Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Characterization
2.2.2. Zeta Potential Measurements
2.2.3. Dispersion/Sedimentation Experiments
3. Results and Discussions
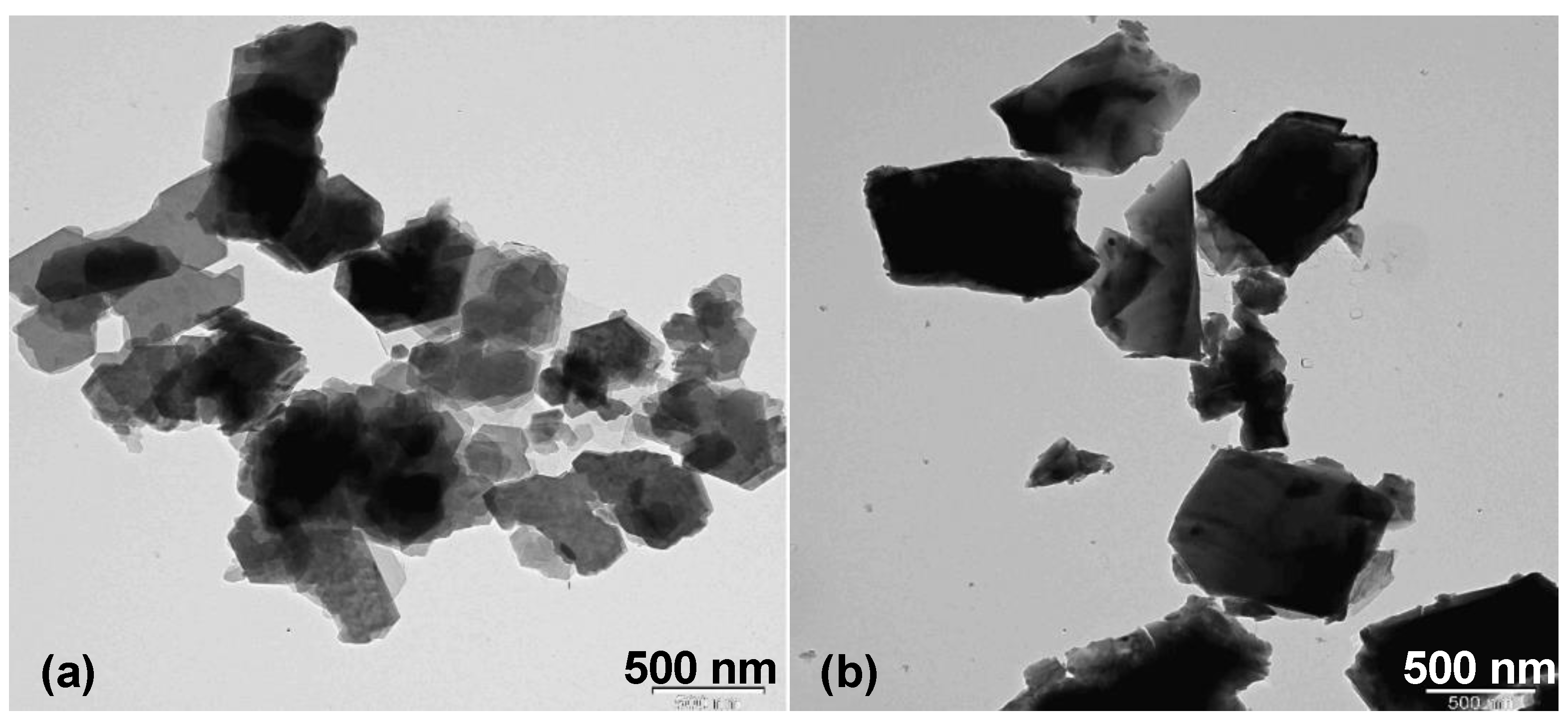
3.1. Sample Characterization
3.2. Zeta Potential Measurements
3.2.1. Without Dispersants
3.2.2. With Dispersants
3.3. Dispersion/Sedimentation Studies
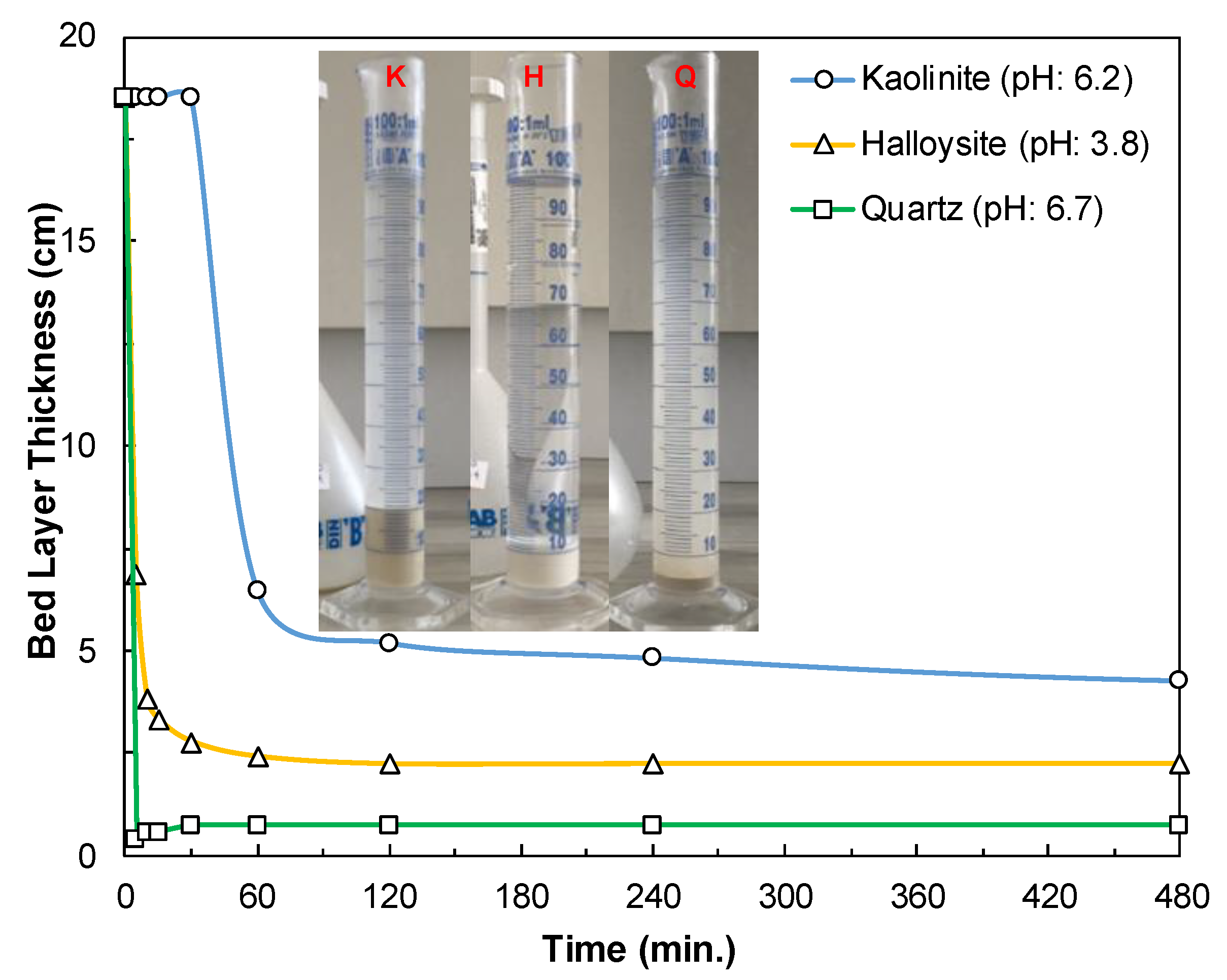
3.3.1. Effect of pH
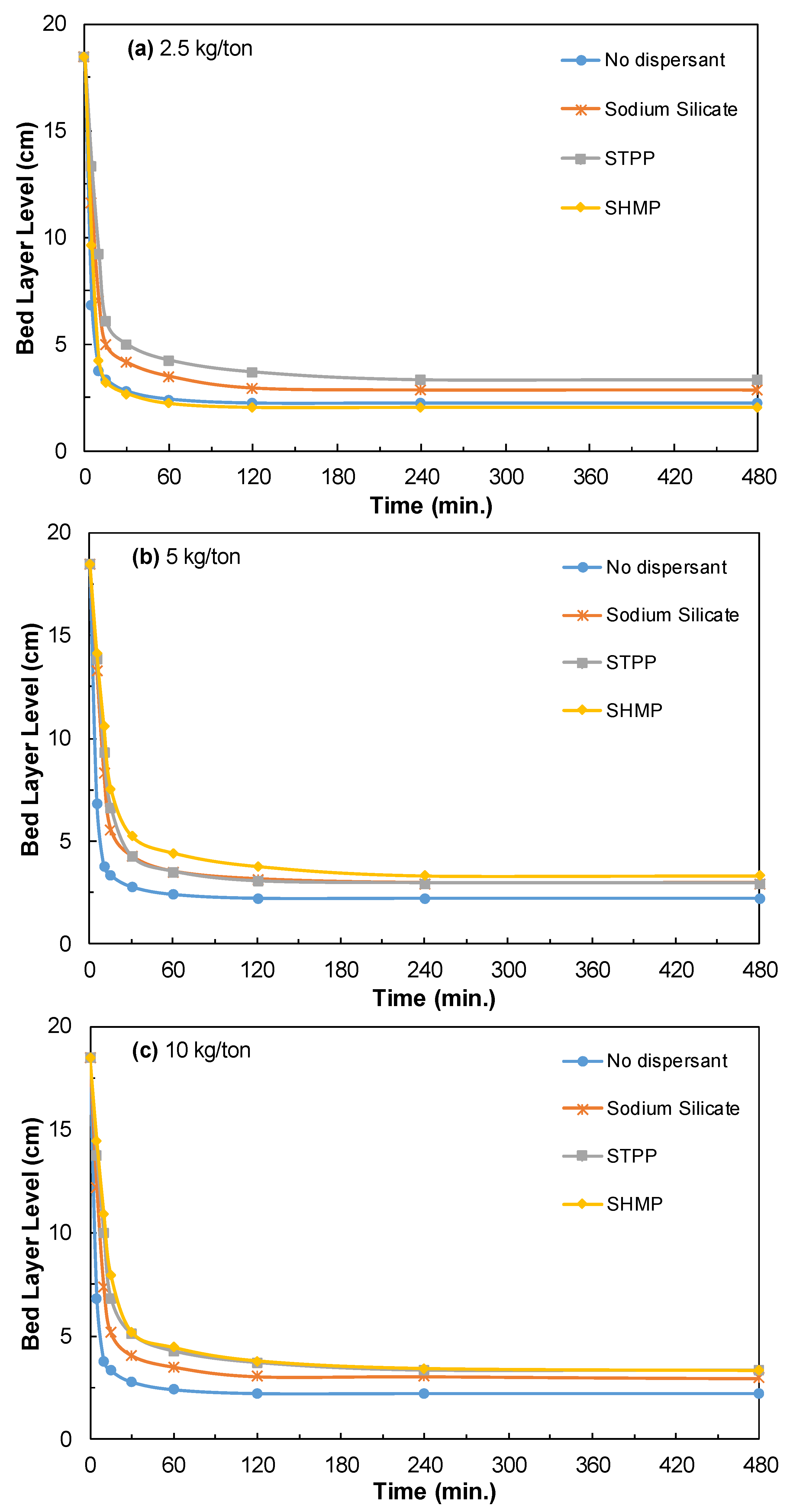
3.3.2. Effect of Dispersants
3.3.3. Effect of Dispersants on Halloysite Ore Dispersion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The history of nanoscience and nanotechnology: From chemical–physical applications to nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, T.F.; Hildebrand, F.A.; Swineford, A. Morphology and structure of endellite and halloysite. Am. Mineral. 1950, 35, 463–484. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, N. On the basic concept of ‘nano-technology’. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Production Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 26–29 August 1974; pp. 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubes of graphite carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Du, C. Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin. Minerals 2018, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchman, G.J.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Hillier, S. The rise and rise of halloysite. Clay Miner. 2016, 51, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lázaro, B.B. Halloysite and kaolinite: Two clay minerals with geological and technological importance. Rev. Real Academia Ciencias. Zaragoza 2015, 70, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Churchman, G. Properties and Processes, Handbook of Soil Sciences, 2nd ed.; Sumner, M.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. F3–F76, 2nd Chapter. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.J.; Kerr, P.F. Halloysite and Allophone; US Geological Survey, Department of the Interior: Washington, WC, USA, 1934; Volume 185-G, pp. 135–148.
- MacEwan, D.M.C. The nomenclature of the halloysite minerals. Mineral. Mag. J. Mineral. Soc. 1947, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchman, G.J.; Carr, R.M. The definition and nomenclature of halloysites. Clays Clay Miner. 1975, 23, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W. Kaolin, serpentine and kindred minerals. In The X-ray Identification and Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals; Brown, G., Ed.; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1961; pp. 51–131. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, P.S.; Brindley, G.W.; Santos, H.D. Mineralogical studies of kaolinite-halloysite clays Part III. A fibrous kaolin mineral from Piedade, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Am. Mineral. 1965, 50, 619–628. [Google Scholar]
- Grim, R.E. Clay Mineralogy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Churchman, G.J.; Whitton, J.S.; Claridge, G.G.C.; Theng, B.K.G. Intercalation method using formamide for differentiating halloysite from kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner. 1984, 32, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, I.D.M.; Eggleton, R.A. Weathering of granitic muscovite to kaolinite and halloysite and plagioclase-derived kaolinite to halloysite. Clays Clay Miner. 1991, 39, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, N.; Fukushima, K.; Fukami, A. Observation of the hydrated form of tubular halloysite by an electron microscope equipped with an environmental cell. Clays Clay Miner. 1978, 26, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawtani., D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Multifarious applications of halloysite nanotubes: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 30, 282–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zubkiewicz, A.; Szymczyk, A.; Franciszczak, P.; Kochmanska, A.; Janowska, I.; Paszkiewicz, S. Comparing Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Halloysite Nanotubes as Reinforcements in EVA Nanocomposites. Materials 2020, 13, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite clay nanotubes: Characterization, biocompatibility and use as drug carriers. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, H.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Enhancing dispersion of halloysite nanotubes via chemical modification. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2014, 41, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgut, E.; Cinar, M.; Terzi, M.; Unver, I.K.; Yildirim, Y.; Boylu, F.; Ozdemir, O. Effect of Blunging/Dispersion Parameters on Separation of Halloysite Nanotubes from Gangue Minerals. Minerals. 2022, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Penumadu, D. Identification of microfabric of kaolinite clay mineral using x-ray diffraction technique. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2007, 25, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobos, I.; Duplay, J.; Rocha, J.; Gomes, C. Kaolinite to halloysite-7A transformation in the kaolin deposit of Sao Vicente de Pereira, Portugal. Clay Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J.; Gates, W.P.; Petit, S. Chapter 5—IR Spectra of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2017, 8, 107–149. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Characterization of Kaolinite from Assam and Meghalaya, Northeastern India. J. Mod. Phys. 2010, 01, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, F.G.; Carlisle, V.W. Infrared spectra of selected Colombian Andosols. Proc. Soil Crop Sci. Soc. Fla. 1972, 31, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Frost, R.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J. Infrared and infrared emission spectroscopic study of typical Chinese kaolinite and halloysite. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, B.J. Spectroscopic estimation of geometrical structure elucidation in natural SiO2 crystal. J. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G.; Sarmah, N.C. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic estimation of crystallinity in SiO2 based rocks. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 31, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Yorozu, Y.; Itami, K. Zeta potentials of clay minerals estimated by an electrokinetic sonic amplitude method and relation to their dispersibilıty. Clay Sci. 2001, 11, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, B.; Evcin, A.; Uygunoglu, T.; Akdemir, Z.B.; Brostow, W.; Joshua, W. Zeta Potential–viscosity relationship in kaolinite slurry in the presence of dispersants. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5451–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarí, G.; Bobos, I.; Gomes, C.S.F.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Modification of surface charge properties during kaolinite to halloysite 7 Å transformation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 210, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eygi, M.S.; Ateşok, G. An investigation on utilization of poly-electrolytes as dispersant for kaolin slurry and its slip casting properties. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorós, J.L.; Sanz, V.; Jarque, J.C. Electrokinetic and rheological properties of highly concentrated kaolin dispersion: Influence of particle volume fraction and dispersant concentration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, S.; Giorgini, L. Overview of the rheological behaviour of ceramic slurries. FME Trans. 2019, 47, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Sim, J.H.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, S.U.; Sohn, D. Opening and blocking the inner-pores of halloysite. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4519–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgen, S.; Çilek, E.C. Effects of some cations to the surface properties of silicates (feldspar and quartz). Erciyes Univ. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, T.; Xu, R.; Zhao, A. Interaction between electric double layers of kaolinite and Fe/Al oxides in suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 297, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Juillerat, F.; Galletto, P.; Bowen, P.; Borkovec, M. Aggregation and charging of colloidal silica particles: Effect of particle size. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5761–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Mencavez, R.; Takai, C.; Fuji, M.; Takahashi, M. Stability of dispersions of colloidal alumina particles in aqueous suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 291, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, H.H. Applied Clay Mineralogy: Developments in Clay Science 2; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. High morphological stability and structural transition of halloysite (Hunan, China) in heat treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önen, V.; Göçer, M.; Taner, H.A. Effect of coagulants and flocculants on dewatering of kaolin suspensions. Omer Halisdemir Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar]
- Chorom, M.; Rengasamy, P. Dispersion and zeta potential of pure clays as related to net particle charge under varying pH, electrolyte concentration and cation type. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 46, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yükselen-Aksoy, Y.; Kaya, A. Zeta potential of kaolinite in the presence of alkali, alkaline earth and hydrolyzable metal ions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 145, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Mineral | LOI * | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halloysite | 17.0 | 44.0 | 38.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Kaolinite | 13.5 | 46.6 | 38.2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| Quartz | 0.2 | 99.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Halloysite ore | 12.0 | 50.9 | 29.7 | 0.7 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.1 |
| Mineral | D10 (µm) | D50 (µm) | D90 (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halloysite | 2.8 | 9.4 | 23.8 |
| Kaolinite | 2.3 | 6.5 | 17.5 |
| Quartz | 3.8 | 14.2 | 32.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durgut, E.; Cinar, M.; Terzi, M.; Kursun Unver, I.; Yildirim, Y.; Ozdemir, O. Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion. Minerals 2022, 12, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111426
Durgut E, Cinar M, Terzi M, Kursun Unver I, Yildirim Y, Ozdemir O. Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion. Minerals. 2022; 12(11):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111426
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurgut, Emrah, Mustafa Cinar, Mert Terzi, Ilgin Kursun Unver, Yildiz Yildirim, and Orhan Ozdemir. 2022. "Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion" Minerals 12, no. 11: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111426
APA StyleDurgut, E., Cinar, M., Terzi, M., Kursun Unver, I., Yildirim, Y., & Ozdemir, O. (2022). Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion. Minerals, 12(11), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111426











