Source and Precipitation Process of Gold in the Linglong Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from Trace Elements of Pyrite and S-Pb Isotopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
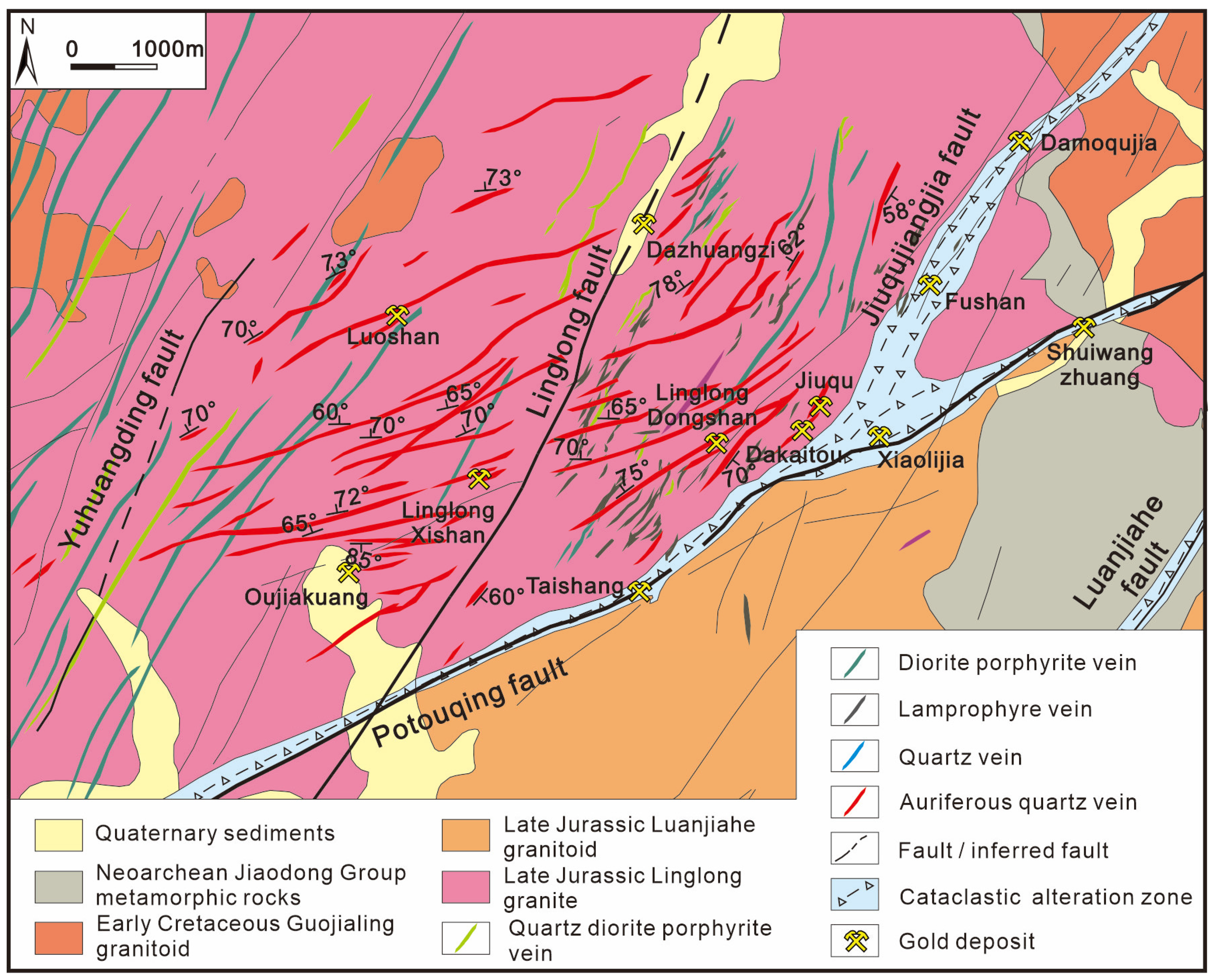
2. Regional Geology

3. Deposit Geology
4. Samples and Analytical Methods
4.1. LA-ICP-MS Analysis of Trace Elements in Pyrite
4.2. LA-MC-ICP-MS Analysis of Sulfur Isotopes in Pyrite
4.3. LA-MC-ICP-MS Analysis of Galena Pb Isotopes
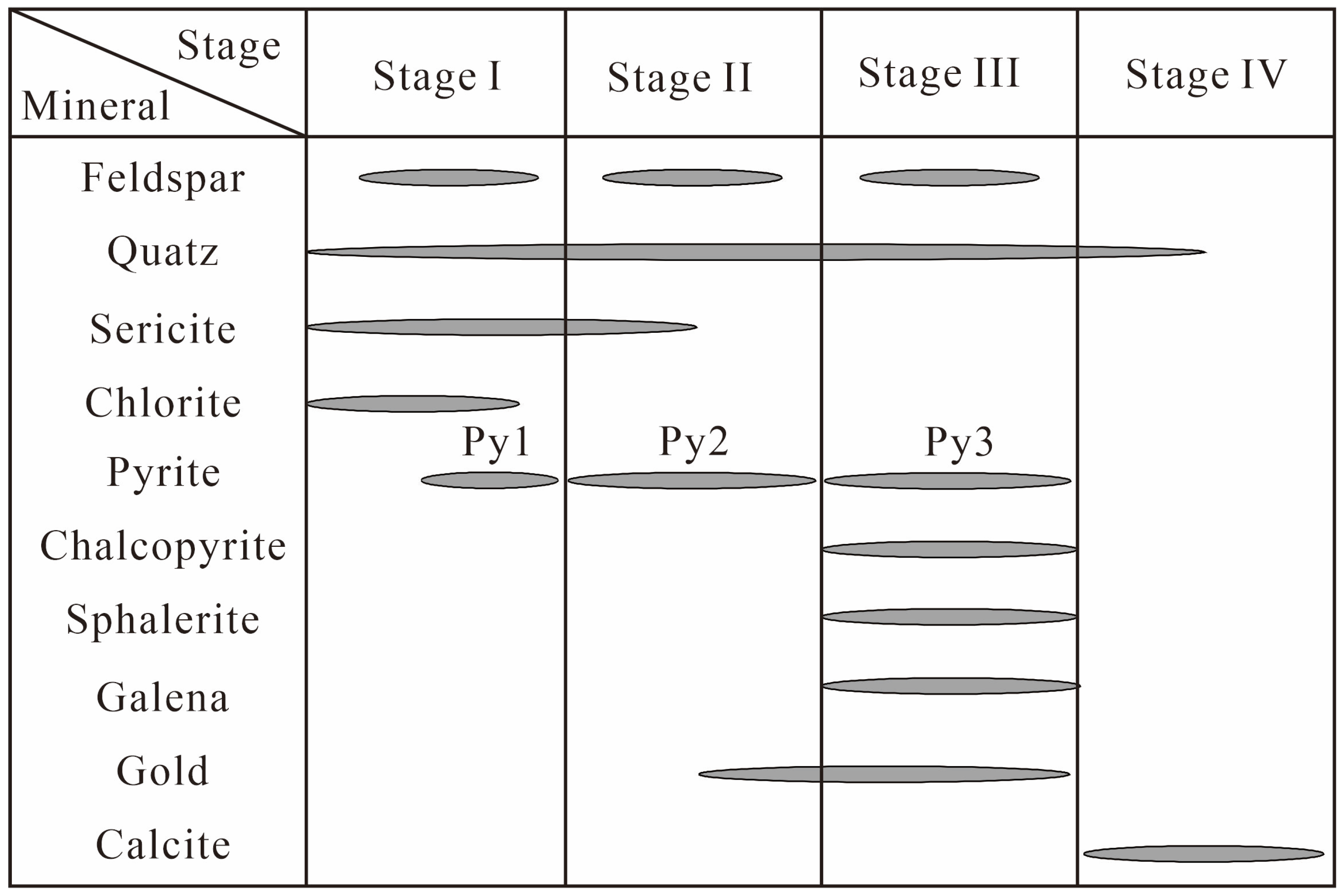
5. Results
5.1. Trace Element Characteristics of Pyrite
5.2. Sulfur Isotope Characteristics
5.3. Lead Isotope Characteristics
6. Discussion
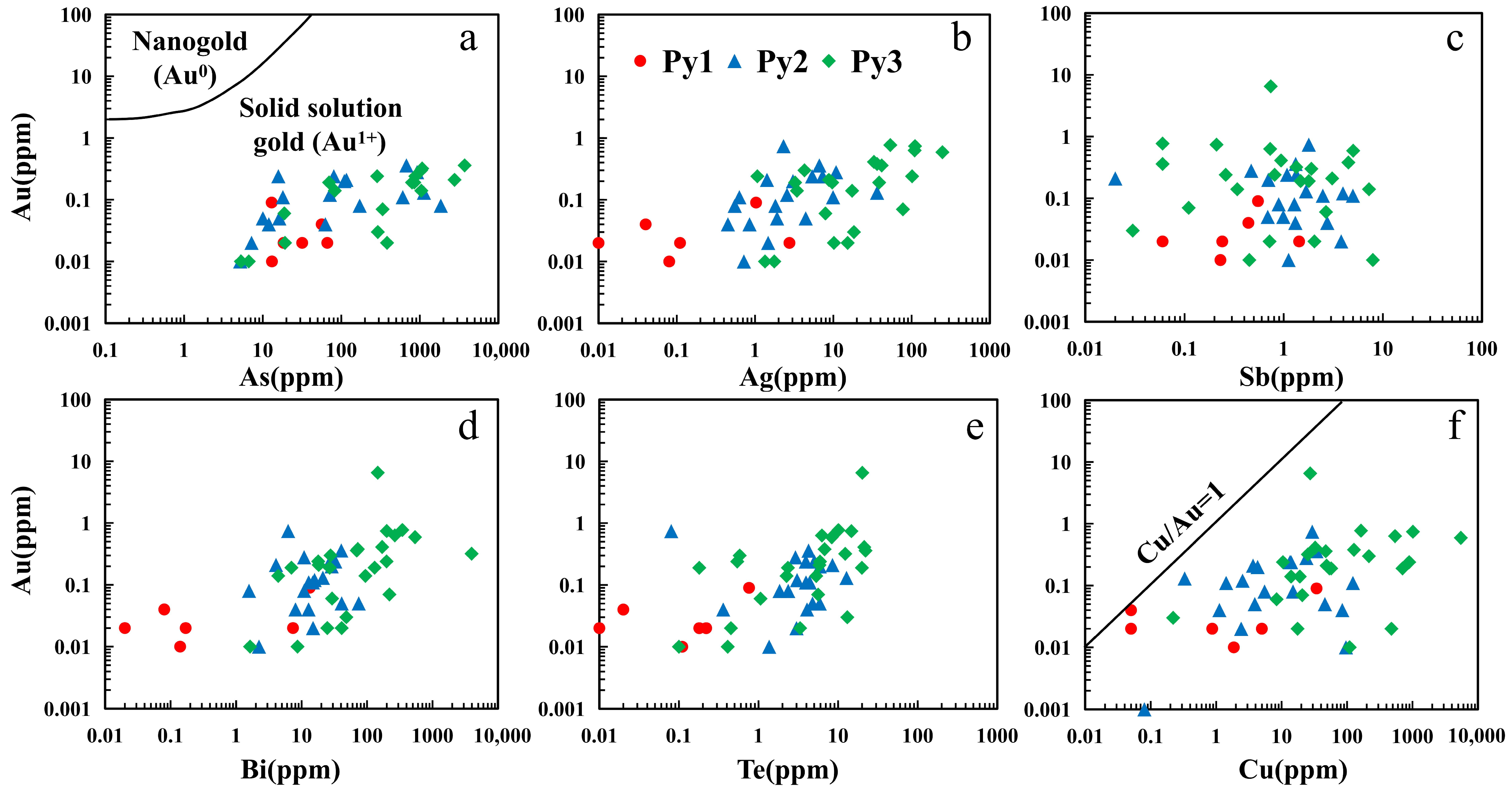
6.1. Occurrence State of Trace Elements in Pyrite
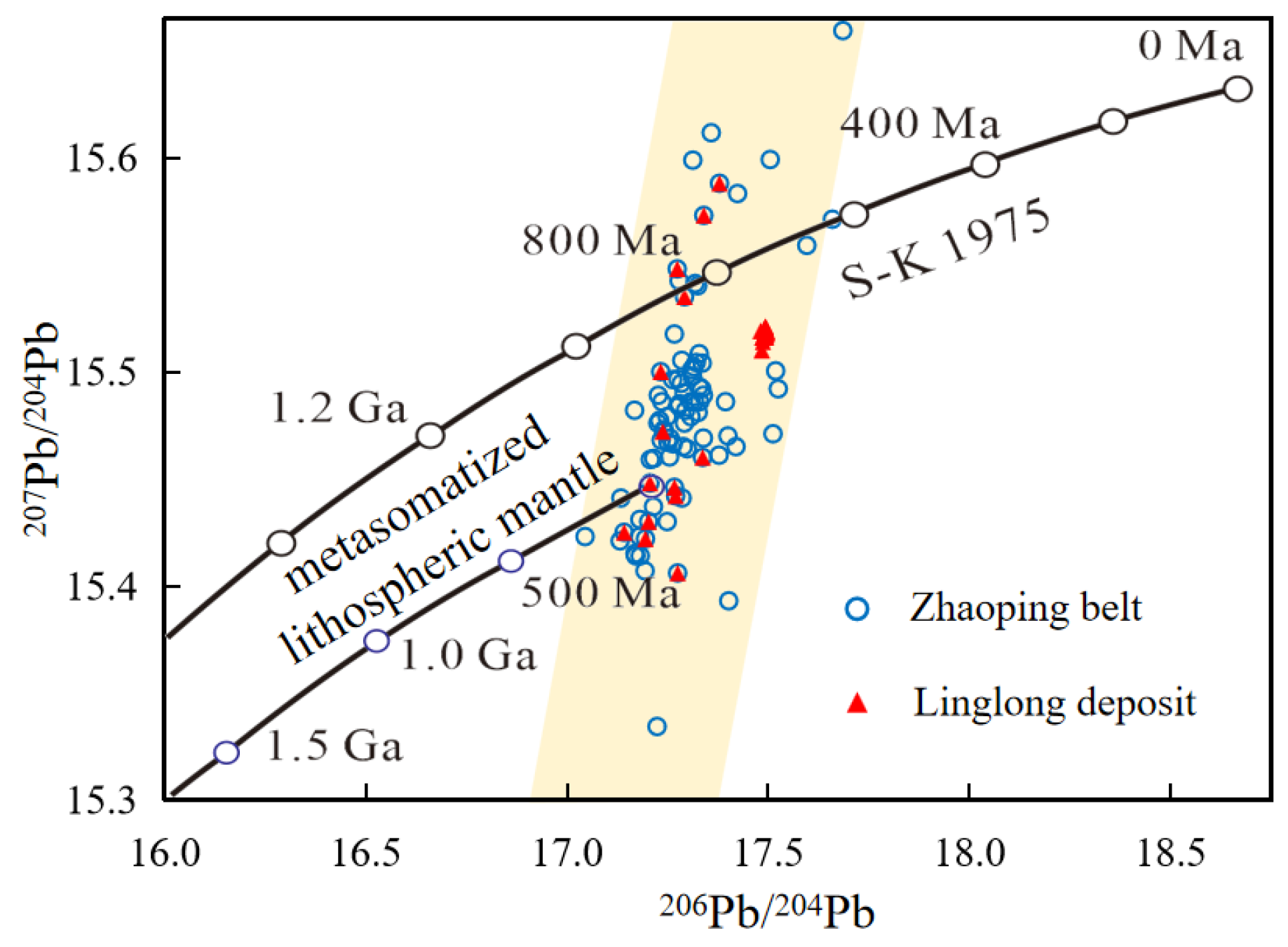
6.2. Sources of Ore-Forming Materials
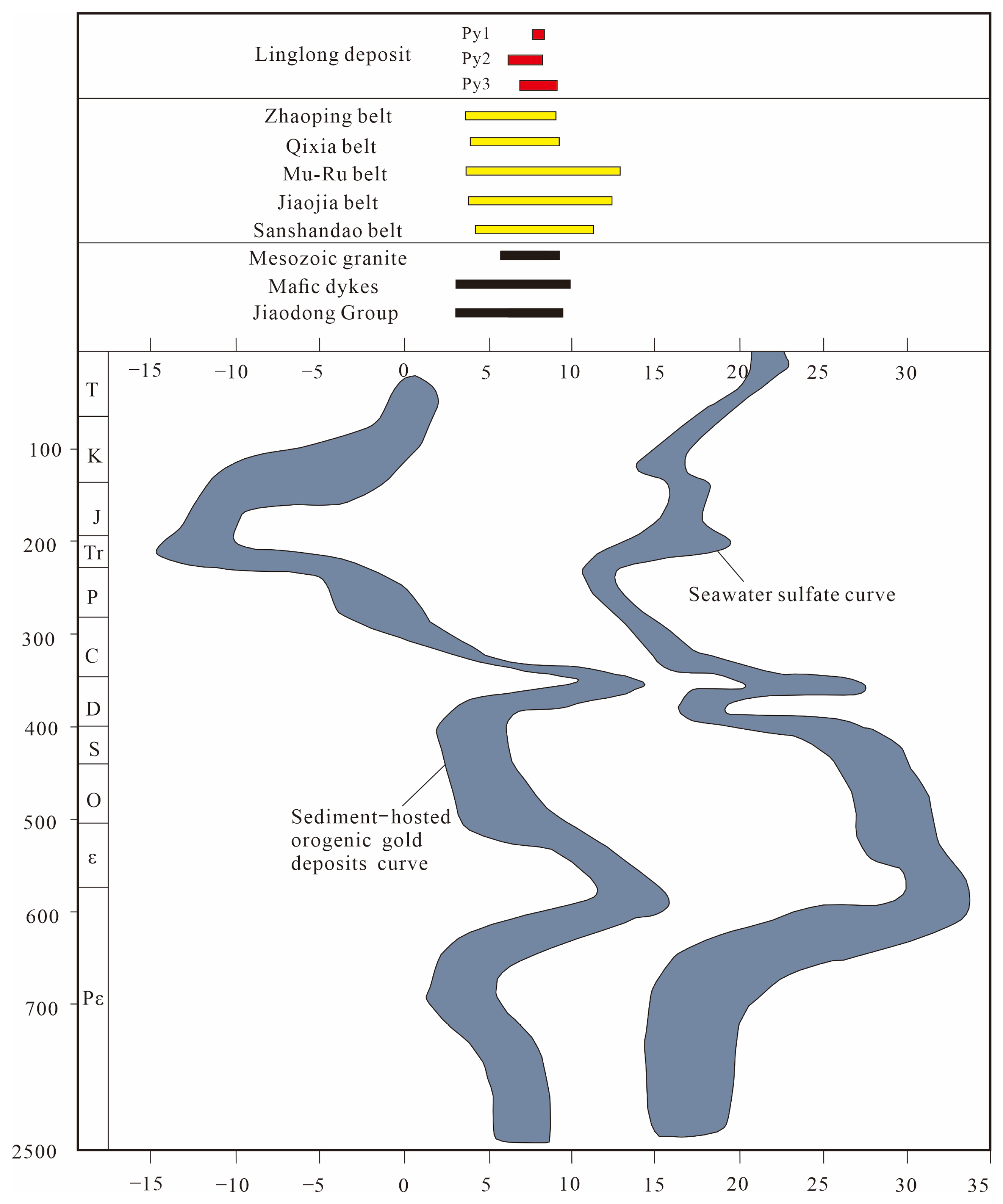
6.3. Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids and Mechanism of Gold Precipitation
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- Trace elements in pyrite show systematic variations across mineralization stages (Py1 → Py3), marked by decreasing Co and Ni and increasing Au, As, Cu, Pb, Zn, Bi, and Te. These trends reflect the continuous evolution of the ore-forming fluids. The early stage (Py1) involved high-temperature, reduced fluids dominated by mantle sources, representing a phase of gold pre-enrichment. During the main ore-forming stages (Py2–Py3), fluid temperature decreased, incorporation of crustal material increased, and water–rock reactions intensified. Gold precipitation was governed by two principal mechanisms: in Py2, Au+ coupled with As3+ and entered the pyrite lattice as a solid solution; in Py3, fluid immiscibility broke down gold complexes, while Bi–Te melts or complexes promoted further gold enrichment and the formation of visible gold.
- (2)
- The S isotope characteristics indicate that sulfur is mainly derived from fluids released by dehydration of the Paleo-Pacific Plate during subduction, and these fluids have metasomatized the overlying lithospheric mantle. The Pb isotope characteristics reflect the ore-forming fluid mixed with crust-derived materials during its ascent. The S-Pb isotope system jointly constrains that the ore-forming materials are mainly derived from the metasomatized lithospheric mantle, with the involvement of crustal materials.
- (3)
- The ore-forming fluid underwent a continuous evolutionary process from early high-temperature, mantle-derived dominance to late low-temperature, crustal-derived mixing. The Py1 stage was dominated by mantle-derived magmatic fluids that were not contaminated by crustal materials. The Py2 stage was accompanied by the incorporation of crustal materials and an increase in As content, triggering the coupled substitution of “As3+ + Au+ → Fe2+” and dissolution–reprecipitation, which promoted the initial activation and enrichment of gold. In the Py3 stage, dissolution–reprecipitation occurred in a low-temperature, open environment, forming fractures and porous structures that facilitated the supernormal enrichment of elements, representing the main mechanism for gold precipitation. Local bismuth–tellurium melt also contributed to gold precipitation.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Santosh, M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique? Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Goldfarb, R.; Yang, L.Q.; Zi, J.W.; Geng, J.Z.; Ma, Y. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Deng, J.; Sai, S.X.; Yu, H.C.; Tamer, M.T.; Ding, Z.J.; Yu, X.F.; Goldfarb, R. Low-temperature thermochronology for defining the tectonic controls on heterogeneous gold endowment across the Jiaodong peninsula, eastern China. Tectonics 2023, 42, e2022TC007669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Bagas, L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Lu, Y. Cretaceous–Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U–Pb, illite K–Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Sun, W. The big mantle wedge and decratonic gold deposits. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wei, B.; Tan, W.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q. The distribution, characteristics and fluid sources of lode gold deposits: An overview. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.G.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny of the North China Craton: Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth. Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, L.; Xue, S.C.; Liu, X.F.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.Q.; Qiu, K.F.; Liang, Y.Y. Metallogenetic model of Jiaodong-type gold deposits, eastern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 2287–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Guo, L.N.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, X.Z.; Li, J.L. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Baker, T.; Dubé, B.; Groves, D.I.; Gosselin, P. Distribution, Character, and Genesis of Gold Deposits in Metamorphic Terranes; One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, Y. Intrusion-related gold deposits of North China Craton, People’s Republic of China. Resour. Geol. 2004, 54, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Pan, R.G. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C–D–O–S–Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Romer, R.L.; Long, Z.Y.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Yu, H.C.; Turner, S.; Wang, Q.F.; Li, S.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Duan, H.R. The role of an oxidized lithospheric mantle in gold mobilization. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Chao, L.; Qing, L.; Wen, Y.M.; Quan, Z.J.; Rong, L.S.; Santosh, M.; Feng, S.J.; Feng, Z.H. Indicators of decratonic gold mineralization in the North China Craton. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.W.; Ye, H.S.; Tang, X.W.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, H.S. Textural, trace element, and sulfur isotope analyses of pyrite from the Yindongpo deposit, East Qinling Orogen: Implications for gold mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 163, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Jiao, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.R.; Zhou, M.F. Constraints of in-situ S-isotopic compositions of pyrite on the genesis of the Bayinqinggeli sandstone-hosted uranium deposit, Ordos Basin, Northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 161, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.J.; Yang, L.Q.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, S.R.; Ren, F.; Dai, Z.H.; Li, D.P.; Shan, W.; Li, Z.S.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Geology, mineralogy and pyrite trace elements constraints on gold mineralization mechanism at the giant Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hollings, P.; Cai, Y.C. Pyrite textures and compositions from the Zhuangzi Au deposit, southeastern North China Craton: Implication for ore-forming processes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2018, 173, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.T.; Sun, L.; Hu, X.K.; Sheng, Y.M.; Zeng, T. Origin and evolution of a porphyry-breccia system: Evidence from zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, in situ sulfur isotope and trace elements of the Qiyugou deposit, China. Gondwana Res. 2021, 89, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Zang, C.J.; Li, L.; Li, S.R.; Tao, W.; Cheng, X. Geochemistry, isotopes, and morphology of coarse-grained pyrite from the Jinqingding gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Implications for episodic ore-forming fluid evolution. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 184, 106742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yan, Z.Q.; Zhao, S.S.; Lu, C.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. Metallogenic mechanism of Ankou gold deposit in the Qixia-Penglai Gold Belt, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from sericite Ar-Ar geochronology, H-O isotope, and in-situ trace element of pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 178, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.M.; Liang, Y.Y.; Shu, L.; Xue, W.H.; Zhang, C.X.; Shen, C.H.; He, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Fang, Y.Y. Genesis of the Jiuqu gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constraints on the texture, mineral geochemistry, and sulfur isotope of pyrite. Acta Geochim. 2024, 44, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.Y.; Xia, R.; Shu, L.; He, B.; Xue, W.H.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Xue, S.M. Geochemistry of pyrite from the Jiaojia gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, north China craton: Implications for source of ore-forming fluids and gold precipitation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, H.M.; Pirajno, F.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, R.T. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D–O–C–S isotope systematics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 33, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor-Ming, J.; Yi, L.D.; Sheng, W.Y.; Biao, S.; Shan, W.J. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry. Am. J. Sci. 2008, 308, 232–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Romer, R.L.; Long, Z.Y.; Yu, H.C.; Turner, S.; Wan, R.Q.; Li, X.Q.; Gao, Z.Y.; Deng, J. Potassium isotopes as a tracer of hydrothermal alteration in ore systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 368, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Gong, B.; Zha, X.P.; Liu, X.M. Zircon U–Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong terrane in the Sulu orogen, China. Precambrian Res. 2007, 161, 389–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.C.; Deng, J.; Yu, H.C.; Qiang, F.; Cui, T.; Wei, S.; Sheng, L.Z.; Li, S.S. Gold occurrence and its indicative significanceto mineralization process in Linglong gold district, Jiaodong gold province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 377–392. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Groves, D.I. Orogenic gold: Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. LITHOS 2015, 233, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.S.; Groves, D.I.; Weng, W.J.; Xue, S.C.; Li, H.J.; Dong, C.Y.; Yang, L.Q.; Li, D.P.; et al. Towards a universal model for orogenic gold systems: A perspective based on Chinese examples with geodynamic, temporal, and deposit-scale structural and geochemical diversity. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 224, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Zhao, H.S.; Yang, L.; Groves, D.I.; Han, J.L.; Qiu, K.F.; Li, D.P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, R.; Deng, J. Formation of the giant Cretaceous Jiaodong-type orogenic gold province of the North China Craton: A consequence of lithospheric multi-layer reworking. Geosci. Front. 2025, 167, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.N.; Song, M.C.; Zheng, X.L. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2447–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Weinberg, R.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Sai, S.X.; Matchan, E.; Phillips, D.; Kohn, B.P.; Miggins, D.P.; Liu, Y. Mesozoic Orogenic Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A Focused Event at 120 +/− 2 Ma During Cooling of Pregold Granite Intrusions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 415–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Hofmann, A.W.; Dai, B.Z.; Hou, M.L.; Zhao, K.D.; Chen, L.H.; Li, J.W.; Jiang, Y.H. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 124, 250–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Q.F.; Deng, J.; Santosh, M.; Liu, X.F.; Liang, Y.Y.; Cheng, H.Y. Characterizing episodic orogenesis and magmatism in eastern China based on detrital zircon from the Jiaolai Basin. Am. J. Sci. 2019, 319, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.K.; Li, Y.F.; Geng, K.; Zhuo, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liang, T.T. Study on the Orogenic Type Gold Deposits in Eastern Shandong Province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2011, 35, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Ling, H.F.; Zhao, K.D. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, east China: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Geol. Mag. 2007, 144, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.H.; Zheng, J.P.; Yu, C.M.; Ping, X.Q.; Ren, H.W. Multistage crust–mantle interactions during the destruction of the North China Craton: Age and composition of the Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Jiaodong Peninsula. LITHOS 2014, 190–191, 52–70. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, N.; Augier, R.; Gumiaux, C.; Monié, P.; Chen, Y.; Faure, M.; Zhu, R. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia). Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Dilek, Y.; Liang, Y.Y. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking—Lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2017, 129, 1379–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B.F.; Wang, Z.L. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steefel, C.; Lichtner, P. Multicomponent reactive transport in discrete fractures: II: Infiltration of hyperalkaline groundwater at Maqarin, Jordan, a natural analogue site. J. Hydrol. 1998, 209, 200–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, S.; Hu, S.H. In situ sulfur isotopes (δ34S and δ33S) analyses in sulfides and elemental sulfur using high sensitivity cones combined with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 911, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belousov, I.; Large, R.R.; Meffre, S.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Steadman, J.; Beardsmore, T. Pyrite compositions from VHMS and orogenic Au deposits in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Implications for gold and copper exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 79, 474–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voute, F.; Hagemann, S.; Evans, N.; Villanes, C. Sulfur isotopes, trace element, and textural analyses of pyrite, arsenopyrite and base metal sulfides associated with gold mineralization in the Pataz-Parcoy district, Peru: Implication for paragenesis, fluid source, and gold deposition mechanisms. Miner. Depos. 2019, 54, 1077–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.R.; Bull, S.W.; Maslennikov, V.V. A Carbonaceous Sedimentary Source-Rock Model for Carlin-Type and Orogenic Gold Deposits. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Walshe, J.; Ewing, R.C. The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 644–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Palenik, C.S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Ewing, R.C. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.C.; Spry, P.G.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Sakellaris, G.-A.; Bristol, S.K.; Melfos, V.; Fornadel, A.P. Bismuthinite derivatives, lillianite homologues, and bismuth sulfotellurides as indicators of gold mineralization in the Stanos shear-zone related deposit, Chalkidiki, northern Greece. Can. Mineral. 2013, 51, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooth, B.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Green, L.; O’Neill, B.; Brugger, J. Bi-melt formation and gold scavenging from hydrothermal fluids: An experimental study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5423–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Wu, Z.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Xu, Z.T.; Liang, Y.Y. Geological characteristics and genesis of Linglong Gold Deposit in Jiaodong. GOLD 2024, 45, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Found. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L. Detecting magmatic-derived fluids using pyrite chemistry: Example of the Chibougamau area, Abitibi Subprovince, Québec. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Guo, L.N.; Li, R.H.; Groves, D.I.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.L.; Zhao, H. Relationships Between Gold and Pyrite at the Xincheng Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for Gold Source and Deposition in a Brittle Epizonal Environment. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Deng, J.; Laflamme, C.; Long, Z.Y.; Wan, R.Q.; Moynier, F.; Yu, H.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Goldfarb, R. Giant Mesozoic gold ores derived from subducted oceanic slab and overlying sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 343, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Santosh, M.; Liu, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, R.; Yang, L. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere: A new model for the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, D.I.; Santosh, M. The giant Jiaodong gold province: The key to a unified model for orogenic gold deposits? Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.-Q.; Groves, D.I.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, K.-F.; Wang, Q.-F. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.D.; Feng, J.Q.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.D. Hydrothermal alteration of the Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 32, 2433–2450. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.Y.; Qiu, K.F.; Simon, A.C.; Pokrovski, G.S.; Yu, H.C.; Connolly, J.A.; Li, S.S.; Turner, S.; Wang, Q.F.; Yang, M.F. Mantle oxidation by sulfur drives the formation of giant gold deposits in subduction zones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2404731121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Qiu, K.F.; Yin, R.; Long, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.C.; Yu, H.C.; Gao, Z.Y.; Deng, J. Lithospheric mantle as a metal storage reservoir for orogenic gold deposits in active continental margins: Evidence from Hg isotopes. Geology 2024, 52, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes in Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.; Finch, A.A.; Boyce, A.J. The sulfur isotope evolution of magmatic-hydrothermal fluids: Insights into ore-forming processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 288, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.; Kontak, D.; Lafrance, B.; Petrus, J.; Sharpe, R.; Fayek, M. Evaluating geochemical discriminants in Archean gold deposits: A Superior province perspective with an emphasis on the Abitibi greenstone belt. Econ. Geol. 2023, 118, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.G.; Wang, H.; Fan, H.R.; Ulrich, T.; Hu, H.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Shu, L. Gold endowment and unloading along pathway for giant gold mineralization: Insights from spatiotemporal variations of in-situ pyrite geochemistry and gold fineness from the Jiaodong gold deposits, north China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2023, 118, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Shu, L.; Ma, P.Y.; Zhang, C.X.; Ma, Y.; Khan, M.; Shen, C.H. Gold source and ore-forming process of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Evidence from textures, mineral chemical compositions and sulfur isotopes of pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 159, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Ding, Z.J.; Bo, J.W.; Ji, P.; Li, T.; Xin, W. In Situ Trace Element and S-Pb Isotope Study of Pyrite from the Denggezhuang Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Peninsula—Insights into the Occurrence of Gold and the Source of Ore-Forming Materials. Minerals 2024, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labidi, J.; Cartigny, P.; Moreira, M. Non-chondritic sulphur isotope composition of the terrestrial mantle. Nature 2013, 501, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.E.; Tomkins, A.G.; Weinberg, R.F.; Fan, H.-R. Implications of pyrite geochemistry for gold mineralisation and remobilisation in the Jiaodong gold district, northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Li, H.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, R.T. The relationship between mantle-derived fluid and gold ore-formation in the Eastern Shandong Peninsula: Evidences from D–O–C–S isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. 2005, 79, 839–857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, X.F.; Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, S.R. In Situ Trace Elements and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite from Jinchiling Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Region: Implications for Ore Genesis. Earth Sci. 2019, 45, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.Z.; Li, Z.K.; Zhao, X.F.; Sun, H.S.; Qiu, H.N.; Li, J.W. New constraints on the genesis of the giant Dayingezhuang gold (silver) deposit in the Jiaodong district, North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.L.; Li, S.R.; Pang, Z.S.; Tao, W.; Sun, W.Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Ore-forming fluids, sources of materials in the Denggezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Penisula and implications for ore genesis. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 1453–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Li, S.R.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhou, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, N. Thermoelectric character of pyrite from Jinqingding glod deposit in eastern Shandong Province and its significance. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.F. Mineralization Characteristics of Gold Deposit in the Guocheng Region, Haiyang, Shandong Province. Geol. Explor. 2010, 46, 462–469. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Liu, S.A.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.T.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, B.X. Zircon geochronology, geochemistry and stable isotopes of the Wang’ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z. Characteristics of the Ore-Forming Fluid and Thermodynamic Simulation of Water-Rock Interaction at the Sanshandao Gold Deposit, Shandong Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.Y. Tectonic Setting, Magmatie Sequence and Fluid of GoldMetallogenic System of the Sanshandao-Cangshang Fault in Jiaodong, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Liu, X.; Shangguan, Y.N.; Cai, Y.C.; Jiang, P. Involvement of anomalously As-Au-rich fluids in the mineralization of the Heilan’gou gold deposit, Jiaodong, China: Evidence from trace element mapping and in-situ sulfur isotope composition. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F. Invisible Gold in Arsenian Pyrite from the High-Grade Daliuhang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong, China: Insights from LA-ICPMS Mappings. In Proceedings of the Twenty-ninth Annual Goldschmidt Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 August 2019; p. 971. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Sun, F.Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, Z.J.; Huang, W.P.; Hu, W.H. Geological characteristics and genesis of Majiayao gold deposit, Qixia City, Shandong Province. Gold 2013, 34, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.D.; Feng, J.Q.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.D. Characteristics of sulfur isotope geochemistryof the Xincheng gold deposit, Northwest Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Y. Sulfur Isotope Studies on the Metallogenic Series of Gold Deposits in the Jiaodong (Eastern Shandong) Area. Miner. Depos. 1994, 13, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zartman, R.; Doe, B. Plumbotectonics—The model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; McNaughton, N.; Groves, D.; Luo, Z.; Huang, J.; Miao, L.; Liu, Y. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the Northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U–Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geol. Rev. 1998, 13, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, J.S.; Kramers, J. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F. The typomorphic characteristics of main metallic minerals in the Luoshan gold deposit, Shandong Province. J. Guilin Inst. Metall. Geol. 1993, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Fan, B.H. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of the Majiayao Gold Deposit, Shandong Province. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 1990, 6, 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.W. A discussion on the Jiaodong Group strata, the source-bed of gold and the strata-bound features of gold ore deposits in northwest part of Jiaodong peninsula. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 1986, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.S.; Zhang, L.G.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, B.C.; Xu, J.F.; Zheng, W.S. A study on lead isotope geochemical backgrounds of geological bodies in Jiaodong region. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 1994, 10, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ling, H.F. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shangdong province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Wei, J.H.; Audétat, A.; Pettke, T. Source of metals in the Guocheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton: Link to early Cretaceous mafic magmatism originating from Paleoproterozoic metasomatized lithospheric mantle. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Li, J.W.; Cooke, D.R.; Danyushevsky, L.; Zhang, L.J.; O’Brien, H.; Lahaye, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, H.J. Textures, trace elements, and Pb isotopes of sulfides from the Haopinggou vein deposit, southern North China Craton: Implications for discrete Au and Ag–Pb–Zn mineralization. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 171, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Li, J.W.; Evans, K.; Koenig, A.E.; Li, Z.K.; O’Brien, H.; Lahaye, Y.; Rempel, K.; Hu, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.P. Ore-forming processes of the Daqiao epizonal orogenic gold deposit, West Qinling orogen, China: Constraints from textures, trace elements, and sulfur isotopes of pyrite and marcasite, and Raman spectroscopy of carbonaceous material. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1093–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricio-Silva, W.; Schutesky, M.E.; Frimmel, H.E.; Fougerouse, D.; Rosière, C.A.; Caxito, F.A.; Bosco-Santos, A. Is there a specific “timing of mineralization” in gold deposits? Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 182, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Fougerouse, D.; Evans, K.; Reddy, S.M.; Saxey, D.W.; Guagliardo, P.; Li, J.W. Gold, arsenic, and copper zoning in pyrite: A record of fluid chemistry and growth kinetics. Geology 2019, 47, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koglin, N.; Frimmel, H.E.; Minter, W.E.L.; Brätz, H. Reply to Reimer and Mossman. Comment on “Trace-element characteristics of different pyrite types in Mesoarchaean to Palaeoproterozoic placer deposits” by Koglin et al. (Mineralium Deposita 42: 259–280, 2010). Miner. Depos. 2011, 46, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Xu, X.-W.; Gao, J.; Peters, S.G.; Li, J.; Cao, M.; Xiang, P.; Wu, C.; You, J. Element migration of pyrites during ductile deformation of the Yuleken porphyry Cu deposit (NW-China). Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 100, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.; Haase, K.M.; Chivas, A.R.; Klemd, R. Phase separation and fluid mixing revealed by trace element signatures in pyrite from porphyry systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 329, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.D.; Large, R.R.; Halpin, J.A.; Baturina, E.L.; Lyons, T.W.; Wu, S.; Danyushevsky, L.; Sack, P.J.; Chappaz, A.; Maslennikov, V.V.; et al. Trace Element Content of Sedimentary Pyrite in Black Shales. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1389–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.T.; Li, J.J.; Shi, G.Y.; Wang, C.G.; Man, R.H. Genetic Mineralogy and Geological Significance of Pyritesfrom the Muping-Rushan gold belt, Jiaodong Peninsula. Geoscience 2025, 39, 667–680. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, N.J.; Han, Z.Z.; Shan, W.; Sun, Y.Q.; Xiong, Y.X.; Shu, L.; Liu, C.E.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.S. Typomorphic Characteristics of Gold-bearing Pyrite in Jiaojia Fault DeepZone of Northwest Jiaodong Peninsula and Its Geological Significance. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 949–962. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, W.F.; Sun, S.-S. The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.L.; Hickey, K.A.; Cline, J.S.; Dipple, G.M.; Kilburn, M.R.; Vaughan, J.R.; Longo, A.A. Uncloaking invisible gold: Use of nanoSIMS to evaluate gold, trace elements, and sulfur isotopes in pyrite from Carlin-type gold deposits. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, M.; Alfredsson, M.; Brodholt, J.; Wright, K.; Catlow, C.R.A. Arsenic incorporation into FeS2 pyrite and its influence on dissolution: A DFT study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.C.; Kontak, D.J.; Lafrance, B. Gold remobilization: Insights from gold deposits in the Archean Swayze greenstone belt, Abitibi subprovince, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougerouse, D.; Micklethwaite, S.; Ulrich, S.; Miller, J.; Godel, B.; Adams, D.T.; McCuaig, T.C. Evidence for two stages of mineralization in West Africa’s largest gold deposit: Obuasi, Ghana. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A. Mineral replacement reactions. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2009, 70, 87–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y. Electron back-scattered diffraction and LA-ICP-MS analysis of pyrite from the Dahu lodegold deposit, southern North China craton: Insights into geochemistry and distribution of trace element connection to microstructure of pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.C.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, D.Z.; Sha, W.J.; Li, S. Forming conditions of tellurides and their constraints on gold enrichment in Linglong gold district, Jiaodong gold province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 63–77. [Google Scholar]




| Sample | Analyzed Minerals (Stage) | δ34S (‰, VCDT) | 2σ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 19LL17-1 | Pyrite (Py1) | +7.80 | 0.10 |
| 19LL17-2 | Pyrite (Py1) | +7.75 | 0.09 |
| 19LL17-3 | Pyrite (Py1) | +8.10 | 0.14 |
| 19LL17-4 | Pyrite (Py1) | +8.25 | 0.08 |
| 19LL37-1 | Pyrite (Py1) | +7.70 | 0.11 |
| 19LL37-2 | Pyrite (Py1) | +7.60 | 0.10 |
| D007B1-1 | Pyrite (Py2) | +8.15 | 0.13 |
| D007B1-2 | Pyrite (Py2) | +7.90 | 0.09 |
| D007B1-3 | Pyrite (Py2) | +8.05 | 0.08 |
| D007B4-1 | Pyrite (Py2) | +7.25 | 0.14 |
| D007B4-2 | Pyrite (Py2) | +7.55 | 0.10 |
| D007B4-3 | Pyrite (Py2) | +6.40 | 0.07 |
| D012B1-1 | Pyrite (Py2) | +6.15 | 0.11 |
| D012B1-2 | Pyrite (Py2) | +6.70 | 0.09 |
| 670-B1-3-1 | Pyrite (Py3) | +8.21 | 0.10 |
| 670-B1-3-2 | Pyrite (Py3) | +7.64 | 0.09 |
| 670-B1-3-3 | Pyrite (Py3) | +7.37 | 0.14 |
| 670-B3-1 | Pyrite (Py3) | +6.90 | 0.08 |
| 670-B3-2 | Pyrite (Py3) | +8.40 | 0.11 |
| 670-B3-3 | Pyrite (Py3) | +7.88 | 0.09 |
| 670-B3-4 | Pyrite (Py3) | +8.10 | 0.10 |
| 670-B3-5 | Pyrite (Py3) | +7.90 | 0.27 |
| 670-B4-1 | Pyrite (Py3) | +7.30 | 0.08 |
| 670-B4-2 | Pyrite (Py3) | +9.10 | 0.09 |
| Sample | Analyzed Minerals | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | TCDT/Ma | μ | ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 670-B1-3-1 | Galena | 17.491 | 15.518 | 38.075 | 729 | 8.440 | 34.710 |
| 670-B1-3-2 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.518 | 38.078 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.720 |
| 670-B1-3-3 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.517 | 38.083 | 726 | 8.450 | 34.740 |
| 670-B1-3-4 | Galena | 17.492 | 15.516 | 38.080 | 726 | 8.440 | 34.730 |
| 670-B1-3-5 | Galena | 17.493 | 15.521 | 38.085 | 731 | 8.440 | 34.750 |
| 670-B1-3-6 | Galena | 17.492 | 15.518 | 38.083 | 728 | 8.440 | 34.740 |
| 670-B2-1-1 | Galena | 17.487 | 15.516 | 38.062 | 729 | 8.440 | 34.660 |
| 670-B2-1-2 | Galena | 17.493 | 15.520 | 38.083 | 730 | 8.440 | 34.740 |
| 670-B2-1-3 | Galena | 17.492 | 15.520 | 38.082 | 730 | 8.440 | 34.740 |
| 670-B2-1-4 | Galena | 17.490 | 15.517 | 38.080 | 728 | 8.440 | 34.730 |
| 670-B2-1-5 | Galena | 17.493 | 15.521 | 38.084 | 731 | 8.440 | 34.750 |
| 670-B2-1-6 | Galena | 17.495 | 15.519 | 38.084 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.750 |
| 670-B2-1-7 | Galena | 17.487 | 15.514 | 38.063 | 727 | 8.440 | 34.660 |
| 670-B2-1-8 | Galena | 17.495 | 15.519 | 38.077 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.720 |
| 670-B2-1-9 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.518 | 38.058 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.640 |
| 670-B2-1-10 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.518 | 38.087 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.760 |
| 670-B4-1-1 | Galena | 17.484 | 15.510 | 38.042 | 725 | 8.440 | 34.580 |
| 670-B4-1-2 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.516 | 38.085 | 724 | 8.450 | 34.750 |
| 670-B4-1-3 | Galena | 17.486 | 15.516 | 38.064 | 730 | 8.440 | 34.660 |
| 670-B4-1-4 | Galena | 17.495 | 15.518 | 38.083 | 726 | 8.450 | 34.740 |
| 670-B4-1-5 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.520 | 38.080 | 729 | 8.450 | 34.730 |
| 670-B4-1-6 | Galena | 17.495 | 15.519 | 38.085 | 727 | 8.450 | 34.750 |
| 670-B4-1-7 | Galena | 17.494 | 15.517 | 38.082 | 726 | 8.450 | 34.740 |
| 670-B4-1-8 | Galena | 17.238 | 15.472 | 37.883 | 857 | 8.180 | 33.930 |
| 670-B4-2-1 | Galena | 17.481 | 15.519 | 38.040 | 737 | 8.430 | 34.570 |
| 670-B4-2-2 | Galena | 17.206 | 15.448 | 37.829 | 853 | 8.150 | 33.720 |
| 670-B4-2-3 | Galena | 17.340 | 15.573 | 38.151 | 893 | 8.290 | 35.020 |
| 670-B4-2-4 | Galena | 17.270 | 15.442 | 37.808 | 801 | 8.210 | 33.630 |
| 670-B4-2-5 | Galena | 17.275 | 15.406 | 37.731 | 758 | 8.220 | 33.320 |
| 670-B4-2-6 | Galena | 17.203 | 15.430 | 37.751 | 836 | 8.150 | 33.400 |
| 670-B4-2-7 | Galena | 17.195 | 15.422 | 37.731 | 833 | 8.140 | 33.320 |
| 670-B5-1-1 | Galena | 17.379 | 15.588 | 38.271 | 882 | 8.330 | 35.500 |
| 670-B5-1-2 | Galena | 17.337 | 15.460 | 37.866 | 774 | 8.280 | 33.870 |
| 670-B5-1-3 | Galena | 17.267 | 15.446 | 37.785 | 808 | 8.210 | 33.540 |
| 670-B5-1-4 | Galena | 17.292 | 15.535 | 38.061 | 886 | 8.240 | 34.650 |
| 670-B5-1-5 | Galena | 17.233 | 15.500 | 38.008 | 890 | 8.180 | 34.440 |
| 670-B5-1-6 | Galena | 17.142 | 15.425 | 37.720 | 874 | 8.080 | 33.280 |
| 670-B5-1-7 | Galena | 17.274 | 15.548 | 38.154 | 912 | 8.220 | 35.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, F.; Ding, Z.-J.; Bao, Z.-Y.; Wang, J.-W.; Ma, S.-X.; Niu, T.; Geng, K.-Q.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Li, G.-J.; et al. Source and Precipitation Process of Gold in the Linglong Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from Trace Elements of Pyrite and S-Pb Isotopes. Minerals 2025, 15, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111220
Ren F, Ding Z-J, Bao Z-Y, Wang J-W, Ma S-X, Niu T, Geng K-Q, Wang B, Li C, Li G-J, et al. Source and Precipitation Process of Gold in the Linglong Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from Trace Elements of Pyrite and S-Pb Isotopes. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111220
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Fei, Zheng-Jiang Ding, Zhong-Yi Bao, Jun-Wei Wang, Shun-Xi Ma, Tao Niu, Kai-Qiang Geng, Bin Wang, Chao Li, Gui-Jie Li, and et al. 2025. "Source and Precipitation Process of Gold in the Linglong Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from Trace Elements of Pyrite and S-Pb Isotopes" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111220
APA StyleRen, F., Ding, Z.-J., Bao, Z.-Y., Wang, J.-W., Ma, S.-X., Niu, T., Geng, K.-Q., Wang, B., Li, C., Li, G.-J., & Li, S.-S. (2025). Source and Precipitation Process of Gold in the Linglong Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from Trace Elements of Pyrite and S-Pb Isotopes. Minerals, 15(11), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111220






