Prediction Models for Evaluating the Strength of Cemented Paste Backfill: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Experimental Tests
2.2. Applied Machine Learning Models
2.3. Building Waste Heat Simulation with EnergyPlus
3. Results and Discussion
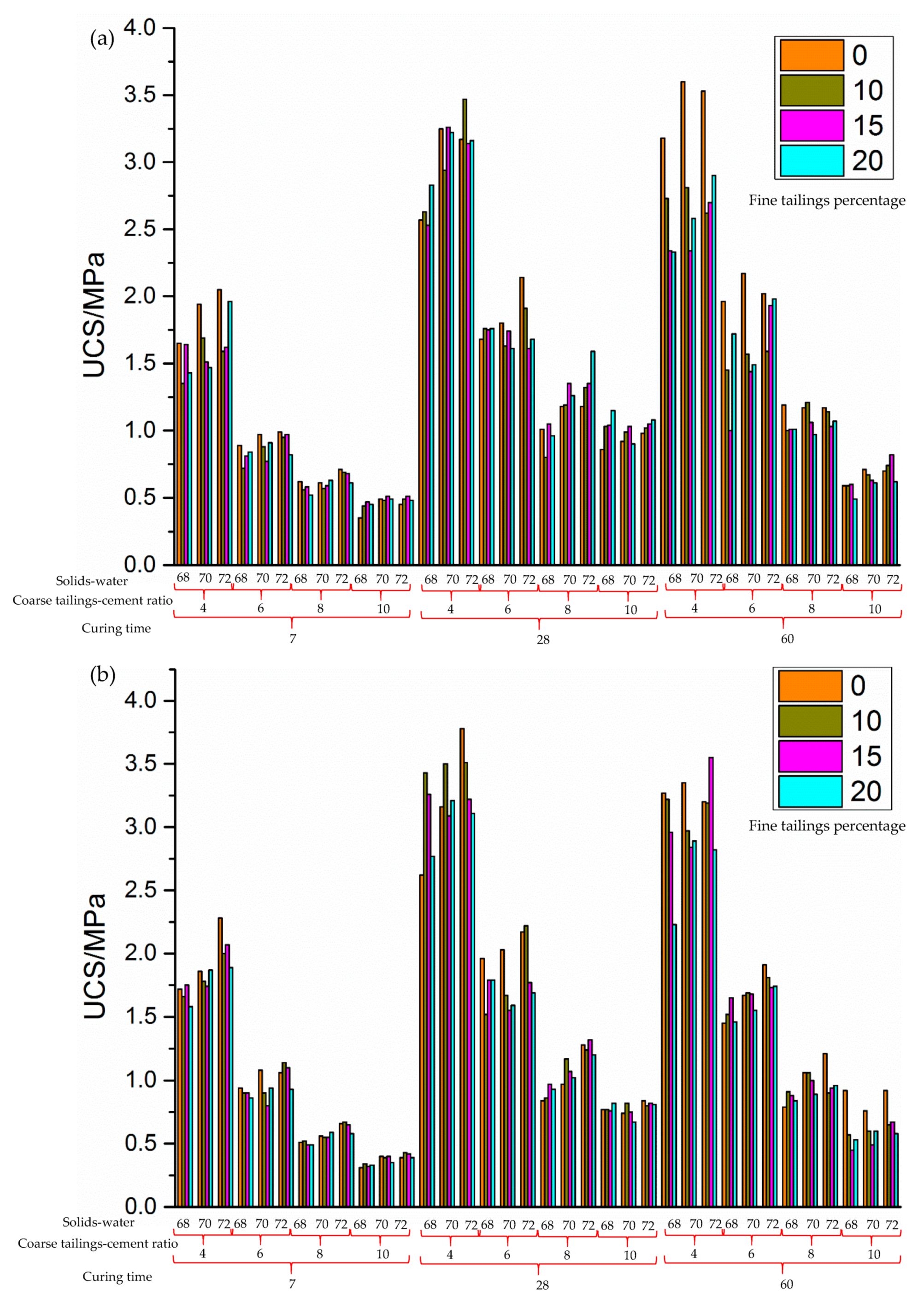
3.1. The Results of UCS of Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB)
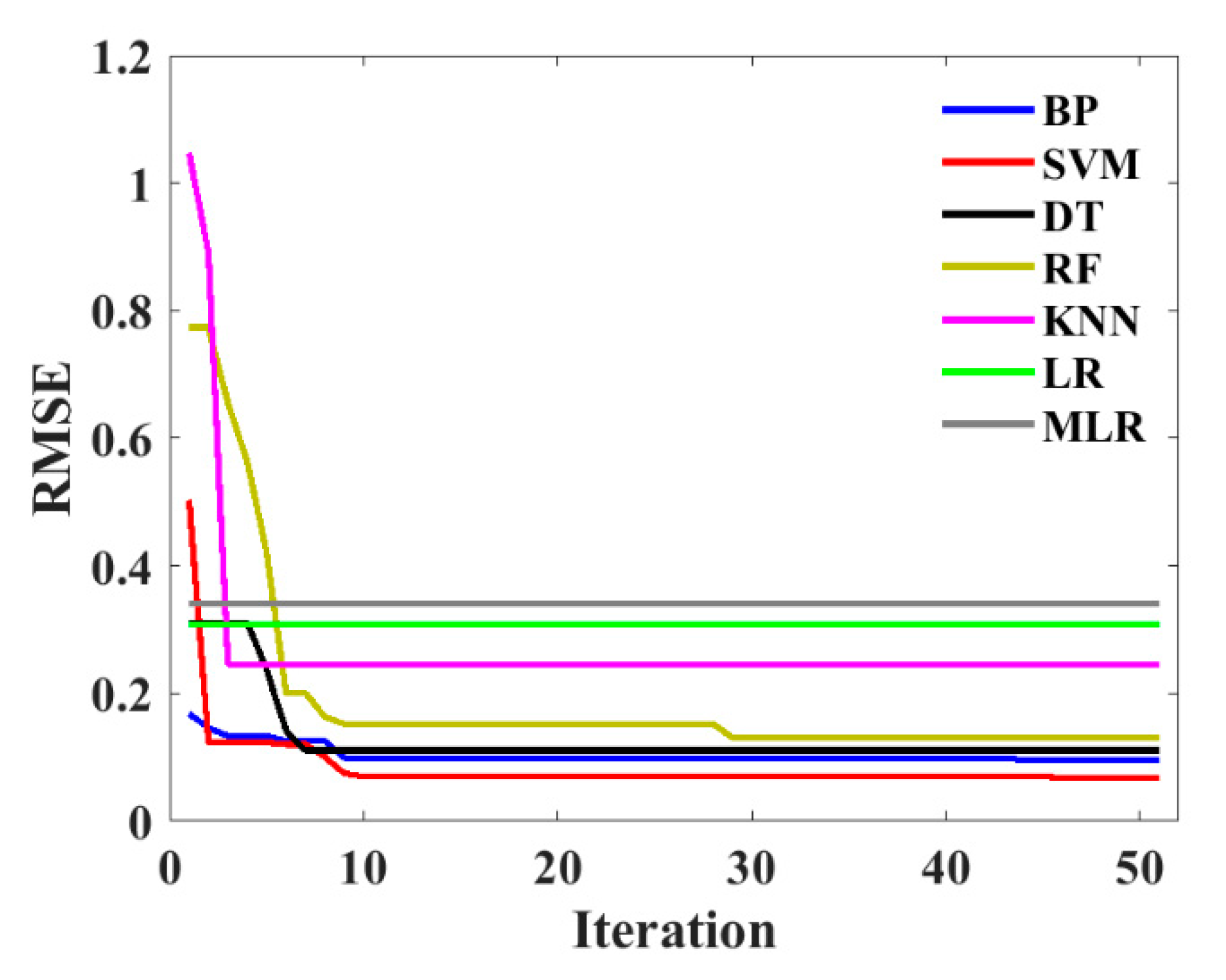
3.2. Hyper-Parameters Tuning
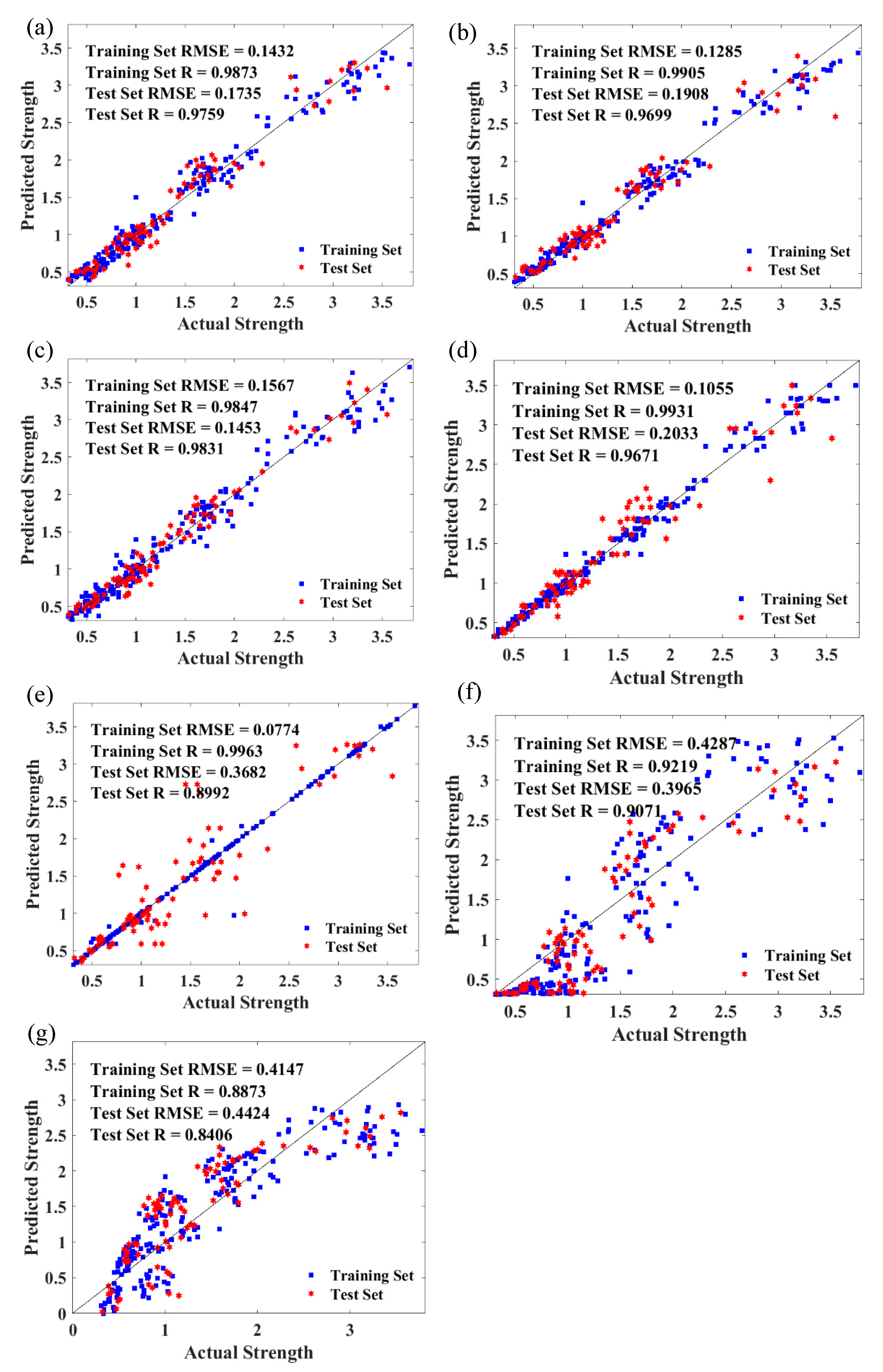
3.3. Model Evaluation
3.4. Spatial Variations of Anthropogenic Heat Intensity
4. Conclusions
- The results of UCS of CPB shows that with the increase of ratio between solids and water ratio, as well as curing time, the UCS of CPB increased, while the strength of CPB declined with the increase of fine sand percentage and the tailing to cement ratio.
- According to the prediction models, the SVM RF, BP and DT models can predict the UCS of CPB effectively and accurately, although the KNN, LR and MLR have a relatively worse performance on the prediction.
- The tailing to cement ratio can affects the strength of CPB obvious, followed by Curing time, solids to water ratio, fine sand, and cement type, which can guide the CPB application in the field.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q. A strength prediction model using artificial intelligence for recycling waste tailings as cemented paste backfill. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-S.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Fourie, A.; Chen, X.; Qi, C.-C. Experimental investigation on the strength characteristics of cement paste backfill in a similar stope model and its mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. Cemented paste backfill for mineral tailings management: Review and future perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2019, 144, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B. Mechanical behaviour of cemented paste backfill. In Proceedings of the 53rd Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–18 October 2000; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Demers, I.; Aubertin, M.; Fried, É.; Blier, A. Integrated mine tailings management by combining environmental desulphurization and cemented paste backfill: Application to mine doyon, Quebec, Canada. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Tang, X.; Dong, X.; Chen, Q.; Fourie, A.; Liu, E. Towards intelligent mining for backfill: A genetic programming-based method for strength forecasting of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2019, 133, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Chen, Q.; Fourie, A.; Zhang, Q. An intelligent modelling framework for mechanical properties of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2018, 123, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, M.; Pokharel, M. Coupled effects of sulphate and temperature on the strength development of cemented tailings backfills: Portland cement-paste backfill. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurlu, E.; Kesimal, A.; Demir, S. Experimental and numerical analyses on determination of indirect (splitting) tensile strength of cemented paste backfill materials under different loading apparatus. Geomech. Eng. 2016, 10, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, J. Development of an ensemble intelligent model for assessing the strength of cemented paste backfill. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5198583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helinski, M.; Fahey, M.; Fourie, A. Behavior of cemented paste backfill in two mine stopes: Measurements and modeling. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2011, 137, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashrei, M.A.; Seracino, R.; Rahman, M. Application of artificial neural networks to predict the bond strength of frp-to-concrete joints. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Taboada, I.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F.; Pérez-Ordóñez, J.L. Prediction of the mechanical properties of structural recycled concrete using multivariable regression and genetic programming. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.D.; Bawden, W.F.; Grabinsky, M. In situ measurements of cemented paste backfill at the cayeli mine. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Developing hybrid machine learning models for estimating the unconfined compressive strength of jet grouting composite: A comparative study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovos, K.G.; Asteris, P.G.; Tsivilis, S. Properties of sandcrete mixtures modified with metakaolin. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, s18–s37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, S.; Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M.; Benzaazoua, M. Microstructural evolution of cemented paste backfill: Mercury intrusion porosimetry test results. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Toward intelligent construction: Prediction of mechanical properties of manufactured-sand concrete using tree-based models. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, G. Prediction of permeability and unconfined compressive strength of pervious concrete using evolved support vector regression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Qian, D. Prediction of the strength of rubberized concrete by an evolved random forest model. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1643529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, G.; Sun, J.; Nener, B. A metaheuristic-optimized multi-output model for predicting multiple properties of pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.; Dou, J.; Zhou, J. A comparative study of pso-ann, ga-ann, ica-ann, and abc-ann in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, C. Optimized neural network using beetle antennae search for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of jet grouting coalcretes. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2019, 43, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBT50107-2019. Standard for Inspection and Evaluation of Concrete Strength; Ministry of urban and rural construction and environmental protection of the people’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Ma, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Nener, B. Determination of young’s modulus of jet grouted coalcretes using an intelligent model. Eng. Geol. 2019, 252, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Chen, Q. Neural network and particle swarm optimization for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of cemented paste backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.-C. Big data management in the mining industry. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, N.; Chang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Development of ensemble learning models to evaluate the strength of coal-grout materials. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G.; Nener, B. A hybrid intelligent system for designing optimal proportions of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, G. Multi-objective optimization of concrete mixture proportions using machine learning and metaheuristic algorithms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

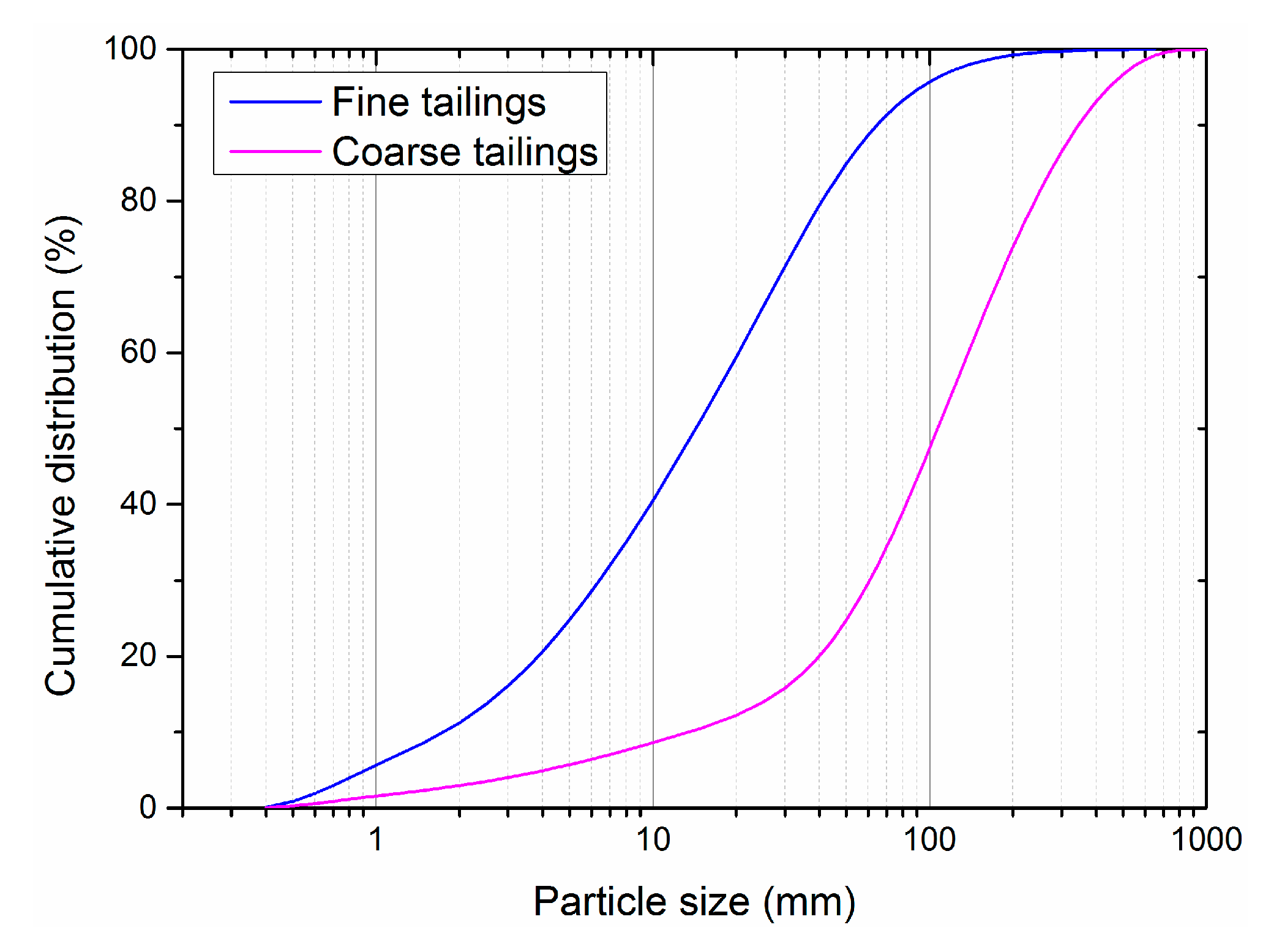

| Elements | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe | FeO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content % | 46.52 | 6.2 | 7.86 | 5.44 | 8.99 | 19.2 | 1.64 |
| Elements | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | S | Cu | Zn |
| Content % | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 0.11 | 5.08 |
| Elements | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe | FeO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content % | 43.4 | 5.67 | 8.56 | 7.43 | 10.65 | 18.89 | 1.44 |
| Elements | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | S | Cu | Zn |
| Content % | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.2 | 6.14 |
| Sample | Fineness (<0.0045 mm/%) | Initial Setting Time/min | Final Setting Time/min | 28d-UCS/MPa | 28d-Flexural Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 23.2 | 240 | 305 | 30.7 | 6.5 |
| #2 | 6 | 180 | 255 | 39.8 | 8 |
| Program | Results/(mg/L) | Program | Results/(mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 0.39 | Li | <0.05 |
| As | <0.05 | Mg | 20.8 |
| Ba | 0.058 | Mn | 0.22 |
| Be | <0.05 | Ni | <0.05 |
| Bi | 0.074 | Pb | <0.05 |
| Ca | 6.26 | Sb | <0.05 |
| Cd | <0.05 | Sn | <0.05 |
| Co | <0.05 | Sr | 6.74 |
| Cr | <0.05 | Ti | <0.05 |
| Cu | <0.05 | V | <0.05 |
| Fe | 0.15 | Zn | <0.05 |
| Cement Types | Coarse Tailings-Cement Ratio | Fine Tailings Percentage | Solids-Water Ratio | Curing Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 4 | 0% | 0.68 | 7 |
| #2 | 6 | 10% | 0.70 | 28 |
| 8 | 15% | 0.72 | 60 | |
| 10 | 20% |
| Cement Type | Curing Time (Days) | Standard Deviations of UCS |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | 7 | 0.47 |
| 28 | 0.81 | |
| 60 | 0.85 | |
| #2 | 7 | 0.57 |
| 28 | 0.96 | |
| 60 | 0.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Huang, J. Prediction Models for Evaluating the Strength of Cemented Paste Backfill: A Comparative Study. Minerals 2020, 10, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111041
Liu J, Li G, Yang S, Huang J. Prediction Models for Evaluating the Strength of Cemented Paste Backfill: A Comparative Study. Minerals. 2020; 10(11):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiandong, Guichen Li, Sen Yang, and Jiandong Huang. 2020. "Prediction Models for Evaluating the Strength of Cemented Paste Backfill: A Comparative Study" Minerals 10, no. 11: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111041
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, G., Yang, S., & Huang, J. (2020). Prediction Models for Evaluating the Strength of Cemented Paste Backfill: A Comparative Study. Minerals, 10(11), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111041







