Abstract
Estonian phosphorite ore contains trace amounts of rare earth elements (REEs), many other d-metals, and some radioactive elements. Rare earth elements, Mo, V, etc. might be economically exploitable, while some radioactive and toxic elements should be removed before any other downstream processing for environmental and nutritional safety reasons. All untreated hazardous elements remain in landfilled waste in much higher concentration than they occur naturally. To resolve this problem U, Th, and Tl were removed from phosphorite ore at first using liquid extraction. In the next step, REE were isolated from raffinate. Nitrated Aliquat 336 (A336[NO3]) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phosphate (D2EHPA) were used in liquid extraction for comparison. An improved method for exclusive separation of radioactive elements and REEs from phosphorite ore in 2-steps has been developed, exploiting liquid extraction at different pH values.
1. Introduction
Rare earth elements (REE), REEs alloys, and compounds possess important magnetic, spectroscopic, and optical features, and therefore, REEs are applicable in many areas of modern technology [1,2,3]. For example, REE complex oxides and complex hydrides are important construction elements in energy storage devices and components, including Li-ion and Na-ion batteries, solid oxide fuel cells [4,5], high-temperature electrolyzers [6,7,8], co-catalysts in polymer membrane electrolyte fuel cells [9,10], and direct methanol oxidation fuel cells [11,12].
The estimated consumption of REEs is about 250 million tons per year. To overcome any supply risk, novel high-technology recovery methods in addition to modern raw material processing methods should be worked out and industrially applied [13,14,15].
During recent years, the phosphate rock containing trace amounts of REEs has been considered as one of the potential new resources to produce REEs due to its huge, about 300 billion tons reserves worldwide [13,14,15,16,17].
REEs have been observed in many different phosphate rocks, mainly in monazite, xenotime, loparite, apatite, and ion-absorbed clay [18,19,20]. Some researchers have pointed out that phosphate rock might be a new source for REEs [15,16] in addition to re-cycling different REE-containing devices, recovery from phosphate rock minerals might relieve an increasing demand for some REEs [3,19].
Extensive literature analysis about REE processing and recovery [3,21] shows that the first studies in phosphate rock processing were made in the Soviet Union about 90 years ago [18,19]. Since that time, the acid leaching with sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and phosphoric acid has been developed followed by different recovery routes such as crystallization and precipitation, ion exchange, and multistep solvent extraction. Nowadays solvent extraction method seems to be the most promising technology for large-scale environmentally-friendly REEs separation, since other methods consume a lot of energy, generate huge quantities of waste products, and collected REEs contain different impurities [19].
It should be noted that separation of an individual REE is a very complicated, energy- and time-consuming task [13,15,22]. During the liquid extraction process many other elements co-extract together with REE, the most noticeable example is the co-extraction of uranium and thorium. These elements pose a threat to the environment and nutritional safety if these elements are not removed during phosphate rock processing. Some researchers have reported the co-extraction of radioactive elements together with REE [19]. Some research groups have conducted extraction experiments with natural phosphate rock acid leachate [18,22]. while some research groups use REE stock solutions which represent the content of REE in natural phosphate rock [21,23,24,25]. As the current study indicates, extraction results obtained from stock solutions are not always comparable with extraction results from phosphate rock acid leachate. The chemical content of natural phosphate rock is significantly more complicated.
Different extractants, including organic phosphorus-based compounds, quaternary ammonium salts, and different ionic liquids have been used in the liquid extraction process [19,21,23,26]. At present, phosphate rock is mainly dissolved in sulfuric acid—a process that decomposes the raw material to produce phosphoric acid and phosphogypsum [18,27,28]. This method distributes the REEs in phosphoric acid (15–30%) and phosphogypsum (PG) (70–85%) requiring separate technological processes for full recovery of REE. It should be noted that the production of 1-ton H3PO4 produces 4–5 tons of PG (about 280–300 million tons of PG per year), leading to worldwide landfill problems and other environmental issues [14,28]. The nitric acid and hydrochloric acid-based processes are mainly challenged by the difficulties of Ca2+ removal. However, the use of nitric acid in the nitrophosphate route gives a very efficient and quick dissolution of REEs from ore and leaves no PG. The nitrophosphate route is described by the following reaction, expressed by Equation (1):
Ca10(PO4)6F2 + 20 HNO3 ⇄ 10 Ca(NO3)2 + 6 H3PO4 + 2 HF
In nature, rare earth elements substitute calcium ions in phosphorite ore and after the nitric acid treatment, they form as different REE trinitrate salts.
Utilizing phosphate rock as a source of REE or even as a source of phosphate fertilizers raises environmental threats. In agreement with the results of previous studies, our current study shows that Estonian phosphorite samples contain a significant amount of radioactive uranium and a smaller amount of thorium [29,30,31]. In addition to radioactive elements, phosphate rock also contains different amounts of hazardous metals as cadmium, lead, thallium, and arsenic [31]. At elevated concentrations, rare earth elements also contribute to environmental pollution caused by the intensive use of phosphate fertilizers, contamination of agricultural soils takes place [27,32]. Thus, it is desirable to remove these elements from phosphorite ore before any other downstream processing, such as saponification for REE extraction.
Estonia has the biggest, but unexploited phosphorite deposits in Europe [30]. These resources might be exploitable commercially for phosphate fertilizer production but results of the current study indicate that some chemical elements should be separated from Estonian phosphorite as byproducts, including REEs.
The improved two-step extraction process for the isolation of U and Th in concentrated nitric acid media and REE in partly neutralized nitric acid media from Estonian phosphorite ore has been worked out and presented in this paper.
2. Experimental
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
Samples of Estonian concentrated phosphorite ore from Iru outcrop were obtained from geological collections of Tallinn University of Technology.
Trioctylmethyl ammonium chloride (Aliquat 336), HNO3 and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (D2EHPA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The structure of extractants is shown in Figure 1. NaOH was purchased from Merck and KNO3 was purchased from Lach-ner. All chemicals had the purity of analytical grade.
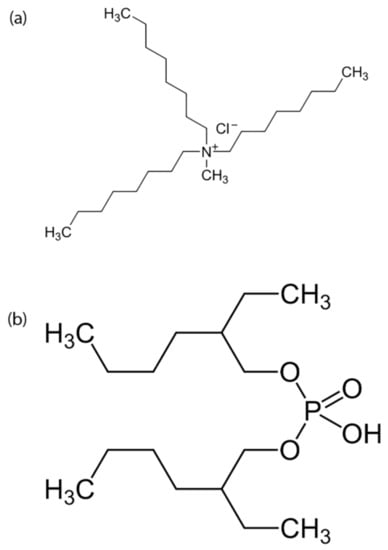
Figure 1.
The structures of (a) Trioctylmethyl ammonium chloride (A336) and (b) bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (D2EHPA).
2.2. Modification of Aliquat 336 with 2.5M KNO3
To obtain better selectivity towards REEs and to decrease the extractant viscosity, and thus, initiate a quicker mass transfer, Aliquat 336 was treated with potassium nitrate to exchange Cl− with NO3−. In most cases, A336[NO3] was diluted with an organic solvent such as n-heptane, xylene, or kerosene [3,21,33], though undiluted A336[NO3] has also been used, like in the paper by Larsson and Biennemans [23]. In addition to REEs extraction A336[NO3] has also been used to extract other metals such as vanadium from chromium [34]. For the preparation of A336[NO3], Aliquat 336 was pre-equilibrated 3 times with 2.5M KNO3 for at least 1 h each time.
2.3. Feed Solution
Then, a 2.46 g sample of concentrated Estonian phosphorite powder from Iru deposit was dissolved in 100 mL 7.5M HNO3 aqueous solution for 24h at room temperature and filtered to remove any indissoluble substance. The solution received was used throughout all the experiments conducted. To determine the difference in extraction efficiency of REEs from Estonian phosphorite ore and water stock solution, the extraction efficiency of A336[NO3] was also measured for REE[NO3]3 stock solution. REE[NO3] salts were dissolved in dilute nitric acid to prepare a 1-liter solution, with a pH equal to 1.5. The pH of the stock solution was established using an Elmetron pH meter CP-411.
The stock solution compositions prepared from some selected REE[NO3]3 salts are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of millimolar concentrations of selected REE in REE[NO3]3 salt stock solution used for testing extraction performance of A336[NO3].
2.4. Equipment
The quantitative analysis of REEs and trace elements in untreated solution and extracted solution samples was established using an Agilent 8800 QQQ ICP-MS (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) in the NoGas mode regime. Corresponding metal cations like 45Sc, 89Y, 137Ba, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 146Nd, 147Sm, 153Eu, 157Gd, 159Tb, 163Dy, 165Ho, 166Er, 169Tm, 172Yb, 175Lu, 232Th, and 238U were quantified from aliquots that were diluted 400-fold with 2% HNO3 aqueous solution before the analysis. All extraction experiments were carried out in 100 mL plastic separation funnels.
2.5. Experimental Conditions
Samples of concentrated Estonian phosphorite ore were dissolved in 7.5M nitric acid and extracted with undiluted nitrated Aliquat 336 (A336[NO3]) or with undiluted D2EHPA in the first extraction step. Aqueous feed solution and extractant were fixed at a constant 9:1 (aqueous/organic) ratio in all cases. The mixture was shaken carefully in a separation funnel for 1 min and kept silent for equilibration for 1 h. Raffinate received was extracted 2 more times with a fresh amount of A336[NO3] to promote a more complete extraction of U and Th, as well as Tl.
Reaction equilibria for A336[NO3] extraction can be expressed as Equation (2):
where M3+ designates the metal cation, (R3N+CH3)NO3−IL represents A336[NO3], and (R3NCH3)M(NO3)IL represents the metal cation and ionic liquid complex. IL represents the ionic liquid phase and aqueous phase.
Equilibrium constant K can be rewritten as:
Reaction equilibria for D2EHPA extraction can be expressed as Equation (4):
where M3+ represents the metal cation, [HA] is the extractant in the organic phase, and [MA3(HA)3] represents the metal-extractant complex in the organic phase.
M3+ + 3 [HA]2 ⇄ [MA3(HA)3] + 3 H+
Equilibrium constant K can be rewritten as:
Only one extraction step was performed with D2EHPA due to the very high extraction efficiency established. In the next step, raffinate was saponified with 1M NaOH to pH 1.5, and REEs were extracted with the same extractant one more time. The sample of raffinate was characterized quantitatively after each extraction step using the ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) measurement method.
Comparative parallel extraction experiment with stock solution, i.e., a mixture of different REE[NO3] salts, was performed in order to control quantitatively the results obtained for REEs tests. REE[NO3] salts were dissolved in moderately diluted nitric acid (pH of a solution was 1.5) and extracted with A336[NO3].
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of REEs Extraction
For detailed quantitative analysis, the extraction efficiency is calculated using Equation (6):
where E stands for extraction efficiency and c for concentrations of REEs (or other metal cations) in the final and initial states, respectively.
The distribution ratio of the element under study was calculated using Equation (7):
where c(extractant) and c(aqueous phase) are concentrations of the element under analysis in extractant and water phases, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study Estonian phosphorite ore was leached in concentrated nitric acid. The nitrophosphate route helps to prevent the formation of phosphogypsum which is the main byproduct in sulfuric acid treatment. Phosphogypsum might be considered as waste with a significant number of radioactive elements and some part of REE would also be incorporated in phosphogypsum. In that sense, the nitrophosphate route seems to be superior to that of sulfuric acid leaching [19]. The main problem in the nitrophosphate route is calcium removal since in fertilizer production it is not the desired element. Historically, calcium has been removed by cooling of phosphorite ore solution leading to precipitation of calcium nitrate. In this study, calcium was not removed since the main goal was to compare the extraction performance of two different extractants: A336[NO3] and D2EHPA. A negligible effect of calcium on the extraction process was presumed.
The concentrations of rare earths, radioactive and toxic elements, and some d- elements in Estonian phosphorite ore dissolved in 7.5M HNO3 aqueous solution are given in Table 2. Very high content of Ce, Y, Nd, and La was observed in agreement with data discussed earlier in papers [18,30]. A high amount of some radioactive (U, Th) and toxic (Pb, As) elements was observed. The content of toxic Tl and Cd (5 × 10−4 ppm) was low.

Table 2.
Content of rare earths, some radioactive elements, toxic elements, and d-metals in concentrated phosphorite ore. 2.46 g phosphorite ore powder was dissolved in 100 mL 7.5M HNO3. Dissolution was performed in a 200 mL plastic bottle for 1 h. Dissolution was performed at room temperature.
The 2-step solvent extraction process of REEs from Estonian phosphorite ore was developed in this study. The main goal was to isolate radioactive U, Th, and toxic Tl in the first extraction step without extracting any other element. Phosphorite ore was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid and extracted thereafter. The extraction performances of A336[NO3] and D2EHPA were tested for comparison. In the second extraction step, the main goal was the extraction of REE using a partly neutralized nitric acid medium (pH = 1.5). Again, the extraction performance of A336[NO3] and D2EHPA was tested for comparison. Change of pH value was based on the observation that REE did not extract from concentrated acid and extracted well from diluted acid solutions.
3.1. First Extraction Step for U, Th, and Tl Removal from Concentrated Nitric Acid Media
3.1.1. Extraction with A336[NO3]
Results of the current study showed that it was possible to extract U, Th, and Tl from the concentrated nitric acid medium using A336[NO3]. Cumulative efficiencies after three consecutive extractions are 85% for uranium, 66% for thorium, and 99% for thallium. The extraction process was very selective and no other elements were co-extracted. Extraction efficiencies were significantly smaller compared to D2EHPA. The only exception was thallium, which was extracted only by nitrated Aliquat 336. It can be concluded that Aliquat 336[NO3] is suitable, but not the best option for U, Th, and Tl removal. Extraction of REE from concentrated nitric acid media using A336[NO3] has been discussed by Kumari et al. [35]. It has been suggested that EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) promotes REE extraction. Since no complexing agents were used in the current study, poor extraction performance can be a result.
3.1.2. Extraction with D2EHPA
The extraction of U and Th was very efficient in concentrated nitric acid media using D2EHPA as an extractant (Figure 2). The extraction efficiency of D2EHPA was superior compared to nitrated A336, except for Tl, which was not extracted with D2EHPA at all. Other toxic elements such as, Cd, and Pb did not extract with D2EHPA. The extraction selectivity of D2EHPA was not as good as selectivity with A336[NO3]. Some HREE were extracted along with U and Th, showing similar extraction behavior. Most REEs were not extracted at all and the selectivity of D2EHPA could still be regarded as very good.

Figure 2.
Extraction efficiencies of REE and other selected elements from phosphorite ore dissolved in concentrated and dilute partly neutralized nitric acid using D2EHPA as an extractant. 7.5M nitric acid designates the concentrated acid and raffinate at pH 1.5 value designates diluted nitric acid media. The time of extraction was 1 h all time. Extraction was performed at room temperature. Undiluted D2EHPA was used as an extractant.
After the removal of harmful and toxic U and Th, it was safer to treat the raffinate in any other downstream process such as partial neutralization of nitric acid for REE extraction. This was the main justification for the 2-step extraction.
3.2. Extraction of REE from Partially Neutralized Nitric Acid Media
3.2.1. Extraction with A336[NO3]
The extraction efficiency of REEs from partly neutralized nitric acid solution with A336[NO3] was very low (data in Figure 3) and A336[NO3] was not a suitable option for REE extraction. To investigate the extraction performance of A336[NO3] further, some REE from the stock solution of selected REE nitrate salts (for content see Table 1) were extracted using A336[NO3]. Extraction efficiencies were much higher this time—all efficiency values were between 57–61%. Significant differences that were established between the real and stock solutions could be explained by the very complicated chemical composition of Estonian phosphate ore, containing in addition to U, Th, Tl, and REEs many other metals (Table 2). Competitive effects in extraction may occur as a result.
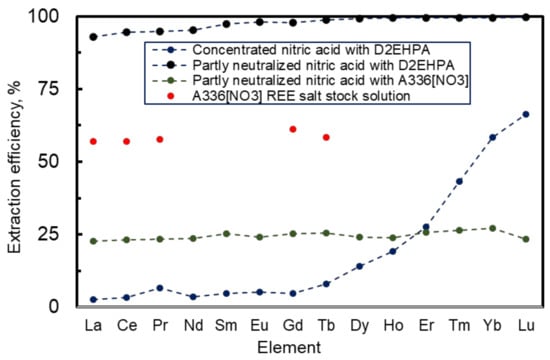
Figure 3.
Extraction efficiencies of REE using D2EHPA and A336[NO3] as the extractants from phosphorite ore nitric acid solution and extraction efficiency of A336[NO3] from a stock solution of selected REE nitrates (content described in Table 1. 7.5M nitric acid designates the concentrated acid and raffinate at pH 1.5 value designates diluted nitric acid media. The time of extraction was 1 h all time. Extraction was performed at room temperature. Undiluted D2EHPA and A336[NO3] were used as extractants.
3.2.2. Extraction with D2EHPA
The results of D2EHPA extraction efficiency in partly neutralized nitric acid are given in Figure 2 and Table 3. As these results show, very high extraction efficiency and distribution ratio was calculated for all REEs.

Table 3.
Extraction efficiency (E in %), distribution ratio (D) of REE, Sc, Y, U, Th, and Tl in concentrated nitric acid and from partly neutralized nitric acid (pH = 1.5) using D2EHPA as an extractant.
The selectivity of D2EHPA was not so high anymore. With the decrease of acidity of the solution to pH = 1.5, the d-metals (Mo, Zr, Fe, Ti, V) and some sp-metals such as Ga, Zn, Ca, Cd, and Pb were extracted with high or moderate extraction efficiency in addition to REEs. Toxic Cd was extracted with 38% efficiency (overall concentration of cadmium is very low), Pb (35%), and As (10%). Thus, REE needs to be separated from other elements in the next steps and individual REE needs to be separated from each other as individual elements or subgroups of elements. Still, extraction from dilute nitric acid using D2EHPA is a good starting point for the following steps.
It is important to emphasize that the first extraction step in concentrated nitric acid media should not be excluded. If only one extraction step is performed, around pH 1.5 U and Th will be co-extracted with REE with very high efficiency.
4. Conclusions
The two-step extraction method for separation at first of U, Th, Tl, and thereafter, all rare earth elements has been developed using tri-n-octylmethylammonium nitrate (Aliquat A336 [NO3] noted as A336[NO3]) and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (D2EHPA) as the extractants. Estonian phosphorite ore was leached in concentrated (7.5 M) nitric acid and extracted in the first phase to isolate the radioactive and toxic elements. It was found that U, Th, and Tl can be selectively extracted using A336[NO3] from concentrated nitric acid media. However, extraction of REEs from partly neutralized nitric acid (pH = 1.5) was poor. Thus, A336[NO3] cannot be suggested as a good extractant for REEs.
D2EHPA extraction efficiency of radioactive elements from concentrated nitric acid and all REEs from partly neutralized nitric acid media was very high. However, some d-elements (Mo, V, Zr, Nb, Ta, etc.) besides REEs have been co-extracted from partly neutralized nitric acid media. Thus, extraction of REEs and other d-elements with D2EHPA was not selective. Thus, the separation of individual REE elements still needs to be developed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J.; methodology, S.J.; validation, P.P. and S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.J.; writing—review and editing, S.J. and E.L.; supervision, E.L.; project administration, C.S. and L.S.; funding acquisition, E.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research was funded by Estonian Research Council’s program RITA and TK 141 (2014-2020.4.01.15-0011) supported by RDF.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, W.; Wen, D.; Ho, J.C.; Qu, Y. Incorporation of rare earth elements with transition metal–based materials for electrocatalysis: A review for recent progress. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Extraction and separation of neodymium and dysprosium from used ndfeb magnets: An application of ionic liquids in solvent extraction towards the recycling of magnets. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Adidharma, H.; Radosz, M.; Wan, P.; Xu, X.; Russell, C.K.; Tian, H.; Fan, M.; Yu, J. Recovery of rare earth elements with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4469–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Shen, F.; Bommier, C.; Zhu, H.; Ji, X.; Hu, L. Na-ion battery anodes: Materials and electrochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, J.; Yin, D.; Luo, M.; Yan, C.; Du, Y. Rare earth incorporated electrode materials for advanced energy storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 390, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, J.T.S.; Neagu, D.; Verbraeken, M.C.; Chatzichristodoulou, C.; Graves, C.; Mogensen, M.B. Evolution of the electrochemical interface in high-temperature fuel cells and electrolysers. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivi, I.; Aruväli, J.; Kirsimäe, K.; Möller, P.; Heinsaar, A.; Nurk, G.; Lust, E. Influence of humidified synthetic air feeding conditions on the stoichiometry of (La1-XSrx)YCoO3−δ and La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ CATHODES under Applied potential measured by electrochemical in situ high-temperature XRD method. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestli, M.; Lust, E.; Nurk, G. Characterization of Terbium and samarium co-doped ceria films prepared using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F812–F820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, M.B.; Hauch, A.; Sun, X.; Chen, M.; Tao, Y.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Hansen, K.V.; Hendriksen, P.V. Relation between ni particle shape change and ni migration in Ni-YSZ electrodes—a hypothesis. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillmaa, K.; Maide, M.; Kanarbik, R.; Nurk, G.; Lust, E. Electrochemical characteristics and gas composition generated by La 0.8 Sr 0.2 Cr 0.5 Mn 0.5 O 3–δ cathode at electrolysis and co-electrolysis modes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F3190–F3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk, P.; Nerut, J.; Kanarbik, R.; Tallo, I.; Aruväli, J.; Lust, E. Synthesis and characterization of platinum-cerium oxide nanocatalysts for methanol oxidation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F315–F323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk, P.; Nerut, J.; Kanarbik, R.; Aruväli, J.; Paiste, P.; Tallo, I.; Lust, E. Synthesis and characterization of platinum-praseodymium oxide nanocatalysts for methanol electrooxidation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards zero-waste valorisation of rare-earth-containing industrial process residues: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castor, S.B. Rare earth deposits of north america. Resour. Geol. 2008, 58, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Graedel, T.E. The potential for mining trace elements from phosphate rock. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, C. The Occurrence states of rare earth elements bearing phosphorite ores and rare earth enrichment through the selective reverse flotation. Minerals 2019, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Z.; DePaoli, D. Rare Earth and phosphorus leaching from a flotation tailings of florida phosphate rock. Minerals 2018, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorovarov, J.I.; Kosynkin, V.D.; Moiseev, S.D.; Rura, N.N. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphorites in the USSR. J. Alloys Compd. 1992, 180, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; El-Shall, H.; Moudgil, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphate rock by hydrometallurgical processes—a critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 774–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; El-Shall, H.; Moudgil, B.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z. Simultaneous recovery of rare earths and uranium from wet process phosphoric acid using solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komasawa, I.; Hisada, K.; Miyamura, M. Extraction and separation of rare-earth elements by Tri-n-Octylmethylammonium nitrate. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1990, 23, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. The Recovery of the lanthanides from phosphate rock. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Chem. Technol. 2007, 35, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.; Binnemans, K. Separation of rare earths by solvent extraction with an undiluted nitrate ionic liquid. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.; Binnemans, K. Separation of rare earths from transition metals by liquid–liquid extraction from a molten salt hydrate to an ionic liquid phase. Dalton Trans 2014, 43, 3186–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.-H.; Li, S.-W.; Wu, W.-Y.; Bian, X.; Peng, J.-H.; Zhang, L.-B. Extraction and separation of Ce(III) and Pr(III) in the system containing two complexing agents with Di- (2-Ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid. RSC Adv 2014, 4, 59997–60001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Lee, J.Y.; Thriveni, T.; Jha, M.K.; Pathak, D.D. Extraction of rare earth metals (REMs) from chloride medium by organo-metallic complexation using D2EHPA. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, M.T.; Aide, C. Rare Earth Elements: Their importance in understanding soil genesis. ISRN Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarikova, M.; Tomaskova, I.; Soudek, P. Rare earth elements in plants. Biol. Plant. 2019, 63, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürjo, S.; Siinor, L.; Siimenson, C.; Paiste, P.; Lust, E. Extraction of Thallium, Thorium and Uranium from Estonian Phosphorite and Phosphogypsum Using Aliquat 336 2018. Available online: https://sisu.ut.ee/sites/default/files/webform/Silvester_Jurjo.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Raudsep, R. Estonian georesources in the european context. Est. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 57, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.; Boutin, C.; Allison, J.E.; Parsons, J.L.; Ellis, D.M. Uptake and effects of six rare earth elements (rees) on selected native and crop species growing in contaminated soils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, P.A.; Kamalam, N.V.; Krishna Prabhu, R.; Sekhar, J.K.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Mahalingam, T.R.; Kumar, C.E.A. Rare earth element fluxes in diverse soils and their absorption by coconut palm. J. Plant Nutr. 2003, 26, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černá, M.; Volaufová, E.; Rod, V. Extraction of light rare earth elements by amines at high inorganic nitrate concentration. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 28, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Efficient Separation of vanadium from chromium by a novel ionic liquid-based synergistic extraction strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sahu, K.K.; Sahu, S.K. Solvent Extraction and Separation of nd, pr and dy from leach liquor of waste NdFeB Magnet using the nitrate form of Mextral® 336At in the presence of aquo-complexing agent EDTA. Metals 2019, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).