Abstract
The production of lithium from spodumene ores generates huge amounts of residues mainly composed of aluminosilicates. The main objective of the present study was to synthesize NaX zeolites with good ion-exchange capacity from these aluminosilicate residues, without using the fusion step or chemically modifying their initial Si/Al ratio. A physico-chemical (chemical composition, sorption capacity) and mineralogical (XRD, SEM) characterization of the zeolite synthesized using the conventional hydrothermal process (Process_1) was performed and compared with zeolite produced using a fusion step followed by a hydrothermal treatment process (Process_2) and commercial zeolite 13X. Then, the effect of operating parameters such as aging time and temperature, crystallization time and solid/liquid ratio on the sorption capacities of the synthesized zeolites using the conventional hydrothermal process was assessed. Initial aluminosilicate residues were mainly composed of Al2O3 (24.6%) and SiO2 (74.0%), while containing low amounts of potential contaminants (<1.6%). Based on its chemical composition, the fine fraction (<53 µm) was identified as the most suitable fraction to produce zeolites, while coarser fractions which contained higher Li content can be used to produce glass and ceramics. Physico-chemical and mineralogical characterization results show that zeolite produced using the conventional hydrothermal process (Process_1) had similar properties compared to zeolites 13X. Therefore, Process_1 was identified as the most performant while reducing operating costs related to alkaline fusion pre-treatments, which did not significantly improve zeolite properties. Finally, the optimum conditions for converting the residues into zeolite NaX, which had an ion-exchange capacity of 58 mg Ca/g were 8 h of aging at 75 °C and 16 h of crystallization at 100 °C, with a solid/liquid ratio of 1/10 (w/v).
1. Introduction
Electric vehicles using lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are gaining more and more attention as a promising option to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with transport, which cause climate change issues. Several countries around the world, including Canada, are looking at the possibility of extracting Li from Li-rich pegmatite deposits, in which the main Li-bearing mineral is spodumene, LiAlSi2O6 [1]. In addition, the production of Li generates huge amounts of residues (with approximatively 10 tons or 20–40 tons per ton of lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) and hydroxide (LiOH), respectively) [2,3]. Over time, it becomes more complicated to manage them into landfills or open-air storage sites, especially since these residues may potentially generate environmental problems [2,3].
One avenue to reduce the environmental footprint of Li production from spodumene ore is to produce zeolites from these aluminosilicate residues, considering their high content in alumina and silica [2]. Zeolites are microporous crystalline aluminosilicates with high ion-exchange and sorption properties [4,5]. Synthetic zeolites X, which have a low Si/Al molar ratio (1.0–1.5), are excellent ion exchangers [5] and are characterized by high sorption capacity due to their unique crystal structure [6]. Zeolite 13X, the Na-form of type X zeolite (NaX), is added in some detergents because of its higher Mg2+ ion-exchange capacity compared to zeolite A [7]. Synthetic zeolites are produced under hydrothermal conditions requiring a large quantity of water and high alkalinity [2,8]. The use of pure aluminate and silicate to produce zeolites is very expensive in addition to them being unsustainable materials [9]. Therefore, the search for less expensive and renewable materials has been the goal of several studies [10].
So far, several studies have been carried out to synthesize zeolite from more sustainable, cost-effective and environmentally friendly raw material, such as kaolinite [11,12], coal fly ash [13,14,15,16,17], bagasse fly ash [18], bauxite tailings [19] and K-feldspar [20]. Lithium slag, considered an emergent waste, can also be used to synthesize zeolite [2,3,7,21,22,23]. However, data regarding the production of zeolites from lithium residues is relatively scarce compared to other residues [2,23].
The conventional hydrothermal process has been used for the simultaneous extraction of lithium from α-spodumene and the synthesis of hydroxysodalite zeolite [10]. A co-crystalline zeolite X/A (with 18% and 82% of X and A zeolite phase, respectively), with good calcium and magnesium ion-exchange capacity compared to commercial zeolite A, was synthesized by conventional hydrothermal process from Li-slag [7]. The incomplete dissolution of the Si and Al from the initial product and the presence of unreacted elements in the final zeolite are among the main drawbacks of this approach [2,13,24]. To improve the efficiency of the process, some pre-treatments should be considered. An alkaline fusion-assisted hydrothermal (AFH) method has been used to efficiently solubilize Si and Al from Li-slag [21,23], favoring zeolite formation in the subsequent hydrothermal treatment. A patented process has been developed to produce zeolite A from aluminosilicate residues originating from Li extraction using the conventional hydrothermal process assisted by alkaline fusion with adjustment of the initial Si/Al ratio to 1/1 [22]. In addition, zeolite X was successfully synthesized from spodumene leachate residue (Li-slag) after adjusting the initial Si/Al ratio to 2/1 using a hydrothermal process assisted by alkaline fusion [21]. Zeolite NaX with adsorption capacity for water vapor comparable to X commercial was obtained from lithium slag, using the fusion step (4 h at 600 °C) followed by hydrothermal treatment [3]. Finally, the higher energy needed during the fusion step (temperature between 500 and 600 °C) is the major drawback of this process [13,24].
It has been noticed that a higher synthesis temperature (>100 °C) is suitable for crystal growth, while lower temperatures favor the nucleation step [25]. It was found that reaction temperatures of 90, 95 or 100 °C were suitable for zeolite X production from Li- slag [3,21]. However, increasing temperatures to 110 and 120 °C leads to zeolite sodalite formation instead of zeolite X [21]. Zeolite NaX produced from fly ash was achieved after 15 h of crystallization at 90 °C, while no to limited crystallization occurred after 3 and 7 h, respectively [26]. Zeolite X was successfully produced from Li-slag after 8 h of crystallization [3]. An aging temperature of 50 °C increases the dissolution of Al and Si, reaching its critical concentration for nucleation [27]. In addition, longer aging time allows the production of zeolites with higher crystallinity [28]. Zeolitization efficiencies are also affected by the dissolution step, where the solid/liquid (S/L) ratio plays a crucial role. Increasing the S/L ratio led to a lower degree of crystallization. For example, a S/L ratio lower than 5 g/L improves Al and Si dissolution, therefore, increasing the zeolitization efficiency. However, the large amount of chemicals used limits their application on an industrial scale [29].
According to the literature, converting Li-residues into zeolites 13X is achievable but requires a pre-activation through alkaline fusion [3,21]. The aim of the present study was to propose an efficient but simpler approach to convert aluminosilicate residues from Li extraction into zeolite NaX without using the fusion step or chemically modifying their initial Si/Al ratio. The performance of the proposed synthesis was evaluated through the ion-exchange capacity of the produced zeolite and compared to that of commercial zeolite 13X. Finally, the effect of operating parameters on the ion-exchange capacity, such as crystallization time, aging time and temperature and solid to liquid ratio, were tested to find the most efficient conditions for converting these residues into value-added by-products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Aluminosilicate Residue and Commercial Zeolite
The Whabouchi property represents one of the largest spodumene deposits in the world. It is located in the territory of Eeyou Istchee/Baie-James in the northern of Quebec, near the Cree community of Nemaska. Owing to the global increase in demand for Li for batteries, Nemaska Lithium, NLI, has developed an acid roasting process to produce LiOH and Li2CO3 from a spodumene concentrate. The process consists of the conversion of α-spodumene to β-spodumene by calcination at high temperatures (at least 1000 °C for 30 min), followed by a roasting step in the presence of H2SO4 [1,30]. The reaction between β-spodumene and sulfuric acid is based on a substitution of the Li atom by a H atom inside the structure of spodumene, leading to the production of an aluminosilicate residue [30].
The plant is expected to produce 205,000 t of residues per year, mainly composed of aluminosilicate. A quantity of 17 kg of these aluminosilicate residues was provided by NLI to conduct this research work. To obtain representative samples for characterization and zeolite synthesis tests, the received batch of aluminosilicate residue was spread into a circular flat cake. Afterwards, the retained circular was divided into four quarters. Two opposite quarters were discarded, and the other two quarters were combined to form a subsample, which was subsequently spread out and then divided into six quarters. The two opposite quarters were mixed to finally obtain three representative samples. These samples were dried at 60 °C for 12 h and then sieved using a series of different sieves (500, 250, 160, 75 and 53 µm). Based on its chemical characterization (Table 1), the small fraction (<53 µm) was selected for the synthesis of zeolite because its Si/Al ratio is equivalent to the commercial zeolite 13X used as a reference material.

Table 1.
Concentrations of major (expressed as oxides in %) and minor elements (mg/kg) as well as Si/Al molar ratio of aluminosilicate residue.
Commercial 13X zeolite powder was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Mississauga, Canada (2 µm average particle size, chemical formula: Na86[(AlO2)86(SiO2)106].xH2O). This zeolite was used as a reference material for comparison with the zeolites synthetized from aluminosilicate residues. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reagent with 97% purity (Fisher Scientific) was used for zeolite synthesis.
2.2. Zeolite Synthesis Testing
The conventional hydrothermal process is widely used and is considered a simple and cost-effective technique [2]. The zeolitization steps from the raw materials (aluminosilicate residue) involve the following: (i) the dissolution of Si and Al using an alkaline solution, (ii) the formation of an aluminosilicate gel, (iii) crystalline nucleation and (iv) crystal growth of zeolites [2,13,24,31]. So, the conventional hydrothermal process (Process_1) was applied on aluminosilicate residue from NLI to synthesize zeolite NaX. As a comparison and to ensure that it is as effective, an alkaline fusion step was applied to the residue, followed by hydrothermal treatment (Process_2). The steps followed for the synthesis of zeolite from aluminosilicate residues are presented in Figure 1. Each synthesis route was undertaken in triplicate to evaluate their reproducibility.
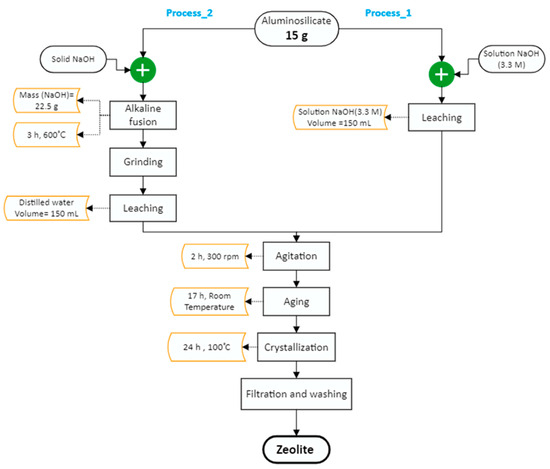
Figure 1.
Zeolites synthesis steps using (i) conventional hydrothermal process (Process_1) and (ii) conventional hydrothermal process assisted by alkaline fusion step (Process_2).
Process_1: Firstly, 15 g of aluminosilicate residue were mixed, at room temperature, with 150 mL of a solution of NaOH (3.3 M) and agitated vigorously for 2 h at 300 rpm, using an orbital shaker (Lab-Line adjustable speed orbital shaker, model 3540) to solubilize Al and Si. Then, the pulp was transferred into a 400 mL beaker and left to age for 17 h at ambient temperature. After aging, the pulp was kept in an electrical oven at 100 °C (Isotemp oven) for crystallization during 24 h. Finally, the solid was separated from the supernatant by vacuum filtration (glass fiber filter G6, 1.6 µm particle size) and washed with distilled water (S/L ratio of 1/10, w/v) to remove excess amounts of NaOH. The recovered solids were dried for 24 h at 60 °C before characterization.
Process_2: For the synthesis of zeolite using the conventional hydrothermal assisted by alkaline fusion process, 15 g of the residue were mixed with 22.5 g of solid NaOH and heated at 600 °C for 3 h in the muffle furnace. Then, the fused product was manually ground using a mortar and a pestle. The same proportion of residue/water was kept from the conventional hydrothermal treatment by mixing thoroughly the fused and ground material with 150 mL of distilled water. Then, the pulp was agitated at room temperature for 2 h at 300 rpm, using the orbital shaker. Aging, crystallization, filtration, rinsing and drying steps are the same as for Process_1.
2.3. Evaluation of Operational Parameters
Two series of tests were conducted to evaluate the effect of (i) crystallization time as well as aging time and temperature and (ii) solid/liquid ratio on the quality of the zeolite produced (i.e., ion-exchange capacity).
2.3.1. Effect of Crystallization Time as well as Aging Time and Temperature
The effect of different parameters, crystallization time as well as aging time and temperature, on the performances of zeolite synthesis (i.e., ion-exchange capacity) was evaluated. For this purpose, two series of tests were realized. For both series of experiments, for the first step, 15 g of aluminosilicate residue were mixed with 150 mL of a solution of NaOH (3.3 M) at 300 rpm for 2 h at room temperature. The first series of tests (n = 5), performed to evaluate the robustness of the process, was carried out based on optimal conditions found in the literature for the synthesis of zeolites 13X [3,6,21,26,28] and on previous tests (results not shown). After mixing, the slurry was transferred into a 400 mL beaker for aging for 16 h at 50 °C. After that, the aged solution was put in an oven for crystallization during 16 h at 100 °C. Finally, the solid was separated by filtration (G6, 1.6 µm pore size) and rinsed thoroughly with distilled water until having a pH of 10–11.
For the second series of tests (n = 12), each experiment was realized just one time because of the good reproducibility of the process (according to the results of the previous series of experiments). In the second series of tests, after mixing the slurry was transferred into a 400 mL beaker for aging. Different aging times (8, 16 and 24 h) and aging temperatures (25, 50 and 75 °C) were tested to evaluate their performances on the produced zeolite ion-exchange capacity. After aging, the aged solution was put in an oven for crystallization at 100 °C during 8, 16 and 24 h.
For both series of experiments, the obtained products were dried for 24 h at 60 °C before characterization.
2.3.2. Effect of Solid/Liquid Ratio
Once the selected conditions for zeolite synthesis that gave NaX zeolites with a higher ion-exchange capacity were found, the effect of the solid/liquid ratio on the performances of synthesized zeolite (i.e., ion-exchange capacity) was investigated by varying the ratio between 10 and 30% (w/v), using a one-factor response surface design. Response surface methodology (RSM) is a mathematical and statistical technique used to establish a relationship between a response (output) and operating parameters (input) [32]. The data analysis was carried out using Design Expert® software version 13 (V. 13.0.11.0 Stat-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA), applying a one-factor methodology design. According to this design, the total number of experiments was fixed at 7, and the ion-exchange capacity of the produced zeolite was used as the response.
In this series of experiments, the volume of NaOH solution (3.3 M) was fixed at 150 mL, and the amount of the aluminosilicate residue was changed to reach the desired S/L ratio (from 10 to 30%, w/v). The slurry was agitated for 2 h at 300 rpm at room temperature and then aged for 8 h at 75 °C. After aging, the mixture was subjected to crystallization for 16 h at 100 °C. Finally, the solid was recovered by filtration (G6, 1.6 µm pore size). Then, the final product was washed with distilled water (S/L ratio of 10%, w/v) to remove excess NaOH and dried for 24 h at 60 °C.
2.4. Determination of Ion-Exchange Capacity
Ion-exchange capacity experiments were carried out by mixing 2 g of zeolite with 100 mL of a solution of CaCl2·2H2O (0.05 M—Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). NaOH and HNO3 were used to have a pH-neutral solution. The pulp was agitated at 250 rpm for 24 h to ensure that equilibrium was reached. Then, the solid was separated by filtration, and the residual Ca concentration in the solution was measured by ICP-AES. The amount of the Ca2+ adsorbed on the zeolite (mg Ca/g zeolite) was calculated using Equation (1).
where Co is the initial concentration of Ca2+ (mg/L), Ce is the remaining concentration of Ca2+ after 24 h of sorption (mg/L), V is the volume of the solution (L), and m is the amount of zeolite used (g).
Ion-exchange capacity (Ca2+) = (Co − Ce) × V/m
2.5. Analytical Methods
The particle size distribution of the aluminosilicate residue and zeolite was determined using a Horiba Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer (model LA-950). Specific surface area of the zeolites was measured using the Sync 210 surface area and pore analyzer (Altamira Instruments, Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Prior to the nitrogen sorption isotherm at 77K, samples were degassed under vacuum for 17 h at 250 °C. BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) equation was used to determine the surface area.
Alkaline fusion with lithium metaborate is an efficient method to completely solubilize solid samples [33]. A quantity of 0.1 g of dried and ground sample was mixed with 1 g of lithium metaborate (LiBO2). This mixture was heated until the sample was completely dissolved in the flux and then poured into the melting acid (0.5% HCl + 10% HNO3) before being stirred for a few minutes to obtain a homogeneous solution. The chemical composition of the aluminosilicate residue and zeolites was then determined using an Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES; Varian, Model 725-ES, Palto Alto, CA, USA).
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were performed on aluminosilicate residue and zeolites, using a Malvern Panalytical Aeris instrument in an external laboratory (Mining Department at Laval University), using a Cu-anode (8 mA, 40 kV) scanning with 2θ ranging from 5° to 85° with a 0.02° step-size scanning with 48 s scan time. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM—Carl ZEISS EVO® 50 Smart, Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC, White Plains, NY, USA), equipped with Everhart-Thornley Secondary Electron detector (SE), was employed to observe the morphology of the aluminosilicate residue and zeolites. The samples for SEM were coated with gold, using SPITM sputter coater module, USA. The morphology of the aluminosilicate residue, zeolite produced using Process_1 and Process_2, as well as commercial zeolite 13X was given by imaging in high-vacuum state at 15 kV and different magnifications (Mag) with working distance of 7 to 8 mm.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization of Aluminosilicate Residue
The particle size distribution of the aluminosilicate residue, presented in Table 1, shows that more than 56% of the residue has a particle size inferior to 53 µm, while for other fractions, the percentage is between 6 and 12%. In addition, the median size (D50) of aluminosilicate residue is 21.5 µm, whereas D10 = 4.9 µm and D90 = 264 µm.
The chemical composition of each fraction is presented in Table 1. The major elements found are silicon (between 70 and 88% as SiO2) and aluminum (between 9 and 29% as Al2O3), which is in accordance with the origin of the residue (extraction of Li from spodumene). The Si/Al ratio found in each fraction ranged from 2.06 (in the fraction <53 µm) up to 8.37 (in the fraction >500 µm). Iron, potassium, calcium and sodium are present in very small amounts (less than 1.6%). As for minor elements, Li concentration in the initial product (aluminosilicate residue) and the different fractions are very low (0.30–1.16%), indicating that aluminosilicate residues contained low amounts of potential impurities, which is beneficial for their use in the synthesis of zeolite. The composition of Li-slag described in other studies was found to be variable and dependent on the location of the deposit [21].
The small fraction (<53 µm), which represents more than 56% of the initial residue, contained high silica and alumina content and a low concentration of other elements in comparison to the other fractions. In addition, Li concentration in this small fraction is around 0.34%, which is quite low compared to other fractions that can be used for other applications, such as glass and ceramics production, due to their higher Li content (up to 1.16%) [1,23]. The Si/Al molar ratio of 2/1 measured in the <53 µm fraction is the closest, compared to other fractions, to the conventional ratio measured in commercial zeolite 13X (Si/Al molar ratio of 1.32/1). Based on these observations, the <53 µm fraction of the present aluminosilicate residues seems to be the most suitable material for the synthesis of zeolite NaX.
XRD patterns of the aluminosilicate residue are shown in Figure 2 and compared with the zeolites produced from the two different processes tested. The diffractogram of the aluminosilicate residue has a main peak at 2θ = 25.7°, consisting of a HAlSi2O6 structure like a β-spodumene structure [30], which is in accordance with the mechanisms involved in the extraction of Li from β-spodumene. An SEM image of the fraction inferior to 53 µm is presented in Figure 3 in comparison with the zeolites produced from the two different processes tested. The fine fraction of aluminosilicate residue consists of small and fractured particles with an amorphous shape, which can be due to the calcination step used to convert the refractory α-spodumene to the less refractory β-spodumene before Li extraction.
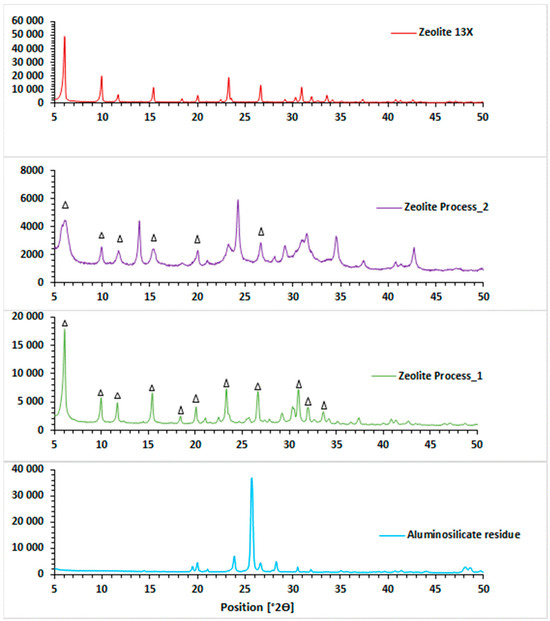
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the aluminosilicate residue (<53 µm), zeolite process_1 (zeolite-without pre-treatment), zeolite process_2 (zeolite-alkaline fusion). ∆ zeolite 13X.

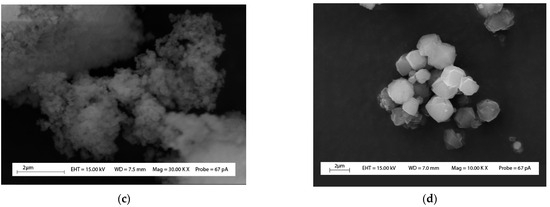
Figure 3.
Scanning electron micrographs of (a) aluminosilicate residue (fraction inferior to 53 µm), (b) zeolite_process_1, (c) zeolite_process_2, (d) zeolite 13X.
3.2. Characterization of the Zeolite Produced
3.2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Synthesized Zeolite
The chemical composition of the zeolites produced by the two different synthesis routes is given in Table 2. Alumina content (29.8–31.2%) was found to be the same in zeolites produced via the two different routes, which is also like commercial zeolite 13X (32.8%). For silica, the concentrations in zeolites produced (44.8–51.7%) were lower than the initial aluminosilicate residue (70.4%). This decrease in SiO2 content leads to an important decrease in the Si/Al ratio from 2.06 (aluminosilicate residues) to 1.22–1.47, which is closer to commercial zeolite 13X (1.32). It can be noticed that SiO2 contents measured in zeolite produced from Process_1 (51%) is higher than SiO2 content in zeolite synthesized from Process_2 (44.8%), highlighting a higher dissolution of Si when adding an alkaline fusion step. Similar trends were observed in previous studies when an alkaline fusion method was used to improve Si and Al solubilization from fly ash before producing zeolite with high purity in the subsequent hydrothermal treatment [13,34]. This was explained by the conversion of fly ash into alkali silicate and aluminate, which are very soluble in aqueous solutions [13,35,36].

Table 2.
Composition in major (expressed as percentage of oxides) and minor (expressed in mg/kg) elements as well as Si/Al molar ratio of zeolites.
A significant increase in Na2O concentration (17.8–23.1%) was observed in the zeolites produced, no matter the synthesis route used, compared to the initial aluminosilicate residue (0.13% of Na2O). This can be explained by the fact that Na contributes to zeolite nucleation and crystallization [17]. However, the final Na2O concentration measured in the zeolite produced from Process_2 is around 23%, which is higher than Process_1 (17%) and closer to commercial zeolite 13X, highlighting potential higher ion-exchange capacities. Magnesium, calcium, manganese and minor elements are present in very low concentrations in the zeolite produced by the two different process routes, reducing the potential risks of contamination of zeolite once used for water treatment or other applications.
3.2.2. Mineralogical Characterization of Synthesized Zeolite
XRD patterns of zeolites produced from the two synthesis routes showed that several diffraction peaks appeared in comparison with the initial aluminosilicate residue, highlighting significant changes in the structure of the aluminosilicate residues, regardless of the synthesis route used (Figure 2). For the zeolites produced using Process_1 and Process_2, the replacement of peaks specific to the presence of aluminosilicate (2θ = 25.7°) by some peaks specific to zeolite 13X is a good indicator of an efficient conversion of aluminosilicate residue into zeolites using the conventional hydrothermal process assisted by alkaline fusion or not.
According to the XRD diagrams of the 13X commercial zeolite, the main peaks attributed to this type of zeolite are at 2θ = 6.1°, 9.9°, 11.7°, 15.4°, 19.9°, 23.3°, 26.6° and 30.9°. The sharpness of the peaks with high diffraction intensity and the absence of background (meaning the absence of amorphous phase) are the most important features of the diffractogram of this highly crystalline zeolite 13X produced from pure chemicals.
XRD diagrams of zeolites produced from the two different processes showed that the final products have a structure quite similar to that of commercial zeolite 13X in terms of diffraction peaks, while a background appeared that can be explained by the presence of amorphous phases.
The diffractogram of Process_1 zeolite showed that all the characteristic peaks of 13X zeolite are present with a good sharpness, but that the intensity of the diffraction peaks is lower. However, for Process_2 zeolite, it was found that the peaks were not well-defined (low sharpness) and that the number of peaks characteristic of 13X zeolite decreased compared to Process_1 zeolite. According to the literature, alkaline melting prior to subsequent hydrothermal treatment improves zeolite synthesis performance. In fact, several studies have demonstrated that when using this step, the raw material can be converted into a large quantity of soluble silicate and aluminate species, producing a high concentration of Si and Al, which participate in zeolite formation. It is, therefore, clear that NaX zeolite (characterized by a metastable structure) was produced using this method. However, after 24 h of crystallization, the NaX zeolite formed began to change its structure, which could be explained by the presence of peaks characteristic of 13X zeolite, but with less intensity and sharpness. This could also explain the lack of sharpness of the peaks and the presence of the background justifying the presence of amorphous particles.
Finally, the formation of NaX can be explained by the similar Si/Al ratio (equal to 2) of the aluminosilicate residue (fraction <53 µm) and zeolite 13X. Indeed, the Si/Al ratio plays an important role in determining the crystal structure of the zeolite produced [8,18]. In a previous study, XRD results showed that when the Si/Al ratios in the reaction mixture were lower than 2.0, between 2.0 and 2.4 or between 2.4 and 3.0, zeolites Na-A, Na-X or Na-Y were formed, respectively [37].
SEM images of initial aluminosilicate residue (fraction inferior to 53 µm) and zeolites are presented in Figure 3. Octahedral crystalline shape like those observed for zeolite 13X particles (Figure 3d) can be seen in the SEM images of zeolites produced by Process_1 (Figure 3b). The apparition of octahedral particles observed for zeolite produced from Process_1 (Figure 3b) compared to initial aluminosilicate residues, where no octahedral particles were observed (Figure 3a), confirms that Process_1 allowed the conversion of aluminosilicate residues to by-products with properties like zeolite 13X. However, for zeolite produced using Process_2 (Figure 3c), it was difficult to identify the morphology even with high magnification (30 kx), which can be explained by the small size of the particles present, confirmed by the higher sorption capacity obtained with this route of synthesis of zeolites (Table 3). In a previous study, it had been found that formation of smaller particles size leads to a higher sorption capacity of zeolite [27].

Table 3.
Calcium ion-exchange capacity (mg/g) of the aluminosilicate residue and zeolites produced using two processes in comparison to certified zeolite 13X.
3.3. Ion-Exchange Capacity of Synthesized and Commercial Zeolites
Ion-exchange capacities of the initial aluminosilicate residue as well as synthesized and commercial zeolites towards Ca2+ sorption from synthetic effluents are summarized in Table 3. Zeolites synthesized using Process_1 and Process_2 demonstrated higher sorption capacities compared to the initial aluminosilicate residue (60–65 mg Ca/g vs. 1.1 mg Ca/g). These results indicate that the conventional hydrothermal process assisted or not by alkaline fusion significantly improved the properties of the residues to fix elements from synthetic effluents, improving the potential to valorize them (t-values = 74.7–129 vs. t-theoretical (α = 0.05) = 2.1–2.3).
A significantly higher ion-exchange capacity was obtained for zeolite Process_2 compared to Process_1 (t-values of 4.99 vs. t-theoretical (α = 0.05) = 2.35), which can be explained by the higher amount of exchangeable Na+ found in zeolite Process_2 (23% of Na2O). However, it can be noticed that Ca2+ sorption capacities of synthesized zeolites were slightly lower than for commercial zeolite 13X (76 mg Ca/g). These lower sorption capacities can be balanced by the fact that these zeolites were produced from residues available in large amounts instead of pure chemicals, thus reducing operating costs.
Based on the physico-chemical (including Ca2+ sorption capacities) and mineralogical characterization of the zeolite produced, the conventional hydrothermal process was the most performant approach (i.e., Si/Al ratio of 1.47/1, presence of octahedral particles showing the presence of zeolite X, ion-exchange capacity of 60 mg/g) for further testing. It is worth noting that the conventional hydrothermal process is the easiest synthesis process in terms of consequential steps for the synthesis of zeolite and is, therefore, less expensive compared to the hydrothermal process assisted by alkaline fusion.
3.4. Evaluation of Operating Parameters on the Performances of the Conventional Hydrothermal Process to Produce Zeolite
Additional experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of operating parameters (i.e., aging time and temperature, crystallization time) of the conventional hydrothermal process on the properties (i.e., Ca2+ ion-exchange capacity) of the synthesized zeolites (Table 4). The first series of tests (n = 5) was performed to evaluate the robustness of the process. The mean and standard deviation of the Ca2+ sorption capacities were 55.64 and 0.88, respectively. So, the coefficient of variation for these replicates was 1.58%, which is very low, indicating good reproducibility of the conventional hydrothermal process to convert aluminosilicate residue into zeolites. So, for further series of experiments, tests were conducted just once.

Table 4.
Effect of operating conditions of the conventional hydrothermal process on the sorption capacity of synthesized zeolites.
3.4.1. Effect of Aging Time
Regarding the aging step, this period preceding the crystallization step is a crucial step to synthesize a desired zeolite. Partial dissolution or depolymerization of the silica (SiO2) is one of the most important steps occurring during the period of aging [38]. The subsequent crystallization step, which is carried out at high temperatures, proceeds more quickly when applied to aged gel compared to gel without aging [38]. Indeed, it has been noted that nuclei can be formed in the gel or solution during the aging period, increasing its size upon the elevated temperature used during the crystallization step [38].
The effect of aging time on the sorption capacities of synthesized zeolites was evaluated between 8 and 24 h (Table 4). The results show that increasing aging time from 8 to 24 h seemed to have a negligible effect on Ca2+ sorption capacities of synthesized zeolites. For example, for a crystallization time of 16 h, sorption capacities are quite similar (56–57 mg Ca/g) when increasing aging time from 8 to 24 h for aging experiments performed at both 25 and 75 °C. These results show that an aging time of 8 h was sufficient to effectively dissolve Al and Si from aluminosilicate residue and form nuclei when the crystallization time is quite long (16 h or more).
However, for lower crystallization time (8 h), increasing the aging time from 8 to 24 h (at 50 °C) improved sorption capacities by 1.45-fold (experiments 7 and 8, respectively), which can be due to improvements in zeolite crystallinity occurring with higher aging time [28,39] and allowing the formation of smaller particles with higher ion-exchange capacity [27]. These results are consistent with previous studies highlighting that aging is an important step in the zeolitization process since it reduces crystallization time and crystals size while increasing the nucleation rate [8,28].
3.4.2. Effect of Aging Temperature
The effect of aging temperature (from 25 to 75 °C) on the sorption capacities of synthesized zeolites was also evaluated (Table 4). As can be observed, increasing the aging temperature from 25 to 75 °C led to an important increase in sorption capacities from 27 (experiment 6) to 56 mg Ca/g (experiment 9) after 8 h of crystallization at 100 °C. Similar improvements in sorption capacities while increasing aging temperature were observed after 16 or 24 h of crystallization. This can be due to a better solubilization of Al and Si, leading to higher crystallinity of the produced zeolites. Based on these results, increasing aging temperature from 25 to 75 °C will allow a significant decrease in crystallization time (from 24 to 8 h) without affecting the final properties of the synthesized zeolites. These results are consistent with previous studies explaining that a complete dissolution of metakaolin occurring at a higher aging temperature (50 °C vs. room temperature) led to the formation of gel containing more crystalline particles [27].
3.4.3. Effect of Crystallization Time
According to our results, crystallization time is the main parameter affecting the sorption capacity of the synthesized zeolite. It can be noticed that zeolites with very low sorption capacities (around 27 mg Ca/g) were synthesized at low crystallization time (8 h), while higher sorption capacities were reached (around 55–57 mg Ca/g) when increasing crystallization time to 16 or 24 h, irrespective of aging time or temperature (Table 4). Moreover, the sorption capacities of zeolite reached a plateau after 16 h of crystallization time compared to 24 h. These results suggest that zeolite crystallization was complete within 16 h, which is consistent with a previous study [6]. Indeed, Zhang et al. (2013) found that at 90 °C, longer crystallization time (15 h) allowed the production of well-crystallized Faujasite, while no crystalline structure of zeolite was observed after 3 h of crystallization [26].
3.4.4. Effect of Solid/Liquid Ratio on Zeolite Properties
The effect of the solid/liquid (S/L) ratio (from 10 to 30%) on the sorption capacities of the synthesized zeolite was evaluated using a one-factor design approach (Table 5). ANOVA was used for testing the statistical significance of the established mathematical model. According to the ANOVA, the high F-value of 378 and Prob > F (p-value) lower than 0.05 indicate that the cubic model established is significant. In addition, the p-value of the lack of fit > 0.05 and the correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.997, adjusted R2 = 0.994 and predicted R2 = 0.987) imply that the proposed cubic model fit very well with the experimental data. The cubic model, expressed in terms of coded factors, is represented by Equation (2).
where Y is the sorption capacity and X is the S/L ratio.

Table 5.
Effect of the S/L ratio (%) on sorption capacity (mg Ca/g) of zeolite using one-factor design.
As expected, an increase in the S/L ratio led to an important decrease in the sorption capacities of synthesized zeolite. It can be noticed that zeolite with two times lower sorption capacities were synthesized when increasing the S/L ratio from 10 to 30%. This loss of efficiency to produce zeolite with satisfactory properties can be due to a lower volume of NaOH used, which might not be sufficient to adequately solubilize Si and Al from aluminosilicate residue, thus decreasing zeolite crystallinity and, therefore, sorption capacities. The best sorption capacity for produced zeolite was obtained with a S/L ratio of 10%.
Finally, the most efficient conditions to produce zeolite NaX from aluminosilicate residue were found to be a S/L ratio of 10%, 8 h of aging at 75 °C and 16 h of crystallization at 100 °C. The physico-chemical characteristics of the zeolite produced under the most performant conditions, initial aluminosilicate residue (<53 µm) and commercial zeolite 13X are summarized in Table 6. The Si/Al ratio of zeolite produced (1.48/1) was found to be lower than the initial residue (2.06/1) and closer to commercial zeolite 13X (1.32/1). Regarding sorption capacity, it was found that the zeolite produced (58.4 mg Ca/g) had a higher ion-exchange capacity compared to the initial residue (1.1 mg Ca/g) and was closer to zeolite 13X. The medium particle size of the zeolite produced (10.2 µm) was lower than that of aluminosilicate residue (21.5 µm) while being higher than commercial zeolite 13X (3.8 µm). However, the specific surface area of the synthesized zeolite (371 m2/g) was higher than initial aluminosilicate residue (5.6 m2/g) but was found to be lower than commercial zeolite 13X (962 m2/g). The crystallization process began on the surface of undissolved particles’ residue [29], allowing the production of larger particles. It has been noted that larger particle size leads to having a lower specific surface area [18], while using pure aluminate and silicate chemicals to produce commercial 13X zeolite gives a zeolite with smaller particle size and higher specific surface area.

Table 6.
Characterization of zeolite-efficient conditions, aluminosilicate residue (<53 µm) and commercial zeolite 13X.
4. Conclusions
Zeolite NaX with a high ion-exchange capacity (60 mg Ca/g) was synthesized from aluminosilicate residues originating from lithium extraction from spodumene using the conventional hydrothermal process. Crystallization time was identified as the main parameter influencing the zeolite sorption capacity. Indeed, a significant increase in the sorption capacity from 29 to 56 mg Ca/g was observed when increasing crystallization time from 8 to 16 h, while a plateau was observed between 16 and 24 h. These results show that 16 h of crystallization was enough to produce zeolite with a good sorption capacity. It was noticed that aging time did not influence zeolite properties, while increasing the aging temperature from 25 to 75 °C for 8 h of crystallization significantly improved the sorption capacity of the zeolite produced. Finally, the most performant conditions to synthesize zeolite from aluminosilicate residue were identified as follows: S/L ratio of 1/10 (w/v), aging time of 8 h, aging temperature of 75 °C and crystallization time of 16 h. The maximum sorption capacity of zeolite produced was around 58 mg Ca/g, which is close to commercial zeolites 13X (76 mg Ca/g). These results demonstrate the high potential to use aluminosilicate residue (low-cost material) generated from Li extraction from spodumene to synthesize zeolite NaX, which can be used as an ion exchange for water treatment. Finally, the synthesis of zeolite using aluminosilicate residues instead of pure sodium silicate and aluminate products (expensive and not sustainable materials) has two important advantages, which are that it reduces both the environmental footprint of these residues generated from the Li production process and the cost of the preparation of synthetic zeolite.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis and writing—original draft: F.I.; Funding acquisition and project administration: J.-F.B.; Supervision and writing—review and editing: D.A., J.D., L.H.T., L.C., L.-C.P. and J.-F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada via the Collaborative Research and Development Grants program (CRDPJ/533857-2018), Nemaska Lithium and the Canada Research Chairs Program.
Data Availability Statement
The relevant datasets analyzed in this study are all presented in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dessemond, C.; Lajoie-Leroux, F.; Soucy, G.; Laroche, N.; Magnan, J.F. Spodumene: The lithium market, resources and processes. Minerals 2019, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, D.; Ibsaine, F.; Dionne, J.; Pasquier, L.C.; Coudert, L.; Blais, J.F. Microporous and macroporous materials state-of-the-art of the technologies in zeolitization of aluminosilicate bearing residues from mining and metallurgical industries: A comprehensive review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 318, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H.; Yao, H. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite X from lithium slag. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 59–60, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, B.J.P.; Yenkie, M.N. Novel Applications in Polymers and Waste Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; 364p. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, S.M.; Carrado, K.A.; Dutta, P.K. Handbook of Zeolite Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; 1184p. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, Z.; Shen, X.; Guo, M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M. A simple hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite X from bauxite tailings for highly efficient adsorbing CO2 at room temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 287, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhuang, Q.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H.; Yao, H. Synthesis and adsorption property of zeolite FAU/LTA from lithium slag with utilization of mother liquid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejka, J.; van Bekkum, H.; Corma, A.; Schueth, F. Introduction to Zeolite Science and Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, T.; Harun, Z.; Othman, M.H.D. A review on sustainable synthesis of zeolite from kaolinite resources via hydrothermal process. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Wang, C.; Zeng, L.; Ma, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C. Lithium extraction and hydroxysodalite zeolite synthesis by hydrothermal conversion of α-spodumene. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9498–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Hopa, Ç.; Yilmaz, Z.; Güler, H. The effect of alkali concentration and solid/liquid ratio on the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite NaA from natural kaolinite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Morales-Ospino, R.; Finocchio, E.; Busca, G.; Sapag, K.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Bastos-Neto, M.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Kaolinite-based zeolites synthesis and their application in CO2 capture processes. Fuel 2022, 320, 123953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C. State-of-the-art applications of fly ash from coal and biomass: A focus on zeolite synthesis processes and issues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 65, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere Ozdemir, O.; Piskin, S. A novel synthesis method of zeolite X from coal fly ash: Alkaline fusion followed by ultrasonic-assisted synthesis method. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 10, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wan, Z.; Daniels, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, G.; Yu, J.; Xu, D.; Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; May, E.F.; et al. Synthesis of high quality zeolites from coal fly ash: Mobility of hazardous elements and environmental applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Han, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y. Synthesis of Na-X zeolite from low aluminum coal fly ash: Characterization and high efficient As(V) removal. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qian, X.; Yuan, P.; Bai, H.; Miki, T.; Men, F.; Li, H.; Nagasaka, T. Green synthesis of zeolite 4A using fly ash fused with synergism of NaOH and Na2CO3. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, C.W.; Salim, C.; Hinode, H. Synthesis of pure Na–X and Na–A zeolite from bagasse fly ash. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 162, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Feasible conversion of solid waste bauxite tailings into highly crystalline 4A zeolite with valuable application. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Ma, H.; Chuan, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite A from K-feldspar and its crystallization mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outram, J.G.; Collins, F.J.; Millar, G.J.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Beer, G. Process optimisation of low silica zeolite synthesis from spodumene leachate residue. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 189, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y. Synthesis of Zeolites. With International Search Report (Art. 21(3)), Australia. Patent N° WO 2019/068135 A1, 1 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Hao, W.; Zhang, S.; Lan, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.N.; et al. Facile activation of lithium slag for the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite A with commercial quality and high removal efficiency for the isotope of radioactive 90Sr. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Azat, S.; Baibatyrova, A. A mini-review on coal fly ash properties, utilization and synthesis of zeolites. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2020, 42, 1968–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Li, J.S.; Wang, L.J.; Sun, X.Y. Influence of NaOH concentrations on synthesis of pure-form zeolite A from fly ash using two-stage method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, D.; Zhang, M.; Yang, R. Synthesis of NaX zeolite: Influence of crystallization time, temperature and batch molar ratio SiO2/Al2O3 on the particulate properties of zeolite crystals. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, L.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Chebude, Y.; Díaz, I. Synthesis of zeolite A from Ethiopian kaolin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 215, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, L.S.M.; Yeong, Y.F.; Sabdin, S. Formation of pure NaX zeolite: Effect of ageing and hydrothermal synthesis parameters. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing, China, 17–19 August 2018; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 458, p. 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Wałek, T.T.; Saito, F.; Zhang, Q. The effect of low solid/liquid ratio on hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from fly ash. Fuel 2008, 87, 3194–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salakjani, N.K.; Singh, P.; Nikoloski, A.N. Production of lithium—A literature review. Part 2. Extraction from spodumene. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2019, 42, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldi, M.; Fuentes-Ordoñez, E.G.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A. Zeolite synthesis from industrial wastes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 287, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuri, A.I.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Response surface methodology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingamells, C. Lithium metaborate flux in silicate analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 1970, 52, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayalu, S.; Meshram, S.; Hasan, M. Highly crystalline faujasitic zeolites from fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 77, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Soe, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Ahn, J.W.; Park, M.B.; Ahn, W.S. Synthesis of nanoporous materials via recycling coal fly ash and other solid wastes: A mini review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 821–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto, N.; Hayashi, H.; Miyaura, K. Selective formation of Na-X zeolite from coal fly ash by fusion with sodium hydroxide prior to hydrothermal reaction. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 4781–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotovat, F.; Kazemian, H.; Kazemeini, M. Synthesis of Na-A and faujasitic zeolites from high silicon fly ash. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrappa, K.; Yoshimura, M. Handbook of Hydrothermal Technology; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oyinade, A.; Kovo, A.S.; Hill, P. Synthesis, characterization and ion exchange isotherm of zeolite Y using Box–Behnken design. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).