Pore Diagenetic Evolution and Its Coupling Relationship with Natural Gas Accumulation in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan
Abstract
1. Introduction
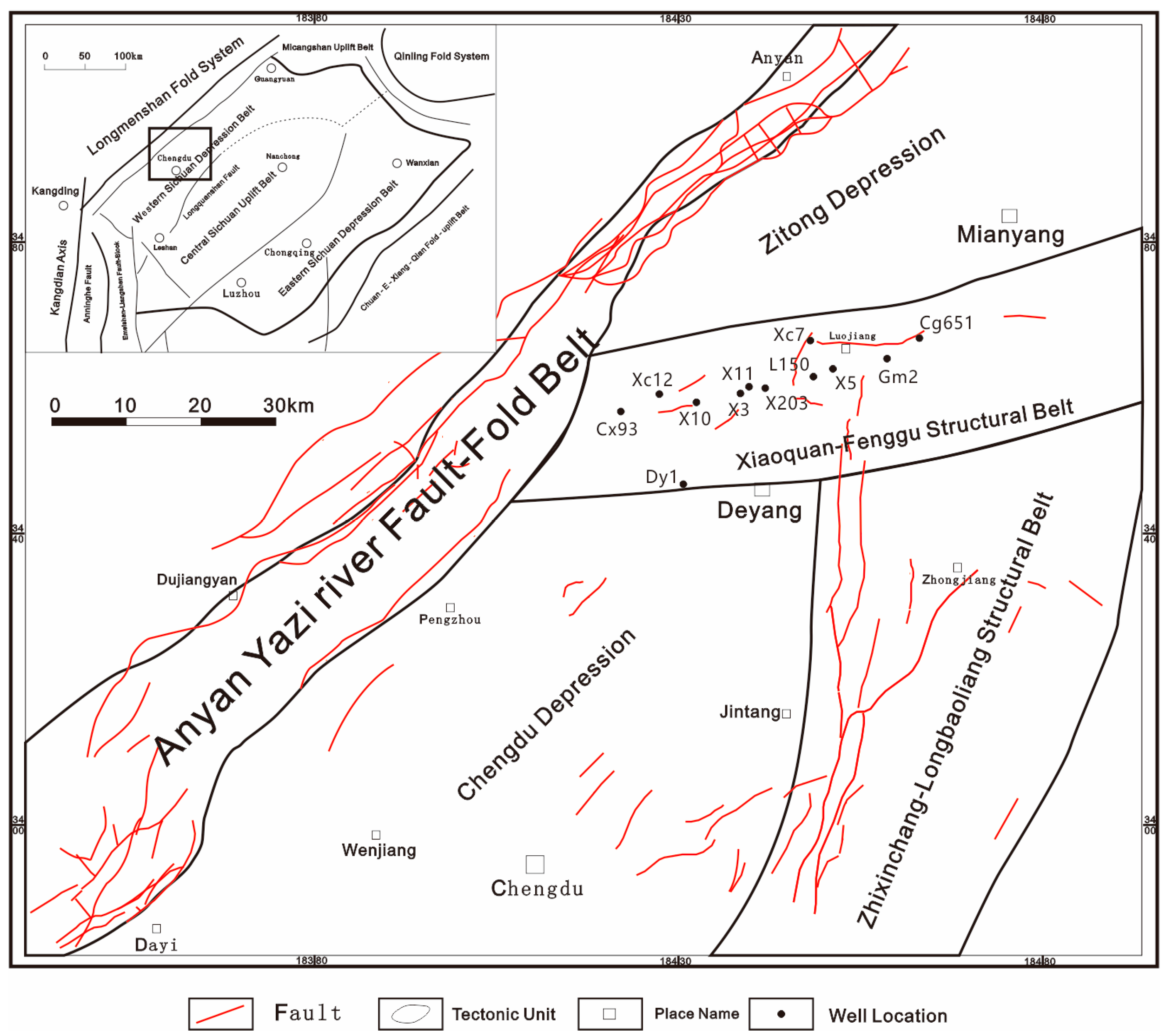
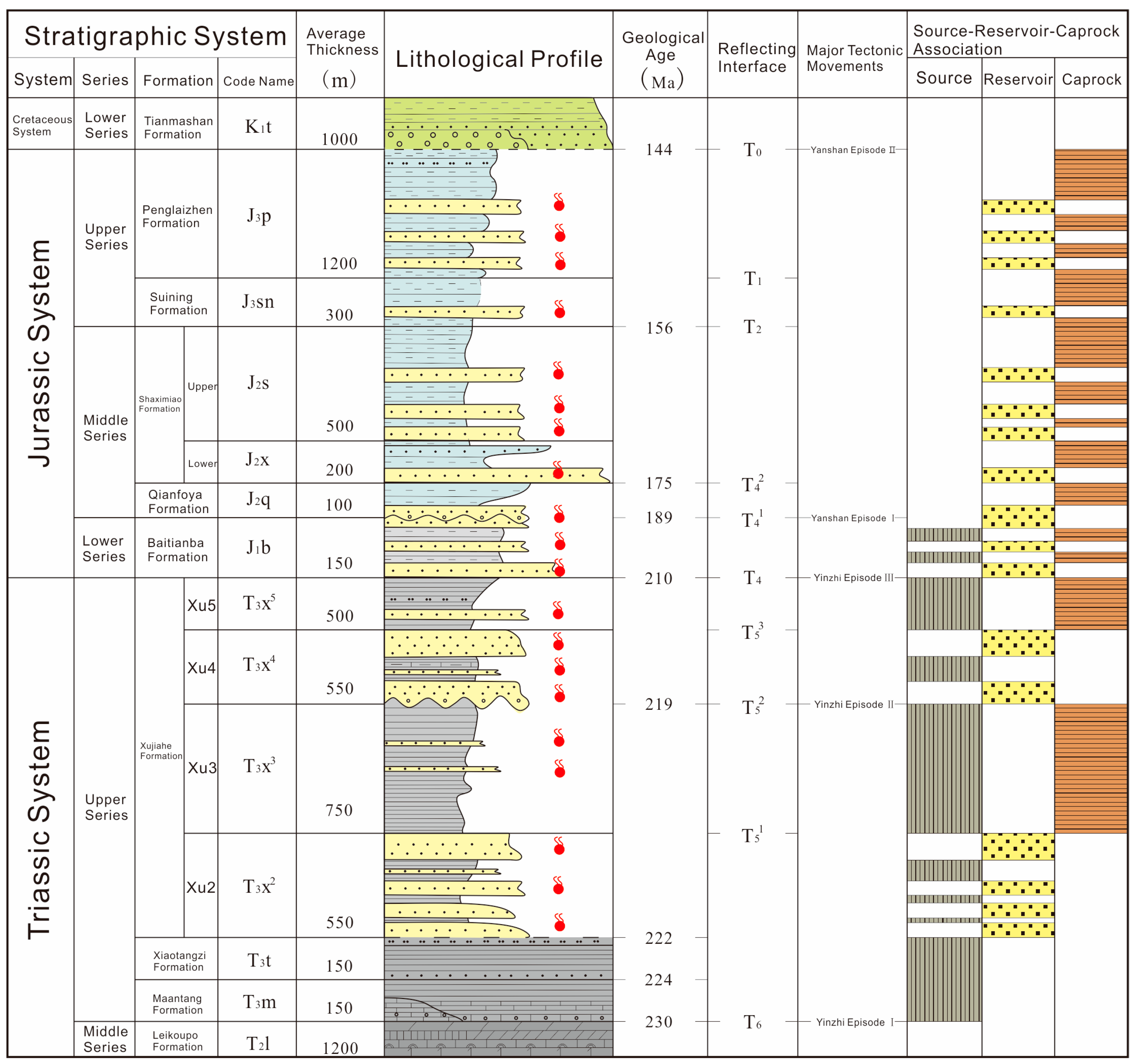
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
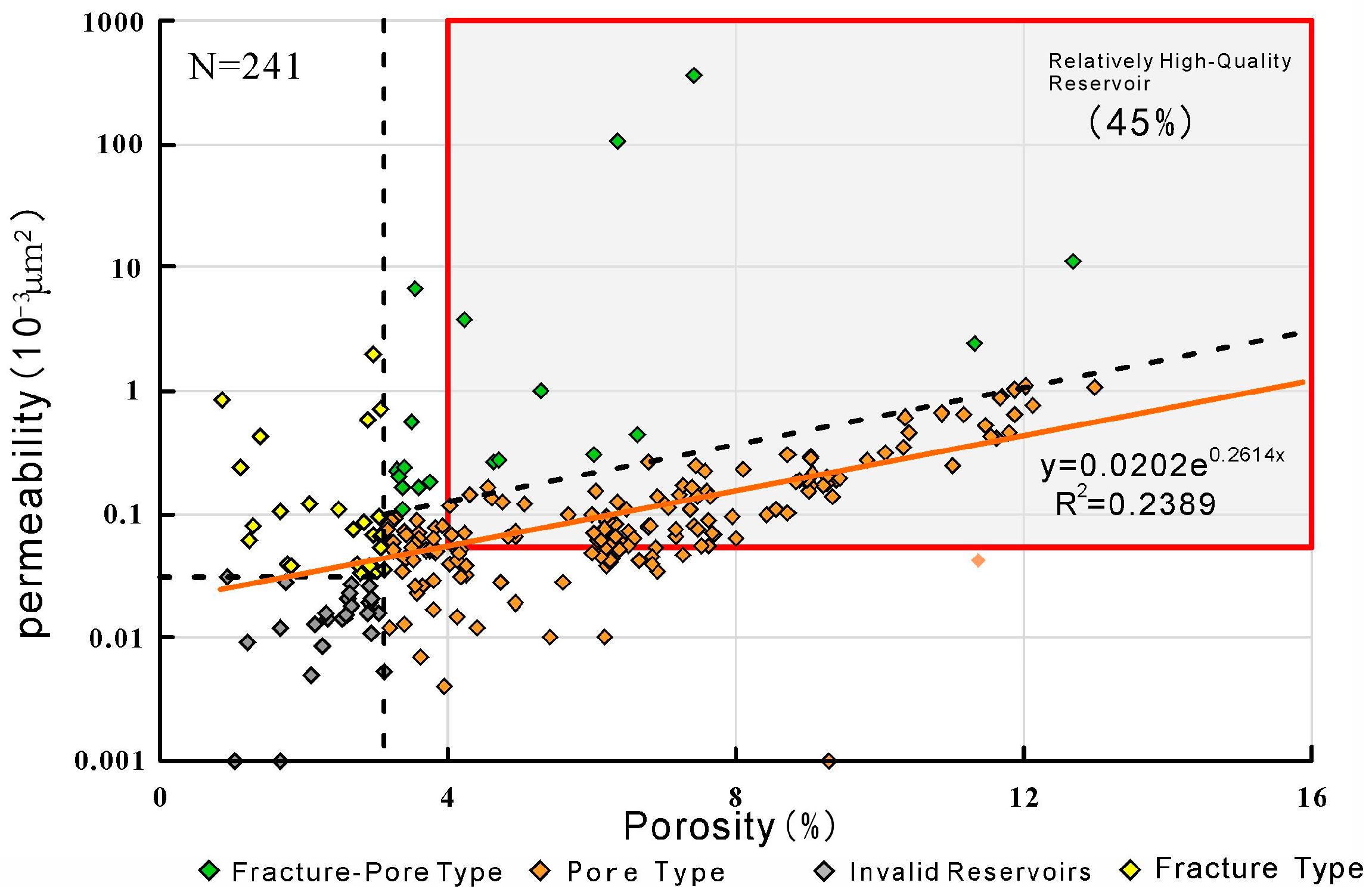
4.1. Reservoir Characteristics
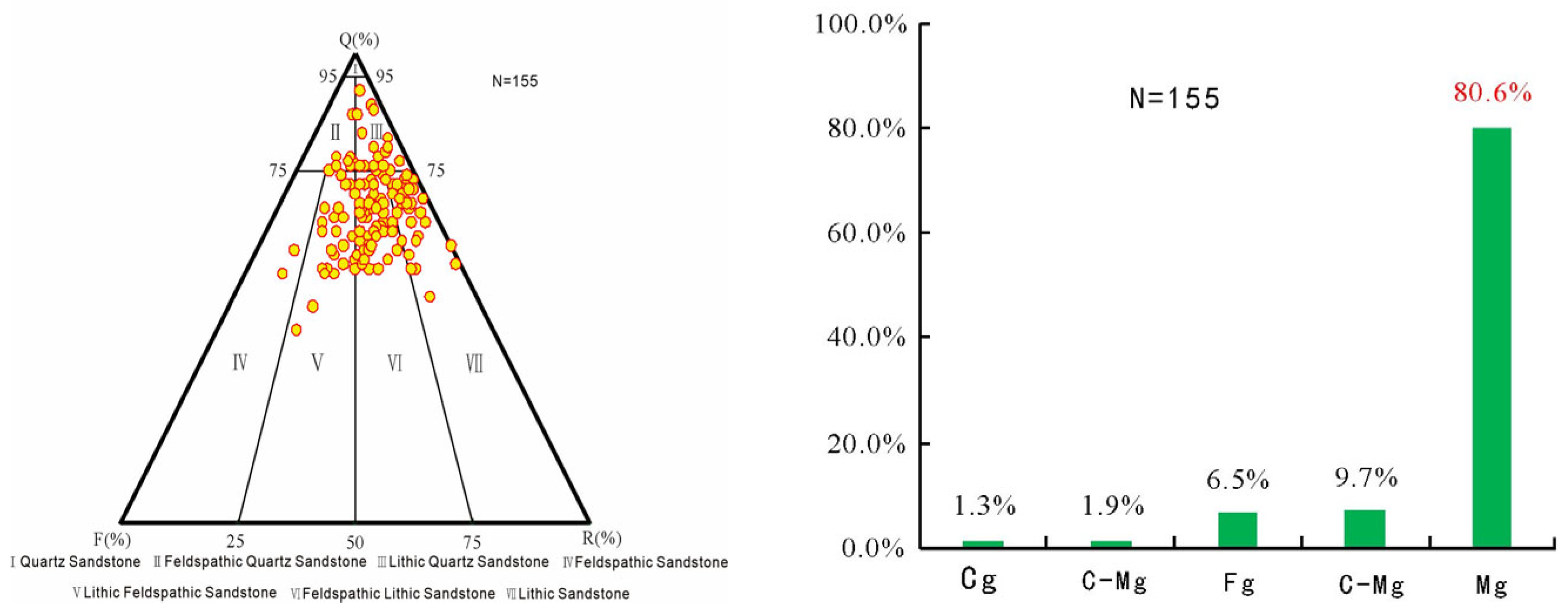
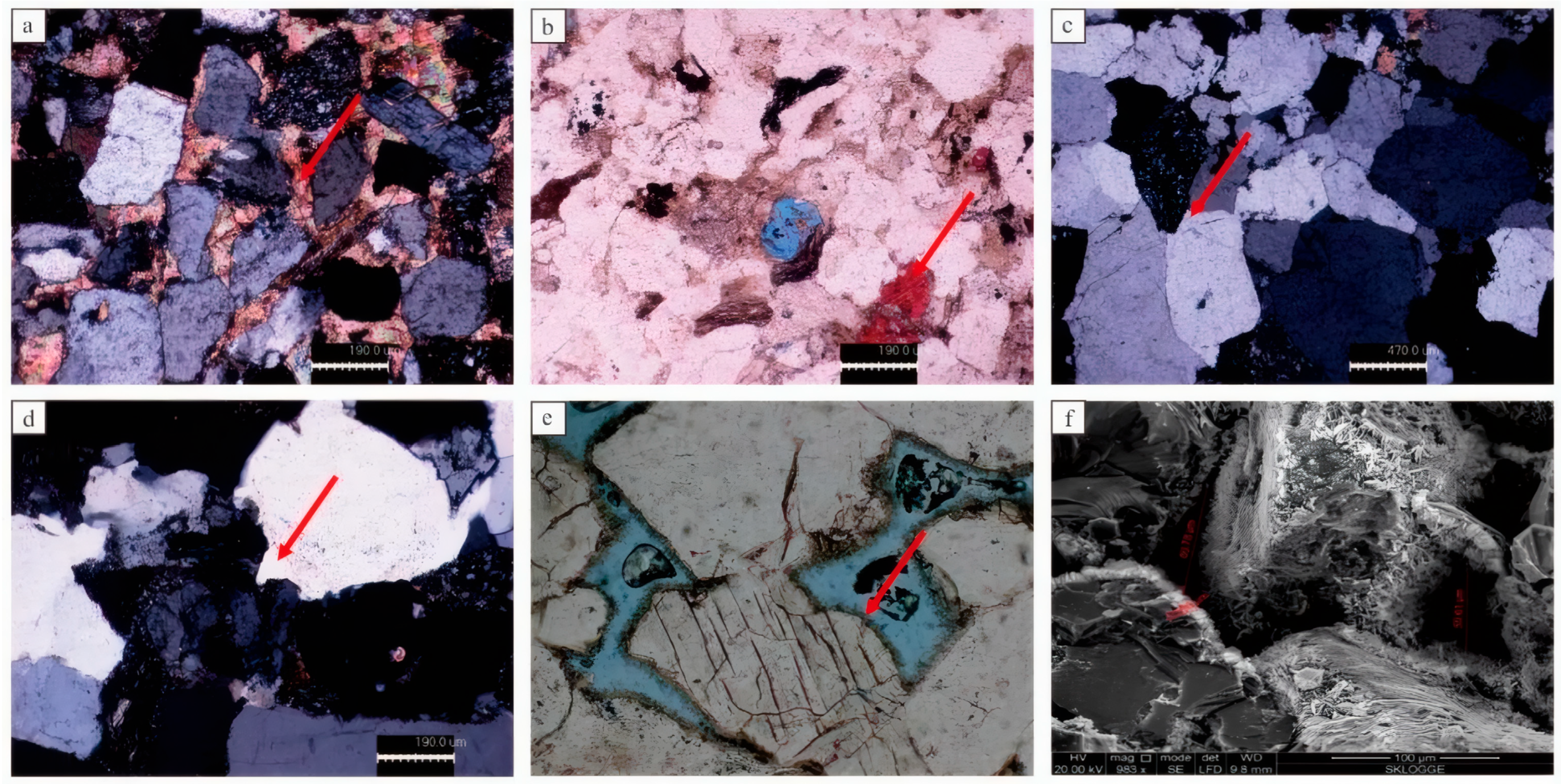
4.1.1. Petrological Features
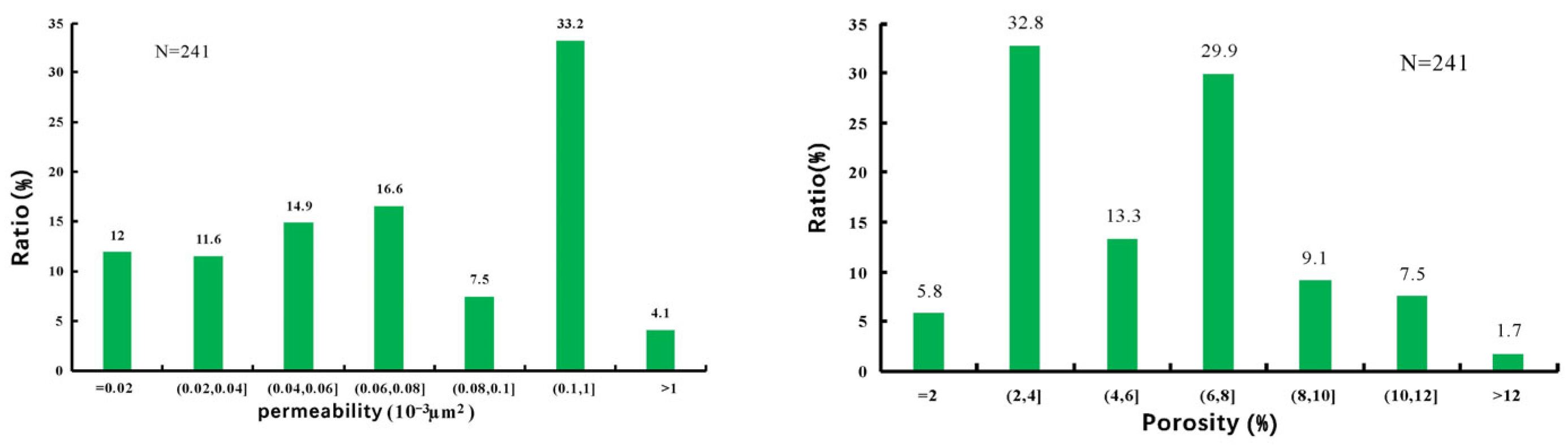
4.1.2. Reservoir Physical Properties
4.2. Controls on Reservoir Porosity
4.2.1. Compaction Effects
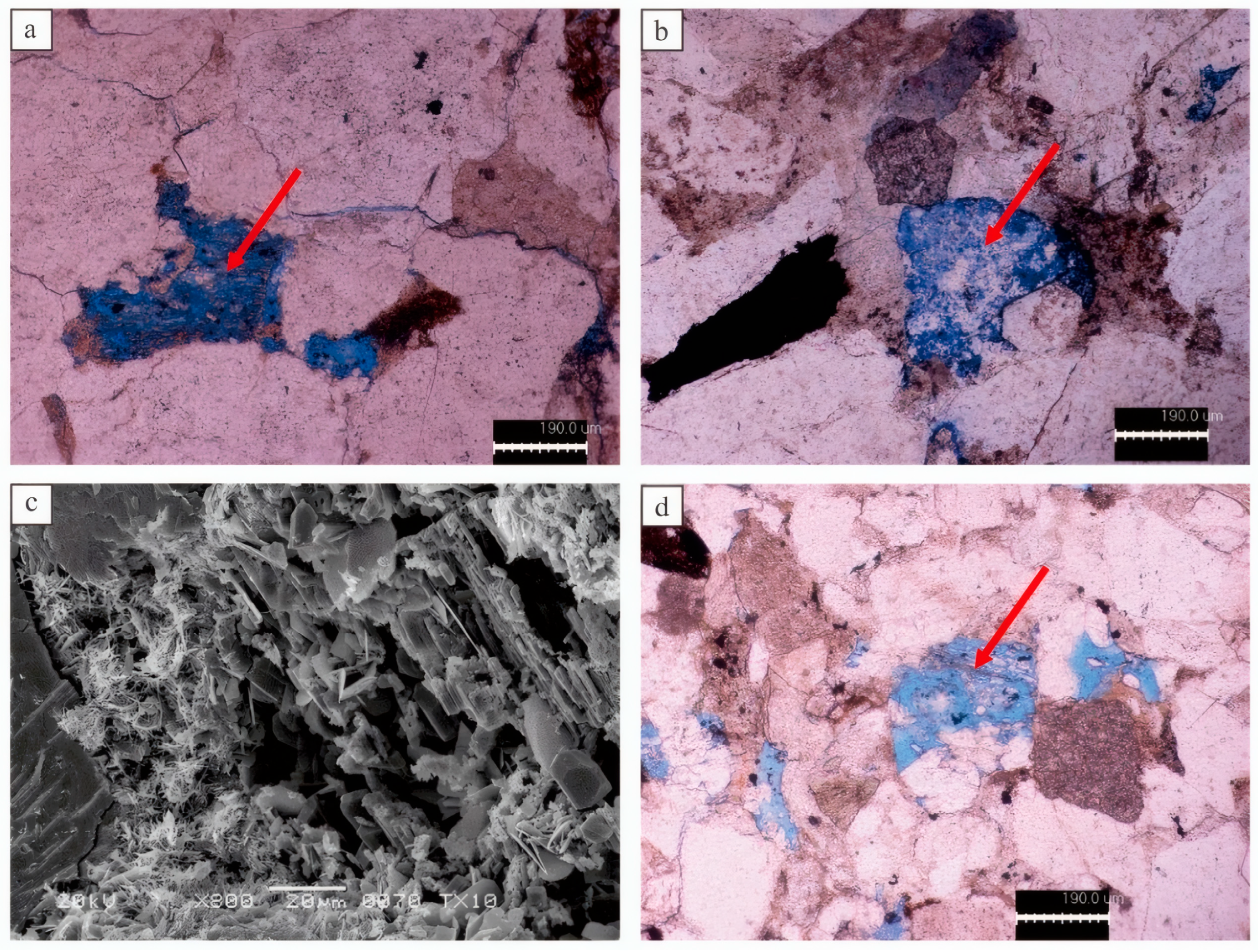
4.2.2. Cementation Effects
4.2.3. Dissolution Effects
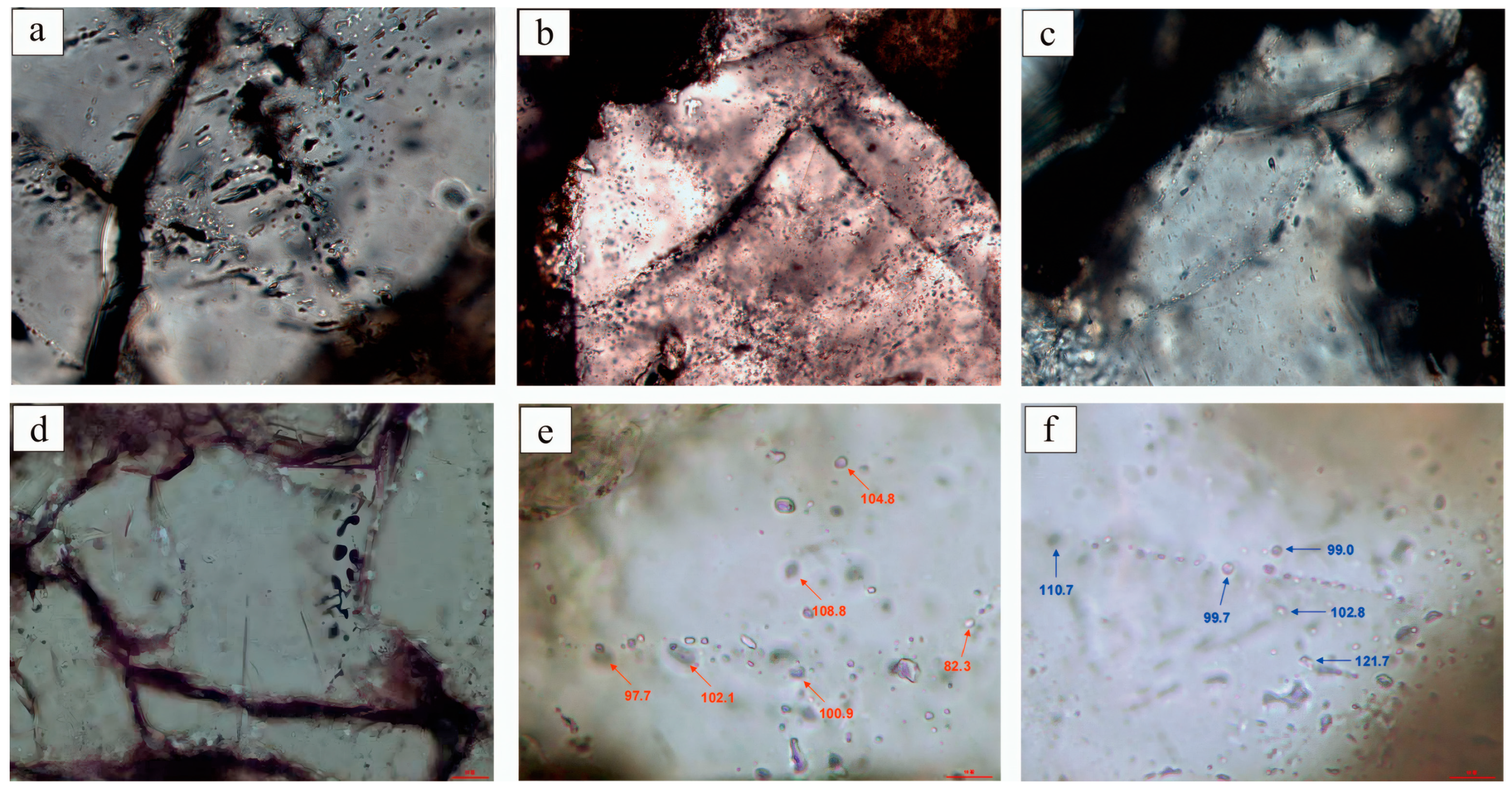
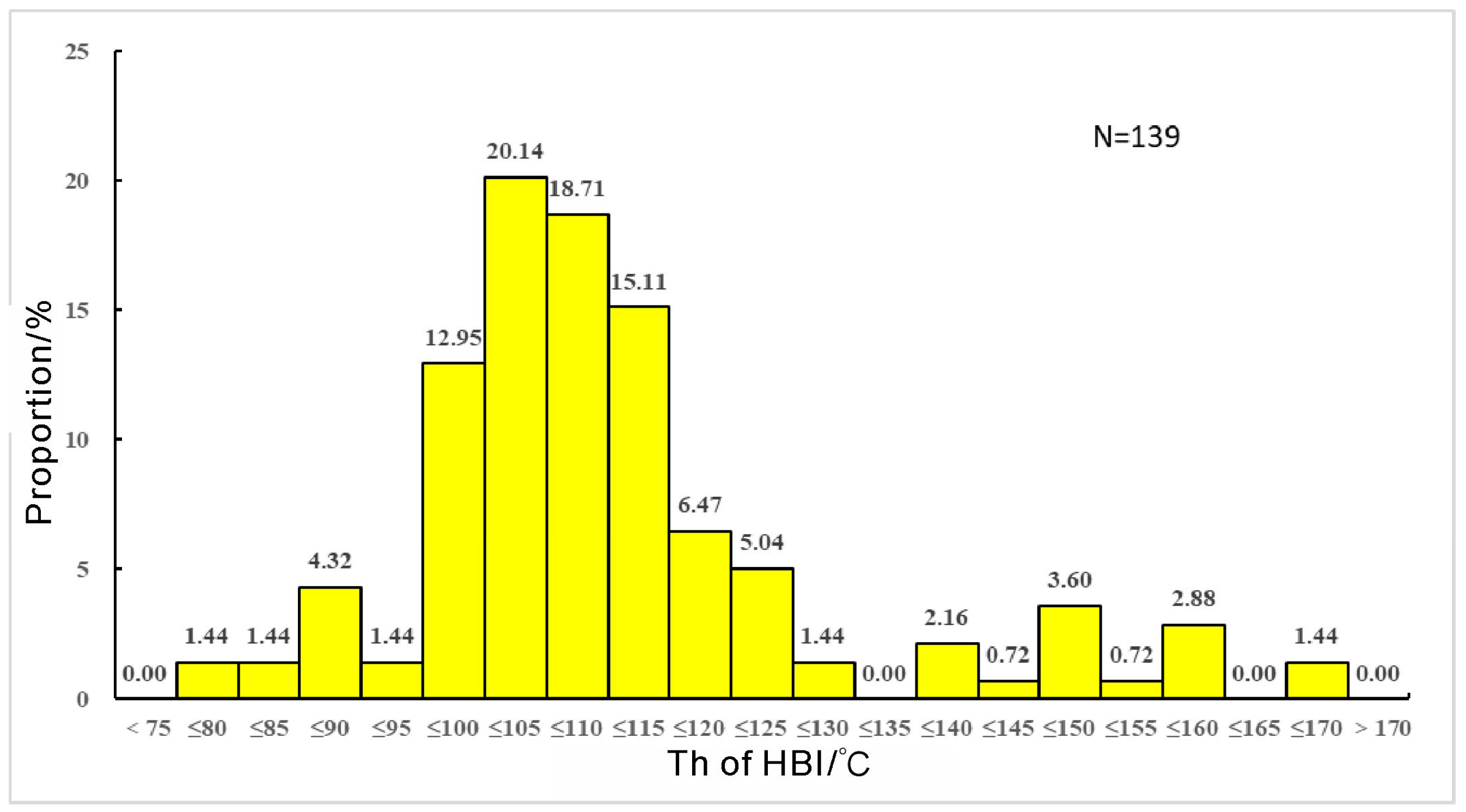
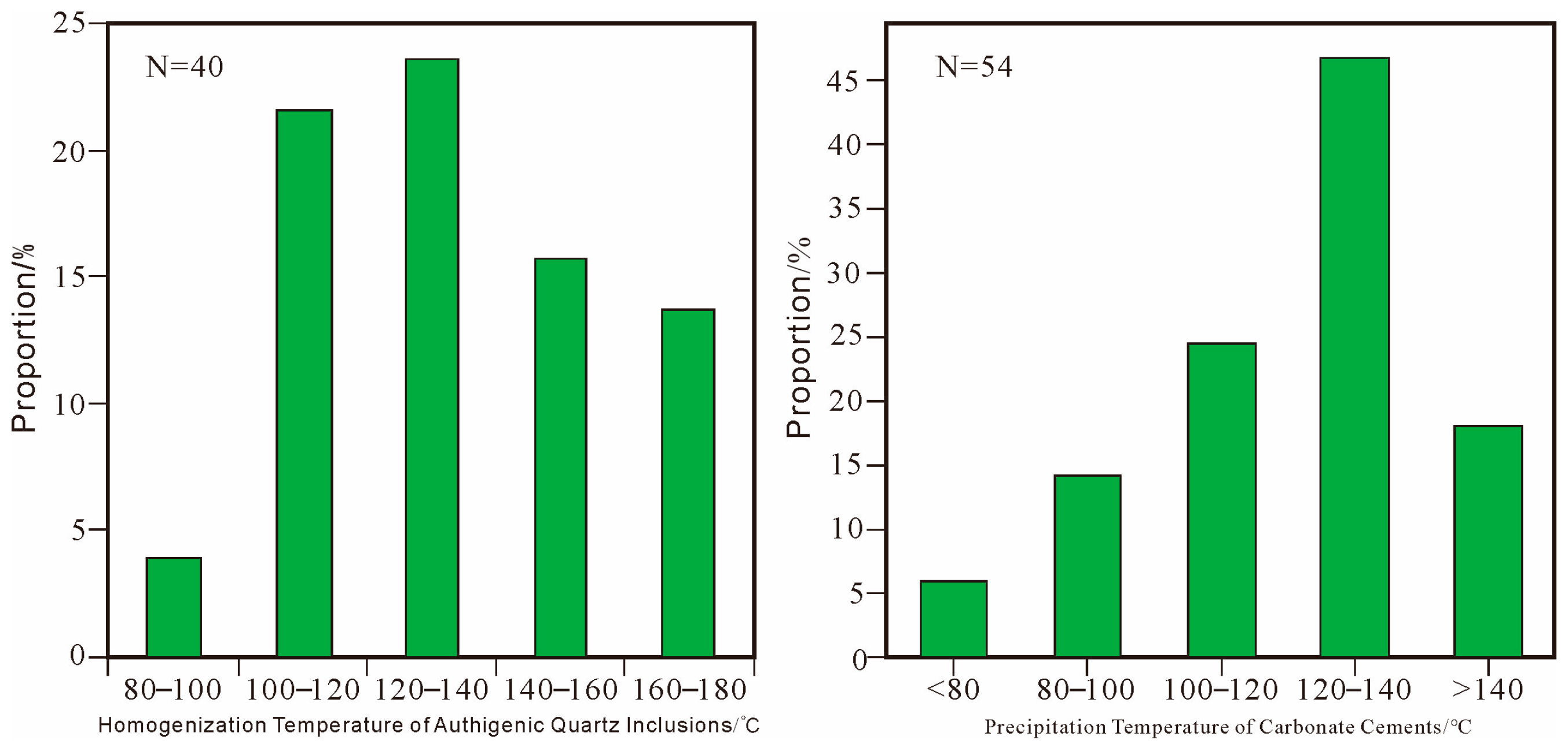
4.3. Fluid Inclusion Characteristics
4.4. Homogenization Temperatures of Fluid Inclusions
5. Discussion
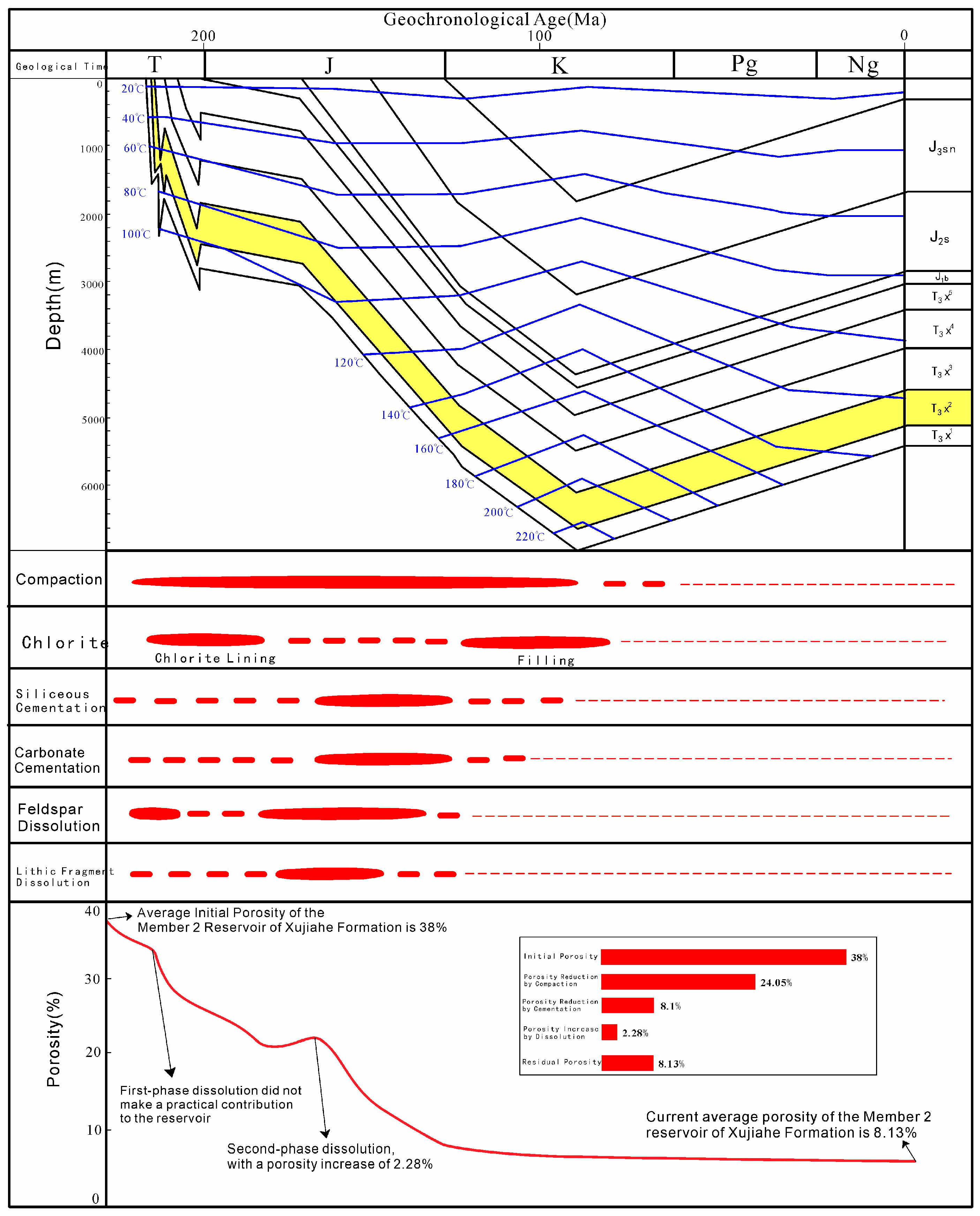
5.1. Quantitative-Temporal Reconstruction of Porosity Evolution
5.1.1. Initial Porosity Restoration (Φ1)
5.1.2. Post-Compaction/Pressure Solution Porosity (Φ2)
5.1.3. Cementation-Induced Porosity Loss
5.1.4. Dissolution-Enhanced Porosity
5.1.5. Reservoir Porosity Evolution Process
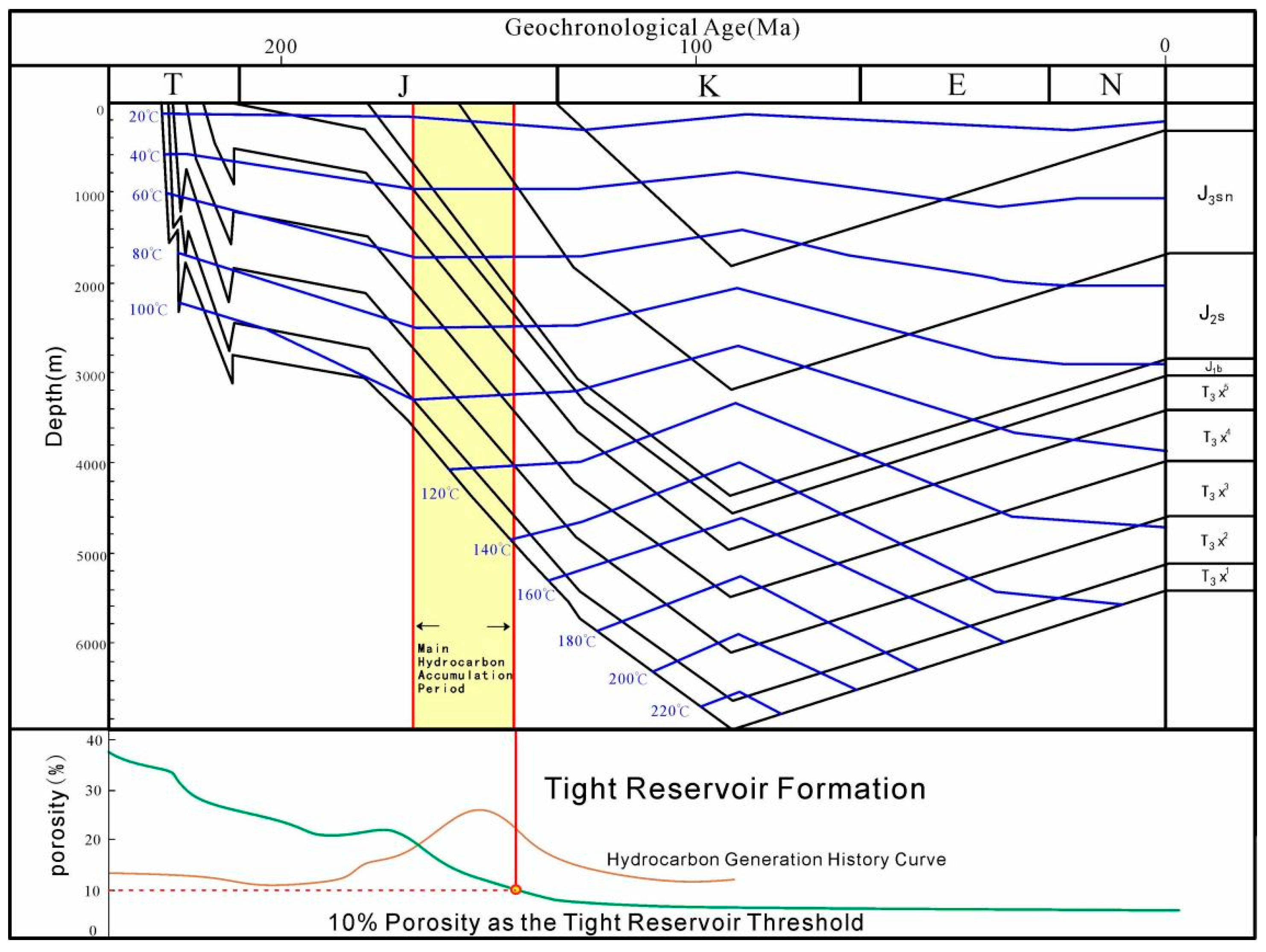
5.2. Coupling Relationship Between Reservoir Densification and Gas Accumulation
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The study demonstrates three principal findings regarding diagenetic controls on the Xu 2 Member reservoirs. Compaction emerges as the dominant factor degrading reservoir quality, reducing primary porosity from an initial 40% ± 5% to 31.72% ± 5% at 1000 m depth, 26.59% ± 5% at 2000 m, 22.11% ± 5% at 3000 m, 18.46% ± 5% at 4000 m, and 15.41% ± 5% at 5000 m.
- (2)
- Cementation exerts substantial impacts through three key phases: authigenic chlorite precipitates early at 600–800 m burial depth, while authigenic quartz and carbonate cements persistently reduce porosity by 10%–21% during 2000–5000 m burial. Dissolution initiates at ~3500 m depth, generating secondary porosity of 2%–16%.
- (3)
- Critical coupling exists between reservoir densification and gas accumulation. Hydrocarbon generation/expulsion peaks occur at 3250–4050 m burial depth, whereas reservoir tightness develops below 4050 m. Large-scale gas accumulation predates reservoir densification, with primary charging during the Late Jurassic preceding Early Cretaceous tightness development. This temporal decoupling highlights favorable conditions for hydrocarbon preservation in the Xu 2 Member.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H. Distribution Characteristics of Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs of Xujiahe Formation in Central Sichuan Basin. In Proceedings of the International Field Exploration and Development Conference 2021, Qingdao, China, 16–18 September 2021; Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Xuefeng, B.; Yu, Y.; Junhui, L.; Youzhi, W. Accumulation conditions and exploration prospects of tight gas reservoirs in the fifth member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Yilong–Pingchang area, Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2025, 30, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, W.; Bo, D.-M.; Hong, F.; Gong, Y.-J.; Hao, J.-Q. Tight sandstone gas accumulation mechanisms and sweet spot prediction, Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin, China. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Yong, Z. Characteristics of Tight Gas Reservoirs in the Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Depression: A Systematic Review. Energies 2024, 17, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-T.; Zeng, L.-B.; Dong, S.-Q.; Li, H.-M.; Liu, J.-Z.; Ji, C.-Q. The characteristics and controlling factors of high–quality reservoirs of ultra–deep tight sandstone: A case study of the Dabei Gas Field, Tarim Basin, China. Pet. Sci. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, R.H.; Walderhaug, O. Porosity prediction through simulation of sandstone compaction and quartz cementation. AAPG Bull. 1999, 83, 433–449. [Google Scholar]
- Paxton, S.T.; Szabo, J.O.; Ajdukiewicz, J.M.; Klimentidis, R.E. Construction of an intergranular compaction curve for evaluating and predicting compaction and porosity loss in rigid grained sandstone reservoirs. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, J.O.; Paxton, S.T. Intergranular volume (IGV) decline curves for evaluating and predicting compaction and porosity loss in sandstones (abs.). AAPG Bull. 1991, 75, 678. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, D.; Lei, W.; Yang, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, T.; Geng, C.; et al. Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoir Types and Formation Mechanisms in the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Anyue Area, Sichuan Basin. Energies 2025, 18, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.; Tang, D.; Yin, H.; Pei, S. Formation and evolution of overpressure system in tight sandstone gas reservoir of Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic in the Western Sichuan foreland basin and its relationship with natural gas accumulation. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. Source of quartz cement in tight gas sandstone: Evidence from the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the western Sichuan Basin, SW China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yu, Y.; Nan, H.; Chen, H. Petrologic and geochemical characteristics of carbonate cements in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation tight gas sandstone, western Sichuan Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2022, 106, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liu, M.; Cao, B.; Ren, Y.; Tan, X.; Zeng, W.; Lian, C. Formation mechanism of carbonate cement in tight sandstone reservoirs in the depression zone of foreland basin and its impact on reservoir heterogeneity: The upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan foreland basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 167, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Meng, W.; Gluyas, J.; Tan, X.; Gao, X.; Feng, M.; Kong, X.; Shao, H. Diagenetic characteristics, evolution, controlling factors of diagenetic system and their impacts on reservoir quality in tight deltaic sandstones: Typical example from the Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Foreland Basin, SW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 103, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. The genesis of authigenic minerals and the porosity evolution of various lithologies and their implications for identifying high–quality reservoirs in the fourth member of Xujiahe Formation Northeast–Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, S. Investigation on pore structure characteristics of ultra–tight sandstone reservoirs in the upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the northern Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 138, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D.; Cui, Y.; Jin, Z. An Intelligent Approach for Gas Reservoir Identification and Structural Evaluation by ANN and Viterbi Algorithm—A Case Study From the Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5904412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gu, F. An Integrated Machine Learning–Based Approach to Identifying Controlling Factors of Unconventional Shale Productivit. Energy 2023, 266, 126512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lin, L.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Wen, L.; Deng, X.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zheng, C.; et al. Chronology and geofluids characteristics of calcite cement in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation tight sandstone reservoir, Wstern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 170, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, G.; Xu, F.; Yuan, H.; Chen, F. Sequence of densification and hydrocarbon charging of Xu2 reservoir in Anyue–Hechuan area, Sichuan Basin, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Liao, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, G. Microscopic pore structures of tight sandstone reservoirs and their diagenetic controls: A case study of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the Western Sichuan Depression, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Pang, X.; Bai, T. Geological characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation models of the tight–sand gas reservoirs in upper Triassic Xujiahe formation in western Sichuan depression of China. In Proceedings of the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference 2013 (URTC), Denver, CO, USA, 12–14 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; Yin, S.; Tian, L. Controls of Multi–Scale Fractures in Tight Sandstones: A Case Study in the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan Depression. Lithosphere 2024, 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Lu, G.; Deng, B.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yang, R.; Jin, X. Tectonic–paleogeographic evolution of the Late Triassic in the Sichuan basin, SW China: Constraints from sedimentary facies and provenance analysis of the Xujiahe Formation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ran, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Lv, F.; Jiang, X. A Late Triassic depositional age for the Xujiahe formation, Sichuan basin: Implications for the closure of the Paleo–Tethys Ocean. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SY/T 5336-2006; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China-Practices for core analysis. National Development and Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2006.
- SY/T 6010-1994; Method for Determination of Homogenization Temperature and Salinity of Inclusions in Sedimentary Rocks. China National Petroleum Corporation: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lyu, W.; Sun, D.; Chen, S.; Guan, C.; Tang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J. Natural fractures in tight gas sandstones: A case study of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang gas field, Western Sichuan Basin, China. Geol. Mag. 2021, 158, 1543–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, X.; Liu, B. Reservoir Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors of Tight Sandstone in Member 2 of the Xujiahe Formation in Northwest Sichuan. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2023, 30, 50–57+66. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.-L.; Luo, P.-Y. Current status and prospect of key techniques for exploration and production of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in China. Shiyou Kantan Yu Kaifa/Pet. Explor. Dev. 2007, 34, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Jin, W. Types of the deep tight sandstone reservoirs and their different controlling in the T3x2 member of Xujiahe formation in Xinchang area, western Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2024, 35, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Fu, Q.; Dan, W.; Zhao, S.; Pang, J.; Chu, M. Diagenesis fluid stagnation effect and genesis of tight sandstone reservoir in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2018, 39, 858–868. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, H.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Fu, M.; Ling, C.; Duan, B.; Chen, Q.; Chen, G. The conditions and modelling of hydrocarbon accumulation in tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study from the Jurassic Shaximiao formation of western Sichuan Basin, China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 225, 211702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Song, J.; Bai, D. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and accumulation stages of Sinian Dengying Formation in Penglai Area, central Sichuan. Unconv. Oil Gas 2023, 10, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.H. Fluid inclusion in the sedmentary and diageneticsystems. Liths 2001, 55, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Liu, Z.; Qu, L.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q. Jurassic hydrocarbon accumulation period division in Huanjiang oilfield: Evidence from fluid inclusions. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2025, 37, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyser, K.; Hiatt, E.E. Fluid in sedmentary basin: Anintrocduction. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 80, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M. Parameters Influencing Porosity in Sandstones: A Model for Sandstone Porosity Prediction. AAPG Bull. 1987, 71, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, D.C.; Weyl, P.K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand. AAPG Bull. 1973, 57, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Tan, X.; Tu, L.; Zeng, Q.G.; Liu, S.B.; Liu, H.L.; Liu, W. Control factors and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoir of the Second Member of Shaximiao Formation in the transition zone between central and western Sichuan Basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2020, 47, 460–471. [Google Scholar]
- Athy, L.F. Density, Porosity and Compaction of Sedimentary Rocks. AAPG Bull. 1930, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z. Further understandingof differential accumulations of oil and water in tight sandstones withlimited charging power: A case study of Chang 8 member in Huachiarea, Ordos Basin, China. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar]



| Well Location | Drilling Depth | Average Porosity /% | Total Cement Content /% | Primary-to-Secondary Porosity Ratio | Primary Porosity | Compaction-Reduced Porosity | Secondary Porosity | Compaction Porosity Loss | Compaction Porosity Reduction Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY-1 | 5550.00 | 8.13 | 8.10 | 0.72 | 5.85 | 13.95 | 2.28 | 24.05 | 63.29 |
| XC-7 | 5190.00 | 10.50 | 4.86 | 0.75 | 7.88 | 12.74 | 2.63 | 25.27 | 66.49 |
| CG-561 | 4985.50 | 8.19 | 5.10 | 0.74 | 6.06 | 11.16 | 2.13 | 26.84 | 70.62 |
| X-11 | 4949.00 | 9.16 | 5.39 | 0.55 | 5.04 | 10.43 | 4.12 | 27.57 | 72.55 |
| XC-12 | 4790.00 | 6.43 | 6.12 | 0.55 | 3.54 | 9.66 | 2.89 | 28.34 | 74.59 |
| GM-2 | 5068.00 | 8.67 | 3.99 | 0.60 | 5.20 | 9.19 | 3.47 | 28.81 | 75.81 |
| X-5 | 4948.00 | 7.72 | 4.04 | 0.45 | 3.47 | 7.51 | 4.25 | 30.49 | 80.23 |
| X-203 | 5067.00 | 7.90 | 2.81 | 0.55 | 4.35 | 7.16 | 3.56 | 30.85 | 81.17 |
| L-150 | 4860.00 | 8.48 | 3.41 | 0.28 | 2.37 | 5.78 | 6.11 | 32.22 | 84.78 |
| CX-93 | 4836.00 | 7.79 | 3.88 | 0.24 | 1.87 | 5.75 | 5.92 | 32.25 | 84.87 |
| Well Location | Horizon | Carbonate Cement Content/% | Siliceous Cement Content/% | Chlorite Cement Content/% | Total Cement Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY-1 | XU2 | 3.80 | 1.64 | 2.66 | 8.10 |
| XC-7 | XU2 | 0.88 | 1.10 | 2.88 | 4.86 |
| CG-561 | XU2 | 2.32 | 0.37 | 2.41 | 5.10 |
| X-11 | XU2 | 2.92 | 1.10 | 1.37 | 5.39 |
| XC-12 | XU2 | 3.69 | 1.54 | 0.89 | 6.12 |
| GM-2 | XU2 | 2.82 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 3.99 |
| X-5 | XU2 | 1.93 | 1.34 | 0.77 | 4.04 |
| X-203 | XU2 | 1.23 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 2.81 |
| L-150 | XU2 | 1.98 | 1.33 | 0.10 | 3.41 |
| CX-93 | XU2 | 2.55 | 1.23 | 0.10 | 3.88 |
| Well Location | Horizon | Primary Porosity Proportion/% | Primary Porosity/% | Secondary Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY-1 | XU2 | 72 | 5.85 | 2.28 |
| XC-7 | XU2 | 75 | 7.88 | 2.63 |
| CG-561 | XU2 | 74 | 6.06 | 2.13 |
| X-11 | XU2 | 55 | 5.04 | 4.12 |
| XC-12 | XU2 | 55 | 3.54 | 2.89 |
| GM-2 | XU2 | 60 | 5.20 | 3.47 |
| X-5 | XU2 | 45 | 3.47 | 4.25 |
| X-203 | XU2 | 55 | 4.35 | 3.56 |
| L-150 | XU2 | 28 | 2.37 | 6.11 |
| CX-93 | XU2 | 24 | 1.87 | 5.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, M.; Wang, J.; Gao, H. Pore Diagenetic Evolution and Its Coupling Relationship with Natural Gas Accumulation in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan. Minerals 2025, 15, 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101052
Li Z, Liu S, Bi Y, Li J, Deng M, Wang J, Gao H. Pore Diagenetic Evolution and Its Coupling Relationship with Natural Gas Accumulation in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zongze, Sibing Liu, Youyi Bi, Junqi Li, Meizhou Deng, Jinxi Wang, and Hengyi Gao. 2025. "Pore Diagenetic Evolution and Its Coupling Relationship with Natural Gas Accumulation in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101052
APA StyleLi, Z., Liu, S., Bi, Y., Li, J., Deng, M., Wang, J., & Gao, H. (2025). Pore Diagenetic Evolution and Its Coupling Relationship with Natural Gas Accumulation in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang Area, Western Sichuan. Minerals, 15(10), 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101052





