mechanism and diagenetic reformation of basement reservoirs in Beier Sag, Hailar Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.F.; Liang, C.; Cao, Y.C.; Han, Y. Types, genesis and significance of quartz in shales. J. Palaeogeogr. 2024, 26, 487–501. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, M.L.; Weber, J.N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1786–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, N.J. Attainment of isotopic equilibrium between ocean water and the benthonic foraminifera genus Uvigerina: Isotopic changes in the ocean during the last glacial. Environ. Sci. 1974, 219, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, I.; O’Neil, J.R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. In Data of Geochemistry, 6th ed.; Fleischer, M., Ed.; Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1977; pp. 440–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.H.; Wamg, C.W.; Li, Q.; Li, P.J. Densification mechanism and diagenesis fluid evolution of low-porosity and low-permeability tight sandstone reservoir: An example from Huagang formation in the northern of the central anticlinal zone in Xihu depression, East China Sea. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 972–981+1029. [Google Scholar]
- Veizer, J.; Hoefs, J. The nature of O18/O16 and C13/C12 secular trends in sedimentary carbonate rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1976, 40, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veizer, J.; Holser, W.T.; Wilgus, C.K. Correlation of 13C/12C and 34S/32S secular variations. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.E. Magmatic volatiles: Isotope variation of C, H, and S. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1986, 16, 185–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Syst ematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.Q.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.T.; Sui, S.L. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics and Palaeoenvironmental Implications of Lacustrine Carbonate Rocks from the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag. Earth Environ. 2009, 37, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.F. The Space-Time Relationship of Gold to Lead-Zinc Mineralization and Its Application. Miner. Depos. 2001, 20, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Ren, Y.S.; Du, G.F.; Wu, Z.J. Genesis of interlayer oxidation zone-type uranium deposit in the channel conglomerates, Beisantai area, Junggar Basin: An insight into uranium mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; He, Y.; Ding, T.P. Mantle fluids involved in metallogenesis of Jiaodong (East Shandong) gold district: Evidence of C, O and H isotopes. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xue, C.J.; Liu, S.W.; Wang, X.H. Research on the Paragenesis (Coexist) Relationship of Lead—Znic and Gold Mineralization in the Bafangshan—Baguamiao Deposit, Fengxian County, Southern Qinglin Mountains. Geol. Rev. 2007, 53, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.J.; Lv, Z.X.; Peng, M.; Xiao, L.; Li, X.; Liao, Z.Y.; Xv, B.; Qian, Y.X. Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of Permian Fengcheng Formation Tuff Reservoir in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin. Mineral. Petrol. 2023, 43, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Hu, K.; Jiang, X.Q.; Liu, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, H.Y. Effect of aid fluid on carbonate reservoir reconstruction. Geochimica 2009, 38, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.J.; Qiao, Z.F.; She, M.; Meng, S.X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Prediction of burial dissolved vugs in carbonates based on dissolution simulation; Acase study of the Longwangmiao Formation dolostone reservoirs, Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 690–701. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.H.; Cao, Y.C.; Qiu, L.W.; Chen, Z.H. Genetic mechanism of high-quality reservoirs in Permian tight fan delta conglomerates at the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China. AAPG Bull. 2017, 101, 1995–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshri, I.D. On the Reactivity of Carbonic and Organic Acids and Generation of Secondary Porosity; SEPM Specical Publication; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Claremore, OK, USA, 1986; Volume 28, pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wei, G.Q.; Tang, D.Z.; Wu, S.X.; Shao, X.J. The feature analysis and geological significance of organic fluid inclusions in the west Sichuan. Geoscience 2004, 03, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Q.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, H.L. Fluid inclusions analysis of the Ordovician reservoir in Tahe Oilfield. Acta Pet. Sin. 2005, 26, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Wang, K.Y.; Cai, W.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, Y.C. Fluid inclusion and H-O isotope study of the Jiguanshan porphyry Mo deposit, Xilamulun Metallogenic Belt: Implications for characteristics and evolution of ore-forming fluids. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Bao, Z.D.; Shen, Y.W.; Gao, Y.S.; Lin, Y.B.; Zhu, L.H.; Chen, X.H.; Ding, S.; Zhu, B.H.; Qi, Q.; et al. Diagenetic evolution and sources of main cements within palaeochannel sandstone reservoirs of the Jurassic Yan’an Formation in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2023, 25, 906–919. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.C.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, S.M.; Xi, K.L.; Xue, X.J. Diagenesis and Reserving Space Characteristics of Tight Oil Reservoirs of Per-mian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Sag of Junggar Basin, China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2019, 41, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.S.; Meng, Y.L.; Huan, J.L.; Dai, T.J.; Xiao, L.H.; Zhou, W. Quantitative evaluation of impact of authigenic chlorite on reservoir quality: A case study of the Member 3 of Weizhou Formation in Weixinan sag, Beibu Gulf Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2021, 23, 639–650. [Google Scholar]



| No. | Depth/m | Mineral Volume Fraction/% | Clay Minerals Mineral Mass Fraction/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | K-Feldspar | Plagioclase | Carbonate | Clay Mineral | Illite/Smectite Mixed Layer | Illite | Chlorite | |||
| A | 1 | 2203.66 | 47.3 | 2.4 | 34.7 | / | 15.6 | 59 | 26 | 15 |
| 2 | 2204.46 | 26.3 | 3.8 | 23.1 | / | 46.8 | 71 | 26 | 3 | |
| 3 | 2204.86 | 41.8 | 2.8 | 33.8 | 1.7 | 19.9 | 70 | 21 | 9 | |
| 4 | 2206.6 | 37.7 | 2.6 | 17.8 | 13.2 | 28.7 | 80 | 17 | 3 | |
| 5 | 2208.31 | 40.6 | 2.5 | 29.8 | 2.6 | 24.5 | 81 | 13 | 6 | |
| 6 | 3275.30 | 41.3 | 3.5 | 21.5 | 0.5 | 29.1 | 86 | 13 | 1 | |
| 7 | 3276.00 | 43.7 | 3.9 | 21.5 | 0.4 | 24.1 | 90 | 9 | 1 | |
| 8 | 3036.38 | 34.4 | 1.5 | 18.4 | 20.2 | 24.6 | 86 | 13 | 1 | |
| 9 | 2323.50 | 13.5 | 7.5 | 31.5 | 8.5 | 38.2 | 78 | 8 | 10 | |
| 10 | 2329.09 | 37.8 | 7.6 | 30.7 | 1.3 | 21.6 | 66 | 16 | 11 | |
| Average | 36.4 | 3.8 | 26.3 | 6.1 | 27.3 | 76.7 | 16.2 | 6.0 | ||
| B | 1 | 1435.46 | 44.7 | / | 9.3 | 1.2 | 42.9 | 97 | 1 | / |
| 2 | 1436.07 | 51.1 | / | 6.3 | 1.2 | 39.2 | 95 | 3 | / | |
| 3 | 1436.90 | 50.8 | / | 6.1 | 3.8 | 37.1 | 98 | 2 | / | |
| 4 | 1437.95 | 49.5 | / | 11.2 | 2.7 | 34.3 | 98 | 2 | / | |
| 5 | 1438.88 | 46.7 | / | 7.1 | 1.2 | 42.6 | 96 | 4 | / | |
| 6 | 1439.86 | 41.2 | / | 4.6 | 1.5 | 51.4 | 96 | 4 | / | |
| 7 | 1440.81 | 44.2 | / | 7.3 | 0.4 | 47.1 | 96 | 4 | / | |
| 8 | 1442.73 | 40.9 | / | 4.1 | 1.4 | 53.2 | 94 | 6 | / | |
| 9 | 1443.10 | 37.1 | / | 12.7 | 3 | 45.3 | 99 | 1 | / | |
| Average | 45.1 | / | 7.6 | 1.8 | 43.7 | 96.6 | 3.0 | / | ||
| No. | Depth/m | δ13CV-PDB (‰) | δ18OV-PDB (‰) | δ18OV-SMOW (‰) | T/°C | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3282.1 | −5.119 | −20.476 | 9.801 | 148.51 | 106.6 |
| 2 | 3282.1 | −4.737 | −20.614 | 9.659 | 149.68 | 107.3 |
| 3 | 3282.1 | −5.215 | −20.371 | 9.910 | 147.62 | 106.5 |
| 4 | 3282.1 | −5.479 | −19.042 | 11.280 | 136.56 | 106.6 |
| 5 | 3282.1 | −5.061 | −18.742 | 11.589 | 134.12 | 107.6 |
| 6 | 3282.1 | −7.022 | −17.216 | 13.162 | 121.95 | 104.3 |
| 7 | 3282.1 | −5.261 | −18.231 | 12.116 | 129.99 | 107.4 |
| 8 | 3230.6 | −6.404 | −19.657 | 10.646 | 141.64 | 104.4 |
| 9 | 3230.6 | −7.587 | −19.442 | 10.867 | 139.86 | 102.1 |
| 10 | 3230.6 | −5.698 | −19.82 | 10.478 | 142.99 | 105.8 |
| 11 | 3230.6 | −5.565 | −19.926 | 10.368 | 143.88 | 106.0 |
| 12 | 3283.7 | −4.407 | −20.268 | 10.016 | 146.75 | 108.2 |
| 13 | 3283.7 | −3.014 | −19.989 | 10.303 | 144.41 | 111.2 |
| 14 | 3283.7 | −3.171 | −19.873 | 10.423 | 143.44 | 110.9 |
| 15 | 3501.6 | −20.923 | −11.021 | 19.548 | 77.32 | 79.0 |
| 16 | 3502.0 | −20.748 | −11.235 | 19.328 | 78.73 | 79.2 |
| 17 | 3502.0 | −21.079 | −10.382 | 20.207 | 73.15 | 79.0 |
| 18 | 3506.5 | −19.570 | −5.700 | 25.034 | 45.12 | 84.4 |
| 19 | 3922.6 | −1.923 | −17.514 | 12.855 | 124.29 | 114.6 |
| 20 | 3922.6 | −3.311 | −16.668 | 13.727 | 117.69 | 112.2 |
| 21 | 3922.6 | −1.906 | −16.993 | 13.392 | 120.21 | 114.9 |
| 22 | 3926.7 | −2.538 | −18.818 | 11.511 | 134.73 | 112.7 |
| 23 | 3926.7 | −2.656 | −18.215 | 12.132 | 129.86 | 112.8 |
| 24 | 3930.0 | −4.978 | −20.673 | 9.598 | 150.19 | 106.8 |
| 25 | 3930.0 | −6.993 | −17.345 | 13.029 | 122.96 | 104.3 |
| 26 | 3930.0 | −5.387 | −19.775 | 10.524 | 142.62 | 106.4 |
| 27 | 3930.0 | −6.282 | −16.801 | 13.590 | 118.72 | 106.1 |
| 28 | 3932.0 | −4.361 | −19.912 | 10.383 | 143.76 | 108.5 |
| 29 | 3932.0 | −5.443 | −15.195 | 15.245 | 106.54 | 108.6 |
| 30 | 3932.0 | −5.286 | −15.339 | 15.097 | 107.61 | 108.8 |
| 31 | 3932.5 | −4.556 | −19.147 | 11.171 | 137.42 | 108.4 |
| 32 | 3932.5 | −5.016 | −16.785 | 13.606 | 118.59 | 108.7 |
| 33 | 3932.5 | −5.158 | −16.978 | 13.407 | 120.09 | 108.3 |
| 34 | 2205.0 | −20.605 | −4.985 | 25.771 | 41.22 | 82.6 |
| 35 | 2205.0 | −21.451 | −3.619 | 27.179 | 34.06 | 81.6 |
| 36 | 2205.0 | −20.178 | −4.556 | 26.213 | 38.93 | 83.7 |
| 37 | 2205.0 | −22.049 | −8.402 | 22.248 | 60.76 | 78.0 |
| 38 | 2205.0 | −18.325 | −1.825 | 29.029 | 25.23 | 88.9 |
| 39 | 2205.0 | −17.134 | −0.838 | 30.046 | 20.64 | 91.8 |
| 40 | 2206.5 | −9.939 | −18.938 | 11.387 | 135.71 | 97.5 |
| 41 | 2206.5 | −9.348 | −18.732 | 11.599 | 134.03 | 98.8 |
| 42 | 2206.5 | −9.346 | −19.038 | 11.284 | 136.53 | 98.7 |
| 43 | 1435.7 | −18.926 | −9.358 | 21.263 | 66.65 | 83.9 |
| 44 | 2481.1 | −25.076 | −9.885 | 20.720 | 69.97 | 71.0 |
| 45 | 2481.1 | −23.238 | −8.116 | 22.543 | 59.04 | 75.7 |
| 46 | 2481.1 | −26.596 | −10.271 | 20.322 | 72.44 | 67.7 |
| 47 | 3506.0 | −29.742 | −3.280 | 27.529 | 32.34 | 64.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Gao, J.; Xue, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, C. Diagenetic Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Middle to High-Porosity and Ultralow-Permeability Tuff Reservoirs in the Huoshiling Formation of the Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030319
Lin S, Guo X, Li L, Gao J, Xue S, Yang Y, Tang C. Diagenetic Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Middle to High-Porosity and Ultralow-Permeability Tuff Reservoirs in the Huoshiling Formation of the Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030319
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Siya, Xiaobo Guo, Lili Li, Jin Gao, Song Xue, Yizhuo Yang, and Chenjia Tang. 2025. "Diagenetic Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Middle to High-Porosity and Ultralow-Permeability Tuff Reservoirs in the Huoshiling Formation of the Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin" Minerals 15, no. 3: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030319
APA StyleLin, S., Guo, X., Li, L., Gao, J., Xue, S., Yang, Y., & Tang, C. (2025). Diagenetic Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Middle to High-Porosity and Ultralow-Permeability Tuff Reservoirs in the Huoshiling Formation of the Dehui Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Minerals, 15(3), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030319