Abstract
Volcanic tuffs have a historical tradition of usage in Northern Hungary as dimension stones for monumental construction, Ottoman architecture, common dwellings, etc., admirable at its best in the medieval castles of Eger and Sirok. This research explores tuff deterioration in the castle walls, dealing with the mineralogical composition, microstructure, trace-element geochemistry, and microporosity of the surface weathering products and the near-surface stone substrate. The classic microscopic and mineralogical techniques–optical microscopy, SEM-EDS, and XRD–were supported by ICP-MS and nitrogen adsorption analyses. The textures and mineral assemblages of the tuffs are partly diverse, and so are the weathering characteristics, although including common features such as secondary crystallization of gypsum, swelling clay minerals, and iron oxides-hydroxides; deposition of airborne pollutants, i.e., carbon particles and heavy metals; formation of crusts and patinas; decreased surface microporosity. Nonetheless, the entity of deterioration varies, in relation to air pollution–involving changing emissions from road and rail transport–and the specific tuff texture, porosity, and durability–affecting pollutant absorption. The studied stone monuments offer the possibility to examine materials with analogue composition and petrogenesis but utilized in different environmental contexts, which allow pointing out the environmental and lithological constraints and cause-effect relationships related to surface weathering.
1. Introduction
The exploitation and usage of volcanic tuffs as dimension stones in Hungary represent part of a quarrying tradition having a great historical significance, commenced as early as the Roman imperial rule in the 1st century BCE. In Northern Hungary, acid tuffs have been exploited since the Middle Ages and used as building and carving stones for numerous public and private works: monumental construction such as churches and castles, Ottoman architectures like mosques and spas, common dwellings, etc. [1]. Tuff outcrops, carved or excavated, were also adapted into cave houses, or became sites for ritual practices or burials like the “beehive stones”, or hosted cellars for storing the prestigious local wine [2,3,4,5].
The castles of the town of Eger and the village of Sirok (Heves County) represent the grandest examples of monumental architecture made almost exclusively of those local stones (Figure 1). Eger Castle was built from 1248 to 1261 from the ruins of a preexisting fortification destroyed during the Mongol invasion. It went through several modifications and reconstructions until the 18th century when it lost its military defensive role. The castle’s name is linked to a battle fought in 1552 by a Hungarian garrison of 2000 units, who triumphed over a massive Ottoman army, sieging with 80,000 soldiers. The structure today appears fully integrated in the modern urban fabric. Sirok Castle was also built in the 13th century, about 15 km from Eger, and had a complex history of renovations and reconstructions. It was a private residence for local lords, then reinforced in the 16th century with a bastion fortification, in the attempt to halt the Ottoman advance. The last major damages were committed by the Habsburgs, who blew up and partly destroyed the castle in 1713 after the unsuccessful Rákóczi’s War of Independence. The fortification towers above the village, isolated on the top of a hill.
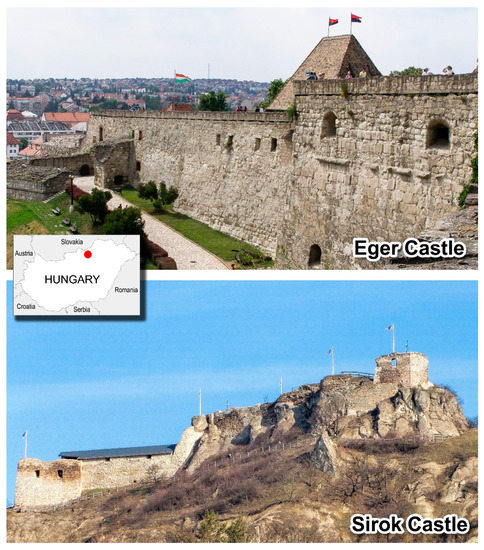

Figure 1.
The medieval castles of Eger and Sirok in Northern Hungary.
The soft and porous tuffs from Northern Hungary exhibit a diverse and severe deterioration, jeopardizing the preservation of monuments and artworks. Although their durability can be inferred from relevant petrophysical and mechanical properties [6,7,8,9,10,11], only one study has documented the weathering of the monumental stone: the most recurring decay patterns, i.e., differential erosion, crust formation, crumbling, and other detachment morphologies, are dependent on mineralogy, pore-size distribution, and proportions of matrix, lithics, and pumice [7]. Indeed, the literature about tuffs in cultural heritage generally gives much broader consideration to technical characterization, and relatively few works deal with weathering-related mineralogical and geochemical changes of the stone in historical sites and buildings, this being a matter traditionally focused on carbonate rocks (the known case studies, from Europe, Asia, and Central America, are in [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]). The studies mentioned report tuff weathering in terms of surface enrichment in clay minerals and gypsum typically.
This research will tackle the theme of tuff deterioration, exploring the mineralogical composition, microstructure, trace-element geochemistry, and microporosity of the surface weathering products and the near-surface stone substrate in historical monuments. The subject of study, namely the building stones of the castles of Eger and Sirok, allows examining materials with analogue composition and petrogenesis but utilized in different environmental contexts. In this regard, the lithological and environmental constraints and cause-effect relationships related to surface weathering are discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
The studied tuffs are part of a sequence of Miocene pyroclastic rocks formed between 18.2 and 14.4 Ma, during the initial acid stage of the volcanic activity associated with the tectonic evolution of the Carpathian-Pannonian Region. The relevant explosive events produced welded and unwelded pumiceous tuffs and subordinate pyroclastic fall beds, having a prevailing high-K rhyolitic and dacitic composition of the juvenile components [29,30,31,32,33].
A set of 22 samples were collected from the eastern walls of Eger Castle–running along Bástya Street and the railway–and the eastern and southeastern walls of Sirok Castle. In both cases, the historical stone materials were sampled. In addition, in Eger Castle, the ashlars used in restored wall sectors, showing major lithological differences, were sampled as well (the eastern walls were rebuilt in the first years of the 20th century, when the railway was realized intersecting the castle area, using old ashlars and new stone blocks). The sampling was performed on the crusts, patinas, and deposits observed on the tuff surfaces (Figure 2), as well as on the underlying host rock in each sampling spot. Finding a compromise between the sampling restrictions and the usual problems of representativeness and tuff heterogeneity, the sample set was selected based on the macroscopic features observed in the field; later, the mineralogical composition was investigated during a comprehensive exploratory experimental session, so as to better target further analyses.

Figure 2.
Details of the walls and the weathering observed on the tuff ashlars of Eger Castle (black crusts, patinas, and surface recession with detached crusts, and differential erosion) and Sirok Castle (black crusts and orange patinas).
The mineralogical composition was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), with a diffractometer Siemens D5000 (Siemens AG, Munich, Germany) equipped with Cu anode operated at 40 kV and 40 mA, measuring in the range 3–65°2θ with scan steps of 0.05°2θ.
The mineralogical and microstructural features were investigated on thin sections perpendicular to the exposed surface (1–2 cm cross sections) with a polarized-light microscope, and analyzed on uncoated samples with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) Zeiss EVO MA10 (Carl ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with W cathode and operated in low-vacuum conditions, integrated by a system EDAX for energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS).
The geochemical composition of the non-silicate fractions was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), using a tandem triple-quadrupole spectrometer Agilent 8800 ICP-QQQ (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) after acid digestion with HNO3.
Microporosity was investigated by N2 adsorption, measuring the adsorption and desorption isotherms at −196 °C with an analyzer Quantachrome NOVA 2000 (Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). Total pore volume and specific surface area by the multipoint BET method (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) were determined within a pore-diameter range from about 3 to 200 nm. Complementary calculations of mean pore diameter and pore-size distribution by the BJH method (Barrett–Joyner–Halenda) were done, and porosity was estimated from skeletal density [11].
3. Environmental Setting
The continental climate of Hungary (Köppen classification: “Dfb”) can be defined, in the studied locations, as moderately warm and dry [34], featuring warm summers and cold winters. July is the warmest month (averaging 20 °C, with a mean maxima of 27 °C) and January the coldest (averaging −3 °C, with a mean minima of −6 °C). Annual mean temperature is 10 °C, and precipitations, the highest in May and June, are around 550 mm yearly [35].
Concerning air pollution, Hungary has followed the general European trend of air quality improvement registered in the past 20 years [36], ranking among the countries producing the lowest total emissions [37]. The concentration of the main pollutants recorded in Eger is shown in Table 1, compared to Budapest–the capital and largest city of Hungary–where NOX is three times more abundant, and CO and PM10 concentrations are noticeably higher too [38]. No data were available for Sirok; it is worth reporting, however, that the village is just 15 km away and is much smaller than the town of Eger; the population is about 2000, against the 50,000 of Eger. The relatively low pollution level in the region could also be inferred by comparing the data from other populated areas in Northern Hungary [39]. Heves County and, more generally, Norther Hungary used to have an important industrial role–involved in coal mining, metallurgy, heavy-machinery production, and the chemical industry–that, after the end of the communist era (1989), gradually declined [40]. Today, the most important industry still operating is a coal power station, among the largest plants in all of Hungary, 20–25 km from Eger and Sirok to the east; due to the prevailing northeasterly winds, however, most of its pollution plumes do not affect the studied sites.

Table 1.
Average daily concentrations of air pollutants in Eger and Budapest, measured from 2012 to 2020 and expressed in µg/m3 [38].
4. Petrographic Study
The volcanic stone used in the historical walls of the castles of Eger and Sirok is a greyish-creamy pumice tuff, with pseudo-porphyritic texture and glassy matrix. The pumice clasts and phenocryst fragments, typically of plagioclase, display a diverse grain size, which can reach lapilli size, with dimensions of several centimeters. The quantitative relationships among pumice, crystal fragments, and matrix may be highly variable in Sirok tuff, as per previous findings [11]. The tuff from the restored walls of Eger Castle, instead, is a fiamme-bearing pumice tuff with finer and a more seriate grain size, and is easily distinguished by its reddish-brownish color. The microscopic appearance and mineralogical composition of these three tuff types are presented in Figure 3. Further data about the major mineralogical phases are provided by the XRD patterns and the relevant semi-quantitative analysis (Table 2), which also confirm the high amorphous content.
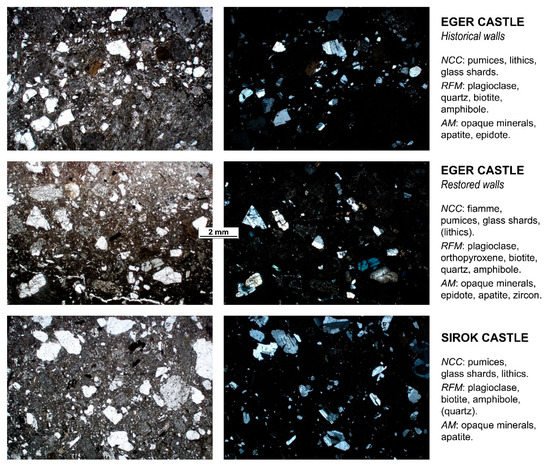
Figure 3.
Thin-section photomicrographs in plane- and cross-polarized light of the studied tuffs, at the same magnification, with the rock components listed in order of abundance (NCC = non-crystalline components and lithoclasts; RFM = rock-forming minerals; AM = accessory minerals).

Table 2.
Semi-quantitative composition of the studied tuffs calculated from the relevant XRD patterns considering the major mineral phases (Ab = albite; Act = actinolite; Bt = biotite; Crs = cristobalite; mHal = meta-halloysite; Mnt = montmorillonite; Qz = quartz).
The petrographic study helps identify the quarry sources of the three tuff varieties [11]. The tuffs of the historical walls of Eger Castle come from the nearby quarries of Demjén or Eger, whereas those of the restored walls from the area of Bogács, a few kilometers apart. The provenance of the tuff of Sirok Castle is the hill itself where the structure was built, or the nearby outcrops. In those locations, the rock composition (bulk and of juvenile components) is mostly dacitic [33].
5. Surface Weathering
5.1. Mineralogy and Microstructure
The weathering layers observed on the tuff surfaces have diverse color, morphology, and extension, and the mineralogical and microscopic analyses reveal the most significant components being C particles, gypsum, and swelling clay minerals, from both Eger Castle and Sirok Castle.
Soiling and black crusts contribute to the most typical discolorations, produced by the deposition and cementation at different degrees of blackish C particles (Figure 4). These crusts frequently have mid-high levels of Cl and a variable extension. In Eger Castle, they reach the greatest thickness, exceeding 100 µm. This is consistent with the more polluted environment of a larger town like Eger. There, motor vehicle exhaust emissions–typically composed of spherical C particles, coated with NOx, VOC, sulfates, metals, etc. [41,42,43]–are supposedly more abundant, even more so considering that a major road runs just 20–30 m from the castle walls. Likewise, a railway runs a few meters away, between the road and the castle, so that the steam and, later, diesel locomotives in transit since 1908 represent a further source of soot.
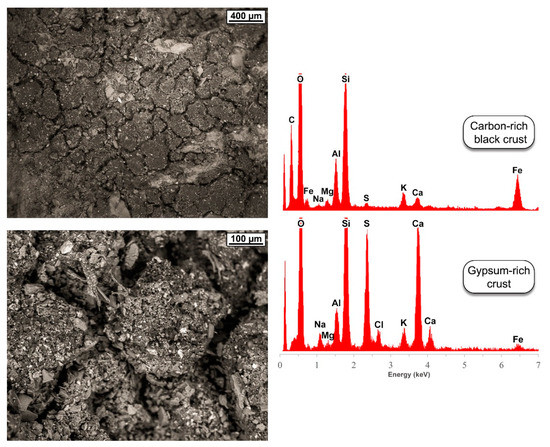
Figure 4.
SEM-BSE photomicrographs showing at different magnifications a microcracked C-rich black crust on the historical walls of Eger Castle. The EDS spectra show the microchemical composition of the same crust and of a gypsum-rich crust from another sampling point.
The occurrence of gypsum is determined at different degrees, from a general sulfation of the tuff surfaces to the presence of discrete discernible crystals (Figure 4). Their grain size is the largest in Eger Castle. The XRD results indicate that gypsum is the secondary phase most frequently detected (Figure 5). Nevertheless, it is often finely dispersed on the stone surface, without forming compact aggregates of coarse-grained crystals. This last observation is explained by the low air concentration of SO2 (about 7 µg/m3, Table 1), typical of a rural environment [44], and the lack of a major intrinsic source of Ca. CaO concentration in the studied tuffs is typically below 3% [33], so that the plausible source is external and represented by lime-mortar joints, from which CaCO3 dissolves and then reprecipitates. The role of mortars in gypsum formation on volcanic rocks has been already postulated in the literature [43,45,46], although some studies indicate the possible contribution of the rock-forming minerals, e.g., calcic plagioclases [15,47]. Generally, the possible role of wind-blown carbonate grains, from loess or calcite-rich rocks, needs also to be considered [48,49].
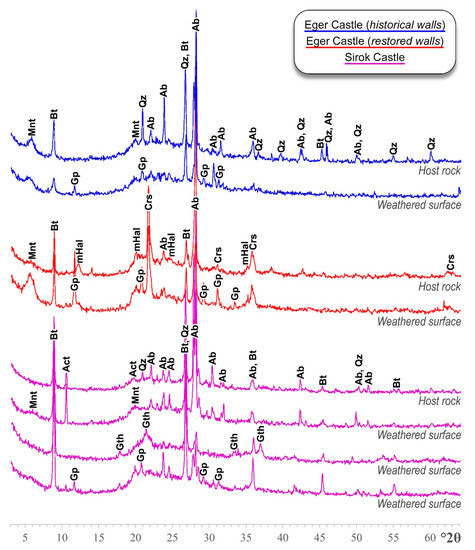
Figure 5.
Powder XRD patterns indicating the mineralogical composition of the studied tuffs and the extra phases detected on their weathered surfaces (Ab = albite; Act = actinolite; Bt = biotite; Crs = cristobalite; Gp = gypsum; Gth = goethite; mHal = meta-halloysite; Mnt = montmorillonite; Qz = quartz).
The deterioration risk associated with weathering crusts with a mix of organic and inorganic components is the formation of surface layers with different physico-mechanical and chemical properties in respect to the substrate. As such, they differently respond to environmental changes and stresses, producing strongly localized mechanical fatigue at the interface with the underlying host rock. The stresses generated by cyclic salt crystallization alone are acknowledged as a major decay cause [50,51,52,53].
As for the clay minerals, specifically montmorillonite, their crystallization seems generally more widespread on the exposed surfaces. This arises after comparing the XRD signals from the host rock and the surface (Figure 5) and the examination of the outermost layers under the microscope: there, the alteration degree of feldspar phenocryst fragments is higher, and the matrix, typically having very low crystallinity, shows several domains of devitrification to cryptocrystalline aggregates (Figure 6a). Indeed, the clay minerals derived from the hydrolysis of the feldspars and, to a greater extent, the glassy matrix. Volcanic glass is thermodynamically unstable and alters more rapidly than the associated minerals and, when it has a silicic composition, montmorillonite is the most common product [54]. Enrichments in swelling clay minerals may enhance stone vulnerability during wetting/drying alternating phases, producing damaging cycles of dilation/contraction [55,56,57,58]. Differential erosion may also increase [7,11]. Figure 6b shows a characteristic surface topography of the tuff from the historical walls of Eger Castle (c.f. Figure 2): the surface outline follows the coarse crystals, pumice, and lithic clasts standing out in relief in respect to the weaker matrix, which is further stressed by the action of clay minerals.
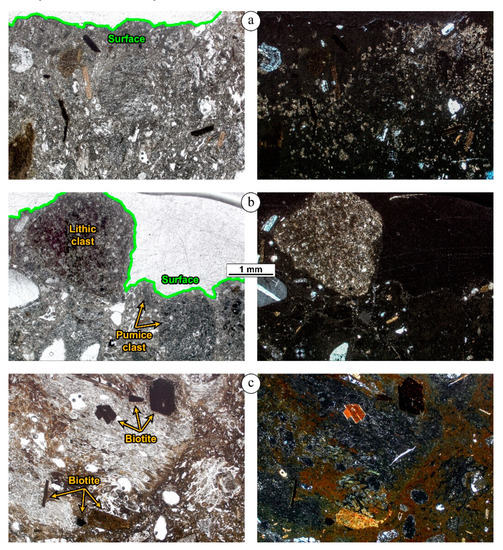
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs in plane- and cross-polarized light of cross sections, at the same magnification, showing different weathering patterns: (a) near-surface alteration and devitrification of the glassy matrix, visible in the birefringent areas (Sirok Castle); (b) irregular surface morphology caused by differential erosion (Eger Castle, historical walls); (c) dispersion of brownish Fe oxides and hydroxides around biotites, in the matrix, and in the outer pores of pumice clasts (Sirok Castle).
Finally, it is worth mentioning a weathering pattern observed more frequently at Sirok Castle, i.e., orange patinas mainly constituted of goethite (Figure 5). This phase might derive from the leaching of Fe-bearing minerals and subsequent Fe mobilization [43], especially from biotite–which releases Fe2+ from the octahedral layers–or the basaltic-andesitic lithoclasts [29]. Another source might be the glassy matrix that, during hydration, is subjected to the strong oxidation of the Fe contained therein [54]. In fact, an enrichment in Fe oxides and hydroxides was observed nearby biotites and in the matrix, spreading out following the pore channels and penetrating into the pumice clasts (Figure 6c). This was also in agreement with the higher biotite concentration in Sirok tuff, estimated by XRD (Table 2), which exceeds 50% in some samples.
5.2. Trace-Element Chemical Composition
The ICP-MS analyses of the non-silicate fraction of crusts, patinas, and deposits on the tuff surfaces, as well as of the host rock, allow outlining the concentration patterns of trace elements. The most interesting data are related to heavy metals (Figure 7). Generally, compared to the bulk stone, the weathered surfaces are noticeably richer in As, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Sn, V, and Zn. The absolute maximum concentrations for some illustrative elements are: As 40 ppm, Cr 28 ppm, Cu 48 ppm, Ni 28 ppm, Pb 89 ppm, V 135 ppm, Zn 79 ppm. The lowest and highest average concentrations are both detected at Eger Castle, on the historical and restored walls, respectively. As for the balance of trace-element concentration between the surface and the host rock, the historical walls of Eger Castle report the lowest decrease of heavy metals in the inner layers, i.e., less than 30% on average: for instance, Fe is 10,027 ppm on the surface and 8579 ppm underneath, instead Pb is 5.6 ppm versus 4.3 ppm. On the contrary, the other tuffs record mean differences between 45% (Eger Castle) and 55% (Sirok Castle), pointing out that the accumulation of those trace elements is mostly superficial.
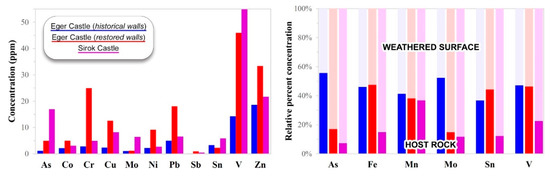
Figure 7.
Average concentration of heavy metals determined by ICP-MS on the weathered surface of the studied tuffs, and comparison with the relative abundance of selected elements in the host rock.
Heavy metals represent air pollution markers and are useful for understanding the environmental context. The anthropogenic sources may be numerous, e.g., transports, industry, construction, electricity and heat production, petroleum refining, incinerators [59]. However, in this case, the only actual influential source was assessed to be transports. Road transport is associated with diverse major emissions, mostly coming from the wear of car brakes and tires and composed of Cu, Zn, Pb and, secondarily, Cr and Ni, although including a variety of other elements (As, Cd, Hg, Sb, Se, V) and sources (motor fuel and oil, asphalt abrasion) [59,60,61]. In the case of Eger Castle, the contribution of rail transport also needs to be accounted for, in view of the steam and diesel engines and the abrasion of metallic train elements and rails releasing Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu, Cr, and Fe mainly [62,63,64,65,66].
These observations are only partly concordant with the experimental results. In fact, the concentration of heavy metals determined at Eger Castle can be higher than the levels of Sirok Castle, consistent with the different localization of the monuments in respect to the surrounding pollution sources. However, those somehow narrow geochemical differences do not indicate two much different environmental contexts. Moreover, within Eger Castle, so in the same higher-pollution scenario, stone chemical alteration can even be the least intense, depending on the tuff variety, as already pointed out. Pb concentration can be taken as a representative example: the average values recorded, ranging from about 5 to 20 ppm, are very far from the 100s and 1000s ppm detected in black crusts from Budapest and other European cities [49]. In other terms, the boundary environmental conditions of the castles of Eger and Sirok and air quality may be less significant than the lithological constraints in defining the accumulation of metallic pollutants.
Therefore, metal mobility and its dependence on the rock properties must be taken into account too. The tuff from the historical walls of Eger Castle, if compared to the others, has a significantly higher open porosity (by a factor of 1.4 to 1.6) given almost totally by large pore-size classes (i.e., capillary pores and macropores [11]), those mainly affected by water infiltration and movement. These characteristics allow for a boosted pollutant absorption and deeper migration inwards, even in liquid solution when the surface gets wet. That explains the low heavy-metal concentrations on the surface and the relative geochemical balance with the inner layers. Finally, that tuff is also the softest and most prone to disintegration, so that, during the enhanced surface recession (Figure 2), the accumulation of airborne particulate may reset frequently.
5.3. Microporosity
The results of the N2 adsorption tests provide evidence that weathering produces measurable changes even in the pore network, and most importantly may lead to a decrease in microporosity. The microporosity of the surface layers is 3/5 that of the host rock for the tuff from the historical walls of Eger Castle, and about 4/5 for Sirok tuff. The microporosity range measured goes from 11% (host rock) down to 1.8% (weathered surface). The pore-size distributions point out another trend, namely the general decrease of pore size in the weathered surface: while the finest micropores apparently are almost unaffected, the quantity of those with a diameter larger than 5–10 nm decreases significantly (Figure 8).
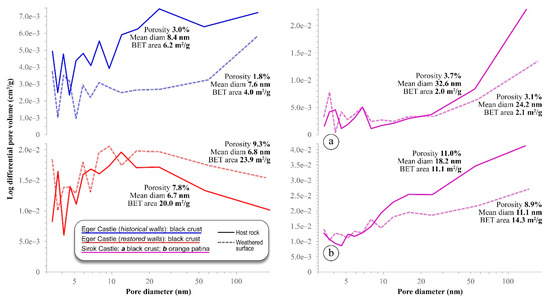
Figure 8.
Pore-size distribution, porosity, mean pore diameter, and BET surface area of the studied tuffs, measured by N2 adsorption separately on the host rock (continuous lines) and the weathered surface (dashed lines). Left graphs show samples of Eger Castle, right graphs of Sirok Castle.
These data indicate that the deposition of exogenous pollutants and surface crystallization of secondary phases lead to micropore filling, or that the weathering crusts may reach a higher density than the deteriorated underlying host rock. The grain size of the weathering-related components is constrained by the lower limit of 5–10 nm that marks the main pore-size changes. When an increase of BET surface area is also recorded, that translates to a higher chemical reactivity, i.e., larger surfaces accessible to decay processes [67]. Nevertheless, a microporosity decrease may also result in hindering further absorption of water vapor and dissolved pollutants; in fact, microporosity is strictly associated with hygroscopic condensation, which can occur in micropores even for values of relative air humidity much lower than 100%–the smaller the pore, the lower the humidity of condensation [68,69,70].
The aforementioned considerations refer only to the investigated size range of micropores, which have a different weight depending on the tuff variety. A previous study of Eger Castle, in fact, reports a weathering-related increase of larger pores, involved in possible enhanced processes driven by liquid water [7]. One example is the increased accumulation of heavy metals in the historical walls, mentioned previously.
Finally, it is worth mentioning the only data that do not conform to the general trend, obtained on the tuff of the restored walls of Eger Castle. Its weathered surface has a porosity increased by a factor of 1.2, compared to the host rock. This might indicate a less advanced stage of compaction, influenced by, among other things, the shorter exposure time from the restorations and the relative lowest open porosity [11].
6. Conclusions
The stone materials used for building and restoring the medieval castles of Eger and Sirok are acid tuffs featuring diverse textures and mineral assemblages, which allow for the recognition of the local quarry sources. Some differences are also noticeable in the characteristics of surface weathering of the stone walls. The most representative features involve the crystallization of secondary phases such as gypsum, swelling clay minerals, and Fe oxides-hydroxides and the deposition of airborne pollutants–C particles and heavy metals–acting as catalysts. Those weathering products may form crusts and patinas, and fill the smallest surface pores. The decreased microporosity measured on the stone surface enhances the chemical and technical differences with the host rock and the tuff vulnerability. The general decay mechanisms are dependent on the chemical alteration of rock components (glass, feldspars, biotite, and lithoclasts) and mineral phases in the mortars, and the air pollution, mainly deriving from motor vehicle exhaust emissions. Nevertheless, the entity of deterioration varies, in relation to both environmental and lithological constraints. Eger Castle rises in the middle of a town, close to a busy road and a railway, whereas Sirok Castle stands isolated on a hill, nearby a much smaller village. The emissions from the road (and rail) transport in Eger are higher, and that reflects a higher average concentration of the associated trace elements, e.g., C, Pb, Zn, Cu, and Cr. In some cases, these general observations do not apply, so that the boundary environmental conditions of the two monuments cannot be considered drastically different, from the viewpoint of air pollution. Rock texture and physical properties are other critical parameters to consider; even in a higher-pollution scenario, softer, more porous, and less durable tuffs may report only a slight surface deposition of pollutants, which instead migrate into the inner substrate or are removed because of a more severe stone disintegration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, validation, writing–review and editing, L.G. and Á.T.; formal analysis, visualization, writing–original draft, L.G.; project administration, resources, supervision, Á.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by SIMP (Italian Society of Mineralogy and Petrology, scholarship for short-term mobility to L.G.) and NKFI (National Research, Development and Innovation of Hungary, funds K-116532 of Á.T.).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Krisztina László and György Bosznai for their support in the nitrogen adsorption analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Török, Á. Hungarian dimensional stones: An overview. Z. Der Dtsch. Ges. Geowiss. 2007, 158, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleb, B. Eger Múltja a Jelenben–The Past in the Present Life of Eger; Eger Városi Tanács VB Műszaki Osztálya: Közdok, Budapest, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kleb, B. Engineering-geological test on settlements with cellar difficulties. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 1988, 32, 99–129. [Google Scholar]
- Baráz, C.; Kiss, G. Marked Stones and Places of Fable in the Mátra Forest (NE-Hungary); Bükk National Park Directorate: Eger, Hungry, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Harangi, S. Volcanic heritage of the Carpathian-Pannonian Region in eastern-central Europe. In Volcanic Tourist Destinations; Erfurt-Cooper, P., Ed.; Geoheritage, Geoparks and Geotourism; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 103–123. [Google Scholar]
- Forgó, L.Z.; Török, Á. Influence of petrophysical and petrographical properties on the behaviour of rhyolite tuff, example from Eger, Hungary. In International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering, 5th ed.; Walraven, J., Blaauwendraad, J., Scarpas, T., Snijder, B., Eds.; Special Publications 271; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2004; pp. 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Török, Á.; Forgó, L.Z.; Vogt, T.; Löbens, S.; Siegesmund, S.; Weiss, T. The influence of lithology and pore-size distribution on the durability of acid volcanic tuffs, Hungary. In Building Stone Decay: From Diagnosis to Conservation; Přikryl, R., Smith, B.J., Eds.; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2007; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Stück, H.; Forgó, L.Z.; Rüdrich, J.; Siegesmund, S.; Török, Á. The behaviour of consolidated volcanic tuffs: Weathering mechanisms under simulated laboratory conditions. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, G.; Mlinárik, L.; Török, Á. Adsorption and chemical precipitation of lead and zinc from contaminated solutions in porous rocks: Possible application in environmental protection. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 122, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, Á.; Barsi, Á.; Bögöly, G.; Lovas, T.; Somogyi, Á.; Görög, P. Slope stability and rockfall assessment of volcanic tuffs using RPAS with 2-D FEM slope modelling. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Török, Á. Variability of technical properties and durability in volcanic tuffs from the same quarry region–examples from Northern Hungary. Eng. Geol. 2019, 262, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, P.L.; Lombardi, G.; Marini, S.; Meucci, C. The volcanic rocks of the monuments of the Forum and Palatine (Rome): Characterization, alterations, and results of chemical treatments. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- De Casa, G.; Giglio, G.; Lombardi, G.; Mariottini, M. Characterization and state of decay of the volcanic tuff of the Tabularium in the Roman Forum, Italy. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Paterno, M.C.P. A Study of the Weathering of Volcanic tuffs In a Tropical Environment, Including the Evaluation of a Consolidant. Master’s Thesis, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumov, M.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Carreón-Nieto, H.; Lozano-Santa Cruz, R. Mineralogía y geoquímica de los procesos de degradación en monumentos históricos: Primer acercamiento a un caso mexicano (Morelia, Michoacán). Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2003, 20, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Topal, T.; Sözmen, B. Deterioration mechanisms of tuffs in Midas monument. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, T.G.; Brendle, S.; van Hees, R.P.J.; de Haas, G.J.L.M. Decay of Rhenish tuff in Dutch monuments. Part 1: Use, composition and weathering. Heron 2004, 48, 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Doehne, E.; Simon, S.; Mueller, U.; Carson, D.; Ormsbee, A. Characterization of carved rhyolite tuff–The Hieroglyphic Stairway of Copán, Honduras. Restor. Build. Monum. 2005, 11, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedef, V.; Kocak, K.; Doyen, A.; Ozsen, H.; Kekec, B. Effect of salt crystallization on stones of historical buildings and monuments, Konya, Central Turkey. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedel, H. Salt-induced alveolar weathering of rhyolite tuff on a building: Causes and processes. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Salt Weathering on Buildings and Stone Sculptures”, Copenhagen, Denmark, 22–24 October 2008; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Erguler, Z.A. Field-based experimental determination of the weathering rates of the Cappadocian tuffs. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccioli, P.; Cattuto, C.; Plescia, P.; Valentini, V.; Negrotti, R. Geochemical and engineering geological properties of the volcanic tuffs used in the Etruscan tombs of Norchia (northern Latium, Italy) and a study of the factors responsible for their rapid surface and structural decay. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, C.; Takaya, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Ohnishi, R.; Thidar, A.; Hatta, T. High acidic sulphate salt production on the cave wall in the Yoshimi Hyaku-Ana historic site, central Japan. In Proceedings of the XIX CBGA Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–26 September 2010; pp. 413–419. [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi, C.T.; Yuasa, H. Simultaneous wetting/drying, freeze/thaw and salt crystallization experiments of three types of Oya tuff. In Natural Stone Resources for Historical Monuments; Přikryl, R., Török, Á., Eds.; Special Publications 333; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2010; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Zamudio, V.; Angeles-Chávez, C.; Cervantes, J. Clay minerals in historic buildings. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, A.B. Durability assessment of the Alaçatı tuff (Izmir) in western Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosonyi, E.; Cobârzan, N. Weathering, conservation state and compatibility studies on the construction materials used for renovation of the historical Dej reformed church fortifying walls. Rom. J. Mater. 2016, 46, 542–551. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Araki, N. Evaluation of nondestructive diagnosis and material characteristics of stone lantern at Damyang Gaeseonsaji temple site in Korea. J. Conserv. Sci. 2019, 35, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harangi, S. Neogene to Quaternary volcanism of the Carpathian-Pannonian Region–A review. Acta Geol. Hung. 2001, 44, 223–258. [Google Scholar]
- Harangi, S.; Lenkey, L. Genesis of the Neogene to Quaternary volcanism in the Carpathian-Pannonian region: Role of subduction, extension, and mantle plume. In Cenozoic Volcanism in the Mediterranean Area; Beccaluva, L., Bianchini, G., Wilson, M., Eds.; Special Paper 418; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Seghedi, I.; Downes, H. Geochemistry and tectonic development of Cenozoic magmatism in the Carpathian-Pannonian region. Gondwana Researh 2011, 20, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, F.; Musitz, B.; Balázs, A.; Végh, A.; Uhrin, A.; Nádor, A.; Koroknai, B.; Pap, N.; Tóth, T.; Wórum, G. Evolution of the Pannonian basin and its geothermal resources. Geothermics 2015, 53, 328–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, R.; Harangi, S.; Guillong, M.; Bachmann, O.; Fodor, L.; Buret, Y.; Dunkl, I.; Sliwinski, J.; von Quadt, A.; Peytcheva, I.; et al. Early to Mid-Miocene syn-extensional massive silicic volcanism in the Pannonian Basin (East-Central Europe): Eruption chronology, correlation potential and geodynamic implications. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Péczely, G. Éghajlattan; Nemzeti Tankönyvkiadó: Budapest, Hungry, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Climate-Data.org Hungary Climate. 2018. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/hungary-20 (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe–2019 Report; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009.
- EEA Air Pollutant Emissions Data Viewer (Gothenburg Protocol, LRTAP Convention). 2017. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/air-pollutant-emissions-data-viewer (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- OLM. Hungarian Air Quality Network–Automatic Monitoring Network. 2020. Available online: http://www.levegominoseg.hu/automatic-monitoring-network (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- Lantai, K.; Wopera, Á.; Nagy, G. Air quality in the Northern Hungarian region. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tiner, T. Far from the core–regions and industrial parks in economic shadow in Hungary. Part one. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2010, 59, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, S.W. The effects of ozone and NOx on the deterioration of calcareous stone. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Agarwal, A.K.; Bharathi, K.V.L. Characterization of exhaust particulates from diesel engine. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Maritan, L.; Simon, K.; Mazzoli, C. Trachyte weathering in the urban built environment related to air quality. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charola, A.E.; Ware, R. Acid deposition and the deterioration of stone: A brief review of a broad topic. In Natural Stone, Weathering Phenomena, Conservation Strategies and Case Studies; Siegesmund, S., Weiss, T., Vollbrecht, A., Eds.; Special Publications 205; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2002; pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Graue, B.; Siegesmund, S.; Oyhantcabal, P.; Naumann, R.; Licha, T.; Simon, K. The effect of air pollution on stone decay: The decay of the Drachenfels trachyte in industrial, urban, and rural environments–a case study of the Cologne, Altenberg and Xanten cathedrals. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1095–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C.; de’ Gennaro, M.; Aiello, R. Use of zeolitic tuff in the building industry. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 45, 551–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzner, B. Volcanic tuffs: The description and quantitative recording of their weathered state. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.J.; Török, Á.; McAlister, J.J.; Megarry, J. Observations on the factors influencing stability of building stones following contour scaling: A case study of the oolitic limestones from Budapest, Hungary. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, O.; Siegesmund, S.; Licha, T.; Török, Á. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of black weathering crusts on limestones from seven different European countries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Oguchi, C.T. Role of pore size distribution in salt uptake, damage, and predicting salt susceptibility of eight types of Japanese building stones. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, W.; Ruedrich, J.; Siegesmund, S. Natural building stones of Mexico–Tenochtitlán: Their use, weathering and rock properties at the Templo Mayor, Palace Heras Soto and the Metropolitan Cathedral. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Doncel, R.; Wedekind, W.; Leiser, T.; Molina-Maldonado, S.; Velasco-Sánchez, A.; Dohrmann, R.; Kral, A.; Wittenborn, A.; Aguillón-Robles, A.; Siegesmund, S. Salt bursting tests on volcanic tuff rocks from Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, M.; Özvan, A.; Dinçer, İ.; Topal, T. Evaluation of the physico-mechanical parameters affecting the deterioration rate of Ahlat ignimbrites (Bitlis, Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.V.; Schmincke, H.U. Pyroclastic Rocks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Steindlberger, E. Volcanic tuffs from Hesse (Germany) and their weathering behaviour. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, W.; López-Doncel, R.; Dohrmann, R.; Kocher, M.; Siegesmund, S. Weathering of volcanic tuff rocks caused by moisture expansion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1203–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, M.J.; Farquharson, J.I.; Kushnir, A.R.; Lavallée, Y.; Baud, P.; Gilg, H.A.; Reuschlé, T. The influence of water on the strength of Neapolitan Yellow Tuff, the most widely used building stone in Naples (Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2018, 80, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötzl, C.; Siegesmund, S.; Dohrmann, R.; Koning, J.M.; Wedekind, W. Deterioration of volcanic tuff rocks from Armenia: Constraints on salt crystallization and hydric expansion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Heavy Metal Accumulation in Mosses in Europe (1990–2005); Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Winther, M.; Slentø, E. Heavy Metal Emissions for Danish Road Transport; NERI Technical Report No. 780; National Environmental Research Institute: Aarhus, Danmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Comite, V.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Barca, D.; Belfiore, C.M.; Bonazza, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Randazzo, L.; Ruffolo, S.A. Damage monitoring on carbonate stones: Field exposure tests contributing to pollution impact evaluation in two Italian sites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.H.; Chu, C.J.; Li, J.; Song, B. Heavy metal pollution in soils on railroad side of Zhengzhou-Putian section of Longxi-Haizhou Railroad, China. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, I.; Pósfai, M.; Kovács, K.; Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Posta, J. Properties and sources of individual particles and some chemical species in the aerosol of a metropolitan underground railway station. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiłkomirski, B.; Sudnik-Wójcikowska, B.; Galera, H.; Wierzbicka, M.; Malawska, M. Railway transportation as a serious source of organic and inorganic pollution. WaterAir Soil Pollut. 2011, 218, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierżanowski, K.; Gawroński, S.W. Heavy metal concentration in plants growing on the vicinity of railroad tracks: A pilot study. Chall. Mod. Technol. 2012, 3, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Ai, Y.W.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Fang, C. The effects of railway transportation on the enrichment of heavy metals in the artificial soil on railway cut slopes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, C.M.; Murray, M. Characteristics of carbonate building stones that influence the dry deposition of acidic gases. Constr. Build. Mater. 1999, 13, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, M.; Charola, A.E.; Sterflinger, K. Weathering and deterioration. In Stone in Architecture. Properties, Durability, 5th ed.; Siegesmund, S., Snethlage, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 225–316. [Google Scholar]
- Germinario, L.; Andriani, G.F.; Laviano, R. Decay of calcareous building stone under the combined action of thermoclastism and cryoclastism: A laboratory simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Maritan, L.; Mazzoli, C. Petrophysical and mechanical properties of Euganean trachyte and implications for dimension stone decay and durability performance. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
