Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Granite with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive Transport Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Toki Granite
2.2. Description of Fluids
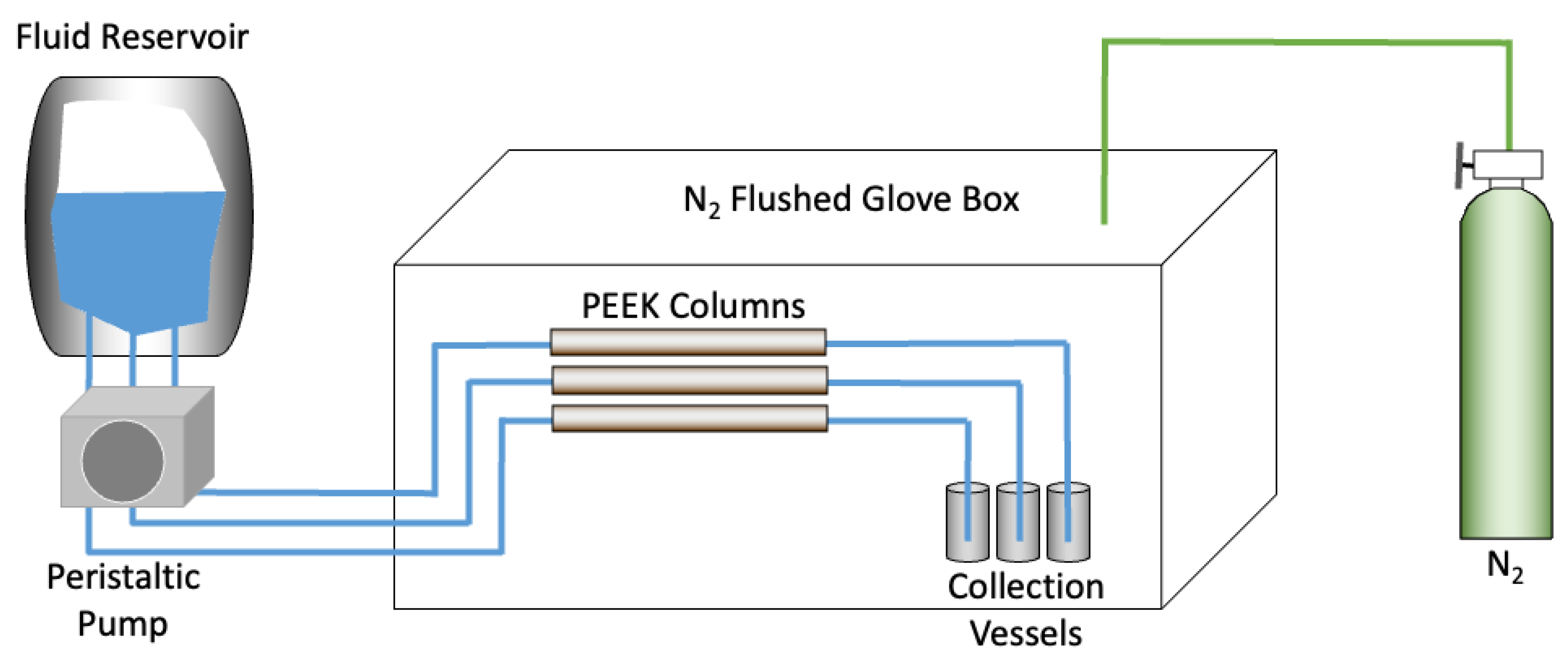
2.3. Description of the Column Experiment
2.4. Fluid Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Solid Samples
2.6. Mineral Saturation State Calculations
3. Reactive Transport Modelling
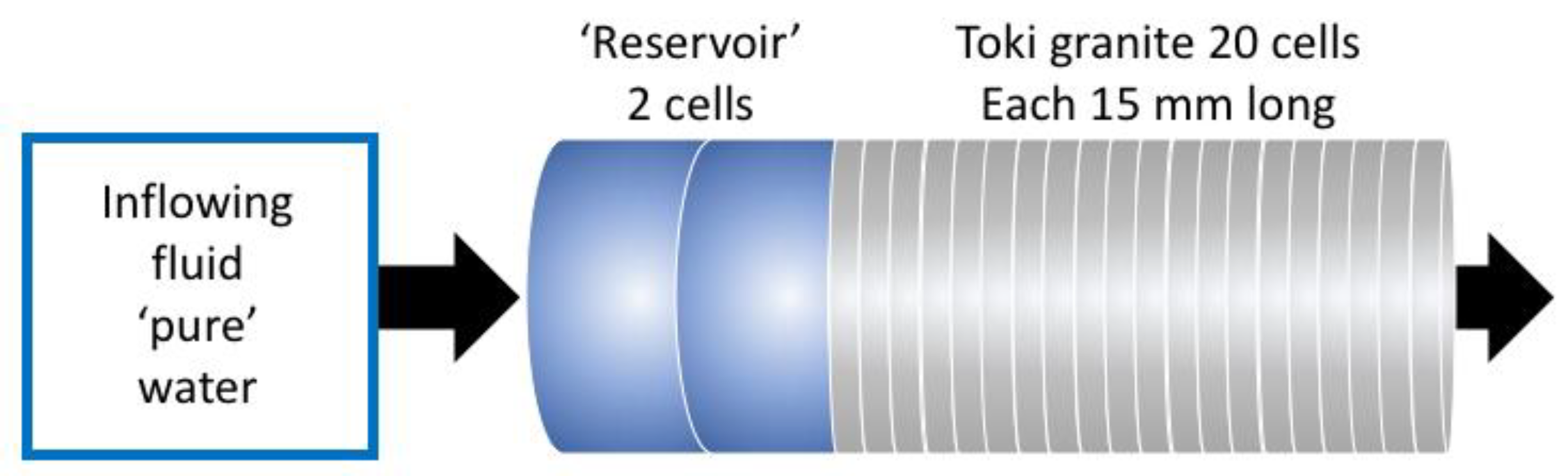
3.1. CABARET Model Concept
3.2. CABARET Model Setup and Parameters
4. Results of Experiments
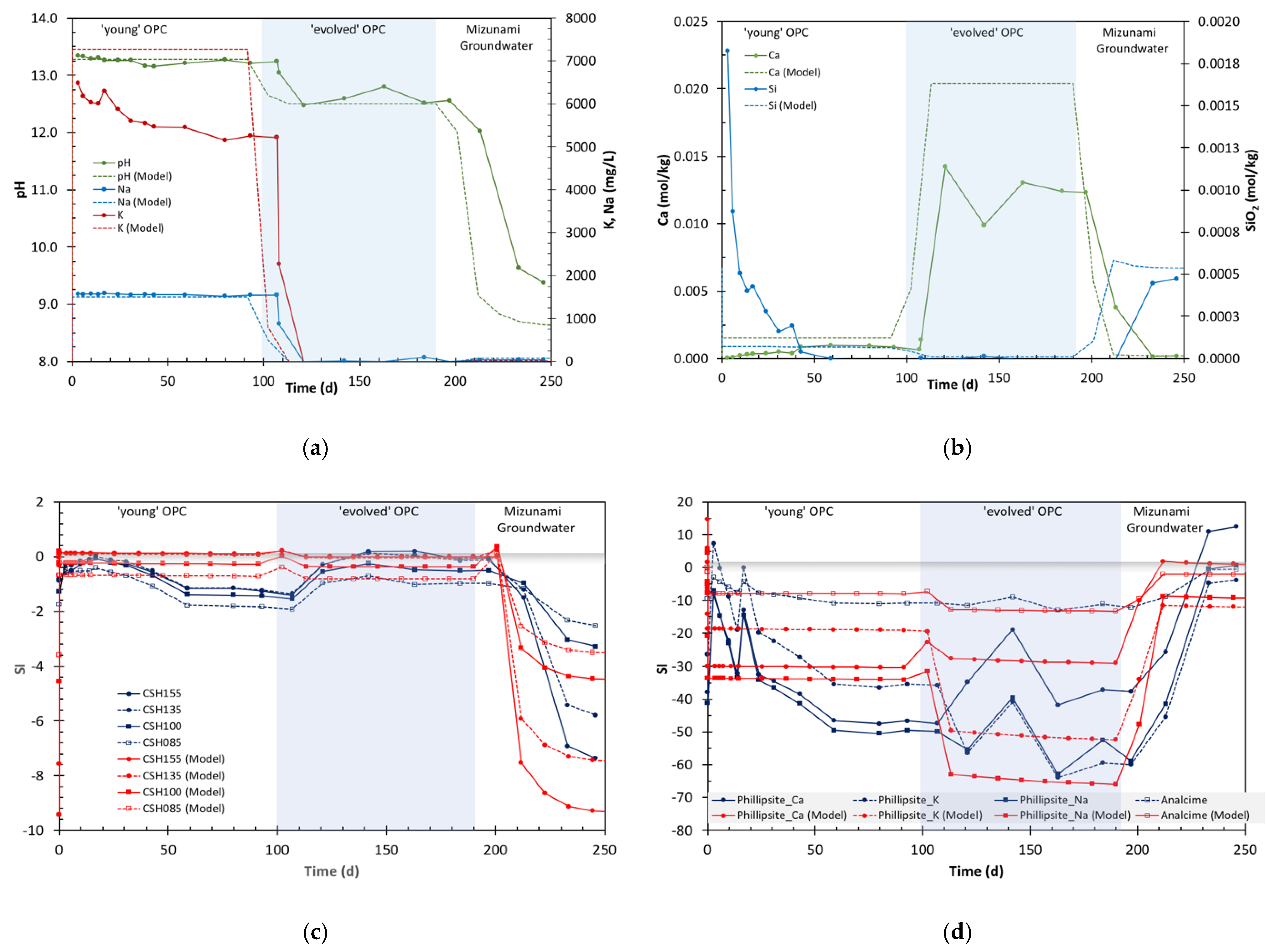
4.1. Aqueous Chemistry
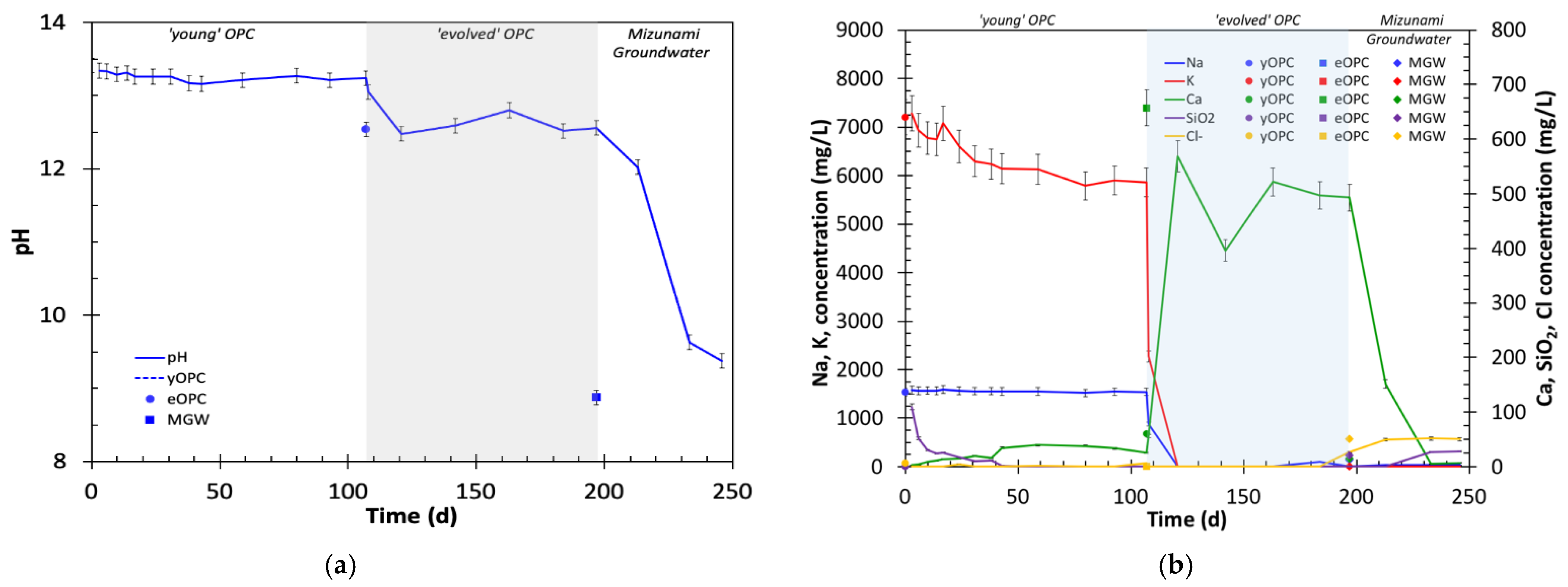
4.1.1. Changes in pH
4.1.2. Changes in Na Concentration
4.1.3. Changes in K Concentration
4.1.4. Changes in Ca Concentration
4.1.5. Changes in Silica Concentration
4.1.6. Changes in Other Ions
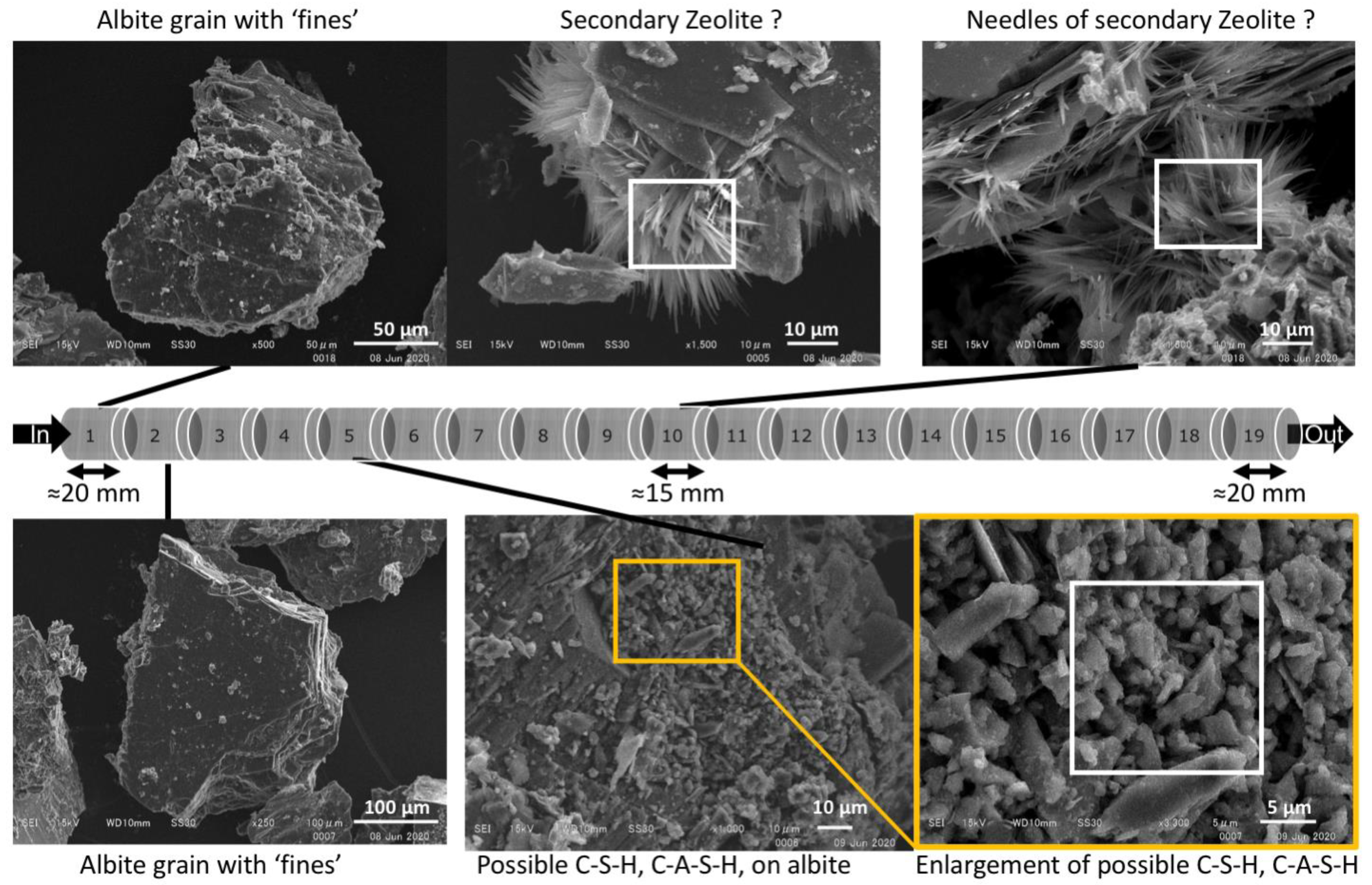
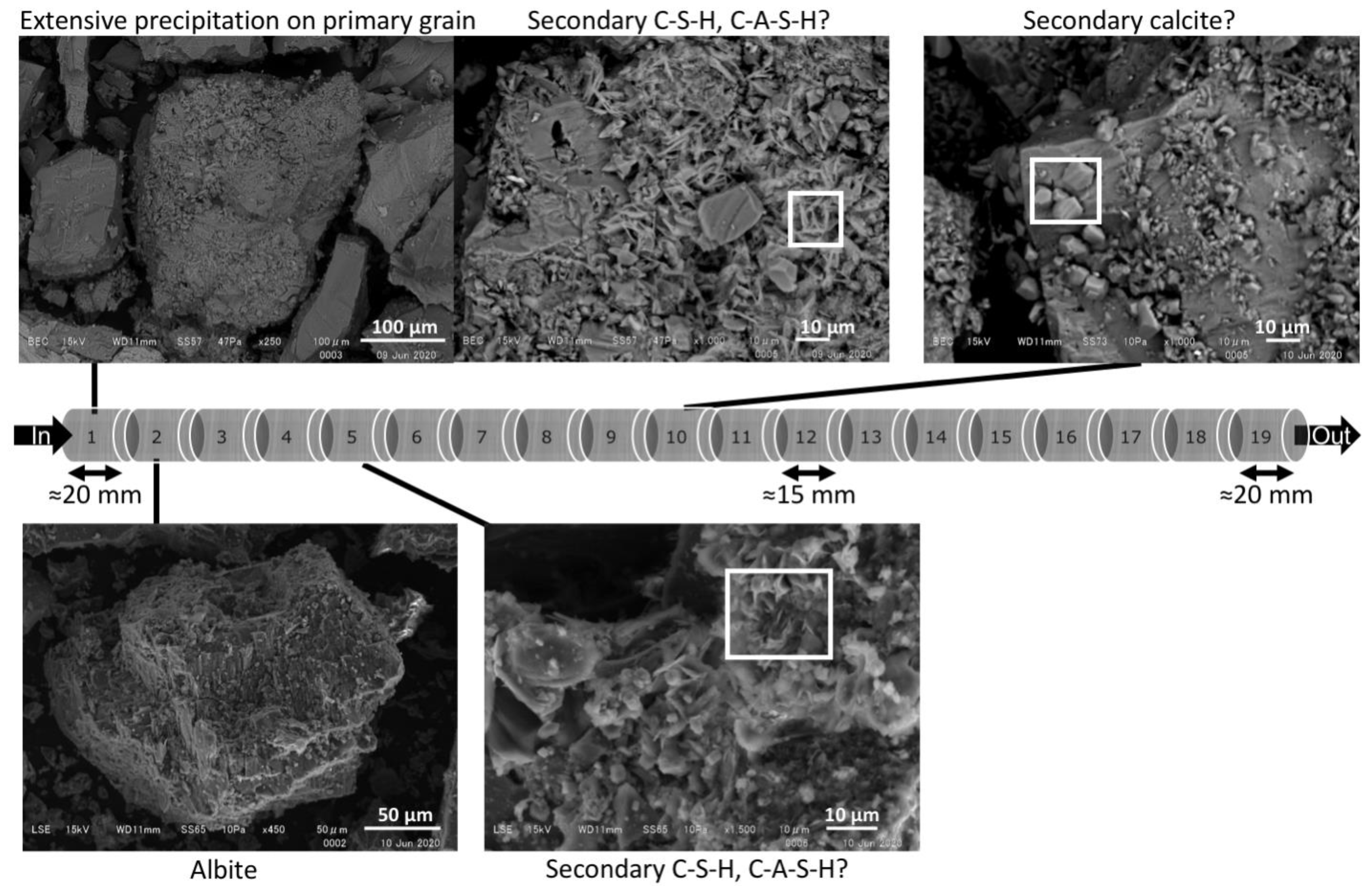
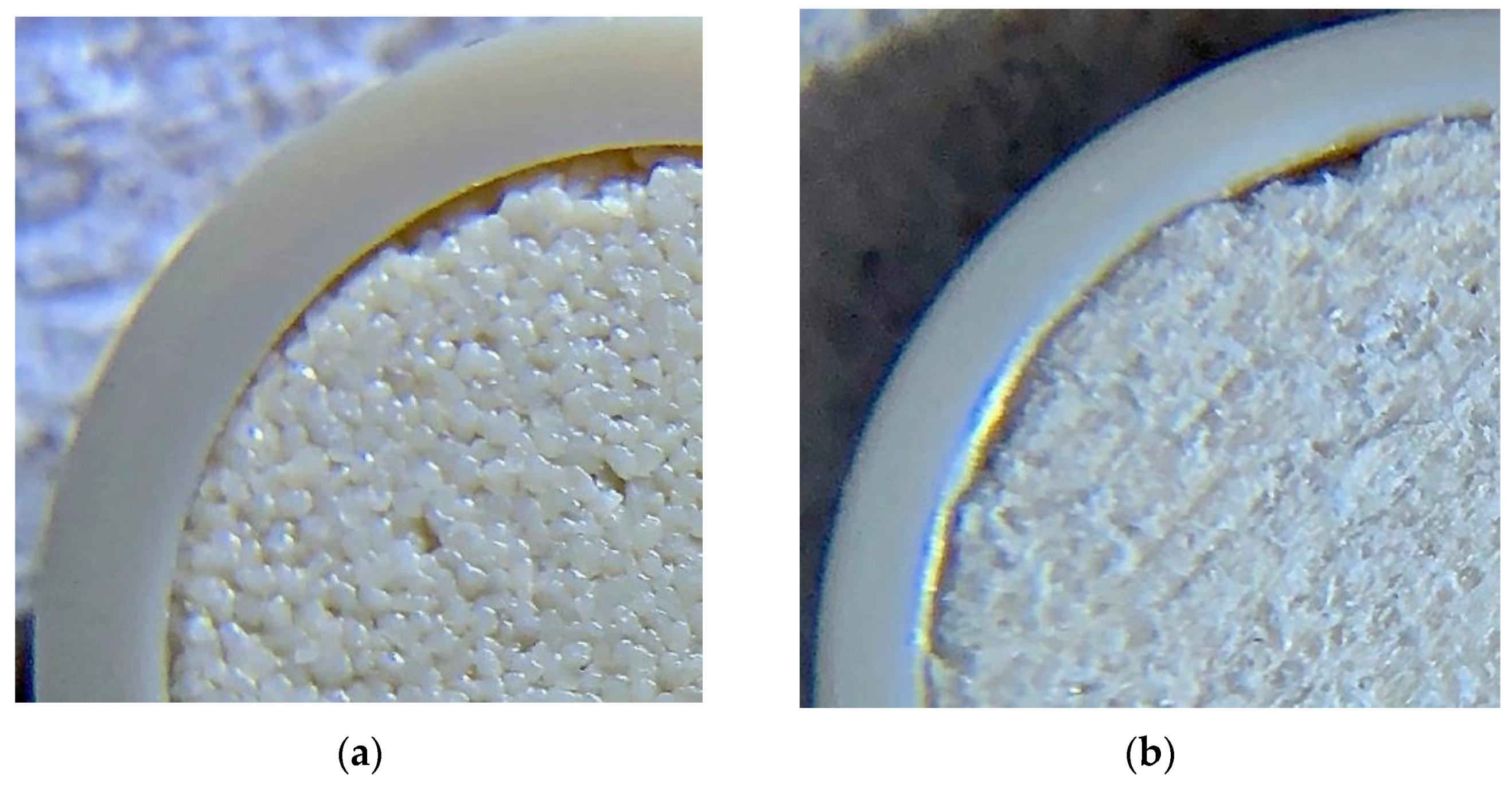
4.2. Mineralogical Analysis
4.2.1. ‘Young’ OPC Leachate Experiment (Col-1)
4.2.2. ‘Young’ and Then ‘Evolved’ OPC Leachate Experiment (Col-2)
4.2.3. OPC Leachates Then MGW (Col-3)
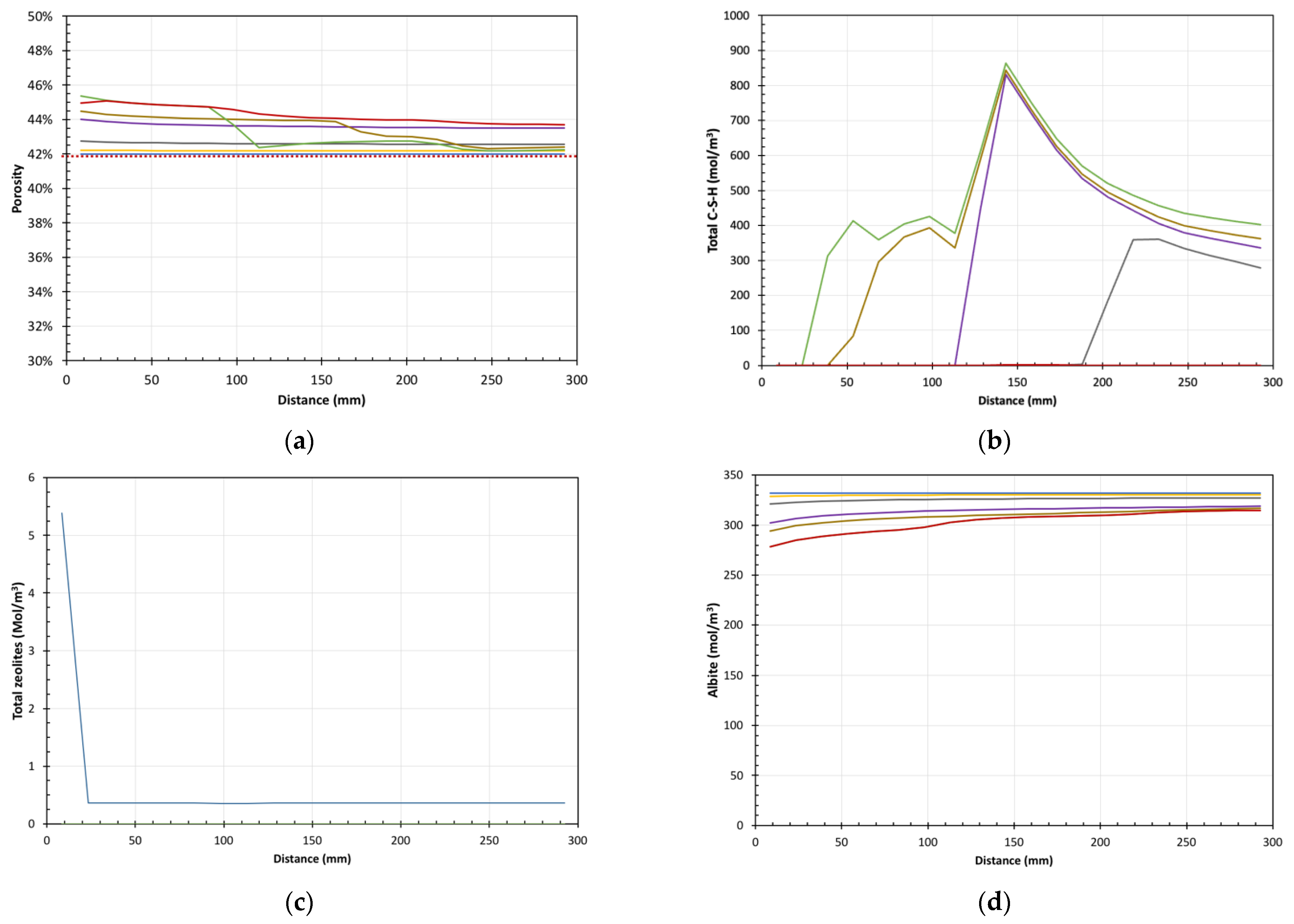
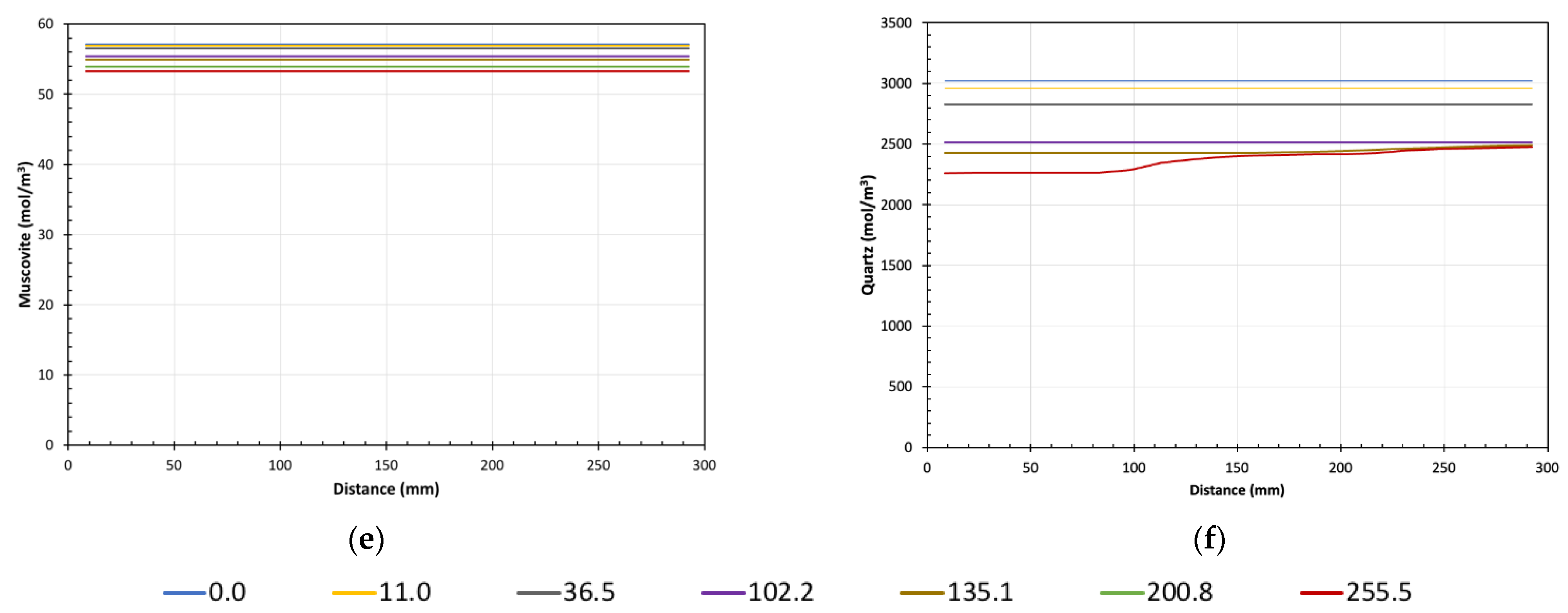
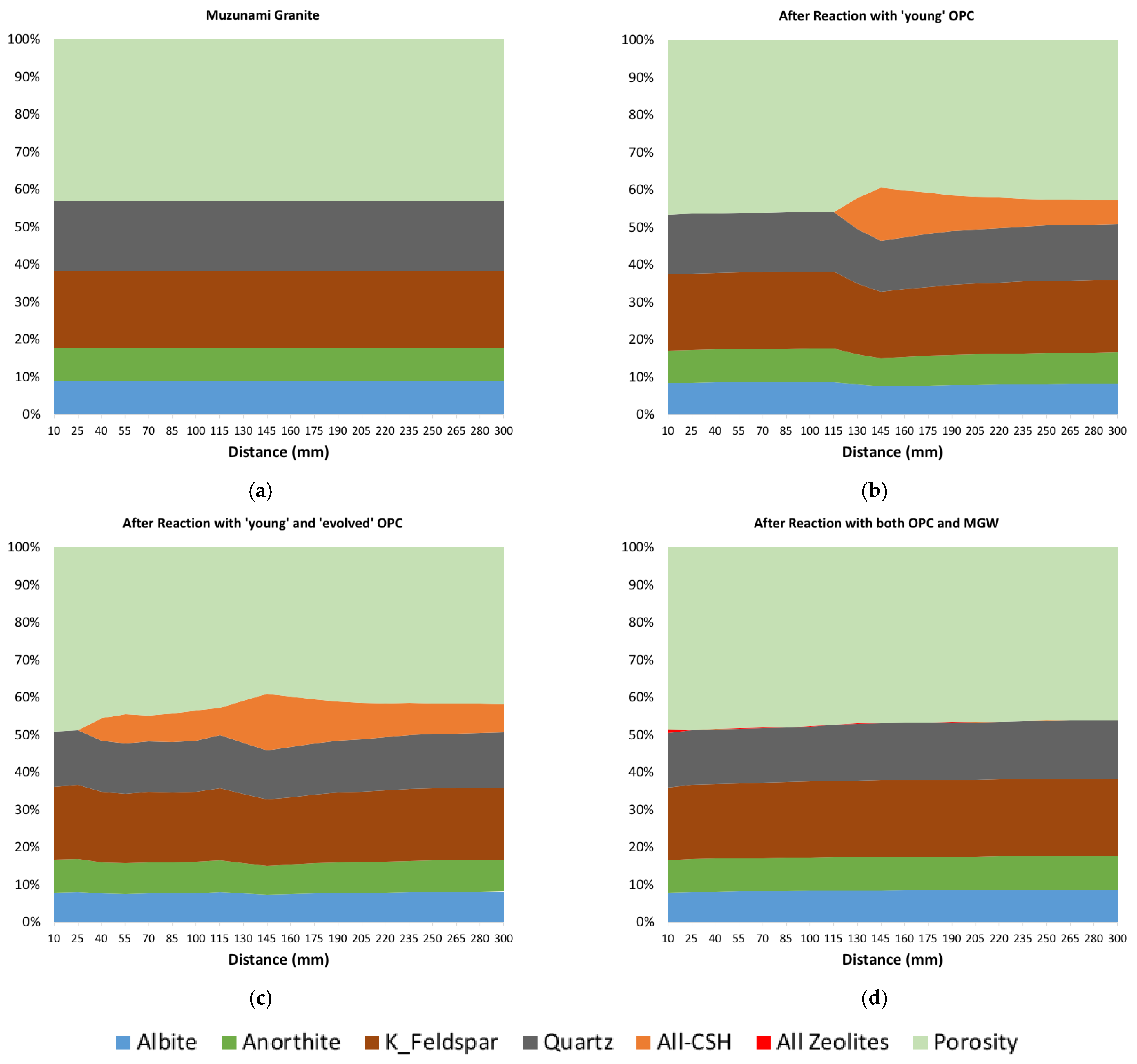
5. Results of Reactive Transport Modelling
Model Predictions vs. Experimental Data
6. Discussion
6.1. Chemistry and Mineralogy
6.2. Extent of Reaction
6.3. Recommendations for Model Improvements and Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- JNC. H12: Project to Establish the Scientific and Technical Basis for HLW Disposal in Japan, Project Overview Report and Three Supporting Reports. JNC TN1410 2000-001~004. 2000. Available online: https://jopss.jaea.go.jp/pdfdata/JNC-TN1410-2000-003.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Baker, A.J.; Bateman, K.; Hyslop, E.K.; Ilett, D.J.; Linklater, C.M.; Milodowski, A.E.; Noy, D.J.; Rochelle, C.A.; Tweed, C.J. Research on the Alkaline Disturbed Zone Resulting from Cement-Water-Rock Reactions around a Cementitious Repository; UK Nirex Ltd.: Oxfordshire, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- JAEA. Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan; Repository Design, Safety Assessment and Means of Implementation in the Generic Phase (TRU-2). JAEA-Review 2007-010, 2007/03. 2007. Available online: https://www.jaea.go.jp/04/be/documents/doc_02.html (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Falck, W.E.; Nilsson, K.-F. Geological Disposal of Radioactive Waste-Moving towards Implementation. In JRC Reference Reports, JRC45385 (EUR 23925 E); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009; Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/566e802a-2eb5-45af-ba47-787d3df4b05d/language-en (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Atkinson, A. The time dependence of pH within a repository for radioactive waste disposal. In UKAEA Report AERE-R 11777; UKAEA: Oxfordshire, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, U. Evolution of pore water chemistry during degradation of cement in a radioactive waste repository environment. Waste Manag. 1992, 12, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Bateman, K.; Tachi, Y. The impact of cement on argillaceous rocks in radioactive waste disposal systems: A review focusing on key processes and remaining issues. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 130, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-471-25424-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, K.; Coombs, P.; Pearce, J.M.; Wetton, P.D. Nagra/Nirex/SKB Column Experiments; Fluid Chemical and Mineralogical Studies. In British Geological Survey Report WE/95/26; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, K.; Coombs, P.; Pearce, J.M.; Noy, D.J.; Wetton, P.D. Fluid Rock Interactions in the Disturbed Zone: Nagra/Nirex/SKB Column Experiments-Phase II. In British Geological Survey Report WE/99/5; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Taubald, H.; Bauer, A.; Schafer, T.; Geckeis, H.; Satir, M.; Kim, J.I. Experimental investigation of the effect of high-pH solutions on the Opalinus Shale and the Hammerschmiede Smectite. Clay Miner. 2000, 35, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.S.; Byran, N.; Lloyd, J.R.; Milodowski, A.E.; Shaw, S.; Morris, K. Summary of the BIGRAD project and its implications for a geological disposal facility. In Report NNL; RWM: Oxfordshire, UK, 2016; Volume 16, p. 13817. Available online: https://rwm.nda.gov.uk/publication/summary-of-the-bigrad-project-and-its-implications-for-a-geological-disposal-facility/ (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Bateman, K.; Murayama, S.; Hanamachi, Y.; Wilson, J.; Seta, T.; Amano, Y.; Kubota, M.; Ohuchi, Y.; Tachi, Y. Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Mudstone with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive-Transport Modelling. Minerals 2021, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, M.; Mallants, D.; Wang, L. Radionuclide and Metal Sorption on Cement and Concrete; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle, C.A.; Milodowski, A.E.; Bateman, K.; Moyce, E.B.A. A long-term experimental study of the reactivity of basement rock with highly alkaline cement waters: Reactions over the first 15 months. Mineral. Mag. 2016, 80, 1089–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bateman, K.; Amano, Y.; Kubota, M.; Ohuchi, Y.; Tachi, Y. Reaction and Alteration of Mudstone with Ordinary Portland Cement and Low Alkali Cement Pore Fluids. Minerals 2021, 11, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, N.; Bildstein, O.; Blanc, P.; Claret, F.; Cochepin, B.; Gaucher, E.C.; Jacques, D.; Lartigue, J.E.; Liu, S.; Mayer, K.U.; et al. Benchmarks for multicomponent reactive transport across a cement/clay interface. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 19, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.; Noy, D.; Mihara, M. Modelling the Interaction of Bentonite with Hyperalkaline Fluids. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Hane, K.; Savage, D.; Benbow, S.; Cuevas, J.; Fernandez, R. Reaction and diffusion of cementitious water in bentonite: Results of ’blind’ modelling. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 45, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, T.; Hagiwara, H.; Ohmori, K.; Munemoto, T.; Onoe, H. Hydrochemical disturbances measured in groundwater during the construction and operation of a large-scale underground facility in deep crystalline rock in Japan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakai, T. Data-Base of Bulk Chemical Compositions and Modal Compositions of TOKI Granitic Body; JAEA-Data/Code 2018-006; Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA): Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2018; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, D.; Hughes, C.R.; Milodowski, A.E.; Bateman, K.; Pearce, J.; Rae, E.; Rochelle, C.A. The evaluation of chemical mass transfer in the disturbed zone of a deep geological disposal facility for radioactive wastes. I. Reaction of silicates with Calcium hydroxide fluids. In Nirex Report NSS/R244; UK Nirex Ltd.: Oxfordshire, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, D.; Bateman, K.; Hill, P.; Hughes, C.R.; Milodowski, A.E.; Pearce, J.; Rochelle, C.A. The evaluation of chemical mass transfer in the disturbed zone of a deep geological disposal facility for radioactive wastes. II. Reaction of silicates with Na-K-Ca- hydroxide fluids. In Nirex Report NSS/R283; UK Nirex Ltd.: Oxfordshire, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, T.; Munemoto, T.; Kubota, M.; Hayashida, K.; Kato, T. Characterization of rare earth elements (REEs) associated with suspended particles in deep granitic groundwater and their post-closure behavior from a simulated underground facility. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 82, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3-A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. 2013. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/ (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- JAEA. The Project for Validating Assessment Methodology in Geological Disposal System. In Annual Report for JFY2016; JAEA Technical Report; Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA): Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2017. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- JAEA. 2014: H25 Project for Technical Study on Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste. In Report on Development of Advanced Cement Material Impact Assessment Technology; Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA): Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan; Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/category/electricity_and_gas/nuclear/rw/library/2013/25-13-1.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022). (In Japanese)
- JAEA. 2019: H29 Project for Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste. Technology Development Project for Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste. Development of Technology for Confirmation of Evaluation of Disposal System. Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/category/electricity_and_gas/nuclear/rw/library/2017/29fy_hyoukakakushou.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022). (In Japanese)
- Trapote-Barreira, A.; Cama, J.; Soler, J.M. Dissolution kinetics of C-S-H gel: Flow-through experiments. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2014, 70–71, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steefel, C.I.; Lichtner, P.C. 1998 Multicomponent reactive transport in discrete fractures: II: Infiltration of hyperalkaline groundwater at Maqarin, Jordan, a natural analogue site. J. Hydrol. 1998, 209, 200–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Sasaki, R. RAdio-Nuclides Migration DAtasets (RAMDA) on Cement, Bentonite and Rock for TRU Waste Repository in Japan. JNC TN1410 2000-001~004. 2005. Available online: https://jopss.jaea.go.jp/pdfdata/JNC-TN8400-2005-027.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Benbow, S.J.; Watson, C.E. 2014 QPAC Reactive Transport Module: Theory and Testing. Quintessa Report QRS-QPAC-RTM-2 v1.1; Quintessa Limited: Henley-on-Thames, UK.
- Savage, D.; Watson, C.; Benbow, S.; Wilson, J. Modelling iron-bentonite interactions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steefel, C.I.; Van Cappellen, P. A new kinetic approach to modeling water-rock interaction: The role of nucleation, precursors, and Ostwald ripening. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2657–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fluid | pH @ 24 °C | Components (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Young’ OPC leachate | Na | K | Ca | SiO2 | Mg | Cl | HCO3− | |
| (Na-K-Ca-OH) | 13.4 | 1500 | 7300 | 60 | - | - | - | - |
| ‘Evolved’ OPC leachate | Ca | SiO2 | Mg | Cl | HCO3− | |||
| (saturated Ca(OH)2) | 12.5 | 800 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Mizunami groundwater | Na | K | Ca | SiO2 | Mg | Cl | HCO3− | |
| BH 09MI20—mean * | 8.70 | 80 | 0.4 | 9 | 32 | 0.1 | 65 | 75 |
| Sampled 25 December 2019 | 8.77 | 141 | <0.10 | 15 | 20.8 | 3.21 | 50.3 | - |
| Vol % | Formula in Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB, [26]) | |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | 42 | |
| Quartz | 18.1 | SiO2 |
| Anorthite | 8.71 | CaAl2Si2O8 |
| Albite | 8.71 | NaAlSi3O8 |
| K_Feldspar | 20.1 | KAlSi3O8 |
| Muscovite | 2.27 | K(Al2)(AlSi3)O10(OH)2 |
| Portlandite | Ca(OH)2 | |
| CSH055 to CSH165 | (CaO)1.65(SiO2)(H2O)2.1167, (CaO)1.55(SiO2)(H2O)2.0167, (CaO)1.45(SiO2)(H2O)1.9167, (CaO)1.35(SiO2)(H2O)1.8167, (CaO)1.25(SiO2)(H2O)1.7167, (CaO)1.15(SiO2)(H2O)1.6167, (CaO)1.05(SiO2)(H2O)1.5167, (CaO)1.00(SiO2)(H2O)1.4667, (CaO)0.95(SiO2)(H2O)1.4167, (CaO)0.90(SiO2)(H2O)1.3667, (CaO)0.85((SiO2)(H2O)1.3167, (CaO)0.80(SiO2)(H2O)1.248, (CaO)0.75(SiO2)(H2O)1.17, (CaO)0.65(SiO2)(H2O)1.014, (CaO)0.55(SiO2)(H2O)0.858 | |
| Stratlingite_Al | (Ca2Al(OH)6)(AlSiO2(OH)4)(H2O)3 | |
| Analcime (Analcite) | NaAlSi2O6(H2O) | |
| Clinoptilolite_alk, | K2.3Na1.7Ca1.4(Al6.8Si29.2O72)(H2O)26 | |
| Clinoptilolite_Ca | Ca3(Al6Si30O72)(H2O)20 | |
| Clinoptilolite_K | K6(Al6Si30O72)(H2O)20 | |
| Clinoptilolite_Na | Na6(Al6Si30O72)(H2O)2 | |
| Phillipsite_alk | K1.4Na1.6Ca0.4(Al3.8Si12.2O32)(H2O)12 | |
| Phillipsite_Ca | Ca3(Al6Si10O32)(H2O)12 | |
| Phillipsite_K | K6(Al6Si10O32)(H2O)12 | |
| Phillipsite_Na | Na6(Al6Si10O32)(H2O)12 | |
| Brucite | Mg(OH)2 | |
| MSH06 to MSH15 | (MgO)0.6(SiO2)(H2O)1.08, (MgO)0.7(SiO2)(H2O)1.2, (MgO)0.8(SiO2)(H2O)1.32, (MgO)0.9(SiO2)(H2O)1.44, (MgO)1(SiO2)(H2O)1.56, (MgO)1.1(SiO2)(H2O)1.68, (MgO)1.2(SiO2)(H2O)1.8, (MgO)1.3(SiO2)(H2O)1.92, (MgO)1.4(SiO2)(H2O)2.04, (MgO)1.5(SiO2)(H2O)2.16 | |
| Monocarbonate_Al | (Ca2Al(OH)6)2(CO3)(H2O)5 | |
| Monosulfate_Al | (Ca2Al(OH)6)2(SO4)(H2O)8 | |
| Magnesite | MgCO3 | |
| Thaumasite | Ca3Si(OH)6(SO4)(CO3)(H2O)12 | |
| Calcite | Ca(CO3)2 | |
| Dolomite | CaMg(CO3)2 | |
| Gypsum | CaSO4(H2O)2 | |
| Ettringite_Al | Ca6(Al(OH)6)2(SO4)3(H2O)26 | |
| Friedel_Salt_Al | (Ca2Al(OH)6)2(Cl)2(H2O)4 | |
| Kuzel_Salt_Al | (Ca2Al(OH)6)2((SO4)0.5Cl)(H2O)6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bateman, K.; Murayama, S.; Hanamachi, Y.; Wilson, J.; Seta, T.; Amano, Y.; Kubota, M.; Ohuchi, Y.; Tachi, Y. Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Granite with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive Transport Modelling. Minerals 2022, 12, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070883
Bateman K, Murayama S, Hanamachi Y, Wilson J, Seta T, Amano Y, Kubota M, Ohuchi Y, Tachi Y. Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Granite with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive Transport Modelling. Minerals. 2022; 12(7):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070883
Chicago/Turabian StyleBateman, Keith, Shota Murayama, Yuji Hanamachi, James Wilson, Takamasa Seta, Yuki Amano, Mitsuru Kubota, Yuji Ohuchi, and Yukio Tachi. 2022. "Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Granite with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive Transport Modelling" Minerals 12, no. 7: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070883
APA StyleBateman, K., Murayama, S., Hanamachi, Y., Wilson, J., Seta, T., Amano, Y., Kubota, M., Ohuchi, Y., & Tachi, Y. (2022). Evolution of the Reaction and Alteration of Granite with Ordinary Portland Cement Leachates: Sequential Flow Experiments and Reactive Transport Modelling. Minerals, 12(7), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070883







