Role of Mg Impurity in the Water Adsorption over Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates: A DFT-D Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Methods
3. Computational Results
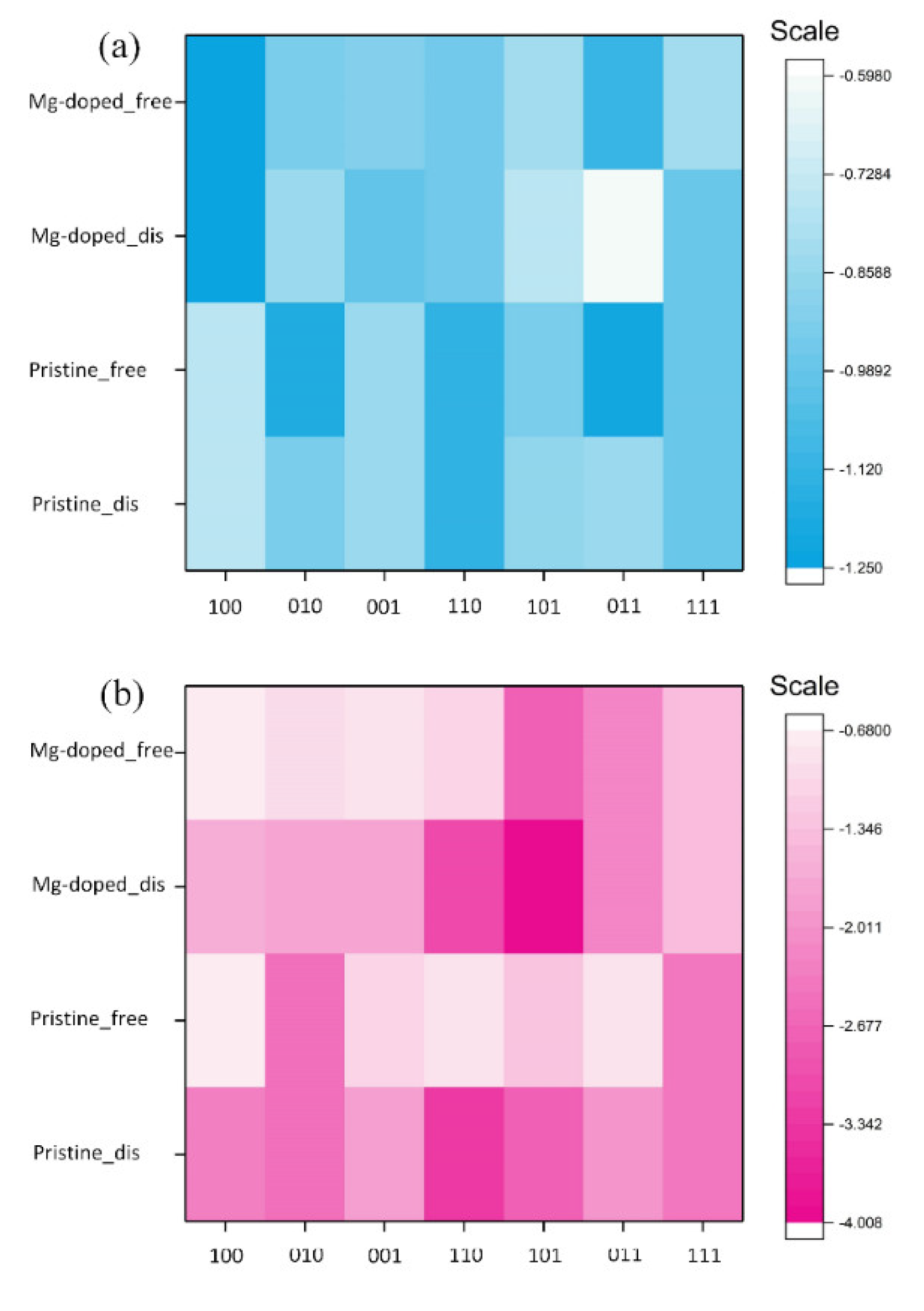
3.1. Impurity Formation Energy
3.2. Adsorption Energy
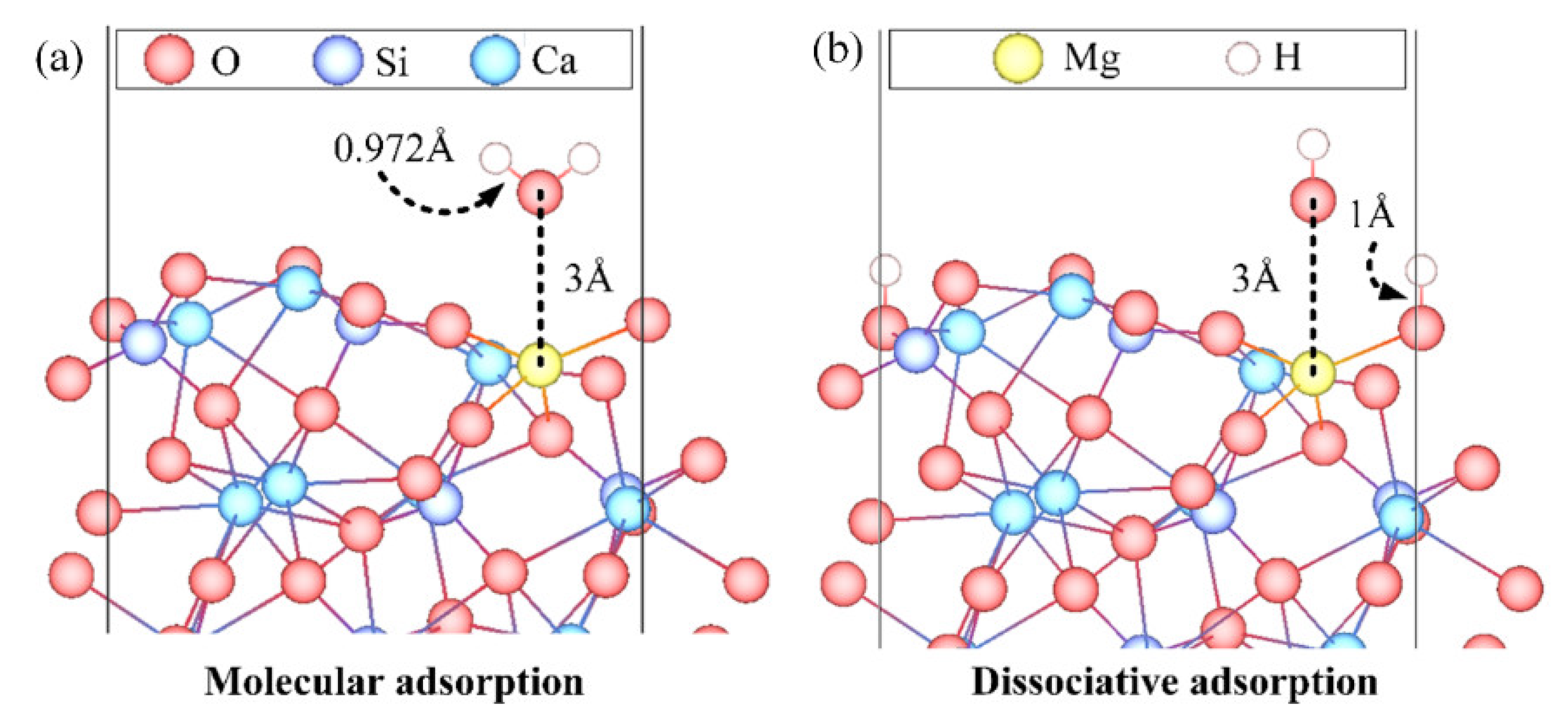
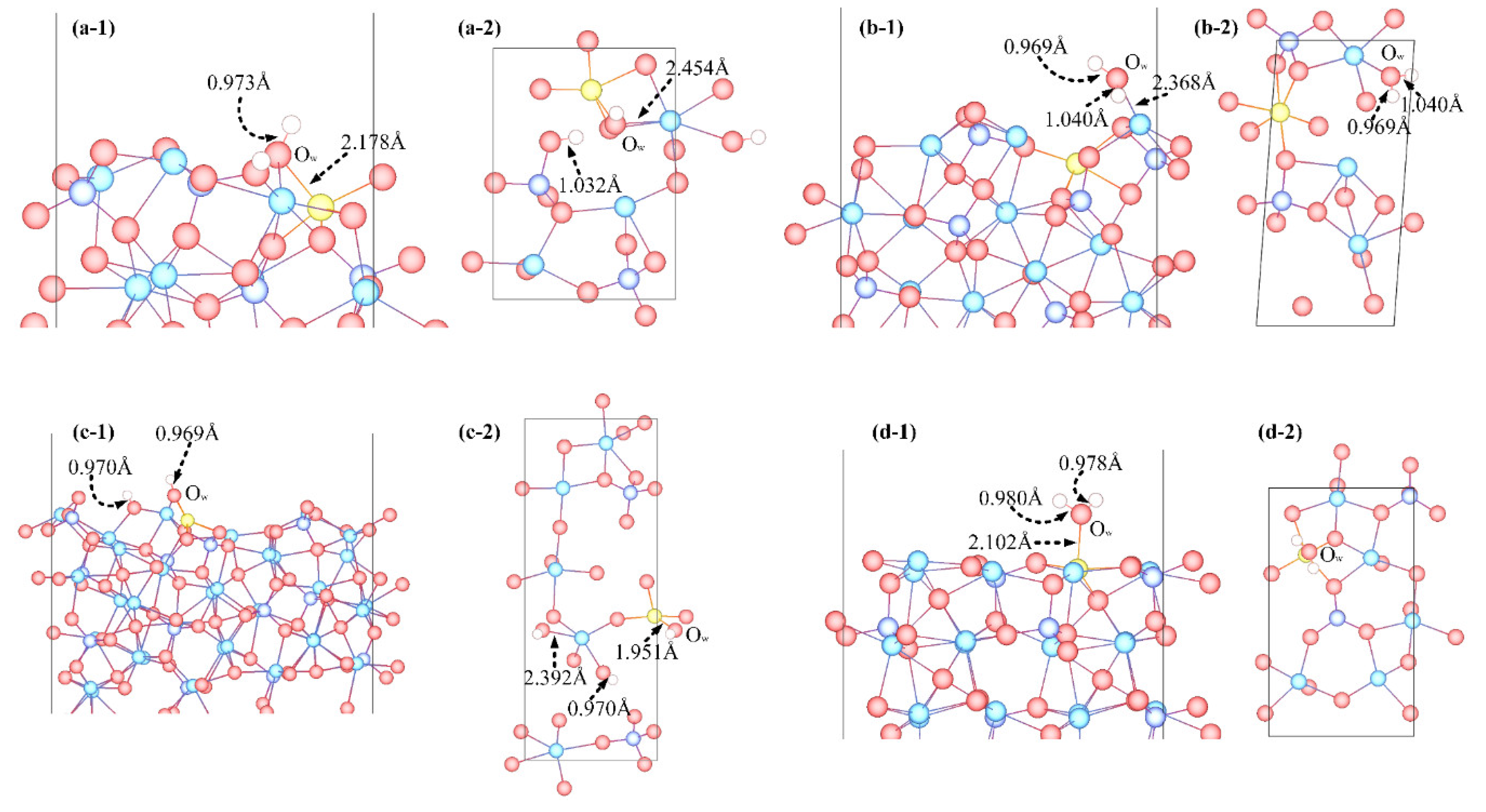
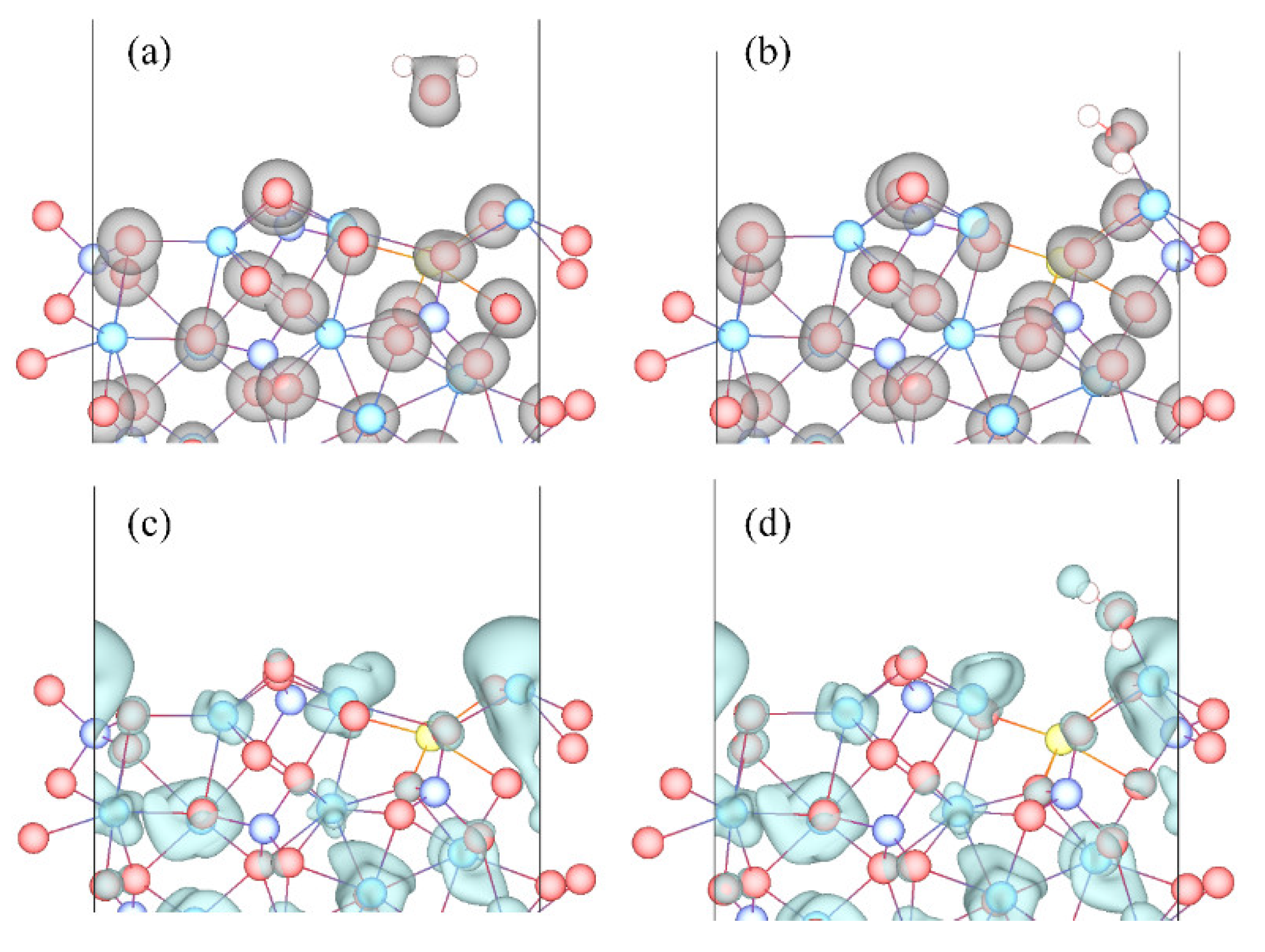
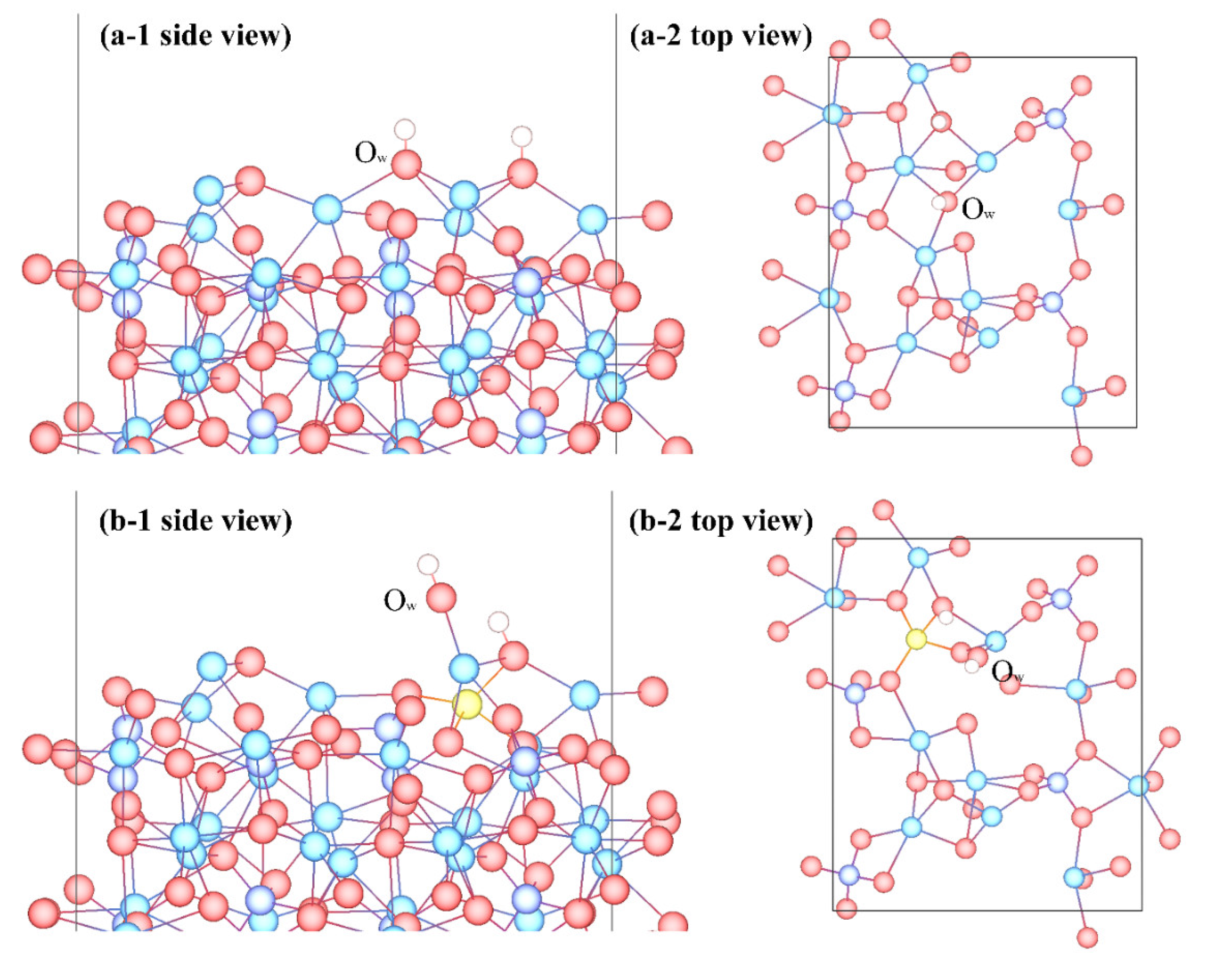
3.3. Adsorption Configuration
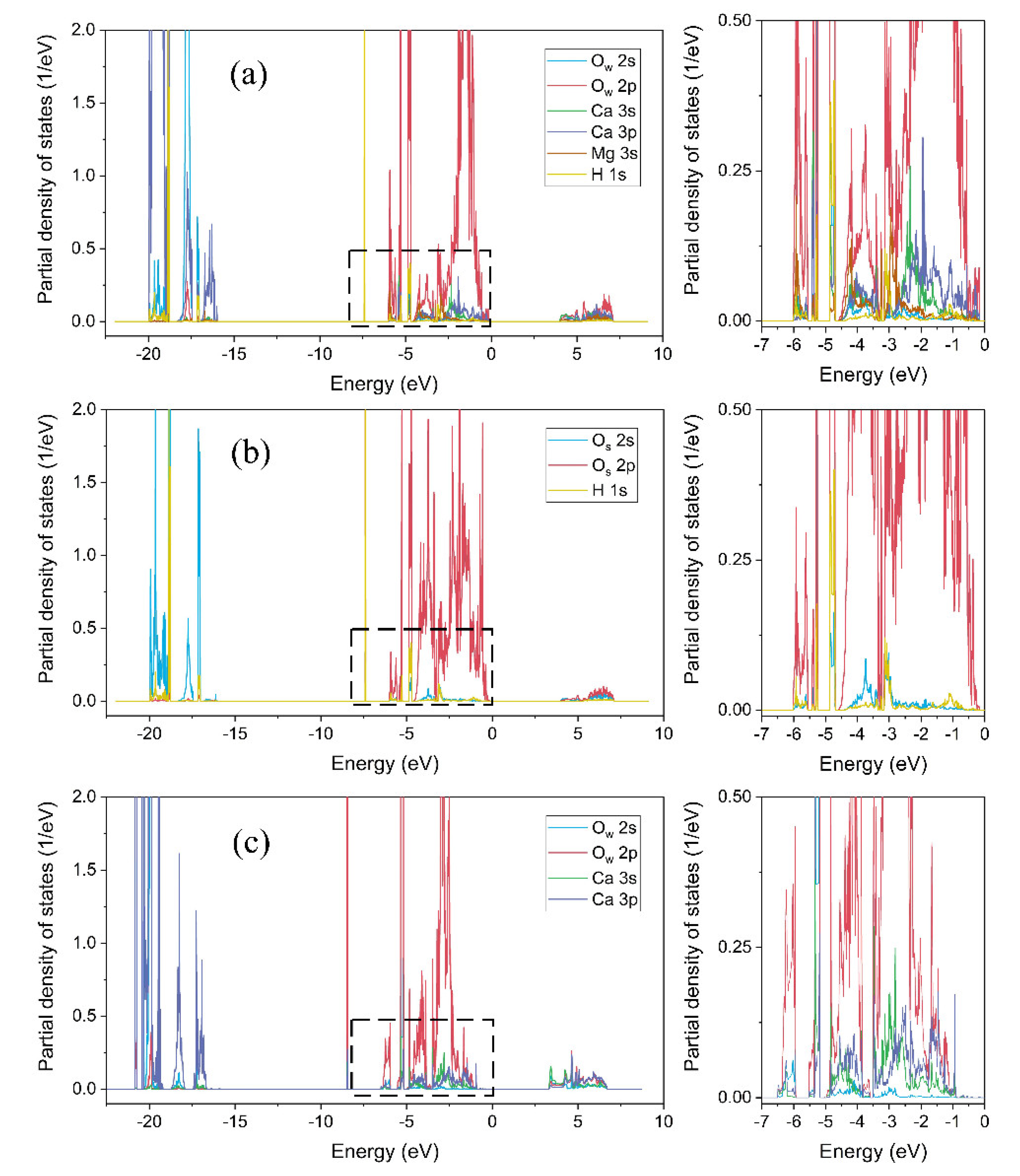
3.4. Partial Density of States
4. Discussion
4.1. What Does the Positive Efor Imply?
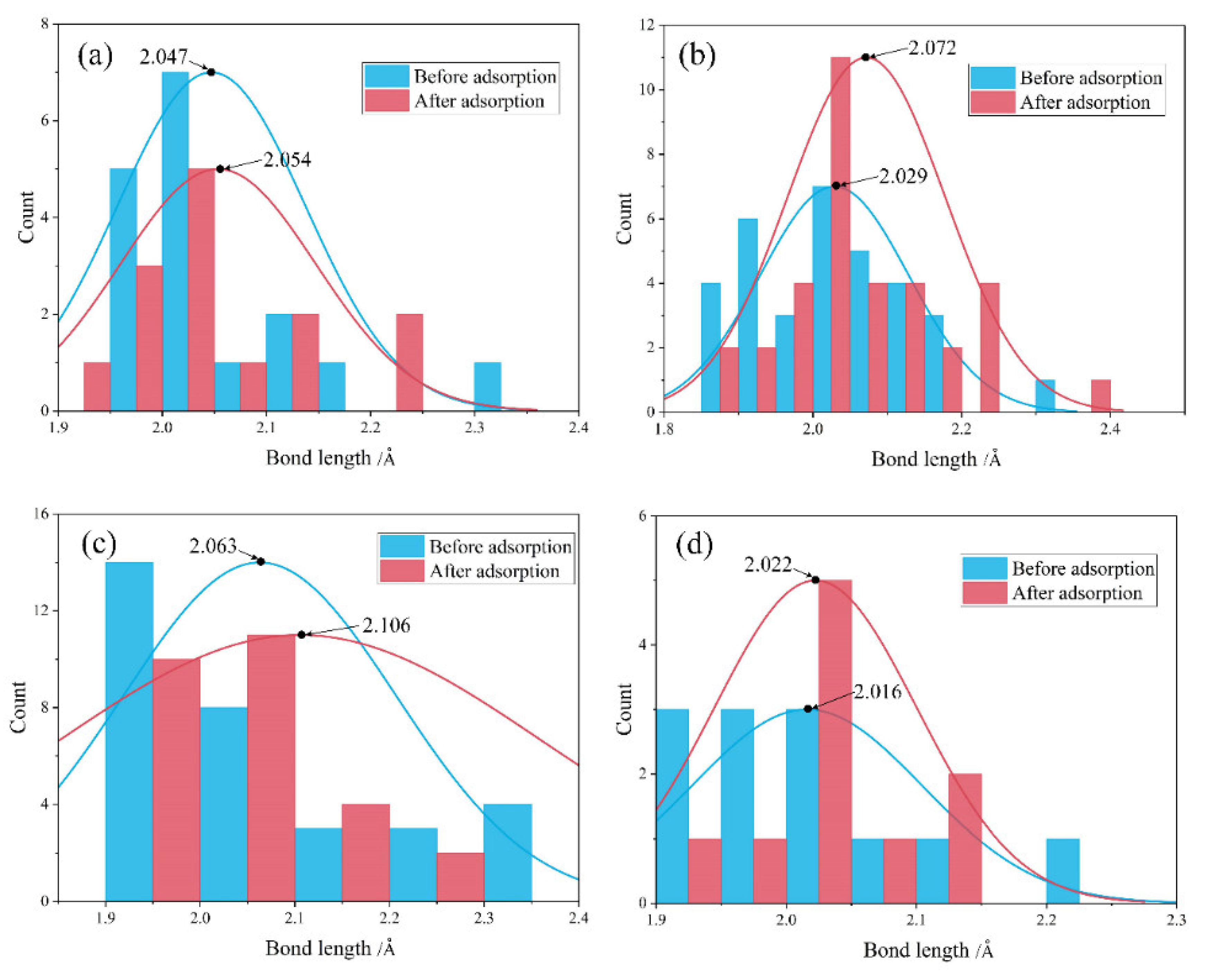
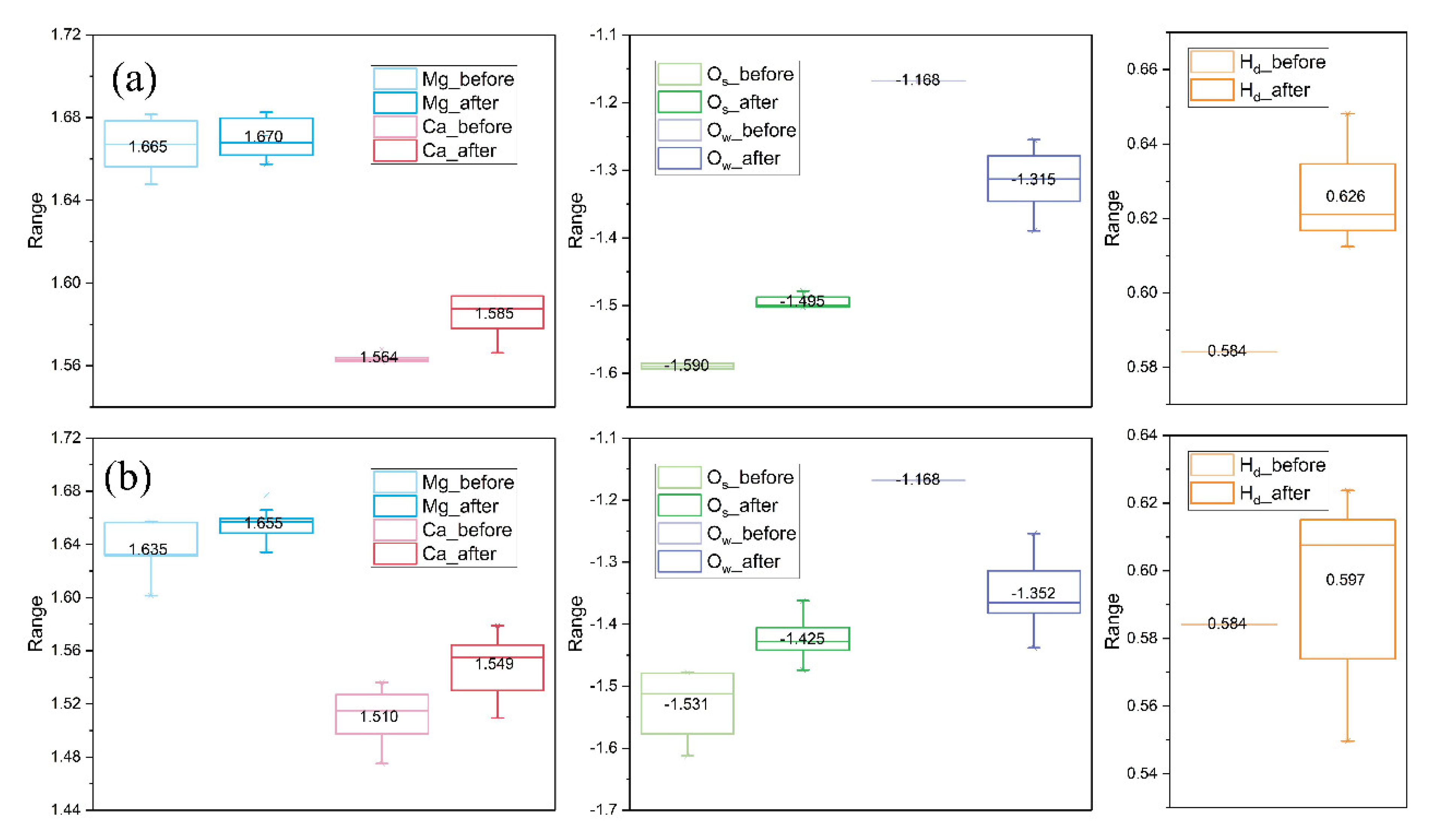
4.2. Comparison before and after Water Adsorption
4.3. Comparison with Pristine Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates
5. Conclusions
- The Efor of Mg substituting for Ca ranged 0.51 to 1.21 eV on β-C2S surfaces and −0.02 to 1.58 eV on M3-C3S surfaces.
- The Ead of an H2O over Mg-doped surfaces of β-C2S and M3-C3S ranged from −0.598 to −1.249 eV and −0.699 to −4.008 eV, respectively. Generally speaking, molecular adsorption was more energetically favorable on β-C2S surfaces and dissociative adsorption was more favorable on M3-C3S surfaces.
- Molecular adsorption was characterized by the Mg-Ow bond and/or the Ca-Ow bond, and in some cases, was also influenced by the attraction between Os and H. Dissociative adsorption was mainly characterized by the Ca-Ow bond, Mg-Ow bond, Os-Hd bond, or was influenced by the attraction between Os and Hd.
- Ow-Mg bonds were originated from the Ow 2p orbital and the Mg 3s orbital, Ow-Ca bonds were originated from the Ow 2p orbital and the Ca 4s/3p orbitals, and Os-Hd bonds was mainly originated from the Os 2p and the Hd 1s orbitals.
- Water adsorption increased the bond length of surface Mg-O and promoted the Mg dissolution. Such a bond-weakening effect was more evident for the molecular adsorption over β-C2S surfaces and the dissociative adsorption over M3-C3S surfaces. The electron transfer was observed from the surface to H2O upon adsorption.
- Mg doping influenced the reactivity of surface Ca/Mg sites, the Ead of the single water adsorption, as well as the adsorption configuration compared with the water adsorption on pristine surfaces.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, B.; Vashistha, P. Application of thermo-chemically activated lime sludge in production of sustainable low clinker cementitious binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, Q.S.; Qi, C.C.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, C.C. Temperature variation characteristics in flocculation settlement of tailings and its mechanism. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Guo, H. Modification of glass structure via CaO addition in granulated copper slag to enhance its pozzolanic activity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, P. Determination of mechanical, flowability, and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill containing rice straw. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, P. Fiber-Reinforced Cemented Paste Backfill: The Effect of Fiber on Strength Properties and Estimation of Strength Using Nonlinear Models. Materials 2020, 13, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Atomic occupancy mechanism in brownmillerite Ca2FeAlO5 from a thermodynamic perspective. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 103, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Chen, Q.; Liu, P.-F. Application of first-principles theory in ferrite phases of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2019, 133, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Valenzano, L.; Singh, T.V.; Pandey, R.; Sant, G. Influence of (Al, Fe, Mg) Impurities on Triclinic Ca3SiO5: Interpretations from DFT Calculations. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, E.; Manzano, H.; Kumar, P.V.; Grossman, J.C. The Characterization, Stability, and Reactivity of Synthetic Calcium Silicate Surfaces from First Principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15214–15219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, H.; Durgun, E.; Qomi, M.J.A.; Ulm, F.-J.; Pellenq, R.J.M.; Grossman, J.C. Impact of Chemical Impurities on the Crystalline Cement Clinker Phases Determined by Atomistic Simulations. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Spagnoli, D.; Fourie, A. DFT-D study of single water adsorption on low-index surfaces of calcium silicate phases in cement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 518, 146255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Song, D.; Liu, S. The adsorption of a single water molecule on low-index C3S surfaces: A DFT approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, H.; Durgun, E.; López-Arbeloa, I.; Grossman, J.C. Insight on Tricalcium Silicate Hydration and Dissolution Mechanism from Molecular Simulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14726–14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Manzano, H.; Guo, Y.; López-Arbeloa, I.; Shen, X. Hydration Mechanism of Reactive and Passive Dicalcium Silicate Polymorphs from Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 19869–19875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, E.; Manzano, H.; Pellenq, R.J.M.; Grossman, J.C. Understanding and Controlling the Reactivity of the Calcium Silicate phases from First Principles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laanaiya, M.; Bouibes, A.; Zaoui, A. Understanding why Alite is responsible of the main mechanical characteristics in Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 126, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovál, M.; Palou, M.; Mojumdar, S.C. Hydration behavior of C2S and C2AS nanomaterials, synthetized by sol–gel method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 86, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thissen, P.; Natzeck, C.; Giraudo, N.; Weidler, P.; Wöll, C. Hydration of Concrete: The First Steps. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 8603–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; He, Z.; Song, D. Molecular and dissociative adsorption of a single water molecule on a β-dicalcium silicate (100) surface explored by a DFT approach. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 101, 2428–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Song, D.; Liu, S. The Adsorption Behavior of a Single and Multi-Water Molecules on Tricalcium Silicate (111) Surface from DFT Calculations. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 102, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Chen, Q.; Yu, L.-J.; Liu, P.-F. Understanding Cement Hydration of Cemented Paste Backfill: DFT Study of Water Adsorption on Tricalcium Silicate (111) Surface. Minerals 2019, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Manzano, H.; López-Arbeloa, I.; Shen, X. Water Adsorption on the β-Dicalcium Silicate Surface from DFT Simulations. Minerals 2018, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Valenzano, L.; Bauchy, M.; Sant, G. Electronic Origin of Doping-Induced Enhancements of Reactivity: Case Study of Tricalcium Silicate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 25991–25999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritas, K.; Ataca, C.; Grossman, J.C. Predicting Electronic Structure in Tricalcium Silicate Phases with Impurities Using First-Principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5074–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Understanding the zinc incorporation into silicate clinker during waste co-disposal of cement kiln: A density functional theory study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shang, D.; Xia, Z.; Li, N.; Ching, W.-Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Comprehending the occupying preference of manganese substitution in crystalline cement clinker phases: A theoretical study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Noirfontaine, M.-N.; Dunstetter, F.; Courtial, M.; Gasecki, G.; Signes-Frehel, M. Polymorphism of tricalcium silicate, the major compound of Portland cement clinker. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Ito, S. Improvement in Reactivity and Grindability of Belite-Rich Cement by Remelting Reaction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 2177–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, R.F.W. A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 084204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, T.; Mansouri, M. Structural effects of substitutional impurities on MoO3 bilayers: A first principles study. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2016, 69, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, K.H.; Ziemer, B.; Seydel, R. Redetermination of the structure of β-dicalcium silicate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1977, 33, 1696–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, P.W. The stability of ionic crystal surfaces. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1979, 12, 4977–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, C. Polar oxide surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, R367–R410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Ching, W.-Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Atomic-level insights into the influence of zinc incorporation on clinker hydration reactivity. Open Ceram. 2020, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, P.C.; Liska, M. Lea’s Chemistry of Cement and Concrete; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.-J.; Kriven, W.M.; Young, J.F. Analytical Electron Microscopic Studies of Doped Dicalcium Silicates. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Calcium Silicate Phase | Low-Index Surfaces | Efor (eV) | Calcium Silicate Phase | Low-Index Surfaces | Efor (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-C2S | (100) | 0.82 | M3-C3S | (100) | 0.46 |
| (010) | 0.74 | (010) | 0.53 | ||
| (001) | 1.21 | (001) | 0.76 | ||
| (110) | 0.78 | (110) | 0.19 | ||
| (101) | 0.51 | (101) | 1.58 | ||
| (011) | 0.94 | (011) | 0.48 | ||
| (111) | 0.51 | (111) | −0.02 |
| β-C2S | Dissociated | Free | M3-C3S | Dissociated | Free |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | −1.249 (D) | (100) | −1.624 (D) | −0.699 (M) | |
| (010) | −0.869 (D) | −0.937 (M) | (010) | −1.786 (D) | −0.938 (M) |
| (001) | −0.994 (M) | −0.915 (M) | (001) | −1.708 (D) | −0.868 (M) |
| (110) | −0.952 (M) | (110) | −3.028 (D) | −1.089 (M) | |
| (101) | −0.765 (M) | −0.831 (M) | (101) | −4.008 (D) | −2.711 (D) |
| (011) | −0.598 (D) | −1.116 (M) | (011) | −2.192 (D) | |
| (111) | −0.982 (M) | −0.817 (M) | (111) | −1.454 (D) | |
| Surfaces | Summary of Bonding |
|---|---|
| (100) | −1.249D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow, Os-Hd, Ow--Hd |
| (010) | −0.869D: Mg-Ow, Os-Hd, Ow--Hd; −0.937M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (001) | −0.994M and −0.915M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (110) | −0.952M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (101) | −0.765M and −0.831M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (011) | −0.598D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow(2), Os-Hd, Os--Hd; −1.116M: Ca-Ow |
| (111) | −0.982M: Ca-Ow, Os-H(2); −0.817M: Ca-Ow, Os-H |
| Surfaces | Summary of Bonding |
|---|---|
| (100) | −1.624D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow(2), Os--Hd; −0.699M: Mg-Ow |
| (010) | −1.786D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow, Os-Hd; −0.938M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (001) | −1.708D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow(2), Os-Hd, Ow--Hd; −0.868M: Mg-Ow, Os--H |
| (110) | −3.028D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow, Os-Hd, Os--Hd; −1.089M: Mg-Ow |
| (101) | −4.008D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow, Os-Hd; −2.711D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow(2), Os-Hd |
| (011) | −2.192D: Mg-Ow, Ca-Ow, Os-Hd, Ow--Hd |
| (111) | −1.454D: Ca-Ow, Os-Hd, Ow--Hd |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, C.; Chen, Q.; Fourie, A. Role of Mg Impurity in the Water Adsorption over Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates: A DFT-D Study. Minerals 2020, 10, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080665
Qi C, Chen Q, Fourie A. Role of Mg Impurity in the Water Adsorption over Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates: A DFT-D Study. Minerals. 2020; 10(8):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080665
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Chongchong, Qiusong Chen, and Andy Fourie. 2020. "Role of Mg Impurity in the Water Adsorption over Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates: A DFT-D Study" Minerals 10, no. 8: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080665
APA StyleQi, C., Chen, Q., & Fourie, A. (2020). Role of Mg Impurity in the Water Adsorption over Low-Index Surfaces of Calcium Silicates: A DFT-D Study. Minerals, 10(8), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080665