In Situ Trace Elemental Analyses of Scheelite from the Chuankou Deposit, South China: Implications for Ore Genesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
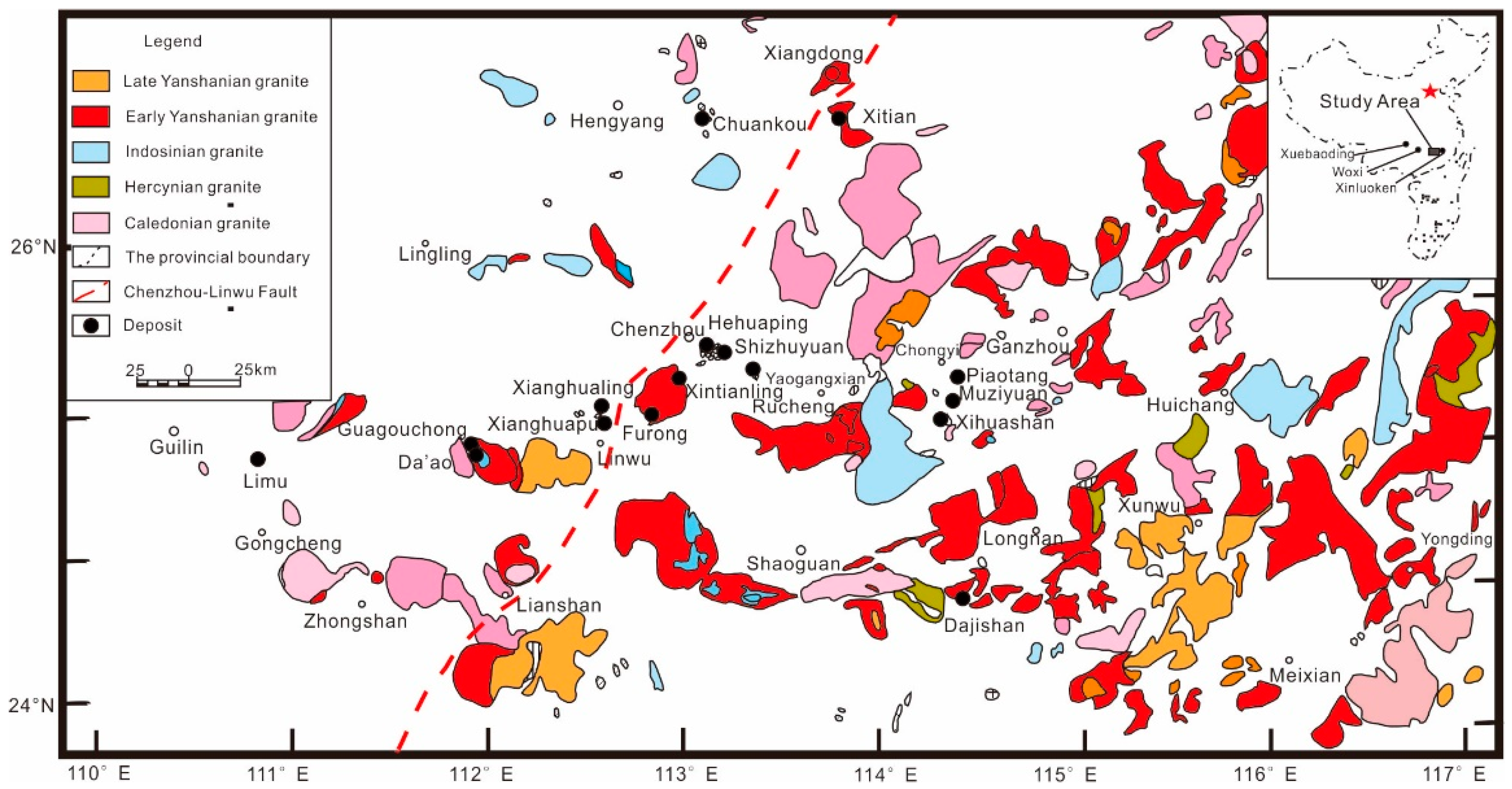
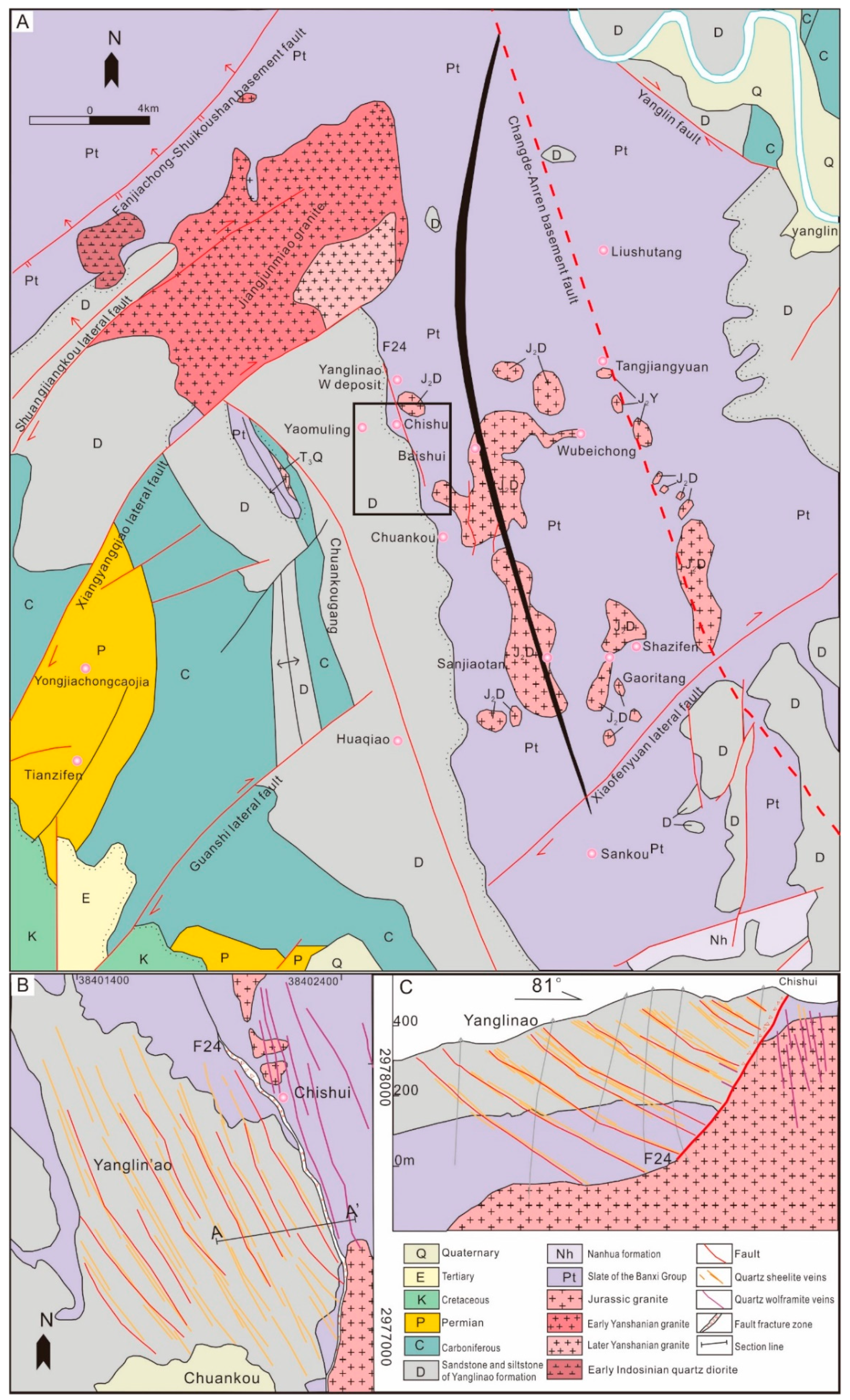
2. Geologic Settings
2.1. Regional Geology
2.2. Ore Deposit Geology
3. Materials and Methods
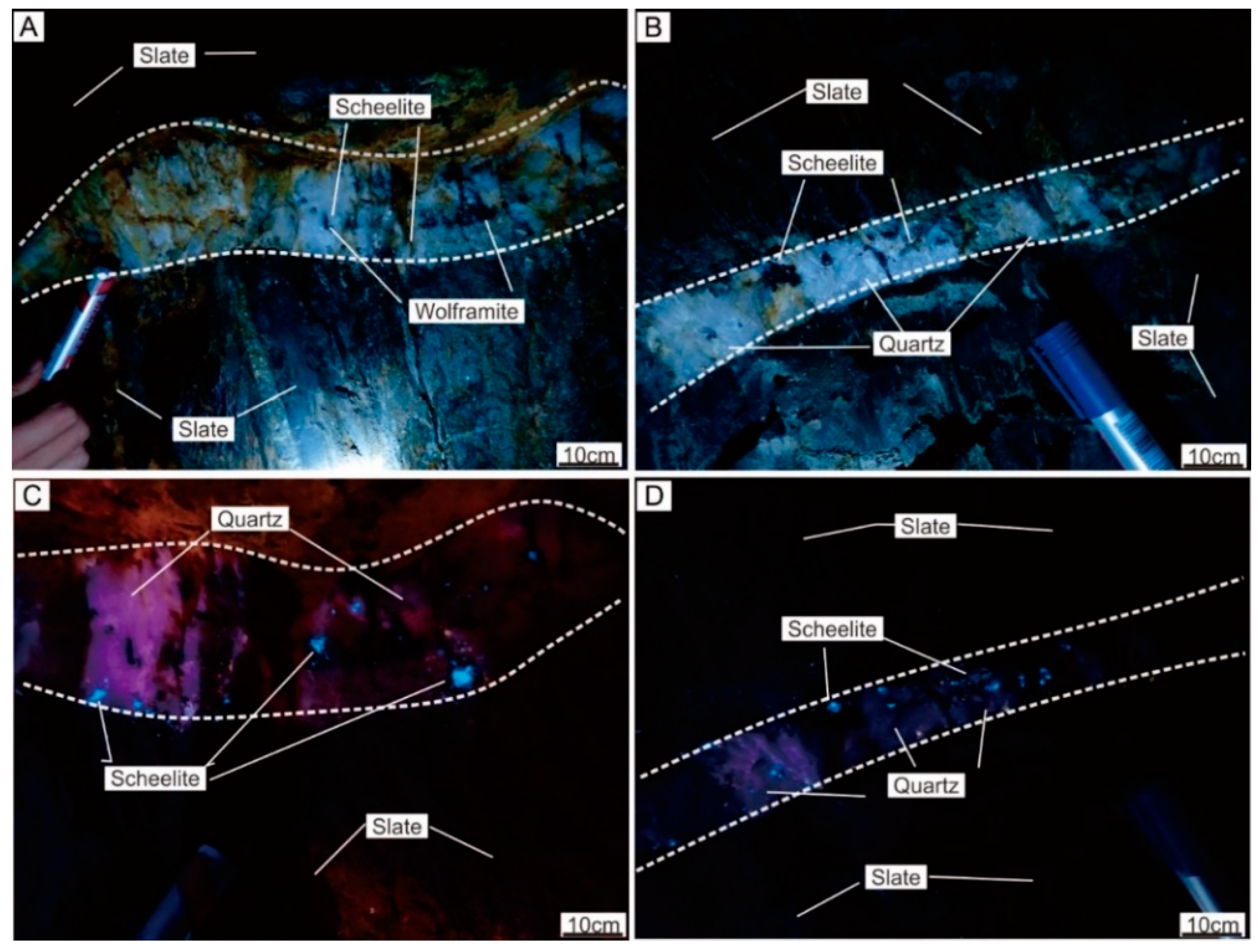
3.1. Optical Microscopy and OM-CL
3.2. LA-ICP-MS Analyses
4. Results
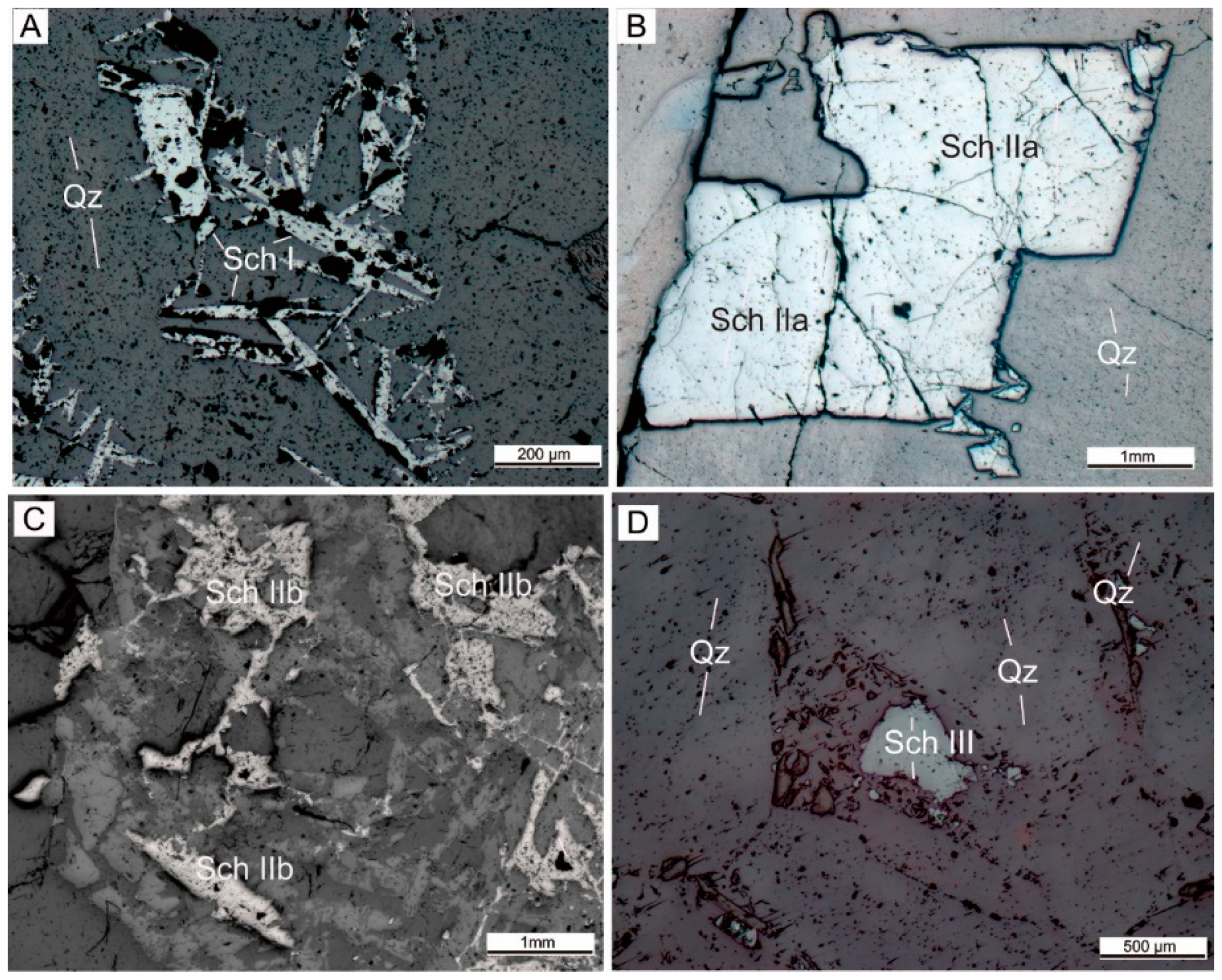
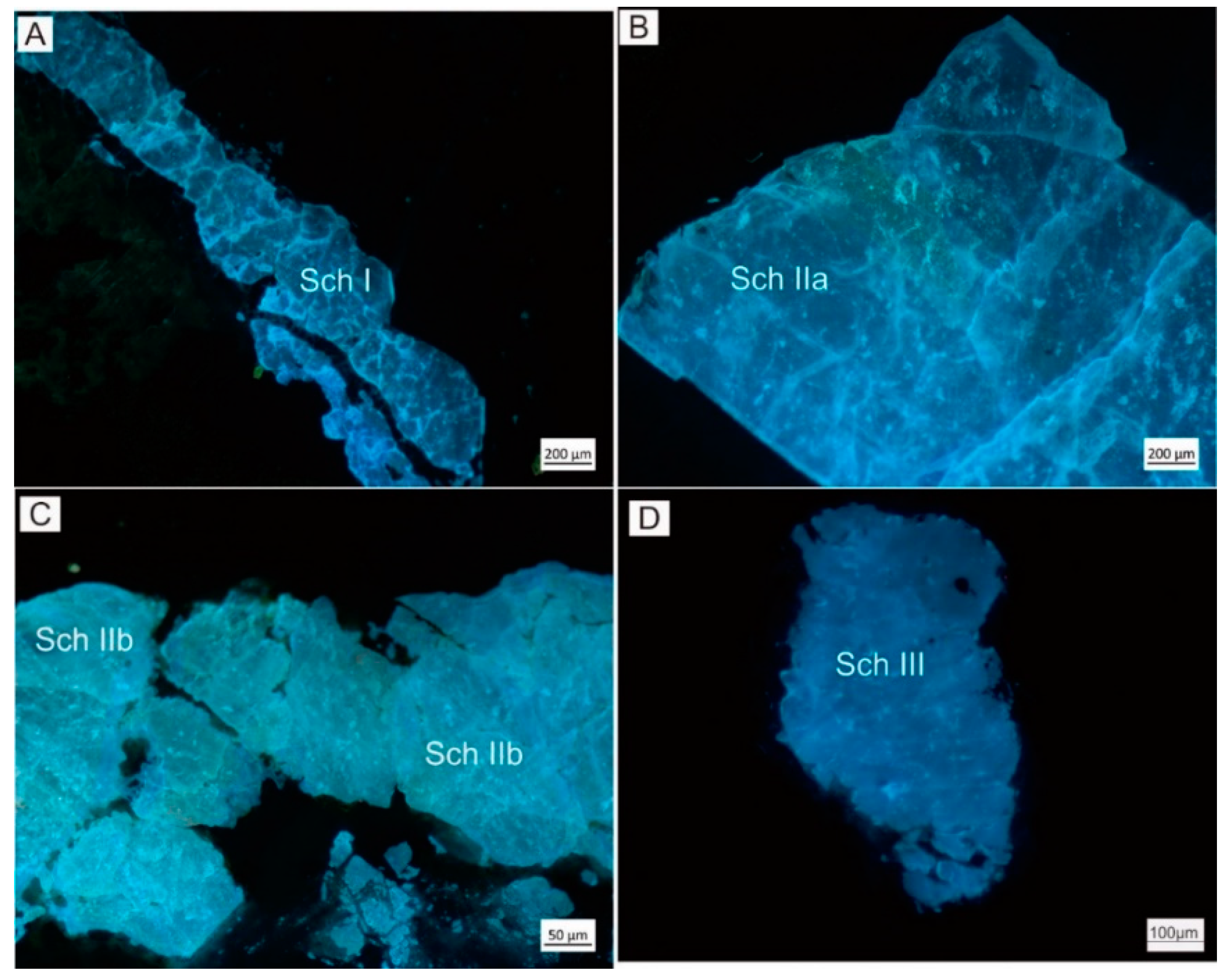
4.1. Optical Microscopy and OM-CL
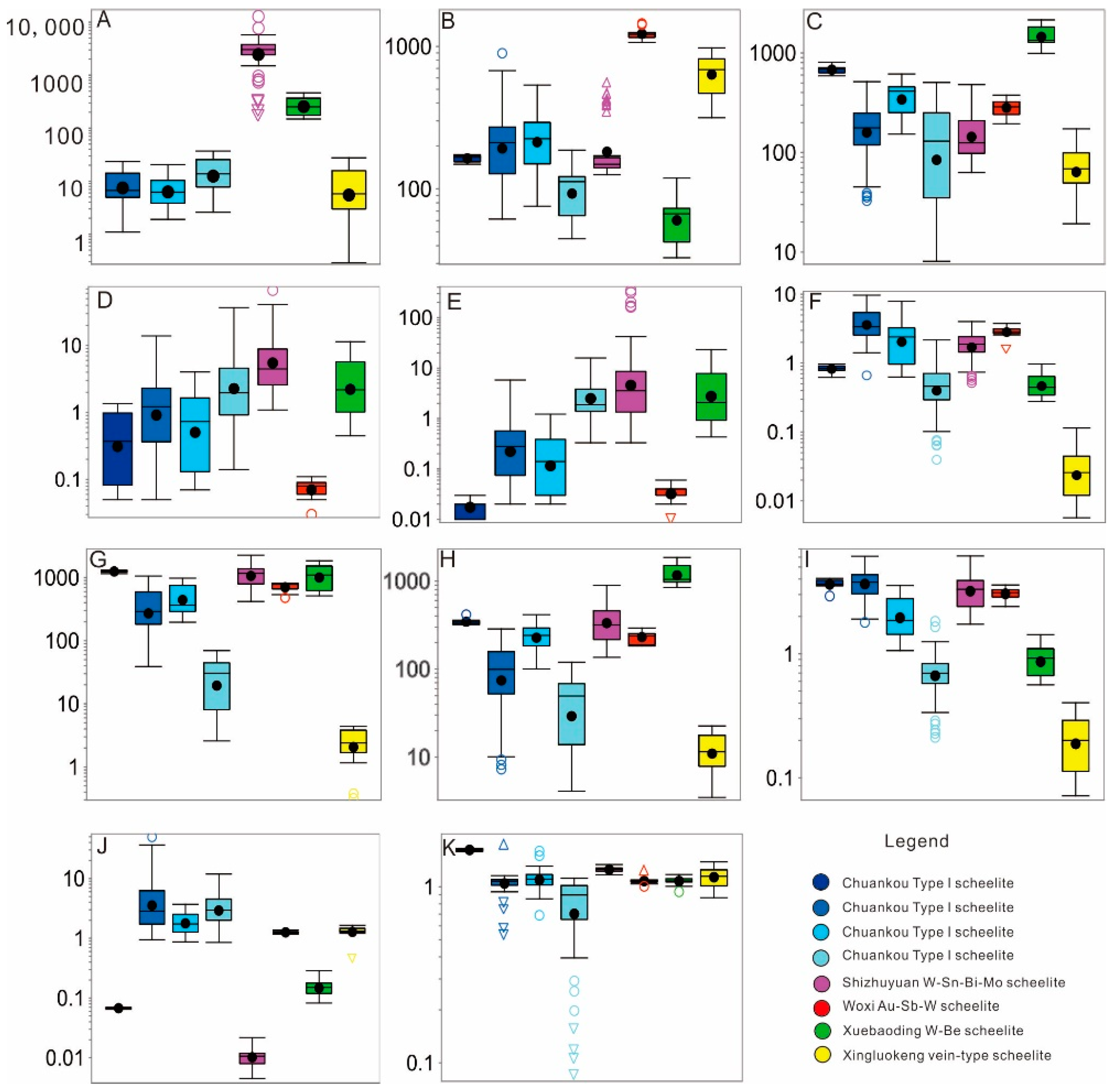
4.2. Trace Element Compositon of Scheelite
4.2.1. Trace Element Characteristics of Scheelite
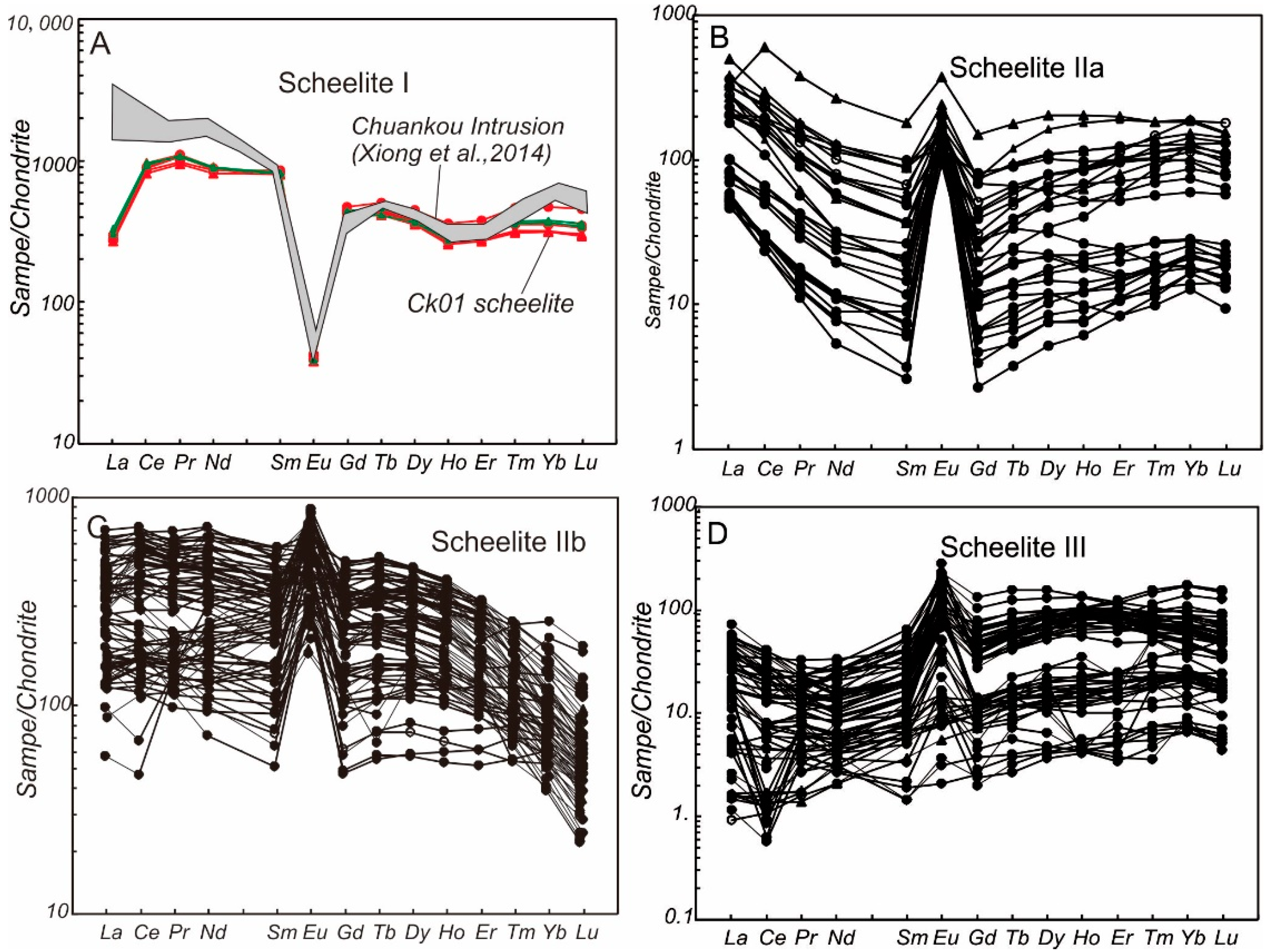
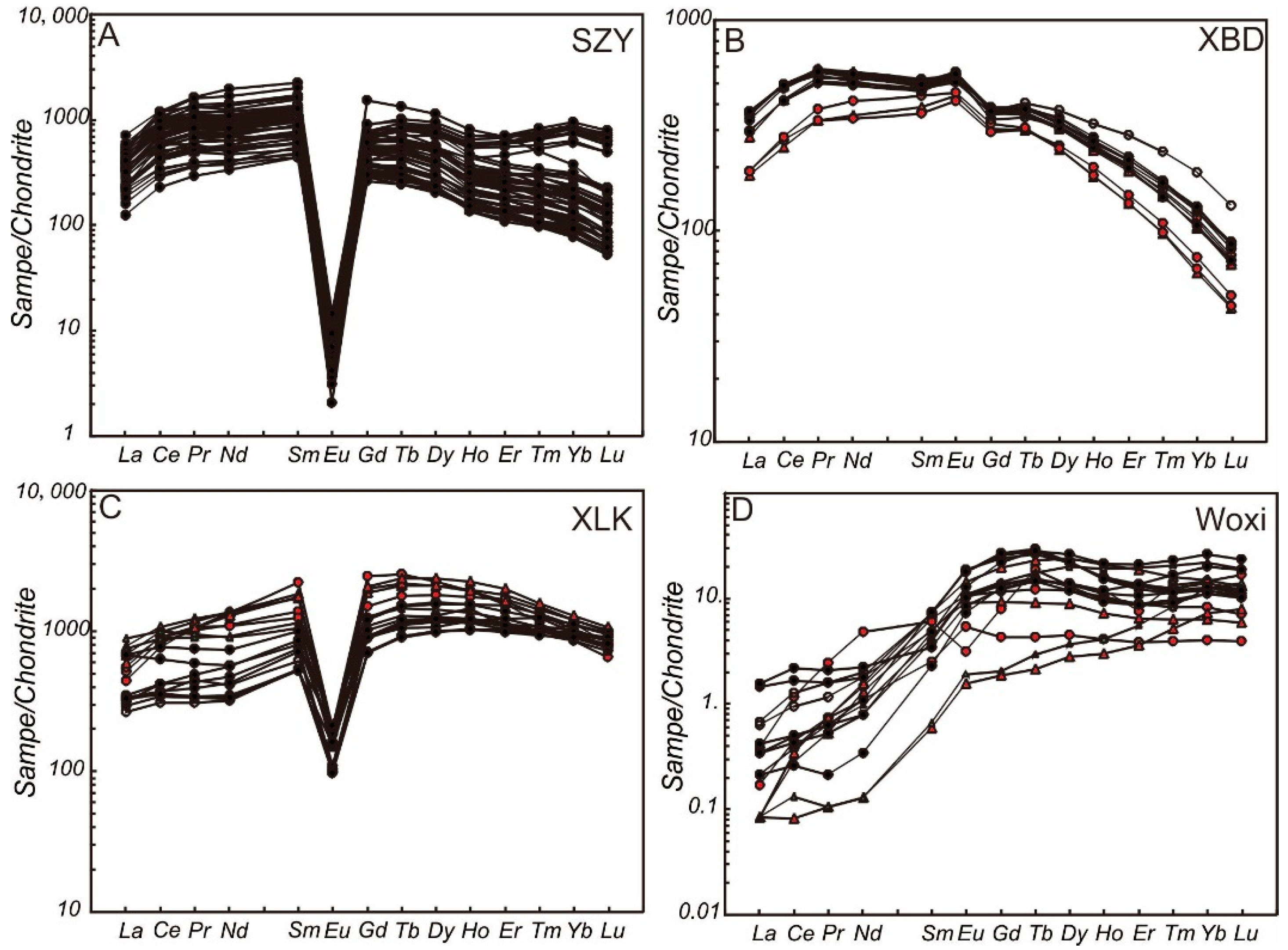
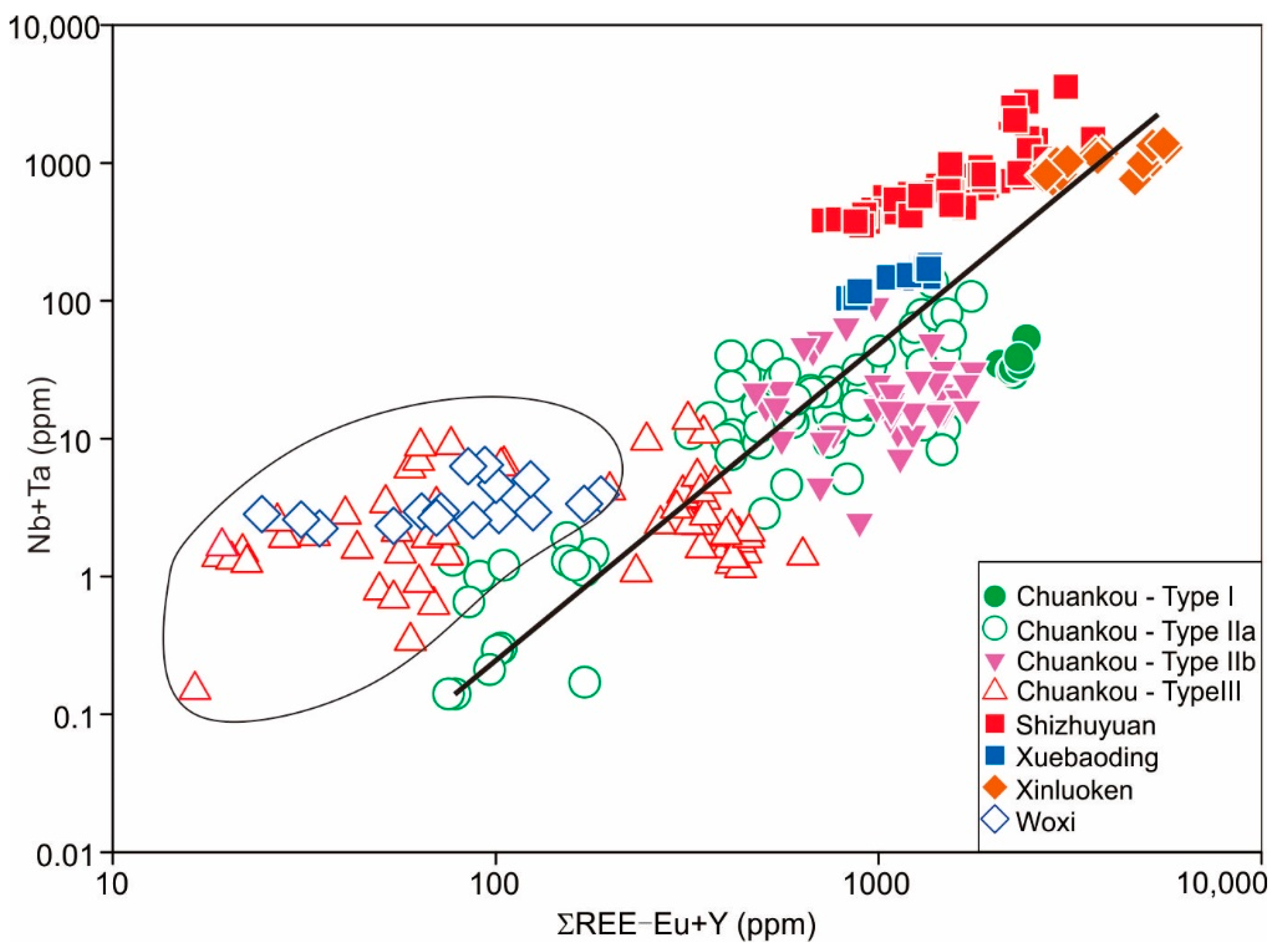
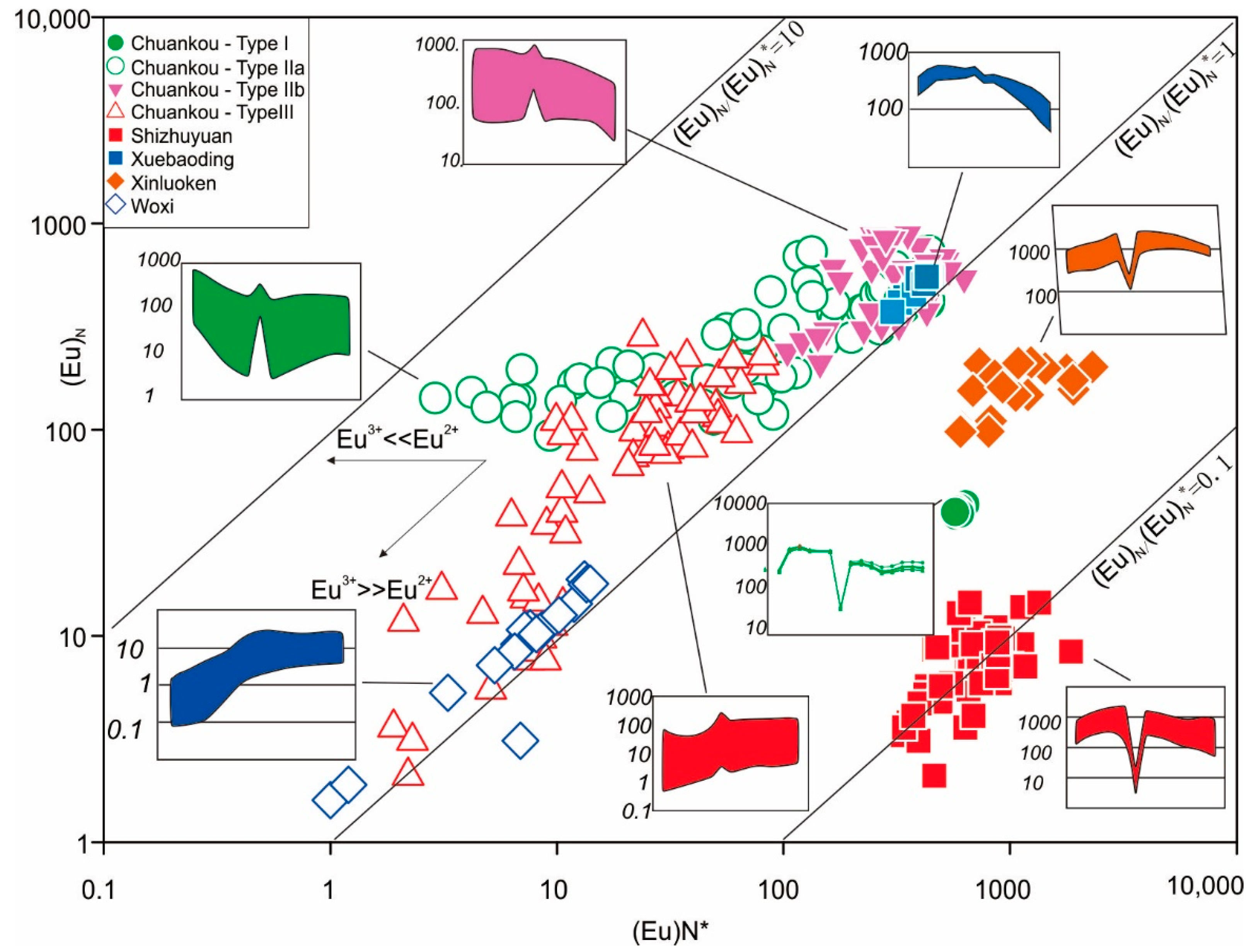
4.2.2. REE Patterns of Scheelite
5. Discussion
5.1. Substitution of Trace Elements into Scheelite
5.2. Nature, and Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids
5.3. Implications for Tungsten Mineralization
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Three generations of scheelite were identified at the Chuankou tungsten deposit.
- (2)
- Two major substitution mechanism occur in scheelite in the Chuankou deposit: 3Ca2+ = 2REE3+ + □(Ca2+ vacancy) and Ca2+ + W6+ = REE3+ + Nb5+, suggesting a middle to high-temperature mineralization system.
- (3)
- REE contents and patterns indicate that two types of fluids were involved in the ore-forming system. The early fluids were derived from the reduced and highly evolved magma. The fluids mixed with oxidizing meteoric water during the opening of fracture system to form later scheelite generations.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brugger, J.; Maas, R.; Lahaye, Y.; McRae, C.; Ghaderi, M.; Costa, S.; Lambert, D.; Bateman, R.; Prince, K. Origins of Nd–Sr–Pb isotopic variations in single scheelite grains from Archaean gold deposits, Western Australia. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Ma, D.; Lu, J.; Zhang, R. Garnet and scheelite as indicators of multi-stage tungsten mineralization in the Huangshaping deposit, southern Hunan province, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal, J.; Kontak, D.J.; Chatterjee, A.K. Trace element geochemistry of scheelite and rutile from metaturbidite-hosted quartz vein gold deposits, Meguma Terrane, Nova Scotia, Canada: Genetic implications. Miner. Pet. 2009, 97, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hollings, P.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Yang, T. In-situ LA-ICP-MS trace elements analysis of scheelites from the giant Beiya gold–polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province, Southwest China and its metallogenic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.S. A Study of the Crystal Chemistry, Cathodoluminescene, Geochemistry and Oxygen Isotopes in Scheelite: Application towards Discriminating among Differing Ore-Deposit Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Laurentian University, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderi, M.; Palin, J.M.; Campbell, I.H.; Sylvester, P.J. Rare earth element systematics in scheelite from hydrothermal gold deposits in the Kalgoorlie-Norseman region, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 1999, 94, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Park, C.; Song, Y. Multistage W-mineralization and magmatic-hydrothermal fluid evolution: Microtextural and geochemical footprints in scheelite from the Weondong W-skarn deposit, South Korea. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 116, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Gao, J.-F.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, W.-H.; Wu, J.-W. Origin of the Muguayuan veinlet-disseminated tungsten deposit, South China: Constraints from in-situ trace element analyses of scheelite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 99, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Deng, T.; Chi, G.; Wang, Z.; Zou, F.; Zhang, J.; Zou, S. Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China: Geological, geochemical and geochronological characteristics, ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 565–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Kang, L.-F.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.-T.; Qi, Y.-Q. Tracing the origin of ore-forming fluids in the Piaotang tungsten deposit, South China: Constraints from in-situ analyses of wolframite and individual fluid inclusion. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 111, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chi, G.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Deng, T.; Geng, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, L. Characteristics of REEs and trace elements in scheelite from the Zhuxi W deposit, South China: Implications for the ore-forming conditions and processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Pownceby, M.; Liu, W.; Grundler, P.; Brewe, D. Oxidation state of europium in scheelite: Tracking fluid–rock interaction in gold deposits. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.-Z.; Wang, J.-G.; Su, B.; Gao, Y.-J.; Wu, F.-Y.; Sein, K.; Yang, Y.-H.; Mao, Q. Scheelite and coexisting F-rich zoned garnet, vesuvianite, fluorite, and apatite in calc-silicate rocks from the Mogok metamorphic belt, Myanmar: Implications for metasomatism in marble and the role of halogens in W mobilization and mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 117, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Gao, J.-F.; Lu, J.-J.; Wu, J.-W. In-situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analyses of scheelite and wolframite: Constraints on the genesis of veinlet-disseminated and vein-type tungsten deposits, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 99, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuba, M.; Beaudoin, G.; Grzela, D.; Makvandi, S. Trace element composition of scheelite in orogenic gold deposits. Miner. Deposita 2019, 55, 1149–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaft, M.; Panczer, G.; Uspensky, E.; Reisfeld, R. Laser-induced time-resolved luminescence of rare-earth elements in scheelite. Miner. Mag. 1999, 63, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.S.; McDonald, A.M.; Kontak, D.J.; McClenaghan, M.B. On the Relationship Between Cathodoluminescence and the Chemical Composition of Scheelite From Geologically Diverse Ore-Deposit Environments. Can. Miner. 2016, 54, 1147–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, J.; Schertl, H.-P.; Neuser, R.D.; Kempe, U.; Hanchar, J.M. Optical microscope-cathodoluminescence (OM–CL) imaging as a powerful tool to reveal internal textures of minerals. Miner. Pet. 2012, 107, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, P.V.S.; Hart, C.J.; Sangurmath, P. Scheelite geochemical signatures by LA-ICP-MS and potential for rare earth elements from Hutti Gold Mines and fingerprinting ore deposits. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 114, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.J.; Ghaderi, M. Trace element analysis of scheelite by excimer laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ELA-ICP-MS) using a synthetic silicate glass standard. Chem. Geol. 1997, 141, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.-Z.; Chen, W.T.; Xu, D.-R.; Zhou, M.-F. Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China: An introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Commodity Statistics and Information. 2020. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Shen, J.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, L.J.; Ying, L.J.; Huang, F.; WANG, D.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zeng, L. Outline of Metallogney of Tungsten Deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar]
- HBGMR. Regional Geology of Hunan Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- HBGMR. Exploration Report of Replaceable Resources in the Zhazixi Sb(W) Ore Deposit; Unpublished Report; Changsha, China, 2010; pp. 10–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zaw, K.; Peters, S.G.; Cromie, P.; Burrett, C.; Hou, Z. Nature, diversity of deposit types and metallogenic relations of South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 31, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.C. Large Scale Mineralization and Large Ore Concentration Area; Geologic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Xiong, S. Structures of the Zhazixi Sb–W deposit, South China: Implications for ore genesis and mineral exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.-P.; Gong, Y.-J.; Hu, X.-L.; Xiong, S.-F. Geology, fluid inclusions, and geochemistry of the Zhazixi Sb–W deposit, Hunan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Schulz, O.; Vavtar, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, L. The Woxi W–Sb–Au deposit in Hunan, South China: An example of Late Proterozoic sedimentary exhalative (SEDEX) mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 57, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hoshino, K. A Study on the Mineralization of the Woxi Au-Sb-W Deposit, Western Hunan, China. Resour. Geol. 2014, 65, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Scheelite Sm-Nd dating and quartz Ar-Ar dating for Woxi Au-Sb-W deposit, western Hunan. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, C.H. Geological characteristics and metallognenic epoch of the Xingluokeng Tugsten Deposit, Fujian Province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2008, 32, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, C.; Shi, G.; Zheng, A. REE composition in scheelite and scheelite Sm-Nd dating for the Xuebaoding W-Sn-Be deposit in Sichuan. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 2543–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Peng, J.; Coulson, I.M.; Hou, L.; Li, S. Cassiterite U–Pb and muscovite40Ar–39Ar age constraints on the timing of mineralization in the Xuebaoding Sn–W–Be deposit, western China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 62, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Raschke, M.B.; Liu, Y. Tourmaline as a Recorder of Ore-Forming Processes in the Xuebaoding W-Sn-Be Deposit, Sichuan Province, China: Evidence from the Chemical Composition of Tourmaline. Minerals 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Geological characteristics and targetting of Chuankou W deposit, Hengyan City, China. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, W.L.; Powell, W.J.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. GLITTER: Data reduction software for laser ablation ICP-MS. In Laser Ablation ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current Practices and Outstanding Issues; Short Course Series; Sylvester, P.J., Ed.; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2008; Volume 40, pp. 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.-F.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Zhao, Z. Constraints on the uptake of REE by scheelite in the Baoshan tungsten skarn deposit, South China. Chem. Geol. 2018, 477, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Rusk, B.; Yang, F.; Zhang, M. Physical and Chemical Evolution of the Dabaoshan Porphyry Mo Deposit, South China: Insights from Fluid Inclusions, Cathodoluminescence, and Trace Elements in Quartz. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, R. In situ LA-ICP-MS analyses of mica and wolframite from the Maoping tungsten deposit, southern Jiangxi, China. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimbault, L.; Baumer, A.; Dubru, M.; Benkerrou, C.; Zahm, A. Ree Fractionation between Scheelite and Apatite in Hydrothermal Conditions. Am. Mineral. 1993, 78, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Lentz, D.R. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of scheelite-bearing skarns, and genetic relations between skarn mineralization and petrogenesis of the associated granitoid pluton at Sargipali, Sundergarh District, Eastern India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 108, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, F. In situ trace elements and Sr isotopes in scheelite and S-Pb isotopes in sulfides from the Shiweidong W–Cu deposit, giant Dahutang ore field: Implications to the fluid evolution and ore genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, J.; Dai, T.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Bayless, R.C.; Gao, J. In Situ Trace Elemental Analyses of Scheelite from the Chuankou Deposit, South China: Implications for Ore Genesis. Minerals 2020, 10, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111007
Pan J, Dai T, Zhang D, Li W, Bayless RC, Gao J. In Situ Trace Elemental Analyses of Scheelite from the Chuankou Deposit, South China: Implications for Ore Genesis. Minerals. 2020; 10(11):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111007
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Junqing, Tagen Dai, Dexian Zhang, Wenshen Li, Richard C. Bayless, and Jianfeng Gao. 2020. "In Situ Trace Elemental Analyses of Scheelite from the Chuankou Deposit, South China: Implications for Ore Genesis" Minerals 10, no. 11: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111007
APA StylePan, J., Dai, T., Zhang, D., Li, W., Bayless, R. C., & Gao, J. (2020). In Situ Trace Elemental Analyses of Scheelite from the Chuankou Deposit, South China: Implications for Ore Genesis. Minerals, 10(11), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10111007




