Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Organically Modified Natural Acid Clay for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Organoclays
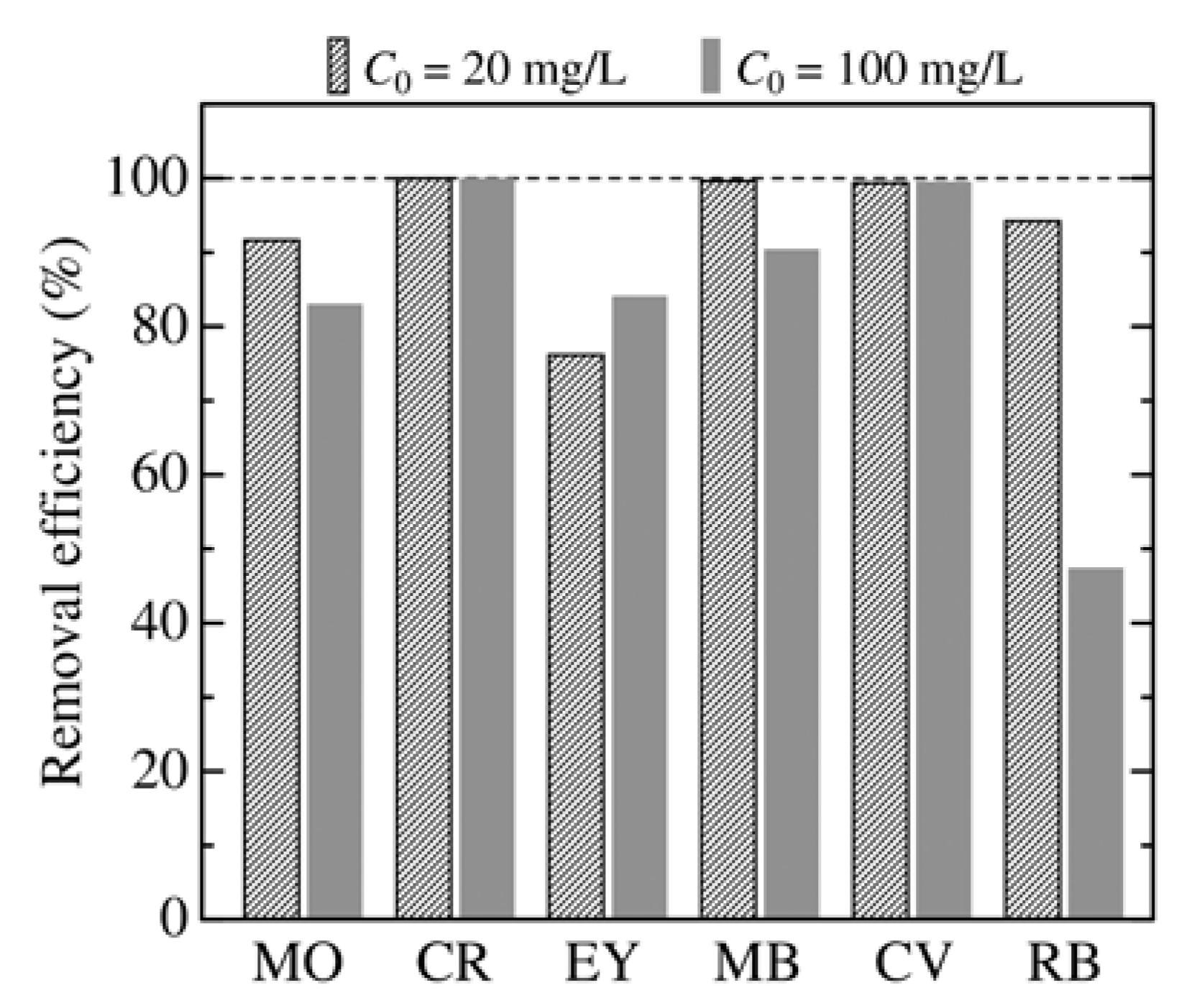
2.2. Dye Adsorption Study
3. Results and Discussion
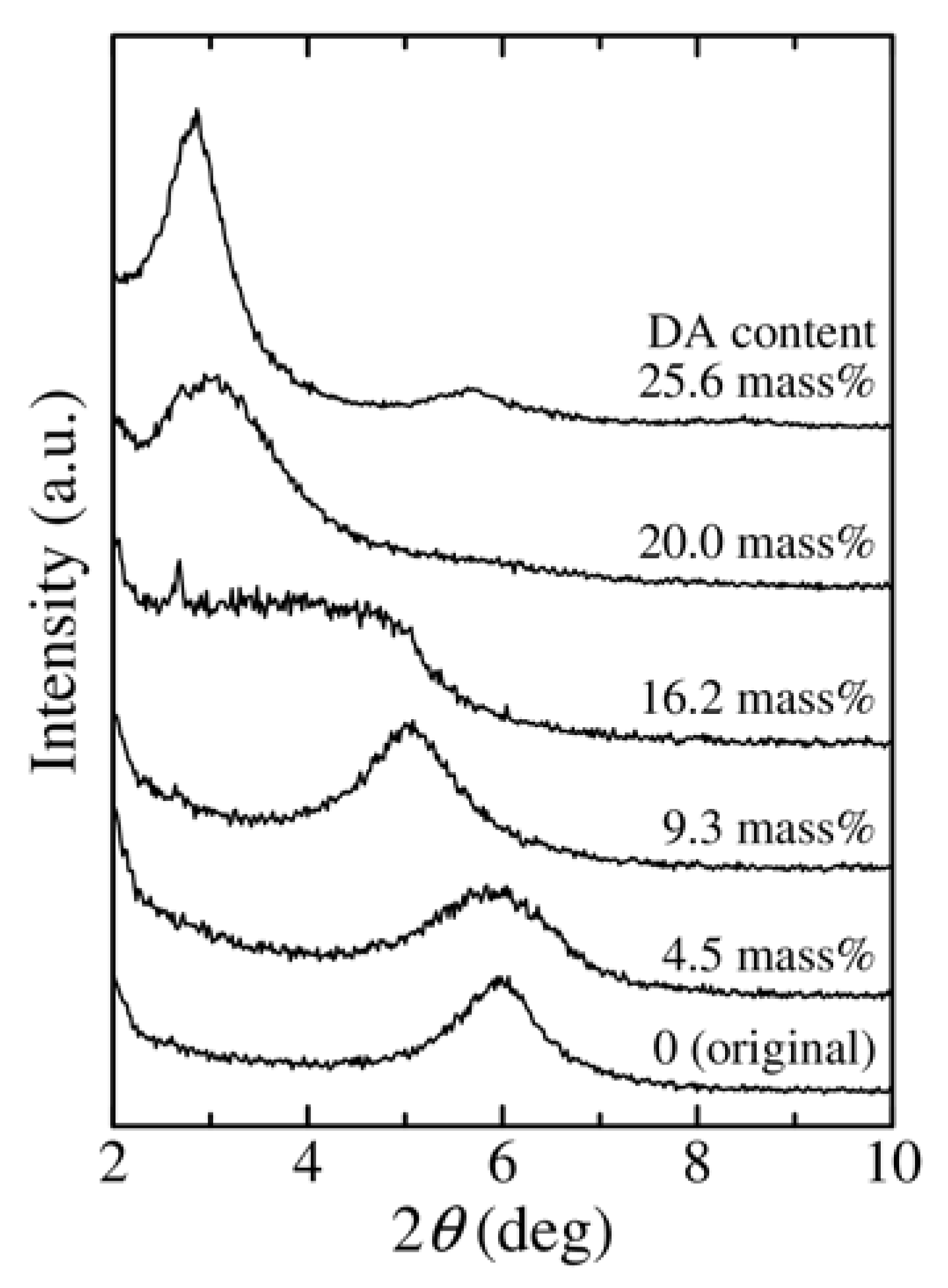
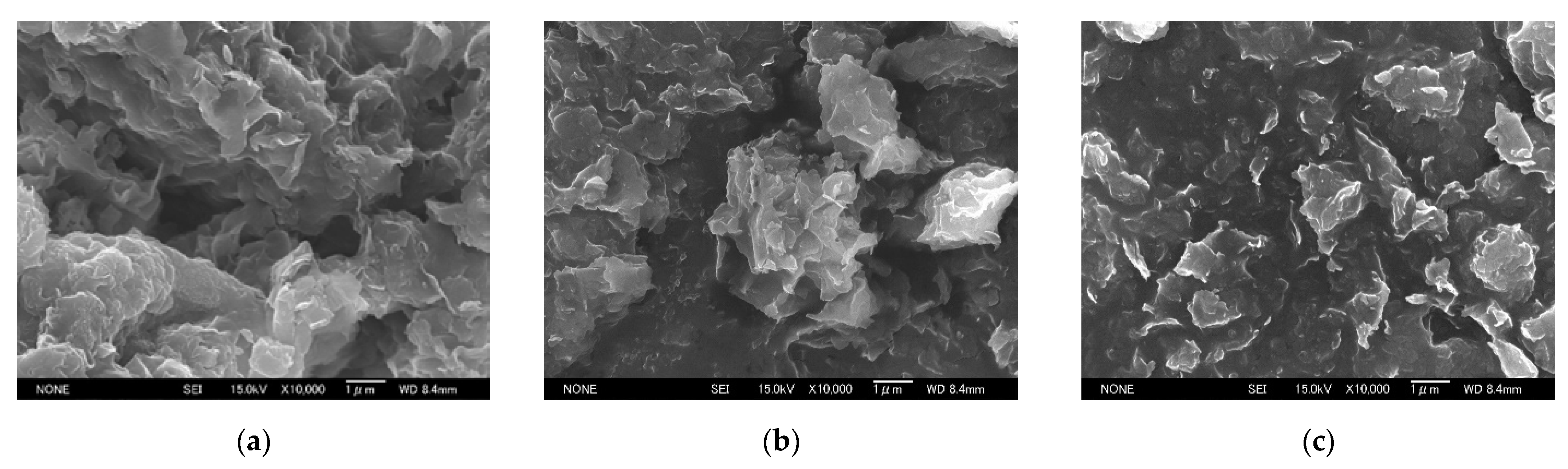
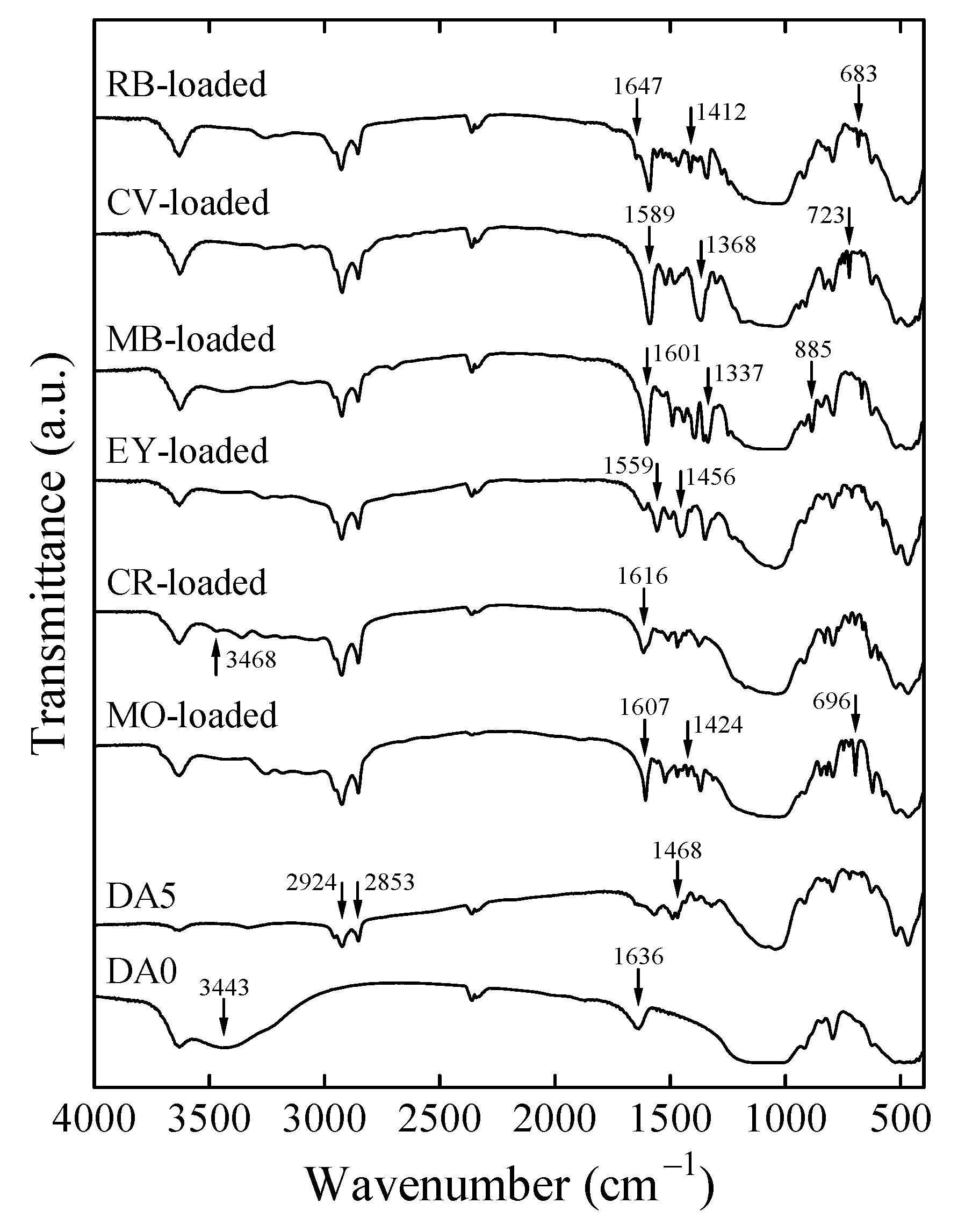
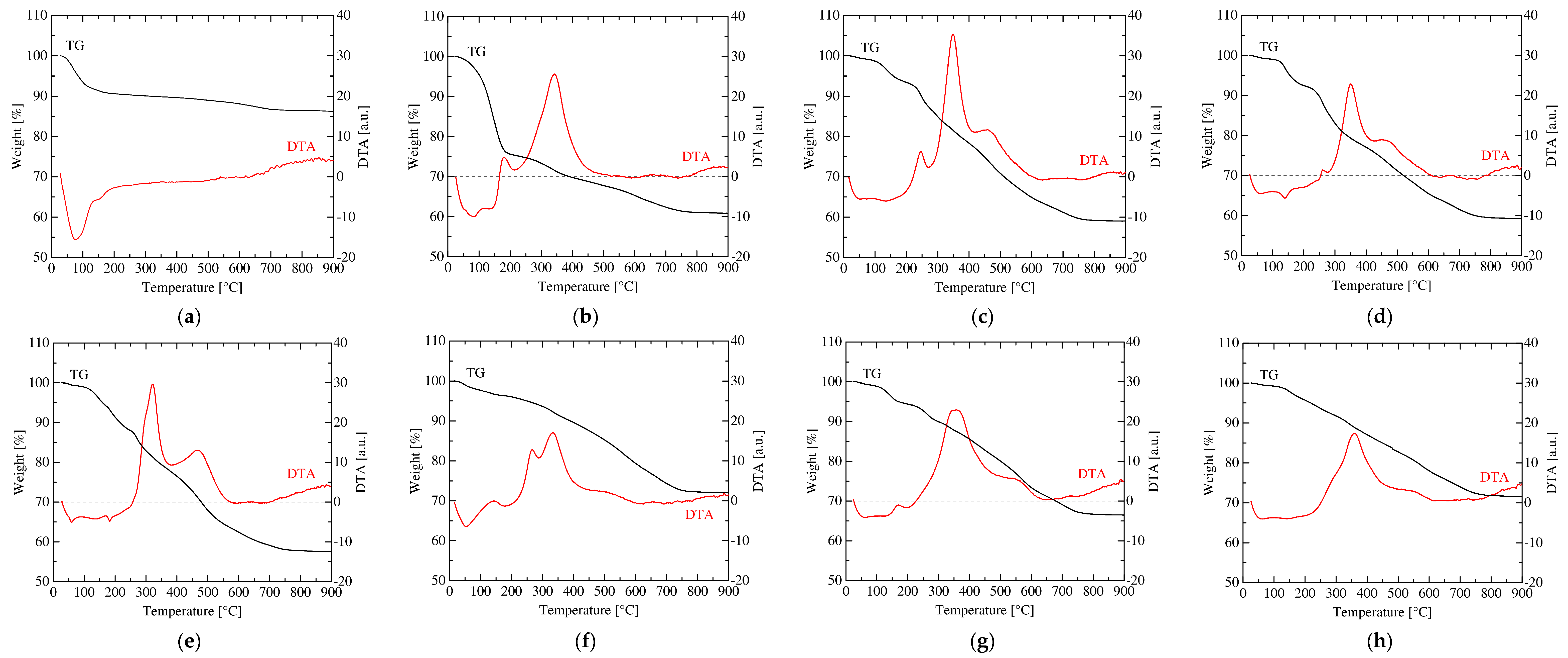
3.1. Change in the Structure of Organoclay with DA Content
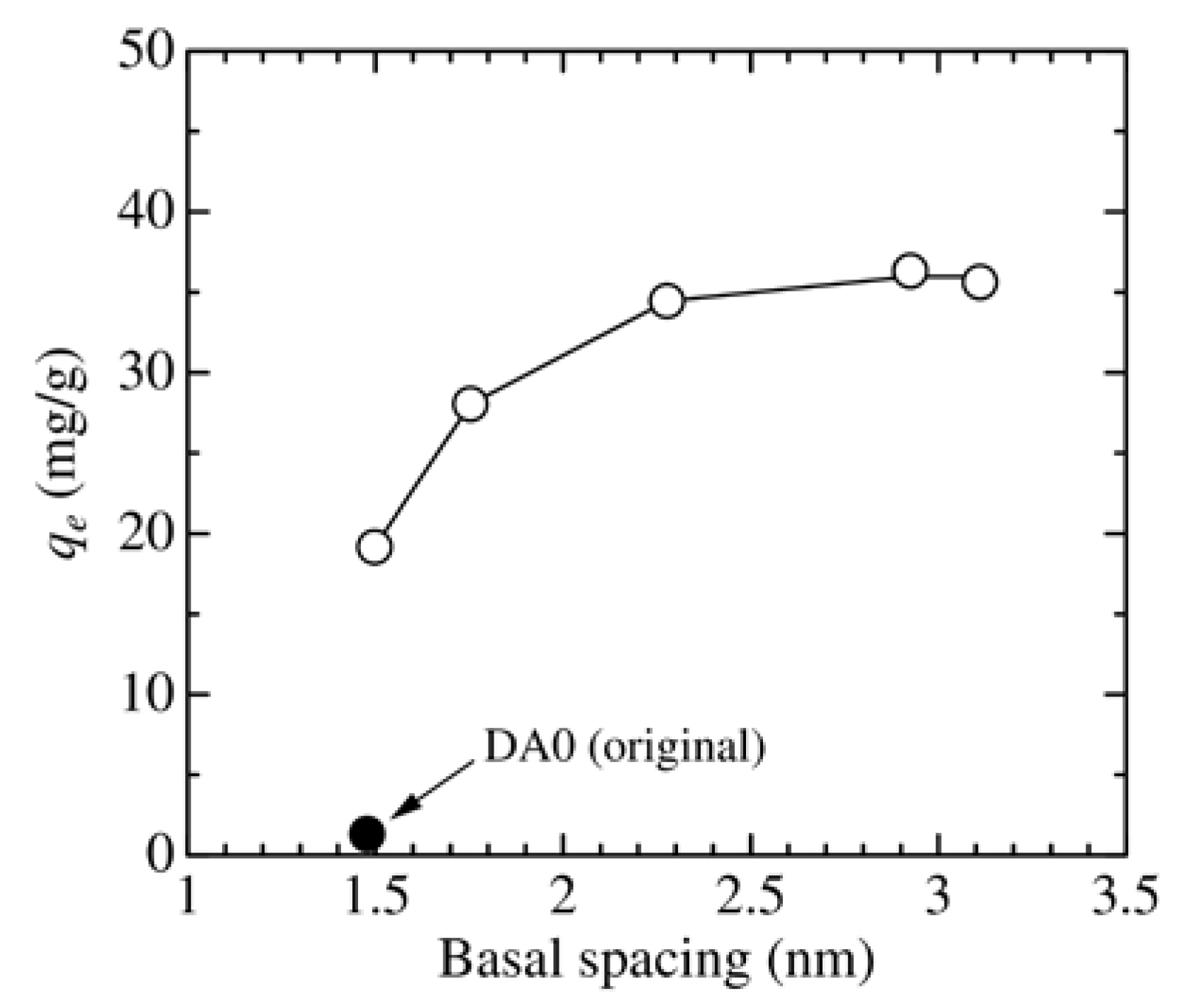
3.2. Effect of Adsorbent Structure on MO Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity
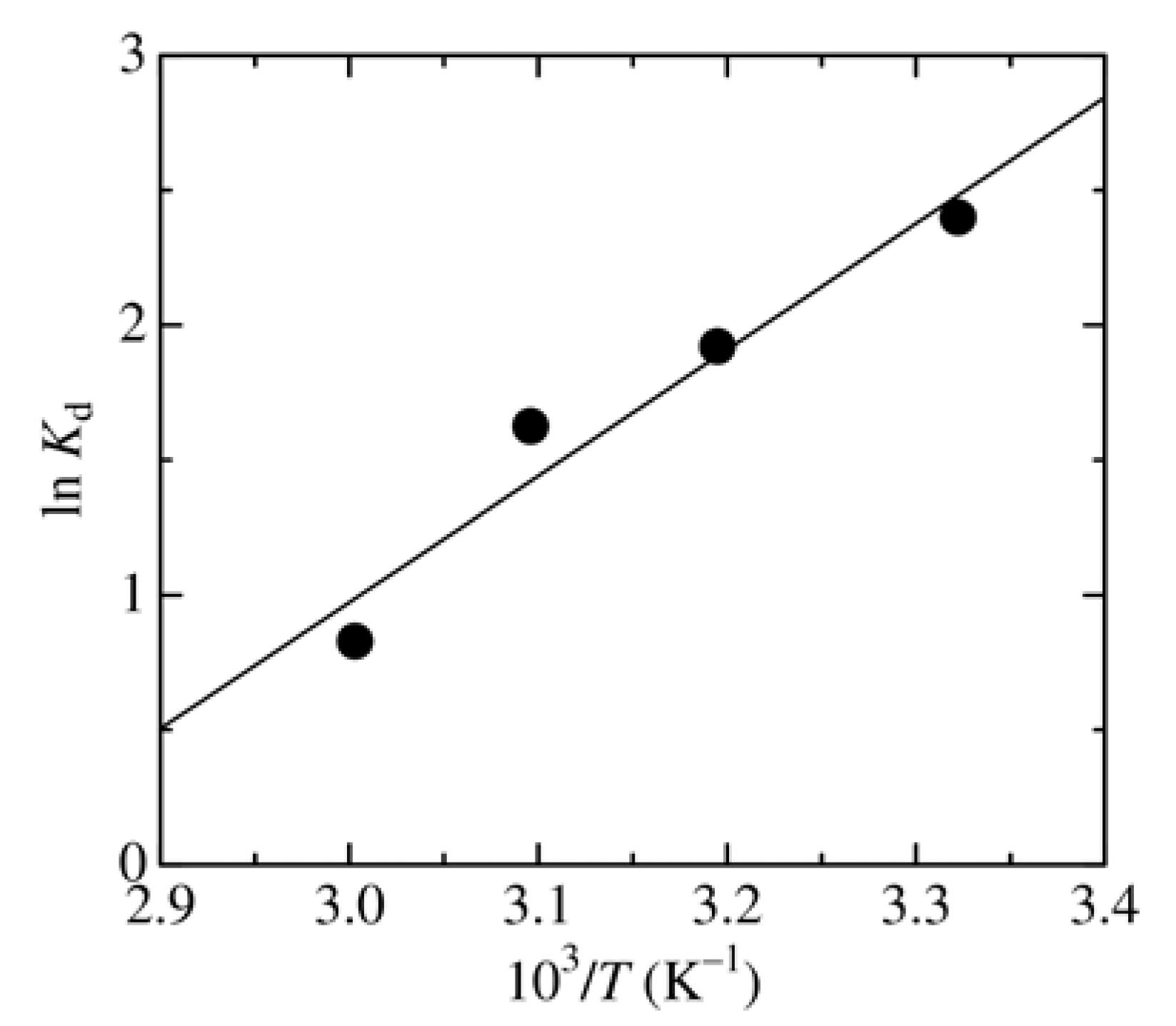
3.3. Dependence of Adsorbent Dosage, pH, and Temperature on MO Removal
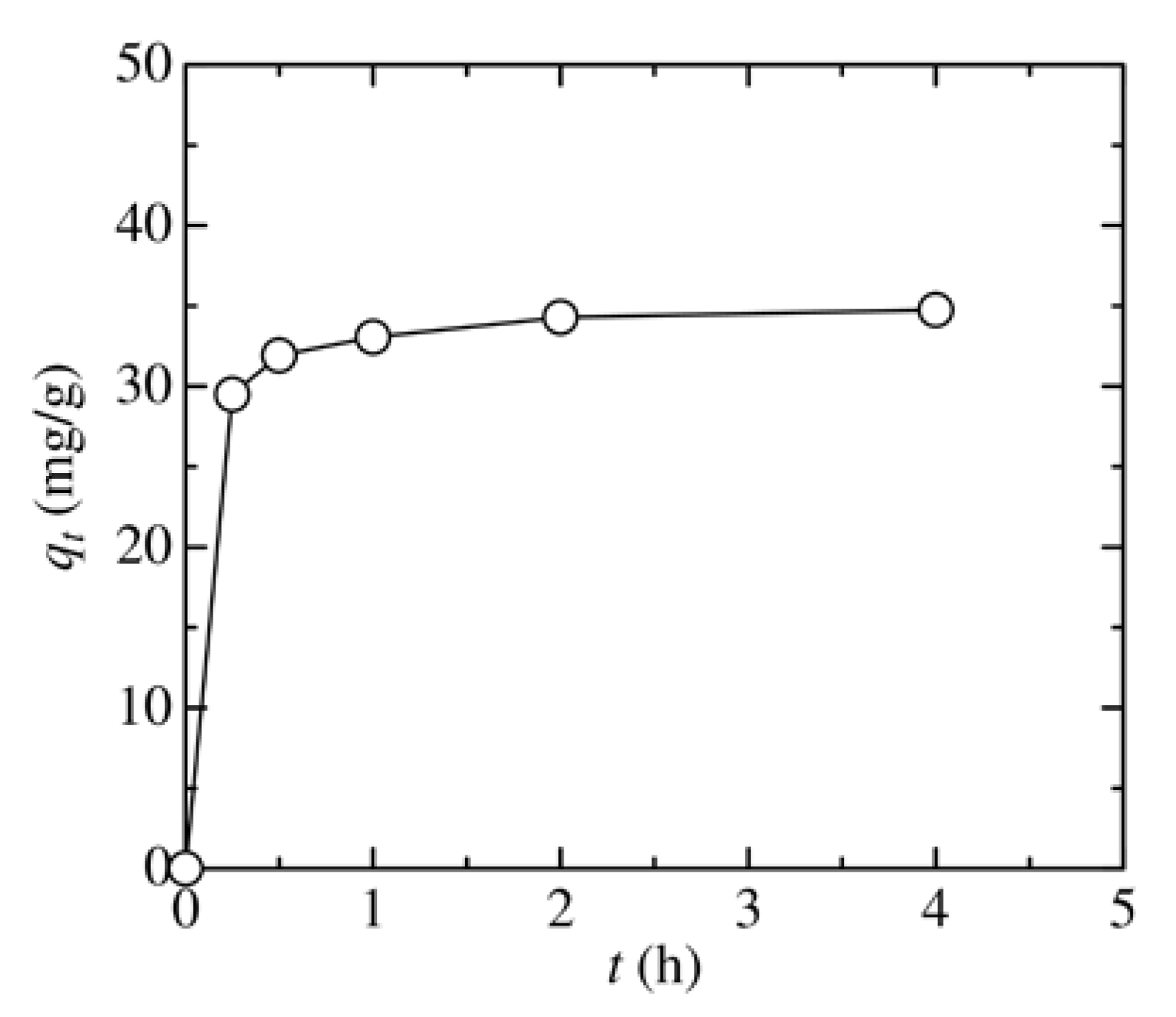
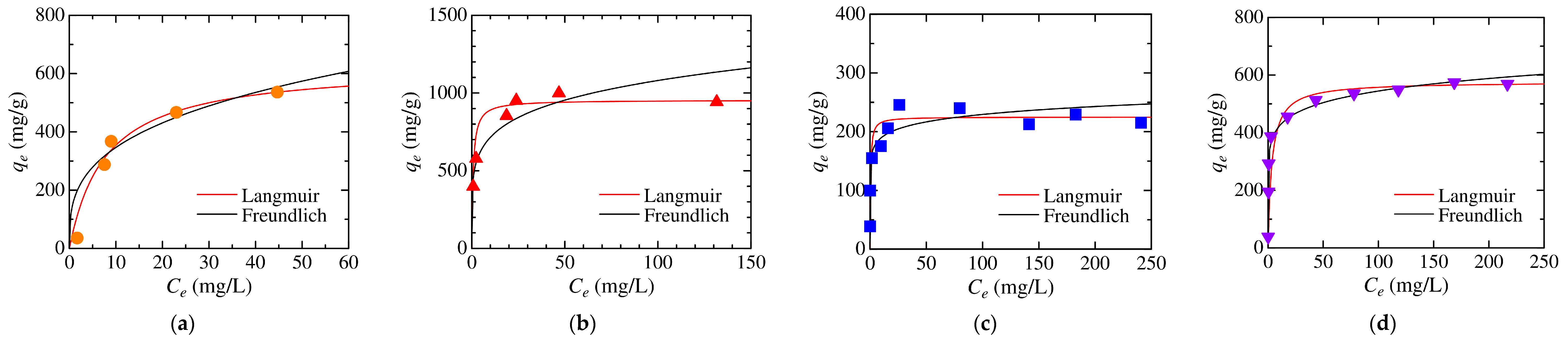
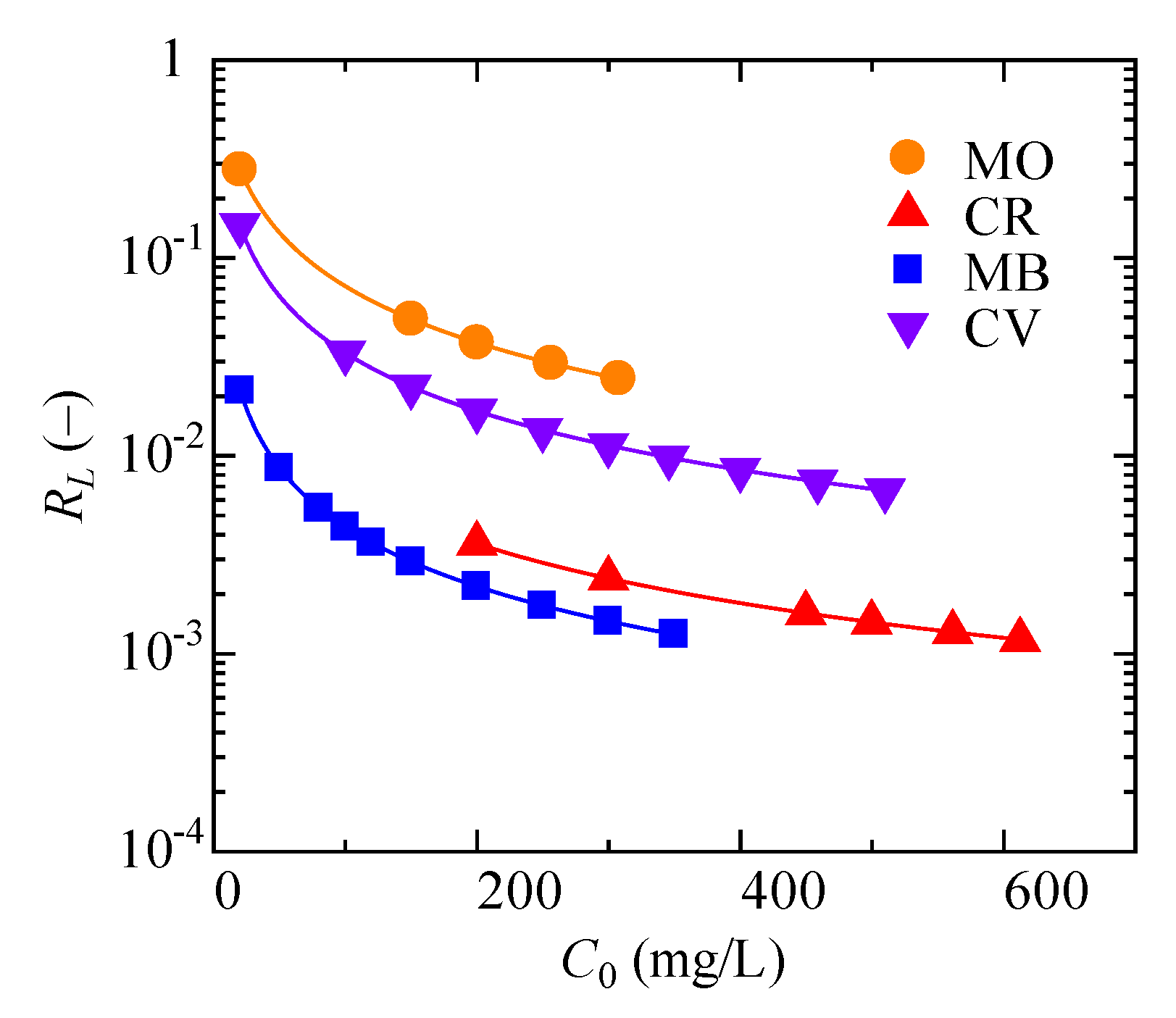
3.4. Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obaideen, K.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Olabi, A.G. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, A.O.; Abiodun, B.A.; Adenuga, D.O.; Nomngongo, P.N. Adsorptive and photocatalytic remediation of hazardous organic chemical pollutants in aqueous medium: A review. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 248, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.K. Novel adsorbents in remediation of hazardous environmental pollutants: Progress, selectivity, and sustainability prospects. Clean. Mater. 2022, 3, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jeevanantham, S.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Saravanan, R. A review on synthesis methods and recent applications of nanomaterial in wastewater treatment: Challenges and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.H.; Ng, C.H.; Islam, A.; Abdulkareem-Alsultan, G.; Joseph, C.G.; Janaun, J.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Khandaker, S.; Islam, G.J.; Znad, H.; et al. Sustainable toxic dyes removal with advanced materials for clean water production: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, T.; Xu, M. Adsorptive removal of organic dyes via porous materials for wastewater treatment in recent decades: A review on species, mechanisms and perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.; Rownok, M.H.; Sabrin, M.; Rahaman, M.H.; Nur Alam, S.M. A review on experimental chemically modified activated carbon to enhance dye and heavy metals adsorption. Cleaner Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, S.; Patil, P.; Jadhav, J. Recent advances in biochar technology for textile dyes wastewater remediation: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Elabiad, M.A.; Mohamed, A.A. Removal of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater using graphene oxide-based nanomaterials: A critical review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magalhães, L.F.; Da Silva, G.R.; Peres, A.E.C. Zeolite application in wastewater treatment. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4544104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Rahman, R.O.; El-Kamash, A.M.; Hung, Y.-T. Applications of nano-zeolite in wastewater treatment: An overview. Water 2022, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y.C.; Jung, H.-Y.; Bhaduri, B.; Kurkuri, M. Recent trends in the application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of toxic dyes and their removal mechanism—A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Calisto, V.; Esteves, V.I.; Otero, M. Overview of relevant economic and environmental aspects of waste-based activated carbons aimed at adsorptive water treatments. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 130984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausor, M.A.; Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Chakrabortty, D. Montmorillonite and modified montmorillonite as adsorbents for removal of water soluble organic dyes: A review on current status of the art. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Sun, R. Rapid modification of montmorillonite with novel cationic Gemini surfactants and its adsorption for methyl orange. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Duan, M.; Liu, P.; Jiang, X. Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions using a bentonite modified with a new gemini surfactant. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Gao, M.; Ye, Y.; Yang, S. Modification of reduced-charge montmorillonites by a series of Gemini surfactants: Characterization and application in methyl orange removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, H. A comparison of trimeric surfactant intercalated montmorillonite with its gemini modified one: Characterization and application in methyl orange removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhouchat, N.; Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Viseras, C. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-P.; Tian, S.-P.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Li, K.-X.; Ma, Q.; Ding, S.-Y.; Gao, J.; Miao, Z. Modification of montmorillonite by Gemini surfactants with different chain lengths and its adsorption behavior for methyl orange. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 151, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamoudi, S.; Srasra, E. Removal of cationic and anionic dyes using purified and surfactant-modified Tunisian clays: Kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic and adsorption–mechanism studies. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Mao, T.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xiao, R.; Sun, Y. Polyhydroxyl gemini surfactant-modified montmorillonite for efficient removal of methyl orange. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Labastida, E.; Díaz-Nava, M.C.; Illescas, J.; Muro, C. Comparison of the removal of an anionic dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption with organically modified clays and their composites. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T. Structure of a layered octosilicate intercalated with alkylamines with different molecular structures in water. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 290, 121545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S. Studies on Japanese acid earth. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1955, 1, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, R.; Takahashi, N.; Sakao, K.; Goto, T. Adsorption of zearalenone to Japanese acid clay and influencing factors. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Oya, M.; Minase, M.; Fujita, K.; Teepakakorn, A.; Ogawa, M. Preparation of sodium-type bentonite with useful swelling property by a mechanochemical reaction from a weathered bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 175, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T. Effect of solvents on the direct intercalation of decylamine into H-octosilicate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.-Y.; Park, K.-W. Intercalation behavior of dodecylamine into layered silicates in organic solvents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2001, 7, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lagaly, G. Interaction of alkylamines with different types of layered compounds. Solid State Ion. 1986, 22, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhemkhem, A.; Pizarro, A.H.; Molina, C.B. Enhancement of the adsorption properties of two natural bentonites by ion exchange: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic study. Clay Miner. 2020, 55, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agcaoili, A.R.; Herrera, M.U.; Futalan, C.M.; Balela, M.D.L. Fabrication of polyacrylonitrile-coated kapok hollow microtubes for adsorption of methyl orange and Cu(II) ions in aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamoudi, S.; Srasra, E. Adsorption of organic dyes by HDPy+-modified clay: Effect of molecular structure on the adsorption. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1193, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Niu, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous-structured MIL-68(Al)/MCM-41-NH2 for methyl orange adsorption: Optimization and selectivity. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, M.; Jiang, H. Soft-template solvent thermal method synthesis of magnetic mesoporous carbon–silica composite for adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 40734–40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, N.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Safajou-jahankhanemlou, M. Synthesis and characterization of solid-state Fe-exchanged nano-bentonite and evaluation of methyl orange adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 49898–49907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horri, N.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz, R.; Frini-Srasra, N.; Srasra, E. Effect of acid activation on the CO2 adsorption capacity of montmorillonite. Adsorption 2020, 26, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Kumai, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Mitsuoka, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Ohta, T.; Nozaki, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Shirai, S.; Nakano, H. Silicon nanosheets and their self-assembled regular stacking structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Jiang, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X. A TiO2 modified abiotic–biotic process for the degradation of the azo dye methyl orange. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58704–58712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Deng, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Guo, X.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z. Fabrication of polystyrene/CuO@calcined layered double hydroxide microspheres with high adsorption capacity for Congo red. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.N.H.; Al-Fazari, A.; Al-Badaei, M.; Al-Mahrazi, R. Utility of eosin Y as a complexing reagent for the determination of citalopram hydrobromide in commercial dosage forms by fluorescence spectrophotometry. Luminescence 2015, 30, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, A.A.; Malik, M.A. Biogenic fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) for proficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under UV irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 16156–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulthana, R.; Taqui, S.N.; Syed, U.T.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Mir, R.A.; Shahapurkar, K.; Khidmatgar, A.; Mohanavel, V.; Syed, A.A.; et al. Biosorption of crystal violet by nutraceutical industrial fennel seed spent equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 43, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dong, B.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Song, H. Multifunctional Au@mSiO2/rhodamine B isothiocyanate nanocomposites: Cell imaging, photocontrolled drug release, and photothermal therapy for cancer cells. Small 2013, 9, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore- and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimonses, V.; Lei, S.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo red adsorption by clay materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H. Spent tea leaves: A new non-conventional and low-cost adsorbent for removal of basic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gamal, S.M.A.; Amin, M.S.; Ahmed, M.A. Removal of methyl orange and bromophenol blue dyes from aqueous solution using Sorel’s cement nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueachot, R.; Wongkhueng, S.; Khankam, K.; Lakrathok, A.; Kaewnon, T.; Naowanon, W.t; Amnuaypanich, S.; Nakhowong, R. Adsorption efficiency of methylene blue from aqueous solution with amine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres by co-condensation biphasic synthesis: Adsorption condition and equilibrium studies. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 14079–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Muntean, S.-G.; Nistor, M.-A.; Putz, A.-M.; Almásy, L.; Săcărescu, L. Highly efficient and fast removal of colored pollutants from single and binary systems, using magnetic mesoporous silica. Chemosphere 2022, 261, 127737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Costişor, O.; Muntean, S.-G.; Nistor, M.-A.; Putz, A.-M.; Ianăşi, C.; Lazău, R.; Almásy, L.; Săcărescu, L. Mesoporous magnetic nanocomposites: A promising adsorbent for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Lan, S.; Rao, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C. Ultrafast and selective adsorption of anionic dyes with amine-functionalized glucose-based adsorbents. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1263, 133150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Z.; Yang, X.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, L. Facile fabrication of quaternary ammonium salt modified cotton linter by radiation grafting and its effective removal of methyl orange: Batch and dynamic flow mode studies. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, X.; Li, B. Investigation the adsorption behavior of functional carbon-based composites for efficient removing anions/cations in single and multicomponent systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishkewich, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Tam, K.C. Synthesis and characterization of modified cellulose nanofibril organosilica aerogels for the removal of anionic dye. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdod, A.S.; Kumar, M.V.P. Adsorption of methylene blue, methyl orange, and crystal violet on microporous coconut shell activated carbon and its composite with chitosan: Isotherms and kinetics. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Lv, F.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, J. Synthesis of nucleoshell γ-AlOOH as an ultra-high-capacity adsorbent for organic pollutants removal. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2022, 50, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Li, Y. Synthesis of MgNiCo LDH hollow structure derived from ZIF-67 as superb adsorbent for Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, N.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Efficient adsorptive elimination of organic pollutants from aqueous solutions on ZIF-8/MWCNTs-COOH nanoadsorbents: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 111, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xia, Z.-Q.; Li, S.-B.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, N. MOF-derived double-shelled Fe(OH)3@NiCo-LDH hollow cubes and their efficient adsorption for anionic organic pollutant. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Han, C.; Wu, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, M. Biotemplated synthesis of hollow nickel silicate fiber for organic dye contaminants and its selective adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Deng, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, W. Limonene-derived hollow polymer particles: Preparation and application for the removal of dyes and heavy metal ions. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Xu, L.; Ke, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Mei, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, S. A highly efficient biomass-based adsorbent fabricated by graft copolymerization: Kinetics, isotherms, mechanism and coadsorption investigations for cationic dye and heavy metal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y. Understanding effects of potassium activator on the porous structure and adsorption performance of bluecoke-based porous powder during microwave heating. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjai, M.; Ferkous, H.; Jebali, Z.; Majdoub, H.; Bourzami, R.; Raffin, G.; Achour, M.; Gil, A.; Boutahala, M. Adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes on a novel mesoporous adsorbent prepared from diatomite and anionic cellulose nanofibrils: Experimental and theoretical investigations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 361, 119670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.R.; Soares, L.C.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Gil, L.F. Use of a new zwitterionic cellulose derivative for removal of crystal violet and orange II from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tang, K.; Kim, T.-H.; Hwang, Y. Selective removal of cationic organic pollutants using disulfide-linked polymer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Fang, Y.; Liu, B. A magnetically recyclable magnetic graphite oxide composite functionalized with polydopamine and β-cyclodextrin for cationic dyes wastewater remediation: Investigation on adsorption performance, reusability and adsorption mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 602, 154338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, A.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. Effective sorptive removal of five cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Omer, A.M. Efficient removal of noxious methylene blue and crystal violet dyes at neutral conditions by reusable montmorillonite/NiFe2O4@amine-functionalized chitosan composite. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Dye | Supplier * | Initial Concentration C0 (mg/L) | Natural pH of 20 mg/L Solution | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anionic: | ||||
| Methyl orange (MO) | KC | 20–300 | 6.9 | 464 |
| Congo red (CR) | NT | 20–600 | 7.1 | 498 |
| Eosin Y (EY) | FW | 20–100 | 5.1 | 517 |
| Cationic: | ||||
| Methylene blue (MB) | KC | 20–350 | 5.7 | 665 |
| Crystal violet (CV) | KC | 20–500 | 5.6 | 595 |
| Rhodamine B (RB) | FW | 20–100 | 4.8 | 554 |
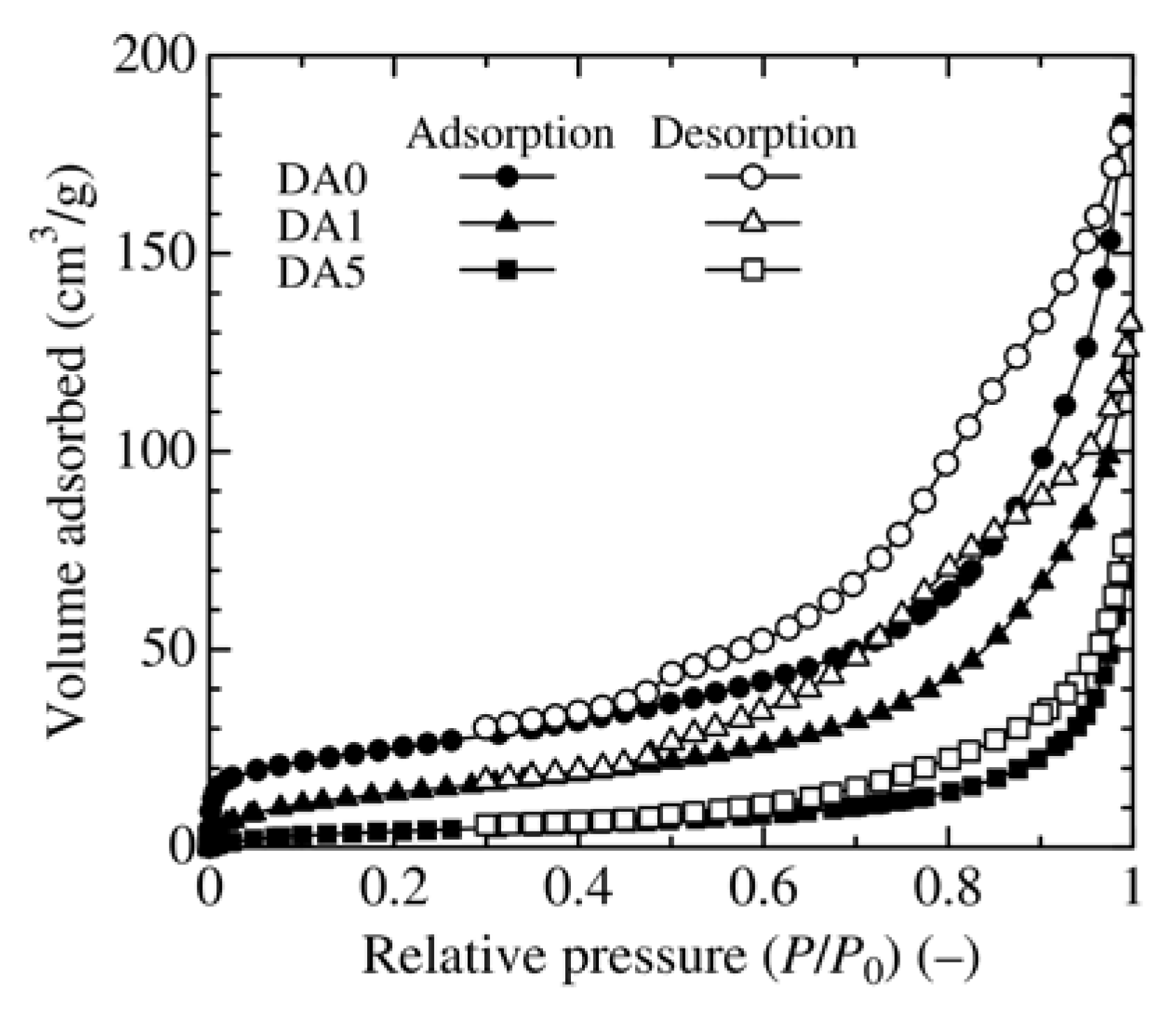
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DA0 | 87.9 | 0.278 | 21.1 |
| DA1 | 52.1 | 0.218 | 18.3 |
| DA5 | 16.4 | 0.118 | 27.8 |
| Temperature (K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/(mol·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 301 | –6.00 | –38.9 | –0.109 |
| 313 | –5.00 | ||
| 323 | –4.36 | ||
| 333 | –2.29 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | qe (mg/g) | 4.88 |
| k1 (h–1) | 0.481 | |
| R2 | 0.876 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qe (mg/g) | 35.2 |
| k2 (g/(h·mg)) | 0.524 | |
| R2 | 0.999 |
| Dye | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qL (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/(g·(mg/L)1/n)) | n | R2 | |
| MO | 629 | 0.129 | 0.996 | 169 | 3.19 | 0.910 |
| CR | 954 | 1.386 | 0.999 | 473 | 5.58 | 0.889 |
| MB | 225 | 2.282 | 0.996 | 157 | 12.16 | 0.652 |
| CV | 577 | 0.292 | 0.999 | 327 | 9.02 | 0.974 |
| Dye | Main Components of Adsorbent | qL (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MO | Japanese acid clay/decylamine | 629 | This work |
| Carbon/ethylenediamine/trimethylamine | 1487 | [56] | |
| Cotton/trimethyl ammonium | 645 | [57] | |
| Carbon/Fe3O4/β-cyclodextrin/chitosan | 269 | [58] | |
| Cellulose/silica | 187 | [59] | |
| Activated carbon/chitosan | 105 | [60] | |
| CR | Japanese acid clay/decylamine | 954 | This work |
| γ-AlOOH | 3881 | [61] | |
| MgNiCo LDH | 1195 | [62] | |
| ZIF-8/MWCNT | 1186 | [63] | |
| Fe(OH)3/NiCo LDH | 658 | [64] | |
| Nickel silicate | 415 | [65] | |
| MB | Japanese acid clay/decylamine | 225 | This work |
| Limonene-derived polymer | 909 | [66] | |
| Peanut shell | 538 | [67] | |
| Bluecoke | 341 | [68] | |
| Nickel silicate | 196 | [65] | |
| Holocellulose | 142 | [69] | |
| CV | Japanese acid clay/decylamine | 577 | This work |
| Cellulose/succinic acid/choline chloride | 2608 | [70] | |
| Trithiocyanuric acid polymer | 1181 | [71] | |
| Carbon/dopamine/Fe3O4/citric acid/β-cyclodextrin | 585 | [72] | |
| MWCNT/iron oxide | 165 | [73] | |
| Montmorillonite/NiFe2O4/ethylenediamine/chitosan | 125 | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwasaki, T. Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Organically Modified Natural Acid Clay for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Minerals 2023, 13, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010041
Iwasaki T. Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Organically Modified Natural Acid Clay for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Minerals. 2023; 13(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwasaki, Tomohiro. 2023. "Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Organically Modified Natural Acid Clay for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes" Minerals 13, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010041
APA StyleIwasaki, T. (2023). Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Organically Modified Natural Acid Clay for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Minerals, 13(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010041







