Abstract
Singular crypto- and microcrystalline hydrothermal zircon aggregates occur in peralkaline granites from the Corupá Pluton of “A-type” granites and syenites in Graciosa Province, Southern Brazil, and are herein characterized for their morphological, textural and geochemical (major, minor and trace elements, and Lu-Hf isotopes) properties. The aggregates were found to present a variety of habits, such as dendritic, oolitic, botryoidal and spherulitic, and they are associated with typical hydrothermal minerals (alkali-feldspars, quartz, fluorite, epidote-group minerals, phyllosilicates and Fe oxides) in micro-fractures and small miarolitic cavities in the host rock. They precipitated directly from a hydrothermal fluid and, compared to magmatic zircon crystals from the host, were found to contain relatively high abundances of the “non-formula” elements (e.g., Fe, Al, and Ca) and HFSEs (High-Field-Strength Elements), particularly the L- and MREEs (Light and Medium Rare Earth Elements), features most typical of hydrothermal zircon, as well as high Th/U ratios, whereas the Lu-Hf isotopic signatures were found to be similar. The formation of the zircon aggregates and the associated epidote-groups minerals was probably due to the interaction between an orthomagmatic, F-bearing, aqueous fluid transporting the HFSEs with the host-rock and/or with an external meteoritic fluid from the country rocks. The preservation of an amorphous-like Zr-silicate compound and crypto-to-microcrystalline zircon varieties is arguably related to the inefficient fluid flux and/or elemental diffusion in a low-temperature oxidizing environment.
1. Introduction
Zircon, ideally ZrSiO4, is an accessory mineral highly stable under most crustal environments and hence widely distributed in rocks and sediments of the Earth’s crust. The elemental and isotopic compositions of zircon provide critical insights into the geochronology and petrology of igneous and metamorphic rocks, provenance studies of sedimentary rocks and sediments, and (therefore) the Earth’s geodynamic evolution in general [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. In magmatic systems, zircon saturation in melts, Ti-in-zircon thermometry, and oxibarometry based on the Ce and Eu oxidation states and/or anomalies allow for the determination of intensive crystallization parameters [8,9,10,11,12,13], while its elemental—particularly the HFSEs (High-Field-Strength Elements, including the REEs, Rare Earth Elements)—and O and Hf isotopic compositions provide invaluable information on magma sources and evolution [14,15,16,17]. Zircon is also the main source of zirconium oxide (ZrO2), an important refractory material, and Zr alloys have multiple applications in modern technology; furthermore, zircon also provides beautiful gemstones [18]. Hence, this mineral has become one of the most studied accessory minerals from the Earth’s crust.
Relatively low-temperature hydrothermal zircon occurs in a variety of geological environments. It may precipitate directly from a fluid phase as isolated crystals or crystalline aggregates (1), form overgrowths on primary zircon crystals of magmatic or metamorphic origin (2), substitute other mineral phases (3), or be the product of dissolution-re-precipitation or diffusion–reaction processes (4) resulting from reactions involving previous zircon crystals and late (generally aqueous and acid) fluid phases [1,19,20,21,22]. Contrasting primary with hydrothermal zircon in magmatic and metamorphic rocks is crucial for accurate U-Pb dating and the determination and modeling of crystallization conditions and primary geochemical signatures [14,19,23,24,25]. On the other hand, hydrothermal zircon allows for U-Pb dating and provides information on the evolution of hydrothermal systems and related ore-forming processes [12,26,27].
Zircon U-Pb dating is one of the most powerful available geochronological methods, so a significant number of studies on hydrothermal zircon have dealt with the effects of hydrothermal processes on the U-Pb systematics of igneous and metamorphic rocks and their implications. Some features, such as the “spongy” texture caused by the abundance of minute “inclusions” and micro- or nano-cavities imprinting a general porous aspect to the crystals [1,19,23], the lobate texture, crystal overgrowths truncating original primary micro-structures, and the relative high contents of so-called “non-formula” elements (such as Fe, Al and Ca) and the LREEs are most typically associated with hydrothermal varieties [20,28]. However, distinguishing primary from hydrothermal zircon is not straightforward in several cases, and the most reliable criterion is the associated mineral assemblage [19,23,29].
In this study, the relatively rare occurrence of crypto- and microcrystalline zircon aggregates in close association with hydrothermal mineral phases in a peralkaline granite from Graciosa Province, South-Southeastern Brazil [30] is described. Morphological, textural, geochemical (major-, minor-, and trace element) and Lu-Hf isotope data are presented. Mineral paragenesis, unusual morphology, textures and microstructures suggest that they precipitated directly from a fluid phase at relatively low temperatures, which—along with inefficient elemental diffusion—prevented the development of larger euhedral crystals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Characterization
The studied rock came from the Corupá Pluton (Figure 1), a Neoproterozoic (ca. 580 Ma, [25,31]) occurrence of the alkaline petrographic association of “A-type” granites and syenites in Graciosa Province, South-Southeastern Brazil [30]. The pluton has a crescent outline and intrudes Archaean granulitic rocks from the Luis Alves microplate. It is a shallow intrusion largely comprising dominant metaluminous, leucocratic, SiO2-oversaturated alkali-feldspar syenites and alkali-feldspar quartz syenites, with subordinate peralkaline alkali-feldspar granites. The granites occur as minor bodies in the central areas of the pluton and represent late products, probably originating from magmatic fractionation and filter-pressing processes acting on previous trachytic-like melts [32,33].
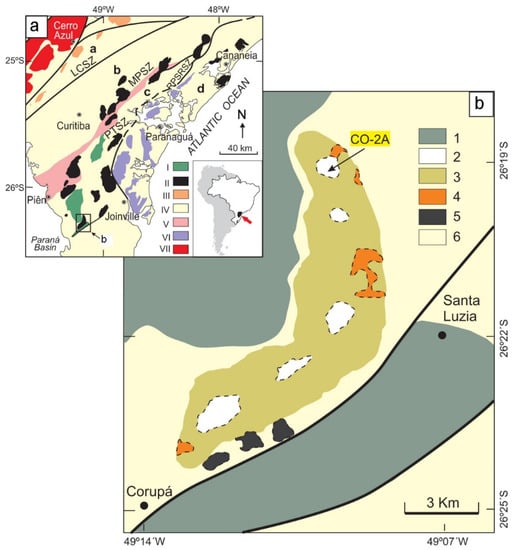
Figure 1.
Simplified geological context (a) and map of the Corupá Pluton (b), Southern Brazil [25,32,33,34]. (a): I: Volcano-sedimentary basins; II: “A-type” granitic and syenitic plutons and complexes from the Graciosa Province; III: “A-type” granitic plutons from the Itu Province; IV. A: Ribeira fold belt; b: Curitiba microplate; c: Luiz Alves microplate; d: Coastal granitoid belt. V: Piên-Mandirutuba Granite batholith; VI: Undifferentiated late- to post-collisional granites; VII: Três Córregos batholith. LCSZ: Lancinha Shear Zone; RPSRSZ: Rio Palmital-Serrinha Shear Zone. (b): 1: Sedimentary and volcanic rocks from Guaratubinha Basin (above) and Corupá Graben (below); 2: Alkali-feldspar granites, 3: Alkali-feldspar syenites, 4: Gabbro-diorites and related hybrid rocks, 5: Basic volcanics, 6: Archaean granulitic rocks from the Luis Alves microplate. The location of the studied CO-2A sample is indicated.
Hydrothermal zircon aggregates were found in a unique granite sample from the northern area of the pluton (sample CO-2A). The rock is homogenous and slightly pinkish, with a massive structure and a medium-grained hypidiomorphic texture. It is leucocratic and composed of mesoperthitic alkali-feldspar, quartz and some interstitial sodic-calcic and sodic amphiboles. Ilmenite, chevkinite, zircon, and minor titanite, apatite, and sphalerite are the main primary accessories, while albite, K-feldspar, quartz, Fe-rich biotite and chlorite, fluorite, epidote-group minerals (allanite-(Ce), ferriallanite-(Ce), epidote and ferriepidote), zircon, and minute magnetite, hematite, and galena are the main hydrothermal minerals [34]. From the geochemical standpoint, the rock comprises SiO2 = 74.63 wt.%, Na2O + K2O = 9.08 wt.%, FeOT/(FeOT + MgO) (wt.%) = 0.98 and is moderately peralkaline, with a peralkaline or agpaitic index ((Na2O + K2O)/Al2O3 molar) of 1.06 [33].
2.2. Analytical Techniques
Qualitative and quantitative chemical and isotopic data and imagery for primary and hydrothermal zircon crystals and crypto- and microcrystalline aggregates were obtained in polished thin (30 and 80 μm) sections at the GeoAnalitica and Geochronological Research Center facilities of the University of São Paulo. After conventional optical analysis under a petrographic microscope, cathodoluminescence (CL), electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA) and laser ablation inductively coupled mass spectrometry (quadrupole, LA-ICPMS and multi-channel LA-MC-ICPMS) analyses were carried out as follows.
Conventional Cl images of hydrothermal aggregates were obtained with a Nuclide ELM-3R luminoscope (Nuclide Corporation, Acton, MA, USA) operating with a 15 kV accelerating voltage and a 0.5 μA beam current.
The EPMA work was carried out with the JXA-8600S and JXA-FE-8530 instruments (JEOL Ltd., Tokio, Japan) and included backscattered electron (BSE, compositional mode), imaging, qualitative and quantitative spot analysis by energy- and wavelength-dispersive spectrometry (EDS and WDS, respectively), and WDS x-ray dot mapping. Quantitative WDS spot analysis was conducted under analytical conditions of 20 kV, 50 nA, and 5 μm for the column accelerating voltage, beam current, and diameter, respectively. Analyzed elements, spectral lines and standards, from the Smithsonian and the laboratory internal collections, were as follows: Si (Kα, zircon), Th (Mα, ThSiO4*), U (Mβ, UO2*), Zr (Lα, zircon), Hf (Lα, HfSiO4*), Ti (Kα, rutile), Al (Kα, Yal-garnet*), Y (Lα, YPO4*), La (Lα, LaPO4*), Ce (Lα, CePO4*), Nd(Lβ, NdPO4*), Sm (Lβ, SmPO4*), Gd (Lβ, GdPO4*), Dy (Lβ, DyPO4*), Er (Lα, ErPO4*), Yb (Lα, YbPO4*), Fe (Kα, hematite), Mn (Kα, Mn-olivine), Mg (Kα, diopside), Ca (Kα, diopside), Na (Kα, jadeite), K (Kα, microcline), P (Kα, CePO4*) and Nb (Lα, met Nb*), where (*) stands for synthetic phases. The total counting times, equally distributed between peak and background, varied from 10 to 50s; matrix effects were corrected with the PROZA software [35]. Spectral interferences over U, Er and Yb lines were corrected following the procedures of Vlach [36]. The estimated analytical precisions were better than 2% for Si and Zr, better than 10% for minor elements, and higher than 10% for the trace elements.
Trace-element LA-ICPMS spot and raster analysis was carried on with the Elan 6100DRC equipment (Perkin-Elmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) provided with an UP-213 laser ablation system (New Wave Research Inc., Fremont, CA, USA) using a 213 nm Nd-doped YAG laser. The analytical routine used in the laboratory was described in detail by Andrade [37]. The raster sampling followed aggregate zoning patterns as observed in BSE images. The energy density and the beam diameter over the samples surface were about 8.5 J/cm2 and 40 (spot) or 30 (raster) μm, respectively, with a 4 Hz repetition rate. Besides 29Si and 91Zr, the isotopes 31P, 49Ti, 55Mn, 88Sr, 89Y, 91Zr, 93Nb, 95Mo, 137Ba, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 143Nd, 147Sm, 151Eu, 155Gd, 159Tb, 163Dy, 165Ho, 166Er, 169Tm, 173Yb, 175Lu, 179Hf, 181Ta, 208Pb, 232Th, and 238U were measured using a signal integration and dwell time of 8.3 and 1.66 ms, respectively. The isotopic interferences of oxide and hydroxide compounds over the selected isotopes (e.g.,135Ba15O+ on 151Eu) are relatively limited in dry plasmas without hydroxyl and oxygen [37]. The daily rate of generation of oxide was controlled holding ThO+ formation lower than 1%. The total acquisition time was set to 120 s, equally distributed between blank and ion signal measures. However, given the higher susceptibility of the hydrothermal aggregates to the laser beam and their dimensions, point and even raster analysis were interrupted earlier to prevent contamination, which resulted in somewhat larger analytical errors. The Glitter software [38] was used for data acquisition, treatment and conversions to elemental concentrations. The synthetic NIST glass SRM-612 and the SiO2 contents previously measured by WDS were used as the external and internal standards, respectively. Analytical errors are quoted along with the presented results. Supplementary Table S1 provides analytical results for the 91500 and GJ-1 zircon references obtained in the laboratory with the applied analytical routine, which showed relatively good agreement with the recommended values (e.g., GeoRem Database [39] and [40,41]).
Lu-Hf LA-MC-ICPMS spot analysis was conducted with the Thermo-Finnigan Neptune Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) coupled with an Excimer ArF Laser (λ = 193 nm) system, according to the procedures described by Sato et al. [42], using a laser spot of 40 µm diameter and 50 s (1 cycle/s) for the ablation time under a frequency of 7 Hz and an energy fluency of 60 mJ (90% of the nominal laser energy: 7.70 J/cm2). 171Yb, 173Yb, 174Yb, 175Lu, 176(Hf + Yb + Lu), 177Hf and 179Hf masses were simultaneously quantified. 176Lu/177Hf ratios were calculated considering 176Lu/175Lu = 0.02669. The GJ-1 zircon standard gave 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282021 ± 0.000008 (2σ, n = 10) during our analysis, which approached the results presented by Liu et al. [41]. Initial 176Hf/177Hf ratios were computed considering λ(176Lu) = 1.867 × 10−11 yr−1 [43].
3. Results
3.1. Textural and Micro-Structural Patterns
The zircon aggregates occur in close association with hydrothermal mineral phases, particularly albite, epidote-group minerals, phyllosilicates, fluorite and Fe oxides. They appear filing in rock micro-fractures, interstices, and small miarolitic cavities, and they have variable dimensions (from ca. 2 to 80 μm; see Figure 2 and Figure 3). Among the hydrothermal HFSE mineral hosts, zircon is subordinated in relation to the epidote-group minerals, and they both occur in small volumes (<0.1%). The zircon aggregates are morphologically and micro-structurally diverse and present singular and variable habits, such as dendritic, rosette, oolitic, lenticular or semi-lenticular fibro-radiated, spherulitic, and botryoidal, with distinct zoning patterns. Some of these habits resemble those described for hydrothermal zircon in some peralkaline granites and related pegmatites, such as the Ambohimirahavavy (Madagascar), Strange Lake (Canada), and Khan Bogd (Mongolia) complexes [22,44,45]. Idiomorphic or typical “spongy”-textured crystals were not found.

Figure 2.
BSE images of hydrothermal zircon aggregates in peralkaline granite from the Corupá Pluton. (a): Dendritic, rosette, oolitic, and other zircon (Zrn) aggregates included in and probably co-precipitated with hydrothermal albite (Ab); note the zoning patterns with grayish or darker core areas and whitish rims. (b): Botryoidal and oolitic hydrothermal zircon, accompanied by minor phyllosilicates (Ph) and fluorite (Flr), filling in fractures in primary quartz (Qz) and protruding a K-feldspar (Kfs) substrate, along with hydrothermal albite. (c): Zoned zircon aggregates with a variety of morphologies, associated with phyllosilicates, fluorite, and allanite-(Ce) (Aln-Ce), filling in a small miarolitic cavity; note the shell-shaped crypto-crystalline aggregate with a concentric zoning pattern in the center of the image. (d): Botryoidal zircon aggregates, with subrounded globules mainly composed of Zr and Si (gZrSi) packed together and enveloped by microcrystalline zircon overgrowths (mZrn); note the dark cores in some globules (gZrSi1) and dark spots in-between globules and overgrowths. (e): Botryoidal aggregate with better-developed microcrystalline aggregates over globular nuclei; note the concentric zoning pattern and Fe-oxide (Fe-ox) “inclusions” and other unidentified dark spots accompanying this pattern. (f): Spherulitic, crypto-to-microcrystalline, fibro-radiated zircon aggregate with concentric zoning pattern, associated with allanite-(Ce) and brighter ferriallanite-(Ce) and epidote (Ep) fibro-radiated aggregate, filling in a miarolitic cavity. White bars measure 10 μm (a–c) and 50 μm (d–f). Mineral abbreviations as recommended by the IMA [46]. See text for discussion.
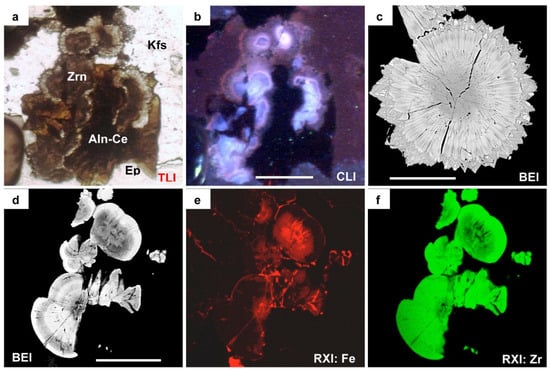
Figure 3.
Images and compositional maps of hydrothermal zircon aggregates in peralkaline granite from the Corupá Pluton. Botryoidal zircon aggregate associated with fibro-radiated allanite-(Ce) and ferriallanite-(Ce) (Aln-Ce, dark brown) + epidote (Ep, green) aggregates between K-feldspar (Kfs) crystals. (a): Transmitted light image emphasizing the brown nuclei and the colorless better-crystallized zircon overgrowths; (b): Cathodoluminescence image displaying zonal and concentric arrangement of light blue, slightly violet, and red colors in zircon. Allanite-(Ce), ferriallanite-(Ce) and epidote are represented in black. (c): BSE image of spherulitic, crypto-to-microcrystalline fibro-radiated zircon aggregate with concentric zoning pattern and minute dark spots (Fe-oxide inclusions and/or micro-pores) accompanying the zoning and crystal fibers arrangements; note the idiomorphic pyramidal termination of the fibers. (d): BSE image of lenticular and semi-lenticular cryptocrystalline aggregates with concentric zoning pattern. (e,f): X-ray dot maps for Fe (e) and Zr (f) of the aggregates shown in (d); note the Fe-rich and Zr-poor irregular nuclei surrounded by a more regular and less Fe-rich, Zr-poor zone and then by a relatively Fe-poor and Zr-rich external zone. White bars measure 50 μm. See text for discussion.
The aggregates present variable crystallization degrees to the extent that could be inferred from optical and BSE images (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Under the optical microscope, the aggregates with relatively smaller dimensions (Figure 2a–c) show variable dark-to-pale brownish colors and undetectable birefringence that suggest an amorphous-like behavior. The largest ones display a well-developed internal fibro-radiated cryptocrystalline arrangement with oscillatory extinction (Figure 3d). BSE images of the smaller aggregates reveal variable zoning patterns given by a relatively darker, grayish, (with lower backscattered coefficients and thus lower mean atomic numbers) internal zone surrounded by a brighter whitish zone, while those of the larger ones depict oscillatory patterns alternating relatively darker, grayish, and whitish μm-sized zones.
The larger botryoidal aggregates comprise brownish globules assembled together, sometimes suggesting coalescence features (Figure 2d,e), with undetectable birefringence; they typically present thin overgrows of tiny radiated colorless zircon microcrystals with pyramidal terminations and normal birefringence. Some globules present subrounded cores that are opaque under transmitted light and much darker in BSE images. In other globules, the external colorless microcrystalline zone is dominant over the internal zone, and they show oscillatory concentric zoning (Figure 2e and Figure 3a). These aggregate types present variable CL colors, from typical bluish to slightly violet in the internal zones and slightly violet to reddish at the most external colorless zones (Figure 3b).
The spherulitic aggregates are almost colorless, transparent, and constituted by fibro-radiated micro-crystals or crystal fibers with well-developed pyramidal terminations and oscillatory extinction (Figure 2f and Figure 3c). BSE images reveal a concentric oscillatory zoning pattern with intercalated, μm-sized slightly grayish and whitish zones.
BSE images depict minute dark spots with quadrangular, rectangular or elongated shapes trapped in-between globules and their overgrowths (Figure 2d,e) or along crystal fibers in the case of the aggregates with fibro-radiated arrangements, distributed according to the radiated and zoning zircon patterns (Figure 2f and Figure 3c).
Qualitative EDS spot analysis carried out simultaneously with BSE imaging indicate that the clearest zones in all aggregates contained Zr, Si and (eventually) some Hf, while the grayish zones additionally contain minor and variable quantities of Al, Ca, Y, REE, and (particularly) Fe. The darkest nuclei observed within some globules (Figure 2d) present (besides Si and Zr) significant quantities of Fe and (eventually) some quantities of Al, Ca and K. The irregular darker zones in the core areas of the fibro-radiated cryptocrystalline aggregates (Figure 3d) are relatively Fe-rich and Zr-poor, as exemplified by the X-ray dot maps presented in Figure 3e,f. Most of the minute dark spots could not be probed; some of them in the botryoidal and spherulitic aggregates with apparent idiomorphic outlines mainly contain Fe and may arguably be hematite or magnetite.
The primary zircon crystals (Figure 4), examined for comparison purposes, are idiomorphic, colorless and pristine, with 40–80 μm along the c crystallographic axis and present both prismatic and pyramidal crystal forms. They occur as isolated crystals and as inclusions in mesoperthite, quartz or amphiboles. BSE images show oscillatory (Figure 4a) or, more typically, slightly patchy (Figure 4c) zoning patterns.
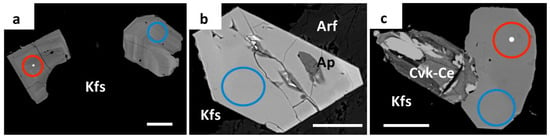
Figure 4.
BSE images of magmatic zircon crystals in peralkaline granite from the Corupá Pluton. (a): Euhedral crystals showing oscillatory zoning patterns included in K-feldspar (Kfs); (b) euhedral crystal with slightly zoning and an apatite (Ap) inclusion between K-feldspar and arfvedsonite (Arf); (c) Euhedral crystal with slightly patchy zoning pattern associated with pristine (main brighter area) and hydrothermally altered (darker areas) chevkinite-(Ce) (Cvk-Ce). White dots, red circles, and blue circles indicate the locations of WDS, LA-ICPMS, and LA-MC-ICPMS spot analysis, respectively. The white bars measure 50 μm.
3.2. Elemental and Isotope Geochemistry
The chemical and Lu-Hf isotopic compositions for primary (magmatic) zircon crystals and hydrothermal aggregates are presented in Table 1 and Table S2 (WDS), 2 (LA-ICPMS), and 3 (LA-MC-ICPMS), and discussed below. Given the spatial resolution, except for some WDS analyses of some relatively thicker crystal fibers, the analytical results for the trace elements and Lu-Hf isotopes of the hydrothermal varieties are representative of the average crystal aggregates.

Table 1.
Representative chemical compositions (wt.%, WDS) and cation proportions for primary (P) and hydrothermal (H) zircon crystals and aggregates, respectively. WDS spot locations for points 1,c and 3,c as given in Figure 4a,c, respectively. H1 = botryoidal aggregates and transparent overgrowth (r); H2 = lenticular fibro-radiated (1,c and 1,r from Figure 3e) and spherulitic fibro-radiated crypto- and micro-crystalline varieties. c = core; I = intermediate zone; r = rim; n.a. = not analyzed; b.d. = below detection limit. All Fe computed as Fe2O3.
The WDS compositions of primary zircon are relatively homogenous and to approach ideal ZrSiO4, with maximum Hf, REE + Y, and Fe values of 0.008, 0.009 and 0.006 cations per formula unit (cpfu), respectively. On the other hand, the hydrothermal varieties contain significantly higher contents of Hf, Th, U, Ti, Al, REE + Y, Fe, Mn, Ca, and Nb amounts of up to 0.015, 0.014, 0.02, 0.007, 0.023, 0.091, 0.044, 0.015, 0.022 and 0.006 cpfu, respectively, a feature common to both natural and synthetic hydrothermal altered zircon [20,21,47]. As a whole, the hydrothermal varieties present lower analytical totals (down to ca. 95 wt.%), which could be explained by the presence of minute pores within or between crystal fibers and/or H2O [48], which led to relatively poor structural formulae and variable cation excess (from 0.02 to 0.04 cpfu) in the Zr site; the total occupancy of this site by elements other than Zr varies between 0.14 and 0.06 cpfu. Some of these, particularly Al, Fe, Ca, Mn, are known as “non-formula” elements because they cannot be well-accommodated in the zircon Si or Zr sites, probably occurring in interstitial sites [46] or nanopores [21,48].
The dark, Fe-rich irregular cores, observed in the cryptocrystalline fibro-radiated aggregates (Figure 3d), contain Fe2O3 up to ca. 39.9 wt.% (0.984 Fe cpfu) and SiO2 and ZrO2 down to 22.4 and 40.8 wt.%, respectively. The structural formulae are incompatible with the zircon structure and give sums up to 2.264 cpfu on the basis of 4 O (see Table 1 and Table S2).
The compositional WDS core-to-rim profile for the pristine spherulitic aggregate shown in Figure 3c is depicted in Figure 5 to illustrate its main zoning pattern. From the core to the most external rim, Fe, Al, Ca, and U show similar behavior, their contents initially decreasing towards the intermediate zone and then increasing towards the aggregate rims; Nb show a similar pattern but significantly decreased in the most external rim, while Th show an abrupt increase and the Th/U ratios increased towards the rim. On the other hand, Y and Dy increase more or less uniformly towards the rim and Hf and Ti remain almost unchanged.
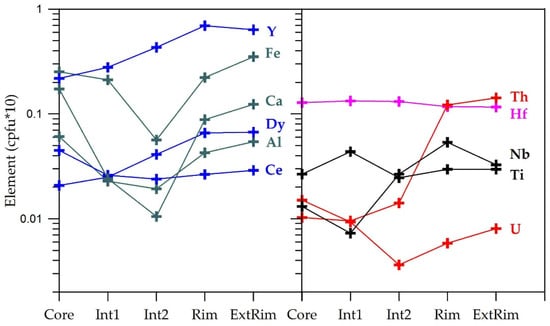
Figure 5.
WDS compositional core-to-rim profile illustrating the main chemical (minor and some trace elements) variations, expressed in cations per formula unit (cpfu), of the spherulitic zircon aggregate shown in Figure 3f.
3.2.1. Trace Element and REE Patterns
Trace-element patterns for hydrothermal and primary zircon are compared in Figure 6. In relation the host granite, both the primary and hydrothermal zircon presented well-developed positive U and Hf and negative Ti anomalies. Except for Ti and Mn, the hydrothermal species are significantly enriched in most of the measured trace elements. Their concentrations are 10–100-fold higher than those observed in the host rock on average, while in the case of the primary zircon, the concentrations of Nb, Ta, La, Ce, Pb, Sr, and Pr are 0.002–0.5-fold those in the host. The ThZircon/ThHost rock and UZircon/UHost rock ratios vary from ca. 10–60 and 100–300 to ca. 3 and 30, respectively. Thus, compared to the primary zircon, the hydrothermal aggregates are particularly rich in Nb, Ta, Pb, Sr, Ti, Mn, and the total REEs; for instance, some of these elements, such as La and Pr, have concentrations of up to 1000-fold higher (see also Table 2). The hydrothermal varieties also have higher Th/U and Ti/Nb (up to 3.9 vs. 1.2 and 1.2 vs. 0.34, respectively) and lower Zr/Hf (up to 45 vs. 74) ratios. The higher Th/U values of the hydrothermal zircon compared to the primary zircon are somewhat unusual because they are opposed to values commonly observed in zircon from several granitic occurrences [4,20].
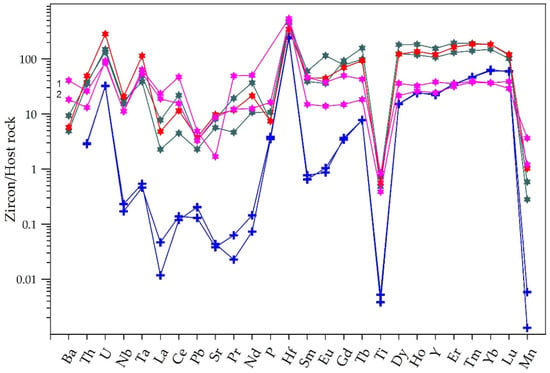
Figure 6.
Trace-element distribution patterns for primary and hydrothermal zircon, normalized to the CO-2A host granite sample. Symbols: blue cross—primary zircon; green star—botryoidal aggregates; magenta star—fibro-radiated crypto-crystalline aggregates; brown core—(1), colorless overgrowth (2); red star—spherulitic fibro-radiated micro-crystalline aggregate in allanite-(Ce).

Table 2.
Trace-element compositions (ppm, LA-ICPMS) of primary (P) and hydrothermal (H) zircon crystals and aggregates, respectively, as well as the associated analytical errors (1σ). P1 and P2 spot locations as provided in Figure 4a,c, respectively. H1 = botryoidal globules; H2a = fibro-radiated crypto-crystalline, brown core; H2b = fibro-radiated crypto-crystalline, colorless overgrowth; H3 = spherulitic, colorless, fibro-radiated aggregate associated with allanite-(Ce), as shown in Figure 2f.
The REE patterns (Figure 7) show that the primary crystals are characterized by high fractionation degrees of the HREE over the LREE and in both the LREE and HREE sides. They display well-developed positive Ce anomalies (2.5 < Ce/Ce* < 7.2 (Ce/Ce* = CeN/(LaN*PrN)0.5, where N stands for normalized to chondritic values)) and negative Eu anomalies (0.02 < Eu/Eu* < 0.03, (Eu/Eu* = EuN/(SmN*GdN)0.5). On the other hand, the hydrothermal zircon presents relatively flat patterns, with HREE over LREE fractionations approaching the unity or even lower values and negative Eu anomalies (0.02 < Eu/Eu* < 0.06). The botryoidal and the spherulitic varieties present the highest HREE/LREE fractionation degrees and subtle positive Ce anomalies. The fibro-radiated cryptocrystalline aggregates are relatively LREE-rich and HREE-poor, with a pattern closer to the host rock and a slight fractionation degree in the LREE side and of the MREE over the HREE; the Ce anomaly was absent. In these varieties, the transparent overgrowths contain higher REE concentrations than the brownish internal zones. The SmN/LaN ratios vary in the ranges of 4.6–15.5 and 0.6–4.8 in the primary and hydrothermal zircon, respectively. These features are much like those described for primary and hydrothermal zircon in igneous rocks elsewhere [3,15,20,49].
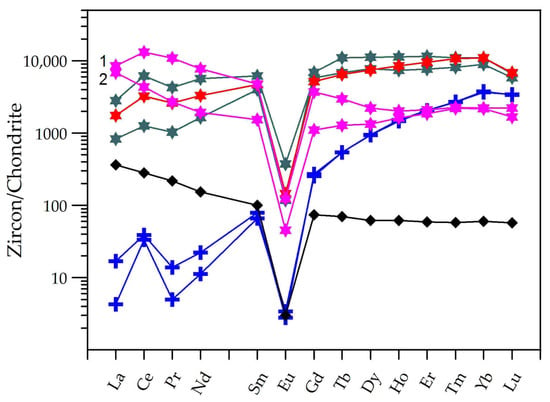
Figure 7.
REE patterns for the primary and hydrothermal zircon and the CO-2A host granite, normalized to the chondritic values of Boynton [50]. Symbols: black diamond—host rock; others as in Figure 6.
3.2.2. Lu-Hf Isotope Geochemistry
Lu and Hf isotope data (Table 3) for primary and hydrothermal zircon are represented in Figure 8. Initial (176Hf/177Hf)t ratios and related εHf(T) parameters were computed for t = 580 Ma in both cases, as the age of the hydrothermal event could not be constrained and it is likely that the it was not much younger than the main magmatism. The (176Hf/177Hf)580 ratios range from ca. 0.28165 to 0.28200, corresponding to −25.8 < εHf(580) < −17.7, thus indicating an isotopically evolved source for the original magma. It must be noted that the values of the hydrothermal varieties are close to those measured in primary zircon crystals, considering the involved analytical errors. These results are compatible with an essentially orthomagmatic source for such elements.

Table 3.
In-zircon Lu and Hf measured (meas) and calculated isotope data for primary (P) and hydrothermal (H) zircon crystals and aggregates, respectively. Points Zr7-3.1, Zr6-2.2 and Zr8-1.1 spot locations are as given in Figure 4a–c, respectively. H1 = crypto- and micro-crystalline fibro-radiated aggregates; H2 = botryoidal globules. Initial (176Hf/177Hf)(t) and related εNd(t) parameter computed for 580 Ma.
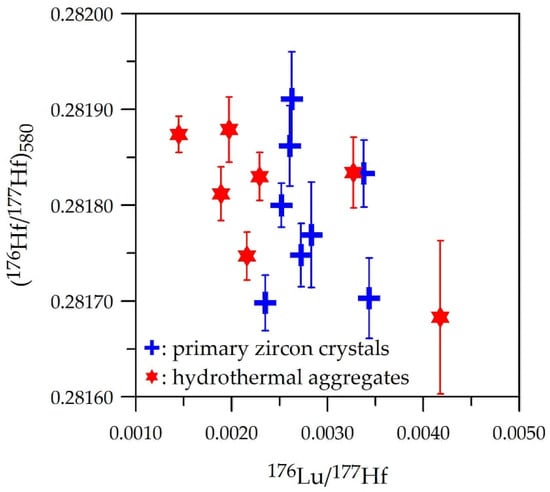
Figure 8.
In-zircon initial (176Hf/177Hf)580 vs. (176Lu/177Hf)meas diagram for primary and hydrothermal zircon crystals and aggregates, respectively. Note the similar variation range.
4. Discussion
The mineral paragenesis associated with the zircon aggregates in the studied peralkaline granite from the Corupá Pluton and their morphology provide undoubted evidence for a hydrothermal origin. Their chemical compositions were found to be characterized by relatively high contents of “non-formula” and HFSs (particularly the L- and MRE) elements, features most commonly associated with hydrothermal dissolution–reprecipitation processes acting on previous magmatic or metamorphic zircon crystals [21].
4.1. The Formation of Crypto- and Microcrystalline Zircon Aggregates
The observed textures and microstructures in the zircon aggregates are relatively rare and intriguing. Their crypto-to-microcrystalline nature contrasts with the epidote-group minerals, whose aggregates are composed of relatively well-formed crystals and should be related to crystal-growth issues and the characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid. For instance, the spherulitic textures observed in chalcedony and other organic and inorganic materials have been interpreted as resulting from spiral crystal growth in a partially polymerized low-temperature fluid [51]. The formation of fibro-radiated hydrothermal or secondary mineral aggregates in low-temperature environments is often interpreted as the result of the precipitation of crypto-to-microcrystals radiating from some kind of seed; if this was the case, a Fe oxide or other Fe compounds are potential candidates in the studied example. The development and partial preservation of globular structures, with some evidence of coalescence, within the botryoidal aggregates are more puzzling and may suggest that during the hydrothermal stage, some process enabled the formation of Zr-rich silicate colloidal solutions or gel-like compounds from which alumino-silicate phases, fluorite, and zircon components unmixed. The preservation of these microstructures and of the amorphous-like Zr-silicate and cryptocrystalline zircon can be tentatively associated with poor element diffusion in a low-temperature environment, as supported by some crystallization experiments starting from synthetic gels [52,53]. Where fluid flux and/or element diffusion were facilitated, as in the outer zones of the globules and in the spherulites, crystal nucleation was reduced and relatively larger crystals developed.
The crystallization of similar zircon aggregates in some occurrences of typically agpaitic granites elsewhere has mainly been related to the substitution of previously crystallized, magmatic and/or post-magmatic Zr-silicates such as eudialyte-group minerals, elpidite and armstrongite–gittinsite [22,44,45]. For instance, pseudomorphs after eudialyte-group minerals constituted by hydrothermal zircon, quartz, and rare-metal-bearing and other hydrothermal phases were described in granites from the Ambohimirahavavy complex [22].
In the studied case, there was no clear evidence indicating a similar origin, as no previous Zr-silicates occurred in the peralkaline granites nor in the enclosing main syenites and the zircon aggregates probably directly precipitated from the hydrothermal fluid. In the granites and syenites, chevkinite (a typical and relatively abundant accessory mineral) and amphiboles contain only minor and trace abundances of Zr, respectively [33,54], so this element is mainly hosted in zircon; however, the analytical results showed that primary zircon from the granite had significantly lower HFSE contents than the hydrothermal varieties. Chevkinite is easily altered by hydrothermal fluids (see Figure 4c), and this process releases significant amounts of REEs (particularly the LREEs) besides Fe and Th [54], which should have contributed to the fluid composition [33]; however, this was not as clear for Zr and Hf, and their source remains unclear. Nevertheless, the Hf isotopic data suggest an orthomagmatic origin.
The transition from the late-magmatic to the post-magmatic stages in the granites from the Corupá Pluton was shown to be marked by a notable change in the chemical environment, and the peralkaline mineralogy characterized by the sodic amphiboles in the former gave way to the precipitation of a Ca- and Al-bearing, metaluminous, assemblage particularly characterized by the precipitation of epidote-group minerals [33]. The occurrence of allanite-(Ce), ferriallanite-(Ce), zircon and fluorite in the hydrothermal assemblage indicates that the fluid phase contained significant amounts of HFSEs (particularly the REEs) and F. It is well-known that the HFSEs form stable complexes and may be concentrated in and transported by aqueous, halogen (F and Cl)-bearing, saline and acid fluids [26,55,56,57,58,59]. Hence, it is suggested here that a similar F-bearing silicate fluid was exsolved from the crystallizing melts during the late evolution of the syenitic–granitic magmatic system and carried these elements.
Subsequent changes in fluid properties, particularly pH neutralization [57,60], allowed for the precipitation of the HFSEs and their incorporation into the structures of hydrothermal epidote-bearing minerals, particularly allanite-(Ce) and ferriallanite-(Ce), and zircon aggregates. These changes are complex and not well-known; they may be driven by the precipitation of hydrothermal mineral phases, interactions with the wall-rock and reactions with previous mineral phases, and/or mixing with fluids derived in the country rocks [26,55,57]. A previous interpretation of the formation of epidote-group minerals in the hydrothermal assemblage did not favor significant external contributions [33]; in this case, the source for Ca and Al must be related to the re-equilibration of the primary alkali-feldspar, which is abundant in the granite host, and the consequent release of its minor anorthite component to the fluid; however, in several occurrences worldwide, such as the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, the involvement of Ca-bearing external meteoritic fluids seems to have been well-demonstrated [55], and this hypothesis cannot be excluded with the available data.
4.2. Crystallization Conditions
The intensive parameters for the late magmatic and hydrothermal crystallization stages in the Corupá Pluton were not precisely constrained. The geological characteristics indicated a relatively low pressure (<ca. 200 MPa) for magma emplacement and crystallization, and the observed mineralogical assemblages suggested relatively reducing (near the quartz–fayalite–magnetite (QFM) buffer) and oxidizing (near the hematite-magnetite, HM buffer) environments at the onset of magmatic and post-magmatic stages, respectively [32,33,54].
The Ti-in-zircon crystallization temperatures of the magmatic analyzed crystals were estimated with the formalism developed by Ferry and Watson [9] while assuming a silica activity (aSiO2) = 1, a reasonable value for evolved granites in which quartz was a close-to-liquidus phase. The estimation of the aTiO2 was somewhat more difficult, as rutile is absent and ilmenite is the unique primary Fe-Ti oxide present in the host rock. Taking aTiO2 values of 0.3, 0.5 and 0.7, as well as the Ti average concentrations and related errors given in Table 2, the obtained temperatures are 772, 738, and 708 °C, respectively, with an estimated error around 50–70 °C for a 95% confidence level. Given the observed mineral paragenesis, it is suggested that the titania activity was moderate to low. The obtained temperatures set an upper limit to the granite solidus, while chlorite thermometry for the main syenites (unpublished data) provided hydrothermal temperature values of around 250–300 °C. Available experimental data suggest that hydrothermal zircon may precipitate in a large range of temperatures, from solidus temperatures down to 150 °C [52,53], and zircon re-equilibration by diffusion–reaction processes may take place even under weathering conditions [21].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min12050628/s1. Table S1: Analytical results for trace elements in zircon reference materials 91500 and GJ-1 and respective recommended values; Table S2: Chemical compositions (WDS, wt.%) and structural formulae for primary and hydrothermal zircon, Pluton Corupá, Sample CO-2. Fb = fibro-radiated; c = core; I = intermediate zone; r = rim; over = overgrowth.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), grants numbers 2008/00562-0 and 2019/17343-4.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the staff of the GeoAnalitica Core Facility and the Geochronological Research Center of the Institute of Geosciences at the University of São Paulo for analytical support. S. Andrade and K. Sato provided invaluable help during trace element and Lu/Hf isotope analyses, respectively; G. Szabó kindly revised the English language manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Wayne, D.M.; Sinha, A.K.; Hewitt, D.A. Differential response of zircon U-Pb systematics to metamorphism across a lithologic boundary: An example from the Hope Valley Shear Zone, southeastern Massachusetts, USA. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 109, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, T.R.; Williams, I.S. Considerations in zircon geochronology by SIMS. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Scharltegger, U. The compositions of zircon in igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, S.L.; Kelly, N.M. Zircon. Tiny but timely. Elements 2007, 3, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, S.L.; Kelly, N.M.; Möller, A. Zircon behavior and thermal histories of Mountain Chains. Elements 2007, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, E.E.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Münker, C. Zircon as a monitor of crustal growth. Elements 2007, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troch, J.; Ellis, B.S.; Schmitt, A.K.; Bouvier, A.-S.; Bachmann, O. The dark side of zircon: Textural, age, oxygen isotopic and trace element evidence of fluid saturation in the subvolcanic reservoir of the Island Park-Mount Jackson Rhyolite, Yellowstone (USA). Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2018, 173, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of magma types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1983, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasoni, F.; Klemme, S.; Rocha-Junior, E.R.; Berndt, J. Zircon saturation in silicate melts: A new and improved model for aluminous and alkaline melts. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 171, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, D.; Finger, F. Application of Ti-in-zircon thermometry to granite studies: Problems and possible solutions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 174, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, J.R.; Palin, M.J.; Campbell, I.H. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(IV)/Ce(III) in zircon: Application to porphyry copper deposits. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 144, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Watson, E.B.; Tailby, N.D. Ce and Eu anomalies in zircon as proxies of the oxidation state of magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Fisher, N.J. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 143, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchar, J.M.; van Westrenen, W. Rare earth element behavior in zircon-melt systems. Elements 2007, 3, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.I.S.; Hawkesworth, C.J. Using hafnium and oxygen isotopes in zircon to unravel the record of crustal evolution. Chem. Geol. 2006, 226, 133–162. [Google Scholar]
- Valley, J.W.; Lackey, J.S.; Cavosie, A.J.; Clechenko, C.C.; Spicuzza, M.J.; Basei, M.A.S.; Bindeman, I.N.; Ferreira, V.P.; Sial, A.N.; King, E.M.; et al. 4.4 billion years of crustal maturation: Oxygen isotope ratios of magmatic zircon. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2005, 150, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B. Zircon in technology and everyday life. Elements 2007, 3, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Corfu, F.; Hanchar, J.M.; Hoskin, P.W.O.; Kinny, P. Atlas of zircon textures. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 469–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O. Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, T.; Schaltegger, U.; Tomaschek, F. Re-equilibration of zircon in aqueous fluids and melts. Elements 2007, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrade, G.; Salvi, S.; Béziat, D. Crystallization and destabilization of eudialyte-group minerals in peralkaline granite and pegmatite: A case study from the Ambohimirahavavy complex, Madagascar. Mineral. Mag. 2018, 82, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.N.; Henry, C.D.; Price, J.G. Hydrothermal zircons and zircon overgrowths, Sierra Blanca Peaks, Texas. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 865–869. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, E.A.; Boehnke, P.; Barboni, M.; Harrison, T.M. Tracking chemical alteration in magmatic zircon using rare earth element abundances. Chem. Geol. 2019, 510, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilalva, F.C.J.; Simonetti, A.; Vlach, S.R.F. Insights in the origin of the Graciosa A-type granites and syenites (Southern Brazil) from zircon U-Pb geochronology, chemistry, and Hf and O isotope data. Lithos 2019, 340–341, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieré, R. Formation of rare earth minerals in hydrothermal systems. In Rare Earth Minerals. Chemistry, Origin and Ore Deposits, 1st ed.; Jones, A.P., Wall, F., Williams, C.T., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996; pp. 105–149. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.; Lin, L.; Sheng-Rong, L.; Santosh, M.; Jun-Feng, S. Geochemistry of hydrothermal zircon as a proxy to fingerprint ore fluids in late Mesozoic decratonic gold deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 143, 104703. [Google Scholar]
- Geisler, T.; Rashwan, A.A.; Rahn, M.K.W.; Poller, U.; Zwingmann, H.; Pidgeon, R.T.; Schleicher, H.; Tomaschek, F. Low-temperature hydrothermal alteration of natural metamict zircons from the Eastern Desert, Egypt. Mineral. Mag. 2003, 67, 485–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, U. Hydrothermal zircon. Elements 2007, 3, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualda, G.A.R.; Vlach, S.R.F. The Serra da Graciosa A-type Granites & Syenites, southern Brazil. Part 1: Regional setting and geological characterization. An. Acad. Bras. Cien. 2007, 79, 405–430. [Google Scholar]
- Vlach, S.R.F.; Siga, O., Jr.; Harara, O.M.M.; Gualda, G.A.R.; Basei, M.A.S.; Vilalva, F.C.J. Crystallization ages of the A-type magmatism of the Graciosa Province (southern Brazil): Constraints from the zircon U-Pb (ID-TIMS) dating of coeval K-rich gabbrodioritic rocks. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2011, 32, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, Y. Mineralogia e Petrologia da Associação Alcalina de Sienitos e Granitos de Tipo-A Do Maciço Corupá (SC). Master´s Dissertation, Institute of Geoscience, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2002. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Vlach, S.R.F. Micro-structural and major-an trace-element compositional variations of hydrothermal epidote-group minerals from a peralkaline granite, Corupá Pluton, Graciosa Province, South Brazil, and their petrological implications. An. Acad. Bras. Ciên. 2012, 84, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazeres Filho, H.J.; Harara, O.M.M.; Basei, M.A.S.; Passarelli, C.R.; Siga, O., Jr. Litoquímica, Geocronologia U-Pb e Geologia Isotópica (Sr-Nd-Pb) das Rochas Graníticas dos Batólitos Cunhaporanga e Três Córregos na Porção Sul do Cinturão Ribeira, Estado do Paraná. Geol. USP 2003, 3, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bastin, G.F.; Heijligers, H.J.M. Progress in electron-probe microanalysis. Materwiss. Werksttech. 1990, 21, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vlach, S.R.F. Th-U-PbT dating by the electron probe microanalyzer, Part 1. Monazite: Analytical procedures and data treatment. Geol. USP Sér. Cient. 2010, 10, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S. Análises por LA-ICPMS em Zircões de Rochas Graníticas da Faixa Ribeira no Estado de São Paulo—SE Brasil: Implicações Genéticas e Geocronológicas. Doctoral’s Thesis, Institute of Geoscience, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2016. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- van Achterbergh, E.; Rayan, C.G.; Griffin, W.L. Glitter User’s Manual; On line interactive data reduction for the LA-ICPMS microprobe v. 4.4; Gemoc National Key Centre, Macquarie University: Ryde, Australia, 2007; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Jochum, K.P.; Nohl, U.; Herwig, K.; Lammel, E.; Stoll, B.; Hofmann, A.W. GeoRem: A new geochemical database for reference materials and isotopic standards. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2005, 29, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.L.; Gao, S.; Daí, M.N.; Zong, C.L.; Gunther, D.; Fontaine, G.H.; Liu, X.M.; Diwu, C. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by Excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zong, K.; Gao, C.G.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.H. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Siga, O.; da Silva, J.A.; Mcreath, I.; Dunyi, L.; Iizuka, T.; Rino, S.; Hirata, T.; Sproesser, W.; Basei, M.A. In situ isotopic analyses of U and Pb in zircon by remotely operated SHRIMP II, and Hf by LA-ICP-MS: An example of dating and genetic evolution of zircon by 176Hf/177Hf from the Ita quarry in the Atuba Complex, SE Brazil. Geol. USP 2009, 9, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, U.; Patchett, P.J.; Vervoort, J.D.; Isachsen, C.E. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu–Hf and U–Pb isotope systematic of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 219, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Zirconosilicate phase-relations in the Strange Lake (Lac-Brisson) pluton, Quebec-Labrador, Canada. Am. Mineral. 1995, 80, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, C. Concentration and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Alkaline Complexes: The Role of Fluids. Doctoral Thesis, Université de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Warr, L.N. IMA-CNMC approved mineral symbols. Min. Mag. 2021, 85, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, T.E.; Davis, G.L. Alteration in zircons and differential dissolution of altered and metamict zircon. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearb. 1975, 74, 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Nasdala, L.; Kronz, A.; Wirth, R.; Váczi, T.; Pérez-Soba, C.; Willner, A.; Kenedy, A.K. The phenomenon of deficient electron microprobe totals in radiation-damaged and altered zircon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1637–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, R.J.; Hanchar, J.M. Structure and chemistry of zircon and zircon-group minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Rare Earth Element Geochemistry, 1st ed.; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Heaney, P.J. A proposed mechanism for the growth of chalcedony. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 115, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frondel, C.; Collette, R.L. Hydrothermal synthesis of zircon, thorite and huttonite. Am. Mineral. 1957, 42, 759–765. [Google Scholar]
- Valéro, R.; Durand, B.; Guth, J.-L.; Chopin, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of porous zircon in basic fluorinated medium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 1999, 29, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlach, S.R.F.; Gualda, G.A.R. Allanite and chevkinite in A-type granites and syenites of the Graciosa Province, southern Brazil. Lithos 2007, 97, 98–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Williams-Jones, A.E. The role of hydrothermal processes in concentrating high-field strength elements in the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, northeastern Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Peters, T.J. Zircon solubility in alkaline aqueous fluids at upper crustal conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 96, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Jones, A.E.; Migdisov, A.A.; Samson, I.M. Hydrothermal mobilization of the rare earth elements—A tale of “Ceria” and “Yttria”. Elements 2012, 8, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrade, G.; Salvi, S.; Béziat, D.; Rakotovao, S.; Rakotondrazafy, R. REE and HFSE mineralization in peralkaline granites of the Ambohimirahavavy alkaline complex, Ampasindava peninsula, Madagascar. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 94, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, H.; Wyllie, P.J. Role of fluids in transport and fractionation of uranium and thorium in magmatic processes. Nature 1990, 348, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Brugger, J.; Caporuscio, F.A. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the RRE: Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations. Chem. Geol. 2016, 439, 12–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).