Lamination Texture and Its Effects on Reservoir and Geochemical Properties of the Palaeogene Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
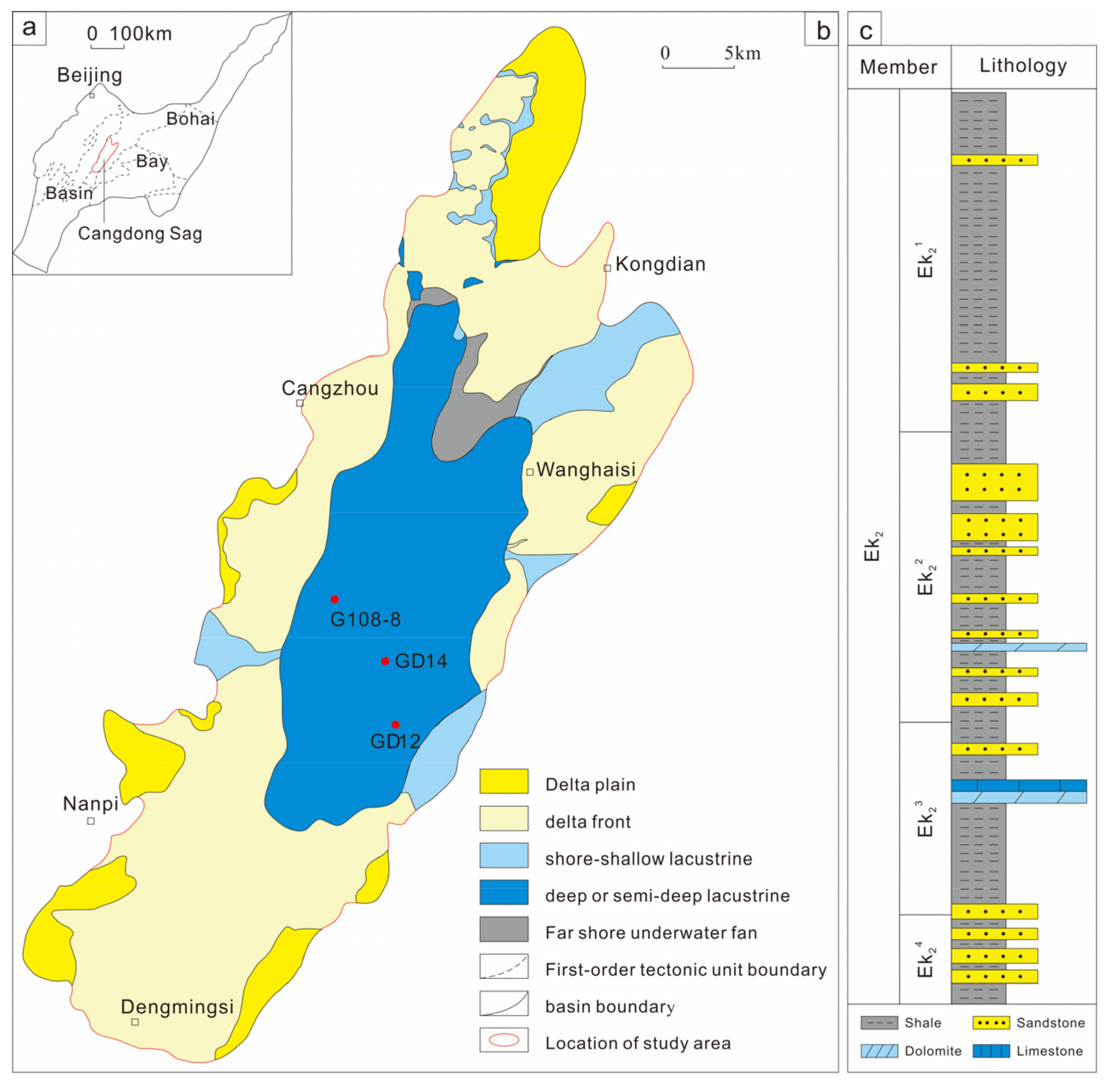
2. Geological Settings
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. TOC and Rock Pyrolysis Analysis
3.2. Polarization Microscope, X-ray Diffraction, and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Laminae Types and Their Combinations
4.2. Lamination Texture Characterization
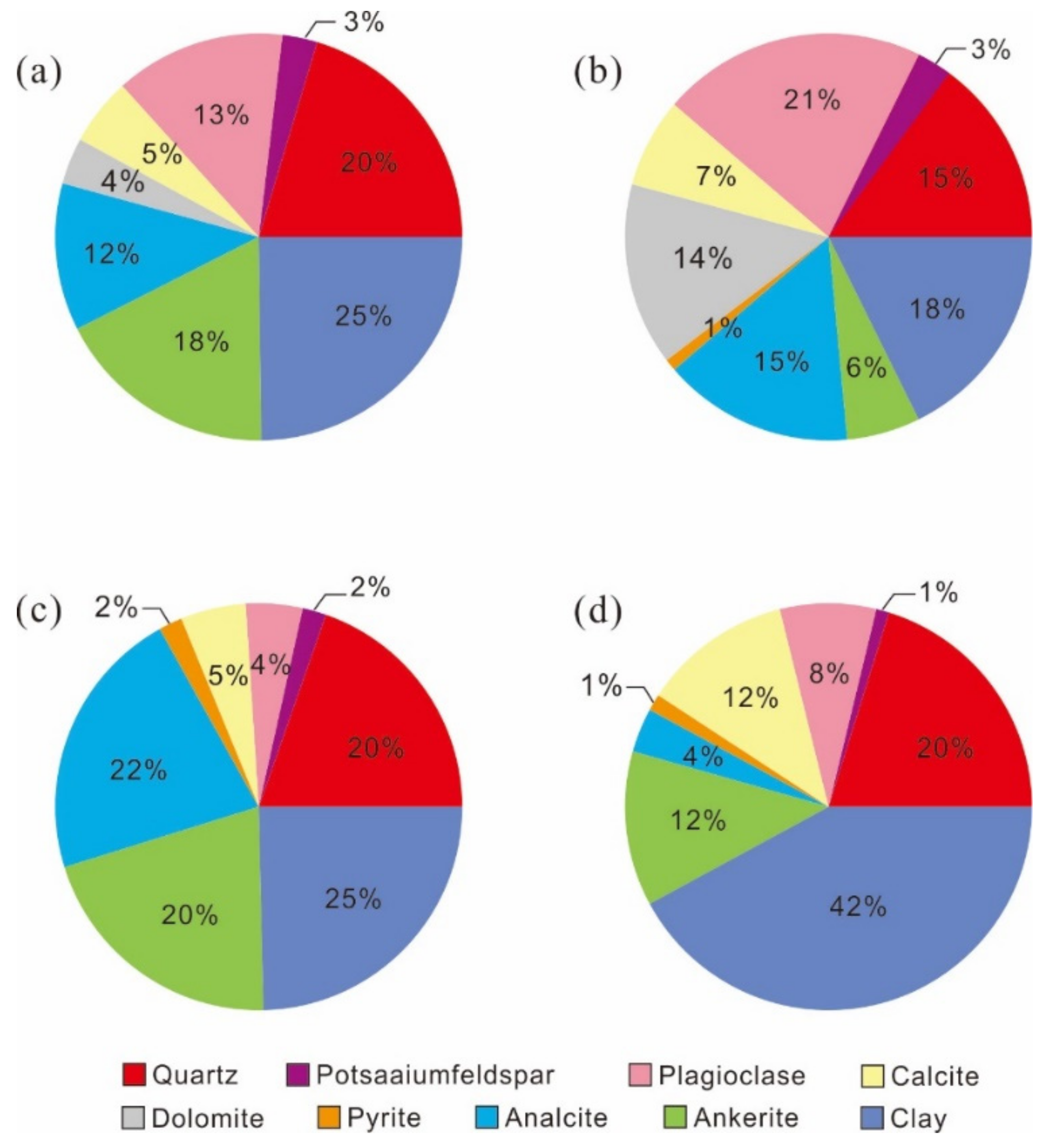
4.2.1. Differences in Mineral Compositions of Lamination Texture
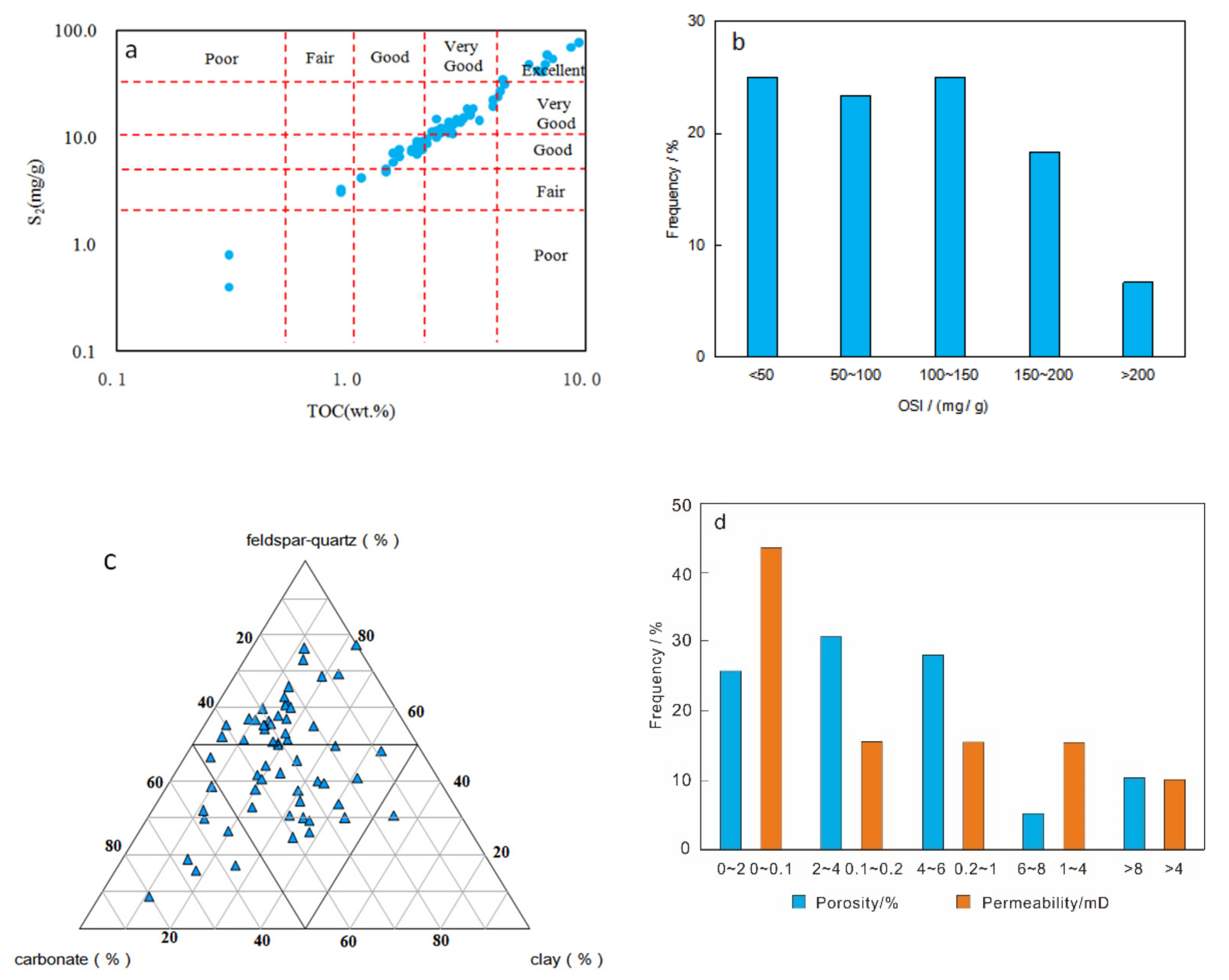
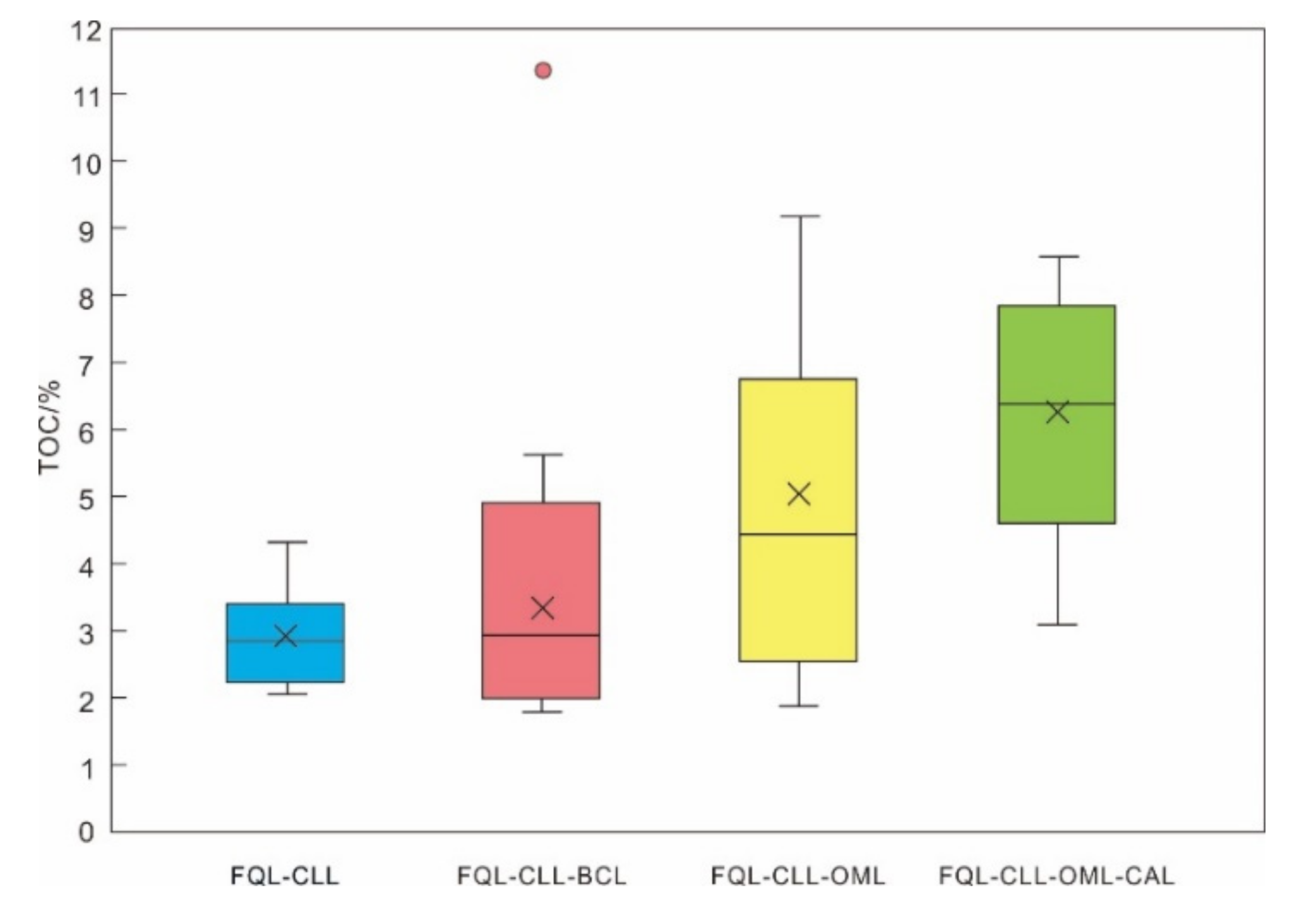
4.2.2. Organic Geochemical Characteristics of Lamination Texture
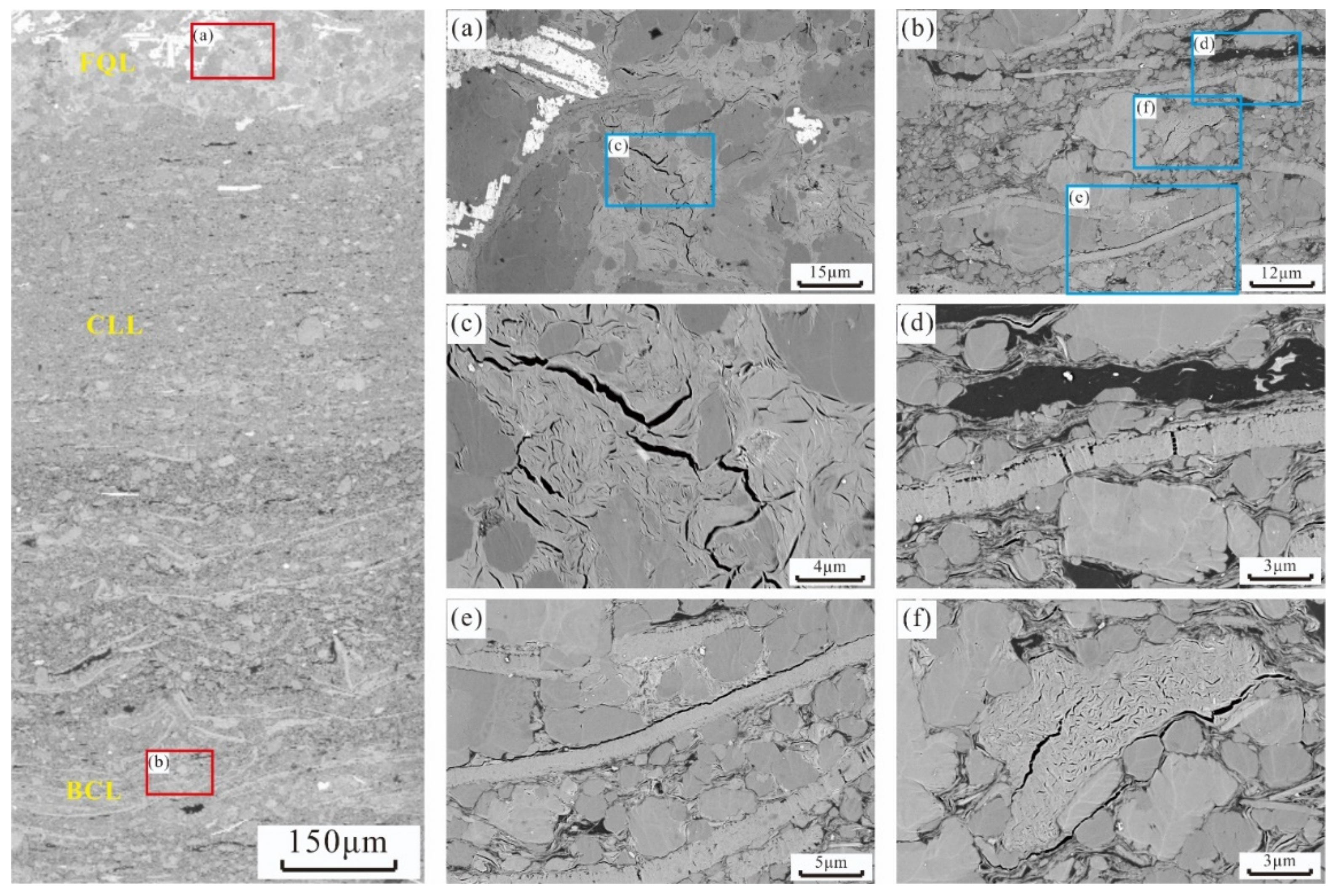
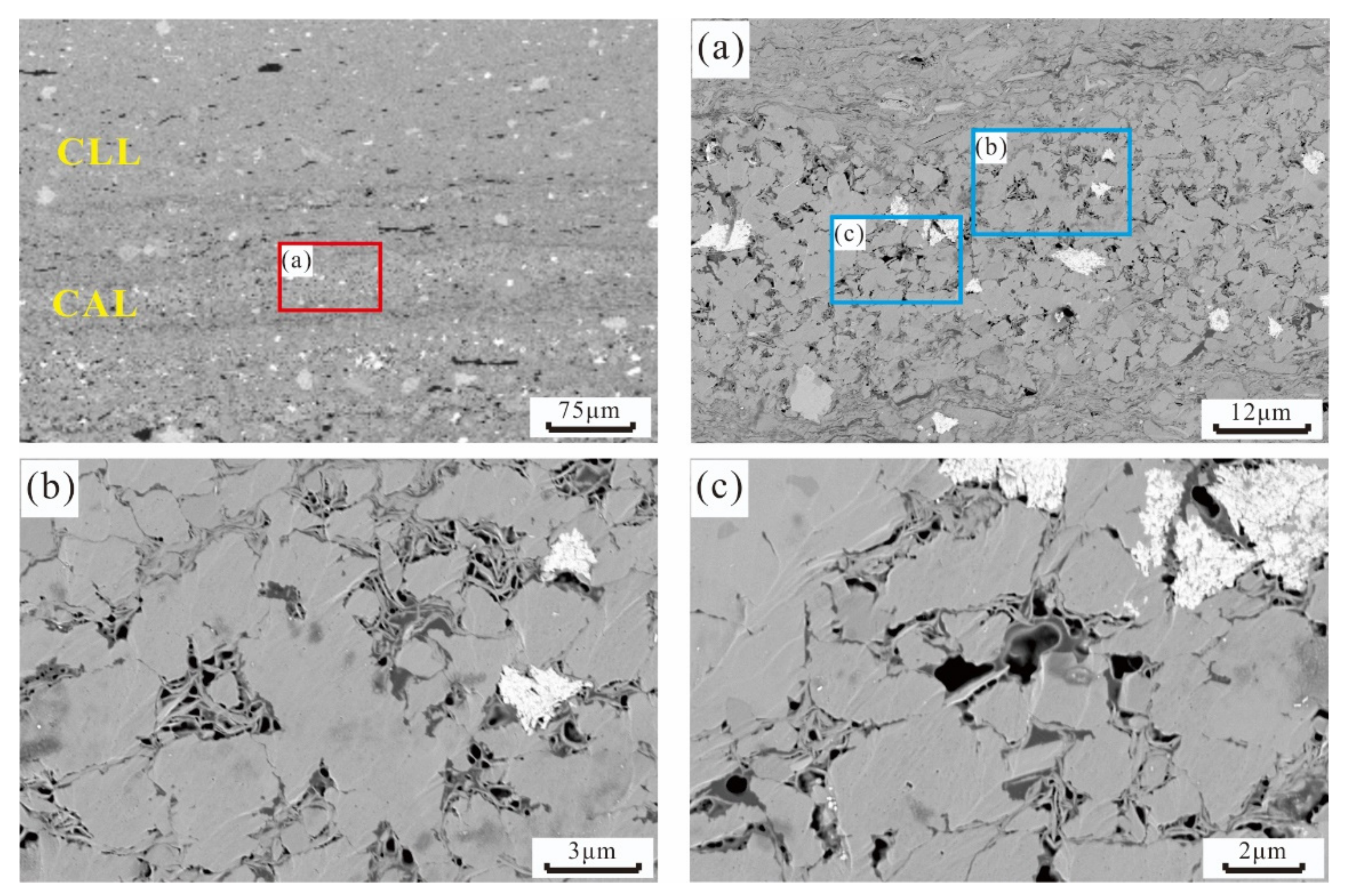
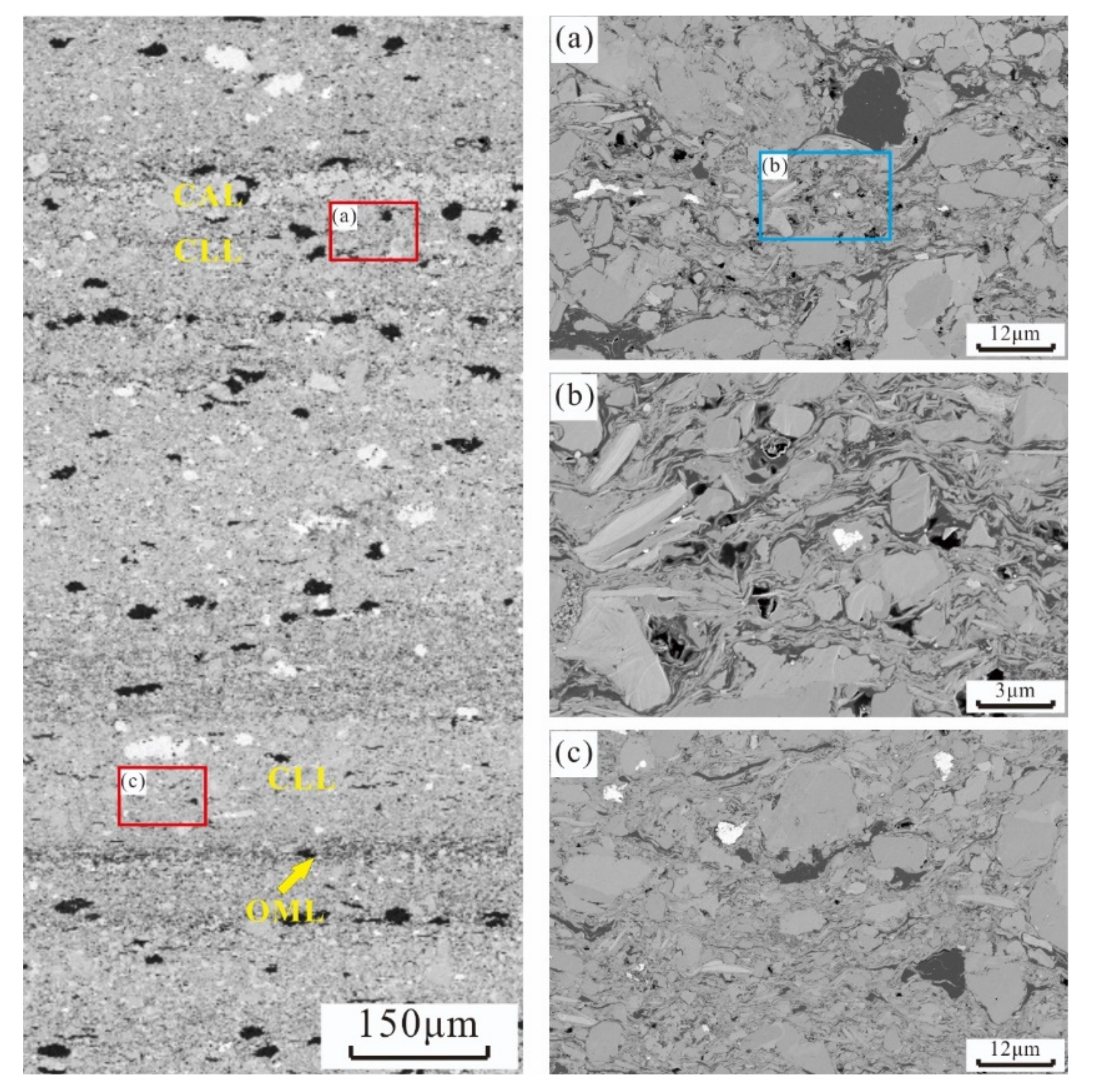
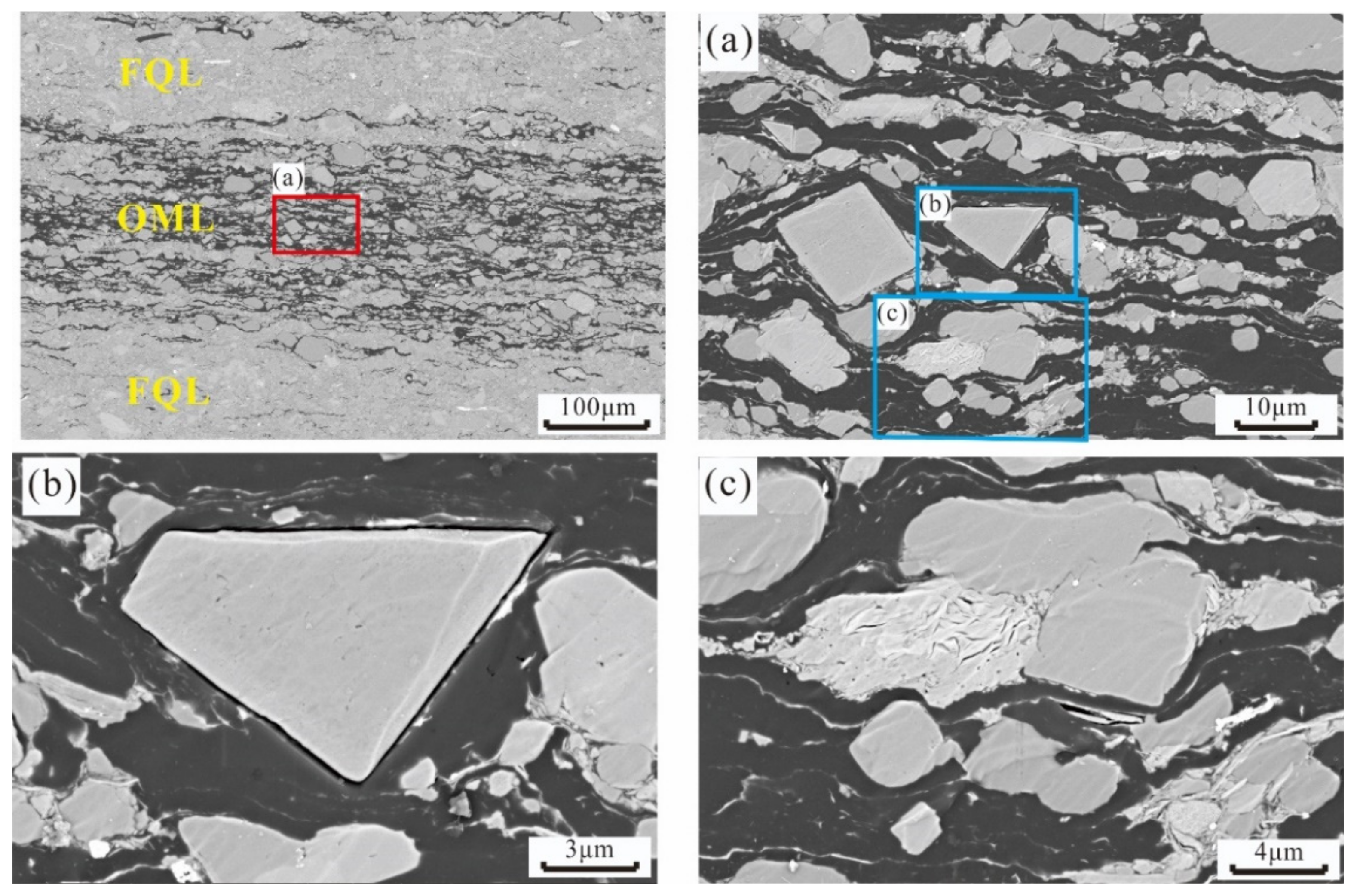
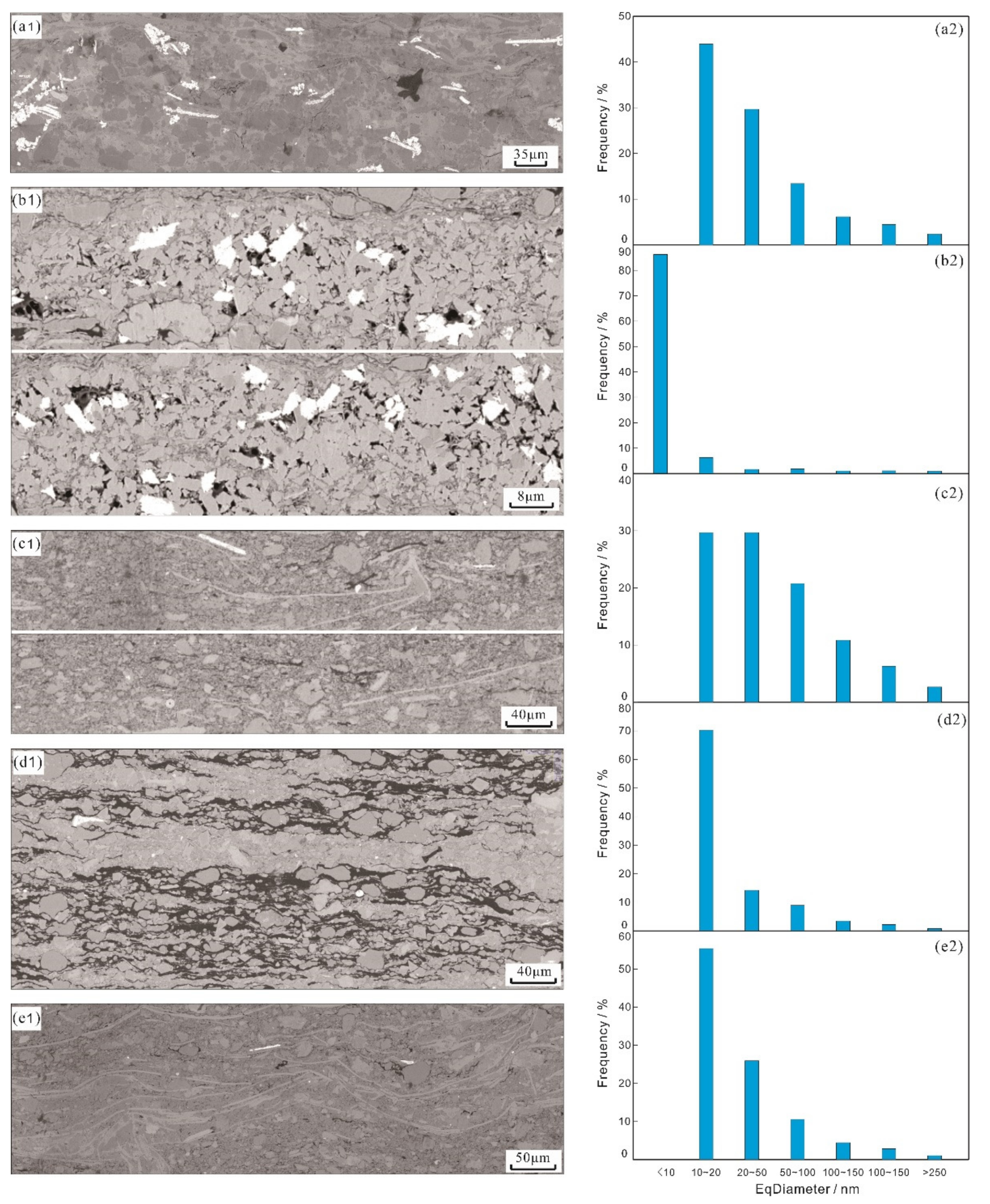
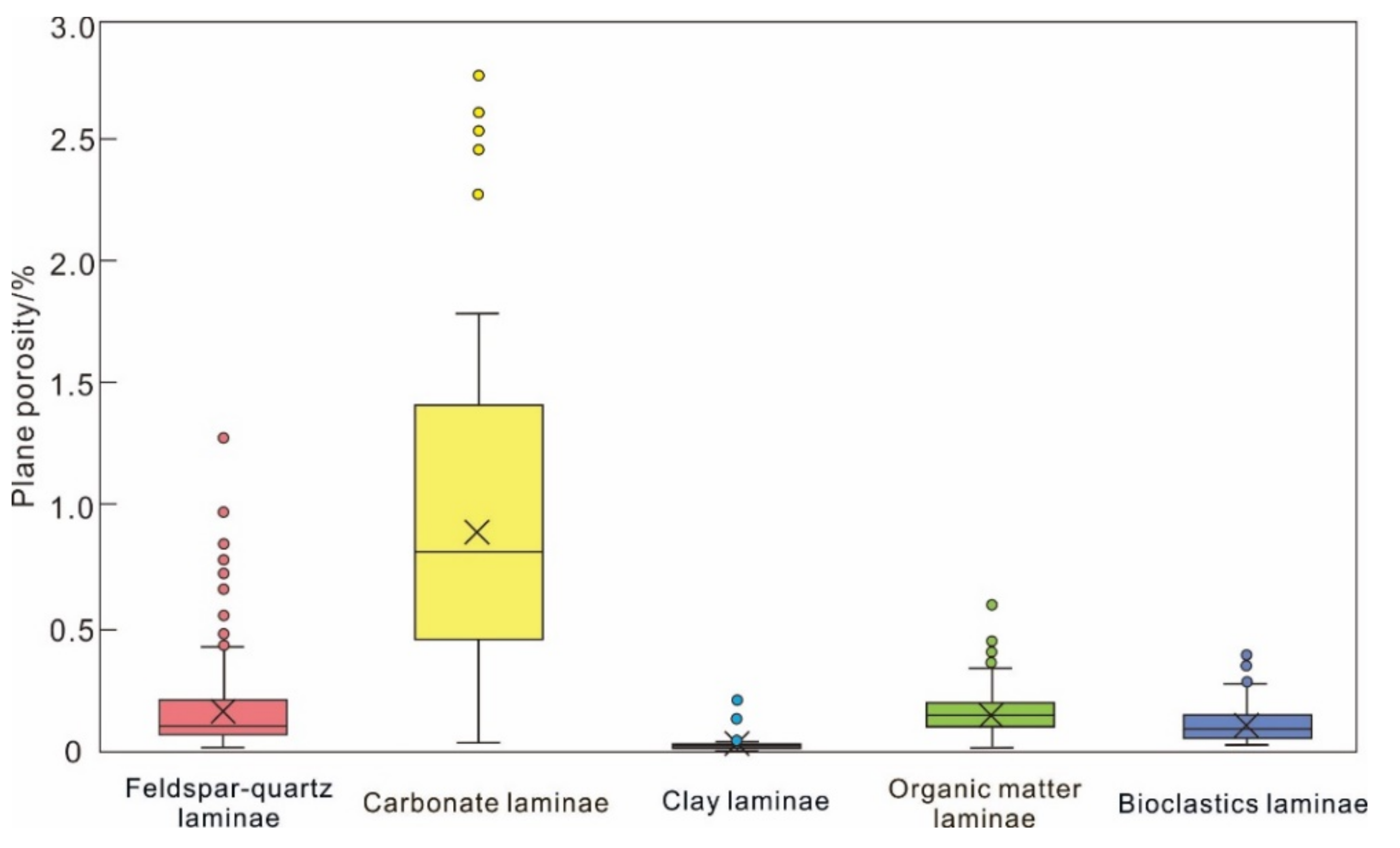
4.2.3. Pore Structures of Lamination Texture
Feldspar-Quartz Laminae
Bioclastic Laminae
Carbonate Laminae
Clay Laminae
Organic Matter Laminae
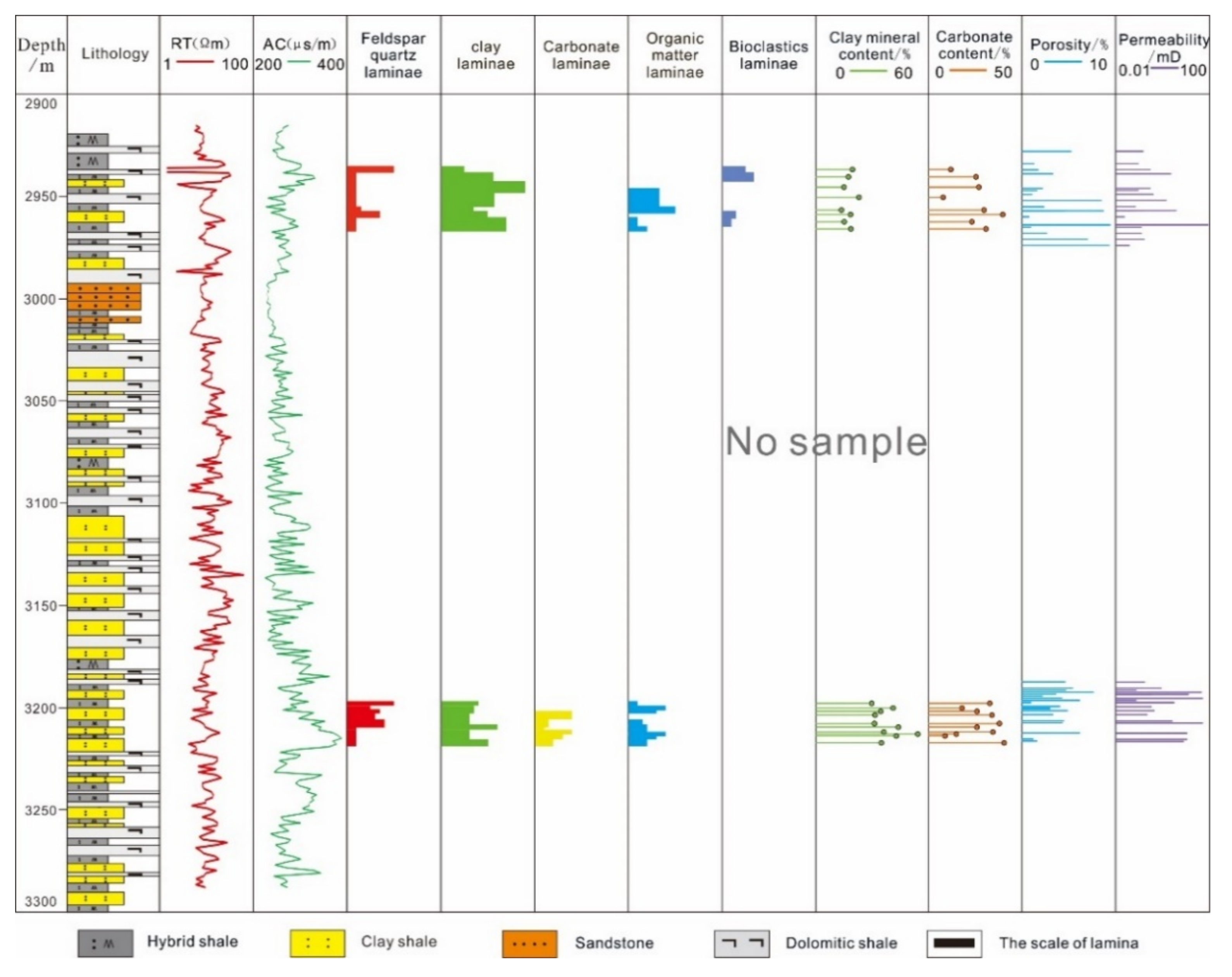
4.3. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Laminae
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The second Member of the Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag has five types of laminae: feldspar-quartz laminae (FQL), clay laminae (CLL), carbonate laminae (CAL), organic matter laminae (OML), and bioclastic laminae (BCL). The laminae occur in four combinations: FQL-CLL, FQL-CLL-BCL, FQL-CLL-OML, and FQL+CAL+CLL+OML.
- (2)
- The differences in mineral composition between the laminae combinations are generally variations in the contents of felsic and clay minerals, while carbonate mineral content varies only slightly. TOC has an obvious correlation with lamination texture that provides a crucial basis for hydrocarbon source potential analysis, with the consistent trend being: FQL-CAL-CLL-OML > FQL-CLL-OML > FQL-CLL-BCL > FQL-CLL.
- (3)
- There are marked disparities in pore types and distribution between different laminae. The pores in FQL, CAL, BCL, and OML are mostly intercrystalline pores of clay minerals. Organic pores are well developed in CAL and CLL, and intragranular pores of bioclastic minerals in BCL. The pores are predominantly mesopores. The equivalent diameter of pores in feldspar-quartz laminae and clay laminae is ascendant, precisely opposite to the equivalent diameter of pores in carbonate laminae. The comparative thin section porosities of laminae can be characterized as: carbonate laminae > feldspar-quartz laminae > organic matter laminae > bioclastic laminae > clay laminae. Carbonate laminae with ‘small but many’ pore characteristics contribute the highest proportion to thin section porosity.
- (4)
- Differentiation between vertical distributions of laminae is accomplished in a single well. FQL and CLL are widely distributed across all the samples, while BCL is concentrated in the upper part of the second Member of the Kongdian Formation, and CAL in the lower part.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stow, D.A.V.; Bowen, A.J. Origin of lamination in deep sea, fine-grained sediments. Nature 1978, 274, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, J. Reverse engineering mother nature-Shale sedimentology from an experimental perspective. Sediment. Geol. 2011, 238, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Hu, S.Y.; Hou, L.H.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Guo, B.C.; Yang, Z. Types and resource potential of lacustrine shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, W.Z.; Hou, L.H.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, R.K.; Wu, S.T.; Bai, B.; Jin, X. Development potential and technical strategy of lacustrine shale oil in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.J.; Bai, Z.R.; Gao, B.; Li, M.W. Has China ushered in the shale oil and gas revolution. Oil Gas Geol. 2019, 40, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.N.; Pan, S.Q.; Jing, Z.H.; Gao, J.L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, S.T.; Zhao, Q. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact. Acta Pet. Sin. 2020, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.X.; Zhu, R.K. Progress, challenges and key issues of unconventional oil and gas development of CNPC. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.H.; Ma, W.J.; Luo, X.; Liu, J.Z.; Lin, S.H.; Zhao, Z.Y. Hydrocarbon generation-retention-expulsion mechanism and shale oil producibility of the Permian lucaogou shale in the Junggar Basin as simulated by semi-open pyrolysis experiments, Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Huang, Z.L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, C.C.; Gao, X.Y. The characteristic and reservoir significance of lamina in shale from Yanchang Formation of Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2015, 26, 408–417. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.V. Lamina, laminaset, bed and bedset. Sedimentology 1967, 8, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAacquaker, J.H.S.; Keller, M.A.; Davies, S.J. Algal blooms and “marine snow”: Mechanisms that enhance preservation of organic carbon in ancient fine-grained sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 2010, 80, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, O.R.; Bohacs, K.M.; Macquaker, J.H.S.; Schieber, J.; Demko, T.M. Capturing key attributes of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in outcrops, cores, and thin sections: Nomenclature and description guidelines. J. Sediment. Res. 2015, 85, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingram, R.L. Terminology for the thickness of stratification and parting units in sedimentary rocks. GSA Bull. 1954, 65, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.M.; Ma, C.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, M.Y. A method of classification of shale set. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2015, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhang, S. Sedimentary environment and Lithofacies of fine-grained hybrid in Dongying Sag: A case of fine-grained sedimentary system of the Es4. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 3543–3555. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, K.L.; Li, K.; Cao, Y.C.; Lin, M.R.; Niu, X.B.; Zhu, R.K.; Wei, X.Z.; You, Y.; Liang, X.W.; Feng, S.B. Laminae combination and shale oil enrichment patterns of Chang 73 sub-member organic-rich shales in the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.S.; Qiu, Z.; Dong, D.Z.; Lu, B.; Liang, P.P.; Zhang, M.Q. Laminae characteristics of gas-bearing shale fine-grained sediment of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation of Well Wuxi 2 in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawar, Z.; Schieber, J. On the origin of silt laminae in laminated shales. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 360, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.S.; Dong, D.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Sun, S.S.; Wu, J. Reservoir characteristics and genetic mechanisms of gas-bearing shales with different laminae and laminae combinations: A case study of Member 1 of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.H.; Deng, Y.; Pu, X.G.; Zhou, L.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Jiao, Y.X. Characteristics and controlling factors of fine-grained mixed sedimentary rocks from the 2nd Member of Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2017, 38, 98–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Cao, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, W.Q. Milankovitch cycle of lacustrine deepwater fine-grained sedimentary rocks and its significance to shale oil: A case study of the upper Es4 member of well NY1 in Dongying sag. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 846–858. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Jin, Z.J.; Jin, Z.K.; Wen, X.; Geng, Y.K.; Yan, C.N.; Nie, H.K. Lithofacies types and sedimentary environment of shale in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 37, 572–586. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, B.Q.; Hu, Q.H.; Shu, Z.G.; Sun, M.D.; Bao, H.Y. Laminae characteristics and influence on shale gas reservoir quality of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Jiaoshiba area of the Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, S.; Yang, C.H.; Guo, Y.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, L. Influence of bedding planes on hydraulic fracture propagation in shale formations. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2015, 34, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Hu, R.L.; Gao, W.; Xia, J.G. Effects of laminated structure on hydraulic fracture propagation in shale. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.X.; Bian, X.B.; Wang, H.T.; Li, S.M.; Jia, C.G.; Liu, H.L.; Sun, H.C. Volume fracturing of deep shale gas horizontal wells. Nat. Gas Ind. 2017, 37, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Pu, X.G.; Han, W.Z.; Zhou, L.H.; Shi, Z.N.; Chen, S.Y.; Xiao, D.Q. A new method for Lithology identification of fine grained deposits and reservoir sweet spot analysis: A case study of Kong 2 Member in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.G.; Jin, F.M.; Han, W.Z.; Shi, Z.N.; Cai, A.B.; Wang, A.G.; Guan, Q.S.; Jiang, W.Y.; Zhang, W. Sweet spots geological characteristics and key exploration technologies of lacustrine shale oil: A case study of Member 2 of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong sag. Acta Pet. Sin. 2019, 40, 997–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.Z.; Zhao, X.Z.; Jin, F.M.; Pu, X.G.; Chen, S.Y.; Mu, L.G.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.N.; Wang, H. Sweet spots evaluation and;exploration of lacustrine shale oil of the 2nd member of Paleogene Kongdian Formation in Cangdong sag, Dagang Oilfield, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.L. Analysis of development mechanism for center anticline high in Dongying Depression. Geotecton. Metallog. 2004, 28, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Dai, L.M.; Zhou, J.T.; Zhao, F.M.; Lu, Y.; Pu, X.G.; Lou, D.; Wu, Q.; et al. Pull-apart basins within the North China craton: Structural pattern and evolution of Huanghua Depression in Bohai Bay Basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2011, 41, 1362–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.W.; Xue, L.F.; Xu, X.K.; Yan, Q.H. Re-establishment of basin framework on member 2 of Kongdian Fomation in Kongnan area Huanghua depression. Acta Sedmentol. Sin. 2007, 25, 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.Y.; Liu, X.P.; Li, H.X.; Liu, Z.C.; Liu, Q.X.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.J. Formation conditions of shale oil reservoir in the second member of Kongdian Formation in southern Kongdian area, Huanghua depression. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.G.; Han, W.Z.; Zhou, L.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.N.; Yang, F.; Liu, S. Lithologic characteristics and geological impLication of fine-grained sedimentation in second Member of the Kongdian Formation high stand system tract of Cangdong Sag, Huanghua depression. China Pet. Explor. 2015, 20, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Zhou, L.H.; Pu, X.G.; Jin, F.M.; Shi, Z.N.; Xiao, D.Q.; Han, W.Z.; Jiang, W.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Favorable formation conditions and enrichment characteristics of lacustrine facies shale oil in faulted lake basin: A case study of Member 2 of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2019, 40, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.H.; Pu, X.G.; Chen, C.W.; Yang, F.; Xia, J.; Guan, Q.S.; Huang, C.Y. Concept, characteristics and prospecting significance of Fine-Grained sedimentary oil gas in terrestrial lake basin: A case from the second member of Paleogene Kongdian Formation of Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 3625–3639. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E.; Cassa, M.R. Applied source rock geochemistry: Chapter 5: Part II. Essential elements. In The Petroleum System–From Source to Trap: AAPG Memoir; Magoon, L.B., Dow, W.G., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Tao, S.Z.; Yuan, X.J.; Hou, L.H.; Zhu, R.K.; Gao, X.H.; Yang, C. Characteristics of Unconventional Oil and Gas Nanopore Reservoirs and Mechanism of Continuous Oil and Gas Accumulation; Chinese society for Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry: Guiyang, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Yuan, X.J.; Yao, J.L.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L.; Bai, B. Reservoir quality characterization of upper Triassic Chang 7 shale in Ordos Basin. Earth Sci. (J. China Univ. Geosci.) 2015, 40, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Zhu, R.K.; Cui, J.G.; Cui, J.W.; Bai, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Jin, X.; Zhu, D.S.; You, J.C.; Li, X.H. Characteristics of lacustrine shale porosity evolution, Triassic Chang 7 member, Ordos basin, NW China, Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.K.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, X.D.; Li, J.M.; Sun, L.; Wu, S.T.; Su, L.; Jiao, H.; Cui, J.W. Multi-scale digital rock evaluation on complex reservoir. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Lin, S.Y.; Chao, D.J.; Zhai, X.F.; Wang, X.R.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.L. Fluid mobility evaluation based on pore structure investigation in tight sandstones: Case study of Upper Triassic Chang 6 tight sandstones in Huaqing Area, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wu, S.; Hu, S.; Zhu, R.; Meng, S.; Yang, J. Lamination Texture and Its Effects on Reservoir and Geochemical Properties of the Palaeogene Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Minerals 2021, 11, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121360
Li M, Wu S, Hu S, Zhu R, Meng S, Yang J. Lamination Texture and Its Effects on Reservoir and Geochemical Properties of the Palaeogene Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Minerals. 2021; 11(12):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengying, Songtao Wu, Suyun Hu, Rukai Zhu, Siwei Meng, and Jingru Yang. 2021. "Lamination Texture and Its Effects on Reservoir and Geochemical Properties of the Palaeogene Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China" Minerals 11, no. 12: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121360
APA StyleLi, M., Wu, S., Hu, S., Zhu, R., Meng, S., & Yang, J. (2021). Lamination Texture and Its Effects on Reservoir and Geochemical Properties of the Palaeogene Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Minerals, 11(12), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121360






