Abstract
A joint-optimization method is proposed for enhancing the behavior of the -norm- and sum-log norm-penalized NLMS algorithms to meet the requirements of sparse adaptive channel estimations. The improved channel estimation algorithms are realized by using a state stable model to implement a joint-optimization problem to give a proper trade-off between the convergence and the channel estimation behavior. The joint-optimization problem is to optimize the step size and regularization parameters for minimizing the estimation bias of the channel. Numerical results achieved from a broadband sparse channel estimation are given to indicate the good behavior of the developed joint-optimized NLMS algorithms by comparison with the previously proposed -norm- and sum-log norm-penalized NLMS and least mean square (LMS) algorithms.
1. Introduction
Recently, adaptive channel estimation has been extensively studied all over the world [1,2]. From these adaptive filtering frameworks, the LMS adaptive filtering algorithm has been deeply discussed for adaptive control, system identification, channel estimation applications owing to its low computational complexity and easy practical realization [3,4,5]. Although the LMS algorithm can effectively estimate the broadband multi-path channel, it has a sensitivity to the input signal scaling, and it is difficult to select an agreeable learning rate to achieve a stable and robust channel estimation behavior [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Subsequently, the NLMS has been proposed by using the normalization of the input training signal power in order to overcome the above addressed problem [12,13]. However, the conventional NLMS algorithm cannot perform well for dealing with sparse channel estimation.
Additionally, the broadband multi-path channel or underwater communication channel might be a sparse channel, which has been studied in recent decades [13,14,15,16,17]. From the measurement of the wireless channel, the channel impulse response can be regarded as sparse channel. This is to say that only a few channel impulse responses in most of the multi-path channels are dominant, while the major channel responses are zeros or their magnitudes are near-zeros. The traditional LMS- and NLMS-based channel estimation methods cannot make use of the inherent sparse properties of these broadband multi-path channels [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. To utilize the sparse structures of the broadband sparse channel, compressed sensing (CS) methods have been introduced for developing various channel estimation algorithms used in sparse cases [18,19,20]. Although some of these CS-based sparse channel estimations can achieve robust estimation performance, these CS algorithms may have high complexity for dealing with time-varying channels or they have difficulty in constructing desired measurement matrices with the restricted isometry property limitation [21]. Thus, simple sparse channel estimation developments have attracted much more attentions in the recent decades.
Sparse LMSs have been presented under the inspiration of the CS techniques [22,23], which are realized by using a norm constraint term in the cost function of the LMS. The first sparse LMS algorithm motivated by the CS technique is carried out by introducing a -norm constraint term into the basic LMS to exploit the in-nature sparse characteristics of broadband multi-path channel [24,25,26,27]. As a result, a zero attractor is given in the updating equation of the sparse LMS algorithm to put forward a zero-attracting (ZA) LMS (ZA-LMS) algorithm. Furthermore, a reweighting ZA-LMS (RZA-LMS) was reported by using a sum-log constraint instead of the -norm penalty in the ZA-LMS algorithm [24,27]. Subsequently, the zero attracting techniques have been widely researched, and a great quantity of sparse LMS algorithms was exploited by using different norm constraints, such as -norm and smooth approximation -norm constraints [28,29,30,31,32]. Furthermore, the zero attracting (ZA) technique has also been expanded into the affine projection algorithm and the normalized NLMS algorithms to further exploit the applications of the ZA algorithms [12,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], which includes ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS algorithms. However, the affine projection algorithm has higher complexity than the NLMS algorithm, which limited its applications. Thus, the sparse NLMS algorithms have been extensively studied and have been used for sparse channel estimations. However, the behavior of these NLMS-based channel estimations was affected by the modified step size and the regularized parameters. The normalized step size has an important effect on the compromise between the channel estimation behavior and convergence speed, while the regularization parameter depends on the SNR of the systems [41]. From [41], we can see that the proposed joint-optimization method cannot utilize the sparsity of the multi-channels. In addition, the step size and the regularization parameters should be selected to address the conflict requirement between the channel estimation behavior and the convergence speed.
In this paper, a joint-optimization method is discussed to enhance the behavior of the ZA- and RZA-NLMS algorithms for estimating finite impulse response (FIR) sparse channels. Their estimation behaviors are discussed via a broadband multi-path channel, which is a prior known sparse channel from the previous studies [6,7,9,12,14,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The proposed algorithms are realized by implementing a joint-optimization on the regularization parameter and step size to achieve a minimization of the channel estimation misalignment, where the joint-optimization method is obtained from [41]. The joint-optimization scheme is derived in detail in the context of zero attraction theory, and it is incorporated into the previously-proposed ZA- and RZA-NLMS algorithms to form zero-attracting joint-optimization NLMS (ZAJO-NLMS) and reweighted ZAJO-NLMS (RZAJO-NLMS) algorithms. The parameter selection and the behavior of our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS are evaluated though a sparse channel, which is similar to [6,7,9,12,14,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The computer simulations indicate that our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms perform better than the previously-presented ZA-NLMS, RZA-NLMS, ZA-LMS, RZA-LMS, traditional LMS and NLMS algorithms for dealing with sparse channel estimation.
The structure is illustrated herein. We review the basic NLMS and the previously-reported ZA-NLMS, as well as the RZA-NLMS algorithms in Section 2 through estimating a broadband multipath wireless communication channel. Section 3 gives the derivation of the joint-optimization scheme and the proposed ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms. In Section 4, our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms will be evaluated though a broadband sparse multipath channel, and their channel estimation behaviors are discussed and compared with the previous ZA-NLMS, RZA-NLMS, ZA-LMS, RZA-LMS, traditional LMS and NLMS algorithms. At last, a short summary is given in Section 5.
2. NLMS-Based Sparse Adaptive Channel Estimation Algorithm
We review the traditional NLMS and its sparse forms, which include the ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS, over a sparse multipath wireless channel, which is given in Figure 1.
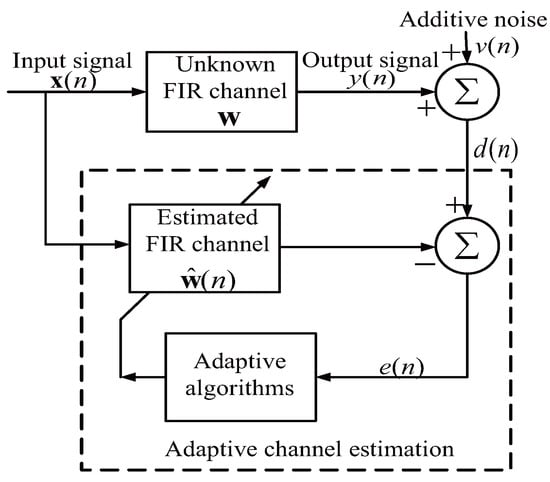
Figure 1.
Typical adaptive filter-based channel estimation system. FIR, finite impulse response.
is used as a training input signal, which is transmitted over an FIR channel . In this paper, N denotes the length of a multipath channel, and is the transpose operation. The channel output is , which is denoted as . The expected signal is acquired at the receiver, and . denotes an additional white Gaussian noise (AWGN). The NLMS-based channel estimation algorithms aim to get the unknown sparse channel by utilizing and to minimize the instant error . We define . denotes the estimated vector. The cost function of the traditional NLMS is depicted as:
By using the Lagrange multiplier method to carry out the desired minimization of (1) and introducing a controlling step size, the updating of the traditional NLMS is obtained [3,4,5]:
denotes a step size of the NLMS algorithm, and represents a regularization parameter with small value, which is to prevent from dividing by zero. Although the NLMS algorithm can give a good estimation of the sparse channel by the use of the update Equation (2), it cannot use the sparsity property of the practical existing multi-path channels. Recently, the ZA technique has been introduced into the original cost function of the traditional NLMS for exploiting the sparseness of the channel. Then, the ZA-NLMS algorithm is presented by using an -norm penalty to modify the original cost function of the traditional NLMS. Thus, the modified cost function for the reported ZA-NLMS is written as:
where denotes a zero attracting strength parameter used to get a balance between the estimation behavior and the sparseness of . Furthermore, the Lagrange multiplier method is utilized to find out a solution of (3). As a result, the updating equation of ZA-NLMS is described as [12]:
where denotes a step size and denotes the zero-attracting strength controlling factor for the ZA-NLMS algorithm, respectively. The ZA-NLMS algorithm utilizes the sparse characteristic of the multi-path wireless channel. However, it exerts a uniform zero attracting on all of the channel taps. Thus, the ZA-NLMS algorithm may reduce the estimation behavior when the designated channel is less sparse. To address this problem, a sum-log penalty [42] is utilized to form the RZA-NLMS algorithm, whose cost function is written as:
We also employ the Lagrange multiplier method to solve Equation (5). Then, the channel coefficients of the RZA-NLMS algorithm are updated by: [12]
or its vector form:
where is a step size, while denotes a zero-attracting strength controlling factor of the RZA-NLMS algorithm, respectively. Here, is a threshold that is used for controlling the reweighted factor /.
From the above discussions, it is observed that the previously-proposed ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS exert the desired zero-attractor on each iteration. The proposed zero attractors attract the zero channel coefficients to zero quickly compared with the traditional NLMS algorithm. Thus, we can say that the sparse NLMS algorithms, namely ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS, utilize different sparse penalties to achieve various zero attractors. The traditional NLMS-based channel estimation algorithm is concluded as follows:
Comparing to the traditional NLMS method mentioned in (8), the mentioned sparse NLMS-based channel estimation algorithms provide amazing zero attractors for both ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS, and hence, their updated equation is:
3. Proposed Sparse Joint-Optimization NLMS Algorithms
Though the proposed sparse NLMS algorithms effectively utilize the in-nature properties of the wireless multi-path channel for achieving a superior channel estimation behavior, their performance will be affected by step size, regularization parameter and the zero-attracting strength controlling factor. After that, various techniques have been presented to enhance the behavior of the ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS algorithms, including variable step size methods and parameter-adjusting techniques [32]. Herein, we concentrate on constructing a joint-optimization method on the regularization parameter and step size.
Next, we will introduce our proposed ZAJO-NLMS algorithm in detail. Here, we consider the updating equation of the ZA-NLMS algorithm:
where denotes a step size, represents a regularization parameter and:
denotes the instantaneous channel estimation error at instant n. As we know, [41]; represents expectation, and represents the variance of . For large N, we can get [43]. Then, we have:
Next, we consider as a channel that can be modeled as a simplified first order Markov model [41],
where represents an AWGN signal with zero mean. Furthermore, we assume that is independent of the channel . Therefore, we can get:
where is an identity matrix. Thus, the variance of gives an important uncertainty on . Here, we define a posteriori bias as:
Here, we can get:
Taking the -norm on (16), using expectation on its left and right sides and getting rid of the uncorrelated products based on the i.i.d. assumptions, we have:
Now, we concentrate on the last five terms in the Equation (17). From the above discussion, the instantaneous error is illustrated as:
By taking the Equation (18) into account, we can get:
where represents the trace operation of a matrix. Assume that the misalignments at the instant n and are uncorrelated. In the stable state, a posteriori bias correlation matrix is approximated as a diagonal matrix [41], which is because the bias of each coefficient tends to be uncorrelated. Thus, we obtain:
Similarly, the cross-correlation can also be obtained based on (18). Therefore, the correlation matrix of can be regarded as a diagonal matrix. By eliminating the uncorrelated terms, we obtain:
Then, the expectation term can also be calculated by taking Equation (18) into consideration. Similarly, we have:
Here, we assume that the correlation matrix of approximates a diagonal matrix, which has been widely used for simplifying the analysis [41,44]. Furthermore, this also motivates us to further develop the second term in Equation (22) based on the Gaussian moment factoring theory [45]. Then, we obtain:
As we know, at the stable status, we get:
and is very small. Thus, Equation (17) can be approximated to be:
From the discussions above, we substitute Equations (20), (21) and (23) into Equation (25) and denote ; we have:
where:
and:
From the result in Equation (26), we can see that the convergence speed and the misadjustment components are separated from each other. The first term of Equation (26) plays a significant role in the convergence speed of adaptive filters, which depends on , , input signal power and filter length. It is worth noting that the convergence speed component does not rely on the and of the model [41]. Thus, the noise power and the uncertainties do not give any effect on the convergence. We can see that fastest convergence speed can be achieved when Equation (27) reaches its minimum. Then, we have:
Therefore, we can get:
where is the fastest convergence speed controlling factor. As we know, the regularization parameter is small, and the length N is large. Thus, for achieving the fastest convergence speed, which is well known in [3,44]. Furthermore, the stability condition is obtained by letting , which results in:
Again, by considering and , the stability conditions of the NLMS and ZA-NLMS algorithms can be obtained, which is written as .
The second term of Equation (26) gives large effects on the misalignment of the proposed algorithm, which significantly depends on the noise power and the uncertainties of the model. With the increment of these two parameters, the misalignment is also increased [41]. The lowest misalignment is obtained when Equation (28) reaches the minimum. Furthermore, by taking the step size into account, we can get the lowest misalignment, which can be expressed as:
As we know, the broadband channel is always time-varying, and hence, . In this case, . This is to say that the lowest misalignment is achieved as the step size approximates zero [3]. From the discussions mentioned above, we follow the optimization criterion to mimic the channel estimation misalignment to obtain the optimized sparse RZA-NLMS and ZA-NLMS algorithms, which is based on the convergence analysis above.
An ideal adaptive filtering algorithm needs low misalignment and a rapid convergence speed rate. Unluckily, the results in Equations (30) and (32) give opposite directions. Thus, we need to optimize the step size to enhance the channel estimation behavior. Furthermore, the regularization affects the behaviors on sparse NLMS algorithms. From (27), we can see that the convergence decreases when the regularization parameter increases, while the misalignment in Equation (28) always increases when regularization parameter decreases. Thus, we should control the step size and to mimic the effects on the performance of the channel estimation algorithms. Additionally, we also follow a minimization problem with respect to the channel estimation misalignment. According to Equation (26) and assuming these two parameters are dependent on time, we can impose [41]:
Then, we can get the same result, which is expressed as:
which gives a joint-optimization procedure. Then, we introduce Equation (34) into Equation (10) to obtain the updating equation of our ZAJO-NLMS algorithm. Then, we can get:
When , we have:
whose solution is expressed as:
Similarly to the extraction of the ZAJO-NLMS, a reweighting factor is incorporating into the ZAJO-NLMS. As a result, the updating equation is obtained for realizing the RZAJO-NLMS algorithm:
From the proposed ZAJO- and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms, we found that the regularization parameter and step size are joint-optimized, while the zero attractor keeps invariable. From the above discussions, we found that there are two additional zero attraction terms, namely and , in the ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms, which are different from [41] due to the zero attractors. In this paper, the proposed ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms are implemented by the combination of the zero-attraction-based NLMS and the joint-optimization method in [41]. As a result, the ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms are constructed to deal with the sparse channel estimation, which can give better performance due to the joint-optimization and the zero attractors and .
Our contributions can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- Two optimized ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms with zero attractors have been proposed for sparse channel estimation, in the context of the state variable model.
- (2)
- The proposed ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms are realized by using the joint-optimization method and the zero attraction techniques to mimic the channel estimation misalignment.
- (3)
- The behaviors of the proposed ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms are evaluated for estimating sparse channels.
- (4)
- The ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms can achieve both faster convergence and lower misalignment than the ZA- and RZA-NLMS algorithms owing to the joint-optimization, which effectively adjusts the step size and the regularization parameter. In the future, we will develop an optimal algorithm to optimize the zero-attractor terms.
4. Results and Discussion
We construct several experiments to look into the estimation behavior of our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms through a multi-path wireless communication channel, which is a general sparse channel model obtained from the measurement [14,17] and which has been widely used for verifying the estimation performance of NLMS-based channel estimations [6,7,9,12,14,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. Moreover, the channel estimation behavior is evaluated using mean-square error, and the channel estimation performance is also compared with the traditional LMS, NLMS, ZA-LMS, RZA-LMS, ZA-NLMS and RZA-NLMS algorithms. Here, a multipath channel has a length of . This channel with varying K is used for predicting the estimation behavior by means of the mean square error (MSE) standard. In the investigation, the channel estimation performance with different sparsity level K is also analyzed in detail. The K dominant coefficients are distributed randomly in the channel, and it is limited by . An example of a typical broadband sparse multi-path wireless channel is given in Figure 2.
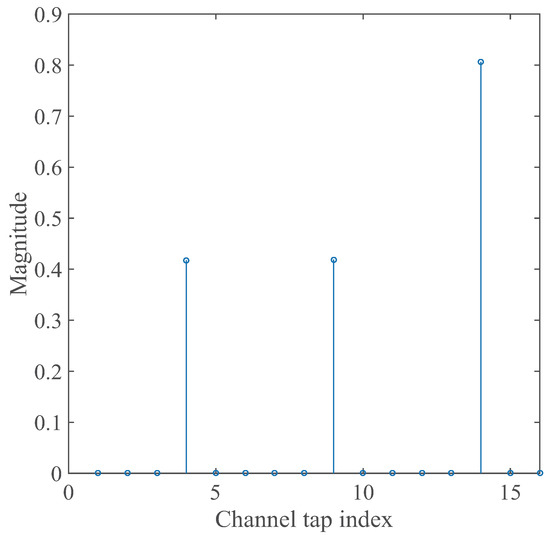
Figure 2.
A typical broadband sparse multi-path channel.
Here, the sparse channel has a length of 16, and it has three dominant coefficients. The number of non-zero coefficients is denoted as sparsity level K. In all of the experiments, is a Gaussian signal, and is a Gaussian noise. The received signal has a power of . The power of the noise is given by . The estimation behaviors of our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms are accessed by the MSE given by:
Since the step size and the regularization parameter have been optimized based on the derivation of our ZAJO-NLMS and RZAJO-NLMS, only the zero-attracting parameter can affect the performance of these proposed algorithms. Thus, we investigated the effects of the and on the MSE. The performance is shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4 for and , respectively.
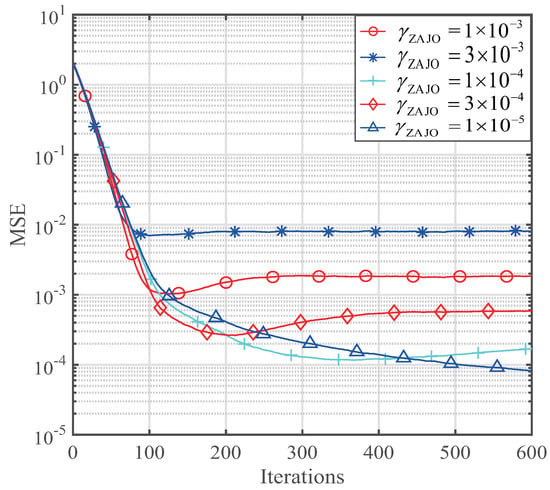
Figure 3.
The effect of the on the zero-attracting joint-optimization (ZAJO)-NLMS for sparse channel estimation.
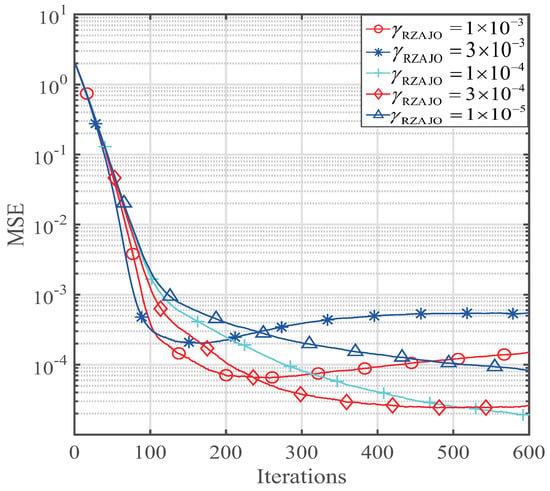
Figure 4.
Effect of the on the reweighted zero-attracting joint-optimization (RZAJO)-NLMS for sparse channel estimation.
We can see that both and have important effects on the sparse channel estimation. With a decrement of the , the MSE of the ZAJO-NLMS algorithm shown in Figure 3 is getting better when ranges from to . As for , both the convergence speed and MSE are deteriorated. From Figure 4, it is observed that has the same trend as that of the . Thus, we can properly select and to achieve desired channel estimation performance. According to the parameter effects in Figure 3 and Figure 4, we choose to investigate the effects of the sparsity level on the sparse channel estimation performance.
Next, we set the sparsity level of the broadband sparse multi-path to to analyze the channel estimation performance. The simulation parameters are , , . The results are comparatively shown in Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 for , , and , respectively. It is observed from Figure 5 that our RZAJO-NLMS algorithm achieves the quickest convergence and smallest steady-state error compared with the traditional LMS, NLMS, ZA-LMS, RZA-LMS, ZA-, RZA- and ZAJO NLMS algorithms. The proposed RZAJO-NLMS algorithm has much more gains than the traditional RZA-NLMS algorithm. Additionally, our proposed ZAJO-NLMS algorithm achieves better channel estimation behaviors than those of the RZA-NLMS algorithm for . When the sparsity level K increases from 2 to 8, the gain between the RZAJO-NLMS and RZA-NLMS algorithm is getting small. However, our proposed RZAJO-NLMS algorithm outperforms all of the other sparse channel estimation algorithms with reference to both the MSE and convergence. When , our proposed ZAJO-NLMS algorithm achieves quicker convergence compared to the traditional NLMS to get the same MSE level. On the contrary, the behavior of the ZA-NLMS becomes worse than that of the traditional NLMS. Thereby, our proposed RZAJO- and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms are more useful for adaptive sparse channel estimation applications.
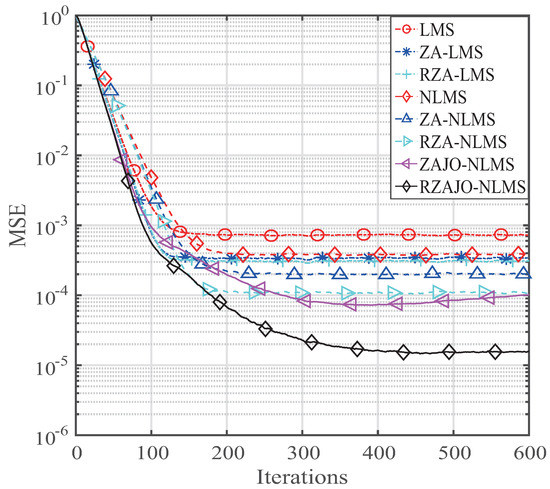
Figure 5.
MSE of our presented ZAJO- and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms for .
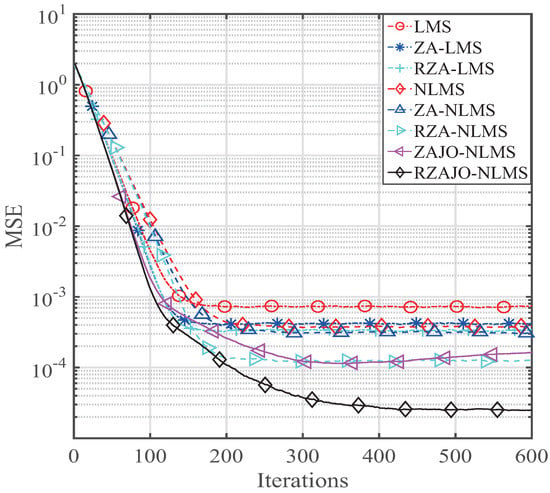
Figure 6.
MSE of our presented ZAJO- and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms for .
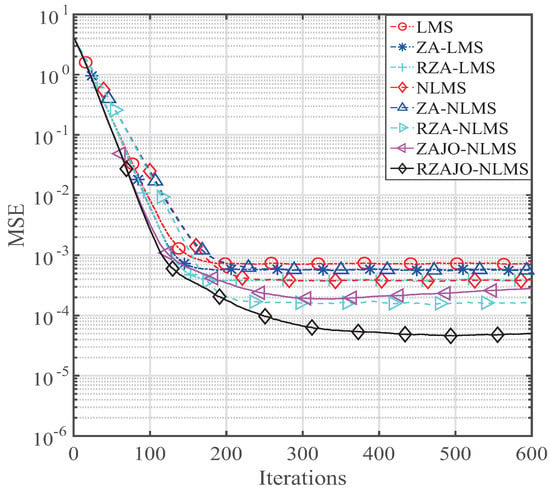
Figure 7.
MSE of our presented ZAJO- and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms for .
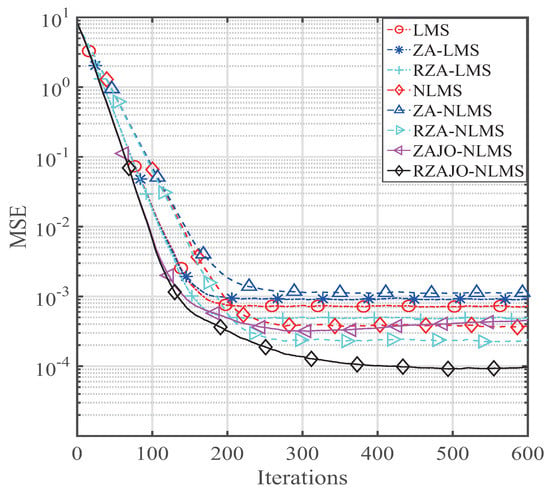
Figure 8.
MSE of our presented ZAJO- and RZAJO-NLMS algorithms for .
5. Conclusions
We proposed joint-optimization sparse NLMS algorithms, namely RZAJO-NLMS and ZAJO-NLMS. The joint-optimization was realized by using a state model to improve the channel estimation performance of both the ZA- and RZA-NLMS algorithms. Our RZAJO- and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms are based on the joint-optimization of step size and the regularization parameter. The proposed joint-optimization was derived in detail. Furthermore, the estimation behavior of our RZAJO- and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms is evaluated on a broadband sparse multi-path channel with different sparsity levels. The results verified that our RZAJO-NLMS algorithm provides the fastest convergence speed rate and lowest MSE. In addition, the proposed ZAJO-NLMS outperforms the previously-reported ZA-NLMS and traditional NLMS algorithms.
This study provided the RZAJO-NLMS and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms based on the zero attracting and the joint-optimization techniques. The proposed joint-optimization technique can be expanded to the -norm constrained NLMS, normalized LMF (NLMF) and normalized least mean mixed norm (NLMMN) to enhance the sparse channel estimation performance or sparse system identification. In addition, the proposed method can be used for exploiting the two-dimensional (2D) adaptive filters for imaging processing, which can be used for medical imaging denoising applications [46]. Moreover, our proposed RZAJO-NLMS and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms can be integrated into the orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) and multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) OFDM systems to improve the quality of the communication systems [47,48].
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China-Government Corporation Special Program (2016YFE0111100), the National Science Foundation of China (61571149), the Science and Technology innovative Talents Foundation of Harbin (2016RAXXJ044), the Projects for the Selected Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars of Heilongjiang Province and Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the People’s Republic of China (MOHRSS) and the PhD Student Research and Innovation Fund of the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HEUGIP201707).
Author Contributions
Yanyan Wang wrote the draft of the paper, wrote the code and did the simulations of this paper. Yingsong Li helped to check the coding and simulations, and he also put forward the idea of the RZAJO-NLMS and ZAJO-NLMS algorithms. He also provided the analysis of the paper. Both of the authors wrote this paper together, and they have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Korowajczuk, L. LTE, WiMAX and WLAN Network Design, Optimization and Performance Analysis; John Wiley: Chichester, West Susses, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Proakis, J.G.; Salehi, M. Digital Communications, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S.; Widrow, B. Least-Mean-Square Adaptive Filters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, P.S.R. Adaptive Filtering Algorithms and Practical Implementation, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, J.; Mareets, I.; Hoang, C. Enhanced detection-guided NLMS estimation of sparse FIR-modeled signal channels. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2006, 53, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Sanguinetti, L.; Mengali, U. Channel estimation for adaptive frequency-domain equalization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2005, 4, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, L.R.; Rey, H.G.; Benesty, J.; Tressens, S. A stochastic model for a new robust NLMS algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2007 15th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO’07), Poznan, Poland, 3–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, R. Sparsity-aware adaptive filter algorithms with mixed controlled l2 and lp error criterions for sparse adaptive channel estimation. Available online: https://doi.org10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.07.036 (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Sparse least mean mixed-norm adaptive filtering algorithms for sparse channel estimation applications. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Sparse multi-path channel estimation using norm combination constrained set-membership NLMS algorithms. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, G.; Peng, W.; Adachi, F. Improved adaptive sparse channel estimation based on the least mean square algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC’13), Shanghai, China, 7–10 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Albu, F. A soft parameter function penalized normalized maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for sparse system identification. Entropy 2017, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, S.F.; Rao, B.D. Sparse channel estimation via matching pursuit with application to equalization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2002, 50, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuokko, L.; Kolmonen, V.M.; Salo, J.; Vainikainen, P. Measurement of large-scale cluster power characteristics for geometric channel models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 3361–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, P.J. Shallow water acoustic response and platform motion modeling via a hierarchical Gaussian mixture model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maechler, P.; Greisen, P.; Sporrer, B.; Steiner, S.; Felber, N.; Brug, A. Implementation of greedy algorithms for LTE sparse channel estimation. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference Record of the Forty Fourth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR’10), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 7–10 November 2010; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Yin, W.; Li, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Zhu, H. Compressive sensing based high-resolution channel estimation for OFDM system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2012, 6, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, W.B.; Haupt, J.; Sayeed, A.M.; Nowak, R. Compressed channel sensing: A new approach to estimating sparse multipath channels. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1058–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub{ock, G.; Hlawatach, F. A compressed sensing technique for OFDM channel estimation in mobile environment: exploting channel sparsity for reducing pilots. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP’08), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 2885–2888. [Google Scholar]
- Candés, E.J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing. C. R. Math. 2008, 346, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Hero, A.O. Sparse LMS for system identification. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP’09), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 3125–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Adaptive channel estimation based on an improved norm constrained set-membership normalized least mean square algorithm. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R. A robust sparse adaptive filtering algorithm with a correntropy induced metric constraint for broadband multi-path channel estimation. Entropy 2016, 18, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Shi, P. Convergence analysis of sparse LMS algorithms with l1-norm penalty based on white input signal. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 3289–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Tong, F. Gradient optimization p-norm-like constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system estimation. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, O.; Vorobyov, S.A. Sparse channel estimation with Lp-norm and reweighted L1-norm penalized least mean squares. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP’11), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 2864–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Jin, J.; Mei, S. L0 norm constraint LMS algorithms for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 16, 774–777. [Google Scholar]
- Niazadeh, R.; Ghalehjegh, S.H.; Babaie-Zadeh, M.; Jutten, C. ISI sparse channel estimation based on SL0 and its application in ML sequence-by-sequence equalization. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. Zero-attracting variable-step size least mean square algorithms for adaptive sparse channel estimation. Int. J. Adap. Control Signal Process. 2015, 29, 1189–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Lamare, R.C.; Nascimento, V.H. Sparsity-aware affine projection adaptive algorithms for system identification. In Proceedings of the Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD 2011), London, UK, 27–29 September 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.V.S.; Martins, W.A.; Diniz, P.S.Z. Affine projection algorithms for sparse system identification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP’13), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 5666–5670. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. An improved proportionate normalized least-mean-square algorithm for broadband multipath channel estimation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. Smooth approximation l0-norm constrained affine projection algorithm and its applications in sparse channel estimation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, W.; Wan, J.; Li, Z. Sparse adaptive channel estimation based on lp-norm-penalized affine projection algorithm. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Low-complexity non-uniform penalized affine projection algorithm for sparse system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Sparse-aware set-membership NLMS algorithms and their application for sparse channel estimation and echo cancelation. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 895–902. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Norm-adaption penalized least mean square/fourth algorithm for sparse channel estimation. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciochina, S.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J. An optimized NLMS algorithm for system identification. Signal Process. 2016, 118, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candés, E.J.; Wakin, M.B.; Noyd, S.P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l1-minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2008, 15, 877–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Rey, H.; ReyVega, L.; Tressens, S. A nonparametric VSS-NLMS algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2006, 13, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isserlis, L. On a formula for the product-moment coefficient of any order of a normal frequency distribution in any number of variables. Biometrika 1918, 12, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulyman, A.I.; Zerguine, A. Convergence and steady-state analysis of a variable step size NLMS algorithm. Signal Process. 2003, 83, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, J.A. Discovery of medical big data analytics: improving the prediction of traumatic brain injury survival rates by datamining patient informatics processing software hybrid hadoop hive. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2015, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, K. Comparative study on the channel estimation for OFDM system using LMS, NLMS and RLS algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Informatics and Medical Engineering (PRIME), Tamilnadu, India, 21–23 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, G.; Adachi, F. Adaptive sparse channel estimation for time-variant MIMO-OFDM systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Sardinia, Italy, 1–5 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).