Abstract
The quartz-vein-type Baiyinhan tungsten deposit is located at the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, NE China. Analyses of fluid inclusions, H-O isotope of quartz and Re-Os isotope of molybdenite were carried out. Three stages of mineralization were identified: The early quartz + wolframite + bismuth stage, the middle quartz + molybdenite stage and the late calcite + fluorite stage. Quartz veins formed in the three stages were selected for the fluid inclusion analysis. The petrographic observation and fluid inclusion microthermometry results revealed three types of fluid inclusions: CO2-H2O (C-type), liquid-rich (L-type) and vapor-rich (V-type). The homogenization temperatures of C-type, V-type and L-type inclusions were 233–374 °C, 210–312 °C, and 196–311 °C, respectively. The salinity of the three types of inclusions was identical, varying in the range of 5–12 wt%. The H-O isotope analyses results showed that quartz had δ18OH2O and δDSMOW compositions of −2.6‰ to 4.3‰ and −97‰ to −82‰, respectively, indicating that the ore-forming fluids were mainly derived from magmatic water with a minor contribution of meteoric water. The addition of meteoric water reduces the temperature and salinity of the ore-forming fluids, which leads to a decrease of the solubility of tungsten and molybdenum in the fluids and eventually the precipitation of minerals. Re-Os isotopic analysis of five molybdenite samples yielded an isochron age of 139.6 ± 7.6 Ma (2σ) with an initial 187Os of −0.05 ± 0.57 (MSWD = 3.5). Rhenium concentrations of the molybdenite samples were between 3.1 ug/g and 8.5 ug/g. The results suggest that the metals of the Baiyinhan deposit have a crust origin, and the mineralization is one episode of the Early Cretaceous tungsten mineralization epoch which occurred at the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt.
1. Introduction
The eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) in NE China is characterized by orogenic events of the Paleo-Asian domain superimposed by the magmatism of the Paleo-Pacific and Ohotsk Ocean tectonic domains, which resulted in extensive distribution of Mesozoic volcanic and granitic rocks together with widespread Cu, Mo, Au, Pb-Zn-Ag and Sn polymetal deposits [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. In recent years, an increasing number of tungsten deposits have been discovered in this region, revealing a great potential of large-scale tungsten mineralization.
The previous geochronology studies of the tungsten mineralization in eastern CAOB have shown Triassic, Jurassic and Early Cretaceous ages [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] and are in close association with the magmatic activities. The mineralization includes porphyry, skarn and quartz-type deposits. The quartz-vein-type tungsten deposits can be divided into two subtypes: Quartz-wolframite and quartz-scheelite vein types. The Baiyinhan quartz-vein-type tungsten deposit belongs to the quartz-wolframite subtype.
At present, there is no unified understanding of the precipitation mechanism of tungsten in ore-forming fluids, especially whether CO2 plays an important role in the migration and precipitation of tungsten. In this study, we selected the newly discovered Baiyinhan deposit, which has not been reported in any article to date. The Re-Os isotope test of molybdenite in the Baiyinhan quartz vein tungsten deposit was carried out to determine the ore-forming age and source of ore-forming materials. Fluid inclusions and quartz H-O isotopes were used to discuss the fluid evolution and fluid source of the deposit, especially the role of CO2 in the migration and precipitation of tungsten.
2. Geological Setting
The eastern CAOB is divided into four tectonic blocks: Erguna, Xing’an, Songliao and Jiamusi massifs, which are separated by the regional-scale Tayuan-Xiguitu, Hegenshan-Heihe and Mudanjiang faults, respectively [1] (Figure 1). The Baiyinhan tungsten deposit is located in the Liaoyuan massif and belongs to the southern part of the Da Hinggan Mountains polymetal metallogenic belt (SDMB) (Figure 2). The SDMB is bounded by the western Hegenshan Fault, the eastern Nenjiang Fault and the southern Xilamulun Fault (Figure 2). The SDMB is composed of the Permian strata and is overlain by the Mesozoic-Cenozoic volcanic and sedimentary rocks and intruded by Mesozoic intrusive rocks (Figure 2). The Permian strata are composed of four units [30]: (1) The Lower Permian Qingfengshan Formation, which consists of graywacke and siltstone with tuffaceous intercalation; (2) the Lower Permian Dashizhai Formation, which is mainly composed of submarine lava and tuff (andesitic, felsic and basaltic) with arenite; (3) the Lower Permian Huanggangliang Formation, which consists of mix-bedded sandstone and shale with limestone and tuffite; and (4) the Upper Permian Linxi Formation, which is mainly composed of terrestrial sandstone, siltstone and mudstone.
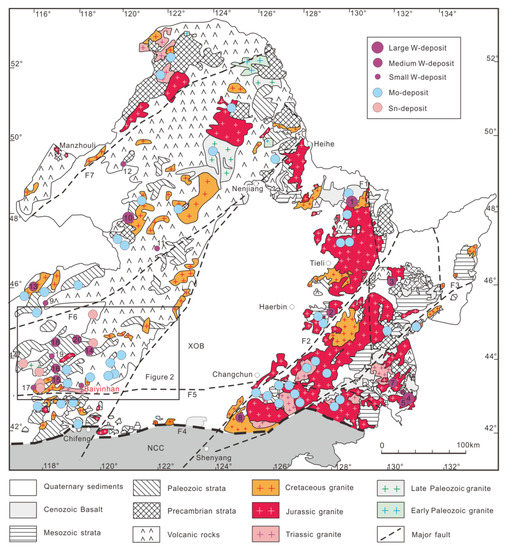
Figure 1.
Geological map of the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and distribution of tungsten deposits in NE China (modified from [3]). Fault: F1—Nengjiang Fault; F2—Yitong-Yilan Fault; F3—Dunhua-Mishan Fault; F4—Chifeng-Kaiyuan Fault; F5—Xilamulun River Fault; F6—Heganshan-Heihe Fault; F7—Xiguitu-Tayuan Fault. Locations: 1—Cuihongshan; 2—Gongpengzi; 3—Yangbishan; 4—Yangjingou; 5—Wudaogou; 6—Liudaogou; 7—Baishilazi; 8—Sanjiazi; 9—Dayana; 10—Honghuaerji; 11—Weilianhe; 12—Zishi; 13—Shamai; 14—Dongshanwan; 15—Xiaolaogualinzi; 16—Weilasituo; 17—Chamuhan; 18—Daolundaba; 19—Wulegerejidaban; 20—Xiaohaiqing.
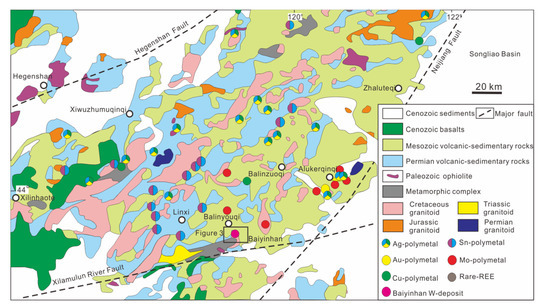
Figure 2.
Regional geological map of south DaHinggan mountains showing the distribution of the metal ore deposits (modified from [34,35]).
The Mesozoic formations include Jurassic and Cretaceous strata. The Jurassic strata are composed of conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, coal bed, volcaniclastic rock, tuff, rhyolite and dacite. The Cretaceous strata consist of andesite, volcaniclastic rock, tuff, tuff sandstone, siltstone and basal conglomerate. The Cenozoic corresponds to continental red strata. The Major structures are the Erlian-Hegenshan Fault, the Xilamulun River Fault and the Nenjiang Fault [31,32].
A scatter of a late Paleozoic granite is exposed at the Haolibao mine area and at the northern part of the Xilamulun River [33]. Mesozoic granites include Triassic, Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous granites [3]. The Mesozoic granites are characterized by low (87Sr/86Sr)i and high εNd(t) values, showing that juvenile crust materials are the major source of the Mesozoic granites [1].
The SDMB is an important polymetal metallogenic belt in China, and contains abundant porphyry Mo deposits, skarn Pb-Zn deposits, skarn Fe-Sn deposits, hydrothermal-vein-type Ag-polymetal, Sn-polymetal, Pb-Zn polymetal and Cu-polymetal deposits (Figure 2).
3. The Baiyinhan Tungsten Deposit
The Baiyinhan tungsten deposit occurs within the Yanshanian granite and is mainly composed of wolframite-bearing quartz veins (Figure 3). The Yanshanian granite (biotite granite, Figure 4A) is constituted of quartz (30–40%), K-feldspar (30–40%), plagioclase (~15%), biotite (~8%), and minor accessory minerals. The xenomorphic granular or granular quartz occurs as clusters, and the grain size varies from 0.2 mm to 2.0 mm. The grain size of K-feldspar varies from 0.5 mm to 2.0 mm and shows a xenomorphic granular texture. The grain size of plagioclase ranges from 0.5 mm to 1.5 mm. The tungsten mineralization at Baiyinhan is spatially confined to gently dipping faults, with a striking length of 10–150 m. The tungsten ore bodies occur mainly as quartz veins, and five ore bodies have been defined (Figure 3). The features of these ore bodies are similar.
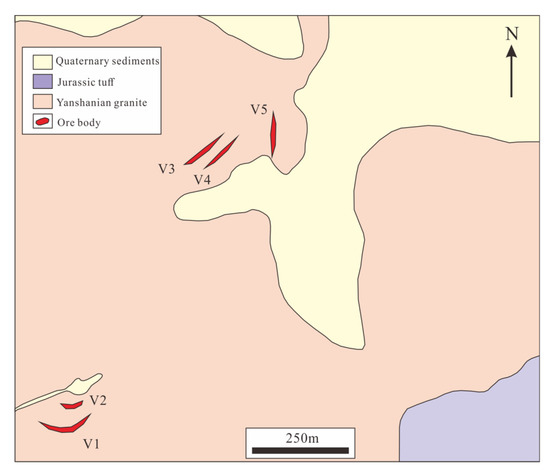
Figure 3.
Geological map of the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.

Figure 4.
Photographs of the biotite granite (A) and the mineralization (B–I) in the Baiyinhan deposit showing: (A) Biotite granodiorite; (B) Wolframite-bearing quartz vein within the granite (dipping to north); (C) Quartz + pyrite + wolframite vein; (D) Quartz + molybdenite + wolframite vein with drusy cavity; (E) Euhedral wolframite in greisen; (F) massive ore; (G) Bismuthinite in massive ore; (H) Veined wolframite in greisen; (I) Veined wolframite in quartz vein. Abbreviations: Bi—biotite, Pl—plagioclase, Kfs—K-feldspar, Mb—molybdenite, Py—pyrite, Gs—greisen, Qv—quartz vein, Qz—quartz, Wf—wolframite, Bm—bismuthinite.
The V1 ore body is located at the southwest part of the ore deposit. It strikes EW and dips north at angles of 10–15°, with a length of 150 m and thickness of 0.1–1.5 m (Figure 3). The V2 ore body is smaller and located at the north of the V1 ore body (Figure 3). It also strikes EW and dips north at an angle of 15°, but the scale of V2 ore body is smaller and thinner than the V1 ore body. The V3, V4 and V5 ore bodies are located at the northern part of ore deposit (Figure 3). The V3 and V4 ore bodies strike NE, and the V5 ore body strike NS. These three ore bodies dip northwest at angles of 12–20°, with a length of several tens to 150 m and thickness of 0.2–1.8 m. The orebody has a WO3 grade of 0.5–2.5%. These orebodies are mainly composed of tungsten-bearing quartz veins and minor greisen alteration rock.
The vein-type ore includes wolframite + pyrite + molybdenite (Figure 4C,D) and minor amounts of bismuthinite (Figure 4G). Gangue minerals consist of quartz and muscovite. The ore minerals occur in major veins and massive structures, along with minor drusy cavity structures (Figure 4F,H,I). The ore minerals are mainly euhedral and subhedral (Figure 4C–E,G). Alteration at Baiyinhan is well-developed and characterized by a fracture-controlled greisen alteration. A small proportion of tungsten mineralization occurs within the greisen (Figure 4E,H). Mineralogically, the greisen alteration comprises quartz and muscovite (Figure 4E).
Based on the structure, texture and mineralogy of the ore veins, three hydrothermal stages can be distinguished: (1) Wolframite + quartz vein stage; (2) molybdenite + quartz + pyrite stage and (3) calcite + fluorite stage. The first stage of quartz-wolframite veins contains significant amounts of disseminated wolframite and minor bismuthinite, accompanying intense greisen alteration. The quartz is typically milky white, coarse-grained, anhedral and fractured. The wolframite is also commonly fractured and is locally cemented together with fractured quartz that was formed during the second and third stages of activity. The second hydrothermal stage is characterized by an enrichment in pyrite and molybdenite. The third stage is characterized by coarse translucent euhedral calcite and fluorite crystals occurring in fractures and veinlets, which crosscut earlier formed veins.
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4.1. Samples
Thirty-six samples of quartz veins were collected from the open pit, all of which were collected from the V3, V4 and V5 ore bodies in the north of the ore deposit for the study of fluid inclusions shape, type, abundance and spatial distribution. Twenty-one of these samples were used for the analysis of microthermometry of fluid inclusions, and 10 samples were used for H-O isotope analysis. Five molybdenite samples were also collected from the ore pile for Re-Os geochronology analysis.
4.2. Analytical Methods
The microthermometric measurements on the fluid inclusions were carried out using a Linkam THMS 600 programmable heating-freezing stage combined with a Zeiss microscope at the China University of Geosciences, Beijing (CUGB), China. The process has been described in detail by Yu et al. [36]. Salinities of H2O-NaCl [37] and CO2-bearing [38] fluids were calculated using the final melting temperatures of ice (Tm-ice) and clathrate (Tm-cla). The pressure of the fluid inclusions was calculated according to Steele et al. [39].
The H-O isotope analyses were accomplished with a MAT253 mass spectrometer at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Oxygen was liberated from quartz through reaction with BrF5 [40] and converted to CO2 on a platinum-coated carbon rod. In accordance with the method described by Simon [41], H isotopic ratios of bulk fluid inclusions in quartz were measured by mechanically crushing ~5 g of quartz grains to a grain size of 1–5 mm. Samples were first degassed of labile volatiles and secondary fluid inclusions by heating under vacuum to 120 °C for 3 h. The released water was trapped and reduced to H2 by reaction with Zn. The analytical precision was better than ±0.2‰ (1σ) for δ18O and ±2‰ (1σ) for δD. H-O isotopic data were reported relatively to the Standard Mean Ocean Water standard. δ18OH2O of fluids were calculated using the equation for quartz-water isotopic equilibrium: 1000 × lnαquartz-water = (3.38 × 106)T−2 − 3.40, where T is the temperature in Kelvins [42], and the average fluid inclusion temperature of each stage was used to calculate the δ18OH2O value.
The Re-Os isotopic analyses were performed at the National Research Center of Geoanalysis, Chinese Academy of Geosciences. The details of the chemical procedure have been described by Du et al. [43,44], Shirey et al. [45] and Stein et al. [46] Five molybdenite samples from the Baiyinhan deposit were collected in the footrill. Microprobe screening of these samples revealed euhedral molybdenite crystals.
5. Results
5.1. Fluid Inclusion Petrography
Fluid inclusions were widely developed in the quartz veins (Figure 5). Most fluid inclusions were isolated or randomly clustered, had relatively regular shapes (polygonal, oval and semicircular) and were interpreted as primary in origin. However, secondary and pseudosecondary inclusions have also been observed as intergranular arrays or aligned along microfractures in transgranular crystal trails [47]. During this study, we focused on the primary inclusions. According to the composition of inclusions and the phase state at room temperature [47,48], fluid inclusions in the Baiyinhan deposit can be divided into three types: C-, L- and V-type (Figure 5). On the basis of the microthermometry results of fluid inclusions, the discussion of fluid evolution corresponded to the aforementioned three hydrothermal stages.
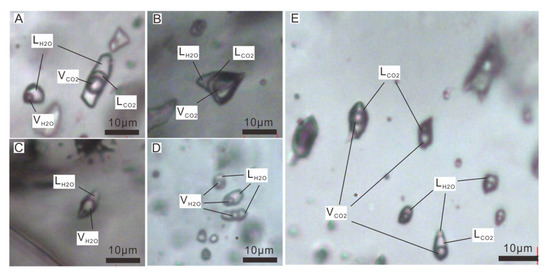
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of typical fluid inclusions in quartz from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit. (A) Liquid-rich C-type inclusion. (B) Vapor-rich C-type inclusion. (C) V-type inclusions. (D) Clustered L-type inclusions. (E) Clustered C-type inclusions. Abbreviation: LCO2 = liquid CO2; LH2O = liquid H2O; VCO2 = vapor CO2; VH2O = vapor H2O.
5.1.1. C-Type (CO2-H2O Inclusions)
C-type inclusions were irregular-shaped to rounded and were ~4–20 μm in size. They usually consisted of three phases at room temperature. In the first phase, the proportion of CO2 was less than 50% (Figure 5A). In the second phrase, the proportion of CO2 was more than 50% and the proportion of VCO2 was larger (Figure 5B). In the third phase, the proportion of CO2 was greater than 50% and the proportion of LCO2 was larger (Figure 5E). Although some inclusions showed only two phases at room temperature, they turned into three phases during cooling. C-type inclusions occurred mainly in veins of early stages. Based on the ratio of liquid to vapor, C-type inclusions can be divided into liquid-rich and vapor-rich inclusions. The liquid-rich inclusions were homogenized to the liquid phase, and the most vapor-rich inclusions were homogenized to the vapor phase.
5.1.2. L-Type (Liquid-Rich Inclusions)
The L-type fluid inclusions were found in quartz veins from all stages. Most L-type inclusions contained liquid and a vapor bubble that occupied ~5–45 vol% of the inclusion (Figure 5D,E). They occurred as irregular to rounded forms of ~4–19 μm in size (mainly 5–9 μm; Figure 5D). In the early stage, different from C-type inclusions, only three L-type inclusions were observed. The massive development of L-type fluid inclusions occurred in the middle and late stages.
5.1.3. V-Type (Vapor-Rich Inclusions)
The V-type fluid inclusions were rarely developed in all quartz veins. They contained two distinct phases, namely liquid H2O and vapor H2O. They were rounded rectangles, and the size ranged from ~3–12 μm (Figure 5C). The bubble usually accounted for >55 vol% of the inclusion. V-type fluid inclusions appeared mainly in the veins of middle and late stages.
5.2. Microthermometry
A summary of the microthermometric data obtained from fluid inclusions from the three mineralization stages is listed in Table 1, and the results are plotted in Figure 6.

Table 1.
Microthermometric data of fluid inclusions from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
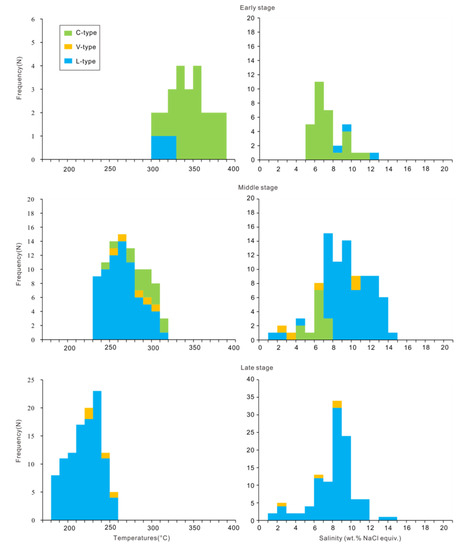
Figure 6.
Histograms of total homogenization temperatures and salinities of different fluid inclusions from the three stages in the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
In the quartz veins of the early stage, there were mainly C-type inclusions and only a few L-type inclusions. C-type inclusions yielded final melting temperatures of solid CO2 ranging from −63.9 to −60.8 °C, lower than the pure CO2 critical point of −56.6 °C. The melting temperatures of the clathrate were 3.9–7.9 °C, and the corresponding salinity were 4.14–10.72 wt% NaCl equiv. The homogenization temperatures of the CO2 phase were 28.1–31.1 °C, and the final homogenization temperatures ranging from 294 °C to 374 °C. Only three L-type inclusions were found in quartz from this stage, yielding ice-melting temperatures ranging from −8.1 °C to −4.4 °C, corresponding to salinities of 7.02–11.82 wt% NaCl equiv. The final homogenization temperatures ranged ~299–311 °C, and the bulk densities of the inclusions were 0.79–0.82 g/cm3. The pressure of L-type inclusions was ~80–92 bars.
The middle stage was dominated by L-type and C-type inclusions with minor V-type inclusions. C-type inclusions yielded final melting temperatures of solid CO2 ranging from −62.2 °C to −60.9 °C, indicating the presence of minor concentrations of other volatiles. The melting temperatures of the clathrate were 6.4–8.1 °C and the corresponding salinity were 3.19–6.81 wt% NaCl equiv. Partial homogenization of CO2 phases occurred between 27.9 °C and 31.1 °C, and the final homogenization temperatures ranged ~233–305 °C. L-type inclusions yielded ice-melting temperatures ranging from −9.5 °C to −0.5 °C, corresponding to salinities of 0.88–13.40 wt% NaCl equiv. The final homogenization temperatures ranged ~228–298 °C, and the bulk densities of the inclusions ranged 0.78–0.93 g/cm3. The pressure of L-type inclusions was ~25–82 bars. V-type inclusions were the least abundant, yielding ice-melting temperatures ranging from −6.6 °C to −0.6 °C, corresponding to salinities of 1.05–9.98 wt% NaCl equiv. The final homogenization temperatures ranged ~248–297 °C, and the bulk densities of the inclusions ranged 0.72–0.88 g/cm3. The pressure of V-type inclusions was ~35–82 bars.
The late stage was dominated by L-type inclusions with minor V-type inclusions. L-type inclusions yielded ice-melting temperatures ranging from −9.4 °C to −0.3 °C, corresponding to salinities of 0.53–13.29 wt% NaCl equiv. The final homogenization temperatures ranged ~171–244 °C, and the bulk densities of the inclusions ranged 0.84–0.96 g/cm3. The pressure of L-type inclusions was ~8–34 bars. Only four L-type inclusions were found in the late stage, yielding ice-melting temperatures ranging from −5.0 °C to −0.6 °C, corresponding to salinities of 1.05–7.86 wt% NaCl equiv. The final homogenization temperatures ranged ~210–245 °C, and the bulk densities of the inclusions ranged 0.81–0.91 g/cm3. The pressure of V-type inclusions was ~14–36 bars.
5.3. H-O Isotopes
Among the 21 quartz vein samples that were analysed for microthermometry, 9 of them were selected and analysed for the O (quartz) and H (fluid inclusions) isotopes. The H-O isotope ratios are listed in Table 2. The δ18O and δD values of hydrothermal quartz samples ranged 8.5–10.2‰ and −97‰ to −92‰, respectively. The calculated δ18OH2O of fluids varied from −2.6‰ to 4.3‰.

Table 2.
Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of quartz from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
5.4. Re-Os Isochron Ages
The abundance of Re and Os and the osmium isotopic compositions of molybdenite from the quartz-vein-type ores of Baiyinhan are shown in Table 3. The concentration range of Re was 3108–8486 ng/g and that of 187Os was 4.52–12.53 ng/g. The Baiyinhan tungsten deposit had low Re and Os contents. The Re content of the Baiyinhan deposit was less than that in the porphyry Mo deposit (where the average value ranged from 14–68 µg/g) [49]. Five samples gave a model age of 137–141 Ma and a weight mean age of 138.8 ± 1.6 Ma (Table 3). Data, processed using the ISOPLOT/Ex program [50], yielded an isochron age of 139.6 ± 7.6 Ma and with MSWD = 3.5 (Figure 7).

Table 3.
Re-Os isotope data for molybdenite samples from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
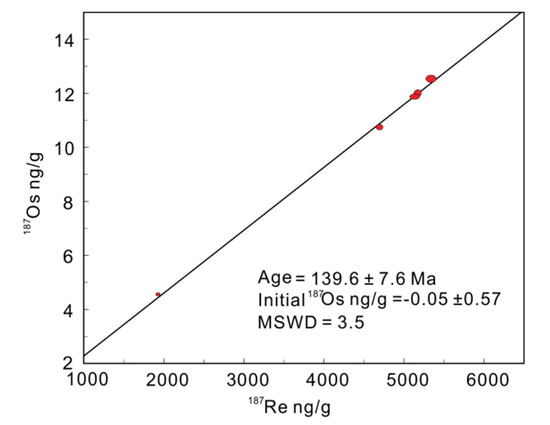
Figure 7.
Re-Os isochron plot for molybdenite samples from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
6. Discussion
6.1. Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids-the Important Role of CO2
The study of fluid inclusions shows that the ore-forming fluid of the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit is a NaCl-H2O-CO2 system with medium temperature and low salinity. The temperature of the fluid gradually decreased from the early stage to the late stage. As indicated from the types and abundance of fluid inclusions in the three stages, the early stage was mainly characterized by high-temperature CO2-rich inclusions, and the middle stage was mainly composed of gas-liquid two-phase inclusions, while the late stage only contained low-temperature gas-liquid two-phase inclusions. The content of CO2 in the ore-forming fluid tended to decrease with the evolution of the fluid.
CO2 is the most abundant gas composition in fluid inclusions in many typical wolframite deposits [52,53]. Rios et al. [54], Li et al. [55] and Chen et al. [48] also found primary fluid inclusions containing CO2 in wolframite, which shows that CO2 is closely related to the dissolution and migration of tungsten. Experimental research has shown that the carbonate or CO2 in the fluid is conducive to the dissolution and migration of tungsten [52,56,57]. Higgins [58] stated that tungsten may migrate in the form of carbonate and bicarbonate in CO2-rich fluids under the condition of high temperature and high pressure. The experimental study on the crystallization of tungsten-manganese ore in alkali carbonate solution showed that tungsten exists mainly in the form of WO42− in the hydrothermal system, and the solubility of wolframite is affected by the pH value of the system. The effect of alkali carbonate or CO2 on the solubility of wolframite cannot be attributed to complexation because it can affect the pH value of the fluid, resulting in the change of tungsten solubility [55]. At the same time, CO2 can act as pH buffer [59,60], and the high content of CO2 in the fluid can maintain the stability and enhance the migration of tungsten [61].
It can be seen from the pressure calculation of the three stages (Table 1) that the pressure of the fluid inclusion gradually decreased. A large number of liquid-rich inclusions were developed in the deposit. There was an obvious negative correlation between density and homogenization temperature (Figure 8). These characteristics may have been caused by the CO2 dissipation during the process of temperature and pressure reduction, resulting in the gradual decrease of CO2 content and increase of fluid density, and the evolution of fluids into a NaCl-H2O system [62,63,64]. The CO2-rich fluid formed during the hydrothermal differentiation in the late magmatism can carry sufficient ore-forming element tungsten. During the migration of ore-forming fluid along the fractures developed in the area, the addition of meteoric water precipitation and decrease of temperature and pressure leads to the immiscibility of the fluid. The escape of CO2 results in the change of pH and the decrease of the solubility of tungsten, which leads to the precipitation and enrichment of WO42− in the ore-forming fluid by combining with cations such as Fe2+ and Mn2+ [65,66,67,68]. The dilution and escape of CO2 can effectively enrich the ore-forming elements and even cause the fluid to supersaturate in an instant [69,70]. The content of CO2 in the ore-forming fluid of the Baiyinhan deposit tends to decrease with the evolution of the fluid, which is similar to that of the Grey River tungsten deposit and Parrila tungsten-tin deposit [71,72]. It also further explains the important role of CO2 in tungsten migration, and that the precipitation and enrichment of wolframite were closely related to the dispersion of CO2 at the Baiyinhan deposit.
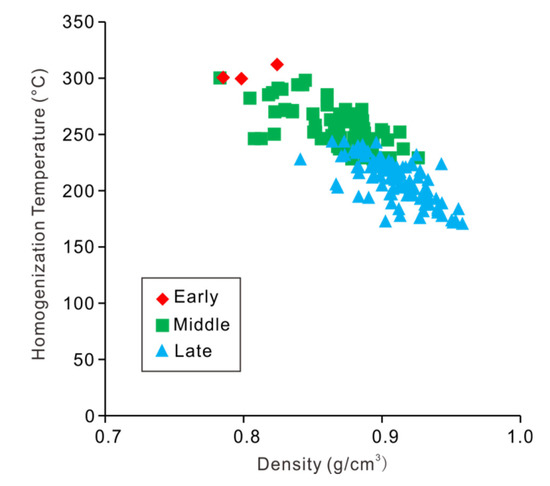
Figure 8.
Temperature-density diagram for fluid inclusions from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit.
6.2. Source of Ore-Forming Fluids and Materials
The H-O isotopes of fluid inclusions show that the samples from three stages have an obvious evolutionary trend, gradually transitioning from early residual magmatic water to late meteoric water (Figure 9). The three samples in the early stage were plotted in the lower part of the residual magma water, and their δD values were lower than the range of the residual magma water. There are two possible explanations for the low fluid δD value for the Baiyinhan deposit: One is the existence of CH4 observed from the Raman test of fluid inclusions and the hydrogen isotope exchange between CH4 and H2 in the fluid, which leads to the fluid depletion of δD [73]. However, in the hydrothermal system containing CH4, the proportion of water was much larger than that of CH4 and H2. Therefore, this process has a trivial impact on hydrogen isotope production [73]. Another possibility is that in actual geological conditions, when magma intrudes into the shallow part of the surface, it is likely to mix with meteoric water directly or indirectly [74]. The mixing of meteoric water and magmatic water has a significant impact on H-O isotopes, and the effect on hydrogen is generally greater than that on oxygen [75]. The second possibility well explains the fact that the δD values of H-O isotopes in quartz in the early stage of the deposit consistently fell in the lower part of the residual magmatic water. Therefore, we conclude that the initial fluid of the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit was a mixture of residual magmatic water and meteoric water. With the migration and evolution of the fluid, the proportion of meteoric water gradually increased.
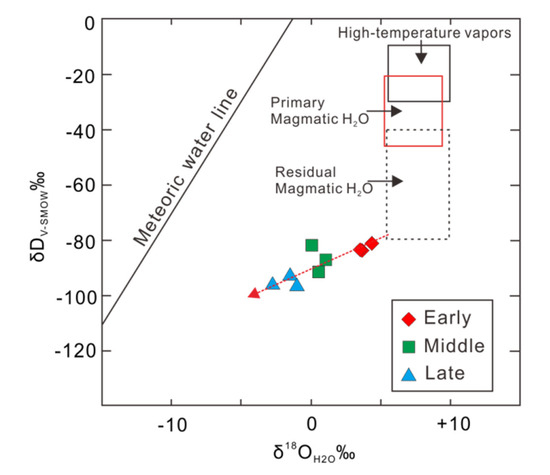
Figure 9.
The quartz δD versus δ18OH2O diagram of the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit (Primary Magmatic H2O after Taylor, [76]; high-temperature vapours after Giggenbach, [77]; residual magmatic H2O after Taylor, [73]).
The Re content in molybdenite from the W-Mo-bearing quartz veins in the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit is consistent with many porphyry Mo deposits but is significantly smaller than those from porphyry Cu-Mo deposits [78]. The average Re contents of molybdenites from porphyry Cu–Mo deposits and porphyry Mo deposits range from 118–19,800 ug/g, and 4–68 ug/g, respectively [76]. The Re content in molybdenites decreases gradually from the mantle source to a mixture of mantle and crust and then to the crustal source [79,80]. The Re contents of molybdenite from the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit ranged from 3.1–8.4 ug/g with an average of 7.1 ug/g (Table 3). The relatively lower Re contents of molybdenites form the Baiyinhan tungsten deposit may indicate that the ore-forming materials source of the ore-bearing quartz vein was a crust source.
6.3. The Significance of Re-Os Age of the Baiyinhan Tungsten Deposit
The analysis of five molybdenite samples yielded an isochron age of 139.6 ± 7.6 Ma with an initial 187Os of − 0.05 ± 0.57. It was shown that the initial 187Os values from the molybdenite were close to zero, and the Re-Os isochron ages reflected the time of sulfide deposition [46,79,80]. Some W (-Mo) deposits were discovered in the eastern part of the CAOB in recent years. The ages of W (-Mo) mineralization in the eastern part of the CAOB were reported and recognized in three periods (Figure 10): Triassic (~230 Ma), Early-Middle Jurassic (198–170 Ma) and Early Cretaceous (~140 Ma). The Baiyinhan deposit was formed in the early Cretaceous with an Re-Os age of 139.6 ± 7.6 Ma, which further indicates that the early Cretaceous is an important metallogenic period with great metallogenic prospect in the eastern part of the CAOB.
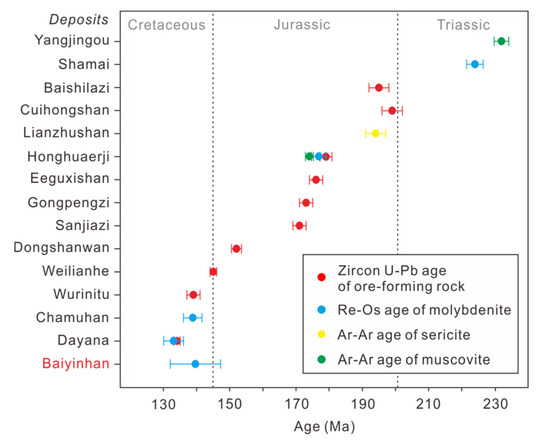
Figure 10.
Ages of W-(Mo) deposits in NE China (data from [11,23,81,82,83,84,85,86] and this paper).
7. Conclusions
(1). The Baiyinhan quartz vein tungsten deposit occurs within the Yanshanian granite. The ore mineral assemblage is wolframite + pyrite + molybdenite ± bismuthinite. The greisen is the main hydrothermal alteration in the deposit.
(2). The thermometric analysis of inclusions showed that the fluid presented a medium-temperature and a low-salinity H2O-CO2-NaCl system. The ore-forming temperature in the three stages gradually decreased, and the CO2 content gradually decreased with the fluid evolution. The mineralization was closely related to CO2 dispersion. The H-O isotope of quartz showed that the ore-forming fluid was a mixture of residual magmatic water and meteoric water.
(3). Five molybdenite samples yielded an isochron age of 139.6 ± 7.6 Ma (MSWD = 3.5), and model ages for individual analyses ranged from ~138–141Ma. Combined with the regional mineralization age data, the tungsten mineralization of the Baiyinhan deposit indicates that the Early Cretaceous is an important tungsten mineralization epoch in the eastern CAOB.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.W. and Q.Z.; formal analysis, R.W.; investigation, R.W., Q.Z. and Y.G.; resources, Q.Z. and J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, R.W.; writing—review and editing, Q.Z. and Z.Z.; visualization, R.W.; supervision, Q.Z.; funding acquisition, Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91962104) and the National Key Research Project of China (Grant No. 2017YFC0601306).
Acknowledgments
We thank Fangming Lai and Xiaoping Zhang from Chifeng Jinghong Mining Company for their help in the field work. We are also grateful to anonymous reviewers for constructive suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Ge, W.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Grant, M.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Jahn, B.M. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Liu, J.M.; Yu, C.M.; Ye, J.; Liu, H.T. Metal DEPOSITS in the Da Hinggan Mountains, NE China: Styles, characteristics, and exploration potential. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 846–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Liu, J.M.; Chu, S.X.; Wang, Y.B.; Sun, Y.; Duan, X.X.; Zhou, L.L. Mesozoic molybdenum deposits in the East Xingmeng orogenic belt, northeast China: Characteristics and tectonic setting. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 54, 1843–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Qin, K.Z.; Liu, J.M.; Li, G.M.; Zhai, M.G.; Chu, S.X.; Guo, Y.P. Porphyry molybdenum deposits in the Tianshan–Xingmeng orogenic belt, northern China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 991–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.G.; Mao, J.W.; Santosh, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Wu, Y.; Hou, L. Geodynamic setting of Mesozoic magmatism in NE China and surrounding regions: Perspectives from spatio–temporal distribution patterns of ore deposits. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 78, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Pei, F.P.; Wang, F.; Meng, E.; Ji, W.Q.; Yang, D.B.; Wang, W. Spatial–temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 74, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.G.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.J.; Men, L.J.; Li, Y.X.; Chai, P.; Yang, F. Timing of formation and geological setting of low-sulphidation epithermal gold deposits in the continental margin of NE China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 608–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.S.; Lei, E.; Zhao, H.L.; Wang, H.; Ju, N. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and ore genesis of Yangjingou large scheelite deposit in Yanbian area, NE China. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2010, 40, 764–772. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.S.; Niu, J.P.; Lei, E.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Geological&geochemical Characteristics and metallogenesis of Sanjiazi scheelite deposit in Siping area. Jilin Province. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2010, 40, 314–320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.S.; Ju, N.; Zhao, H.L.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.Q.; Wu, C.Z. Geological characteristics and fluid inclusions of Wudaogou lode scheelite deposit in eastern Yanbian, Jilin Province. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2011, 41, 1736–1744. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, A.P.; Wang, Y.J.; Qin, D.J.; She, H.Q.; Han, Z.G.; Guan, J.D.; Kang, Y.J. Metallogenic and diagenetic age of Honghuaerji tungsten polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 428–439. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, A.P.; She, H.Q.; Chen, Y.C.; Qin, D.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Han, Z.G.; Kang, Y.J. Ar-Ar age of muscovite from the greisenization alteration zones of the Honghuaerji tungsten polymetallic deposit, inner Mongolia, and its geological significance. Rock Miner. Anal. 2016, 35, 108–116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, A.P.; Chen, Y.C.; She, H.Q.; Li, G.M.; Li, Y.X. Geochronology and geochemical characteristic of biotite granite of the Dayana W-Mo deposit in Dong Uj imqin banner, inner Mongolia, and its geological significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 107–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, A.P.; Chen, Y.C.; She, H.Q.; Li, G.M.; Li, Y.X. Chronology and geochemical characteristics of granite in Weilianhe of Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Geol. China 2018, 45, 963–976. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Li, J.W.; Chang, Y.L.; Han, Z.G.; Dong, X.Z.; Yang, Y.C.; Tian, J.; She, H.Q.; Xiang, A.P.; Kang, Y.J. Genetic types and ore-forming geological significance of granites in the Honghuaerji scheelite deposit, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2015, 34, 322–342. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Li, J.W.; Huang, M.H.; Guo, W.J.; Dong, X.Z.; Tian, J.; Yang, Y.C.; She, H.Q.; Xiang, A.P.; Kang, Y.J. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid in Honghuaerji scheelite deposit, Inner Mongolia. Miner. Depos. 2016, 35, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Fu, C.; Tang, W.L.; Li, H.M.; Lin, Y.X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.G.; Zhao, Z.L.; Dang, Z.C.; Zhao, L.J. The metallogenic age of the Shamai wolframite deposit in Dong Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Bull. China 2016, 35, 524–530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Z.; Wu, G.; Li, T.G.; Liu, R.L.; Wu, L.W.; Zhang, P.C.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.C. LA-ICP-MS zircon and cassiterite U-Pb ages of Daolundaba copper-tungstentin deposit in Inner Mongolia and their geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2018, 37, 225–245. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.P.; Ren, Y.S.; Hao, Y.J.; Lai, K.; Zhao, H.L.; Liu, J. Genesis and Material Source of Scheelite of Yangbishan Iron-Tungsten Deposit in Heilongjiang, NE China. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2018, 48, 105–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.P. Geological characteristics and genesis study of Xiaolaogualinzi W-Mo polymetallic deposit in Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2018, 32, 276–282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Jiang, S.H. Geological setting and origin of Mo–W–Cu deposits in the honggor–shamai District, inner Mongolia, North China. Resour. Geol. 2011, 61, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Ding, Z.J.; He, M.C.; Yao, S.Z.; Zhu, B.P.; Shen, J.; Chen, B. Two epochs of magmatism and metallogeny in the Cuihongshan Fe-polymetallic deposit, Heilongjiang Province, NE China: Constrains from U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology and Lu-Hf isotopes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 143, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Sun, Y.; Chu, S.X.; Duan, X.X.; Liu, J.M. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Dongshanwan porphyry Mo-W deposit, Northeast China: Implications for the Late Jurassic tectonic setting. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 97, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Song, Z.; Dong, X.; Tian, J.; Yang, Y.; She, H.; Xiang, A.; Kang, Y. Sm-Nd dating and REE Composition of scheelite for the Honghuaerji scheelite deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northeast China. Lithos 2016, 261, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-H.; Bagas, L.; Hu, P.; Han, N.; Chen, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H. Zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the highly fractionated granite with tetrad REE patterns in the Shamai tungsten deposit in eastern Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the timing of mineralization and ore genesis. Lithos 2016, 261, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.; Chen, Y.; Bagas, L.; She, H.; Kang, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, C. Molybdenite Re-Os and U-Pb zircon dating and genesis of the Dayana W-Mo deposit in eastern Ujumchin, Inner Mongolia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Santosh, M.; Jin, Z.; Wen, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, L. Highly differentiated magmas linked with polymetallic mineralization: A case study from the Cuihongshan granitic intrusions, Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China. Lithos 2018, 302, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, F.F.; Liu, J.J.; Xue, C.J.; Zhang, Z.C. Genesis of the Wurinitu W-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia, northeast China: Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions and isotope systematics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Mi, K.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Liu, J.; Jia, W.; He, S. Deposit geology, geochronology and geochemistry of the Gongpengzi skarn Cu-Zn-W polymetallic deposit, NE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Neimongol Autonomous Region (BGMR). Regional Geology of Neimonggol Autonomous Region; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991; 532p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Geological Information Were Discovered and Their Plate Tectonic Significance on the Northern Bank of Xarmoron River. Geol. Inn. Mong. 1999, 90, 6–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.J.; Liu, W.S.; Wang, X.C.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, J.M.; Zhao, X.P.; Li, R.L. Geophysical characteristics of Daxinganling gravitational gradient zone in Eastern China and its geodynamic mechanism. Chin. J. Geophys. 2005, 48, 86–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Liu, J.M.; Liu, H.T. Geology and geochemistry of the Bianbianshan Au-Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn deposit, Southern Da Hinggan mountains, Northeastern China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2012, 86, 630–639. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Liu, J.M.; Chu, S.X.; Guo, Y.P.; Gao, S.; Guo, L.X.; Zhai, Y.Y. Poly-metal mineralization and exploration potential in southern segment of the Da Hinggan mountains. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2016, 46, 1100–1123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, G.G.; Jin, W.L.; De, H.Z.; Fei, X.; Han, B.X.; Shuai, J.W.; Tian, L.J. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of igneous rocks from the Dongbulage porphyry Mo deposit, Great Hinggan Range, NE China: Constraints from geology, geochronology, and isotope geochemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 120, 103326. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Zeng, Q.; Frimmel, H.E.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Sun, G.; Zhou, T.; Li, J. Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, northeastern North China Craton: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and pyrite trace element concentrations. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 313–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, R.J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.F. Gas hydrates in CO2-bearing fluid inclusions and the use of freezing data for estimation of salinity. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.M.; Lecumberri, S.P.; Bodnar, R.J. HokieFlincs_H2O-NaCl: A Microsoft Excel spreadsheet for interpreting microthermometric data from fluid inclusions based on the PVTX properties of H2O-NaCl. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 49, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.N.; Mayeda, T.K. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1963, 27, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, K. Does δD from fluid inclusion in quartz reflect the original hydrothermal fluid? Chem. Geol. 2001, 177, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.N.; O’Neil, J.L.; Mayeda, T.K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.D.; He, H.L.; Yin, N.W.; Zou, X.Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Sun, D.Z.; Cheng, S.Z.; Qu, W.J. A study of the rhenium-osmium geochronometry of molybdenites. Acta Geol. Sin. 1994, 68, 339–347. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, A.D.; Wu, S.Q.; Sun, D.Z.; Wang, S.X.; Qu, W.J.; Markey, R.; Stein, H.; Morgan, J.; Malinovskiy, D. Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials: Molybdenite HLP and JDC. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2004, 28, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirey, S.B.; Walker, R.J. Carius tube digestion for low-blank rhenium-osmium analysis. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.J.; Markey, R.J.; Morgan, J.W.; Du, A.; Sun, Y. Highly precise and accurate Re-Os ages for molybdenite from the East Qinling molybdenum belt, Shanxi Province, China. Econ. Geol. 1997, 92, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.Z.; Fan, H.R.; Ni, P.; Ou, G.X.; Shen, K.; Zhang, W.H. Fluid Inclusions; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 1–450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.L.; Ni, P.; Li, W.S.; Ding, J.Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, Y.L. The link between fluid evolution and vertical zonation at the Maoping tungsten deposit, Southern Jiangxi, China: Fluid inclusion and stable isotope evidence. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 192, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzina, A.N.; Sotnikov, V.I.; Economou, E.M.; Eliopoulos, D.G. Distribution of rhenium in molybdenite from porphyry Cu-Mo and Mo-Cu deposits of Russia (Siberia) and Mongolia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2005, 26, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. Users Manual for Isoplot/Ex rev. 2.49; Geochronological Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 1a, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Smoliar, M.I.; Walker, R.J.; Morgan, J.W. Re-Os ages of groupⅡA, ⅢA, ⅣA, and ⅣB iron meteorites. Science 1996, 271, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Ma, D.S. Geochemistry of Tungsten; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987; pp. 1–222. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.A.; Samson, I.M. The hydrothermal geochemistry of tungsten in granitoid environments: I. relative solubilities of ferberite and scheelite as a function of T, P, pH, and mNaCl. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 143–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, F.J.; Villas, R.N.; Fuzikawa, K. Fluid evolution in the Pedra Preta wolframite ore deposit, Paleoproterozoic Musa granite, eastern Amazon craton, Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2003, 15, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhao, Z.; Chou, I.M. Roles of carbonate/CO2 in the formation of quartz-vein wolframite deposits: Insight from the crystallization experiments of huebnerite in alkal-icarbonate aqueous solutions in a hydrothermal diamond-anvil cell. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 95, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Zhang, B.; Han, Y.W. An experimental study on the partitioning of tungsten between aqueous fluid and silicate melts. Geochimica 1992, 3, 272–281. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Li, J.K.; Zhao, Z. A preliminary experimental study of the crystallization of wolframite using hydrothermal diamond anvil cell. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 159–166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, N.C. Fluid inclusion evidence for the transport of tungsten by carbonate complex in hydrothermal solutions. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1980, 17, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, S.E.; Ohmoto, H. Chemical evolution and mineral deposition in boiling hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.N.; Evans, K.A. Role of CO2 in the formation of gold deposits. Nature 2004, 429, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.B.; Zhang, D.H.; Wang, C.S.; Zhao, G.J. Characteristics of fluid inclusion for typical tungsten, stannary vein deposit and porphyry molybdenum deposit in China. Guilin Ligong Daxue Xuebao 2011, 31, 524–532. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Linnen, R.L.; Williams, J.A.E. The evolution of pegmatite-hosted Sn-W mineralization at Nong Sua, Thailand: Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Ni, P.; Yuan, S.D.; Wu, S.H. Fluid inclusion studies of the Huangsha quartz-vein type tungsten deposit, Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 122–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Feng, C.Y.; Li, D.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, Z.L. Fluid inclusions characteristics and ore genesis of Taoxikeng tungsten and tin deposit in Chongyi County, Jiangxi Province. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2012, 42, 374–383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Spycher, N.F.; Reed, M. Evolution of a broadlands-type epithermal ore fluid along alternative P-T paths: Implications for the transport and deposition of base, precious, and volatile metals. Econ. Geol. 1989, 84, 328–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, C.S.; Yun, S.T. Origin and evolution of W-Mo-producing fluids in a granitic hydrothermal system: Geochemical studies of quartz vein deposits around the Susan Granite, Hwanggangri District, Republic of Korea. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupner, T.; Kempe, U.; Dombon, E.; Pätzold, O.; Leeder, O.; Spooner, E.T.C. Fluid regime and ore formation in the tungsten (-yttrium) deposits of Kyzyltau (Mongolian Altai): Evidence for fluid variability in tungsten-tin ore systems. Chem. Geol. 1999, 154, 21–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, L.N.; Zeng, Z.L.; Liu, C.H.; Xu, H. Metallogenic fluid study of the Yanqian skarn type tungsten deposit in eastern Nanling region. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 2485–2507. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.H. Some new advances in ore-forming fluid geochemistry on boiling and mixing of fluids during the progress of hydrothermal deposits. Adv. Earth Sci. 1997, 12, 546–552. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Hinsberg, V.J.; Berlo, K.; Migdisov, A.A.; Williams, J.A.E. CO2-fluxing collapses metal mobility in magmatic vapour. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2016, 2, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Higgins, N.C.; Kerrich, R. Progressive 18O depletion during CO2 separation from a carbon dioxide-rich hydrothermal fluid: Evidence from the Grey River tungsten deposit, Newfoundland. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1982, 19, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangas, J.; Arribas, A. Hydrothermal fluid evolution of the Sn-W mineralization in the Parrilla ore deposit (Caceres, Spain). J. Geol. Soc. 1988, 145, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 843–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, R.O.; Ohmoto, H. Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: A review. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.L. Solubilities of ore minerals. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 404–460. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.E. Degassing of H2O from rhyolite magma during eruption and shallow intrusion, and the isotopic composition of magmatic water in hydrothermal systems. Magmatic contributions to hydrothermal systems. Geol. Surv. Jpn. Rep. 1992, 279, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along convergent plate boundaries and their origin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 113, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Guo, F.; Zhou, L.L.; Duan, X.X. Two periods of mineralization in Xiaoxinancha Au-Cu deposit, NE China: Evidences from the geology and geochronology. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Du, A.D. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenites in the Xiaoliugou W (Mo) deposit in the northern Qian mountains and its geological significance. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1999, 63, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Du, A.; Seltmann, R.; Yu, J.J. Re–Os ages for the Shameika porphyry Mo deposit and the Lipovy Log rare metal pegmatite, central Urals, Russia. Miner. Depos. 2003, 38, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Ren, Y.S.; Ju, N.; Wang, H.; Hou, K.J. Geochronology and geochemistry of metallogenic intrusion in Baishilazi tungsten deposit of eastern Yanbian area, Northeast China. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2011, 41, 1726–1735. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.J.; Ren, Y.S.; Zhao, H.L.; Zou, X.T.; Chen, C.; Hou, Z.S.; Qu, W.J. Re-Os isotopic dating of the molybdenite from the Cuihongshan W-Mo polymetallic deposit in Heilongjiang province and its geological significanc. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2013, 43, 1840–1850. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. The Geological Characteristics and Prospecting Direction of Gongpengzi Cu-Zn-W Deposit in Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.S. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Iron Polymetallic Orefield in Ergu Area, Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.L. Ore Genesis and Geodynamic Settings of Tungsten Deposits in Eastern Jilin and Heilongjiang Provinces. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Sun, J.G.; Tang, C.; Men, L.J.; Li, Y.X.; Cui, P.L. Petrogenic and metallogenic geochronology and its geological implications of Lianzhushan gold deposit, Jiayin, Heilongjiang Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 8, 2435–2449. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).