Symmetry in the Language of Gene Expression: A Survey of Gene Promoter Networks in Multiple Bacterial Species and Non-σ Regulons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Predicted Promoters
2.2. GPNs and Thresholding
2.3. Assessment of Fractal Structure
2.4. Information Entropy
2.5. Footprint Size, Information Entropy, and Fractal Dimension
3. Results
3.1. Visual Pattern
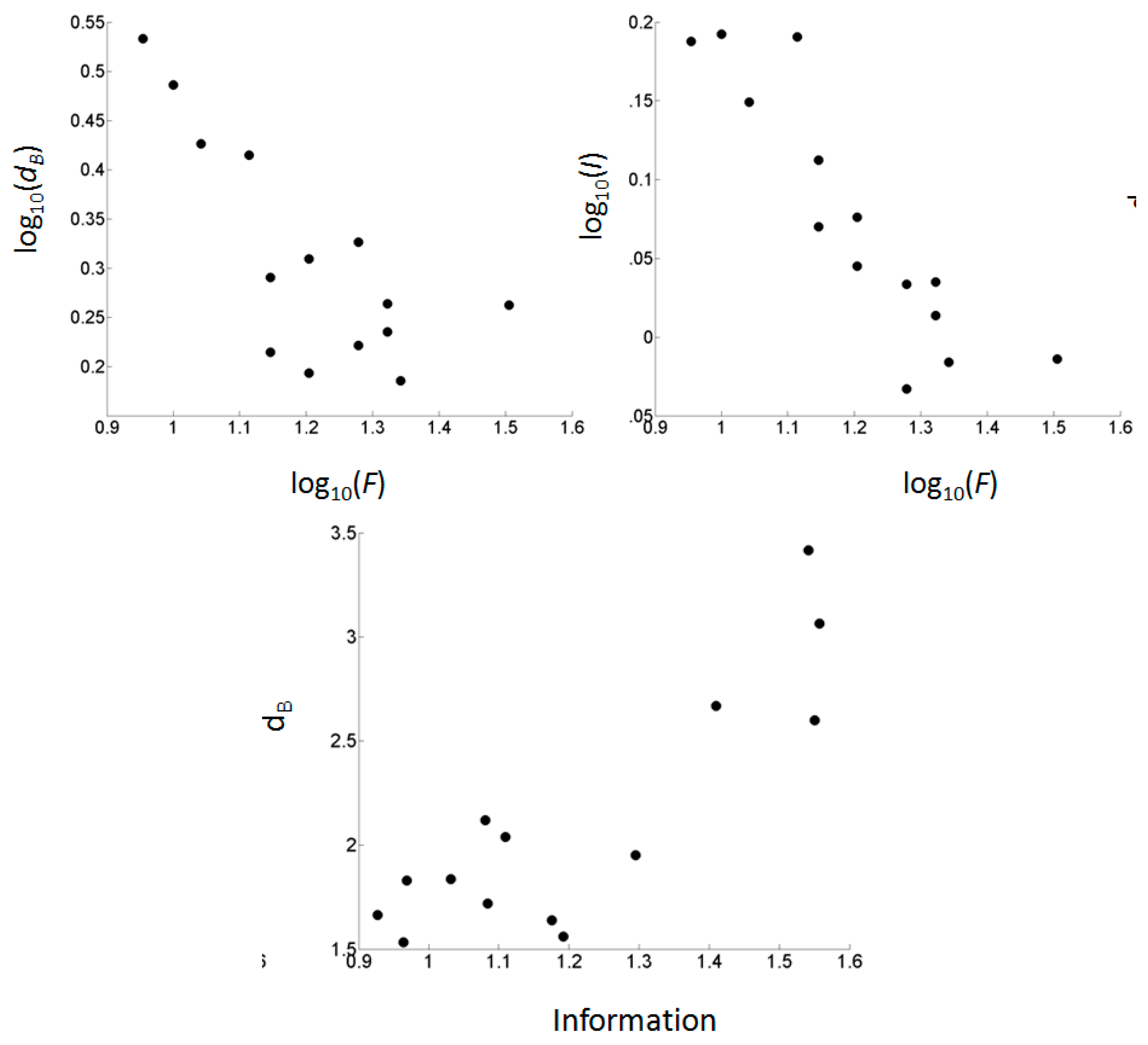
3.2. Fractal Dimensions
3.3. Footprint Symmetry and Information Entropy
3.4. Scaling of Footprint Size, Information (IRMean), and Fractal Dimension
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Watson, J.D.; Crick, F.H.C. A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid. Nature 1953, 171, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Marr, T.G.; Kaneko, K. Understanding long-range correlations in DNA sequences. Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenom. 1994, 75, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegna, R.N.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Goldberger, A.L.; Havlin, S.; Peng, C.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E. Linguistic features of noncoding DNA sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscombe, N.M.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Johnson, T.; Gerstein, M. The dominance of the population by a selected few: Power-law behavior applies to a wide variety of genomic properties. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0040.1–research0040.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Features, patterns, correlations in DNA and protein texts. Available online: http://www.nslij-genetics.org/dnacorr/ (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Molina, N.; Van Nimwegen, E. Scaling laws in functional genome content across prokaryotic clades and lifestyles. Trends Genet. 2009, 25, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nimwegen, E. Scaling laws in the functional content of genomes. Trends Genet. 2003, 19, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, C. Fractals and hidden symmetries in DNA. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 507056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, D.V.; Filatova, M.V.; Kuklinb, A.I.; Islamovb, A.K.; Kentzingerc, E.; Pantinaa, R.; Toperverga, B.P.; Isaev-Ivanova, V.V. Fractal nature of chromatin organization in interphase chicken erythrocyte nuclei: DNA structure exhibits biphasic fractal properties. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedev, D.V.; Filatov, M.V.; Kuklin, A.I.; Islamov, A.K.; Stellbrink, J.; Pantina, R.A.; Denisov, Y.Y.; Toperverg, B.P.; Isaev-Ivanov, V.V. Structural hierarchy of chromatin in chicken erythrocyte nuclei based on small-angle neutron scattering: Fractal nature of the large-scale chromatin organization. Crystallogr. Rep. 2008, 53, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman-Aiden, E.; van Berkum, N.L.; Williams, L.; Imakaev, M.; Ragoczy, T.; Telling, A.; Amit, I.; Lajoie, B.R.; Sabo, P.J.; Dorschner, M.O.; et al. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 2009, 326, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, R.L.; Silvab, R.C.; Pereira, F.G.; Leite, N.J.; Lorand-Metze, I.; Metze, K. The fractal dimension of nuclear chromatin as a prognostic factor in acute precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell. Oncol. 2006, 28, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedin, V.; Adam, R.L.; de Sá, B.C.S.; Landman, G.; Metze, K. Fractal dimension of chromatin is an independent prognostic factor for survival in melanoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, D.P.; Falconi, M.A.; Adam, R.L.; Ortega, M.M.; Lima, C.P.; de Souza, C.A.; Lorand-Metze, I.; Metze, K. Fractal characteristics of May-Grunwald-Giemsa stained chromatin are independent prognostic factors for survival in multiple myeloma. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, S. The Origins of Order: Self-Organization and Selection in Evolution; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.; Levin, M. Gene regulatory networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlebach, G.; Shamir, R. Modelling and analysis of gene regulatory networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.-L.; Oltvai, Z. Network biology: Understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.M.; Luscombe, N.M.; Aravind, L.; Gerstein, M.; Teichmann, S.A. Structure and evolution of transcriptional regulatory networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004, 14, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.-L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Tombor, B.; Albert, R.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.-L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 2000, 407, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giot, L.; Bader, J.S.; Brouwer, C.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kuang, B.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Ooi, C.E.; Godwin, B.; Vitols, E.; et al. A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 2003, 302, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yook, S.H.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabasi, A.-L. Functional and topological characterization of protein interaction networks. Proteomics 2004, 4, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, L.B.; Adam, R.L.; Leite, N.J.; Metze, K.; Rossi, M.A. Shannon’s entropy and fractal dimension provide an objective account of bone tissue organization during calvarial bone regeneration. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2008, 71, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.Ch.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. Fractal dynamics in physiology: Alterations with disease and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvão, V.; Mirandab, J.G.V.; Andradeb, R.F.S.; Andrade, J.S., Jr.; Gallose, L.K.; Maksee, H.A. Modularity map of the network of human cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5750–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, G.B.; Woodruff, W.H.; Brown, J.H. Allometric scaling of metabolic rate from molecules and mitochondria to cells and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, G.B.; Brown, J.H. The origin of allometric scaling laws in biology from genomes to ecosystems: towards a quantitative unifying theory of biological structure and organization. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, V.M.; Allen, A.P.; Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Herman, A.B.; Woodruff, W.H.; West, G.B. Scaling of number, size, and metabolic rate of cells with body size in mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4718–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R. Molecular Biology, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides, J. Grammatical model of the regulation of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9405–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, D.; McClure, W. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 2237–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, A.; Collado-Vides, J. Sigma70 promoters in Escherichia coli: Specific transcription in dense regions of overlapping promoter-like signals. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Jia, H.; Dröge, P.; Li, J. The human genome-wide distribution of DNA palindromes. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2007, 7, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janga, S.C.; Collado-Vides, J. Structure and evolution of gene regulatory networks in microbial genomes. Res. Microbiol 2007, 158, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, P.R.; Horsley, R.K.; Ahmed, Y.A.; Williamson, J.J.; Turcic, S.M. Fractal topology of gene promoter networks at phase transitions. Gene Reg. Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, R.R.; Chakravarti, D.; Lutfeali, S.; Ray, A.; Raval, A. Identifying hubs in protein interaction networks. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supekar, K.; Menon, V.; Rubin, D.; Musen, M.; Greicius, M.D. Network analysis of intrinsic functional brain connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nooy, W.; Mrvar, A.; Batagelj, V. Exploratory Social Network Analysis with Pajek; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W.H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, P.R. Diffusion limited aggregation and the fractal evolution of gene promoter networks. Netw. Biol. 2011, 1, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Havlin, S.; Makse, H.A. Origins of fractality in the growth of complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittgenstein, L. Philosophical Investigations, Translated by G.E.M. Anscombe, 3rd ed.; MacMillan Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer i Cancho, R.; Solé, R.V. Least effort and the origins of scaling in human language. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer i Cancho, R. Zipf’s law from a communicative phase transition. Eur. Phys. J. B 2005, 47, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.A. Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyvers, M.; Tenenbaum, J. The large-scale structure of semantic networks: Statistical analyses and a model of semantic growth. Cogn. Sci. 2005, 29, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münch, R.; Hiller, K.; Grote, A.; Scheer, M.; Klein, J.; Schobert, M.; Jahn, D. Virtual Footprint and PRODORIC: An integrative framework for regulon prediction in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 4187–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münch, R.; Hiller, K.; Barg, H.; Heldt, D.; Linz, S.; Wingender, E.; Jahn, D. Prodoric Database. 2003. Available online: http://prodoric.tu-bs.de/ (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Gama-Castro, S.; Jiménez-Jacinto, V.; Peralta-Gil, M.; Santos-Zavaleta, A.; Peñaloza-Spinola, M.I.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Segura-Salazar, J.; Muñiz-Rascado, L.; Martínez-Flores, I.; Salgado, H.; et al. RegulonDB (version 6.0): Gene regulation model of Escherichia coli K-12 beyond transcription, active (experimental) annotated promoters and Textpresso navigation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D120–D124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batagelj, V.; Mrvar, A. Pajek – program for large network analysis. Connections 1998, 21, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Batagelj, V.; Mrvar, A. Networks/Pajek. Available online: http://vlado.fmf.uni-lj.si/pub/networks/pajek/. (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Kamada, T.; Kawai, S. An algorithm for drawing general undirected graphs. Inf. Process. Lett. 1989, 31, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Havlin, S.; Makse, H.A. Self-similarity of complex networks. Nature 2005, 433, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Gallos, L.K.; Havlin, S.; Makse, H.A. How to calculate the fractal dimension of a complex network: The box covering algorithm. J. Stat. Mech. 2007, P03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, A.; Schult, D.; Swart, P. Exploring Network Structure, Dynamics, and Function Using NetworkX. In Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference (SciPy2008), Pasadena, CA USA, 19–24 August 2008; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg, A.; Schult, D.; Swart, P. NetworkX. Available online: http://networkx.lanl.gov/ (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Schneider, T.D.; Stormo, G.D.; Gold, L.; Ehrenfeucht, A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 188, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence logos: A new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Alamos National Laboratory. HCV Sequence Database: Entropy. Available online: http://hcv.lanl.gov/content/sequence/ENTROPY/entropy_one.html (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Taxonomy. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/guide/taxonomy/ (accessed on 11 November 2011).
- Hook-Barnard, I.G.; Hinton, D.M. Transcription initiation by mix and match elements: Flexibility for polymerase binding to bacterial promoters. Gene Reg. Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, P.P.; Chattoraj, D.K.; Schneider, T.D. Information analysis of sequences that bind the replication initiator RepA. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 233, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.D. Reading of DNA sequence logos: Prediction of major groove binding by information theory. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 274, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liebovitch, L.S. Fractals and Chaos; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zipf, G.K. Human Behaviour and the Principle of Least Effort: An Introduction to Human Ecology; Addison–Wesley: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-I-Cancho, R.; Forns, N. The self-organization of genomes. Complexity 2010, 15, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, R.V. Genome size, self-organization and DNA’s dark matter. Complexity 2010, 16, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misteli, T. Self-organization in the genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6885–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, I.; Scalzo, D.; Tapscott, S.J.; Kosak, S.T.; Groudine, M. Networking the nucleus. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
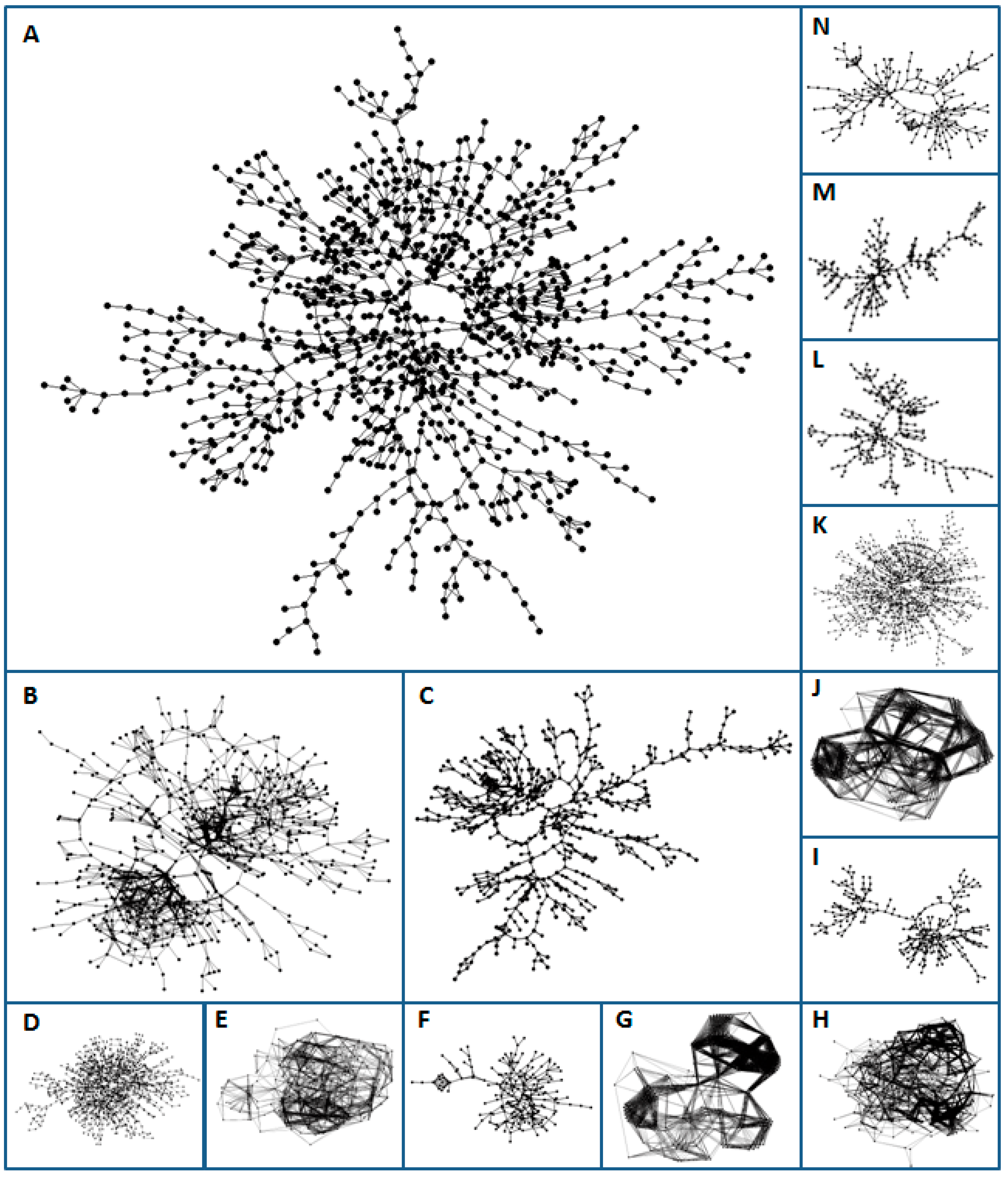

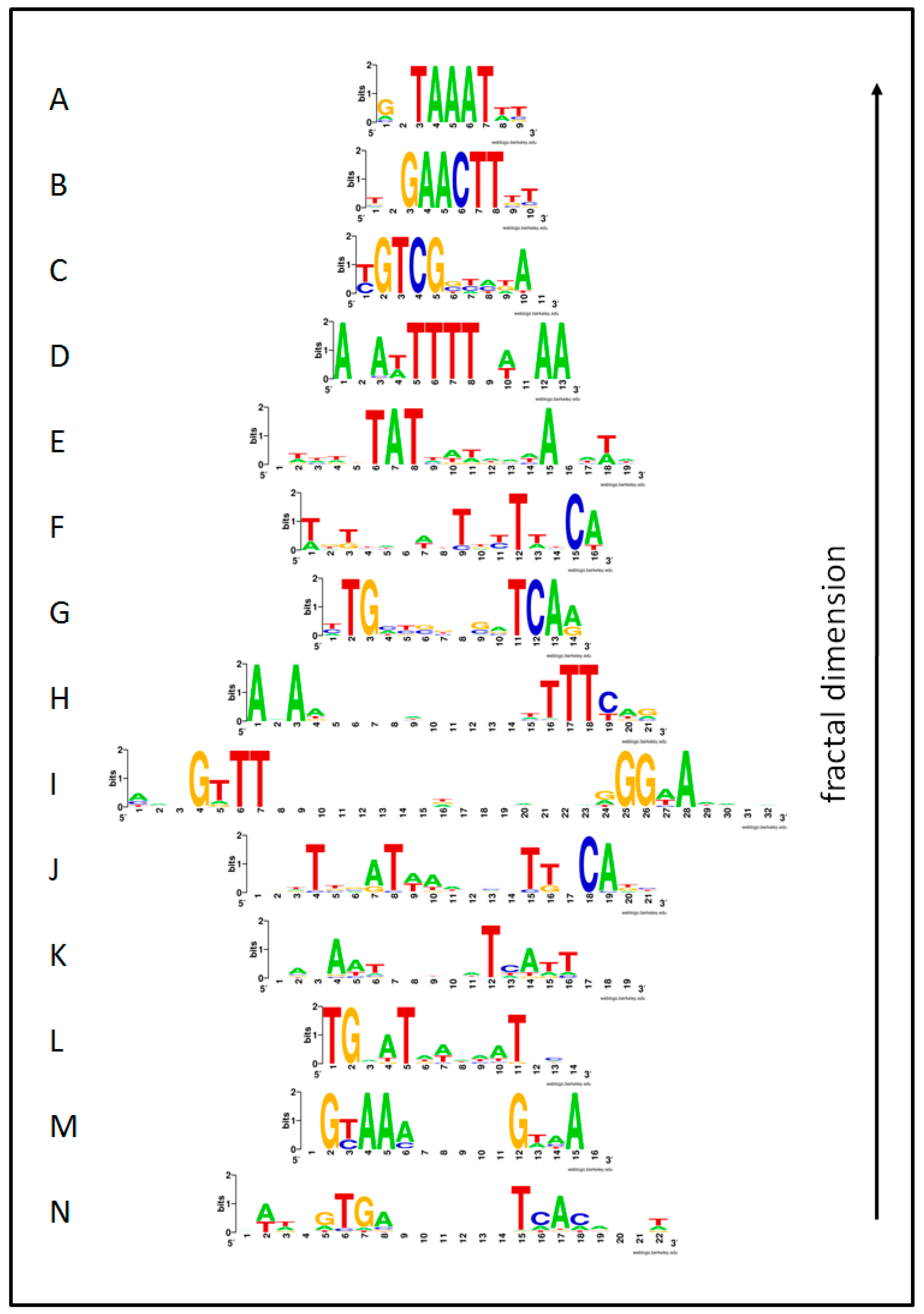
| Image | Regulon | Species | Library | S | X | F | IRMean | dB | R2d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | DegU | BS | Prod | 0.8 | 17 | 21 | 1.032 | 1.837 | 0.921 |
| B | Anr-Dnr(37) | PA | Prod | 1.0 | 13 | 14 | 1.295 | 1.953 | 0.921 |
| C | ArgR | EC | Prod | 0.7 | 13 | 14 | 1.175 | 1.640 | 0.978 |
| D | Hpr | BS | Prod | 0.8 | 16 | 19 | 1.081 | 2.120 | 0.914 |
| E | ResD | BS | Prod | 0.2 | 12 | 13 | 1.551 | 2.599 | 0.960 |
| F | SigB(n14) | BS | Prod | 0.8 | 20 | 32 | 0.967 | 1.831 | 0.945 |
| G | AlgU(-35) | PA | Prod | 0.5 | 9 | 10 | 1.557 | 3.064 | 0.959 |
| H | FleQ | PA | Prod | 0.5 | 10 | 11 | 1.410 | 2.669 | 0.965 |
| I | Fur | PA | Prod | 0.9 | 15 | 19 | 0.927 | 1.665 | 0.972 |
| J | PvdS | PA | Prod | 0.3 | 8 | 9 | 1.541 | 3.415 | 0.938 |
| K | DeoR | EC | Reg | 1.0 | 14 | 16 | 1.109 | 2.040 | 0.906 |
| L | CpxR | EC | Prod | 1.0 | 14 | 16 | 1.192 | 1.561 | 0.966 |
| M | Crp | EC | Prod | 0.6 | 17 | 22 | 0.964 | 1.534 | 0.977 |
| N | MarA | EC | Reg | 1.0 | 16 | 21 | 1.084 | 1.719 | 0.938 |
| x | y | β | A | R2 | r | Fstat | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | dB | –0.064 | 3.205 | 0.431 | –0.656 | 9.079 | 0.010 |
| log10(F) | log10(dB) | –0.560 | 0.986 | 0.569 | –0.754 | 15.821 | 0.002 |
| F | IRMean | –0.031 | 1.726 | 0.669 | –0.818 | 24.245 | <0.001 |
| log10(F) | log10(IRMean) | –0.472 | 0.643 | 0.795 | –0.892 | 46.551 | <0.001 |
| IRMean | dB | 2.236 | –0.579 | 0.734 | 0.857 | 33.088 | <0.001 |
| log10(IRMean) | log(dB) | 1.168 | 0.225 | 0.696 | 0.834 | 27.463 | <0.001 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldrich, P.R.; Horsley, R.K.; Turcic, S.M. Symmetry in the Language of Gene Expression: A Survey of Gene Promoter Networks in Multiple Bacterial Species and Non-σ Regulons. Symmetry 2011, 3, 750-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym3040750
Aldrich PR, Horsley RK, Turcic SM. Symmetry in the Language of Gene Expression: A Survey of Gene Promoter Networks in Multiple Bacterial Species and Non-σ Regulons. Symmetry. 2011; 3(4):750-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym3040750
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldrich, Preston R., Robert K. Horsley, and Stefan M. Turcic. 2011. "Symmetry in the Language of Gene Expression: A Survey of Gene Promoter Networks in Multiple Bacterial Species and Non-σ Regulons" Symmetry 3, no. 4: 750-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym3040750
APA StyleAldrich, P. R., Horsley, R. K., & Turcic, S. M. (2011). Symmetry in the Language of Gene Expression: A Survey of Gene Promoter Networks in Multiple Bacterial Species and Non-σ Regulons. Symmetry, 3(4), 750-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym3040750




