Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
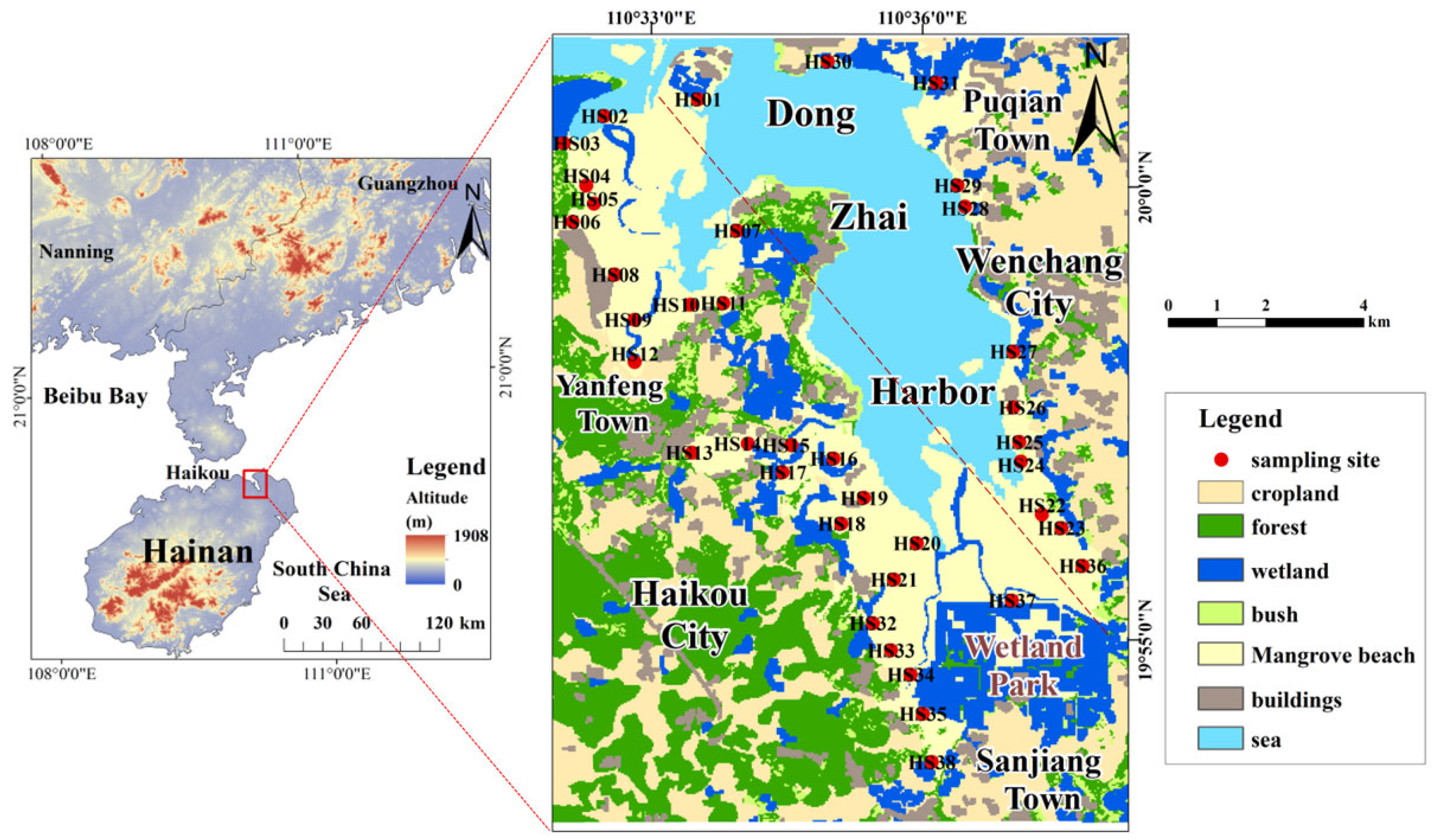
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Risk Assessment Methods
3. Results
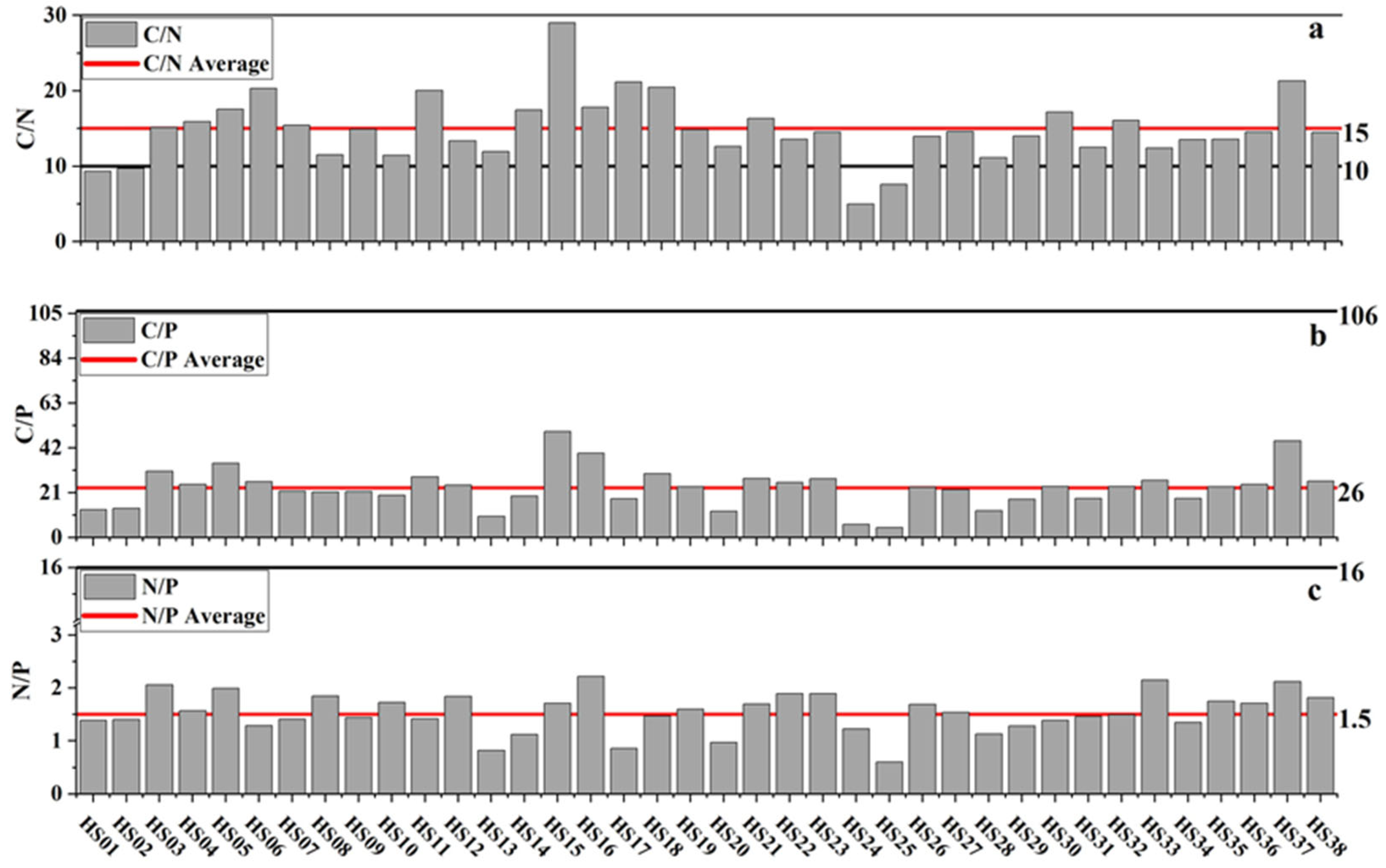
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Physico-Chemical Properties
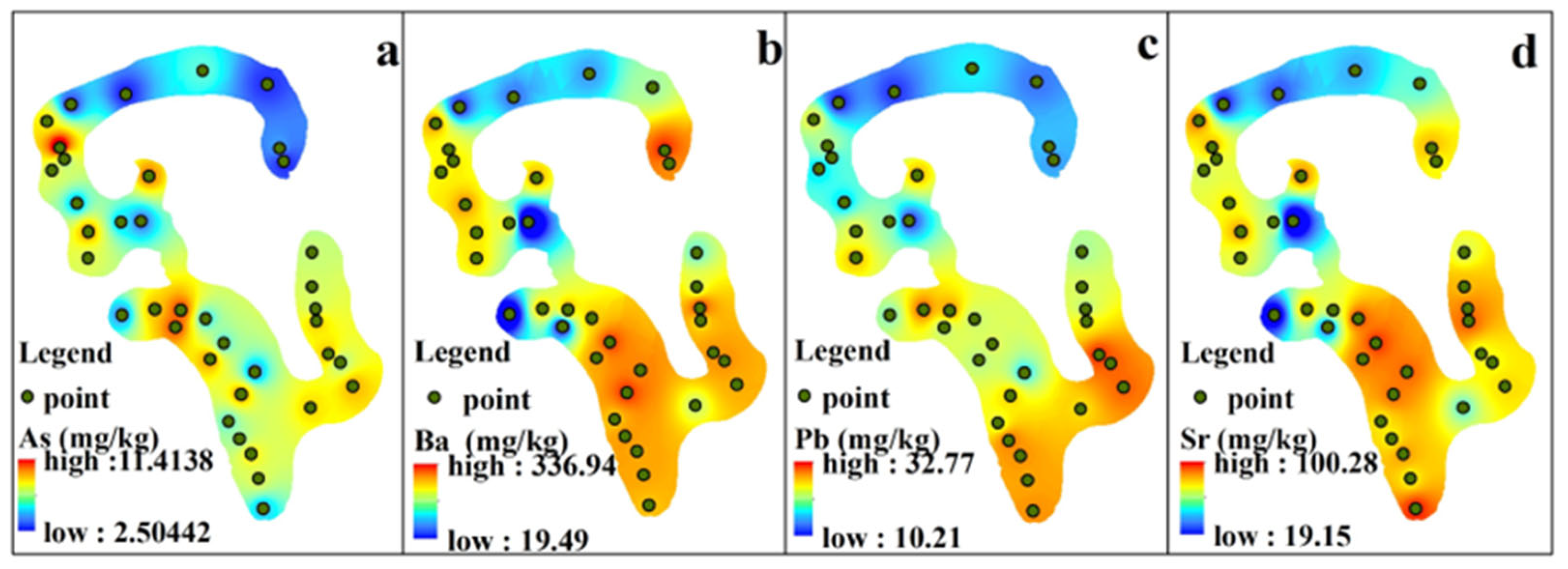
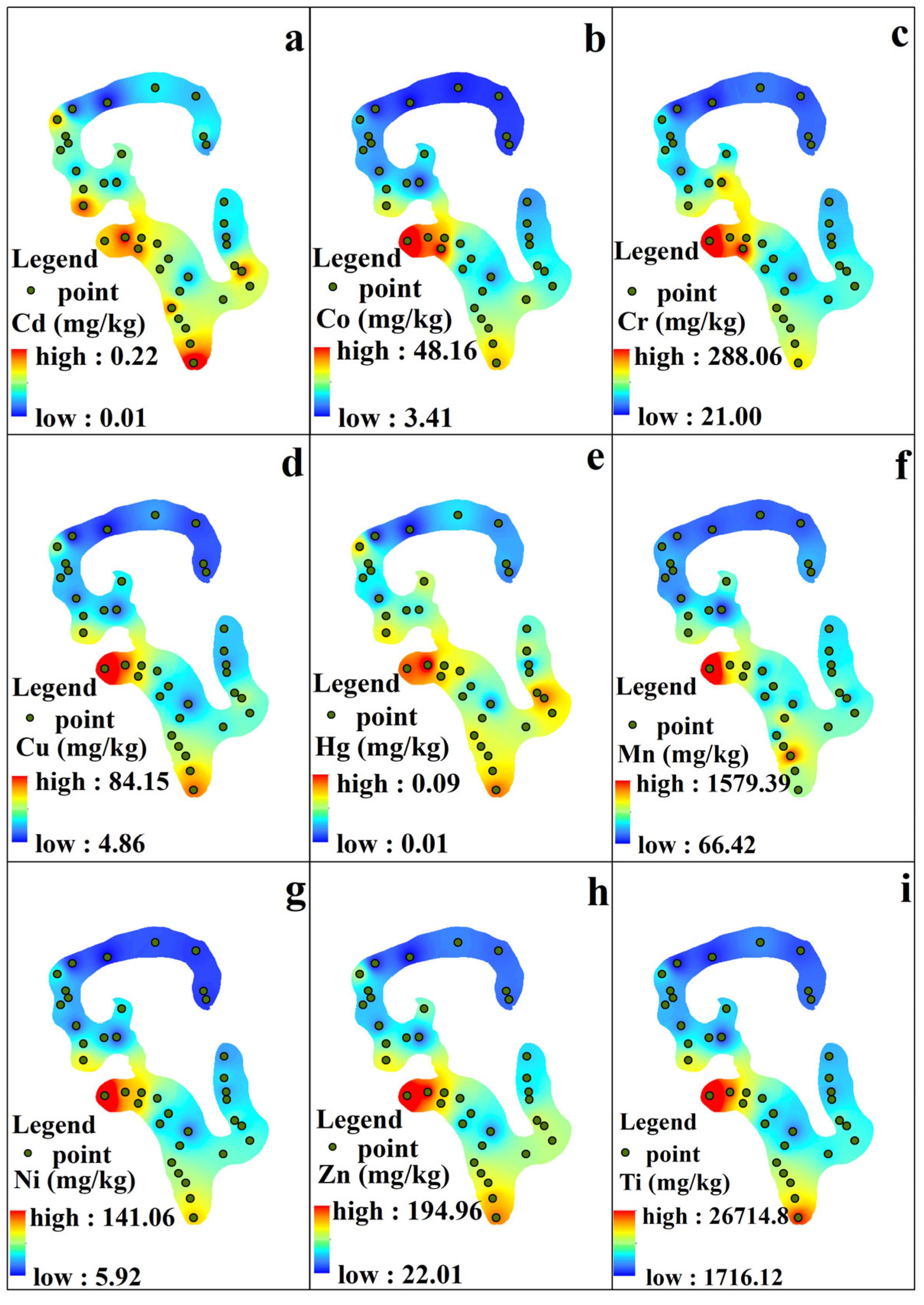
3.2. Spatial Distributions of Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
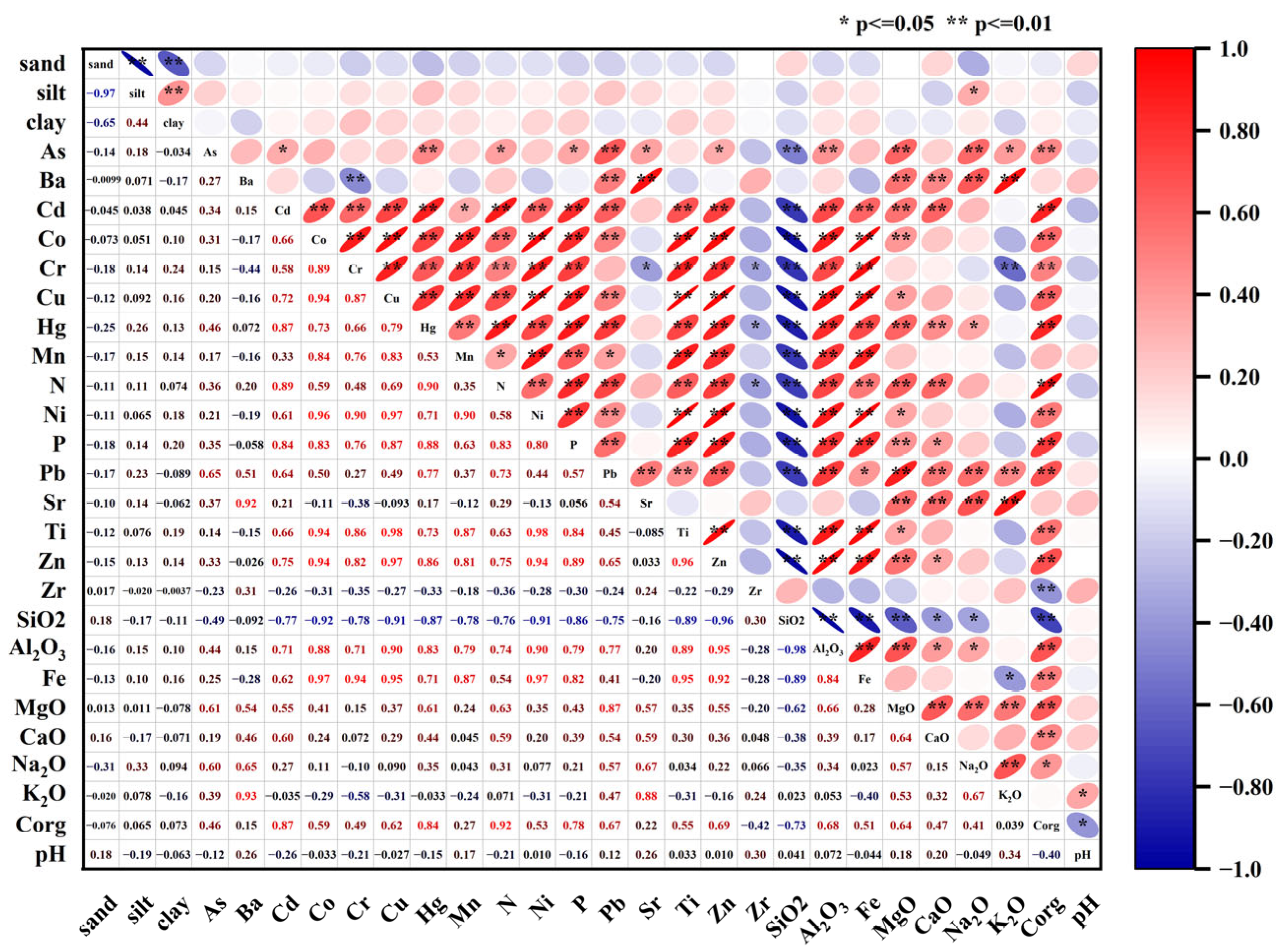
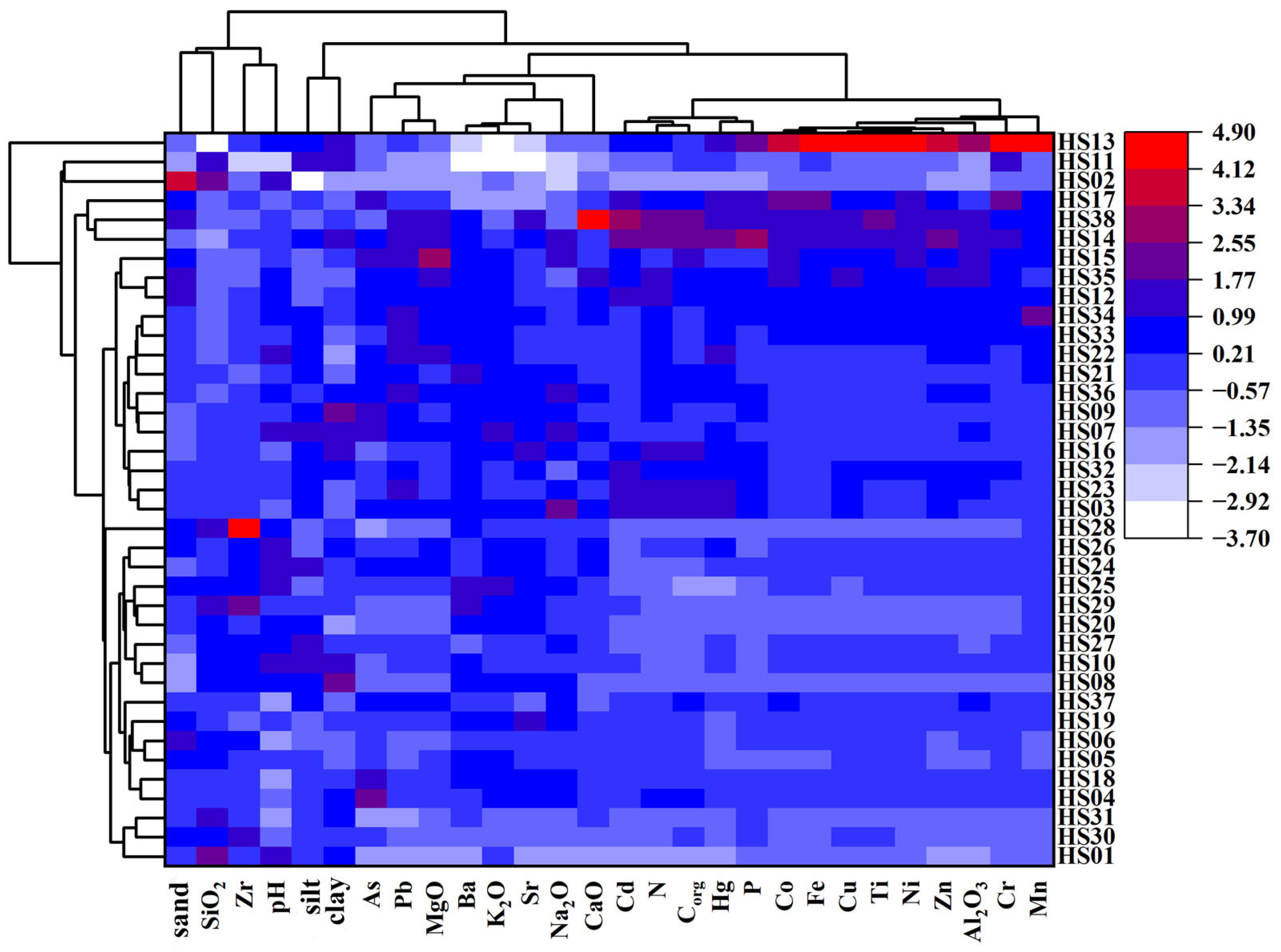
4.1. Source Apportionment of Metals in Sediment
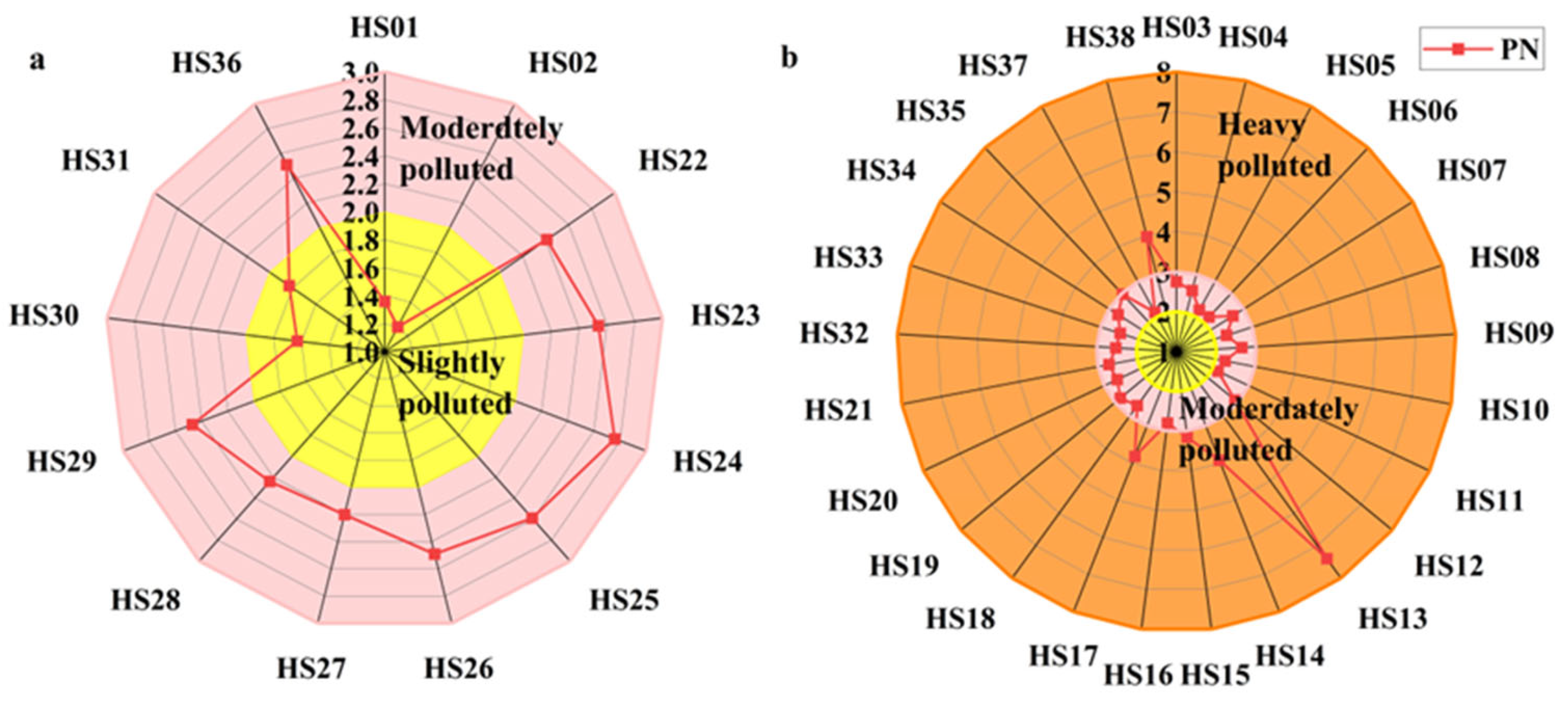
4.2. Contamination Status and Potential Ecological Risk
4.3. Evaluation of the Nemero Index
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In terms of spatial distribution, the contents of heavy metals in the western part of the wetland were significantly higher than those in the eastern part. The heavy metals Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Zn, and Ti were mainly distributed in the area of human activities, and were greatly influenced by human activities. The heavy metals As, Pb, Ba, and Sr were distributed in significantly high levels in all locations except the northern part of the wetland, which might be more strongly influenced by natural factors such as physical sources and tides.
- (2)
- The sources of heavy metals in the wetland sediments were categorized and resolved using correlation analysis and cluster analysis. It was concluded that As, Ba, Pb, and Sr mainly came from natural sources; Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Ti, and Zn mainly came from industrial sources; and the input of heavy metals from agricultural sources mainly included Cd and Hg.
- (3)
- The potential ecological risk index (RI) and the Nemero index (PN) pointed out that the main polluting elements of the wetland were Cd, Hg, and Ni, with agricultural sources as the main source of pollution; furthermore, there were obvious ecological risks of heavy metals in the western and southeastern corners of the wetland, which were in the inland area far away from the coastline, close to the range of human activities, and characterized by dense mangrove vegetation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.Y.; Primavera, J.H.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; McKee, K.; Bosire, J.O.; Cannicci, S.; Diele, K.; Fromard, F.; Koedam, N.; Marchand, C.; et al. Ecological role and services of tropical mangrove ecosystems: A reassessment. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 726–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayen, S. Occurrence, bioavailability and toxic effects of trace metals and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, S.S.; Aich, A.; Sengupta, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Sudarshan, M. Assessment of trace metal contamination of wetland sediments from eastern and western coastal region of India dominated with mangrove forest. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Chaudhuri, P.; Birch, G. Assessment of biotic response to heavy metal contamination in Avicennia marina mangrove ecosystems in Sydney Estuary, Australia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellinen, V.; Cherkashina, T.; Gustaytis, M. Assessment of metal pollution and subsequent ecological risk in the coastal zone of the Olkhon Island, Lake Baikal, Russia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wan, R.-A.; Yu, R.-L.; Hu, G.-R.; Lin, C.-Q.; Huang, H.-B. A comprehensive analysis on source-specific ecological risk of metal(loid)s in surface sediments of mangrove wetlands in Jiulong River Estuary, China. Catena 2022, 209, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Lin, G.; Feng, C.C.; Li, Z.; Qi, F.; Zheng, T.; Xie, L. Trace metals in sediments and benthic animals from aquaculture ponds near a mangrove wetland in Southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, V.X.; Barros, A.; Azevedo, J.A.; Miranda, P.R.; da Costa, J.G. Bioavailability of heavy metals in mangrove soil in Alagoas, Brazil. Biosci. J. 2019, 35, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cadena, J.; Andrade, S.; Silva-Coello, C.; De la Iglesia, R. Heavy metal concentration in mangrove surface sediments from the north-west coast of South America. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 82, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defew, L.H.; Mair, J.M.; Guzman, H.M. An assessment of metal contamination in mangrove sediments and leaves from Punta Mala Bay, Pacific Panama. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrig, H.A.; Pinto, F.N.; Moreira, I.; Malm, O. Heavy metals and methylmercury in a tropical coastal estuary and a mangrove in Brazil. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Du, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Rao, W. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of a Tropical Mangrove Wetland on Hainan Island, China. Water 2022, 14, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Huang, X.; Hu, J.; Li, C.; Yang, X.B.; Arndt, S.K. Land use change impacts on heavy metal sedimentation in mangrove wetlands—A case study in Dongzhai Harbor of Hainan China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.J.; Bai, J.K.; Meng, Y.C.; Diao, X.P.; Pan, K.; Zhu, X.S.; Lin, G.H. Effects of land use on the heavy metal pollution in mangrove sediments: Study on a whole island scale in Hainan China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.; Gao, J.; Song, R.; Song, L.; Ning, D. Uncertainties in Pollution and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments Using Regional Background Soils in China. Toxics 2023, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Huo, Y.R. Uptake and concentration of heavy metals in dominant mangrove species from Hainan Island, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Luo, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in seawater and sediments from Meishan Bay, Zhejiang coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111217–111225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, S.; Naito, R.; Nakamura, Y. Spatial patterns of concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in marine sediments from Japanese port areas. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101135–101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Oyola, S.; García-Martínez, M.-J.; Ortega, M.F.; Chavez, E.; Romero, P.; García-Garizabal, I.; Bolonio, D. Ecological and probabilistic human health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in river sediments affected by mining activities in Ecuador. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4459–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, C.; Fu, B.; He, L.; Fu, Q.; Shen, M.; Zhao, Z. Factors influencing the accumulation of Pd in mangrove wetland sediments in Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Cui, R.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Fang, X.; Ding, X.; Zou, L.; Bai, F. Clay mineralogy of the riverine sediments of Hainan Island, South China Sea: Implications for weathering and provenance. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xi, X.; Xiao, G.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ye, J.; Li, Z. National multi-purpose regional geochemical survey in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zee, C.; Slomp, C.P.; Van Raaphorst, W. Authigenic P formation and reactive P burial in sediments of the Nazaré canyon on the Iberian margin (NE Atlantic). Mar. Geol. 2002, 185, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Al, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Khadka, S.; Idris, A.M. Receptor model-based source apportionment and ecological risk of metals in sediments of an urban river in Bangladesh—ScienceDirect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Environmental Monitoring Center. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ni, S.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, C. Calculation of Heavy Metals Toxicity Coefficient in the Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—A tributary of the Ganges, India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Hassan, R.; Fardous, Z.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Hossain, M.B. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surficial sediments from the lower Meghna River estuary, Noakhali coast, Bangladesh. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, B. Application of Mineral Analysis in Mangrove Wetland Soils. J. Instrum. Anal. 2019, 38, 823–829. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sekula-Wood, E.; Benitez Nelson, C.R.; Bennett, M.A.; Thunell, R. Magnitude and composition of sinking particulate phosphorus fluxes in Santa Barbara Basin, California. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Cai, G.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, L. The concentration distribution and biohazard assessment of heavy metal elements in surface sediments from the continental shelf of Hainan Island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padua, P.C.; Srivastava, P.; de Martini, A.P.; Alves, D.P.; Gabel, V.S.; Ferreira, P.A.d.L.; Jovane, L. A 140-year record of environmental changes in São Sebastião, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 4, 156578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattan, J.; Rao, C.; Higgs, N.; Colley, S.; Parthiban, G. Distribution of major, trace and rare-earth elements in surface sediments of the Wharton Basin, Indian Ocean. Chem. Geol. 1995, 121, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.C.; Wang, D.D.; Yang, Y.; Dai, C.; Han, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Tu, J.Y.; Yang, B.M. Process and Sedimentary records for Holocene coastal environmental changes, Hainan Island: An overview. Quat. Sci. 2016, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Ruan, M.; Wang, Y.; Mao, C. Recognition of Significant Multi- Element Geochemical Signatures of Lower Soil on Hainan Island, China: Implications for Thermal Mineral Water Exploration. Water 2022, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongo, E.; Jin, F.; Mutethya, E.; Wu, D.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Z. Sediment Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment in Changwang and Wuyuan Rivers in Hainan Island, China. Water 2023, 15, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makokha, V.A.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. Concentrations, Distribution, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Huo, X.; Hu, C.; Tao, Y. Contamination, Ecological Risk and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments in the Hailar River, the Upper Source of the Erguna River between China and Russia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemerow, N.L. Scientific Stream Pollution Analysis; Scripta Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Allafta, H.; Opp, C. Spatio-temporal variability and pollution sources identification of the surface sediments of Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Expression | Coefficient of Interpretation | Classification and Contamination Degree | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual potential ecological risk index () | Tir: Toxicity coefficient, according to previous research results, the toxicity response coefficients of Hg, Cd, As, Cu, Pb, Ni, Cr, Co, and Zn are 40, 30, 10, 5, 5, 5, 2, 2, and 1, respectively. Ci: The measured content of element i in sediments (mg/kg). Cref: The geochemical background value of element n (mg/kg). | < 40: Low risk 40 ≤ < 80: Moderate risk 80 ≤ < 160: Heavy risk 160 ≤ < 320: Serious risk ≥ 320: Extremely serious risk | [23] | |
| Potential ecological risk index (RI) | : Individual potential ecological risk index. | RI < 150: Low risk 150 < RI ≤ 300: Moderate risk 300 < RI ≤ 600: Serious risk RI > 600: Extremely serious risk | [24] | |
| Nemerow pollution index (PN) | CFave: The average of contamination factors of investigated metals. CFmax: The maximum contamination factor for a metal in a sample. | PN ≤ 0.7: Safe 0.7 < PN ≤ 1: Warning 1 < PN ≤ 2: Mild contamination 2 < PN ≤ 3: Moderate contamination PN > 3: Serious contamination | [25] |
| Area | Content | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | pH | Corg (mg/kg) | N (mg/kg) | P (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Min. | 14.50 | 7.20 | 2.60 | 4.89 | 2000 | 205.00 | 146.00 |
| Max. | 90.20 | 74.50 | 13.50 | 8.19 | 28200 | 1935.00 | 1024.00 | |
| Average | 37.63 | 52.29 | 10.08 | 7.05 | 9900 | 754.00 | 497.00 | |
| Standard deviation | 18.68 | 17.01 | 3.41 | 0.99 | 8400 | 539.69 | 261.23 | |
| CV (%) | 49.63 | 32.54 | 33.8 | 14.1 | 84.59 | 71.58 | 52.62 | |
| West | Min. | 10.20 | 40.10 | 4.40 | 4.05 | 4300 | 342.00 | 264.00 |
| Max. | 51.20 | 70.90 | 20.30 | 7.70 | 40500 | 2619.00 | 2079.00 | |
| Average | 29.92 | 57.87 | 12.21 | 6.18 | 20600 | 1276.00 | 845.00 | |
| Standard deviation | 13.61 | 10.64 | 4.89 | 0.91 | 9400 | 575.39 | 447.05 | |
| CV (%) | 45.48 | 18.39 | 40.05 | 14.75 | 45.69 | 45.11 | 52.92 | |
| Synthesis | Average | 33.78 | 55.08 | 11.15 | 6.62 | 15250 | 1015.00 | 671.00 |
| Area | Content | Heavy Metals Content (mg/kg) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Ba | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Hg | Mn | Ni | Pb | Sr | Ti | Zn | ||
| East | Min. | 2.50 | 133.00 | 0.01 | 3.40 | 21.00 | 4.90 | 0.01 | 123.00 | 5.90 | 10.20 | 43.00 | 1716.00 | 22.00 |
| Max. | 7.90 | 337.00 | 0.18 | 15.10 | 84.00 | 29.50 | 0.07 | 419.00 | 35.20 | 32.80 | 97.00 | 7221.00 | 90.00 | |
| Average | 5.19 | 254.00 | 0.07 | 8.27 | 52.00 | 14.19 | 0.03 | 239.00 | 18.54 | 20.67 | 76.00 | 4446.00 | 53.00 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.06 | 67.86 | 0.04 | 4.15 | 20.71 | 7.34 | 0.02 | 95.53 | 10.14 | 7.71 | 16.97 | 1728.40 | 23.01 | |
| CV (%) | 39.77 | 26.72 | 66.88 | 50.20 | 39.96 | 51.70 | 63.70 | 40.00 | 54.69 | 37.31 | 22.43 | 38.88 | 43.23 | |
| West | Min. | 3.40 | 19.00 | 0.04 | 4.30 | 44.00 | 9.10 | 0.02 | 66.00 | 10.20 | 11.00 | 19.00 | 2201.00 | 32.00 |
| Max. | 11.40 | 335.00 | 0.23 | 48.20 | 288.00 | 84.20 | 0.09 | 1580.00 | 141.1 | 30.70 | 100.00 | 26719.00 | 195.00 | |
| Average | 6.43 | 265.00 | 0.11 | 16.65 | 97.00 | 26.02 | 0.05 | 390.00 | 38.58 | 23.62 | 81.00 | 7951.00 | 82.00 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.10 | 77.38 | 0.05 | 9.87 | 53.73 | 16.02 | 0.02 | 294.48 | 26.03 | 5.14 | 19.92 | 5078.48 | 37.10 | |
| CV (%) | 32.62 | 29.18 | 42.63 | 59.27 | 55.42 | 61.57 | 36.64 | 75.58 | 67.46 | 21.77 | 24.71 | 63.87 | 45.16 | |
| Synthesis | Average | 6.01 | 261.00 | 0.10 | 13.78 | 82.00 | 21.97 | 0.04 | 338.00 | 31.72 | 22.61 | 79.00 | 6751.00 | 72.00 |
| Level of Potential Ecological Risk | RI | Level of Potential Ecological Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 40 | Low risk | RI < 120 | Low risk |
| 40 ≤ < 80 | Moderate risk | 120 ≤ RI < 240 | Moderate risk |
| 80 ≤ < 160 | Heavy risk | 240 ≤ RI < 480 | Serious risk |
| 160 ≤ < 320 | Serious risk | RI ≥ 480 | Extremely serious risk |
| ≥ 320 | Extremely serious risk |
| East | West | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | < 40 | < 80 | < 160 | < 40 | < 80 | < 160 |
| As | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Ba | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Cd | 9 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 13 | 6 |
| Co | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Cr | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Cu | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Hg | 13 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 1 | 0 |
| Mn | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Ni | 13 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 1 | 0 |
| Pb | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Sr | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Ti | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Zn | 13 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Long, R.; Ma, B.; Chang, Y.; Mao, C. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness. Minerals 2023, 13, 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121476
Zhang G, Chen S, Long R, Ma B, Chang Y, Mao C. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness. Minerals. 2023; 13(12):1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121476
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gucheng, Shenghong Chen, Ruiling Long, Bo Ma, Yu Chang, and Changping Mao. 2023. "Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness" Minerals 13, no. 12: 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121476
APA StyleZhang, G., Chen, S., Long, R., Ma, B., Chang, Y., & Mao, C. (2023). Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness. Minerals, 13(12), 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121476





