Optimizing Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Superfine Tailings Slurry Based on the Response Surface Method and Desirability Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Tailings
2.1.2. Flocculant
2.1.3. Water
2.2. Test Method for Tailings Flocculation and Settling
2.2.1. Process of Flocculation and Settling Test for Tailings Slurry
2.2.2. Measurement Method for MCLF
2.3. Flocculant Selection Test
2.4. Experiment Design and Optimization Methods
3. Results
3.1. Flocculant Selection
3.2. Flocculation and Settling Test Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Establishment and Significance Analysis of RSM Model
4.2. Effects and Mechanistic Analysis of Factors and Their Interactions on Flocculation and Settling Indicators
4.2.1. Effect of Factors and Their Interactions on the Flocculation and Settling Indicators
4.2.2. Exploration of Flocculation and Settling Mechanism of Superfine Tailings
4.3. Verification and Predictive Analysis of RSM Models
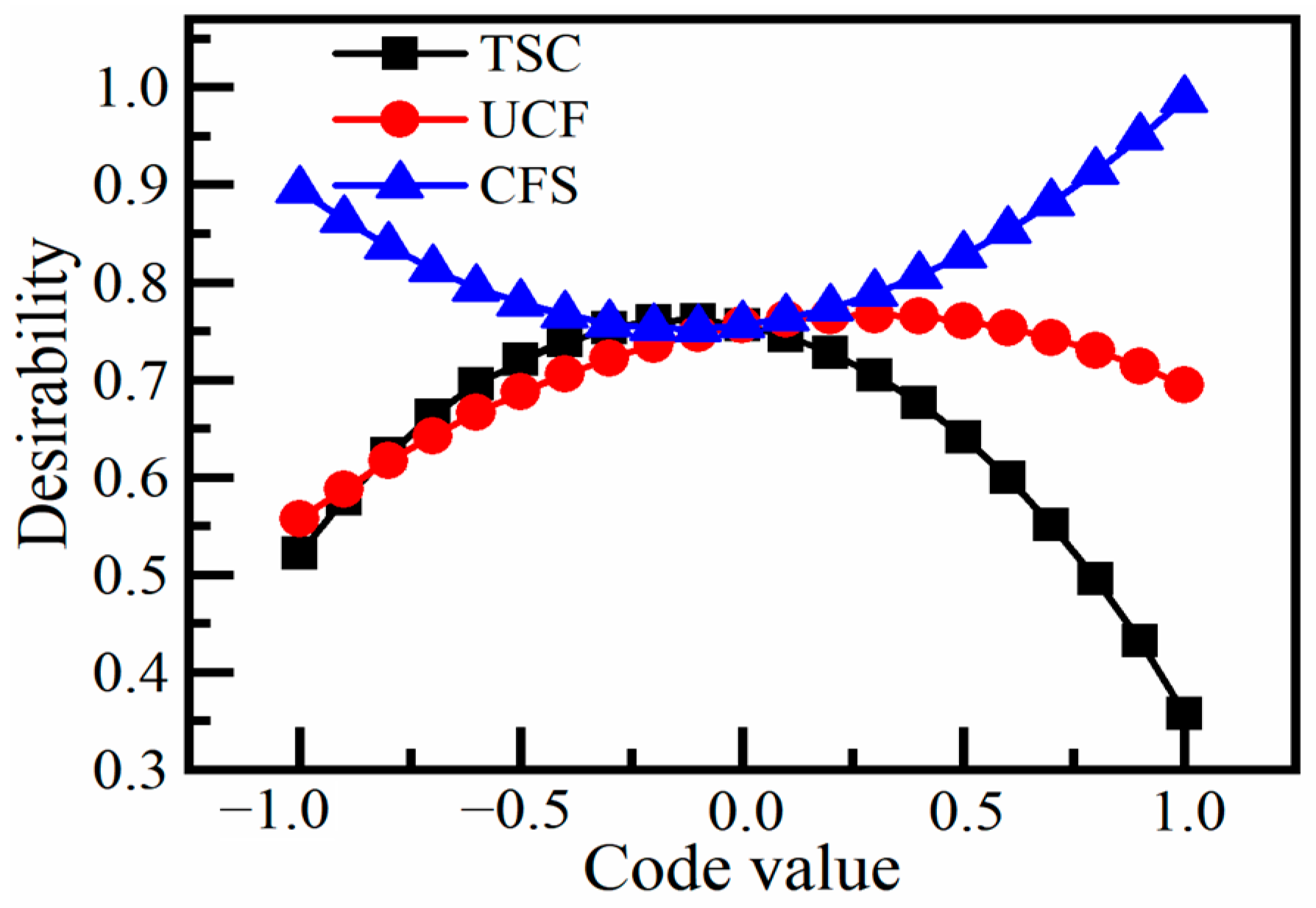
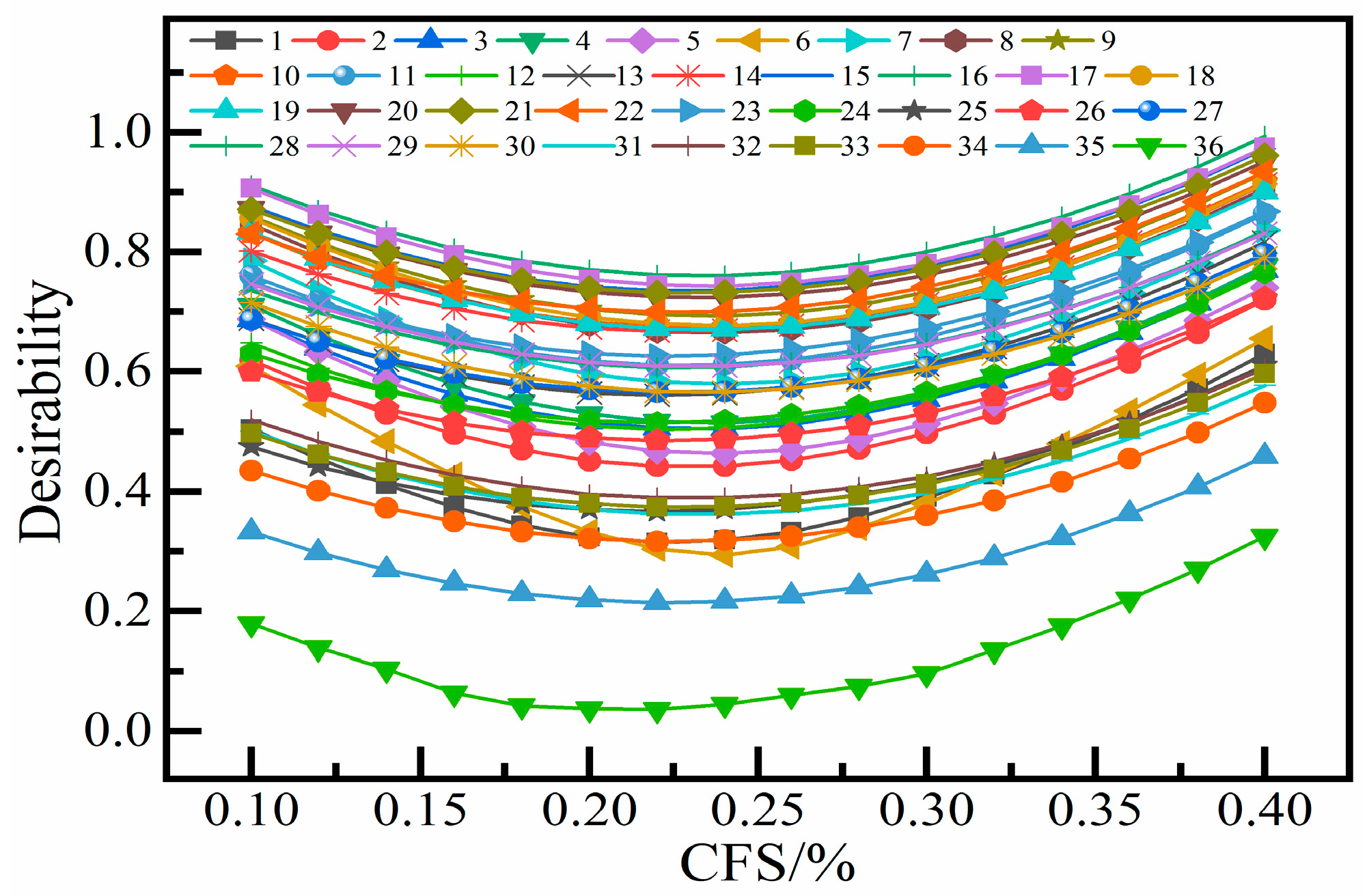
4.4. Multi-Objective Desirability Optimization of Flocculation and Settling Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avadiar, L.; Leong, Y.K.; Fourie, A. Effects of polyethylenimine dosages and molecular weights on flocculation, rheology and consolidation behaviors of kaolin slurries. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. Cemented paste backfill for mineral tailings management: Review and future perspectives. Min. Eng. 2019, 144, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.Z.; Wang, S.F.; Yang, Y.X.; Chen, X.M. Water recovery improvement by shearing of gravity-thickened tailings for cemented paste backfill. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, R.; Massinaei, M.; Behnamfard, A. Improving flocculation and dewatering performance of iron tailings thickeners. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yan, B.; Xie, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, H. A two-step flocculation process on oil sands tailings treatment using oppositely charged polymer flocculants. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguay, M.; Fawell, P.; Adkins, S. Modelling the impact of two different flocculants on the performance of a thickener feedwell. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 4262–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, A.; Ji, X.; Yan, Q.; Li, X. Rule and mechanism of flocculation sedimentation of unclassified tailings. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2010, 32, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Hankins, N.P.; Hilal, N. Effect of chemical composition on the flocculation dynamics of latex-based synthetic activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, L.; Soares, J.B.P. The influence of tailings composition on flocculation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, M.K.R.; Fatehi, P. Influence of pH and ionic strength on flocculation of clay suspensions with cationic xylan copolymer. Colloid. Surf. A 2017, 530, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, L.; Cao, Y.; Gui, X.; Li, Z. Effect of pH on the flocculation behaviors of kaolin using a pH-sensitive copolymer. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Optimal flocculating sedimentation parameters of unclassified tailings slurry. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 47, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D. Optimal prediction model of flocculating sedimentation velocity of unclassified tailings. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2015, 25, 793–798. [Google Scholar]
- Önal, G.; Özer, M.; Arslan, F. Sedimentation of clay in ultrasonic medium. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.R.; Fawell, P.D.; Bahri, P.A.; Swift, J.D. Estimating average particle size by focused beam reflectance measurement (FBRM). Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 19, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaputra, A.; Jones, F.; Fawell, P.D.; Smith, P.G. Focused beam reflectance measurement for monitoring the extent and efficiency of flocculation in mineral systems. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R. Selection research of filling materials. In Theory and Engineering Practice of Cemented Filling in Metal Mines; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J. Thickening dehydration performance and flocculation mechanism of ultrafine tailings based on dual flocculation. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 3597–3608. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 51450-2022; Technical Standard for Metal and Non-metal Mine Filling Engineering. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Ruan, Z.; Wu, A.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; .Wang, Y. Flocculation and settling behavior of unclassified tailings based on measurement of floc chord length. Chin. J. Eng. 2020, 42, 980–987. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Ruan, Z.; Bürger, R.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Optimization of flocculation and settling parameters of tailings slurry by response surface methodology. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.L.; Gunst, R.F.; Hess, J.L. Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments with Applications to Engineering and Science, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Study for Multiple Response Optimization Based on Robust Parameter Design. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Ma, J.; Peng, K.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, L. Mix ratio optimization of alpine mine backfill based on response surface method. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2013, 35, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Candioti, L.V.; De Zan, M.M.; Cámara, M.S.; Goicoechea, H.C. Experimental design and multiple response optimization. Using the desirability function in analytical methods development. Talanta 2014, 124, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y. Multi-objective optimization for mix proportioning of mine filling materials. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2017, 49, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Optimization of Mix Proportioning of Mine Filling Materials Using RSM-DF Experiments Design Method. J. Basic. Sci. Eng. 2019, 27, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z. Selection and optimization of flocculation sedimentation parameters of unclassified tailings slurry based on RSM-BBD. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2020, 30, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, A.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Huo, C. Effect of flocculation settling on rheological characteristics of full tailing slurry. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 47, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.N.; Novak, J.T. Influence of cations on activated-sludge effluent quality. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Wu, A.; Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Chen, H. Research on Flocculation Sedimentation Technology of Unclassified-tailings. Min. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, J.; Peng, J.; Tu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Feng, J. Effect and mechanism of sodium hexametaphosphate on the flocculation sedimentation behaviors of ultrafine iron tailings. Met. Mine 2022, 08, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, A.; Klein, B.; Wang, H. Effect of primary flocculant type on a two-step flocculation process on iron ore fine tailings under alkaline environment. Miner. Eng. 2019, 132, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, J. Study on the flocculation law and mechanism of APAM unit consumption to different particle size in the flocculation and sedimentation of tailings. Min. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Li, S.; Peng, L.; Fan, J. Flocculation and settlement characteristics and thickening mechanism of difficult-to-settle fine tailings. Min. Res. Dev. 2025, 45, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Z. Optimizing complex enzymatic extraction of Chaenomeles cathayensisjuice by response surface methodology combined with desirability function analysis. China Brew. 2011, 9, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
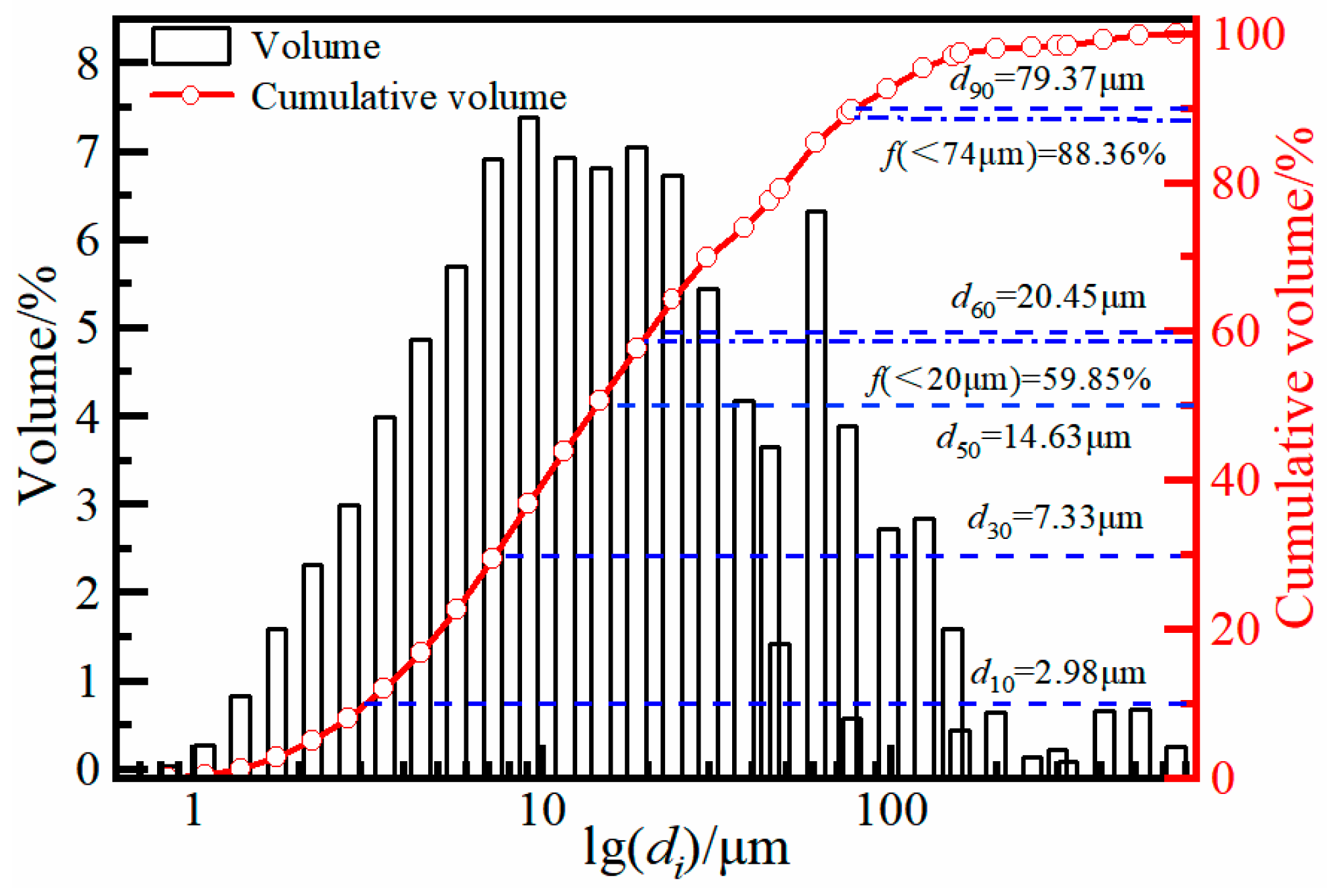

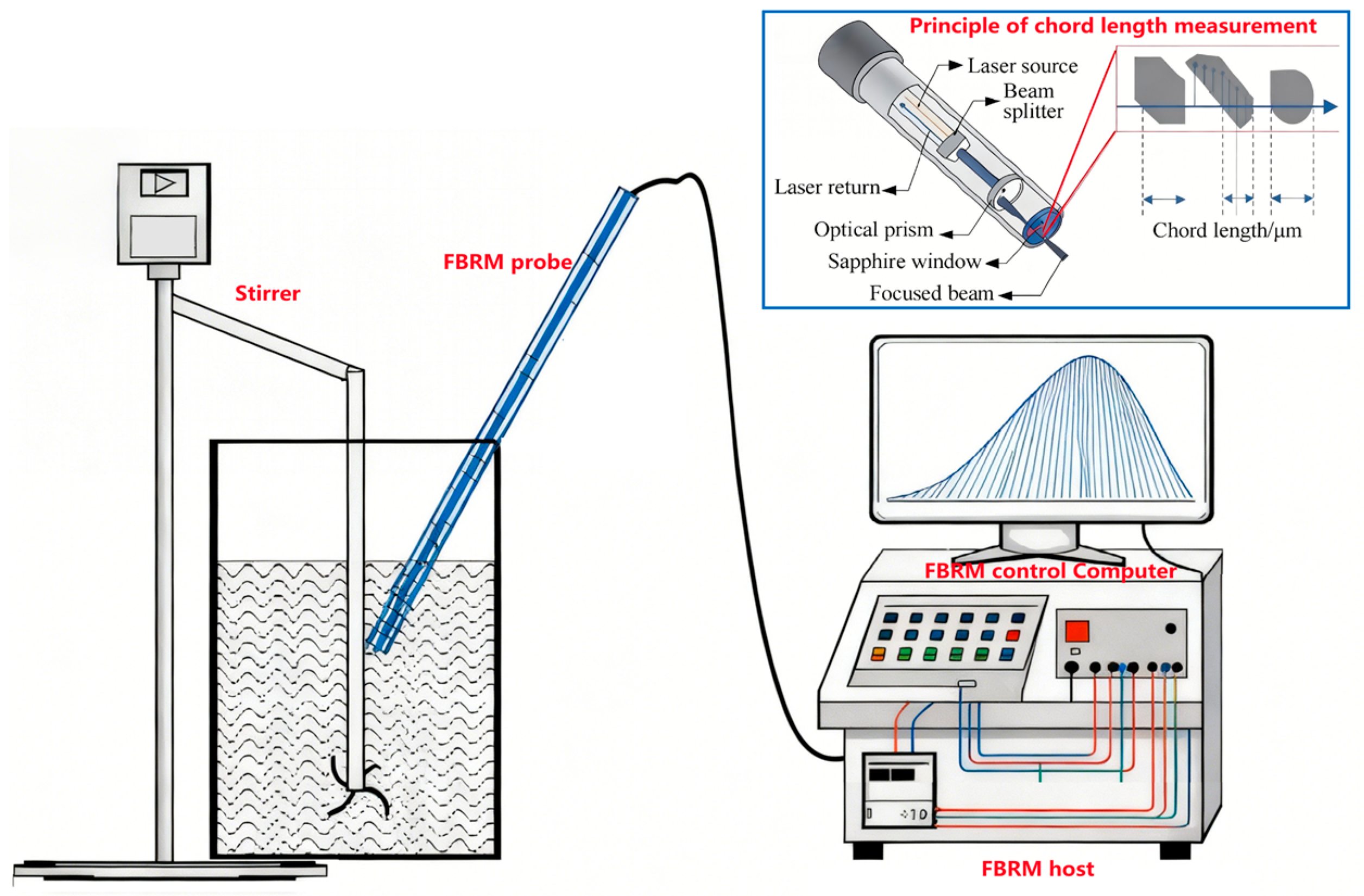
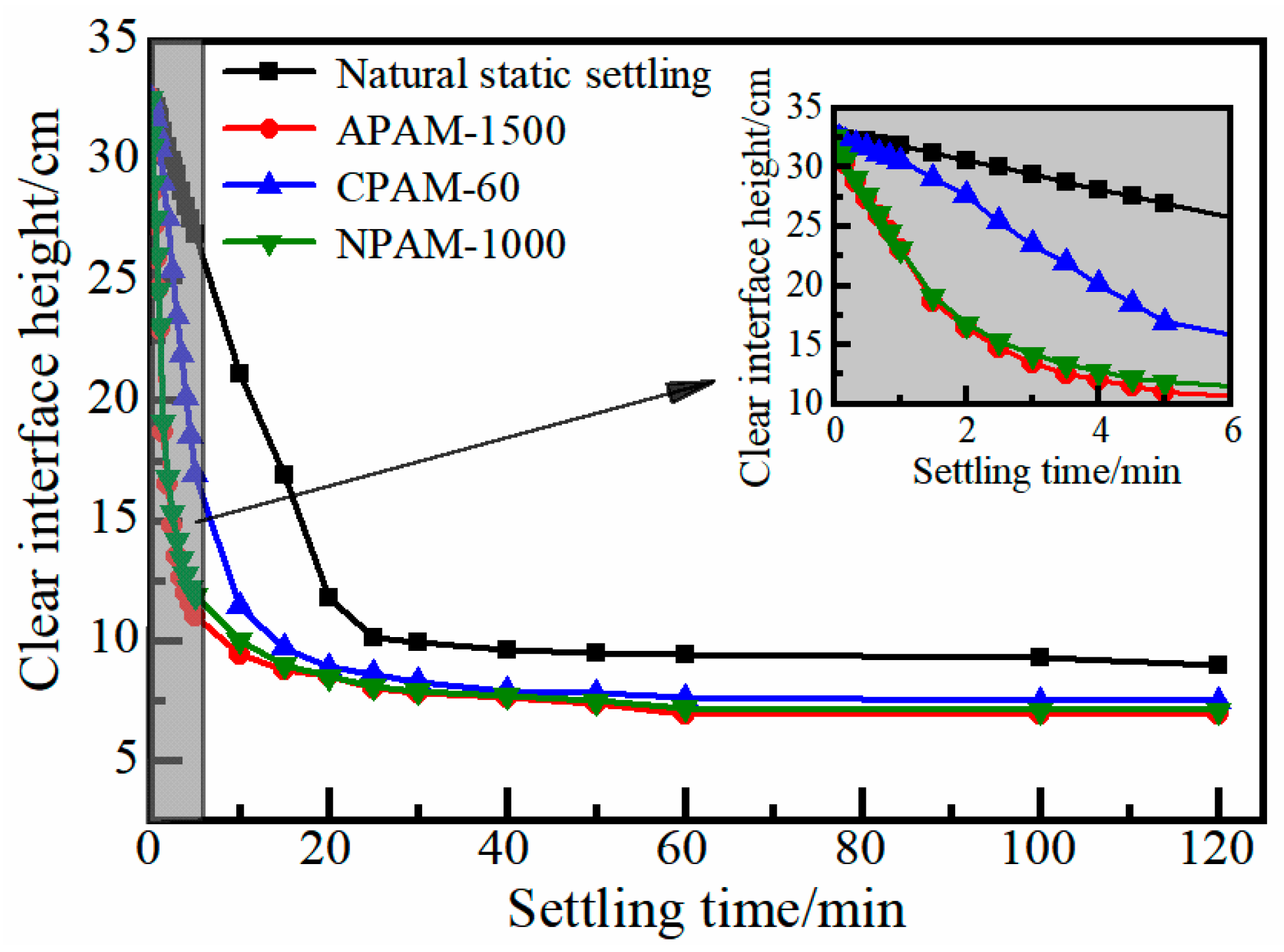

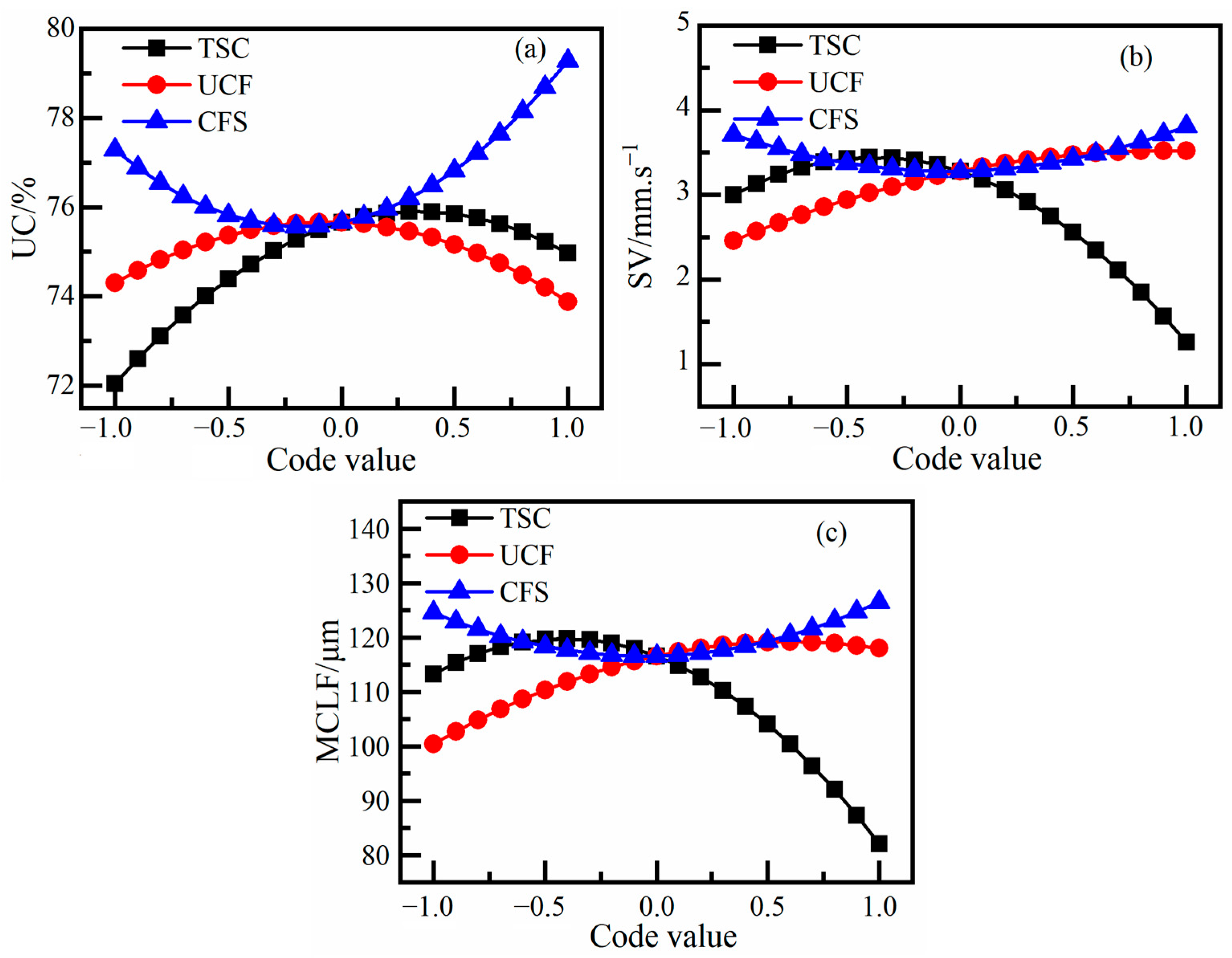


| Physical Properties | Density/(t·m−3) | Loose Bulk Density/(t·m−3) | Tamped Bulk Density/% | Void Fraction/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test result | 2.95 | 1.59 | 2.08 | 46.10 |
| Chemical Composition | CaO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 35.88 | 34.52 | 10.60 | 6.28 | 4.87 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 6.38 |
| Type | TSC */% | UCF/(g·t−1) | CFS */% | UC */% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APAM-1500 | 20 | 15 | 0.2 | 77.86 |
| CPAM-60 | 67.39 | |||
| NPAM-1000 | 75.62 |
| Influence Factor | Code Value | Code Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| TSC/% | x1 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| UCF/g·t−1 | x2 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| CFS/% | x3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| No. | Code Value | Test Results | Prediction Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSC x1/% | UCF x2/g·t−1 | CFS x3/% | UC y1/% | SV y2/mm·s−1 | MCLF y3/μm | UC y1/% | SV y2/mm·s−1 | MCLF y3/μm | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 77.15 | 3.96 | 123.00 | 78.56 | 3.97 | 123.61 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.66 | 3.28 | 116.61 | 76.62 | 3.26 | 116.50 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 69.78 | 3.17 | 115.42 | 70.81 | 3.24 | 110.93 |
| 4 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 77.67 | 2.96 | 113.11 | 78.38 | 3.02 | 112.82 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 73.23 | 1.46 | 88.90 | 71.21 | 1.49 | 89.20 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 76.27 | 4.15 | 124.63 | 73.76 | 4.08 | 123.61 |
| 7 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 70.74 | 2.21 | 103.14 | 69.73 | 2.18 | 102.80 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 75.77 | 1.56 | 91.22 | 76.68 | 1.61 | 90.63 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.66 | 3.28 | 116.61 | 76.62 | 3.26 | 116.52 |
| 10 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 73.88 | 3.42 | 118.01 | 73.96 | 3.46 | 119.41 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.66 | 3.28 | 116.60 | 76.62 | 3.26 | 116.53 |
| 12 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 75.88 | 3.57 | 119.52 | 75.37 | 3.49 | 121.72 |
| 13 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 73.99 | 0.53 | 53.63 | 73.55 | 0.51 | 55.31 |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 78.96 | 1.87 | 97.42 | 75.99 | 1.83 | 96.62 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.66 | 3.28 | 116.60 | 76.62 | 3.26 | 116.54 |
| 16 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 75.73 | 2.82 | 111.41 | 73.55 | 2.81 | 111.31 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.66 | 3.28 | 116.64 | 76.62 | 3.26 | 116.50 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob > F | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y1 | y2 | y3 | y1 | y2 | y3 | y1 | y2 | y3 | y1 | y2 | y3 | |
| Model | 82.15 | 15.13 | 47.61 | 9.13 | 1.68 | 5.29 | 43.92 | 200 | 21.28 | <10−4 | <10−4 | 3 × 10−4 |
| x1 | 17.02 | 6.06 | 19.5 | 17.02 | 6.06 | 19.5 | 81.92 | 721 | 78.42 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
| x2 | 0.36 | 2.24 | 6.25 | 0.36 | 2.24 | 6.25 | 1.74 | 266 | 25.13 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
| x3 | 8.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 8.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 38.59 | 2.50 | 0.31 | 4 × 10−4 | 3 × 10−4 | <10−4 |
| x12 | 19.53 | 5.60 | 15.8 | 19.53 | 5.60 | 15.08 | 93.99 | 667 | 60.65 | <10−4 | <10−4 | 1 × 10−4 |
| x22 | 10.4 | 0.35 | 2.32 | 10.4 | 0.35 | 2.32 | 50.02 | 41.13 | 9.34 | 2 × 10−4 | 0.0004 | 0.0184 |
| x32 | 28.82 | 0.97 | 3.30 | 28.82 | 0.97 | 3.30 | 138.7 | 115 | 12.36 | <10−4 | <10−4 | 0.0083 |
| x1 × 2 | 0.01 | 1 × 10−4 | 1.32 | 0.01 | 1 × 10−4 | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 5.32 | 5 × 10−4 | 0.9162 | 0.8326 |
| x1x3 | 0.35 | 6 × 10−3 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 6 × 10−3 | 0.06 | 1.70 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.6518 | 0.8418 | 2 × 10−4 |
| x2x3 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.35 | 3.24 | 0.11 | 0.2831 | 8 × 10−4 | 0.7504 |
| Residual | 1.45 | 0.06 | 1.74 | 0.21 | 8 × 10−3 | 0.25 | ||||||
| Pure Error | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| No. | Factors | UC y1/% | SV y2/mm.s−1 | MCLF y3/μm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSC/% | UCF /g·t−1 | CFS /% | TR | PR | RE/% | TR | PR | RE/% | TR | PR | RE/% | |
| V1 | 17 | 14 | 0.3 | 75.44 | 74.60 | 1.12 | 3.59 | 3.53 | 1.58 | 119.11 | 117.51 | 1.36 |
| V2 | 17 | 12 | 0.2 | 72.60 | 73.59 | 1.34 | 3.19 | 3.15 | 1.36 | 113.99 | 112.73 | 1.12 |
| V3 | 19.58 | 15.98 | 0.4 | 79.95 | 78.99 | 1.22 | 4.24 | 4.20 | 0.87 | 125.40 | 126.85 | 1.14 |
| V4 | 21 | 16 | 0.1 | 76.59 | 77.41 | 1.06 | 3.92 | 3.86 | 1.43 | 121.91 | 120.19 | 1.43 |
| V5 | 21 | 18 | 0.4 | 77.02 | 78.73 | 2.22 | 4.09 | 4.08 | 0.24 | 123.8 | 123.38 | 0.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.; Shi, S.; Geng, B.; Fu, J.; Huo, S.; Zhang, H. Optimizing Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Superfine Tailings Slurry Based on the Response Surface Method and Desirability Function. Minerals 2025, 15, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111216
Wen Z, Shi S, Geng B, Fu J, Huo S, Zhang H. Optimizing Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Superfine Tailings Slurry Based on the Response Surface Method and Desirability Function. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111216
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zhenjiang, Shihu Shi, Biyao Geng, Jianxun Fu, Si Huo, and Huan Zhang. 2025. "Optimizing Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Superfine Tailings Slurry Based on the Response Surface Method and Desirability Function" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111216
APA StyleWen, Z., Shi, S., Geng, B., Fu, J., Huo, S., & Zhang, H. (2025). Optimizing Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Superfine Tailings Slurry Based on the Response Surface Method and Desirability Function. Minerals, 15(11), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111216








