Synthesis of KAlSiO4 by Hydrothermal Processing on Biotite Syenite and Dissolution Reaction Kinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
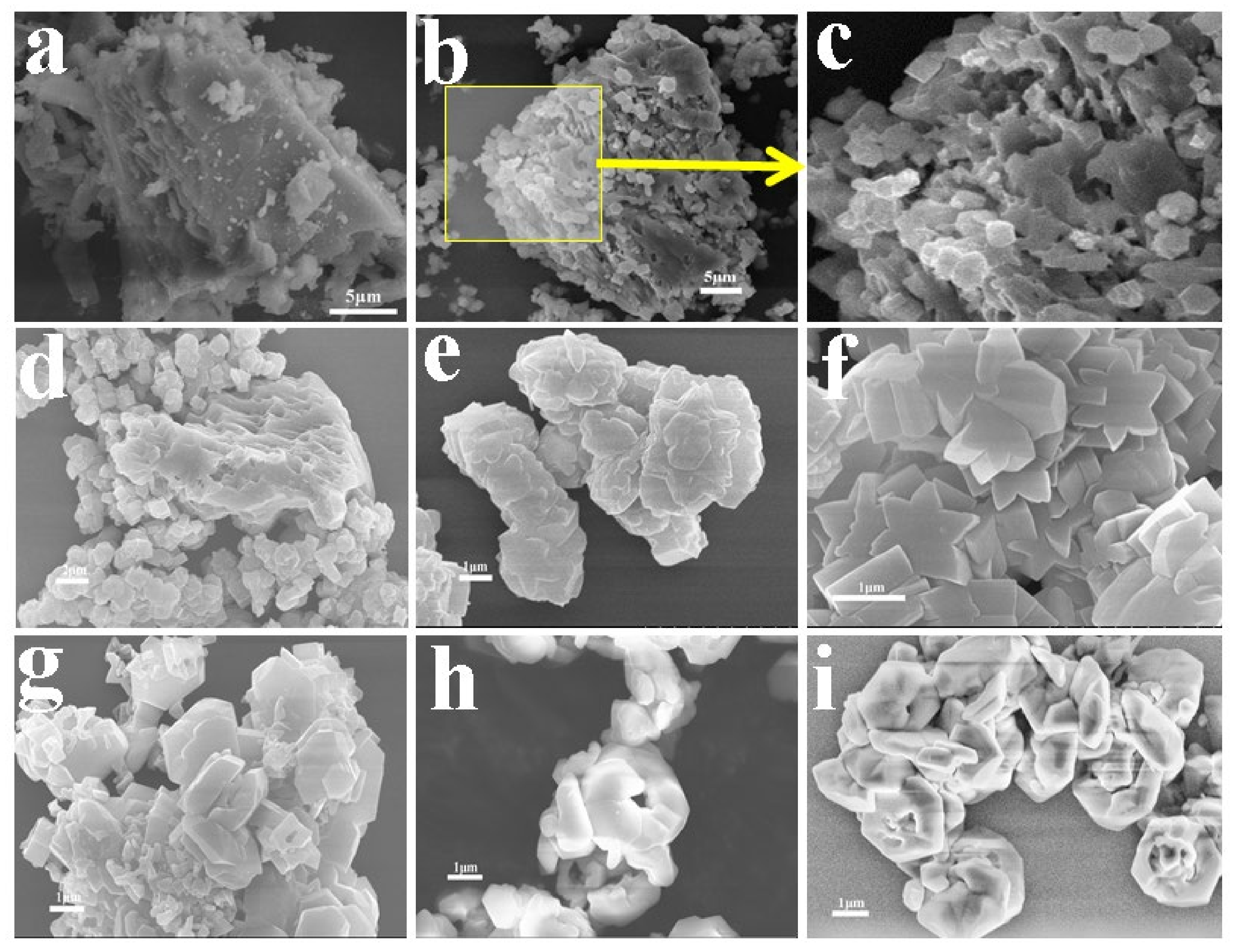
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Two Kinds of KAlSiO4
3.2. Reaction Kinetics
3.2.1. Kinetic Model
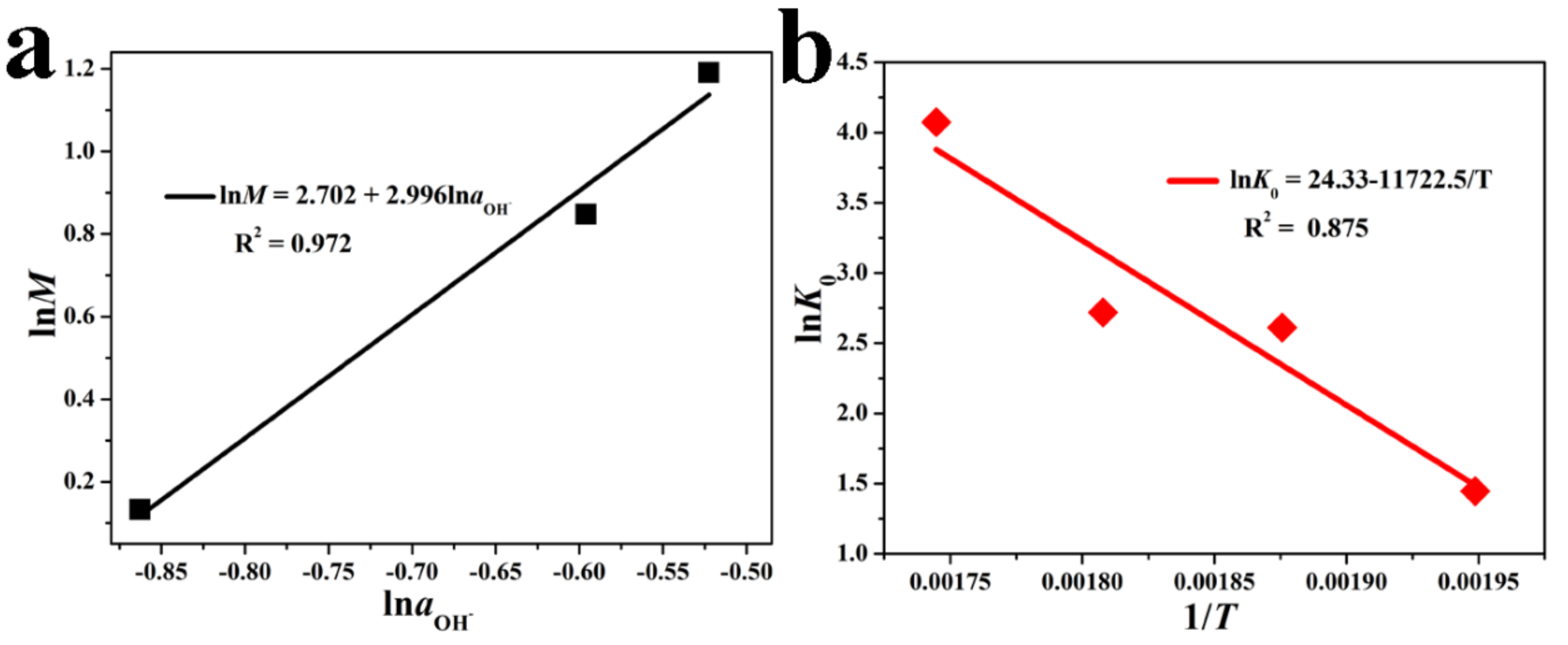
3.2.2. Kinetics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, A.C.M. Mineral sources of potassium for plant nutrition. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 281–294. [Google Scholar]
- Skorina, T.; Allanore, A. Aqueous alteration of potassium-bearing aluminosilicate minerals: From mechanism to processing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.W. Potassic Rocks in China: Resource and Clean Utilization Techniques; Chemical Industy Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 1–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Su, S.; Chang, Q.; Komarneni, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of nano-kaolinite from K-feldspar. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15611–15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.W.; Yang, J.; Su, S.Q.; Liu, M.T.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.B.; Qi, H.B.; Zhang, P.; Yao, W.G. 20 years advances in preparation of potassium salts from potassic rocks: A review. Acta Geol. Sinica 2015, 89, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.J.; Su, S.Q.; Yao, W.G.; Luo, Z.; Liu, M.T.; Yin, C.C.; Chen, J.; et al. Potassic syenite resource in China and reaction mechanism of potash salt processing by hydrothermal alkaline digestion. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ciceri, D.; Manning, D.A.C.; Allanore, A. Historical and technical developments of potassium resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, J.A.; Back, M.E. Fleischer’s Glossary of Mineral Species; The Minerallogical Record Inc.: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2014; p. 420. [Google Scholar]
- Guertal, E.A. Preplant slow-release nitrogen fertilizers produce similar bell pepper yields as split applications of soluble fertilizer. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavit, U.; Shaviv, A.; Shalit, G.; Zaslavsky, D. Release characteristics of a new controlled release fertilizer. J. Control. Release 1997, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Z.; Liu, Y.Q.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Cao, Y. Preparation and properties of macromelecular slow-release fertilizer containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y. Potassium silicate: A slow-release potassium fertilizer. Nutr. Cycling Agroecosyst. 1991, 30, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.G.; Rueda, J.I.P.; Mateos, F.B.; Marin, J.P. Slow-release fertilizer in the form of emulsion. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 1999, 13, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Mangrich, A.; Tessaro, L.; Anjos, A.D.; Wypych, F.; Soares, J. A slow-release K+ fertilizer from residues of the Brazilian oil-shale industry: Synthesis of kalsilite-type structures. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 1030. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.W.; Su, S.Q.; Yang, J.; Cai, B.; Liu, M.; Yao, W.; Peng, H. Preparation of potassium sulfate from K-feldspar by hydrothermal alkaline method: Reaction principle and process evaluation. Ciesc. J. 2014, 8, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ma, H.W.; Yang, J. Sintering preparation and release property of K2MgSi3O8 slow-release fertilizer using biotite acid-leaching residues as silicon source. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ma, H.; Yuan, J.; Guo, R. Synthesis of K2O–MgO–SiO2 compounds as slow-release fertilisers from acid-leached biotite residues. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, W.; Luan, X.; Zhao, P. K2MgSi3O8 in slow-release mineral fertilizer prepared by sintering of by-product of red mud-based flocculant. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovicienė, I.; Jankeviciutė, A.; Pinkas, J.; Kareiva, A. Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of kalsilite-type alumosilicates. Mater Sci. 2007, 13, 1392–11320. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrijevic, R.; Dondur, V. Synthesis and characterization of KAlSiO4 polymorphs on the SiO2-KAlO2 join. J. Solid State Chem. 1995, 115, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerro, A.I.; Mantovani, M.; Escudero, A. Hydrothermal synthesis of kalsilite: A simple and economical Method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2204–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, T.E.; Nagy, K.L.; Lasaga, A.C. Free energy dependence of albite dissolution kinetics at 80 °C. Chem. Geol. 1993, 105, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Lu, P.; Konishi, H.; Dilmore, R.; Xu, H.; Seyfried, W.E.; Zhu, C. Coupled alkali-feldspar dissolution and secondary mineral precipitation in batch systems: 1. New experiments at 200 °C and 300 bars. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachhold, N.; Aneziris, C.G. Synthesis of alkali aluminosilicates—Materials for alkali contaminated environments at high temperatures. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2013, 10, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, C. Hydrothermal synthesis of analcime and hydroxycancrinite from K-feldspar in Na2SiO3 solution: Characterization and reaction mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 54503–54509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Su, S.; Chang, Q.; Komarneni, S. Green synthesis of nano-muscovite and niter from feldspar through accelerated geomimicking process. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 165, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Zhang, P. Thermodynamics of the hydrothermal decomposition reaction of potassic syenite with zeolite formation. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2018, 34, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Gao, Y. Hydrothermal processing on potassic syenite powder: Zeolite synthesis and potassium release kinetics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.Q.; Ma, H.W.; Chuan, X.Y.; Cai, B.Y. Preparation of potassium sulfate and zeolite NaA from k-feldspar by a novel hydrothermal process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 155, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.Y.; Ma, H.W.; Guo, R.Y.; Ma, X.; Komarneni, S. A case study targeting K fertilizer chemical synthesis with complete valorization of extraction by-products as an option. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 654–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Chang, Q. Preparation of Zeolite F as Slow Release Fertilizers from K-Feldspar Powder. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 10722–10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.W. Crystallographic Thermodynamics Software; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, C. Crystal structural transformation and kinetics of NH 4+/Na+ ion-exchange in analcime. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 222, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.C.; von Dreele, R.B. General Structure Analysis System; LANSCE, MS-H805; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1994.
- Khomyakov, A.P.; Nechelyustov, G.N.; Sokolova, E. Megakalsilite, a new polymorph of KAlSiO4 from the Khibina alkaline massif, kola peninsula, Russia: Mineral description and crystal structure. The Candidate Mineralogist. Can. Miner. 2002, 40, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andratschke, M.; Haase, H.; Klement, U. Die Kristallstruktur Von a-KZnPO4. In Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 1249–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann, R.; Tisserand, D. Dissolution kinetics as a function of the Gibbs free energy of reaction: An experimental study based on albite feldspar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, M.S. Feldspar Dissolution Kinetics and Eauilibrium. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kremenović, A.; Vulić, P. Disordered kalsilite KAlSiO4. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2014, 70, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.V.; Bailey, S.W. Second review of Al–O and Si–O tetrahedral distances. Acta Crystallogr. 1963, 16, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Yan, Z.; Smith, M.; Zhang, P.; Wen, B. Kalsilite based heterogeneous catalyst for biodiesel production. Fuel 2010, 89, 2163–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, H.; Han, Z.C.; Liu, L.C. Low-energy synthesis of kaliophilite catalyst from circulating fluidized bed fly ash for biodiesel production. Fuel 2019, 257, 116041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, V.; Hira, S.; Manna, P.; Kumar, P. In vitro Cytotoxicity, Apoptotic and Hemolysis Assay of Kalsilite-Based Glass Ceramics for Dental Veneering Application. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2016, 13, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.H.; Singh, V.K.; Kumar, P. Mechanochemically synthesized kalsilite based bioactive glass-ceramic composite for dental vaneering. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oda, C.; Walker, C.; Chino, D.; Ichige, S.; Honda, A.; Sato, T.; Yoneda, T. Na-montmorillonite dissolution rate determined by varying the Gibbs free energy of reaction in a dispersed system and its application to a coagulated system in 0.3M NaOH solution at 70 °C. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 93, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, Z. Dissolution behavior of aluminum, silicon, and iron of diaspore concentrate in naoh-naal(OH)4 Solutions at elevated temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18429–18439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A.C.; Soler, J.M.; Ganor, J.; Burch, T.E.; Nagy, K.L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2361–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A.C. Transition State Theory. Rev. Miner. 1981, 8, 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseyev, V.A.; Medvedeva, L.S.; Prisyagina, N.I.; Balabin, A.I. Change in the dissolution rates of alkali feldspars as a result of secondary mineral precipitation and approach to equilibrium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.J.B.; Powell, R. An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1998, 16, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Anderko, A.; Young, R.D. A speciation-based model for mixed-solvent electrolyte systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2002, 203, 141–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, P.A.N.; Hui, P.A.N.; Hong, L.U.; Jian, S.U.; Dong, C. Alkli—activated Mechanisms of Kaolinite and Hydrothermal Synthesis of 4A Zeolite. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
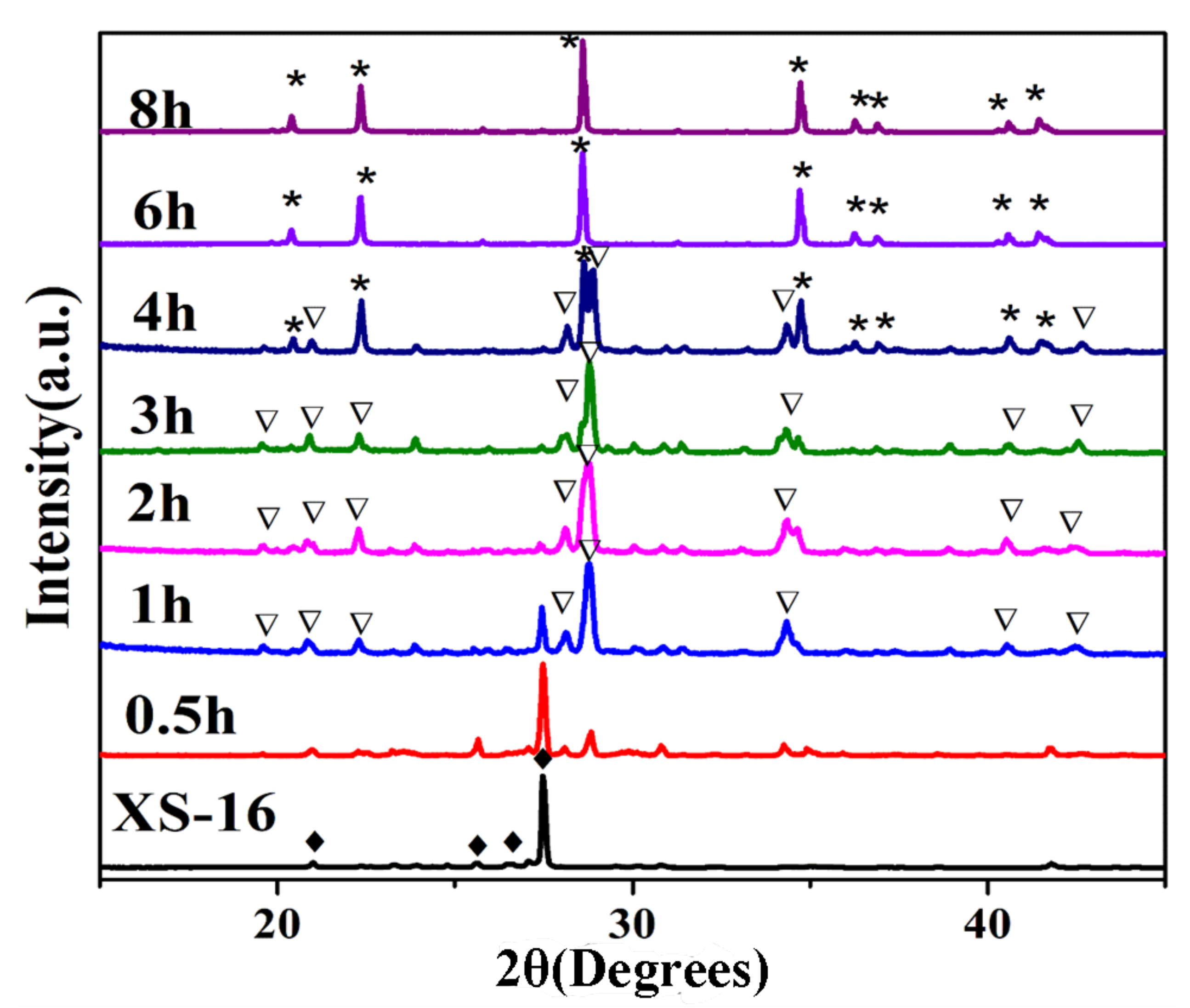

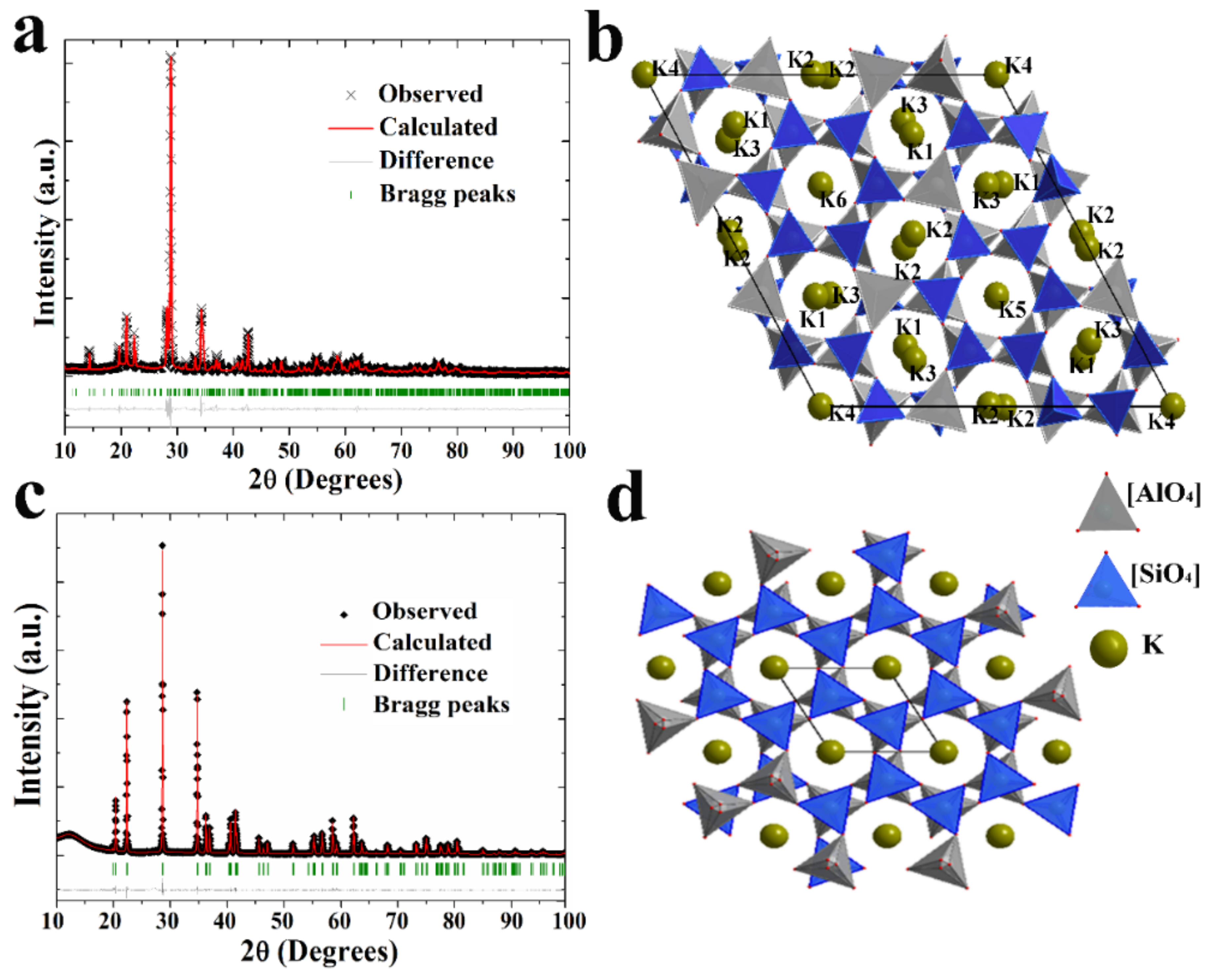
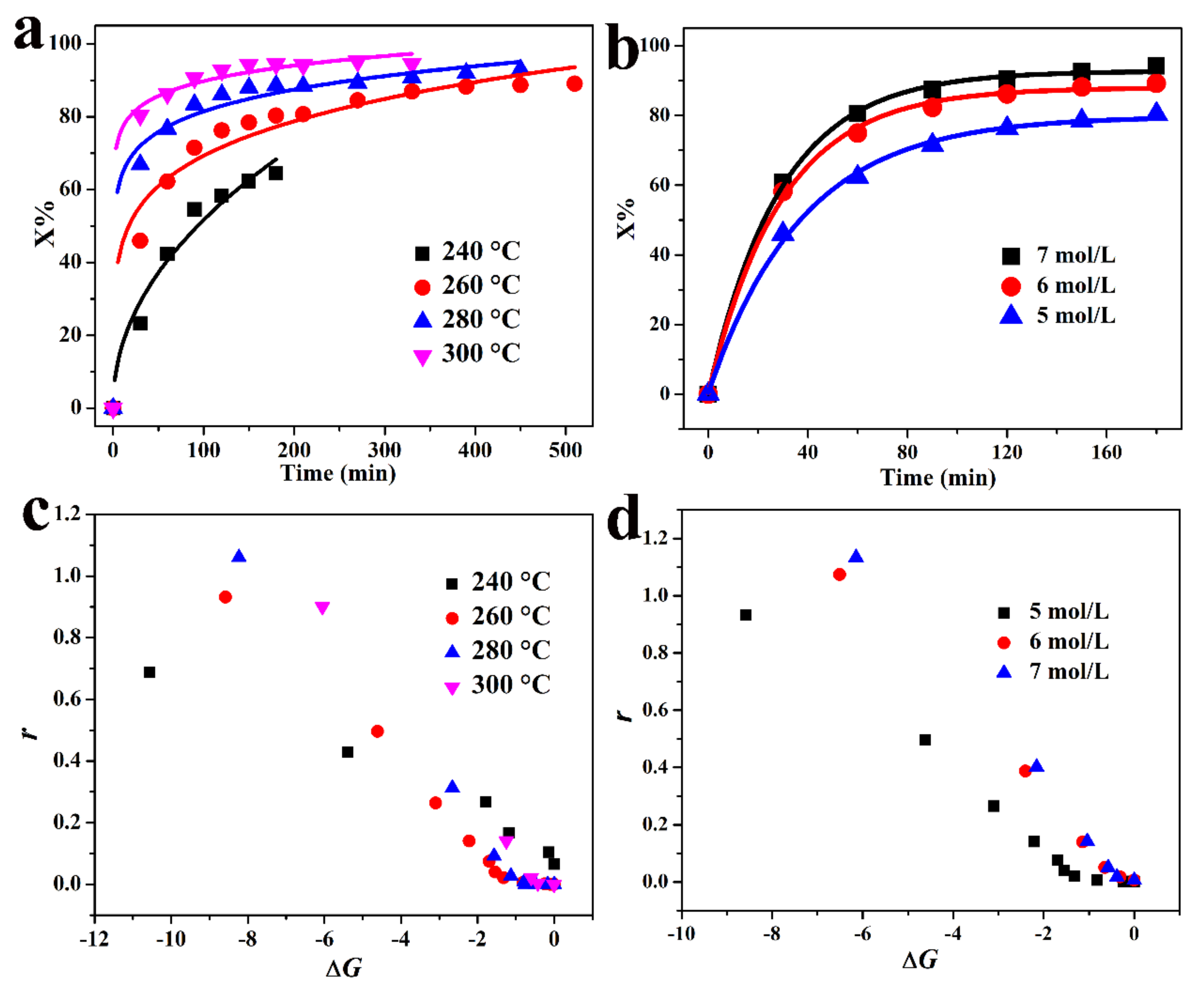
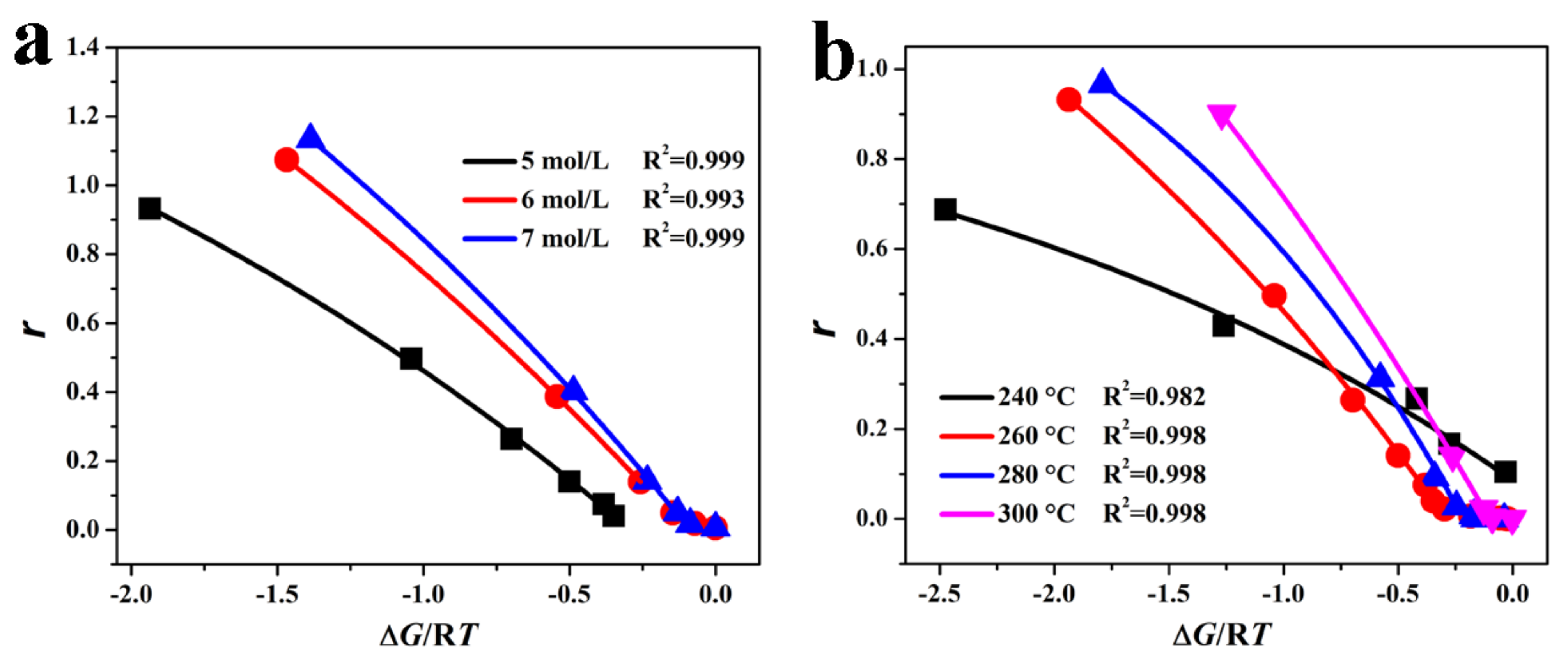
| Sample | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XS-16 | 64.84 | 0.29 | 17.95 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 0.36 | 0.63 | 14.15 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 100.24 |
| microcline | 63.84 | 0.08 | 17.99 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 16.76 | - | - | 99.39 |
| Sample | Time/h | SiO2 | K2O | Al2O3 | C (SiO2)/mol·L−1 | SiO2 (%) | Product Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XS-K-1 | 1 | 44.98 | 21.53 | 28.77 | 2.062 | 57.52 | Mic (68%) + MEK (32%) |
| XS-K-2 | 2 | 38.60 | 28.83 | 30.66 | 2.278 | 63.54 | Mic (31%) + MEK (69%) |
| XS-K-3 | 3 | 38.89 | 28.46 | 30.35 | 2.269 | 63.27 | MEK |
| XS-K-4 | 4 | 37.81 | 29.66 | 30.04 | 2.305 | 64.29 | MEK (42%) + Kls (58%) |
| XS-K-6 | 6 | 37.23 | 29.09 | 29.95 | 2.325 | 64.84 | Kls |
| XS-K-8 | 8 | 37.69 | 29.12 | 30.47 | 2.310 | 64.41 | Kls |
| Atom | x | y | z | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 0 | 0 | 0.2407 | 1.0 |
| Al | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.0379 | 1.0 |
| Si | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.4237 | 1.0 |
| O1 | 0.3831 | 0.9875 | 0.4858 | 1.0 |
| O2 | 0.3339 | 0.7155 | 1/4 | 1/3 |
| Atom | x | y | z | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 0.1511 | 0.3310 | 0.9303 | 1.0 |
| K2 | 0.5222 | 0.5196 | 0.9254 | 1.0 |
| K3 | 0.3346 | 0.1392 | 0.9135 | 1.0 |
| K4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.4655 | 1.0 |
| K5 | 0.3333 | 0.6667 | 0.4183 | 1.0 |
| K6 | 0.3333 | 0.6667 | 0.9277 | 1.0 |
| Al1 | 0.1673 | 0.1535 | 0.7300 | 1.0 |
| Al2 | 0.6649 | 0.0019 | 0.1082 | 1.0 |
| Al3 | 0.4989 | 0.3295 | 0.7370 | 1.0 |
| Al4 | 0.3336 | 0.5023 | 0.7352 | 1.0 |
| Si1 | 0.3287 | 0.3321 | 0.7182 | 1.0 |
| Si2 | 0.3409 | 0.5067 | 0.1269 | 1.0 |
| Si3 | 0.1726 | 0.1591 | 0.1204 | 1.0 |
| Si4 | 0.4956 | 0.6689 | 0.6303 | 1.0 |
| O1 | 0.1283 | 0.0795 | 0.2391 | 1.0 |
| O2 | 0.0441 | 0.1803 | 0.4529 | 1.0 |
| O3 | 0.3843 | 0.2958 | 0.6735 | 1.0 |
| O4 | 0.3555 | 0.4147 | 0.6313 | 1.0 |
| O5 | 0.1151 | 0.2009 | 0.1159 | 1.0 |
| O6 | -0.0755 | 0.5481 | 0.1801 | 1.0 |
| O7 | 0.2847 | 0.5400 | 0.1858 | 1.0 |
| O8 | 0.4059 | 0.6121 | 0.6790 | 1.0 |
| O9 | 0.2576 | 0.2238 | 0.2024 | 1.0 |
| O10 | 0.5291 | 0.7519 | 0.7230 | 1.0 |
| O11 | 0.4130 | 0.1104 | 0.6923 | 1.0 |
| O12 | 0.2747 | 0.0359 | 0.1714 | 1.0 |
| O13 | 0.1950 | 0.4789 | 0.4575 | 1.0 |
| O14 | 0.3310 | 0.3435 | 0.8875 | 1.0 |
| O15 | 0.1381 | 0.5802 | 0.2328 | 1.0 |
| O16 | 0.6184 | 0.4725 | 0.4636 | 1.0 |
| Bond | Bond Length (Å) | Bonds | Bond Length (Å) | Bond | Bond Length (Å) | Bond | Bonds Length (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si1-O3 | 1.51 | Si2-O7 | 1.51 | Al1-O1 | 1.96 | Al2-O6 | 1.93 |
| Si1-O4 | 1.51 | Si2-O11 | 1.58 | Al1-O2 | 1.95 | Al2-O9 | 1.97 |
| Si1-O12 | 1.48 | Si2-O15 | 1.55 | Al1-O5 | 1.89 | Al2-O11 | 1.94 |
| Si1-O14 | 1.45 | Si2-O16 | 1.53 | Al1-O12 | 1.98 | Al2-O14 | 1.89 |
| Si3-O1 | 1.61 | Si4-O6 | 1.48 | Al3-O3 | 1.92 | Al4-O4 | 2.02 |
| Si3-O2 | 1.51 | Si4-O8 | 1.59 | Al3-O7 | 1.89 | Al4-O8 | 1.82 |
| Si3-O5 | 1.57 | Si4-O10 | 1.53 | Al3-O13 | 2.00 | Al4-O10 | 1.80 |
| Si3-O9 | 1.57 | Si4-O13 | 1.64 | Al3-O15 | 1.83 | Al4-O16 | 2.08 |
| Average bond length of Si-O: 1.54 Å | Average bond length of Al-O: 1.93 Å | ||||||
| Parameters | KOH Concentration (mol/L) | Reaction Temperature (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 240 | 260 | 280 | |
| M | 1.142 | 2.334 | 3.291 | 1.122 | 2.334 | 1.582 |
| 0.422 | 0.551 | 0.593 | 0.638 | 0.551 | 0.466 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Ma, H.; Luo, Z.; Ma, X.; Guo, Q. Synthesis of KAlSiO4 by Hydrothermal Processing on Biotite Syenite and Dissolution Reaction Kinetics. Minerals 2021, 11, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010036
Yuan J, Ma H, Luo Z, Ma X, Guo Q. Synthesis of KAlSiO4 by Hydrothermal Processing on Biotite Syenite and Dissolution Reaction Kinetics. Minerals. 2021; 11(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jiangyan, Hongwen Ma, Zheng Luo, Xi Ma, and Qian Guo. 2021. "Synthesis of KAlSiO4 by Hydrothermal Processing on Biotite Syenite and Dissolution Reaction Kinetics" Minerals 11, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010036
APA StyleYuan, J., Ma, H., Luo, Z., Ma, X., & Guo, Q. (2021). Synthesis of KAlSiO4 by Hydrothermal Processing on Biotite Syenite and Dissolution Reaction Kinetics. Minerals, 11(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010036






