Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Behavior of Magnesite and Dolomite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
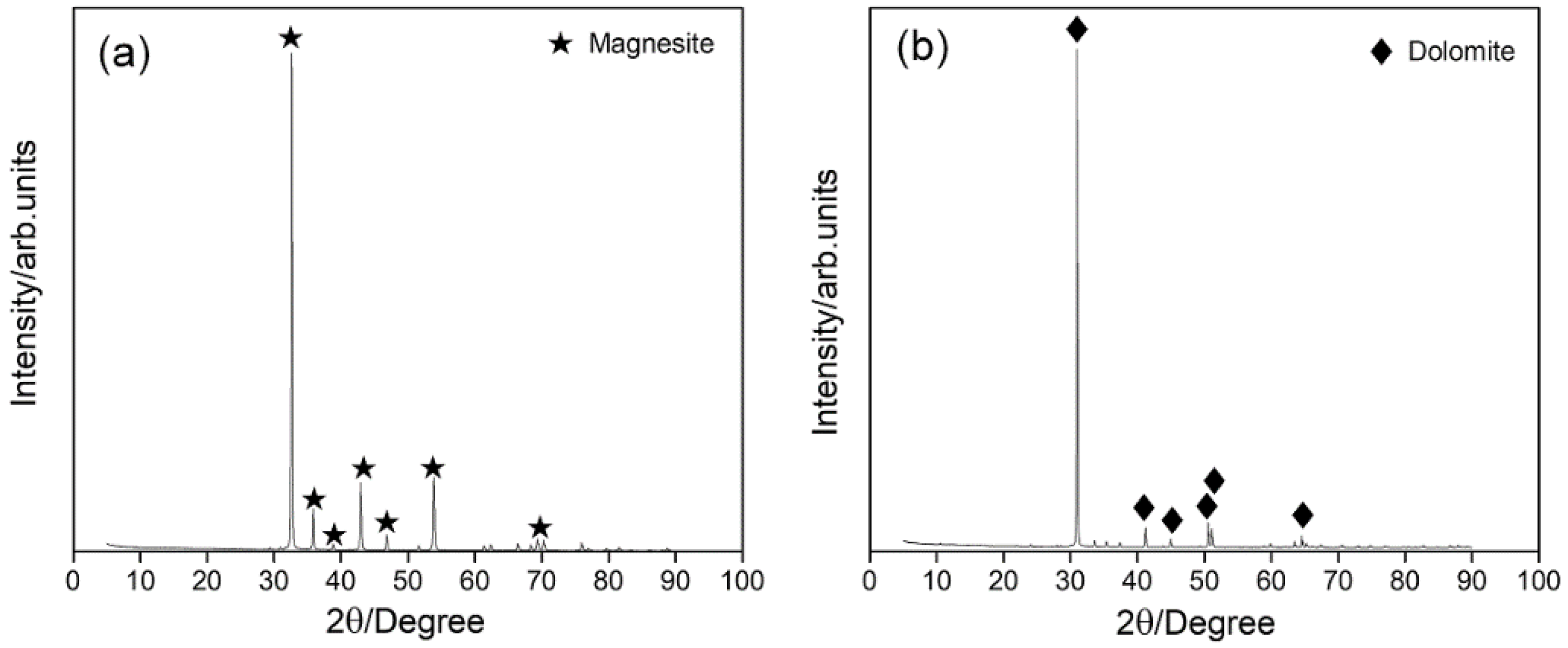
2.1. Minerals and Reagents
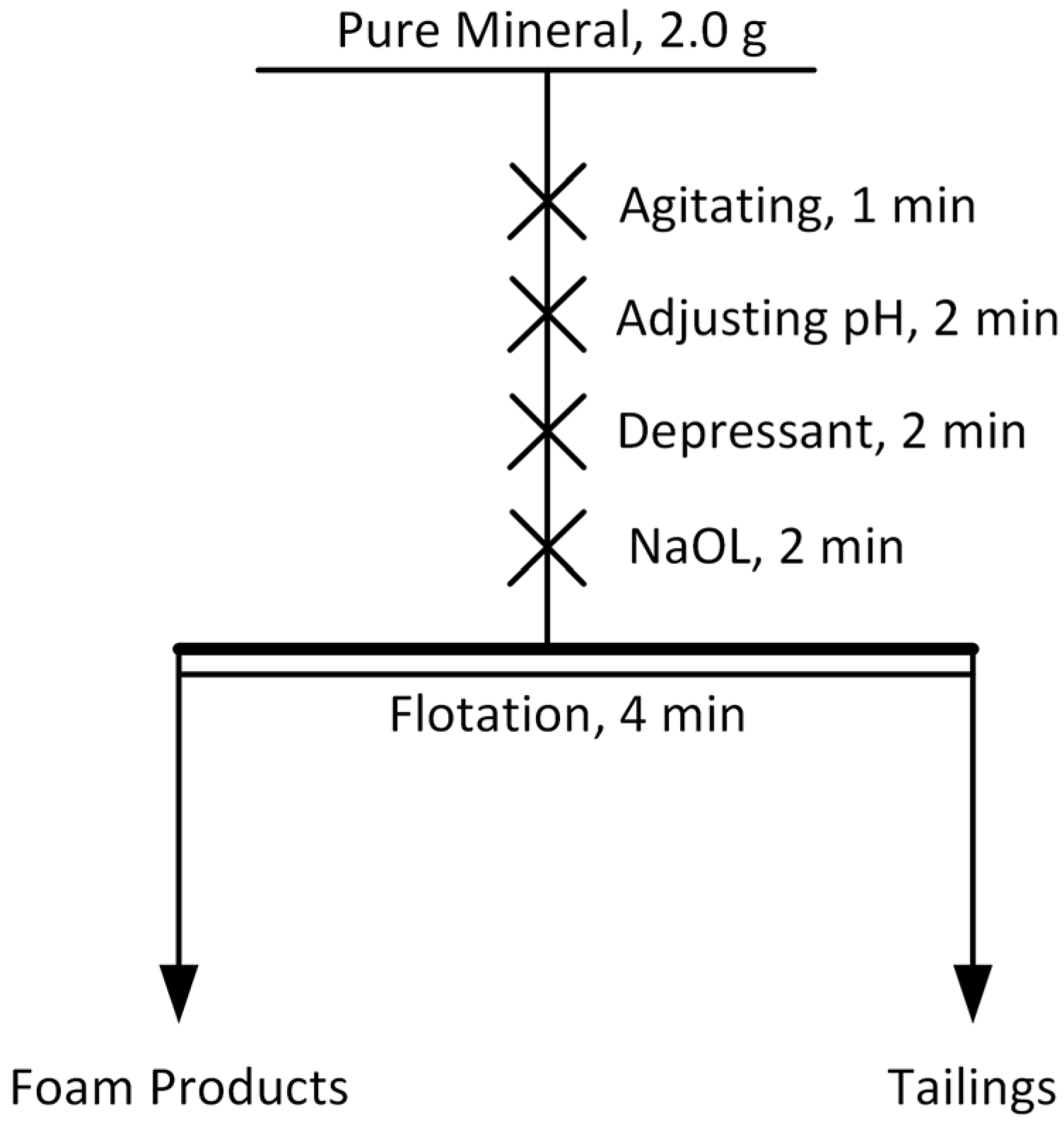
2.2. Flotation Tests
2.3. Contact Angle Measurements
2.4. Contact Angle Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
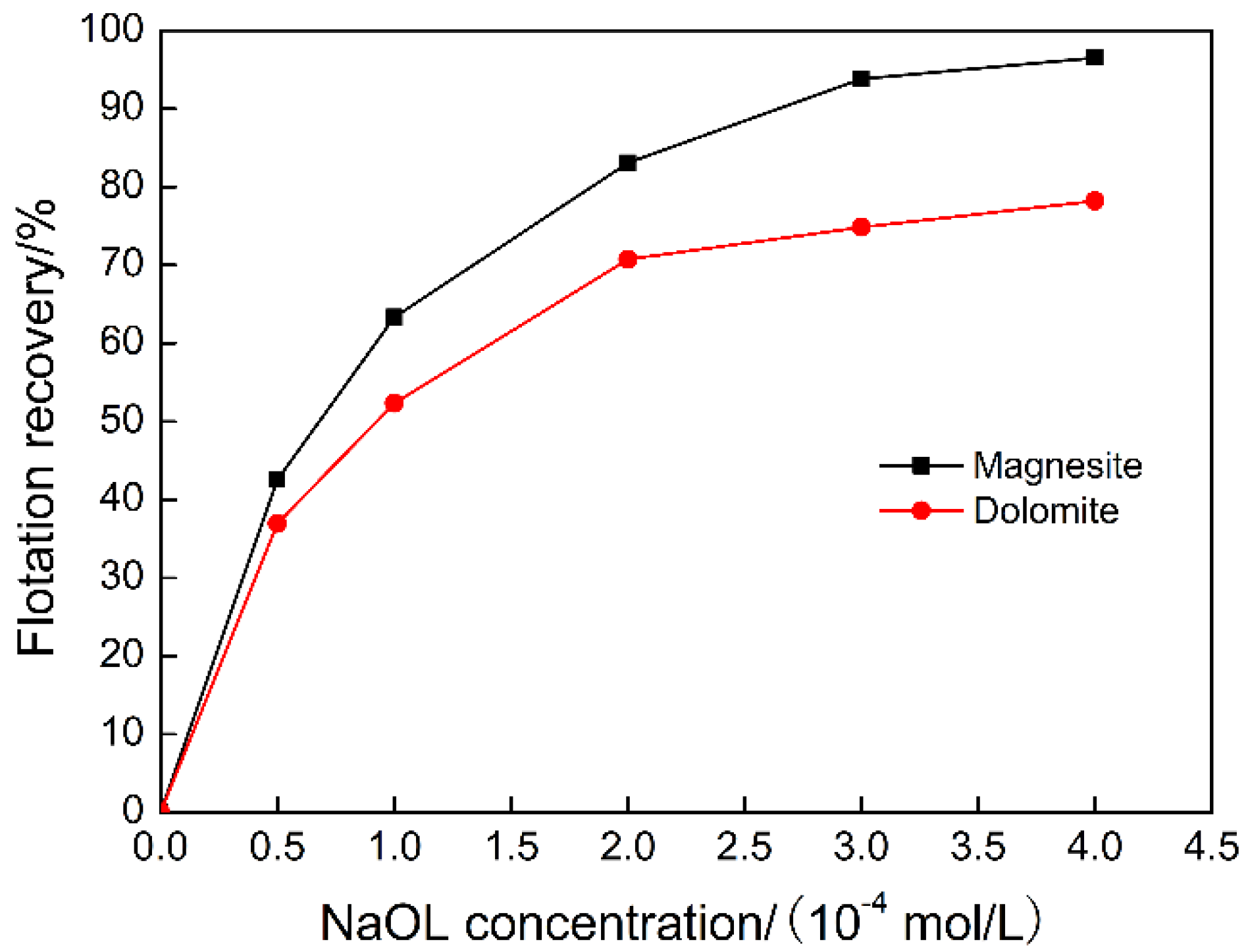
3.1. The Effect of Sodium Oleate on Magnesite and Dolomite
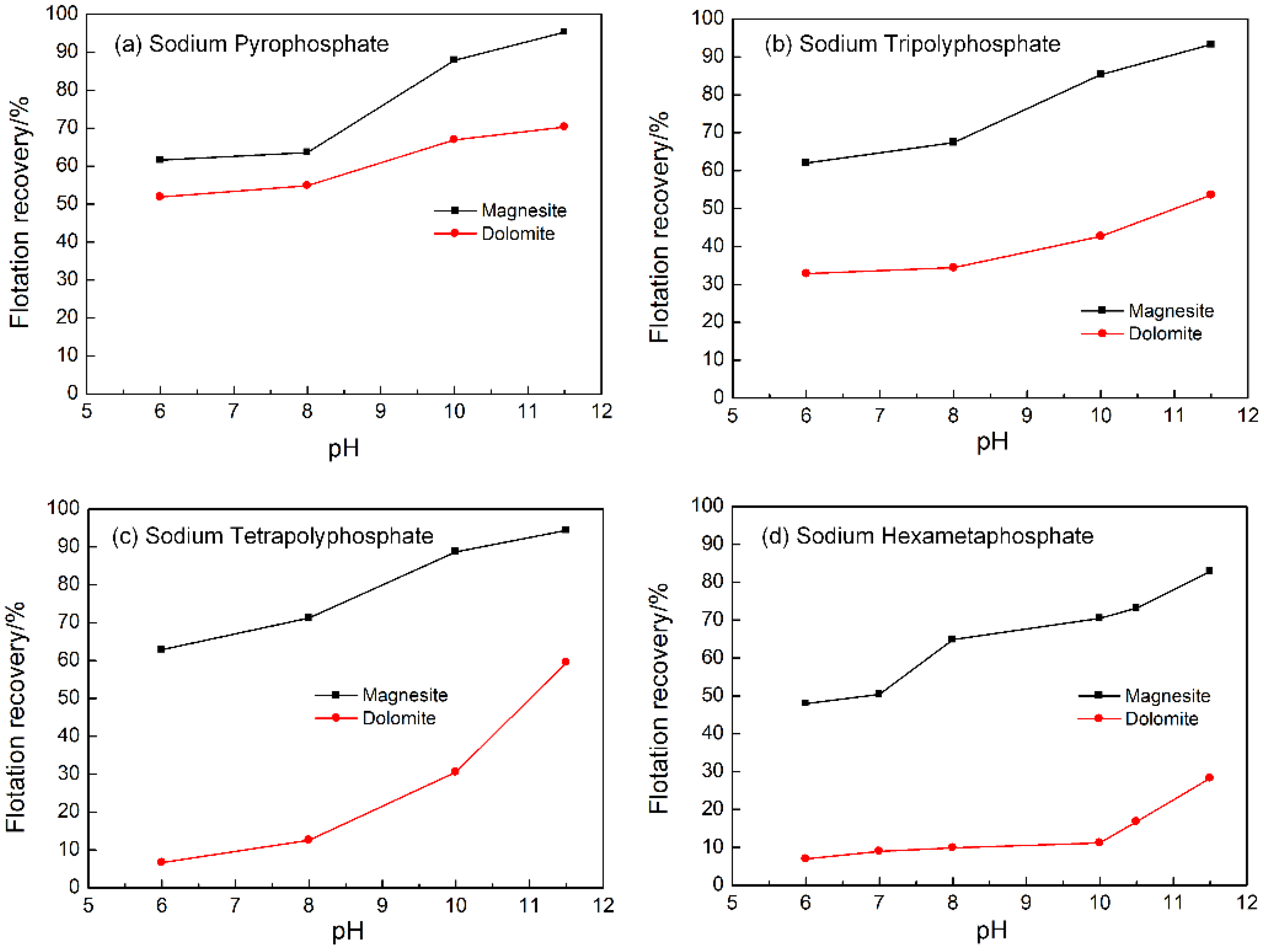
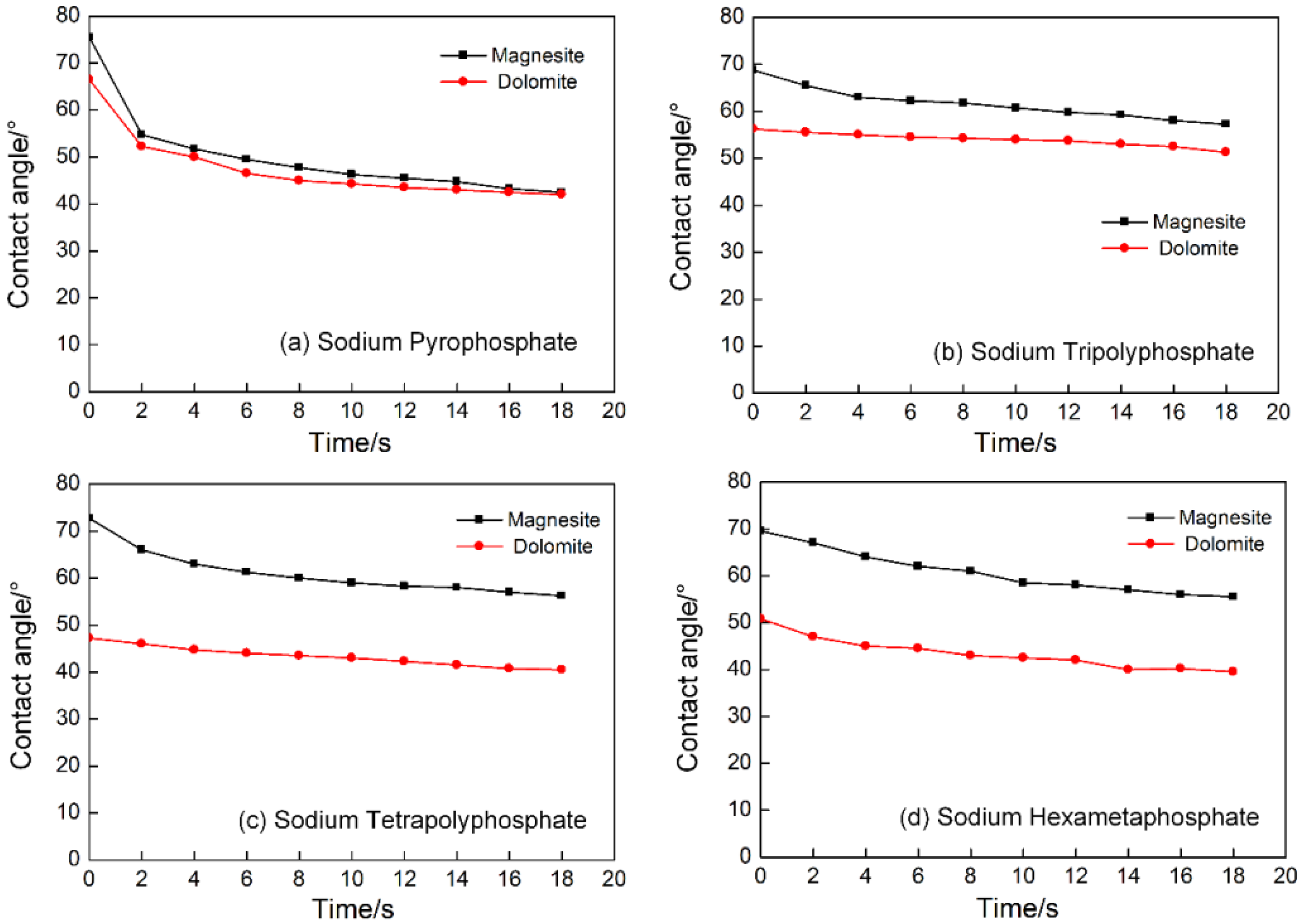
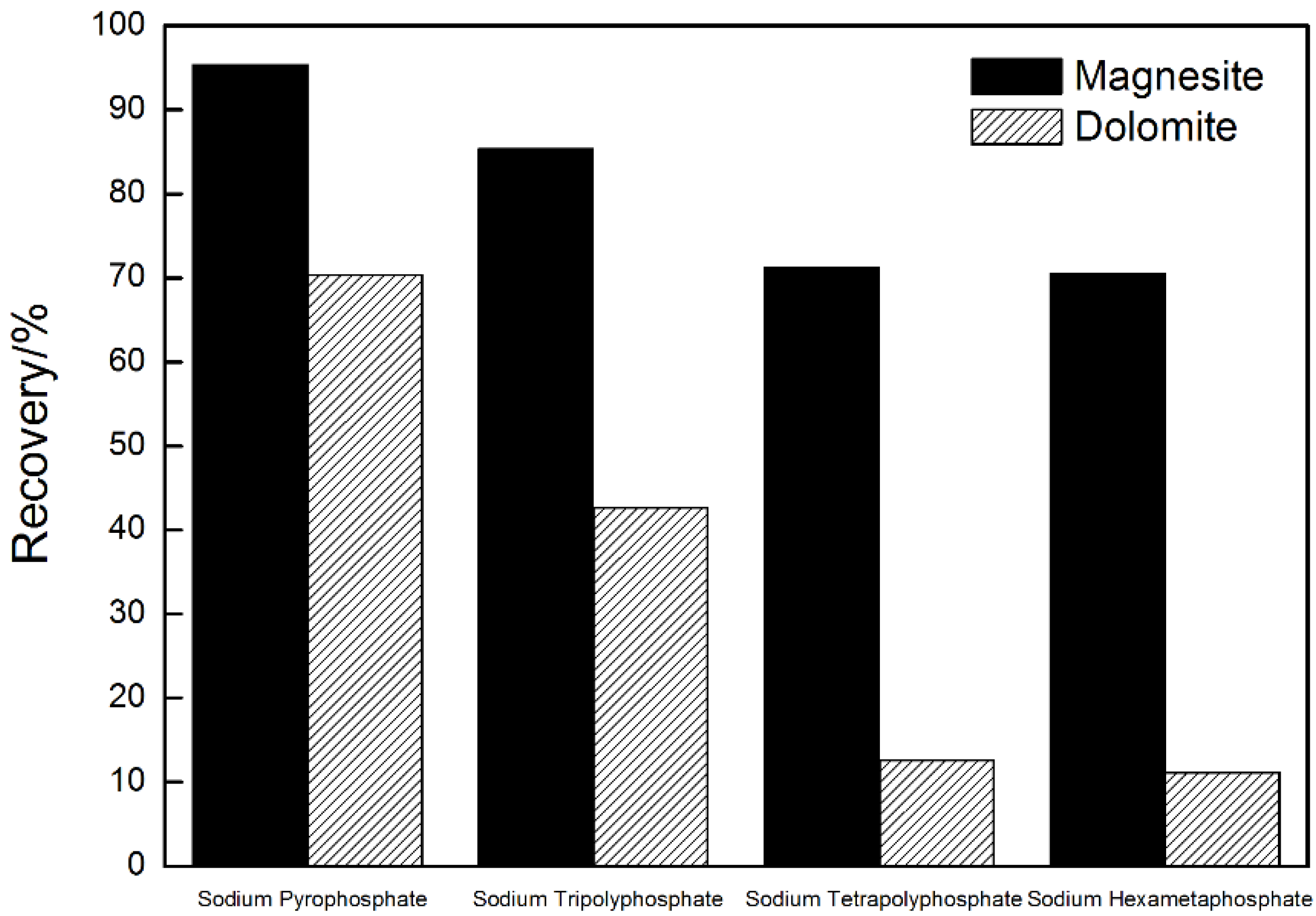
3.2. Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Separation of Magnesite and Dolomite
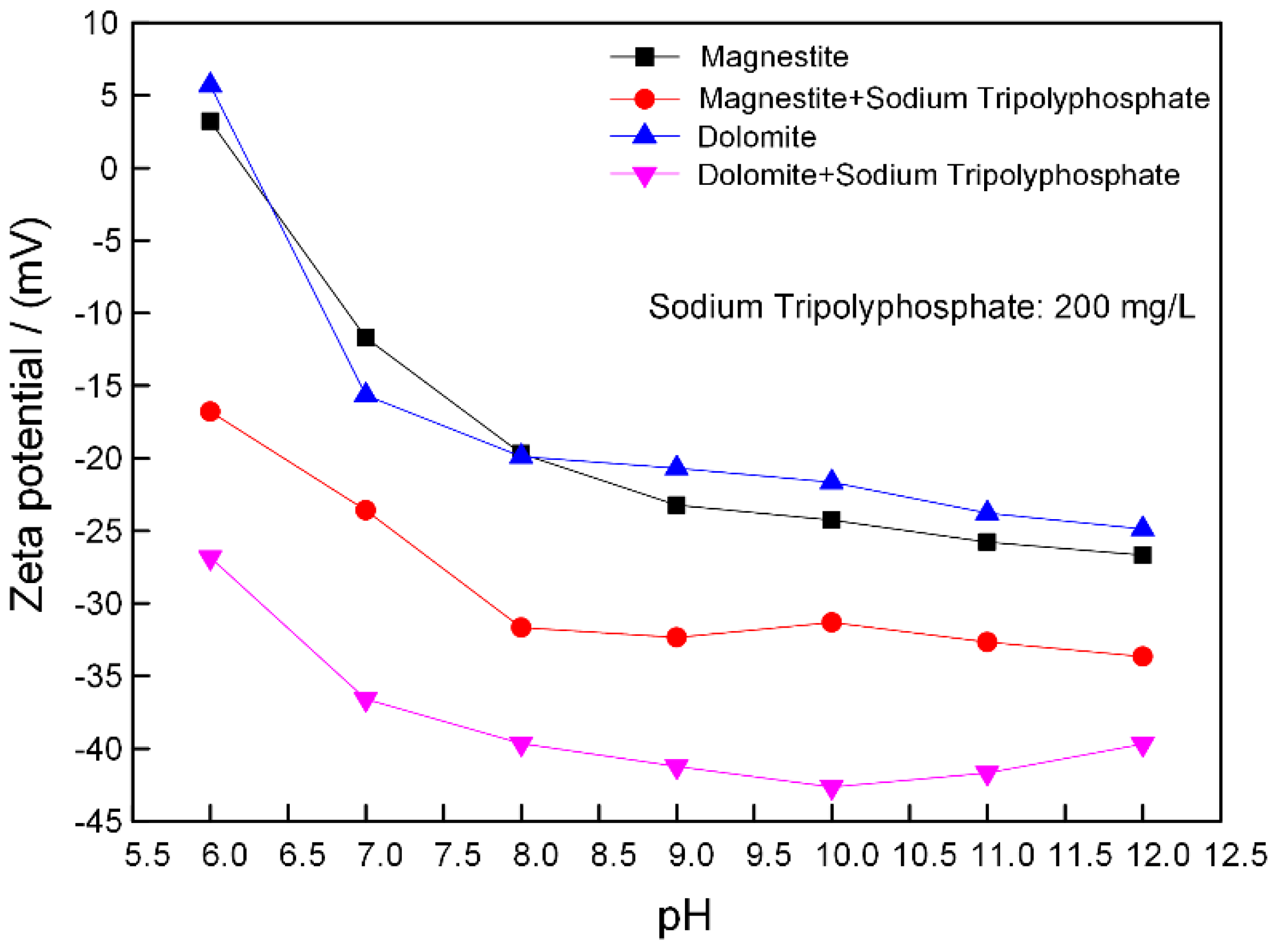
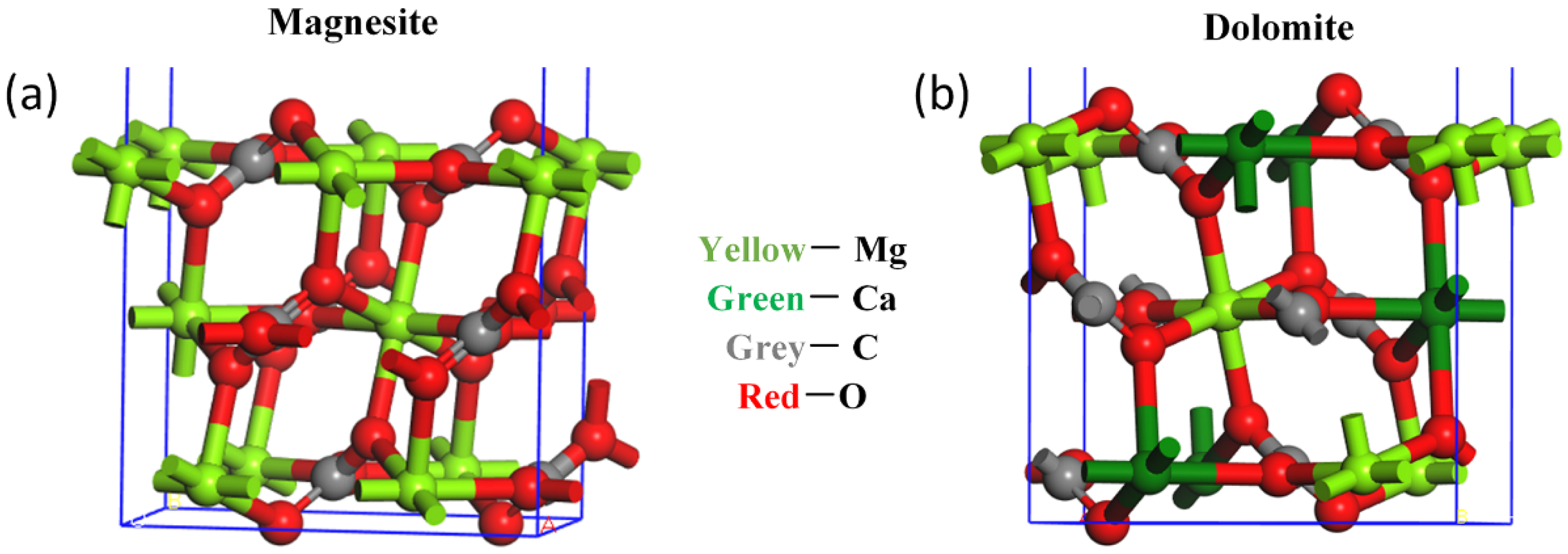
3.3. The Inhibition Mechanism of Sodium Phosphate Salts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, K.T.; Han, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Tran, T. Recovery of magnesium from Uyuni salar brine as hydrated magnesium carbonate. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J. Selective flotation of magnesite from dolomite using α-chloro-oleate acid as collector. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhu, Z. Selective co-adsorption of a novel mixed collector onto magnesite surface to improve the flotation separation of magnesite from dolomite. Powder Technol. 2020, 371, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Cao, S.; Yin, W.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Yao, J. Selective adsorption of a high-performance depressant onto dolomite causing effective flotation separation of magnesite from dolomite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020, 578, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Han, F.; Yin, W.; Hong, J.; Yang, B. Modification of selectivity in the flotation separation of magnesite from dolomite. Colloid Surface. 2020, 606, 125460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yin, W.; Gong, E. Depressing effect of fine hydrophilic particles on magnesite reverse flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 149, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, N.; Wei, D.Z.; Shen, Y.B.; Han, C.; Zhang, C.E. Elimination of the adverse effect of calcium ion on the flotation separation of magnesite from dolomite. Mineral 2017, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.Z.; Sun, H.R.; Tang, Y.; Hong, J.S.; Yang, B.; Fu, Y.F.; Han, H.L. Effect of pulp temperature on separation of magnesite from dolomite in sodium oleate flotation system. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Sun, H.; Hong, J.; Cao, S.; Yang, B.; Won, C.; Song, M. Effect of Ca selective chelator BAPTA as depressant on flotation separation of magnesite from dolomite. Miner. Eng. 2019, 144, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonyen, D.G.; Kromah, V.; Gibson, B.; Nah, S.; Chelgani, S.C. A review of flotation separation of Mg carbonates (dolomite and magnesite). Mineral 2018, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matis, K.A.; Balabanidis, T.N.; Gallios, G.P. Processing of magnesium carbonate fines by dissolved-air flotation. Colloid. Surface 1988, 29, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matis, K.A.; Gallios, G.P. Anionic flotation of magnesium carbonates by modifiers. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1989, 25, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L.; Tao, D. Reverse flotation of magnesite by dodecyl phosphate from dolomite in the presence of sodium silicate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Masuyama, A.; Okahara, M. Preparation and surface-active properties of new amphipathic compounds with two phosphate groups and two long-chain alkyl groups. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gence, N. Wetting behavior of magnesite and dolomite surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 3744–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yin, W.; Kelebek, S. Magnesite-dolomite separation using potassium cetyl phosphate as a novel flotation collector and related surface chemistry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntwampe, I.O.; Waanders, F.B.; Bunt, T.S.S.R. Comparison between mixing and shaking techniques during the destabilization-hydrolysis of the acid mine drainage (AMD) using Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2. J. Chem. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2015, 6, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, L.A.; Barak, P. Solubility and dissolution kinetics of dolomite in Ca–Mg–HCO3/CO3 solutions at 25 °C and 0.1 MPa carbon dioxide. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Cygan, R.T.; Slater, B. Atomistic simulations of the (1014) surface of carbonate minerals. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2000, 620, M2.2.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Cygan, R.T.; Slater, B. Structure of the (1014) surfaces of calcite, dolomite, and magnesite under wet and dry conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Tao, D. Effect of solution chemistry on flotability of magnesite and dolomite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gence, N.; Ozbay, N. pH dependence of electrokinetic behavior of dolomite and magnesite in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8057–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mofty, S.E.; El-Midany, A.A. Role of calcium ions and their interaction with depressants in phosphate flotation. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2641–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.D.R.; Rodrigues, R.T.; Azevedo, A.C.; Rubio, J. Calcium and magnesium ion removal from water feeding a steam generator by chemical precipitation and flotation with micro and nanobubbles. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | MgO/% | CaO/% | SiO2/% | Al2O3/% | FeO/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesite | 47.20 | 0.50 | 0.62 | <0.02 | 0.17 |
| Dolomite | 21.61 | 30.85 | 0.05 | - | - |
| Minerals | Metal Site Density/nm2 | Number of Broken Bonds at Metal Site |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesite (104) | Mg:5.70 | 2 |
| Dolomite (104) | Ca: 2.704; Mg: 2.704 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, W.; Chen, X. Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Behavior of Magnesite and Dolomite. Minerals 2020, 10, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111031
Bai J, Wang J, Yin W, Chen X. Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Behavior of Magnesite and Dolomite. Minerals. 2020; 10(11):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Junzhi, Jizhen Wang, Wanzhong Yin, and Xiangxiang Chen. 2020. "Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Behavior of Magnesite and Dolomite" Minerals 10, no. 11: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111031
APA StyleBai, J., Wang, J., Yin, W., & Chen, X. (2020). Influence of Sodium Phosphate Salts with Different Chain Length on the Flotation Behavior of Magnesite and Dolomite. Minerals, 10(11), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111031




