Abstract
In this paper, a modified GrabCut algorithm is proposed using a clustering technique to reduce image noise. GrabCut is an image segmentation method based on GraphCut starting with a user-specified bounding box around the object to be segmented. In the modified version, the original image is filtered using the median filter to reduce noise and then the quantized image using K-means algorithm is used for the normal GrabCut method for object segmentation. This new process showed that it improved the object segmentation performance a lot and the extract segmentation result compared to the standard method.
1. Introduction
Digital image processing deals with a wide variety of applications ranging from biology, military, medical, space science, art, games and movie industries.
The object segmentation is an important step in image processing and analysis [1]. In computer vision, segmentation divides the input image into background and objects. The purpose of the segmentation is to simplify and make it easy to interpret or convert to more meaningful representation of an image. Segmentation is one of the most difficult subjects in an digital image processing, and many studies on this subject have been done to get more accurate results.
GrabCut method is based on object segmentation algorithm called GraphCut [2,3]. While GraphCut algorithm segments an image without user intervention, GrabCut accepts an interest area defined by a user and extracts objects using the clues given to get better results. Many studies have been done to improve performance of GrabCut detecting objects in unknown regions [4,5].
In the proposed method, the image is smoothed using median filter and the quantized using k-means clustering technique. Then, GrabCut extracts objects from the quantized image [6]. In this way, we got improved performance.
2. Related Work
In general, object segmentation is one of the most fundamental tasks in image processing. Image segmentation is to divide an image into a number of pixel sets on the basis of shape or area. In this work, we following image filters and a clustering technique is applied for an efficient object segmentation.
2.1. Image Filter
Filtering is one of the main tasks of signal processing. Filtering is used to remove noise in the image, to extract visual characteristics of interest, and to resample the image. Representative filters are Gaussian filter, Mean, etc.
Gaussian filter is used to remove the noise using the following equations:
where is the standard deviation.
Mean filter is the representative noise removing filter and is defined as follows:
where is a neighbor pixel and W is a mask of size .
2.2. Image Segmentation
Segmentation is the process of dividing the digital image into a set of multiple pixels to simplify the image representation. Typical methods of image clustering are Mean Shift (MS), Fuzzy C-Means (FCM), etc. [7].
Mean shift (MS) is a procedure for locating the maxima of a given window area by selecting a pixel (mode) most close to the averaged color, then moving the center of the window to the mode to find local maxima repeatedly until it is converged [8,9]. The result of MS is good in low frequency areas, but it has some difficulties to group high frequency areas. The following Figure 1 show the example.
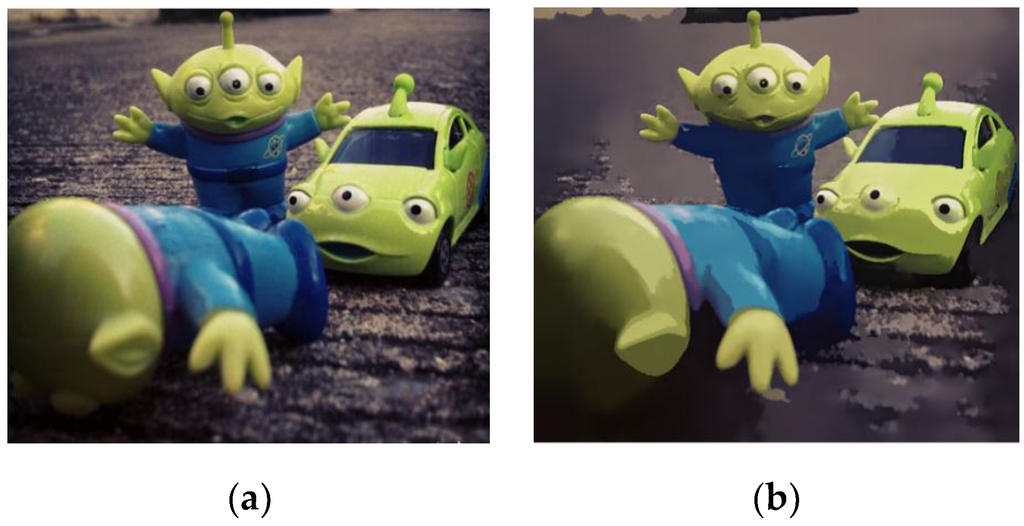
Figure 1.
MS clustering. (a) Original image; (b) Result image.
FCM is to overcome the difficulty of MS by considering belonging or membership degree into the distance. Data-points close to a cluster center have a high belonging degree [10,11].
Let a data set to be clustered, where p is feature dimension, is a real vector space, and N is the number of pixels. Each pixel of color image is expressed as feature vectors like and center of cluster is , where p is feature dimension and C is the number of clusters. FCM calculates matrix U minimizing the target function .
where , and is membership degree that data k belongs to cluster i. is the center of cluster i, defined using Equation (5).
where is the mean value of using fuzzy constant m. One disadvantage of FCM is that the number of clusters should be provided in advance. Figure 2 is the class membership map applying FCM algorithm and Figure 3 is result of FCM clustering.

Figure 2.
FCM class membership map. (a) Class 1; (b) Class 2; (c) Class 3.
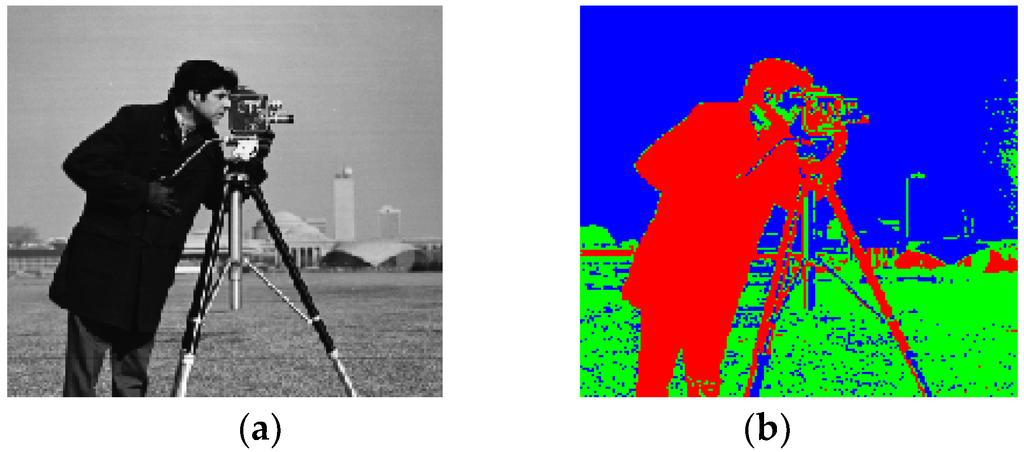
Figure 3.
FCM clustering. (a) Original image; (b) Result image.
Image segmentation can be accomplished also by using GraphCut. Boykov proposed GraphCut to get optimized interactive image segmentation:
where is a vector of either 0 or 1. 0 means background and 1 means object. is continuity between adjacent pixels and is a data term representing how much the data belongs to object or background. Data term requires prior information about object and background, and provided probability density function, data term calculated using Equation (7).
where and are histograms of background and object, p is a pixel and P is a pixel set of an image. is the intensity of pixel P. Figure 4 is result of GraphCut algorithm that is another typical method of image segmentation.

Figure 4.
GraphCut algorithm. (a) Original image; (b) Result image.
3. The proposed Method
The flow of proposed method is show in Figure 5.
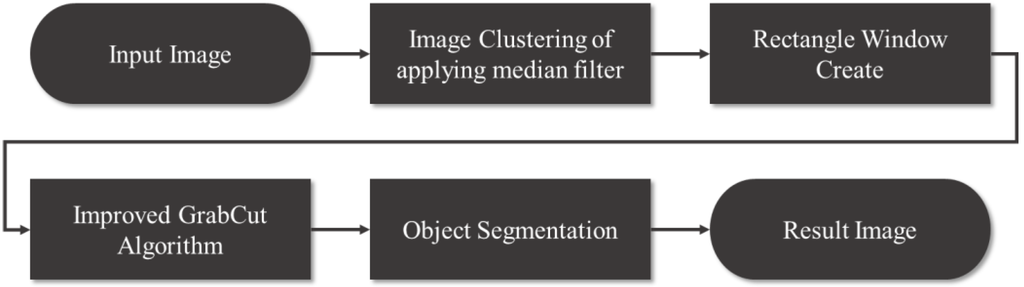
Figure 5.
A flowchart of the proposed method.
3.1. Clustering to Reduce Noise
Digital image can be contaminated during data transmission.
where N is the size of data set. K-means clustering method is applied to the output of the filter. K-means classifies the data set to the predefined number of classes. Let be the center of i-th cluster and be the set of pixels belongs to cluster i. The variance of all the data set is defined as Equation (9).
The goal is to find minimizing V. K-means starts with arbitrary initial values . Allocating pixels to close and recalculating is repeated until it is converged.
Equation (10) is the simplest clustering method minimizing repeatedly. Figure 6 shows applied the median filter in image.
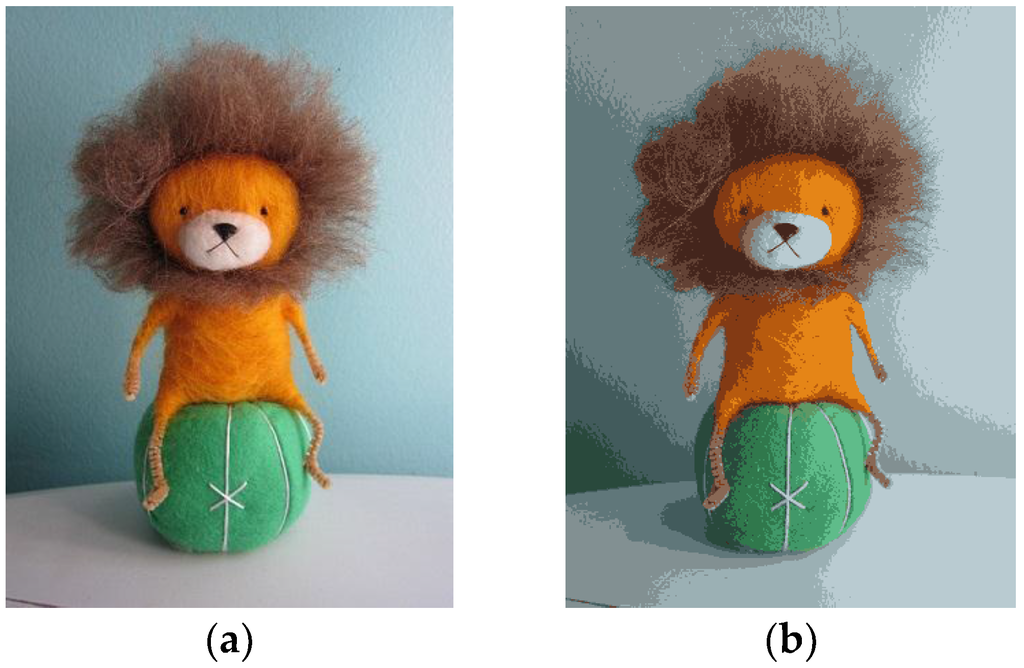
Figure 6.
An image applied the median filter image. (a) Original image; (b) Result image.
3.2. Object Segmentation Using Improved GrabCut
GrabCut accepts an interest area defined by a user and extracts objects using the clue given. Figure 7 shows trimap of foreground of GrabCut algorithm.
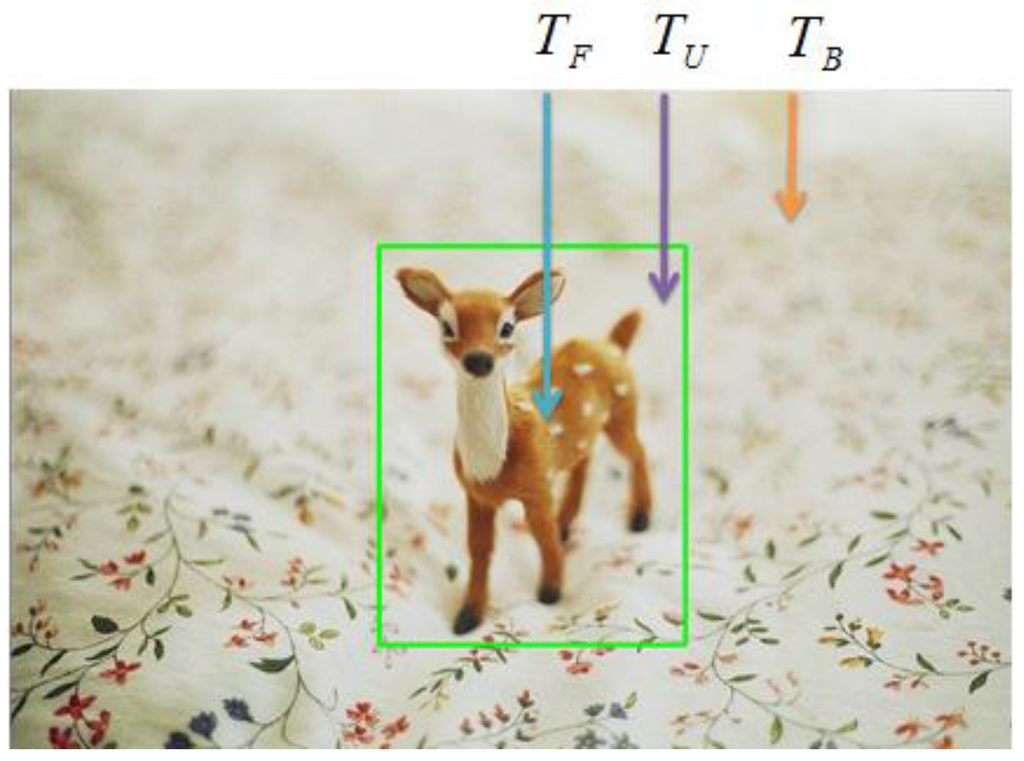
Figure 7.
Composition of trimap; shows trimap of foreground (), background () and unknown region ().
Object and background is mixed in unknown region. Background is defined as Equation (11).
where is the area greater than gradient. Symbol is a dilation operator and S is a structure element for it.
A Gaussian mixture model is a probabilistic model that assumes all the data points are generated from a mixture of a finite number of Gaussian distributions with unknown parameters and is given by:
where i-th vector component is characterized by normal distributions with weights and a pair of mean and covariance . represents relative importance. is defined as follows:
Parameters for GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model) of M components is expressed as Equation (14):
is defined as follows:
Figure 8 shows a result of the improved GrabCut algorithm.

Figure 8.
Improved GrabCut algorithm. (a) Original image; (b) Result image.
4. Experiment and Discussion
The experiments were performed using about 400 photos such as figures, plants, food, etc.
Performance of GraphCut, standard GrabCut and proposed method is compared. Figure 9 shows some results. GrabCut is better than GraphCut and, the proposed method shows better results than GrabCut in most cases by detecting background in unknown area [12,13].

Figure 9.
(a) Original image; (b) GraphCut Algorithm; (c) GrabCut Algorithm; (d) Ref. [12]; (e) Ref. [13]; (f) Proposed Method.
Evaluation is performed using precision and recall. Precision is the fraction of retrieved instances that are relevant, while recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that are retrieved:
where is the number of pixels, is the object and is ground truth objects. Figure 10 shows the precision and recall of three methods. The proposed method gives the best result.
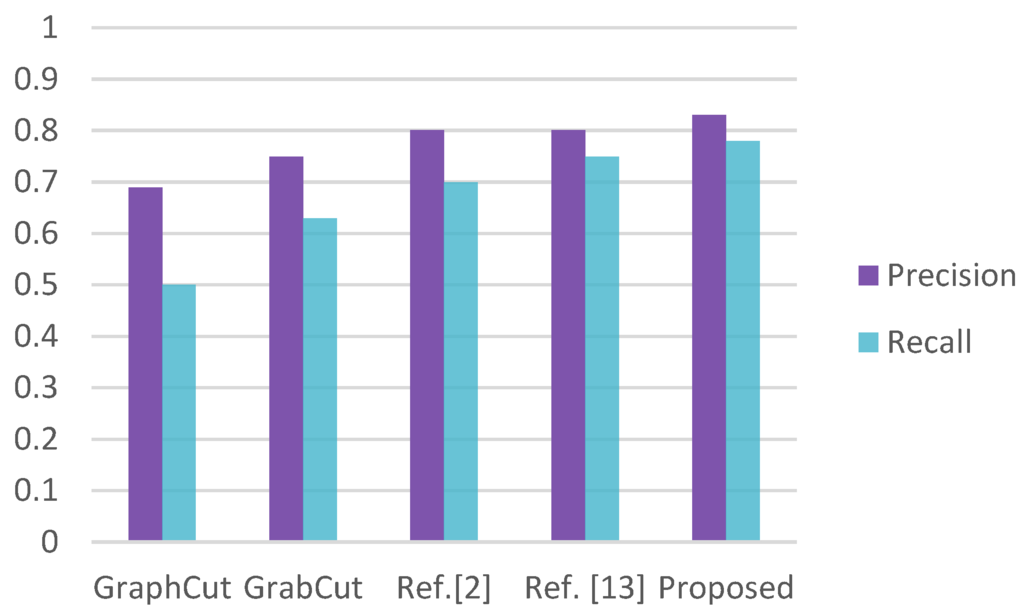
Figure 10.
Precision-recall result.
Experiments are performed using PSNR (Peak Signal to Noise Ratio). PSNR is the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation.
MSE (Mean Squared Error) is the difference between the estimator and what is estimated. Where MSE is defined as follows:
Table 1 shows the quantitative comparison of result experiments.

Table 1.
Result of experiment.as quantitative comparison.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a modified GrabCut method is proposed using median filter and k-means clustering technique to reduce image noise and to extract objects better. An image is preprocessed and then used for the input of standard GrabCut. This method showed better performance than GraphCut or standard GrabCut from the various and complex pictures like medical images, traffic images and people images. This research should be extended further to detect objects in video, and this can be used in many industrial applications.
Acknowledgments
The work reported in this paper was conducted during the sabbatical year of Kwangwoon University in 2013.
Author Contributions
GangSeong Lee provided guidance for this paper; SangHun Lee was the research and academic advisor of editing; GaOn Kim developed and solved the proposed model, carried out this analysis and wrote the manuscript; JongHun Park contributed to the revisions and performed experiments; YoungSoo Park contributed to the revisions and advisor of editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yoo, T.-H.; Lee, G.-S.; Lee, S.-H. Window Production Method based on Low-Frequency Detection for Automatic Object Extraction of GrabCut. In Proceedings of Digital Policy & Management, Seoul, Korea, 20 September 2012; pp. 211–217.
- Tang, M.; Gorelick, L.; Vekler, O.; Boykove, Y. GrabCut in One Cut. In Proceedings of ICCV Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1767–1776.
- Rother, C.; Kolmogorov, V.; Blake, A. GrabCut : Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. In Proceedings of Computer Graphics, Imaging and Visualization (CGIV), Penang, Malaysia, 26–29 July 2004; pp. 309–314.
- Boykov, Y.Y.; Jolly, M.-P. Interactive graph cut for optimal boundary & region segmentation of object in N-D image. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; pp. 105–112.
- Hänsch, R.; Hellwich, O.; Wang, X. Graph-cut segmentation of polarimetric SAR image. In Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1733–1736.
- Malyszko, D.; Wierzchon, S.T. Standard and Genetic k-means Clustering Techniques in Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications, CISIM ’07, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 28–30 June 2007; pp. 299–304.
- Sulaiman, S.N.; Isa, N.A.M. Adaptive fuzzy-K-means clustering algorithm for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2010, 56, 2661–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Wang, P.; Lee, S.-H. Image Compression with Meanshift Based Inverse Colorization. In Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2013; pp. 330–331.
- Lebourgeols, F.; Drira, F.; Gaceb, D.; Duong, J. Fast Integral MeanShift: Application to Color Segmentation of Document Images. In Proceedings of ICDAR Document Analysis and Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 August 2013; pp. 52–56.
- Yang, D.-L.; Zhang, J.-W. Study of Image Quantization Technology Based on FCM Clustering Algorithm. In Proceedings of Intelligent System Design and Engineering Application (ISDEA), Changsha, China, 13–14 October 2010; pp. 421–424.
- Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Tian, J. Histogram Constraint Based Fast FCM Cluster Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Vigo, Spain, 4–7 June 2007; pp. 1623–1627.
- Tang, M.; Ayed, B.I.; Marin, D.; Boykov, Y. Secrets of GrabCut and Kernel K-means. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, London, ON, Canada, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1555–1563.
- Hua, S.; Shi, P. GrabCut color image segmentation based on region of interest. In Proceedings of 2014 7th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP), Dalian, China, 14–16 October 2014; pp. 392–396.
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).