Adsorption Characteristics of Praseodymium and Neodymium with Clay Minerals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Adsorption Experiment
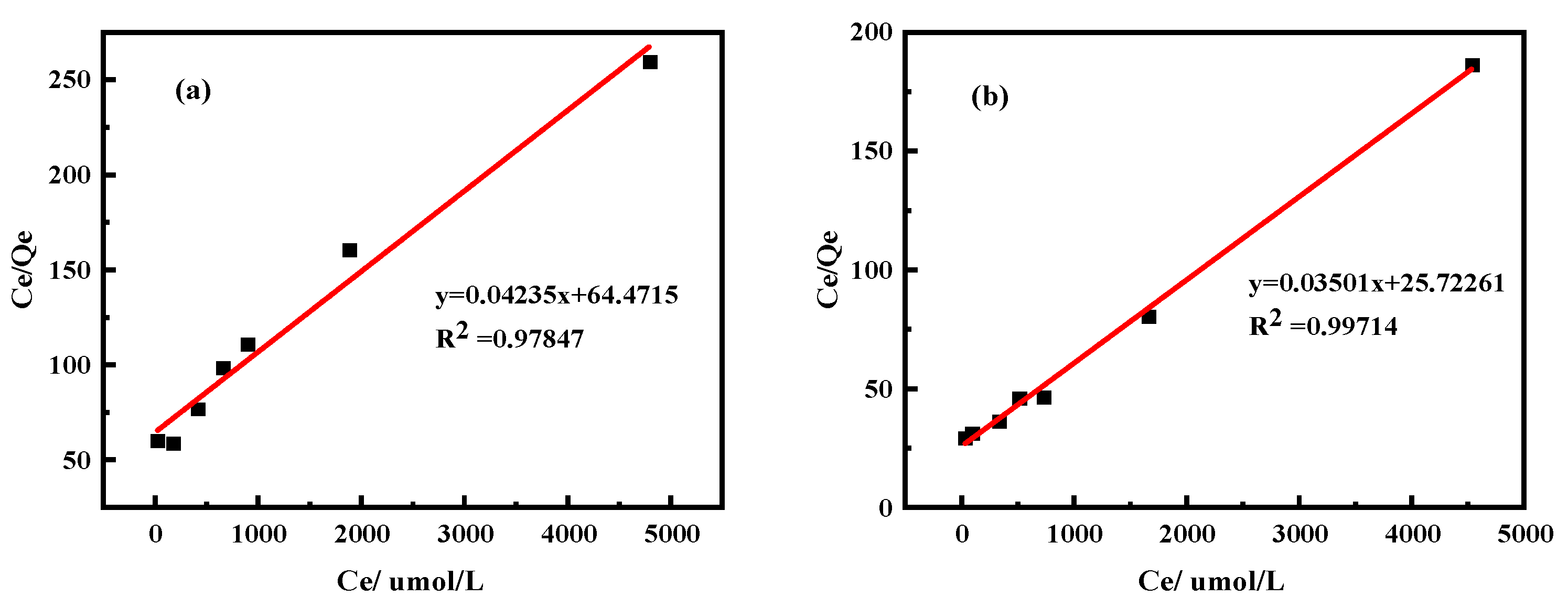
2.2.2. Isothermal Adsorption Model
2.2.3. Quantum Chemical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clay Mineral Composition and Content
3.2. Effects of Initial Solution Concentration on Adsorption Process
3.2.1. Effects of Kaolinite and Halloysite on Pr Adsorption Properties
3.2.2. Effects of Kaolinite and Halloysite on Nd Adsorption Properties
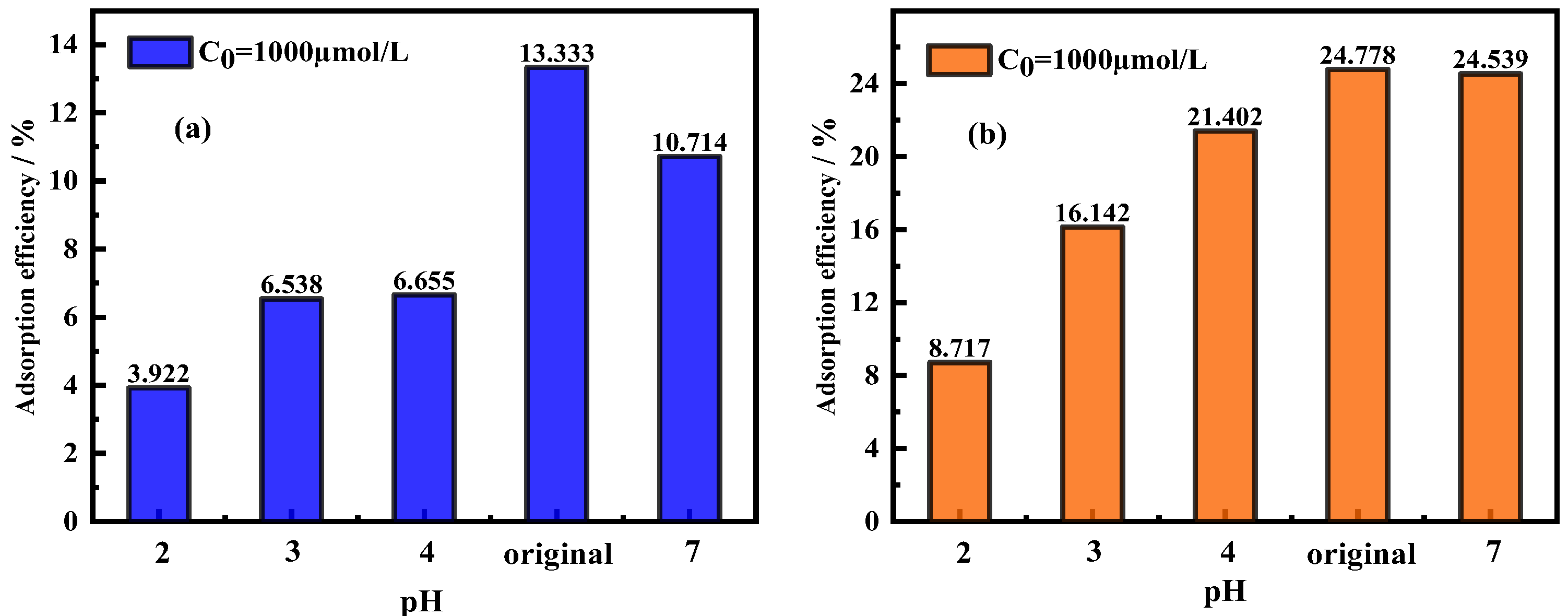
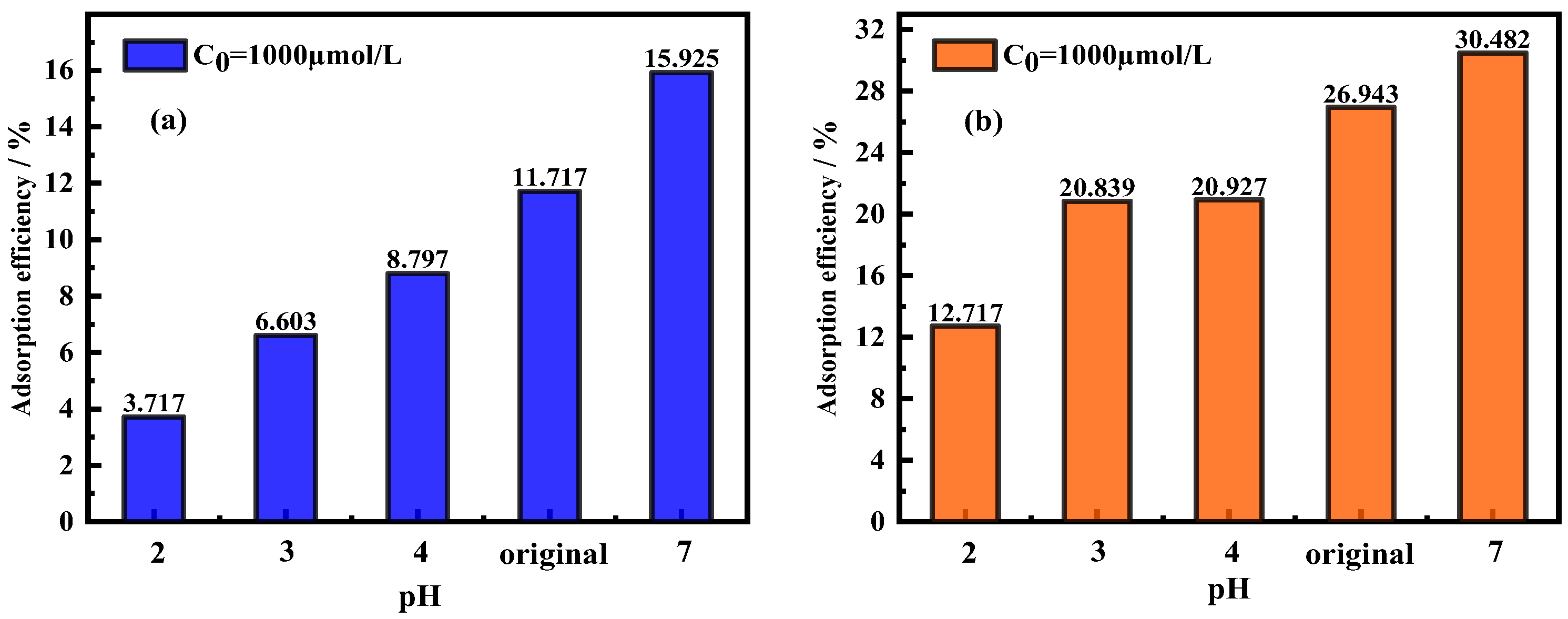
3.3. Effects of pH on Adsorption Efficiency/Adsorption Capacity
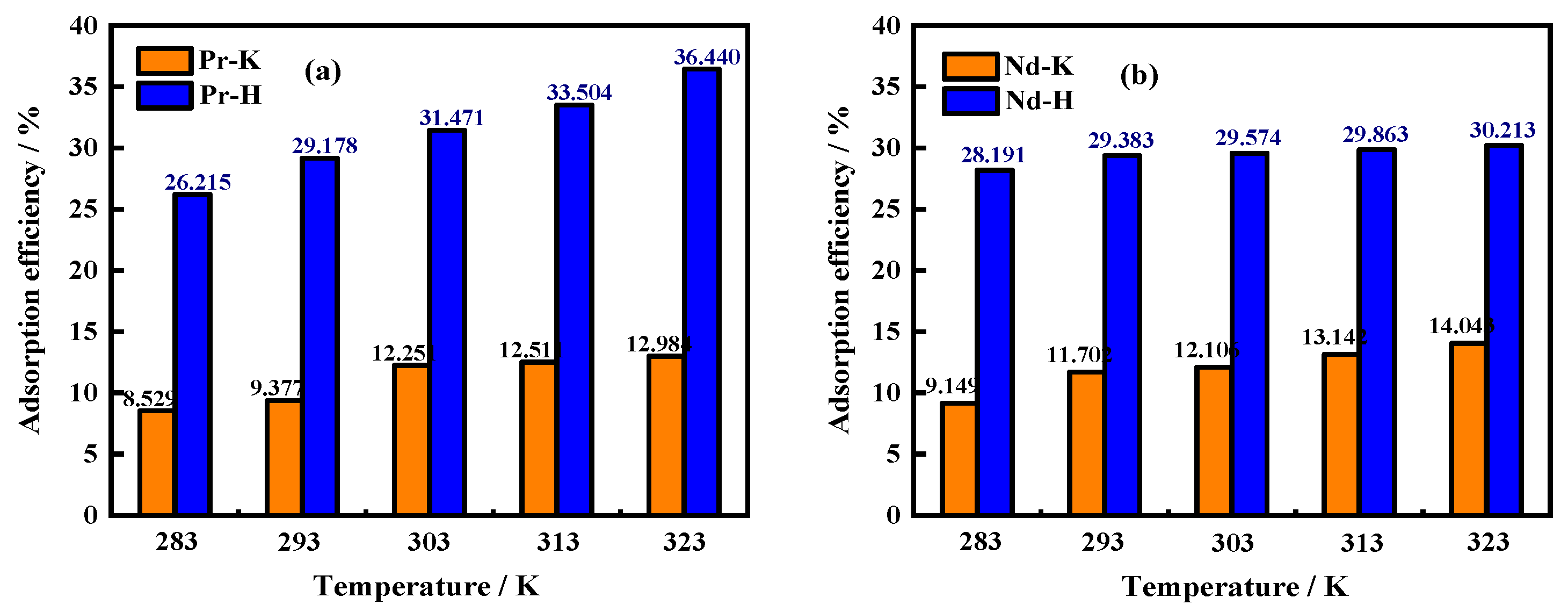
3.4. Effects of Temperature on Adsorption Efficiency/Adsorption Capacity
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism of Rare Earth Elements with Clay Minerals
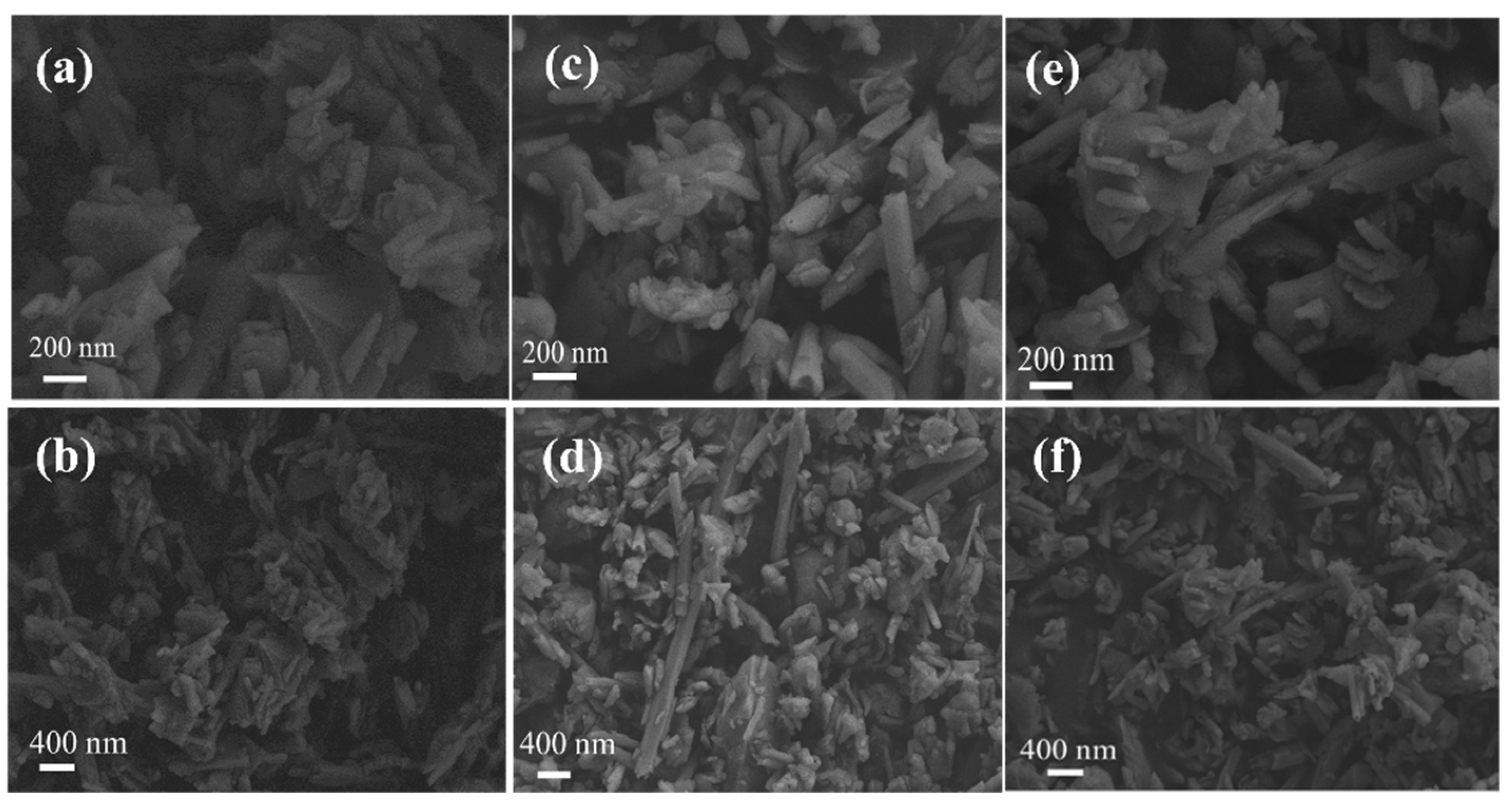
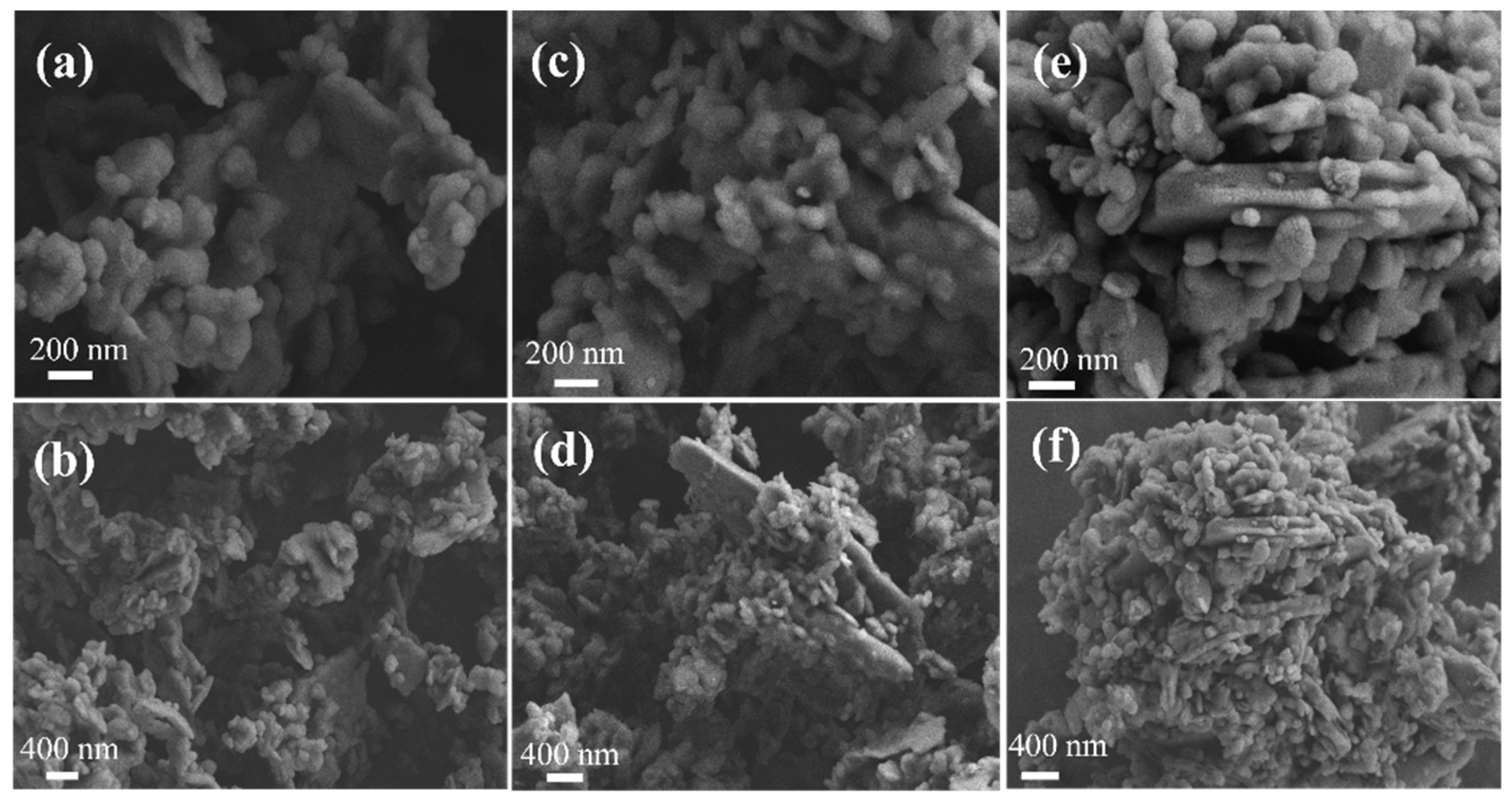
3.5.1. SEM Analysis Results of Adsorption Process
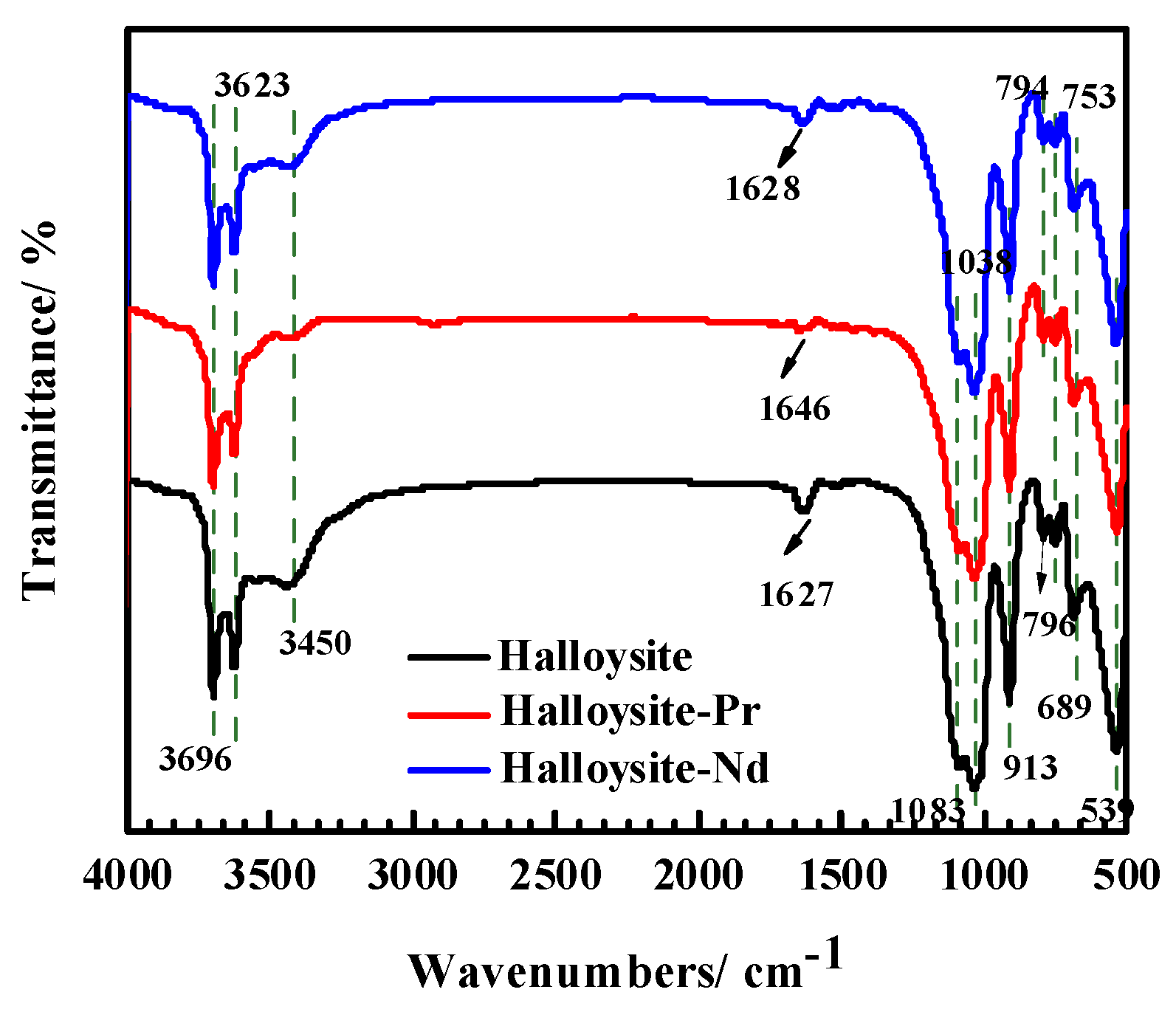
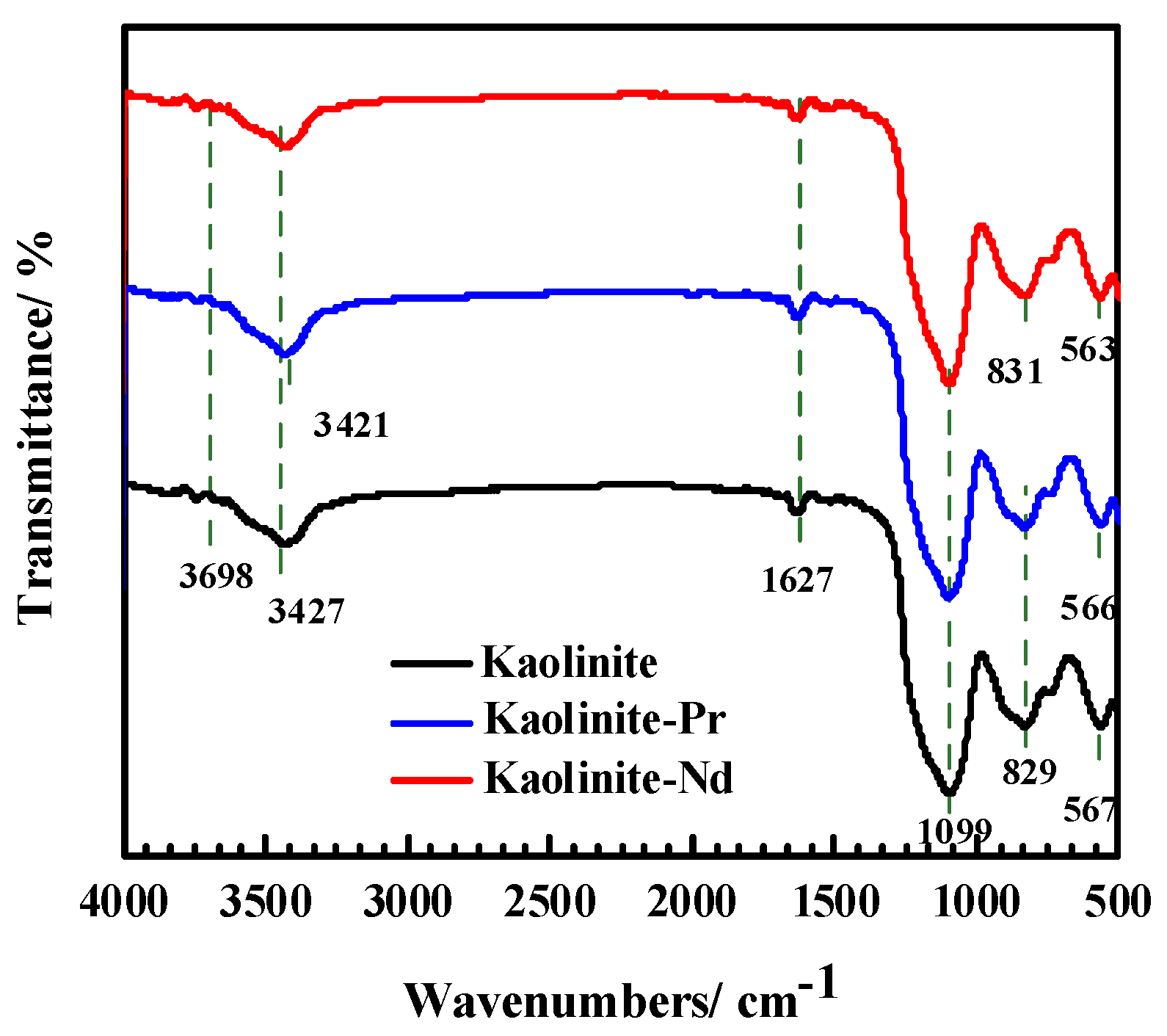
3.5.2. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis Results of Adsorbents
3.5.3. Quantum Chemical Analysis Results of Adsorption Process
3.5.4. Model of the Microscopic Adsorption Structure of Pr and Nd by Kaolinite and Halloysite
3.6. The Relation Between the Adsorption Recovery and Rare Earth Resource Perspective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.J.; Lin, A.; Li, X.L.; Wu, Y.D.; Zhou, W.B.; Chen, Z.H. China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Yan, G.H.; Yuan, H.T.; Zhang, M.R.; Zhang, B. A novel method for low-rank coal drying using steam transient flash evaporation. Fuel 2023, 354, 129238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhao, K.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Xu, S.X.; Liang, Z.P.; Wu, K. Adsorption of La3+ and Ce3+ by poly-γ-glutamic acid crosslinked with polyvinyl alcohol. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, K.M.; Wall, F.; Merriman, D. The rare earth elements: Demand, global resources, and challenges for resourcing future generations. Nat. Resour. Res. 2018, 27, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, R.M.; Izatt, S.R.; Bruening, R.L.; Izatt, N.E.; Moyer, B.A. Challenges to achievement of metal sustainability in our high-tech society. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2451–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.H.; Jiménez-Villacorta, F. Perspectives on permanent magnetic materials for energy conversion and power generation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilburn, D.R. Wind Energy in the United States and Materials Required for the Land-Based Wind Turbine Industry from 2010 Through 2030; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Xiao, Y.F.; Feng, Z.Y.; Hu, G.H.; Huang, L.; Huang, X.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, M.L. Leaching and mass transfer characteristics of elements from ion-adsorption type rare earth ore. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.X.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.Q.; Yu, J.X.; Chi, R.A. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of clay minerals on NH4+ in the leaching agent of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. China Min. Mag. 2021, 30, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.X.; Qin, L.; Wang, G.S.; Luo, S.H.; Peng, C.L.; Li, Q. Metallogenic process of ion adsorption REE ore based on the occurrence regularity of La in kaolin. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, Z.L. Adsorption of La3+, Nd3+ and some heavy metal ions by humic acid in amulti-metal-ion system. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 816–821. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.F. Study on the Green and Efficient Leaching Technology for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earths Ore with Magnesium Salt System; Northeastern University: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.F.; He, X.L.; Liao, C.F.; Jiang, P.G. Studies on the sorption of amino methylene phosphonic acid resin for heavy rare earth metals. Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 2009, 25, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.J.; Liang, X.L.; Ma, L.Y.; Huang, J.; He, H.P.; Zhu, J.X. Adsorption of REEs on kaolinite and halloysite: A link to the REE distribution on clays in the weathering crust of granite. Chem. Geol. 2019, 525, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SY/T 5163-2010[S]; X-Ray Diffraction Analysis Methods for Clay Minerals and Common Non-Clay Mineral in Sedimentary Rocks. Oil and Gas Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Xue, W.L.; Li, F.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.Y.; Huang, B.B. Mixing soil with bentonite to amend its microstructure and permeability. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Wang, Z. Research evolvement of treatment technology of Pb2+ in water with clay mineral. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2009, 37, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.J. Structure and Physical-Chemistry Property Evolution of Heat-Treatment Palygorskite as Well as Adsorption for Phosphorus; Hefei University of Technology: Hefei, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.N.; Cai, Y.T.; Yang, P.J.; Chang, K.K. Ferric oxide on U(VI) adsorption. Biol. Chem. Eng. 2016, 2, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Coppin, F.; Berger, G.; Bauer, A.; Castet, S.; Loubet, M. Sorption of lanthanides on smectite and kaolinite. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, A.F.; Fernandes, A.C.; Pereira, C.; Pires, J.; Freire, C. Physicochemical characterization of organosilylated halloysite clay nanotubes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 219, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hong, S. Application of oxalic acid cross-linking activated alumina/chitosan bio composites in defluorination from aqueous solution. Investigation of adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Wu, H.D.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yao, P.K.; Zhang, Q.P. Intercalation-hydrothermal preparation of submicron 13X zeolite with coal-measure kaolin. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 37, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.S.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, W.; Ning, P. Surface modification of long-chain alkyl silane on hnts. Silicone Mater. 2011, 25, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Kang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ding, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.F. Effect of Kaolinite Particle Size on lts Crystal Structure and Thermal Evolution Behaviors. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 38, 3964–3971. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, S.J.; Segall, M.D.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Probert, M.I.J.; Refson, K.; Payne, M.C. First principles methods using CASTEP. Z. Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 2005, 220, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T. First-Principles Study on Microstructures and Elastic Properties of Clay Mineral; Taiyuan University of Technology: Taiyuan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.S.; Lai, Y.M.; Peng, C.L. Adsorption of rare earth yttrium and ammonium ions on kaolinite surfaces: A DFT study. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2018, 137, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
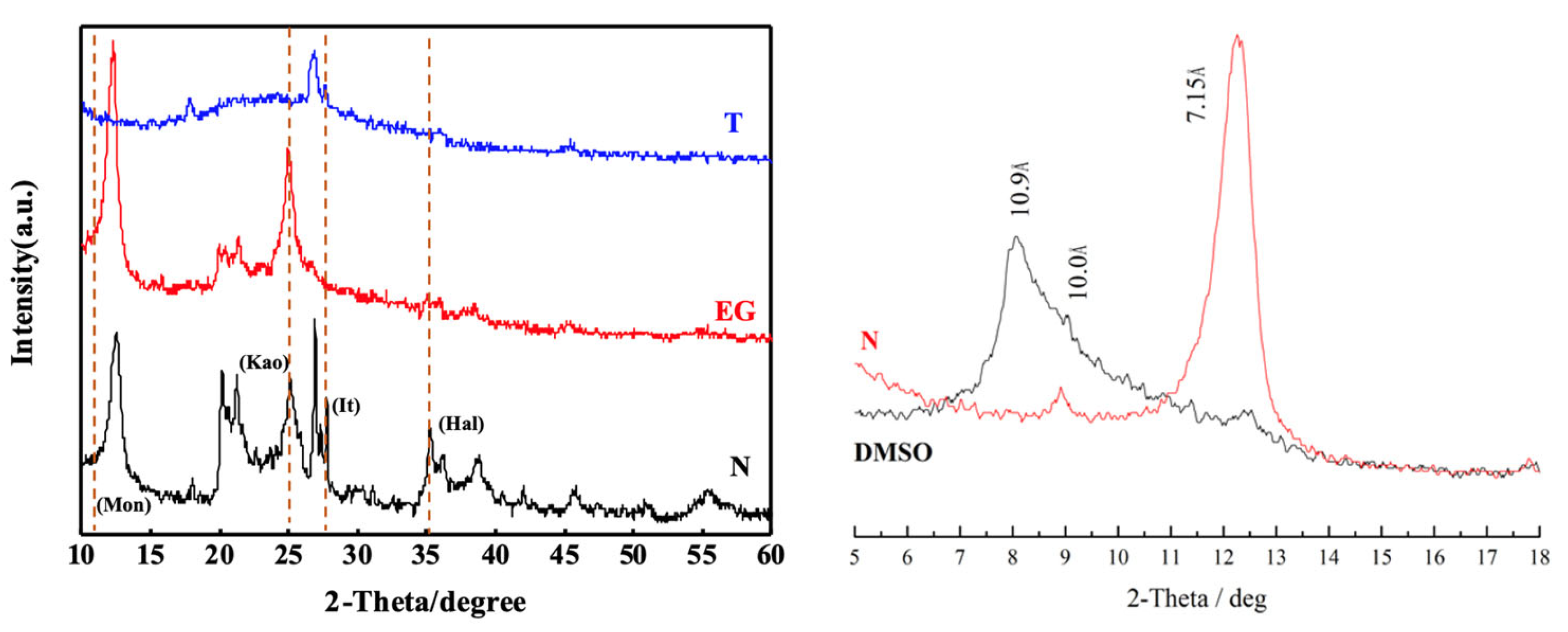
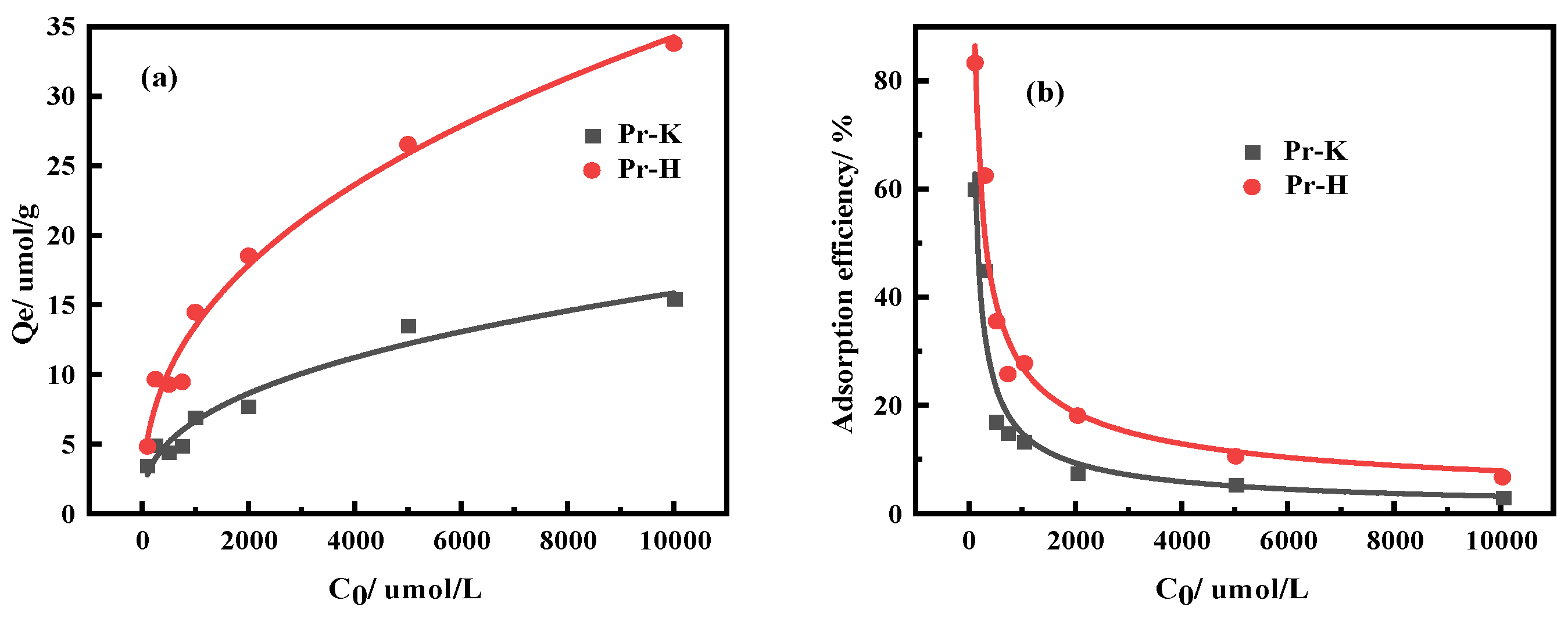
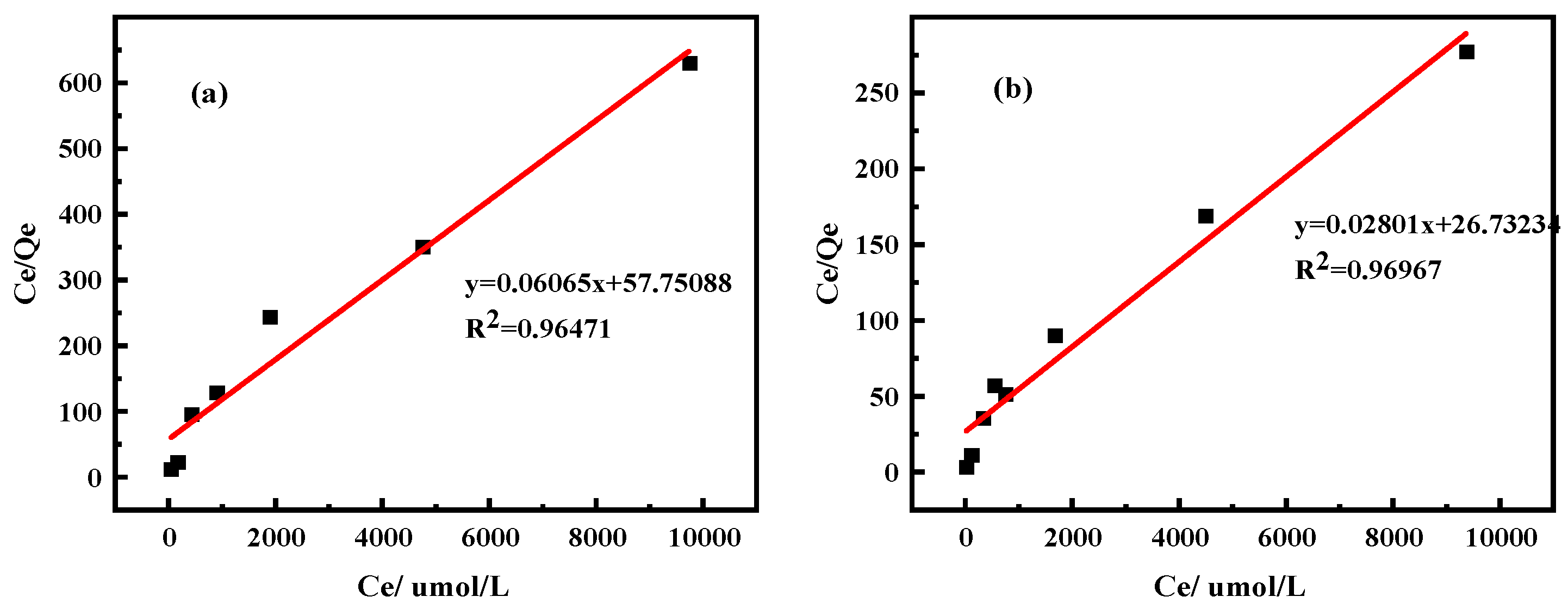
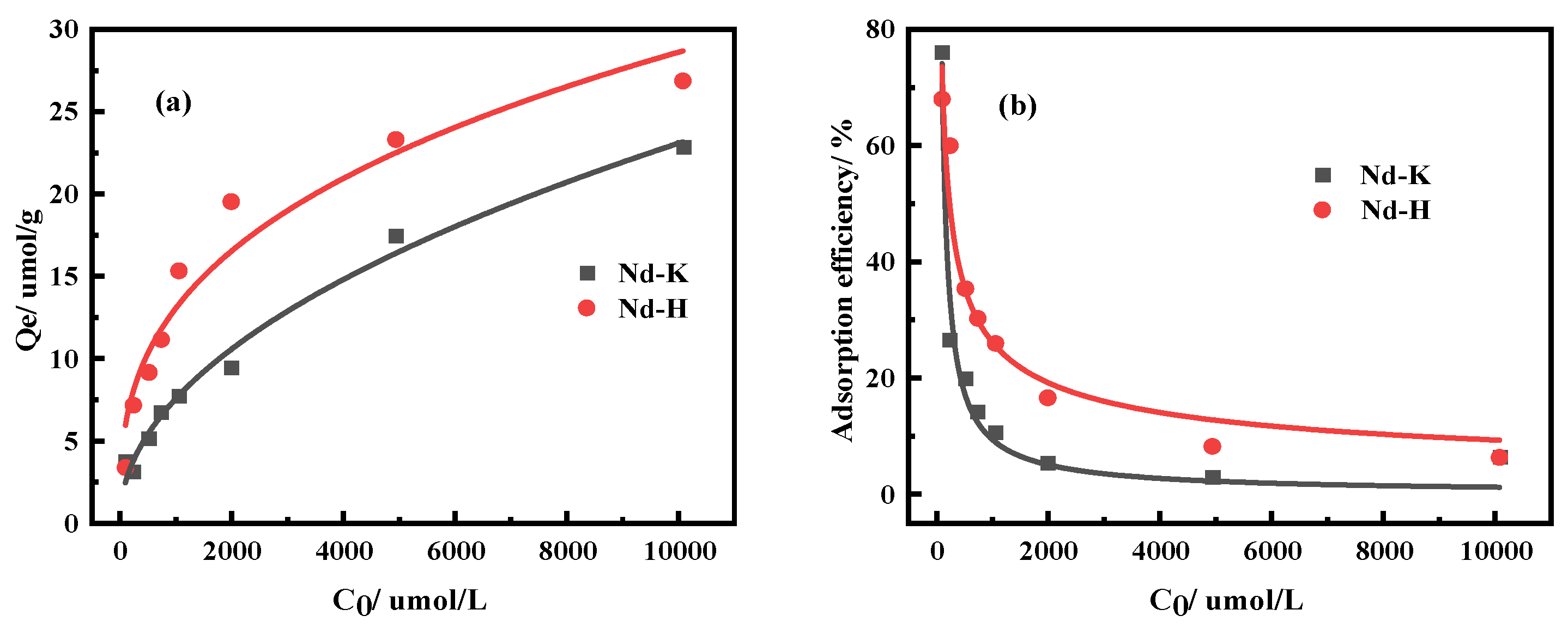

| Ingredient | REO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MnO | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.12 | 66.23 | 18.14 | 0.13 | 4.21 | 0.57 |
| Ingredient | CaO | TiO2 | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Loss |
| Content | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 1.60 | 0.6 | 7.1 |
| Specimen | Kaolinite | Halloysite | Illite | Montmorillonite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ledge | 25.06 | 65.78 | 8.13 | 1.03 |
| Equations | Freundlich Equation | Langmuir Equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In KF | 1/n | R2 | 1/(QmaxKL) | Qm(µmol/g) | R2 | ||
| Clay minerals | Kaolinite | 0.083 | 0.269 | 0.607 | 57.751 | 16.488 | 0.965 |
| Halloysite | 0.590 | 0.311 | 0.937 | 26.732 | 35.702 | 0.970 | |
| Equations | Freundlich Equation | Langmuir Equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In KF | 1/n | R2 | 1/(QmaxKL) | Qm(µmol/g) | R2 | ||
| Clay minerals | Kaolinite | −0.091 | 0.292 | 0.558 | 64.471 | 23.613 | 0.978 |
| Halloysite | 0.177 | 0.358 | 0.951 | 25.723 | 28.571 | 0.997 | |
| Single Atoms | Model 1: Kaolinite (001) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atom | Etot (eV) | Adsorbate | Etot (eV) | Eads (eV) |
| Pr | −0.157 | Pr | −737.186 | −13.28 |
| Nd | −0.156 | Nd | −737.295 | −13.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Chi, R.; Zhang, Z. Adsorption Characteristics of Praseodymium and Neodymium with Clay Minerals. Minerals 2025, 15, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101051
Chen Z, Wang H, Chi R, Zhang Z. Adsorption Characteristics of Praseodymium and Neodymium with Clay Minerals. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101051
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhuo, Han Wang, Ruan Chi, and Zhenyue Zhang. 2025. "Adsorption Characteristics of Praseodymium and Neodymium with Clay Minerals" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101051
APA StyleChen, Z., Wang, H., Chi, R., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Adsorption Characteristics of Praseodymium and Neodymium with Clay Minerals. Minerals, 15(10), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101051








