Effectiveness of Carbaryl, Carbofuran and Metolachlor Retention in Soils under the Influence of Different Colloid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sorbents
2.3. Soil Sampling and Methods
2.4. Sorption and Desorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Characteristics
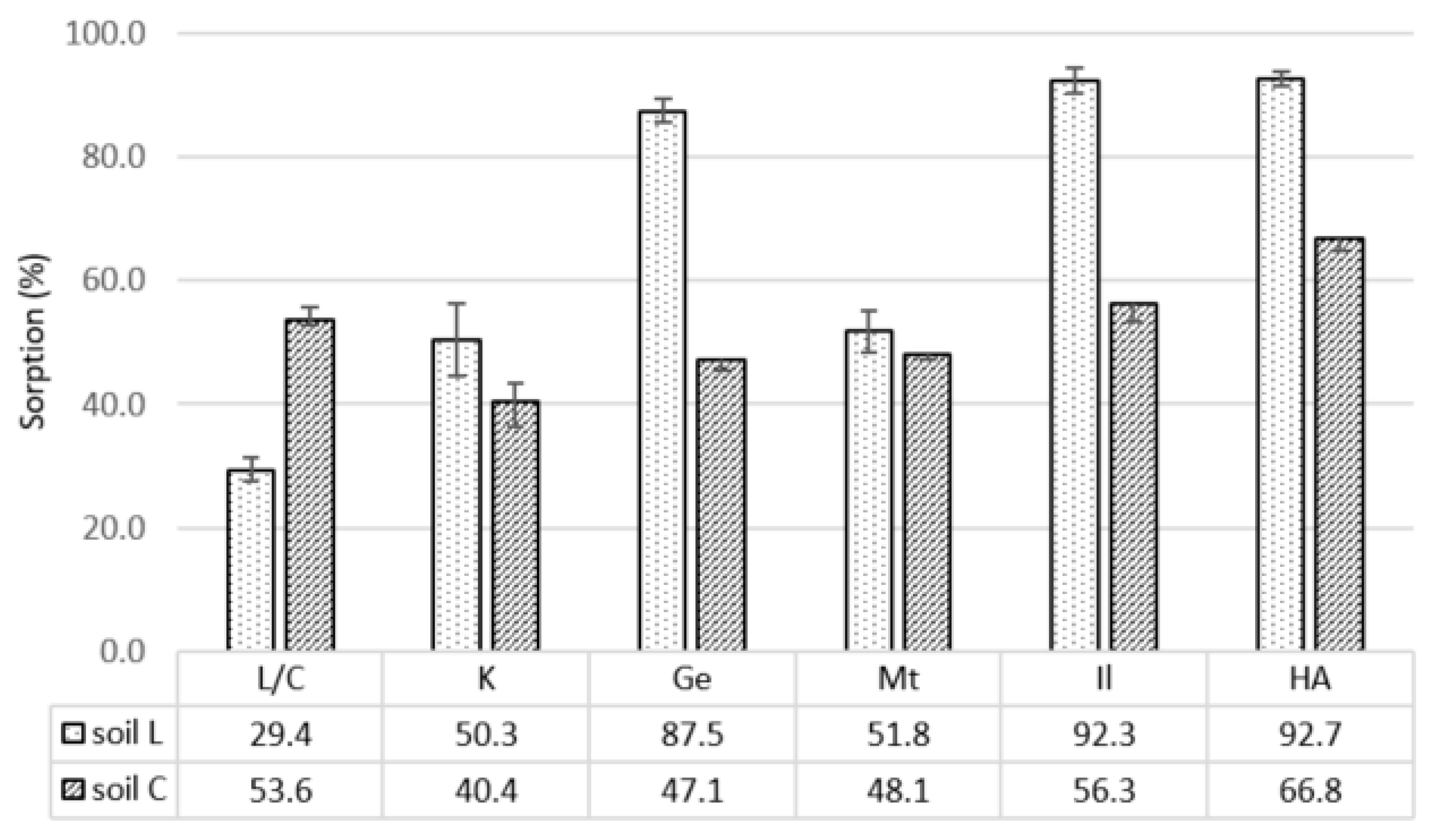
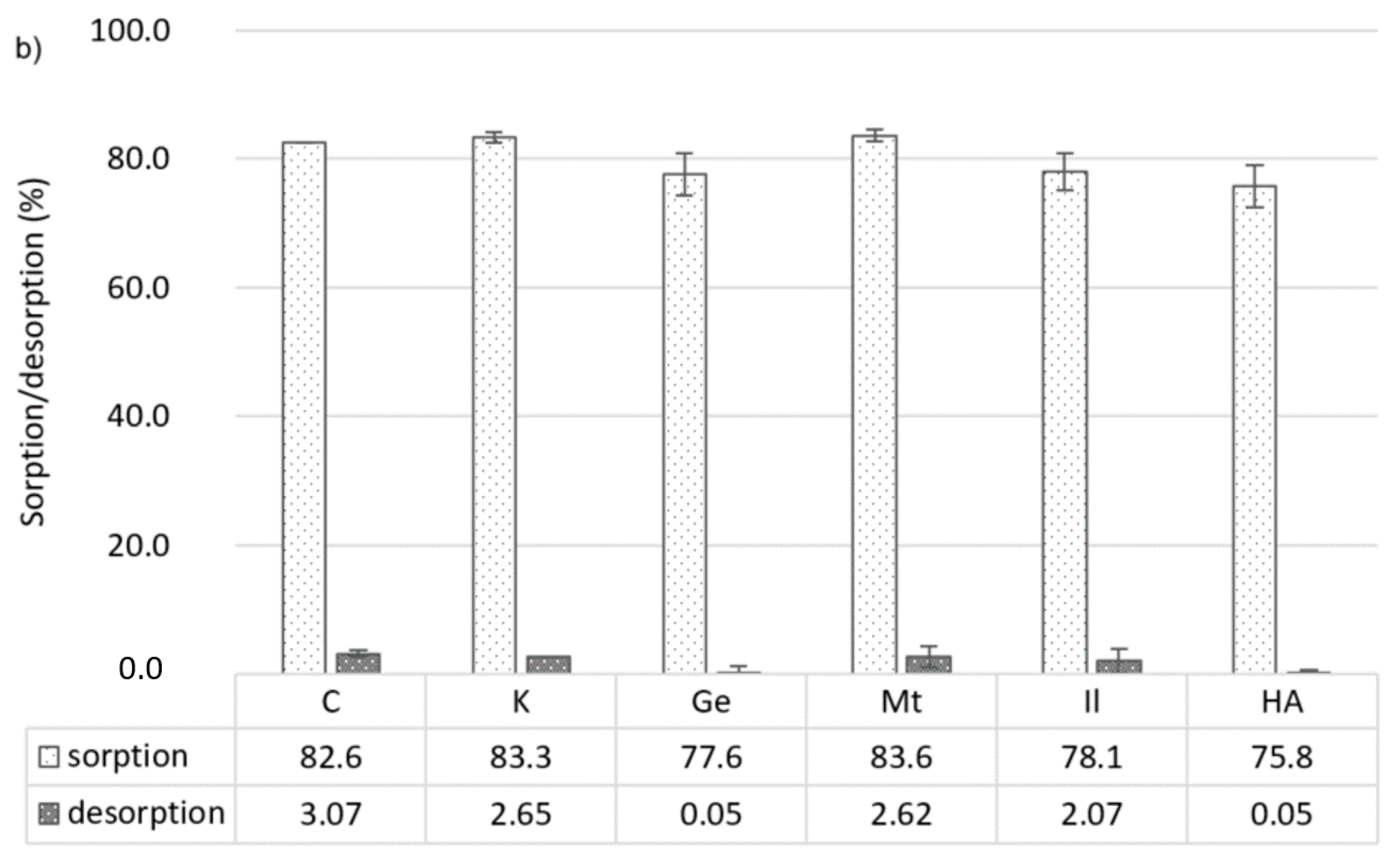
3.2. Sorption of Pesticides
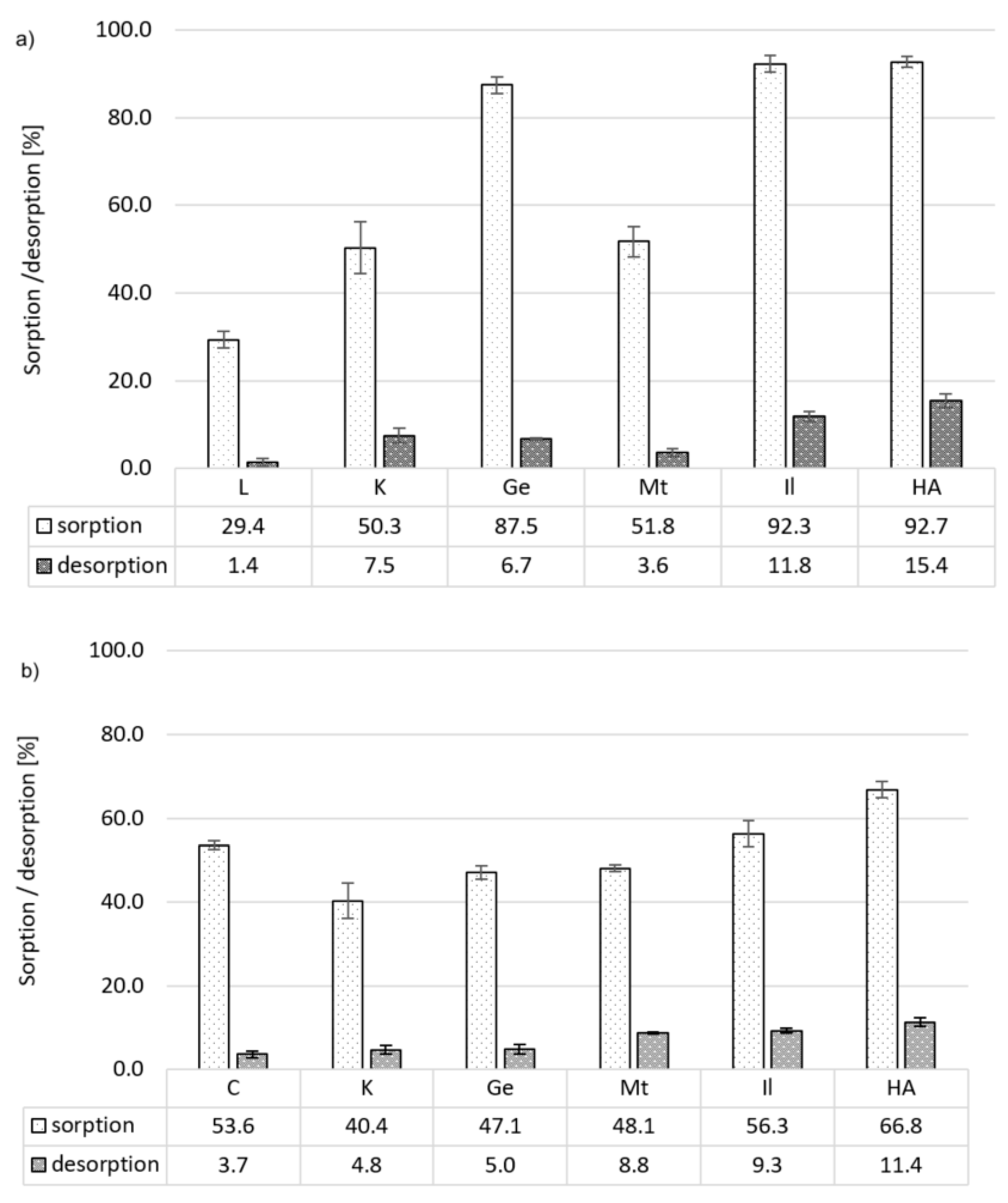
3.2.1. Carbaryl
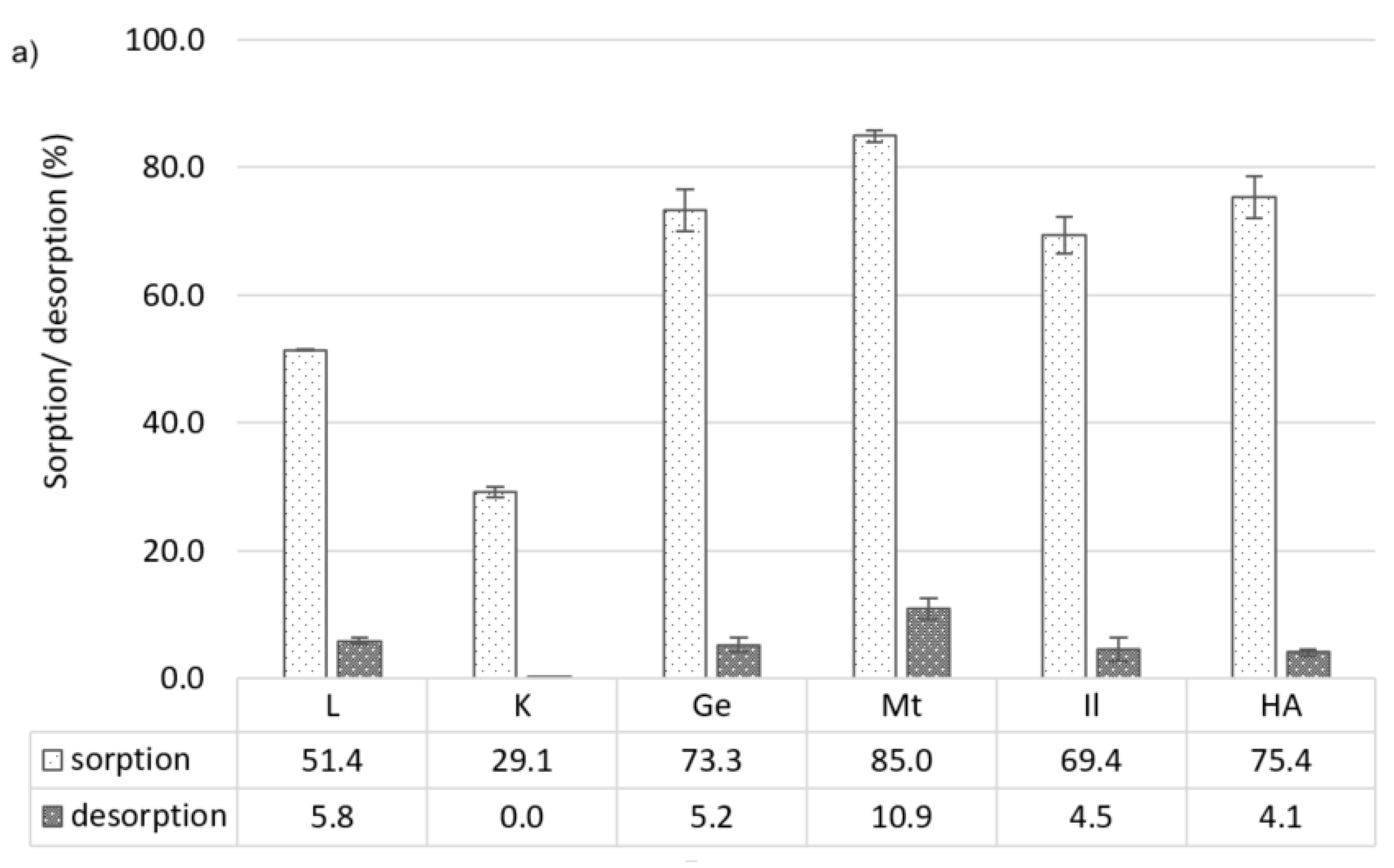
3.2.2. Carbofuran
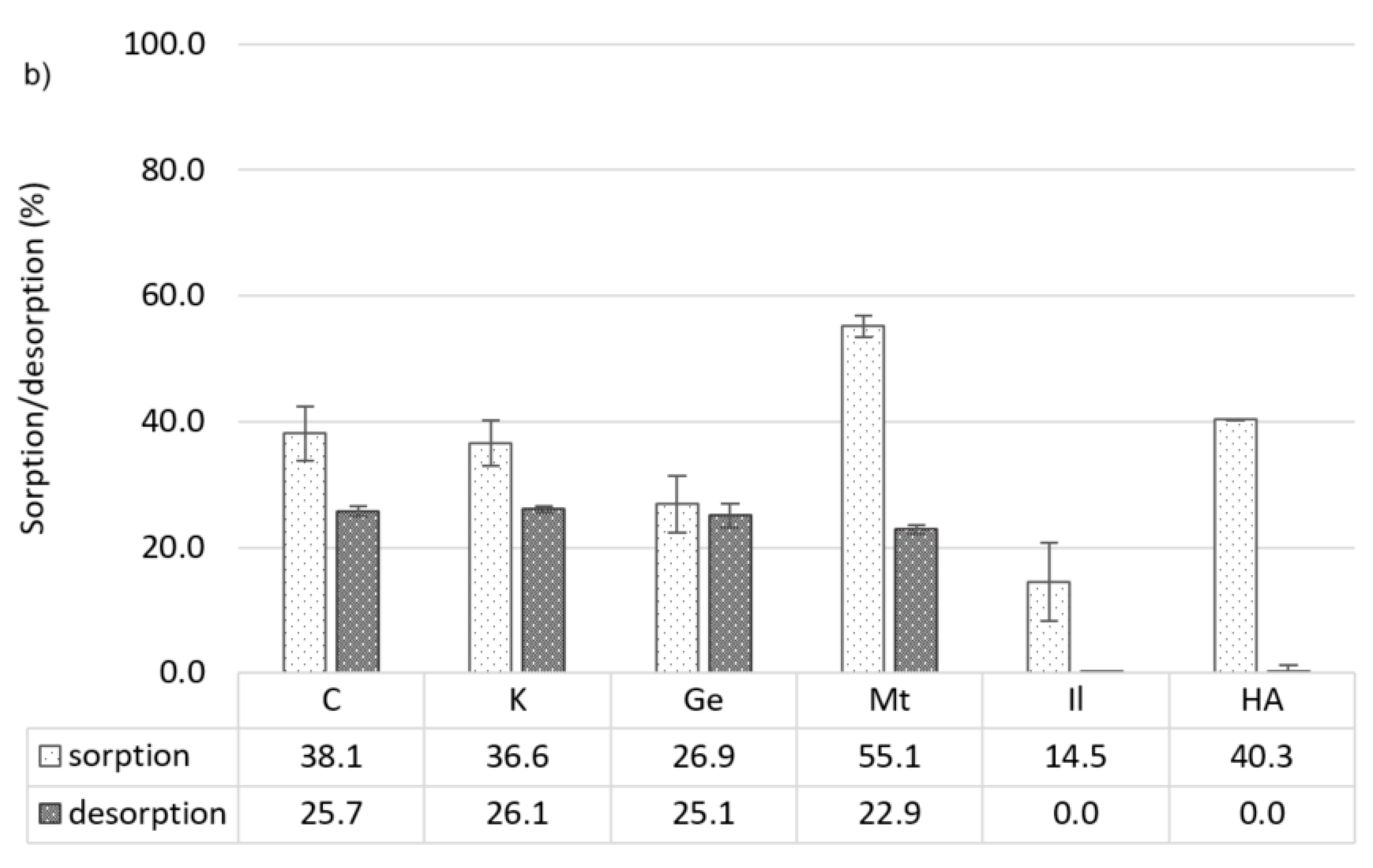
3.2.3. Metolachlor
3.3. Desorption of Pesticides
3.3.1. Carbaryl
3.3.2. Carbofuran
3.3.3. Metolachlor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, J.E.D.; Jabeen, N. The Adsorption of Herbicides and Pesticides on Clay Minerals and Soils. Part 2. Atrazine. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2003, 46, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ge, C.J.; Feng, D.; Yu, G.; Deng, H.; Fu, B. Adsorption–Desorption Behavior of Atrazine on Agricultural Soils in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.W.; White, J.L. Factors influencing the adsorption, desorption, and movement of pesticides in soil. Residue Rev. 1970, 32, 29–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.C.; de Freitas Melo, V.; Bohone, J.B.; Abate, G. Sorption and desorption of atrazine on soils: The effect of different soil fractions. Geoderma 2018, 322, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; He, X.; Xue, A.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Yu, J.; Rong, X.; Liang, W. Bioavailability of methyl parathion adsorbed on clay minerals and iron oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Muhammad, A. Potential contributions of clay minerals and organic matter to pentachlorophenol retention in soils. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nahhal, Y.; Undabeytia, T.; Polubesova, T.; Mishael, Y.G.; Nir, S.; Rubin, B. Organo-clay formulations of pesticides: Reduced leaching and photodegradation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattar, S.F.A.; Zakaria, N.A.; Foo, K.Y. Utilization of Natural Clay as a Reliable Solution for the Adsorptive Treatment of Metolachlor Contaminated Stormwater. In Proceedings of the 37th IAHR World Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–18 August 2017; pp. 4133–4142. [Google Scholar]
- Nir, S.; El Nahhal, Y.; Undabeytia, T.; Rytwo, G.; Polubesova, T.; Mishael, Y.; Rabinovitz, U.; Rubin, B. Chapter 11.2 Clays and Pesticides. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durovic, R.; Gajic-Umiljendic, J.; Dordevic, T. Effects of organic matter and clay content in soil on pesticide adsorption processes. Pestic. Phytomed. 2009, 24, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, X.; Rong, X.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Liang, W.; Li, S.; Huang, Q. Adsorption and biodegradation of carbaryl on montmorillonite, kaolinite and goethite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.H.B.; Mingelgrin, U. Interactions between small organic chemicals and soil colloidal constituents. Interact. Soil Colloid Soil Solut. Interface 1991, 323–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.L.; Kao, M.M. Adsorption of carbofuran on lateritic soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 58, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, J.; Almendros, G. Organo-Mineral Interactions Involved in Herbicide Sorption on Soil Amended with Peats of Different Maturity Degree. Agronomy 2021, 11, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spark, K.M.; Swift, R.S. Effect of soil composition and dissolved organic matter on pesticide sorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 298, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioi, S.; Polati, S.; Roz, M.; Rinaudo, C.; Gianotti, V.; Gennaro, M.C. Sorption studies of chloroanilines on kaolinite and montmorillonite. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.; Hermosín, M.C.; Celis, R.; Cornejo, J. Sorption of two polar herbicides in soils and soil clays suspensions. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotzen, R.A.; Polubesova, T.; Chefetz, B.; Mishael, Y.G. Adsorption of soil-derived humic acid by seven clay minerals: A systematic study. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, H.; Mittelmeijer-Hazeleger, M.C. Adsorption of CO2 and N2 on Soil Organic Matter: Nature of Porosity, Surface Area, and Diffusion Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Liu, F.; Yue, Q.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Hu, B.; Chen, Y. Influence of humic acid on the sorption of pentachlorophenol by aged sediment amended with rice-straw biochar. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 33, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Dębicka, M.; Bekier, J.; Jamroz, E.; Kawałko, D. Humic acid and biochar as specific sorbents of pesticides. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2692–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pedersen, J.A. Sorption of Sulfonamide Antimicrobial Agents to Humic Acid–Clay Complexes. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Pedersen, J.A. Adsorption of Sulfonamide Antimicrobial Agents to Clay Minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9509–9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Wang, H.; Lazouskaya, V.; Du, Y.; Lu, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y. Cotransport of bismerthiazol and montmorillonite colloids in saturated porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etcheverry, M.; Cappa, V.; Trelles, J.; Zanini, G. Montmorillonite-alginate beads: Natural mineral and biopolymers based sorbent of paraquat herbicides. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5868–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes De Oliveira, M.; Johnston, C.T.; Premachandra, G.S.; Teppen, B.J.; Li, H.; Laird, D.A.; Zhu, D.; Boyd, S.A. Spectroscopic study of carbaryl sorption on smectite from aqueous suspension. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9123–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, A.; Jayasundera, S. The sorption of nonionic pesticides onto clays and the influence of natural organic carbon. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojemueller, E.; Nennemann, A.; Lagaly, G. Enhanced pesticide adsorption by thermally modified bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusino, A.; Liu, W.; Gessa, C. Influence of organic matter and its clay complexes on metolachlor adsorption on soil. Pestic. Sci. 1992, 36, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Smreczak, B.; Siebielec, G. Assessment of pesticide residue content in Polish agricultural soils. Molecules 2020, 25, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Brown, K.D. Sorption, Degradation, and Mineralization of Carbaryl in Soils, for Single-Pesticide and Multiple-Pesticide Systems. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, B.; Luan, Z. Sorption of endrin to montmorillonite and kaolinite clays. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, B.S.; Brahmaprakash, G.P.; Reddy, B.R.; Singh, U.D.; Sethunathan, N. Effect and persistence of selected carbamate pesticides in soils. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1984, 93, 87–203. [Google Scholar]
- Raturi, S.; Islam, K.R.; Caroll, M.J.; Hill, R.L. Carbaryl, 2,4-D, and Triclopyr adsorption in thatch-soil ecosystems. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2005, 40, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, T.; Maestroni, B.; Islam, M.; Cannavan, A. Sorption of 14 C-carbofuran in Austrian soils: Evaluation of fate and transport of carbofuran in temperate regions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 956–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pérez, M.; Villafranca-Sánchez, M.; Flores-Céspedes, F.; Garrido-Herrera, F.J.; Pérez-García, S. Use of Bentonite and Activated Carbon in Controlled Release Formulations of Carbofuran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6697–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janaki, J.; Meena, S.; Chinnusamy, C. Dynamics of Metolachlor in Sandy Clay Loam Soil and Its Residues in Maize and Soybean. Trends Biosci. 2015, 8, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.; Novak, J.M.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Long-term tillage effects on soil metolachlor sorption and desorption behavior. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Vryzas, Z.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. S-metolachlor herbicide removal in pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Hertfordshire Pesticides Properties Data Base. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Borden, D.; Giese, R.F. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Cation exchange capacity measurements by the ammonia-electrode method. Clays Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.U.; Dogan, M.; Onal, M.; Sarikaya, Y.; Aburub, A.; Wurster, D.E. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Specific surface area by the Brunauer Emmett Teller (BET) method. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polubesova, T.; Nir, S. Modeling of organic and inorganic cation sorption by illite. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Adsorption and stability of arsenic(III) at the clay mineral-water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosson, G.S.; Sandmann, E. Kinetic Study of Denatonium Sorption to Smectite Clay Minerals. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World reference base for soil resources 2014. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; WRB: Greenwich, CT, USA, 2014; ISBN 9789251083697. [Google Scholar]
- Spark, D.L. Methods of soil analysis. Part 3: Chemical Methods. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. B Ser. 1996, 34, 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.; Chen, Y.; Jamroz, E.; Miano, T. Preface: Humic substances in the environment. J Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U.; Cornell, R.M. Goethite. In Iron Oxides in the Laboratory; Wiley Online Books; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000; pp. 67–92. ISBN 9783527613229. [Google Scholar]
- Reichard, P.U.; Kraemer, S.M.; Frazier, S.W.; Kretzschmar, R. Goethite dissolution in the presence of phytosiderophores: Rates, mechanisms, and the synergistic effect of oxalate. Plant Soil 2005, 276, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Size Analysis BT—Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Pansu, M., Gautheyrou, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 15–63. ISBN 978-3-540-31211-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lončarić, Z.; Kovačević, V.; Rastija, D.; Karalić, K.; Popović, B.; Ivezić, V.; Semialjac, Z. Simple Regression Models for Predicting Soil Zdenko Loncaric, PhD. Eur. Sci. J. 2013, 3, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wierzbowska, J.; Sienkiewicz, S.; Zarczyński, P.; Krzebietke, S. Environmental application of ash from incinerated biomass. Agronomy 2020, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnér, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Untersuchungen uber die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage fur die Beurteilung des Nährstoffzustandes der Böden. II. Chem. Extraktionsmethoden Phosphor Kaliumbestimmung. K. Lantbr. Ann. 1960, 26, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kondratowicz-Maciejewska, K.; Kobierski, M. Content of available magnesium, phosphorus and potassium forms in soil exposed to varied crop rotation and fertilisation. J. Elem. 2011, 16, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-Z-19010-2:1999 Soil Quality—Determination of Soil Specific Surface Area; Measurement by Glycerin Vapor Sorption Method; PKN: Warsaw, Poland, 1999. (In Polish)
- Martin, J.D. XPowderXTM (XPowder, XPowder12). A Software Package for Powder X-Ray Diffraction Analysis. In Qualitative, Quantitative and Microtexture; Godel Editorial: Granada, Spain, 2016; ISBN 9788416478873. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. 106 Adsorption—Desorption Using a Batch Equilibrium Method. OECD Guidel. Test. Chem. 2000, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, O.P. Effect of soil properties on the persistence of carbamate pesticides. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2009, 51, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.C.; Neira-Albornoz, A.; Escudey, M. Herbicides Mechanisms Involved in the Sorption Kinetic of Ionisable and Non Ionisable Herbicides: Impact of Physical/Chemical Properties of Soils and Experimental Conditions. In Kinetic Modeling for Environmental Systems; Rehab, O., Rahman, A., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2019; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.; Johnston, C.T.; Teppen, B.J.; Boyd, S.A. Potential Contributions of Smectite Clays and Organic Matter to Pesticide Retention in Soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polati, S.; Angioi, S.; Gianotti, V.; Gosetti, F.; Gennaro, M. Sorption of Pesticides on Kaolinite and Montmorillonite as a Function of Hydrophilicity. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2006, 41, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, N.K.; Chattoraj, S.; Sadhukhan, B.; Das, B. Evaluation of carbaryl sorption in alluvial soil. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 727–738. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Nabi, S.A.; Singh, S. Adsorption and movement of carbaryl in soils: A verification of cosolvent theory and comparison of batch equilibrium and soil thin layer chromatography results. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2010, 92, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, H. Sorption of Aromatic Compounds to Clay Mineral and Model Humic Substance–Clay Complex: Effects of Solute Structure and Exchangeable Cation. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcke, G.U.; Kulikova, N.A.; Hesse, S.; Kopinke, F.D.; Perminova, I.V.; Frimmel, F.H. Adsorption of humic substances onto kaolin clay related to their structural features. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spark, K.M.; Wells, J.D.; Johnson, B.B. Characteristics of the sorption of humic acid by soil minerals. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Koopal, L.K.; Xiong, J.; Avena, M.; Tan, W. Mechanisms of soil humic acid adsorption onto montmorillonite and kaolinite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Couso, A.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Rodríguez-Salgado, I.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M. Comparison of batch, stirred flow chamber, and column experiments to study adsorption, desorption and transport of carbofuran within two acidic soils. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, G.; Zakaria, Z.; Kuntom, A.; Omar, D.; Ismail, B. Adsorption and desorption of carbofuran in Malaysian soils. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2007, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, A.; López, R.; Gondar, D.; Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Arce, F. Adsorption of MCPA on goethite and humic acid-coated goethite. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Devlin, J.F.; Bi, E. Bonding of monocarboxylic acids, monophenols and nonpolar compounds onto goethite. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Srivastava, G. Adsorption and movement of carbofuran in four different soils varying in physical and chemical properties. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, O.P. Adsorption and desorption of three carbamate pesticides by illite, kaolinite and humic acid-clay complexes. J. Adv. Chem. 2014, 10, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iglesias, A.; López, R.; Gondar, D.; Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Arce, F. Adsorption of paraquat on goethite and humic acid-coated goethite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youbin, S.; Kazuhiro, T.; Akio, I.; Dongmei, Z. Adsorption, desorption and dissipation of metolachlor in surface and subsurface soils. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nennemann, A.; Mishael, Y.; Nir, S.; Rubin, B.; Polubesova, T.; Bergaya, F.; Van Damme, H.; Lagaly, G. Clay-based formulations of metolachlor with reduced leaching. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.J.A.; Tunega, D.; Schaumann, G.E.; Haberhauer, G.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Lischka, H. Proton transfer processes in polar regions of humic substances initiated by aqueous aluminum cation bridges: A computational study. Geoderma 2014, 213, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalah, J.O.; Wandiga, S.O. Adsorption/desorption and mobility of carbofuran in soil samples from Kenya. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 56, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, B.L.; Gent, M.P.N. Hydrophobicity of Clay Surfaces: Sorption of 1,2-Dibromoethane and Trichloroethene. Clays Clay Miner. 1990, 38, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Pesticide | Chemical Structure | Water Solubility (mg L−1) at 20 °C | Octanol–Water Partition Coefficient Log P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbaryl | 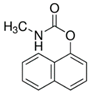 | 9.1 | 2.36 |
| Carbofuran | 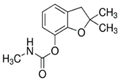 | 322 | 1.8 |
| Metolachlor | 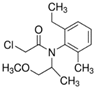 | 530 | 3.4 |
| Clay Minerals | Lattice Structure | CEC (cmolc·kg−1) (NH4Ac Method) | Specific Surface Area (m2 g−1) (N2 BET Method) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite (KGa-1b) | 1:1 | 3.0 a | 13.1 b |
| Illite (IMt-2) | 2:1 | 25.0 c | 24.2 d |
| Montmorillonite (Stx-1b) | 2:1 | 84.4 e | 83.8 e |
| No. | Variant Name | Soil Mass (g) | Colloid Added (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L/C | 2.5 g of L or C soil | - |
| 2 | LK/CK | 2.0 g of L or C soil | 0.5 g of kaolinite |
| 3 | LGe/CGe | 2.0 g of L or C soil | 0.5 g of goethite |
| 4 | LMt/CMt | 2.0 g of L or C soil | 0.5 g of montmorillonite |
| 5 | LIl/CIl | 2.0 g of L or C soil | 0.5 g of illite |
| 6 | LHA/CHA | 2.4 g of L or C soil | 0.1 g of freeze-dried humic acid |
| Soil | pH (H2O) | pH (KCl) | CaCO3 (%) | Ctot | Corg | N | Corg:N | Sand | Silt | Clay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | (%) | |||||||||
| L | 7.3 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 0.95 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 76 | 17 | 7 |
| C | 7.6 | 7.4 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 8.4 | 47 | 34 | 19 |
| Soil | Ca | Mg | K | Na | Σ | Hh | CEC | SSA <2 mm | SSA <2 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cmolc·kg−1 | m2 g−1 | ||||||||
| L | 23.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 26.1 | 0.3 | 26.4 | 40.3 | 370.4 |
| C | 39.1 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 42.0 | 0.3 | 42.3 | 80.5 | 309.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I.; Debicka, M.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A. Effectiveness of Carbaryl, Carbofuran and Metolachlor Retention in Soils under the Influence of Different Colloid. Minerals 2021, 11, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090924
Ćwieląg-Piasecka I, Debicka M, Medyńska-Juraszek A. Effectiveness of Carbaryl, Carbofuran and Metolachlor Retention in Soils under the Influence of Different Colloid. Minerals. 2021; 11(9):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090924
Chicago/Turabian StyleĆwieląg-Piasecka, Irmina, Magdalena Debicka, and Agnieszka Medyńska-Juraszek. 2021. "Effectiveness of Carbaryl, Carbofuran and Metolachlor Retention in Soils under the Influence of Different Colloid" Minerals 11, no. 9: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090924
APA StyleĆwieląg-Piasecka, I., Debicka, M., & Medyńska-Juraszek, A. (2021). Effectiveness of Carbaryl, Carbofuran and Metolachlor Retention in Soils under the Influence of Different Colloid. Minerals, 11(9), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090924








