Abstract
The study of the influence of microorganisms on the formation of deep- and shallow-water ore deposits is a promising topic in environmental science. This problem, along with the role of organic matter in the growth of Fe-Mn nodules, remains understudied. This study focuses on the analysis of the composition and content of fatty acids in fast-growing Fe-Mn deposits and underlying sediments from various regions of the Kara Sea. Fatty acids serve as important biomarkers of diagenetic processes and reflect the different origins of organic matter. This work is based on the results of lipid extract analysis using GC–MS. Various sources of fatty acids were identified, including plankton, bacteria, terrestrial plants, and detrital material. It was found that FA content depends on the size of the nodules. Compared to underlying sediments, Fe-Mn nodules are enriched in FAs of bacterial and detrital origin, with SAFAs > MUFAs and a negligible content of PUFAs.
1. Introduction
Deep-sea ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts are of great interest to scientists and industries due to their potential as a source of valuable metals and rare earth elements. These polymetallic mineral deposits can be found on the ocean floor in areas with very low sedimentation rates, such as the pelagic zones and submarine outcrops of the Pacific and Eastern Indian Oceans [1,2,3,4]. The growth rate of deposits is extremely slow, ranging from just a few millimeters to a few centimeters over millions of years, depending on their origin. Several theories have been proposed regarding the genesis of Fe-Mn nodules, each considering different metal sources: (1) the hydrogenetic precipitation of metals from cold ambient water; (2) oxic/suboxic diagenesis from sediment-pore fluids; and (3) the precipitation of Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides directly from hydrothermal solutions [1,5,6,7,8].
However, the current view on the genesis of Fe-Mn deposits does not take into account the processes that lead to the rapid formation of nodules in shallow-water continental margin areas. These shallow-water deposits are mainly located at depths of up to 300 m and grow about 1000 times faster than their deep-sea analogs [9,10,11].
The idea that microbial activity affects the formation of ferromanganese deposits is increasingly gaining support [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Microorganisms play a crucial role in diagenesis, impacting iron and manganese mineralization. Some prokaryotes can oxidize Fe2+ and Mn2+ and use them as a source of energy. Others can reduce Fe3+ and Mn4+ as terminal electron acceptors in electron transfer chains [27,28]. The ability of microorganisms to both oxidize and reduce metals is essential for understanding the complex processes of Fe-Mn nodule formation.
Driven by the supply of organic matter (OM), diagenetic processes control the element redistribution in the Fe-Mn nodule formation environment [29,30]. Manganese minerals facilitate the transition of stable OM compounds into bioavailable low-molecular components [31]. Many trace elements are capable of forming complex, chelate, and clathrate compounds with the products derived from the incomplete decomposition of OM. Microorganisms and various components of OM in the ocean are part of an integrated biogeochemical system. This system combines a range of interconnected physical, chemical, and biochemical processes, such as sorption and desorption, extracellular hydrolysis of organic macromolecules, and the resynthesis of organic and organic-mineral compounds [29,32].
So far, only a few studies have examined biomarkers in the Fe-Mn deposits [13,33,34,35,36,37]. Biomarkers reflect environmental factors that determine the intensity of biosynthesis and various stages of OM transformation [38].
Fatty acids (FAs) are a significant component of the lipid fraction of OM. Many studies have utilized FAs to estimate the relative contribution of planktonic, bacterial, and terrestrial components to the composition of OM [39,40,41,42,43]. Their prevalence in living organisms, specific origins in terms of individual compounds, and relative lability make FAs effective biomarkers for studying the origins and diagenetic transformation of OM in water column, sediments, and ore deposits lying on the water–sediment interface. The content and composition of individual FAs in the fast-growing Fe-Mn nodules have not been studied previously in the Arctic region.
This work focuses on the qualitative and quantitative analyses of FAs to assess source signatures of OM in the Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and underlying sediments. The term ‘Fe-Mn crust’ in this paper refers to the morphology of samples, and it does not correspond to the classic crusts on oceanic seamounts. The results provide valuable insights into the biogeochemical processes that occur during the formation of fast-growing Fe-Mn deposits in the Kara Sea. This study demonstrates that the formation of ore deposits on the sea floor should be considered as part of global biogeochemical cycles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regional Settings
The Kara Sea is a high-Arctic epicontinental sea lying along the northern shore of Siberia between the Taimyr Peninsula, the Novaya Zemlya, and the Severnaya Zemlya archipelagos (Figure 1). Its depth reaches a maximum of 620 m and averages 118 m. The most prominent morphological features are the East Novaya Zemlya Trough and Saint Anna Trough, with depths over 500 m. The Saint Anna Trough is a main pathway for water, sediment, and ice exchange between the Arctic Ocean, the Barents Sea, and the Kara Sea. The annual river runoff into the Kara Sea is 1100–1350 km3 (including the Ob and Yenisei runoff of 400–450 and 600–630 km3, respectively). These two rivers discharge up to 13.2 and 15.8 million tons of sediment matter annually [44]. Their discharge shows a strong seasonal variability and controls the sedimentation, biological productivity, and hydrological structure in the southern part of the sea. The surface currents demonstrate a cyclonic pattern, driven by the prevailing winds. Deeper portions of the water column are influenced by water mass exchange with the Arctic Ocean and the Barents and Laptev Seas [45]. The Kara Sea, in contrast to the Barents Sea, is completely covered by ice during winter and spring [46].
2.2. Field Sampling
Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and underlying sediments were collected during the research cruise 76 of the RV Akademik Mstislav Keldysh and cruises 128 and 129 of the RV Professor Shtokman (2014, 2015, and 2019). Samples were obtained from four different regions of the Kara Sea with different environmental conditions: open sea (site PSh128-35), inner shelf region with negligible freshwater inflow to the west of the Yamal Peninsula (sites AMK76-6258, AMK76-6259, PSh129-40, and PSh129-64), Stepovoy Bay of the Novaya Zemlya archipelago (site PSh128-64), and the St. Anna Trough (sites AMK76-6236 and AMK76-6238) (Figure 1). Nodule samples were collected using a trawl or box corer. Underlying sediments and crust were obtained using a box corer. The coordinates of the sampling sites and sample descriptions are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
The coordinates and depths of Kara Sea sampling sites and sample descriptions.
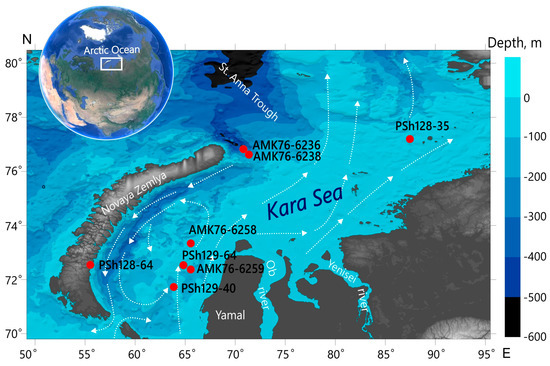
Figure 1.
The bathymetric map of the Kara Sea (GEBCO, 2022) with the location of the sampling sites (red dots) and directions of surface currents (white arrows); the surface circulation shown in the figure was derived from [45].
2.3. Sample Storage and TOC Analysis
Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and sediment samples were frozen onboard at −21 °C prior to being freeze-dried on land. The bulk nodules (3 samples), the individual samples of small (S, 3–5 cm in diameter), medium (M, 5–8 cm), and large (L, >8 cm in diameter) sizes (13 samples), and the underlying sediments (2 samples) were studied (see sample descriptions in Table 1). Dried samples were ground using a mortar and pestle.
Total organic carbon (TOC) was measured on a Shimadzu L-VPH and was determined on decalcified (acidification with 10% HCl) samples. The instrument was calibrated using the standard SDO-2 for sediments and the standard SDO-4 for nodules [47].
2.4. Lipid Extraction and GC–MS
The freeze-dried samples (10–20 g) were ground, homogenized, and subjected to extraction under ultrasonication with a dichloromethane/methanol mixture (9:1, v/v). The total lipid extract (TLE) was purified from sulfur using activated copper. Subsequently, TLE was separated into three fractions using column chromatography with silica gel and elution with hexane/DCM (2:1, v/v; non-polar fraction), DCM/MeOH (1:1, v/v; polar fraction), and MeOH (phospholipid fraction). This paper presents only the results of the analysis of the polar fraction, which contains fatty acids.
Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs): The aliquot of the sample (polar fraction) was evaporated to dryness under a stream of nitrogen. A portion of BF3/MeOH (5 drops) was added, vortex-mixed, and heated for 1 h at 60 °C. A known amount of 2-methyloctadecanoic acid (i-C19 FA) was added to the aliquot as an internal standard prior to derivatization. After cooling the mixture, distilled water and hexane were added. The mixture was then vortexed to neutralize the BF3 and to get of FAMEs into the non-polar solvent. After allowing the layers to settle, the hexane phase with FAMEs was collected. A reagent blank was prepared along with the samples to identify possible contaminations.
GC–MS analyses were performed using a Shimadzu TQ-8040 with a Rxi-5Sil MS 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm capillary column. The temperatures were programmed as follows: the oven temperature was held at 70 °C for 1 min, heated to 130 °C at 20 °C /min, heated to 320 °C at 4 °C /min, and then held at the latter temperature for 10 min. A splitless injection mode was used. The carrier gas was helium, with a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The analysis was performed using a total scan from m/z 50 to 650 (70 eV). The identification and quantification of FAs were made based on the retention times of the calibration mixture (Supelco CRM47885 37 Component FAME Mix, Supelco 47080-U BAME Mix). The concentrations of individual FAs were reported in μg/g of the dry sample. The analytical precision of repeated sample analyses for fatty acids averaged ±15%.
For a detailed description of the internal structures and mineral and element composition of the studied samples, see [13,48,49].
3. Results
3.1. Fe-Mn Nodules and Crusts
TOC content in nodules varied from 0.26 to 1.04% (0.55% on average) and was lower than in the underlying sediments (1.24–1.44%) (Table 2).

Table 2.
The concentration of total organic carbon (%) and grouped FAs (µg/g dry weight and %) in nodules and underlying sediments from the Kara Sea.
The FA compositions of the studied samples are presented in Table 2. Total fatty acid (TFA) concentrations in the nodule and crust samples ranged from 0.78 to 4.73 µg/g of dry weight (Figure 2A and Table 2). The TFA concentration in nodules is the highest in samples of L size from sites AMK76-6258 (4.34 µg/g dw) and AMK76-6259 (4.73 µg/g dw).
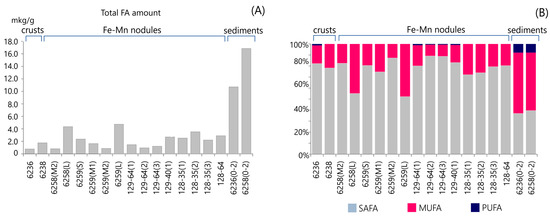
Figure 2.
The distribution of the amount of total fatty acids in Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and underlying sediments from the Kara Sea (A). Relative abundance of saturated (SAFAs), monounsaturated (MUFAs), and polyunsaturated (PUFAs) fatty acids (B).
FAs were identified in a range of C10–C24 and include three groups: saturated (SAFA), monounsaturated (MUFA), and polyunsaturated (PUFA) compounds. The same fatty acids generally occurred in all samples but in different quantities (Table 2 and Figure 2B and Figure 3). In all studied samples, SAFAs and MUFAs, especially those with 14, 16, and 18 carbon atoms, were dominant.
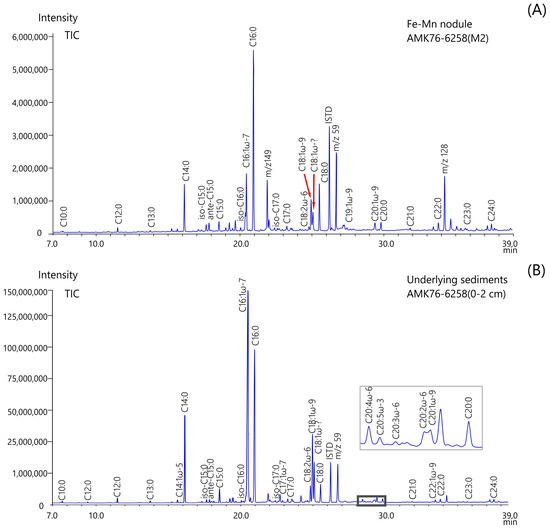
Figure 3.
The gas chromatograms of fatty acid methyl esters extracted from Fe-Mn nodules (A) and underlying sediments (B) collected from site AMK76-6258.
SAFAs are the most abundant group of fatty acids (78%) among all studied nodule and crust samples, with the exception of L samples with a SAFA content of approximately 53%. C14, C16, and C18 are the principal saturated fatty acids, with values of 10%–21%, 33%–58%, and 7%–17%, respectively (Table S1).
The branched fatty acid (iso-, anteiso-C15, iso-C16, and iso-C17) content varied significantly among samples, with a range of 3%–8% of the total fatty acids (Table S1), with the exception of site AMK76-6238, where the concentration of branched acids in the studied crusts reached 21%.
The MUFA concentration varied from 0.10 to 2.25 µg/g dw (Table 2). The proportion of MUFAs in the total fatty acid concentration varied considerably between sites and samples depending on their size (Figure 2B and Table 2). The major contribution to the content of these acids comes from 16:1ω-7 (4%–64%) and 18:1ω-9 (16–83%) (Table S1). The L-sized nodule samples had the highest concentration of MUFAs (45% and 48%, respectively) and were dominated by 16:1ω-7. The sites PSh129-64 and PSh129-40 are noteworthy, where the composition of monounsaturated acids, unlike other sites, was dominated by 18:1ω-9 (Table S1).
The contribution of PUFAs to the total fatty acid concentration was negligible in nodules and crusts (<1.4%) (Figure 2B and Table 2). PUFAs were identified in samples from sites AMK76-6236, PSh129-64, and PSh129-40 and included only C18:2ω-6(cc) (Table S1).
No hydroxy-fatty acids were detected in any of the studied samples.
3.2. Underlying Sediments
The content of TFAs in the sediments was significantly higher than the contribution of MUFAs and PUFAs to nodules and crusts (Figure 2A). Its value reached 10.7 µg/g on site AMK79-6236 and 16.8 µg/g on site AMK76-6258 (Table 2). MUFAs were the predominant group of fatty acids (54% mean), with a maximum concentration of 16:1ω-7 and 18:1ω-9. PUFAs were represented by different components and comprised 8% of TFAs (Table S1). The content of saturated acids was half as low in the sediments than in the ore deposits. In general, the distribution of SAFAs dominated by C14, C16, and C18 was similar in sediments and nodules.
4. Discussion
The analysis of the nodules revealed different origins of FAs: planktonic, bacterial, terrestrial, and detrital (Figure 4). The contribution of phytoplankton (including diatoms, dinoflagellates, and macroalgae) is reflected in specific FA profiles observed. It has been suggested that these FAs were initially accumulated in the sediments due to the vertical settling of OM and were then embedded in nodules during the growth of the latter.
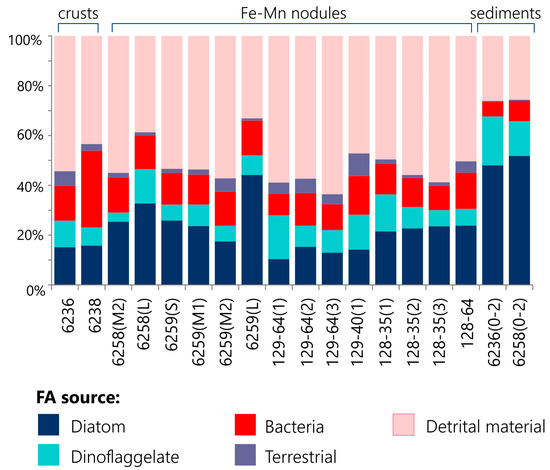
Figure 4.
The relative abundance of fatty acids derived from plankton, bacteria, terrestrial plants, and detrital material in Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and underlying sediments from the Kara Sea.
Diatoms are rich in C14:0, C16:1ω-7, C20:4ω-6, and C20:5ω-3; dinoflagellates produce C18:1ω-9 and C22:6ω-3; and C18:2ω-6, C18:3ω-3, C18:3ω-6, and C18:1ω-7 are synthesized by macroalgae [43,50,51,52]. Planktonic organisms exert a significant influence on the FA composition in studied nodules and crusts (>20%) (Figure 4 and Table 2). A high level of C16:1ω-7 FAs indicates a predominant role of diatoms in the samples. It has also been reported that phytoplankton undergoes intra-seasonal and inter-annual variations, and on certain occasions, dinoflagellates may contribute more than diatoms [53,54]. This may be the reason for the dominance of C18:1ω-9 FAs on sites PSh129-64 and PSh129-40 (Table S1).
Bacteria produce odd-numbered carbons and iso- and anteiso-branched FAs such as C18:1ω-7, C15:0, iso-C15:0, ante-C15:0, C17:0, iso-C17:0, ante-C17:0, which include trans-monounsaturated acids [39,55,56,57,58,59]. Branched FAs are commonly used as specific markers of bacterial involvement in the organic matter connected to suspended particles or sediments [39,60,61]. They do not participate in the vegetal or animal metabolisms of marine or freshwater organisms [55]. The concentration of bacterially derived components in the Fe-Mn nodules and crusts varied significantly (from 0.10 to 0.62 μg/g dw) (Table 2 and Figure 5). The results indicate an increase in bacterial input during the growth of the nodules (L-sized nodules from sites AMK76-6258 and AMK76-6259).
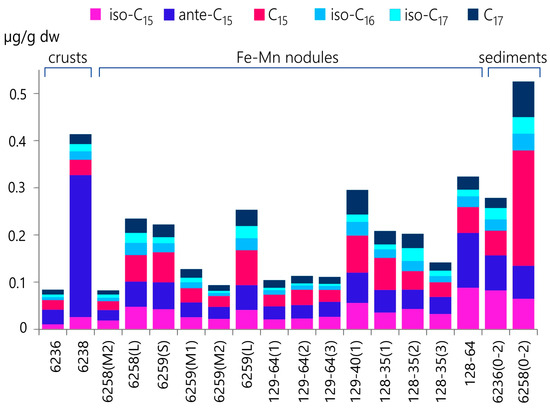
Figure 5.
The comparison of concentration profiles illustrating the changes in the accumulation of specific bacterial fatty acids in Fe-Mn nodules, crusts, and underlying sediments from the Kara Sea.
Individual bacterial FAs accumulate differently, even in nodules from the same site (Figure 5). This finding supports an earlier suggestion that diversity in the microbial community indicates that nodules may be a specific location for a complicated network of bacterial metabolism [13]. The presence of pores within the nodule matrix creates favorable conditions for microbial communities as they provide dissolved metals, carbon substrates, and nutrients. Numerous fossilized microorganisms, resembling bacterial cocci, rods, and biofilm-like structures, were previously found in Fe-Mn deposits in the Kara Sea using scanning electron microscopy [13]. Such fossils were found within Fe-rich (site PSh128-35) and Mn-rich (site AMK76-6259) nodules. Similar formations have been observed in Fe-Mn nodules from the Pacific and Indian Oceans [20,26,62,63]. Well-crystallized Fe and Mn oxides surrounding the fossilized microorganisms suggest a diagenetic process that occurred after nodule formation. The study of thin sections also revealed microbial cell-like structures partially or completely filled with Fe and Mn minerals. The consistent thickness of the ‘microbial cell coatings’ (0.2 μm) within the nodules indicates that the fossilization of all the cells in the colony occurred simultaneously, possibly due to the depletion of organic carbon sources or limited access to mineral electron acceptors (Fe and Mn oxyhydroxides).
The results of 16S rRNA gene sequencing showed that microbial communities in Fe-rich deposits from sites AMK76-6236 and PSh128-35 were enriched in members of the Geopsychrobacteraceae family, which have metal-reducing or metal-oxidizing activities [13]. The microbial communities in Mn-rich nodules from site AMK76-6259 have an increased abundance of Magnetospiraceae and planctomycetes of the Scalinduaceae family, which were poorly represented in the analyzed Fe-rich ore deposits and underlying sediments. These taxa do not include organisms that utilize Mn compounds as electron acceptors or donors for growth. Magnetospirillum is known for its unique ability to produce fine-grained intracellular magnetite crystals, while Scalinduaceae are capable of Fe²⁺ oxidation [64]. Moreover, each of the identified microbial communities contains unique and shared operational taxonomic units, representing bacterial and archaeal families unevenly distributed in the Fe–Mn deposits and sediments.
The accumulation of planktonogenic and bacterial lipids in Fe-Mn deposits increases the ratio of unsaturated to saturated compounds (U/S) (Table 2). This ratio characterizes the degree of the «freshness» of organic matter since unsaturated FAs are less stable in the process of sedimentation and diagenesis than their saturated counterparts without double bonds [65]. According to the results, as the Fe-Mn nodules grow and become larger in size (sites AMK76-6258 and AMK76-6259), the content of unsaturated acids increases (Figure 2B). This may be due to the increasing surface area of the samples, which allows for the accumulation of more components. Another possible reason is the reduced effect of the degradation and autoxidation of labile compounds within these semi-closed ore deposits.
Long-chain and even-carbon predominant series of n-FAs (>n-C20) are characteristic constituents of the surface waxes biosynthesized by higher plants [40]. Higher plant lipids are characterized, along with FAs, by the production of odd-numbered long-chain n-alkanes, with maxima usually in n-C27, n-C29, n-C31, and n-C33 [38].
It is generally accepted that in Arctic sediments, there is a co-occurrence of predominantly odd long-chain n-alkanes and even long-chain n-alkanoic acids in lipid fractions, which indicates a high terrestrial input in the composition of OM [44]. Moreover, the concentrations of n-FAs are higher relative to n-alkanes. This study’s data revealed that long-chain n-FAs are almost absent in the extracts of Fe-Mn nodules and underlying sediments (Figure 3 and Table S1). However, previous studies have suggested that terrigenous n-alkanes are predominant in the OM composition of these samples [13]. Carboxylic acids are known to be particularly susceptible to diagenetic degradation and are more sensitive than most other lipids. The stability of the FAs is controlled by the length of carbon chains and the level of unsaturation, as well as the nature of the matrix to which they are bound [30]. Due to lower microbial availability caused by matrix effects, FAs are generally less sensitive in terrestrial components compared to phytoplankton and bacterial ones. Therefore, long-chain n-fatty acids derived from higher plants are likely to be more stable than short-chain acids produced by marine biota. Consequently, if selective degradation processes took place in the studied nodule and sediment samples, they should have resulted in a shift towards longer-chain products. However, these processes cannot explain the observed absence of long-chain n-FAs.
A similar discrepancy between the distribution of hydrocarbons and FAs, i.e., the presence of long-chain n-alkanes and the absence of long-chain n-FAs, was also documented for lipid extracts of surface sediment samples from the Laptev Sea and Kara Sea [66,67,68,69]. In the paper by Belyaeva and Eglinton [68], the authors compared the composition of free FAs to those bound in complex lipid molecules. The data showed that long-chain FAs derived primarily from terrestrial lipids are supplied into the sediment only in a bound form. This provides them with subsequent resistance during diagenesis. The source of bound lipids is not clearly understood. They may originate from calcite-bound lipids, the process of strong adsorption to the aluminosilicate sediment surfaces, or from the esterification of free lipids with other forms of sedimentary OM [40,65]. Since Fe-Mn nodules are formed and grow on the water–sediment interface, their low concentrations in the terrestrial FAs of the studied samples imply that long-chain FAs in the sediments exist in a bound form.
Ubiquitous FAs C16:0 and C18:0 are found in bacteria, phytoplankton, zooplankton, and land plants and have been utilized as indicators of detrital input [70]. In the studied Fe-Mn nodules and crusts, these FAs had the highest contribution to the total FA pool (31–58%), and their accumulation increased during the growth of the nodules (Table S1).
The differences in FA content were observed between samples from different sites but of the same region as well as between individual samples from the same site. For samples from the same site, the changes in the FA content did not correlate with nodule morphology but depended on their size and, consequently, their age. The L-sized samples of up to 12 cm in diameter (sites AMK76-6258 and AMK76-6259) had the highest concentrations of FAs. The older the nodule, the more time it was exposed to environmental factors on the seafloor surface and the longer it accumulated FAs. This may also be a result of the increasing surface area of the nodule during its growth, as mentioned above. The local changes in organic carbon inflow and local bottom circulation patterns are responsible for variations in FA content in samples from different sites but from the same region. Despite significant variations in FA concentrations, the profile of FAs in the studied nodules was nearly unchanged.
The described groups of sampling sites are located in areas with different geochemistry of bottom sediments [71], total organic carbon (TOC) content in the sediments [72], particulate organic carbon (POC) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations in water [73], hydrological and hydrophysical conditions [74], and ice cover periods [75]. However, the results do not provide evidence for a direct influence of contrasting environmental settings on the content of FAs in nodules on a regional scale.
The distributions of FAs in the underlying sediments sampled from different regions of the Kara Sea were similar to each other (Figure 4 and Table 2). Unlike Fe-Mn deposits, FA composition was characterized by an enhanced accumulation of planktonogenic OM with a predominance of diatom-derived components over dinoflagellates. Furthermore, the accumulation of planktonogenic lipids in the bottom sediments led to an increase in the ratio of unsaturated to saturated compounds (U/S). In the analyzed sediments, the U/S ratio was greater than 1.5. This study’s data support the results of other studies in the Kara Sea [68]. Moreover, the underlying sediments contained a high abundance (8% in total) of C18:3ω-6, C18:2ω-6, C18:3ω-3, C20:5ω-3, C20:3ω-6, and C20:2ω-6 FAs (Figure 3 and Table S1). The synthesis of PUFAs in the cellular membranes of marine organisms represents an adaptation process to the low-temperature Arctic environment [68]. Similar to Fe-Mn nodules, detrital FAs (C14:0, C16:0, and C18:0) are the dominant component of the FA composition of the underlying sediments. This difference could reflect substantial fatty acid losses via degradation during the long-distance transport of terrestrial materials from the Ob and Yenisei estuarial areas to the sampling sites.
5. Conclusions
The study of FAs in shallow-water fast-growing Fe-Mn nodules and their underlying sediments from different parts of the Kara Sea confirmed the importance of the source-specific FA biomarkers for the investigation of diagenetic processes and the origins of OM in marine ore deposits. It was found that FAs in the studied Fe-Mn deposits were mainly derived from detrital material, phytoplankton, and bacteria, with a negligible contribution of terrestrial components. The total FA content in nodules and the contribution of each FA group show a high variability at two scales: (1) between samples from different sites but of the same region and (2) between individual samples from the same site. These variations are suggested to be controlled by multiple factors: size (age) of the nodules, diverse diagenetic processes localized on the particular site during nodule formation, organic matter supply (including the local changes in organic carbon inflow), bottom water circulation, influence of the Ob and Yenisei runoff, primary productivity, and underlying sediment properties. The results do not confirm a direct influence of contrasting environmental conditions in the Kara Sea on the content of fatty acids in nodules at the regional scale. The FA of the studied nodules and crusts contain significant amounts of labile compounds (11%–48%), which suggests a yet unknown mechanism for their preservation, probably associated with the ore matrix of the samples. The accumulation of specific bacterial fatty acids differs among Fe-Mn nodule samples collected from the same site. This difference serves as indirect evidence that bacteria form unique microcosms within each individual nodule.
In contrast to Fe-Mn nodules, the composition of underlying sediments is dominated by fatty acids from phytoplankton, with MUFAs > SAFAs and a high proportion of PUFAs.
Understanding the mechanisms behind the formation and distribution of the nodules is crucial for the effective exploration and utilization of these ore deposits. Further research into the complex interplay of geochemical, biological, and physical processes influencing nodule formation can provide valuable insights for optimizing exploration strategies and enhancing our knowledge of marine mineral deposits.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15010064/s1, Table S1: Concentrations of fatty acids (ng/g dw) in Fe-Mn nodules, crusts and underlying sediments from the Kara Sea.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 24-27-00409.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to scientific parties, masters, and crews of the R/V Akademik Mstislav Keldysh (cruise 76) and R/V Shtokman (cruises 128 and 129) for their professional support in the material collection for this study. The author would like to thank Aleksey Udalov for sampling (Shirshov Institute of Oceanology) and Elena Streltsova (Shirshov Institute of Oceanology) for sample preparation. I also thank Dmitrii Borisov (Shirshov Institute of Oceanology) and the three anonymous reviewers of this paper for their suggestions, who helped improve this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Glasby, G.P. Manganese: Predominant Role of Nodules and Crusts. In Marine Geochemistry; Shulz, H.D., Zabel, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 371–427. [Google Scholar]
- Glasby, G.P.; Stoffers, P.; Sioulas, A.; Thijssen, T.; Friedrich, G. Manganese Nodule Formation in the Pacific Ocean: A General Theory. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1982, 2, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, P.; Friedrich, G.; von Stackelberg, U. The Manganese Nodule Belt of the Pacific Ocean: Geological Environment, Nodule Formation, and Mining Aspects; von Stackelberg, U., Ed.; Enke: Stutgart, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, J.R.; Mizell, K.; Koschinsky, A.; Conrad, T.A. Deep-Ocean Mineral Deposits as a Source of Critical Metals for High- and Green-Technology Applications: Comparison with Land-Based Resources. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baturin, G.N. Geochemistry of Oceanic Ferromanganese Nodules; Nauka: Moscow, Ressia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, J.R.; Koschinsky, A. Deep-Ocean Ferromanganese Crusts and Nodules. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 13, pp. 273–291. ISBN 9780080983004. [Google Scholar]
- Josso, P.; Pelleter, E.; Pourret, O.; Fouquet, Y.; Etoubleau, J.; Cheron, S.; Bollinger, C. A New Discrimination Scheme for Oceanic Ferromanganese Deposits Using High Field Strength and Rare Earth Elements. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 87, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymond, J.; Lyle, M.; Finney, B.; Piper, D.Z.; Murphy, K.; Conard, R.; Pisias, N. Ferromanganese Nodules from MANOP Sites H, S, and R—Control of Mineralogical and Chemical Composition by Multiple Accretionary Processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.B. Some Geochemical Observations on Manganese-Iron Oxide Nodules from Different Depth Environments. Mar. Geol. 1967, 5, 511–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, G.P.; Emelyanov, E.M.; Zhamoida, V.A.; Baturin, G.N.; Leipe, T.; Bahlo, R.; Bonacker, P. Environments of Formation of Ferromanganese Concretions in the Baltic Sea: A Critical Review. Manganese Miner. Geochem. Mineral. Terr. Mar. Depos. 1997, 119, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlawatsch, S.; Neumann, T.; Van Den Berg, C.M.G.; Kersten, M.; Harff, J.; Suess, E. Fast-Growing, Shallow-Water Ferro-Manganese Nodules from the Western Baltic Sea: Origin and Modes of Trace Element Incorporation. Mar. Geol. 2002, 182, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöthe, M.; Wegorzewski, A.; Müller, C.; Simon, F.; Kuhn, T.; Schippers, A. Manganese-Cycling Microbial Communities Inside Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7692–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulga, N.; Abramov, S.; Klyukina, A.; Ryazantsev, K.; Gavrilov, S. Fast-Growing Arctic Fe–Mn Deposits from the Kara Sea as the Refuges for Cosmopolitan Marine Microorganisms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Schröder, H.C.; Schloßmacher, U.; Müller, W.E.G. Organized Bacterial Assemblies in Manganese Nodules: Evidence for a Role of S-Layers in Metal Deposition. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, M.V.; Maillot, B.M.; Shulse, C.N.; Gooday, A.J.; Amon, D.J.; Smith, C.R.; Church, M.J. From the Surface to the Deep-Sea: Bacterial Distributions across Polymetallic Nodule Fields in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone of the Pacific Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yli-Hemminki, P.; Jørgensen, K.S.; Lehtoranta, J. Iron–Manganese Concretions Sustaining Microbial Life in the Baltic Sea: The Structure of the Bacterial Community and Enrichments in Metal-Oxidizing Conditions. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulse, C.N.; Maillot, B.; Smith, C.R.; Church, M.J. Polymetallic Nodules, Sediments, and Deep Waters in the Equatorial North Pacific Exhibit Highly Diverse and Distinct Bacterial, Archaeal, and Microeukaryotic Communities. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Ran, L.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Lu, B.; Xu, X.-W.; Wang, C.-S. Heterogeneous Marine Environments Diversify Microbial-Driven Polymetallic Nodule Formation in the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1430572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molari, M.; Janssen, F.; Vonnahme, T.R.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Boetius, A. The Contribution of Microbial Communities in Polymetallic Nodules to the Diversity of the Deep-Sea Microbiome of the Peru Basin (4130–4198 m Depth). Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 3203–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liao, L.; Wang, C.S.; Ma, W.L.; Meng, F.X.; Wu, M.; Xu, X.W. A Comparison of Microbial Communities in Deep-Sea Polymetallic Nodules and the Surrounding Sediments in the Pacific Ocean. Deep Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 79, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-D.; Sun, X.-M.; Guan, Y. Biogenic Mineralization in the Ferromanganese Nodules and Crusts from the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Okumura, T.; Uematsu, K.; Hirai, M.; Iijima, K.; Usui, A.; Suzuki, K. Heterogeneity of Microbial Communities on Deep-Sea Ferromanganese Crusts in the Takuyo-Daigo Seamount. Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, F.; Mitsunobu, S.; Suzuki, K.; Hoshino, T.; Morono, Y.; Inagaki, F. Dense Microbial Community on a Ferromanganese Nodule from the Ultra-Oligotrophic South Pacific Gyre: Implications for Biogeochemical Cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 447, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, B.J.; Heidelberg, J.F. Microbial Communities Associated with Ferromanganese Nodules and the Surrounding Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Müller, W.E.G. Marine Biominerals: Perspectives and Challenges for Polymetallic Nodules and Crusts. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gan, L.; Wiens, M.; Schloßmacher, U.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Distribution of Microfossils Within Polymetallic Nodules: Biogenic Clusters Within Manganese Layers. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K.; Kappler, A. Geomicrobiology. Dekker, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 0824707648. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Dong, H.; Reguera, G.; Beyenal, H.; Lu, A.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.-Q.; Fredrickson, J.K. Extracellular Electron Transfer Mechanisms between Microorganisms and Minerals. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romankevich, E.A. Geochemistry of Organic Matter in the Ocean; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; ISBN 978-3-642-49966-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wakeham, S.G.; Canuel, E.A. Degradation and Preservation of Organic Matter in Marine Sediments. In Marine Organic Matter: Biomarkers, Isotopes and DNA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 295–321. [Google Scholar]
- Sunda, W.G.; Kieber, D.J. Oxidation of Humic Substances by Manganese Oxides Yields Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Substrates. Nature 1994, 367, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.F.; Brocks, J.J.; Grice, K.; Schwark, L.; Jaraula, C.M.B.; Dick, J.M.; Evans, K.A. Organic Geochemistry and Mineralogy. I. Characterisation of Organic Matter Associated with Metal Deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 50, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, O.A.; Poluyaktov, V.F. Fatty Acid Composition of the Iron-Manganese Nodules and Surrounding Sediments in the Pacific and Indian Oceans Abstract. Saturated, Monosaturated, Polyunsaturated, and Iso Fatty Acids Have Been Investigated in Iron-Manganese Nodules and Surrounding. Okeanologiya 1996, 35, 630–637. [Google Scholar]
- González, F.J.; Somoza, L.; Lunar, R.; Martínez-Frías, J.; Rubí, J.A.M.; Torres, T.; Ortiz, J.E.; Díaz-del-Río, V. Internal Features, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Ferromanganese Nodules from the Gulf of Cadiz: The Role of the Mediterranean Outflow Water Undercurrent. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 80, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulga, N.A. Characteristics of Alkanes in Ferromanganese Nodules of the Clarion–Clipperton Fracture Zone. Oceanology 2018, 58, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulga, N.A. Distribution of N-Alkanes in the Ferromanganese Nodule–Sediment–Pore Water System (Clarion–Clipperton Fracture Zone). Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2017, 52, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, B.E.; Ashton, N.J.; Pattrick, R.A.D. The Formation of Ferromanganese Nodules in the Southwest Indian Ocean; an Abiotic Process. Mineral. Mag. 2014, 78, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 0521837626/9780521837620. [Google Scholar]
- Volkman, J.K.; Johns, R.B.; Gillan, F.T.; Perry, G.J.; Bavor, H.J. Microbial Lipids of an Intertidal Sediment—I. Fatty Acids and Hydrocarbons. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahl, F.G.; Muehlhausen, L.A.; Lyle, M. An Organic Geochemical Assessment of Oceanographic Conditions at Manop Site C over the Past 26,000 Years. Paleoceanography 1989, 4, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niggemann, J.; Schubert, C.J. Fatty Acid Biogeochemistry of Sediments from the Chilean Coastal Upwelling Region: Sources and Diagenetic Changes. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 626–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeham, S.G.; Hedges, J.I.; Lee, C.; Peterson, M.L.; Hernes, P.J. Compositions and Transport of Lipid Biomarkers through the Water Column and Surficial Sediments of the Equatorial Pacific Ocean. Deep Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1997, 44, 2131–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budge, S.M.; Parrish, C.C. Lipid Biogeochemistry of Plankton, Settling Matter and Sediments in Trinity Bay, Newfoundland. II. Fatty Acids. Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.; Macdonald, R.W.; Stein, R.; MacDonald, R.W. The Organic Carbon Cycle in the Arctic Ocean; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, R.; Fahl, K.; Fütterer, D.K.; Galimov, E.M.; Stepanets, O.V. Siberian River Run-off in the Kara Sea: Characterisation, Quantification, Variability, and Environmental Significance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 0080951422. [Google Scholar]
- Hörner, T.; Stein, R.; Fahl, K. Paleo-Sea Ice Distribution and Polynya Variability on the Kara Sea Shelf during the Last 12 Ka. arktos 2018, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, P.J.; Tindle, A.G.; Webb, P.C. Geochemical Reference Material Compositions: Rocks, Minerals, Sediments, Soils, Carbonates, Refractories & Ores Used in Research & Industry; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1992; ISBN 1870325400. [Google Scholar]
- Menendez, A.; James, R.; Shulga, N.; Connelly, D.; Roberts, S. Linkages between the Genesis and Resource Potential of Ferromanganese Deposits in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic Oceans. Minerals 2018, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchagin, O.S.; Perova, E.N.; Brusnitsyn, A.I.; Ershova, V.B.; Khudoley, A.K.; Shilovskikh, V.V.; Molchanova, E.V. Ferro-Manganese Nodules from the Kara Sea: Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 106, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeżyńska, J.; Kędra, M.; Walkusz, W. Identifying Trophic Relationships within the High Arctic Benthic Community: How Much Can Fatty Acids Tell? Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K.; Jeffrey, S.W.; Nichols, P.D.; Rogers, G.I.; Garland, C.D. Fatty Acid and Lipid Composition of 10 Species of Microalgae Used in Mariculture. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1989, 128, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.P.; Volkman, J.K.; Jackson, A.E.; Blackburn, S.I. THE FATTY ACID AND STEROL COMPOSITION OF FIVE MARINE DINOFLAGELLATES. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhanova, I.N.; Flint, M.V.; Sergeeva, V.M.; Kremenetskiy, V.V. Phytoplankton of the South-Western Part of the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2011, 51, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitina, L.S.; Ilyash, L.V. Composition and Abundance of Phytoplankton in the Baidarata Inlet of the Kara Sea in Summer and Autumn. Moscow Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2013, 68, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribe, P.; Fillaux, J.; Laureillard, J.; Denant, V.; Saliot, A. Fatty Acids as Biomarkers of Planktonic Inputs in the Stratified Estuary of the Krka River, Adriatic Sea: Relationship with Pigments. Mar. Chem. 1991, 32, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keweloh, H.; Heipieper, H.J. Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Bacteria. Lipids 1996, 31, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, R.J.; Taylor, J. The Relationship between Fatty Acid Distributions and Bacterial Respiratory Types in Contemporary Marine Sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1983, 16, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Hollander, D.J. Differential Contribution of Bacteria to Sedimentary Organic Matter in Oxic and Anoxic Environments, Santa Monica Basin, California. Org. Geochem. 1997, 26, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, G.J.; Volkman, J.K.; Johns, R.B.; Bavor, H.J., Jr. Fatty Acids of Bacterial Origin in Contemporary Marine Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliot, A.; Goutx, M.; Fevrier, A.; Tusseau, D.; Andrie, C. Organic Sedimentation in the Water Column in the Arabian Sea: Relationship between the Lipid Composition of Small and Large-Size, Surface and Deep Particles. Mar. Chem. 1982, 11, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutx, M.; Saliot, A. Relationship between Dissolved and Particulate Fatty Acids and Hydrocarbons, Chlorophyll a and Zooplankton Biomass in Villefranche Bay, Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Chem. 1980, 8, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Das, S.K.; Munda, P. Biogenic Signature and Ultra Microfossils in Ferromanganese Nodules of the Central Indian Ocean Basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 73, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reykhard, L.Y.; Shulga, N.A. Fe-Mn Nodule Morphotypes from the NE Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, Pacific Ocean: Comparison of Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 110, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R.; Holmes, D.E.; Nevin, K.P. Dissimilatory Fe (Iii) and Mn (Iv) Reduction. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2004, 49, 219–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burdige, D.J. Geochemistry of Marine Sediments; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 069109506X. [Google Scholar]
- Zegouagh, Y.; Derenne, S.; Largeau, C.; Bardoux, G.; Mariotti, A. Organic Matter Sources and Early Diagenetic Alterations in Arctic Surface Sediments (Lena River Delta and Laptev Sea, Eastern Siberia), II.: Molecular and Isotopic Studies of Hydrocarbons. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E.S.; Charkin, A.; Dudarev, O.; Semiletov, I.; Vonk, J.E.; Sánchez-García, L.; Andersson, A.; Gustafsson, Ö. Carbon Isotopes and Lipid Biomarker Investigation of Sources, Transport and Degradation of Terrestrial Organic Matter in the Buor-Khaya Bay, SE Laptev Sea. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, A.N.; Eglinton, G. Lipid Biomarker Accumulation in the Kara Sea Sediments. Oceanology 1997, 37, 634–642. [Google Scholar]
- Fahl, K.; Stein, R. Modern Organic Carbon Deposition in the Laptev Sea and the Adjacent Continental Slope: Surface Water Productivity vs. Terrigenous Input. Org. Geochem. 1997, 26, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killops, S.; Killops, V. Introduction to Organic Geochemistry; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Malden, MA USA, 2004; ISBN 9781118697214. [Google Scholar]
- Rusakov, V.Y.; Kuzmina, T.G.; Toropchenova, E.S.; Zhilkina, A.V. Modern Sedimentation in the Kara Sea: Evidence from the Lithological–Geochemical Investigation of Surface Bottom Sediments. Geochem. Int. 2018, 56, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.; Romankevich, E.; Semiletov, I.; Wild, B.; van Dongen, B.; Vonk, J.; Tesi, T.; Shakhova, N.; Dudarev, O.V.; Kosmach, D.; et al. CASCADE—The Circum-Arctic Sediment CArbon DatabasE. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2561–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, N.A.; Fedulov, V.Y.; Kravchishina, M.D.; Shchuka, S.A. Organic Carbon Content in Dissolved and Particulated Forms in the Kara Sea Water. Oceanology 2024, 64, 217–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, S.V.; Kivva, K.K.; Polukhin, A.A. Application of Statistical Data Analysis Methods for Zoning Kara Sea Waters. Oceanology 2024, 64, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sea Ice Maps. AARI Official Web-Site. Available online: https://www.aari.ru/data/realtime/ledovye-karty-2 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).