Physicochemical Characteristics of the Birnessite and Todorokite Synthesized Using Various Methods
Abstract
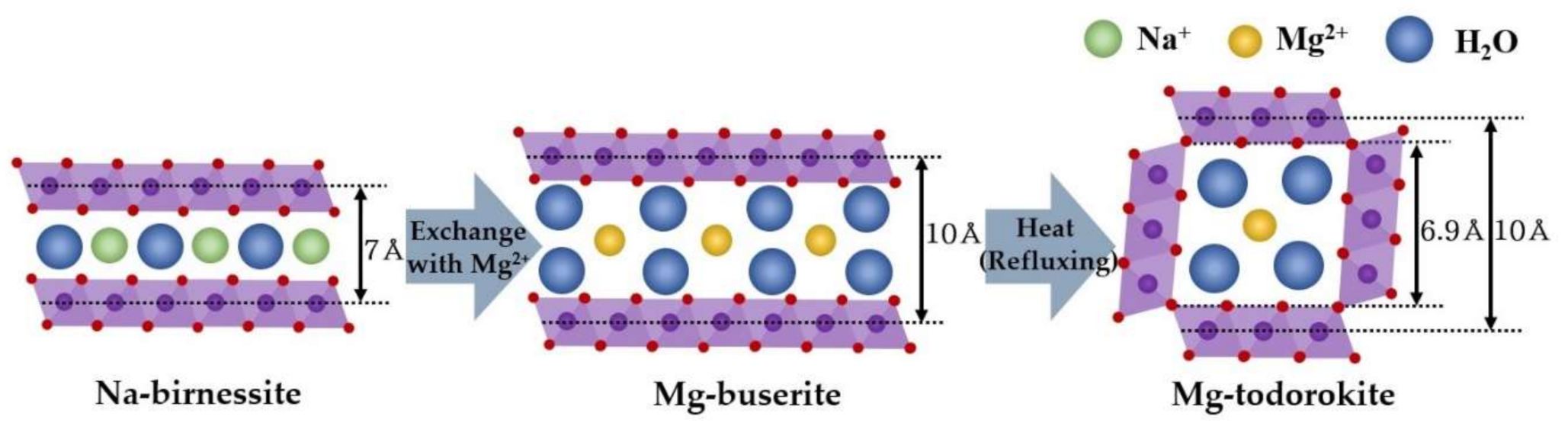
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Na–Birnessite Synthesis (Precursor Preparation)
2.1.1. Oxidation Method
2.1.2. Redox Reaction Method
- Mg-free Na–birnessite
- Mg-doped Na–birnessite
2.1.3. Reduction Method
2.2. Na–Birnessite to Mg–Buserite via the Ion Exchange Process
2.3. Todorokite Synthesis (Hydrothermal Treatment)
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Features
3.2. Chemical Analysis
3.3. Specific Surface Area
3.4. XPS
3.5. TGA
3.6. IR Spectroscopy
3.7. SEM Images
3.8. Characteristics of Birnessite and Todorokite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hlawatsch, S.; Garbe-Schönberg, C.D.; Lechtenberg, F.; Manceau, A.; Tamura, N.; Kulik, D.A.; Kersten, M. Trace metal fluxes to ferromanganese nodules from the western Baltic Sea as a record for long-term environmental changes. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebetrau, V.; Eisenhauer, A.; Gussone, N.; Wörner, G.; Hansen, B.T.; Leipe, T. 226Raexcss/Ba growth rates and U-Th-Ra-Ba systematic of Baltic Mn/Fe crusts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M.A.; Manceau, A.; Kersten, M. Mn, Fe, Zn and As speciation in a fast-growing ferromanganese marine nodule. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3125–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dick, G.J.; Clement, B.G.; Webb, S.M.; Fodrie, F.J.; Bargar, J.R.; Tebo, B.M. Enzymatic microbial Mn(II) oxidation and Mn biooxide production in the Guaymas Basin deep-sea hydrothermal plume. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6517–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.M.; Rossman, G.R. Desert varnish: The importance of clay minerals. Science 1977, 196, 1446–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, D.A.; Post, J.E. Characterization of manganese oxide mineralogy in rock varnish and dendrites using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Bigham, J.M.; Faure, G. Removal of trace metals by coprecipitation with Fe, Al and Mn from natural waters contaminated with acid mine drainage in the Ducktown Mining District, Tennessee. J. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, G.; Heaney, P.J.; Webb, S.M.; Burgos, W.D. Characterization of manganese oxide precipitates from Appalachian coal mine drainage treatment systems. J. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-España, J.; Yusta, I. Coprecipitation of Co2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ with Mn(Ш/IV) oxides formed in metal-rich mine waters. Minerals 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Post, J.E. Manganese oxide minerals: Crystal structures and economic and environmental significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, R.G.; Burns, V.M. Chapter 7 Mineralogy. In Marine Manganese Deposits; Glasby, G.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 185–248. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, D.C.; Chen, C.C.; Dixon, J.B. Synthesis of todorokite. Science 1986, 231, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.F.; Zerger, R.P.; Deguzman, R.N.; Suib, S.L.; McCurby, L.; Potter, D.I.; O’Young, C.L. Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Science 1993, 260, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.F.; Zerger, R.P.; Suib, S.L.; McCurby, L.; Potter, D.I.; O’Young, C.L. Octahedral molecular sieves: Preparation, characterization and applications. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 260, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.M. The synthesis of birnessite, cryptomelane, and some other oxides and hydroxides of manganese. Mineral. Mag. 1971, 38, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Segal, S.R.; Wang, J.Y.; Tian, Z.R.; Suib, S.L. Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity of feitknechtite. Proc. MRS 1996, 431, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yamasaki, N. Transformation of manganese oxides from layered structures to tunnel structures. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1607–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGuzman, R.N.; Shen, Y.F.; Neth, E.J.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L.; Levine, S.; Newsam, J.M. Synthesis and characterization of Octahedral molecular sieves(OMS-2) having the hollandite structure. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, O. Some stability relations in the system Mn-O2-H2O at 25 ℃ and one atmosphere total pressure. Am. Mineral. 1965, 50, 1296–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Ramos, J.P.; Baddour, R. Electrochemical and structural characteristics of some lithium intercalation materials synthesized via a sol-gel process: V2O5 and manganese dioxides-based compounds. Solid States Ion. 1992, 53–56, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.; Pereira-Ramos, J.P.; Baffier, N. Electrochemical sodium insertion into the sol-gel birnessite manganese dioxide. Electrochim. Acta 1993, 38, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.; Pereira-Ramos, J.P.; Baffier, N. Synthesis and characterization of lamellar MnO2 obtained from thermal decomposition of NaMnO4 for rechargeable lithium cells. J. Solid State Chem. 1995, 120, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.; Henry, M.; Baffier, N.; Livage, J. Sol-gel synthesis of manganese oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 1990, 88, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanoli, R.; Stähli, E.; Feitknecht, W. Über oxidhydroxide des vierwertigen mangans mit schichtengitter 1. Mitteilung. Natriummangan(II,III)manganate(IV). Helv. Chim. Acta 1970, 53, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanoli, R.; Stähli, E.; Feitknecht, W. Über oxidhydroxide des vierwertigen mangans mit schichtengitter 2. Mitteilung: Mangan(III)-manganat (IV). Helv. Chim. Acta 1970, 53, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, E.D. Characterization of a marine birnessite. Am. Mineral. 1977, 62, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.; Buseck, P.R. Todorokites: A new family of naturally occurring manganese oxides. Science 1981, 212, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscarson, D.W.; Huang, P.M.; Defosse, C.; Herbillon, A. Oxidative power of Mn(IV) and Fe(III) oxides with respect to As(III) in terrestrial and aquatic environments. Nature 1981, 291, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, B.J.; Kinser, A.K.; Passerini, S.; Smyrl, W.H.; Stein, A. Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties of magnesium birnessite and zinc chalcophanite prepared by low-temperature route. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.; Pereira-Ramos, J.P.; Baffier, N.; Messina, R. Birnessite manganese dioxide synthesized via a sol-gel process: A new rechargeable cathodic material for lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 1991, 36, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, P.; Baffier, N.; Bach, S.; Pereira-Ramos, J.P. Synthesis, ion exchange and electrochemical properties of lamellar phyllomanganates of the birnessite group. Mater. Res. Bull. 1996, 31, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L. Cu containing octahedral molecular sieves and octahedral layered materials. J. Catal. 1996, 161, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P. Layered birnessite-type MnO2 with surface pits for enhanced catalytic formaldehyde oxidation activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5719–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, C.E.; Kurz, P. Water oxidation catalysis by synthetic manganese oxides with different structural motifs: A comparative study. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14958–14968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, J.E.; Bish, D.L. Rietveld refinement of the todorokite structure. Am. Mineral. 1988, 73, 861–869. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, R.G.; Burns, V.M.; Stockman, H.W. A review of the todorokite-buserite problem; implications to the mineralogy of marine manganese nodules. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 972–980. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, D.C.; Dixon, J.B.; Chen, C.C. Ion exchange, thermal transformations, and oxidizing properties of birnessite. Clays Clay Miner. 1986, 34, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straczek, J.A.; Horen, A.; Ross, M.; Warshaw, C.M. Studies of the manganese oxides. IV. Todorokite. Am. Mineral. 1960, 45, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, N.; Komaba, S.; Sakai, H.; Kumagai, N. Preparation of todorokite-type manganese-based oxide and its application as lithium and magnesium rechargeable battery cathode. J. Power Sources 2001, 97–98, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, N.; Komaba, S.; Abe, K.; Yashiro, H. Synthesis of metal-doped todorokite-type MnO2 and its cathode characteristics for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetschi, P.; Giovanoli, R. Cation vacancies in MnO2 and their influence on electrochemical reactivity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1988, 135, 2663–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, H.; Shu, D.; He, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, J. Supercapacitive behavior and high cycle stability of todorokite-type manganese oxide with large tunnels. J. Power Sources 2012, 203, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sagheer, F.A.; Zaki, M.I. Synthesis and surface characterization of todorokite-type microporous manganese oxides: Implications for shape-selective oxidation catalysts. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2004, 67, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.P.; Ashton, W.R.; Tseung, A.C.C. An observation of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis processes in the decomposition of H2O2 over MnO2 and Mn(OH)2. J. Catal. 1991, 131, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, M. Characteristics of manganese nodules as adsorbents and catalysts, a review. Appl. Catal. 1984, 9, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Young, C.L.; Shen, Y.F.; Zerger, R.P.; Suib, S.L. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Octahedral Molecular Sieve. U.S. Patent 5340562, 23 August 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.G.; Xu, W.Q.; Shen, Y.F.; Suib, S.L. O’Young, C.L. Studies of oxygen species in synthetic todorokite-like manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Suib, S.L. Mechanistic and kinetic studies of crystallization of birnessite. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, D.C.; Chen, C.C.; Dixon, J.B. Transformation of birnessite to buserite, todorokite, and manganite under mild hydrothermal treatment. Clays Clay Miner. 1987, 35, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Kanoh, H.; Miyai, Y.; Ooi, K. Metal ion extraction/insertion reactions with todorokite-type manganese oxide in the aqueous phase. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yamasaki, N. Hydrothermal soft chemical process for synthesis of manganese oxides with tunnel structures. J. Porous Mater. 1998, 5, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, W.F.; Wadsley, A.D.; Walkley, A. An X-ray diffraction study of manganese dioxide. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1947, 92, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.; Petrovay, D.J.; Jorgensen, M.L. Sol-gel synthesis of layered birnessite-type manganese oxides. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.; Landrigan, J.A.; Jorgensen, M.L.; Duan, N.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L. Sol-gel synthesis of birnessite from KMnO4 and simple sugars. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 1604–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Luo, J.; Suib, S.L. Syntheses of birnessites using alcohols as reducing reagents: Effects of synthesis parameters on the formation of birnessites. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Suib, S.L. Preparative parameters, magnesium effects, and anion effects in the crystallization of birnessites. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 10403–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, A.; Park, S.H.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L. Crystallization of sodium-birnessite and accompanied phase transformation. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoh, H.; Tang, W.; Makita, Y.; Ooi, K. Electrochemical intercalation of alkali-metal ions into birnessite-type manganese oxide in aqueous solution. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6845–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, L.; Baffier, N.; Bach, S.; Pereira-Ramos, J.P.; Messina, R. Structural and electrochemical characteristics of a lamellar sodium manganese oxide synthesized via a sol-gel process. Solid States Ion. 1993, 61, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.G.; Wei, X.; Gallaway, J.W.; Chaudhry, Z.; Shin, A.; Huang, J.; Yakobov, R.; Nyce, M.; Vanderklaauw, N.; Banerjee, S. Rapid electrochemical synthesis of δ-MnO2 from γ-MnO2 and unleashing its performance as an energy dense electrode. Mater. Today Energy 2017, 6, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.G.; Gallaway, J.W.; Turney, D.E.; Nyce, M.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Banerjee, S. Regenerable Cu-intercalated MnO2 layered cathode for highly cyclable energy dense batteries. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.H.; Zhai, L.M.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F.; He, J.Z. Adsorption and redox reactions of heavy metals on synthesized Mn oxide minerals. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, N.; Lan, S.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Characterisation of hexagonal birnessite with a new and rapid synthesis method-comparison with traditional synthesis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25951–25956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ching, S.; Krukowska, K.S.; Suib, S.L. A new synthetic route to todorokite-type manganese oxide. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 294, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.J.; Feng, X.H.; He, J.Z.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F. Effects of reaction condition on the formation of todorokite at atmospheric pressure. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.J.; Liu, X.W.; Tan, W.F.; Feng, X.H.; Liu, F.; Ruan, H.D. Influence of Mn(III) availability on the phase transformation form layered buserite to tunnel-structured todorokite. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.J.; Qiu, G.H.; Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F. Birnessites with different average manganese oxidation states synthesized, characterized, and transformed to todorokite at atmospheric pressure. Clays Clay Miner. 2009, 57, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.B.; Ruan, H.D. Synthesis of todorokite at atmospheric pressure. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4330–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanoli, R.; Burki, P.; Giuffredi, M.; Stumm, W. Layer structured manganese oxide hydroxides. IV. The buserite group; Structure stabilization by transition elements. Chimia 1975, 29, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Kang, L.; Ooi, K.; Makita, Y.; Feng, Q. Studies on the formation of todorokite-type manganese oxide with different crystalline birnessites by Mg2+-templating reaction. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 285, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, A.; Giraldo, O.; Suib, S.L. Double-aging method for preparation of stabilized Na-buserite and transformations to todorokites incorporated with various metals. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 6106–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.R.; Yin, Y.G.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L. Effect of Mg2+ ions on the formation of todorokite type manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vileno, E.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Suib, S.L. Facile synthesis of synthetic todorokite (OMS-1), co-precipitation reactions in the presence of a microwave field. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 1998, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinger, K.A.; Laubernds, K.; Son, Y.C.; Suib, S.L. Effects of microwave processing on chemical, physical and catalytic properties of todorokite-type manganese oxide. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4296–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.H.; Liu, F.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, X.W.; Hu, H.Q. Synthesis of todorokite by refluxing process and its primary characteristics. Sci. China Earth Ser. D 2004, 47, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, E.A. Chapter 21 Controls on Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn concentrations in soils and water: The significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. In Trace Inorganics in Water; Baker, R.A., Ed.; ACS Advances in Chemistry Series(Am. Chem. Soc.): Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 73, pp. 337–387. [Google Scholar]
- Young, L.B.; Harvey, H.H. The relative importance of manganese and iron oxides and organic matter in the sorption of trace metals by surficial lake sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A. Inorganic ion exchangers: A technology ripe for development. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuki, T.; Kozai, N. Adsorption behavior of radioactive cesium by non-mica minerals. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chitrakar, R.; Makita, Y.; Sonoda, A. Cesium ion exchange on synthetic birnessite (Na0.35MnO2∙0.6H2O). Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.; Makita, Y.; Sonoda, A. Cesium ion uptake by synthetic K-birnessite K0.30(Mn4+0.90Mn3+0.03-0.07)O2∙0.50H2O. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 1032–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.; Makita, Y.; Sonoda, A. Cesium adsorption by synthetic todorokite-type manganese oxides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 87, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.; Pillinger, M.; Newton, J.; Harjula, R.; Möller, T.; Amin, S. Sorption behavior of radionuclides on crystalline synthetic tunnel manganese oxides. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3798–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasany, S.M.; Chaudhary, M.H. Adsorption behavior of microamounts of cesium on manganese dioxide. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1984, 84, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, E.M.; Misak, N.Z. Sorption of cesium and cobalt radionuclides on a new manganese oxide. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A 1988, 39, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.V.; Tandon, S.N. Studies on the adsorption of cesium and strontium radionuclides on hydrated manganese oxide. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1977, 28, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Yu, Q.; Momoki, T.; Kaseyama, T. Adsorption characteristics of Cs+ on biogenic birnessite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Ohnuki, T.; Kozai, N.; Sakamoto, F.; Tanaka, K.; Sasaki, K. Quantitative analysis of radiocesium retention onto birnessite and todorokite. Chem. Geol. 2017, 470, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakhonov, S.V.; Churagulov, B.R.; Gudilin, E.A. Selective cleaning of ions heavy metals form water solutions using the H-form of todorokite synthesized by the hydrothermal method. J. Surf. Investig. 2008, 2, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gadde, R.R.; Laitinen, H.A. Studies of heavy metal adsorption by hydrous iron and manganese oxides. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.Z. Biogenic Mn oxides for effective adsorption of Cd from aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppa, L.D.; Komárek, M.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.C.; Joussein, E. Adsorption of copper, cadmium, lead and zinc onto a synthetic manganese oxide. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 399, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.S.; Wang, M.K. Syntheses and characterization of birnessite by oxidizing pyrochroite in alkaline conditions. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, J.; Suib, S.L. Preparative parameters and framework dopant effects in the synthesis of layer-structure birnessite by air oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, J.C.; Schweitzer, G.K.; Carlson, T.A. Use of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study bonding in Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co compounds. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, M.; Hirokawa, K.; Ikeda, S. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of manganese-oxygen systems. J. Electron Spectrosc. 1975, 7, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, M.; Hirokawa, K. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of Co3O4, Fe3O4, Mn3O4, and related compounds. J. Electron Spectrosc. 1976, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junta, J.L.; Hochella, M.F. Manganese (II) oxidation at mineral surfaces: A microscopic and spectroscopic study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 4985–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.P.; Sen, S.K. Calculation of multiplet structure of core p-vacancy levels. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 10, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.P.; Sen, S.K. Calculation of multiplet structure of core p-vacancy levels. II. Phys. Rev. B 1975, 12, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drits, V.A.; Silvester, E.; Gorshkov, A.I.; Manceau, A. Structure of synthetic monoclinic Na-rich birnessite and hexagonal birnessite: I. Results from X-ray diffraction and selected-area electron diffraction. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Hanson, J. Rietveld refinement of a triclinic structure for synthetic Na-birnessite using synchrotron powder diffraction data. Powder Diffr. 2002, 17, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, A.L.; Shaw, S.; Peacock, C.L. Nucleation and growth of todorokite from birnessite: Implications for trace-metal cycling in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 144, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wertheim, G.K.; Hufner, S.; Guggenheim, H.J. Systematics of core-electron exchange splitting in 3d-group transition-metal compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Banerjee, D. Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Dillard, J.G.; Giovanoli, R.; Moers, H.; Stumm, W. Oxidation of Mn(II): Initial mineralogy, oxidation state and ageing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Bae, J.; Lee, G. Determination of Mn oxidation state in Mn-(hydr)oxides using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS). Econ. Environ. 2009, 42, 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Feng, Q.; Yanagisawa, K. Characterization of birnessite-type sodium manganese oxides prepared by hydrothermal reaction process. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parant, J.P.; Olazcuaga, R.; Devalette, M.; Fouassier, C.; Hagenmuller, P. Sur quelques Nouvelles phases formule NaχMnO2(χ ≤ 1). J. Solid State Chem. 1971, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.L. Effects of inorganic cation templates on octahedral molecular sieves of manganese oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 11020–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, D.L.; Post, J.E. Thermal behavior of complex, tunnel-structure manganese oxides. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gadsden, J.A. Infrared Spectra of Minerals and Related Inorganic Compounds; Butterworths: London, UK, 1975; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, R.M.; Rossman, G.R. The tetravalent manganese oxides: Identification, hydration, and structural relationships by infrared spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1979, 64, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Ooi, K. IR spectra of manganese oxides with either layered or tunnel structures. Spectrochim. Acta A 2007, 67, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Oxi-BIR | Rdx-BIR | RdxMg-BIR | Red-BIR | Birnessite [103] | ||||||||||
| 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | hkl | d/Å | I (%) |
| 12.4 | 7.14 | 100.0 | 12.4 | 7.12 | 100.0 | 12.3 | 7.18 | 100.0 | 12.4 | 7.14 | 100.0 | 001 | 7.14 | 100.0 |
| 24.9 | 3.57 | 24.5 | 19.2 | 4.62 | 21.5 | 19.0 | 4.67 | 22.6 | 24.9 | 3.57 | 25.2 | 002 | 3.57 | 25.3 |
| 36.2 | 2.48 | 3.41 | 25.0 | 3.55 | 23.1 | 25.2 | 3.54 | 15.5 | 35.6 | 2.52 | 3.52 | 011 | 2.52 | 9.0 |
| 51.2 | 1.78 | 0.77 | 33.4 | 2.68 | 2.01 | 36.1 | 2.48 | 9.56 | 36.2 | 2.48 | 2.03 | 100 | 2.48 | 1.5 |
| 63.1 | 1.47 | 1.19 | 36.1 | 2.49 | 7.27 | 37.0 | 2.43 | 8.95 | 36.9 | 2.43 | 4.75 | 110 | 2.43 | 6.7 |
| 65.5 | 1.42 | 2.67 | 37.9 | 2.37 | 5.78 | 63.3 | 1.47 | 2.91 | 42.0 | 2.15 | 2.18 | 003 | 2.37 | 0.5 |
| 80.6 | 1.20 | 0.32 | 42.0 | 2.15 | 1.72 | 65.6 | 1.42 | 3.50 | 62.9 | 1.47 | 1.69 | 102 | 2.14 | 5.9 |
| 49.6 | 1.84 | 2.48 | 76.9 | 1.24 | 0.83 | 64.5 | 1.44 | 1.47 | 121 | 1.47 | 1.8 | |||
| Oxi-TOD | Rdx-TOD | RdxMg-TOD | Red-TOD | Natural Todorokite [35] | ||||||||||
| 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | 2θ | d/Å | I (%) | hkl * | d/Å | I (%) |
| 9.12 | 9.69 | 100.0 | 9.08 | 9.73 | 8.03 | 9.15 | 9.66 | 100.0 | 9.08 | 9.73 | 100.0 | 001 | 9.76 | 100.0 |
| 18.25 | 4.86 | 77.26 | 12.23 | 7.23 | 100.0 | 12.38 | 7.14 | 8.16 | 12.52 | 7.06 | 17.42 | 10 | 7.05 | 29.9 |
| 26.17 | 3.40 | 14.41 | 19.07 | 4.65 | 16.78 | 18.29 | 4.85 | 81.01 | 18.26 | 4.86 | 52.80 | 002 | 4.88 | 9.4 |
| 27.57 | 3.23 | 7.69 | 24.74 | 3.59 | 13.31 | 27.49 | 3.24 | 7.93 | 25.30 | 3.52 | 4.25 | 20 | 3.52 | 3.2 |
| 37.19 | 2.42 | 24.44 | 36.51 | 2.46 | 11.83 | 36.00 | 2.49 | 4.13 | 36.43 | 2.46 | 6.71 | 003 | 3.25 | 0.8 |
| 40.66 | 2.22 | 6.20 | 38.40 | 2.34 | 5.09 | 37.20 | 2.41 | 4.56 | 37.26 | 2.41 | 10.30 | 210 | 2.43 | 7.3 |
| 45.55 | 1.99 | 4.20 | 65.69 | 1.42 | 5.77 | 40.63 | 2.22 | 3.37 | 40.44 | 2.23 | 3.10 | 20 | 2.23 | 0.0 |
| 65.48 | 1.42 | 9.48 | 77.56 | 1.23 | 0.93 | 65.55 | 1.42 | 1.96 | 65.46 | 1.42 | 3.81 | 414 | 1.42 | 0.0 |
| Sample | Chemical Composition | BET (m2/g) | Bes (Mn2p3/2, eV) | Bes (Mn3s, eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxi-BIR | Na0.91Mn6O12∙4.54H2O | 80 | 642.1 | 4.5 |
| Oxi-TOD | Na0.27Mg0.62Mn6O12∙5.07H2O | 185 | 641.9 | 4.5 |
| Rdx-BIR | Na0.4K0.02Mn6O12∙2.67H2O | 52 | 641.8 | 5.1 |
| Rdx-TOD | Na0.08K0.03Mg0.23Mn6O12∙4.31H2O | 146 | 641.8 | 4.9 |
| RdxMg-BIR | Na0.36K0.06Mg1.04Mn6O12∙4.44H2O | 67 | 642.1 | 4.5 |
| RdxMg-TOD | Na0.11K0.04Mg0.73Mn6O12∙5.24H2O | 95 | 642.0 | 4.2 |
| Red-BIR | Na1.5Mg0.62Mn6O12∙3.99H2O | 76 | 642.4 | 4.4 |
| Red-TOD | Na0.39Mg0.62Mn6O12∙4.77H2O | 153 | 642.0 | 4.8 |
| Features | Oxidation | Redox Reaction | Reduction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Mg2+ | Mg2+ Doped | |||||||
| BIR | TOD | BIR | TOD | BIR | TOD | BIR | TOD | |
| XRD | Single phase | Single phase | Birnessite + Feitknechtite | Not clear * | Birnessite + Feitknechtite | Single phase | Single phase | Single phase |
| Crystal Structure | Turbostratic | - | Roughly monoclinic | - | Roughly turbostratic | - | Monoclinic | - |
| Morphology | Irregularplaty | Long acicular (1–10 μm) | Parallelogram plate | Fibrous fragment (~5 μm) | Thin line entangled | Fibrous fragment (~5 μm) | Hexagonal | Fibrous fragment (~5 μm) |
| Other Features | The highest BET value among birnessite and todorokite | BET increase rate was the largest during the transition from birnessite to todorokite | BET value difference between birnessite and todorokite was the smallest | Highest crystallinity | - | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, S.; Kim, Y. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Birnessite and Todorokite Synthesized Using Various Methods. Minerals 2020, 10, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100884
Min S, Kim Y. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Birnessite and Todorokite Synthesized Using Various Methods. Minerals. 2020; 10(10):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100884
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Soyoung, and Yeongkyoo Kim. 2020. "Physicochemical Characteristics of the Birnessite and Todorokite Synthesized Using Various Methods" Minerals 10, no. 10: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100884
APA StyleMin, S., & Kim, Y. (2020). Physicochemical Characteristics of the Birnessite and Todorokite Synthesized Using Various Methods. Minerals, 10(10), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100884




